668346b5cf3861b4495ab4d24487318c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 136
 Chapter 8 Stacks and Queues 1
Chapter 8 Stacks and Queues 1
 This is a stack of books. 2
This is a stack of books. 2
 This is a queue of people. 3
This is a queue of people. 3
 Chap. 8 Contents 8. 1 Stacks 8. 1. 1 The Pure. Stack Interface 8. 1. 2 Implementations of the Pure. Stack Interface 8. 1. 3 Stack Application 1: How Compilers Implement Recursion 8. 1. 4 Stack Application 2: Converting from Infix to Postfix 8. 1. 5 Prefix Notation 8. 2 Queues 8. 2. 1 The Pure. Queue Interface 8. 2. 2 Implementations of the Pure. Queue Interface 8. 2. 3 Computer Simulation 8. 2. 4 Queue Application: A Simulated Car Wash 4
Chap. 8 Contents 8. 1 Stacks 8. 1. 1 The Pure. Stack Interface 8. 1. 2 Implementations of the Pure. Stack Interface 8. 1. 3 Stack Application 1: How Compilers Implement Recursion 8. 1. 4 Stack Application 2: Converting from Infix to Postfix 8. 1. 5 Prefix Notation 8. 2 Queues 8. 2. 1 The Pure. Queue Interface 8. 2. 2 Implementations of the Pure. Queue Interface 8. 2. 3 Computer Simulation 8. 2. 4 Queue Application: A Simulated Car Wash 4
 8. 1 Stacks 5
8. 1 Stacks 5
 6
6
 Object-Oriented (O-O) Terms Stack, Queue 是特別的 List. 以O-O 術語, 它們 EXTEND (延伸) List (不論是 Array. List 或是 Linked. List) General concepts (通用觀念) are Super classes such as Array. List Specialized concepts (專用觀念 ) are Sub classes such as Stack 7
Object-Oriented (O-O) Terms Stack, Queue 是特別的 List. 以O-O 術語, 它們 EXTEND (延伸) List (不論是 Array. List 或是 Linked. List) General concepts (通用觀念) are Super classes such as Array. List Specialized concepts (專用觀念 ) are Sub classes such as Stack 7
 8
8
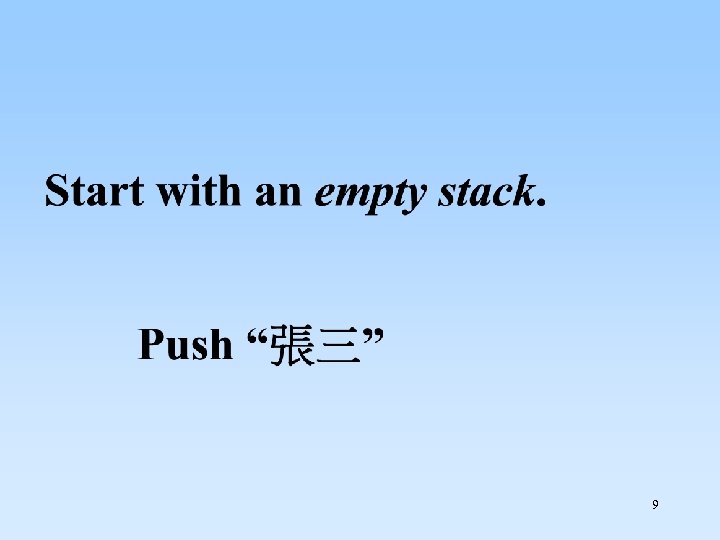 9
9
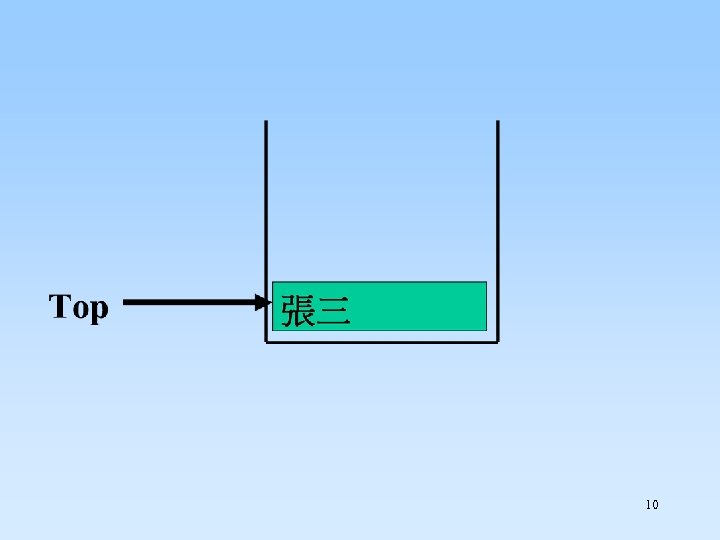 10
10
 11
11
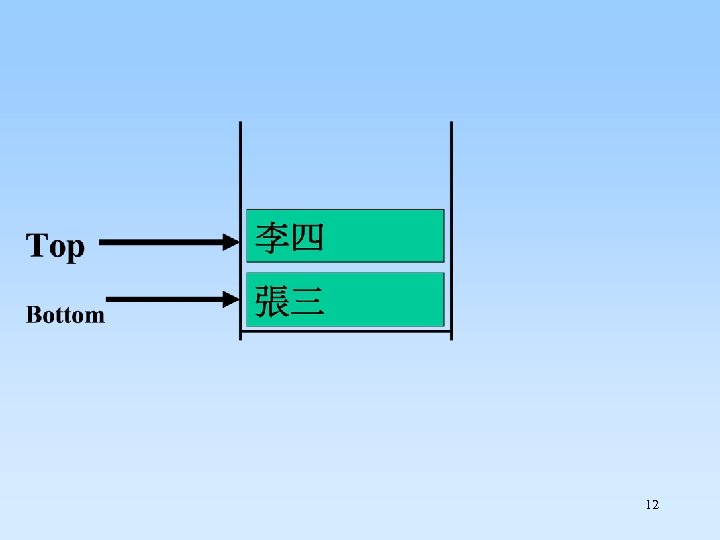 12
12
 13
13
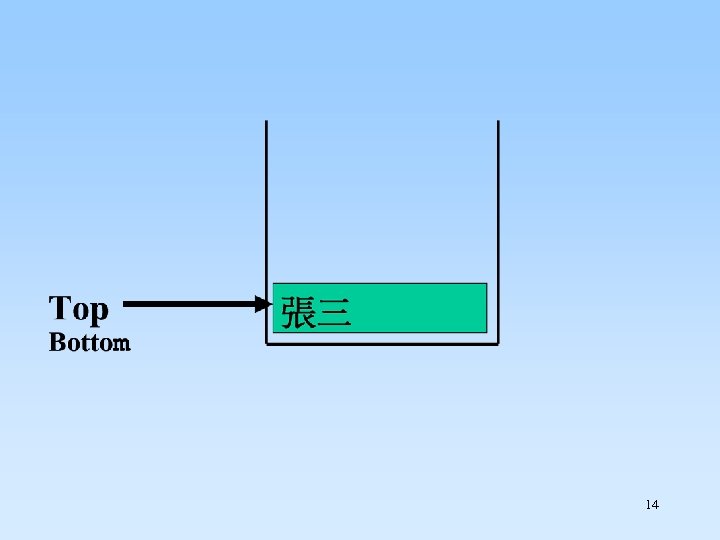 14
14
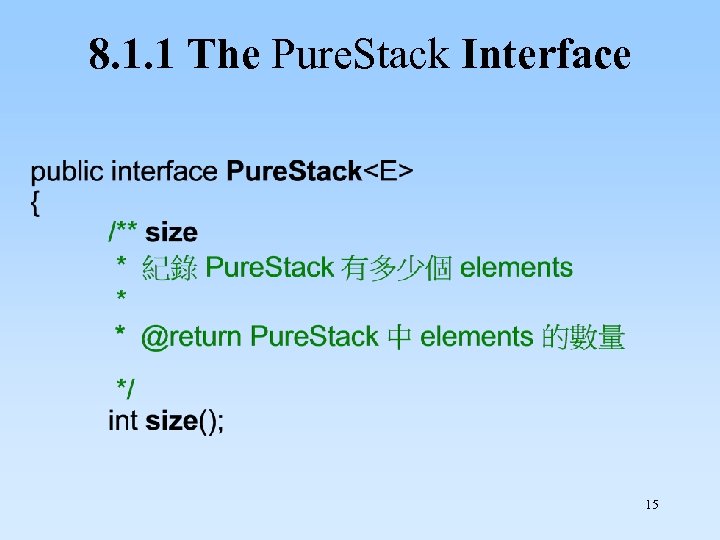 8. 1. 1 The Pure. Stack Interface 15
8. 1. 1 The Pure. Stack Interface 15
 16
16
 17
17
 8. 1. 2 實作Pure. Stack Interface 18
8. 1. 2 實作Pure. Stack Interface 18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
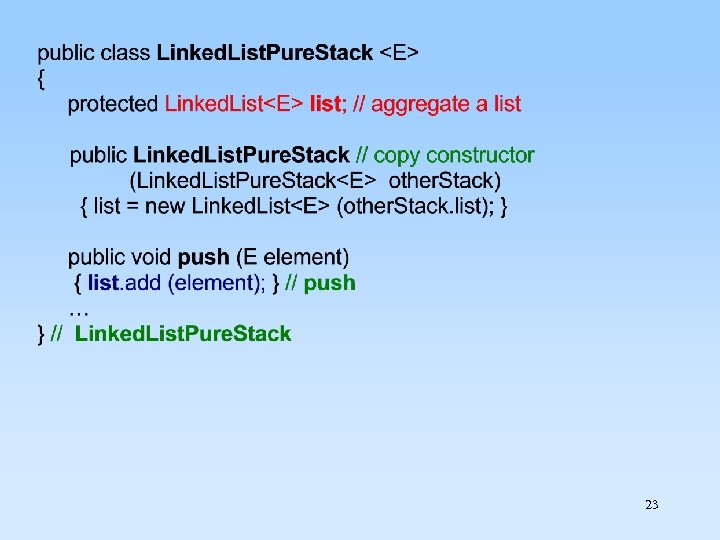 23
23
 寫出下列的輸出結果: Linked. List. Pure. Stack
寫出下列的輸出結果: Linked. List. Pure. Stack
 8. 1. 3 Stack 的應用 1: Compiler如何實作Recursion 25
8. 1. 3 Stack 的應用 1: Compiler如何實作Recursion 25
 26
26
 Run-time stack 處理 activation records. Push: When method is called Pop: When execution of method is completed (returned) 27
Run-time stack 處理 activation records. Push: When method is called Pop: When execution of method is completed (returned) 27
 28
28
 Run-time Stack: n=1 return “ 1” n=2 return “ 10” n =5 return “ 101” 29
Run-time Stack: n=1 return “ 1” n=2 return “ 10” n =5 return “ 101” 29
 30
30
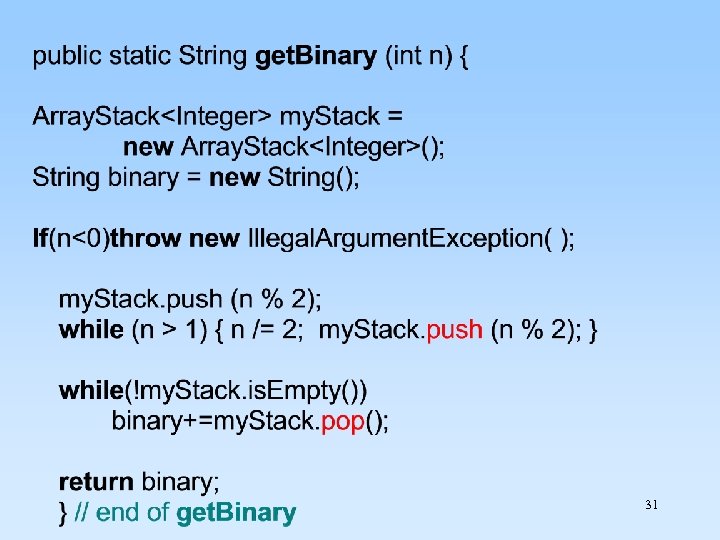 31
31
 32
32
 33
33
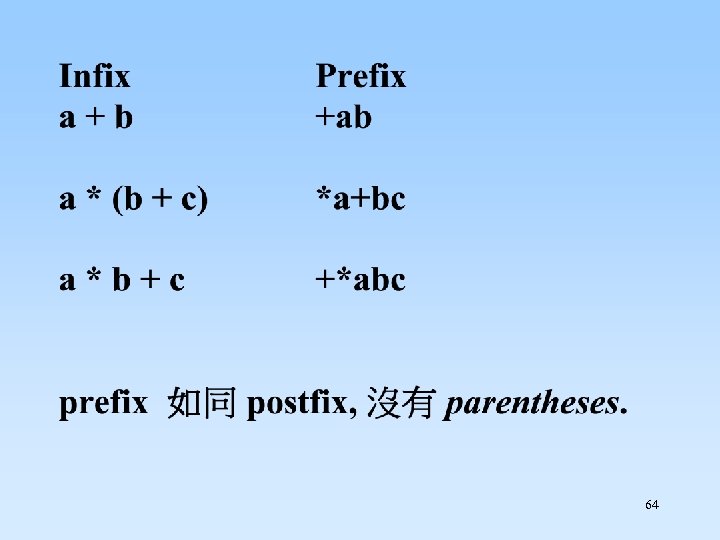
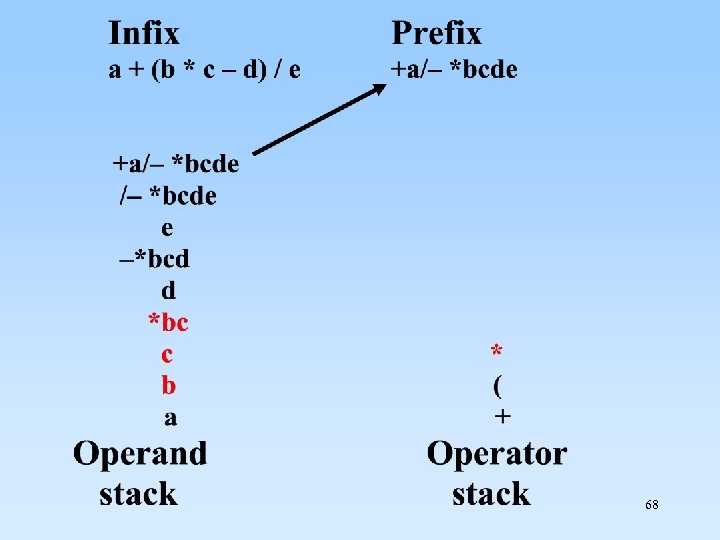
 8. 1. 4 Stack 應用 2: 轉換Infix(中置式) 到 Postfix(後置式) 在 infix 表示法中, operator(運算子) 放置於 operands(運算元) 之間. For example: a + b c – d + (e * f – g * h) / i 34
8. 1. 4 Stack 應用 2: 轉換Infix(中置式) 到 Postfix(後置式) 在 infix 表示法中, operator(運算子) 放置於 operands(運算元) 之間. For example: a + b c – d + (e * f – g * h) / i 34
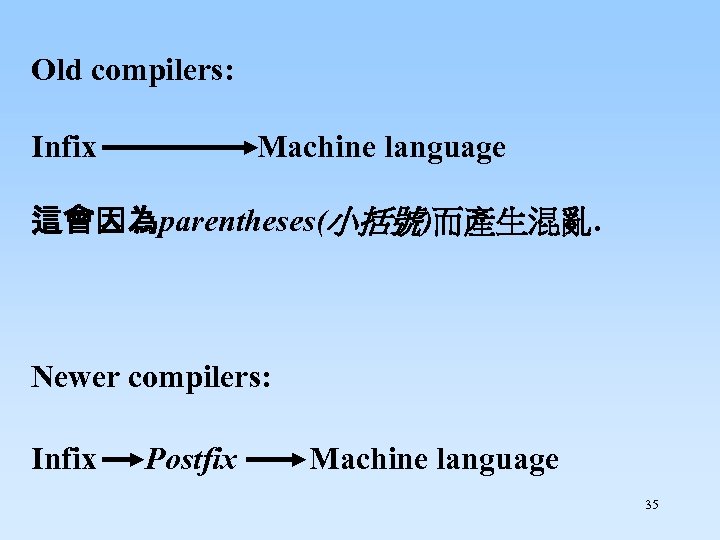 Old compilers: Infix Machine language 這會因為parentheses(小括號)而產生混亂. Newer compilers: Infix Postfix Machine language 35
Old compilers: Infix Machine language 這會因為parentheses(小括號)而產生混亂. Newer compilers: Infix Postfix Machine language 35
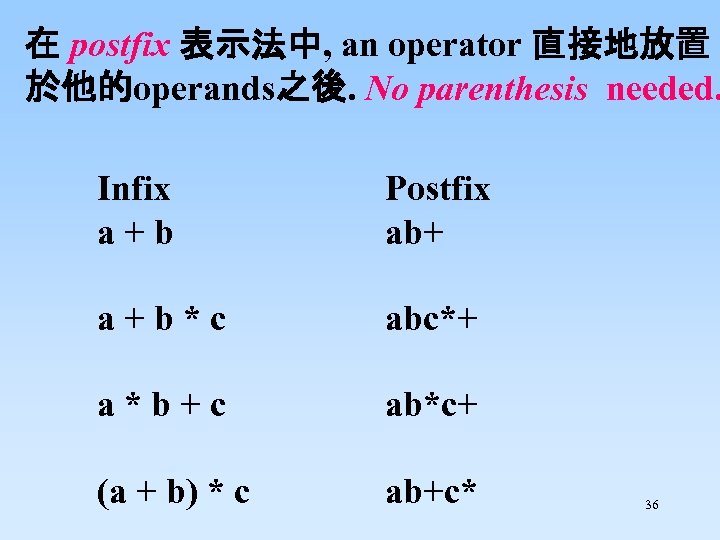 在 postfix 表示法中, an operator 直接地放置 於他的operands之後. No parenthesis needed. Infix a + b Postfix ab+ a + b * c abc*+ a * b + c ab*c+ (a + b) * c ab+c* 36
在 postfix 表示法中, an operator 直接地放置 於他的operands之後. No parenthesis needed. Infix a + b Postfix ab+ a + b * c abc*+ a * b + c ab*c+ (a + b) * c ab+c* 36
 postfix 不必使用 Parentheses 很棒! 37
postfix 不必使用 Parentheses 很棒! 37
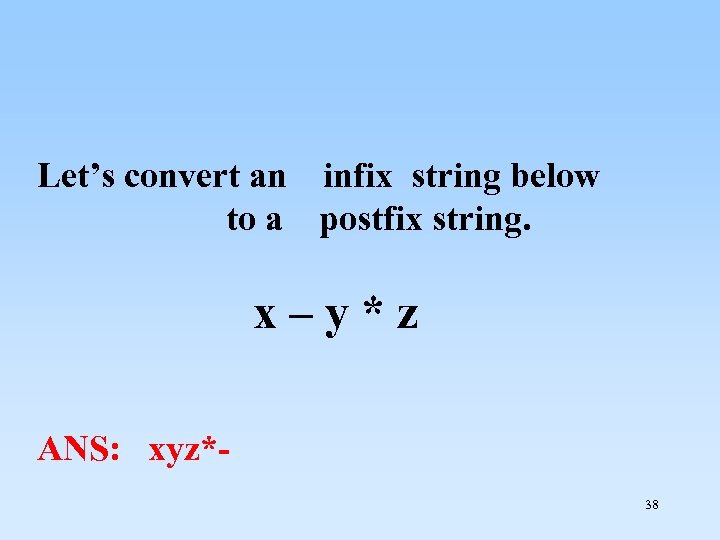 Let’s convert an infix string below to a postfix string. x – y * z ANS: xyz*38
Let’s convert an infix string below to a postfix string. x – y * z ANS: xyz*38
 Postfix 保留 operands的先後順序, so an operand can be appended to postfix as soon as that operand is encountered in infix. 39
Postfix 保留 operands的先後順序, so an operand can be appended to postfix as soon as that operand is encountered in infix. 39
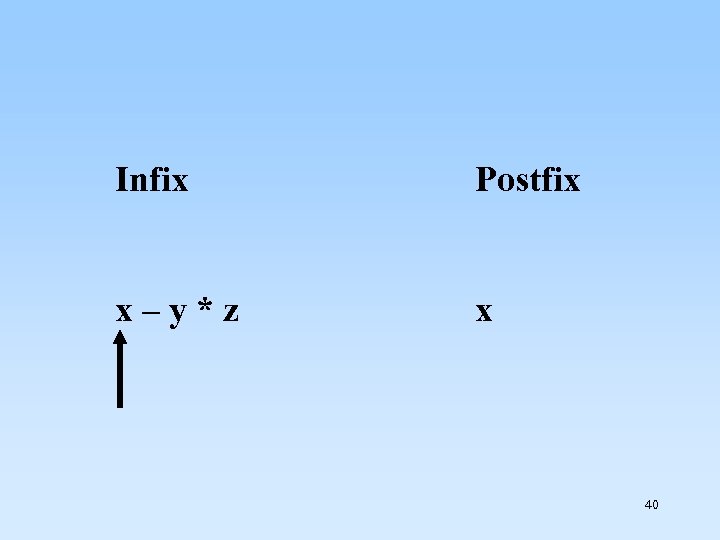 Infix x – y * z Postfix x 40
Infix x – y * z Postfix x 40
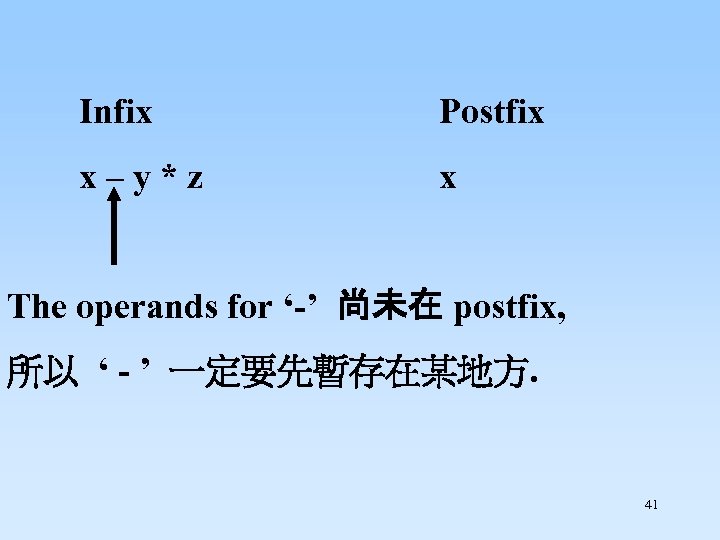 Infix x – y * z Postfix x The operands for ‘-’ 尚未在 postfix, 所以 ‘ - ’ 一定要先暫存在某地方. 41
Infix x – y * z Postfix x The operands for ‘-’ 尚未在 postfix, 所以 ‘ - ’ 一定要先暫存在某地方. 41
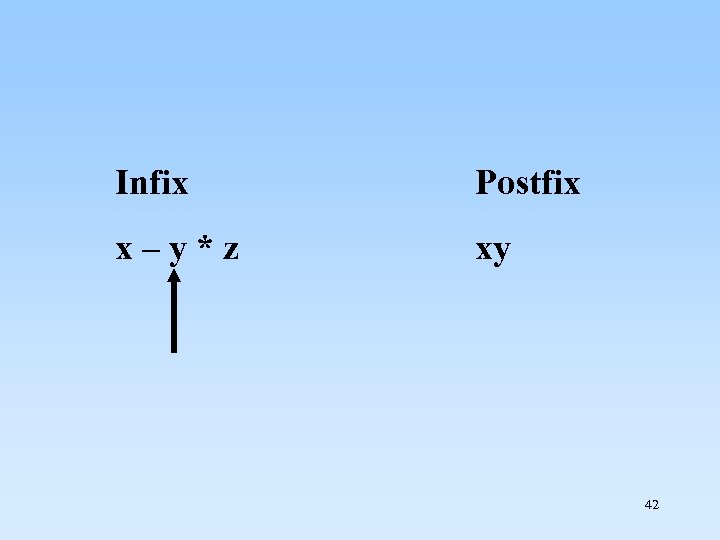 Infix x – y * z Postfix xy 42
Infix x – y * z Postfix xy 42
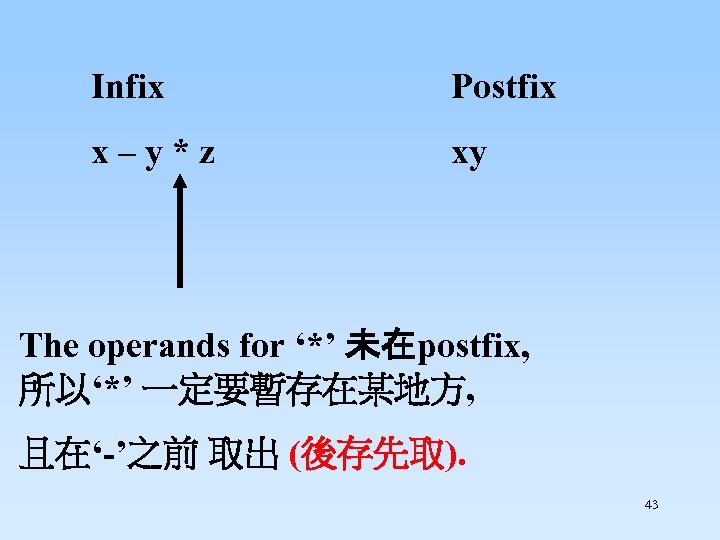 Infix x – y * z Postfix xy The operands for ‘*’ 未在postfix, 所以‘*’ 一定要暫存在某地方, 且在‘-’之前 取出 (後存先取). 43
Infix x – y * z Postfix xy The operands for ‘*’ 未在postfix, 所以‘*’ 一定要暫存在某地方, 且在‘-’之前 取出 (後存先取). 43
 Infix x – y * z Postfix xyz 44
Infix x – y * z Postfix xyz 44
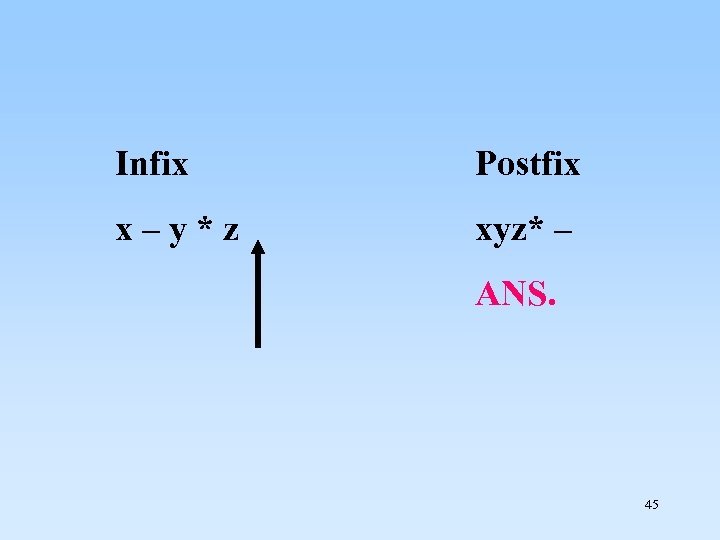 Infix x – y * z Postfix xyz* – ANS. 45
Infix x – y * z Postfix xyz* – ANS. 45
 As another test case, we start with x*y-z. After moving ‘x’ to postfix, ‘*’ is temporarily saved, and then ‘y’ 被加到postfix. What happens when ‘-’ is accessed? Infix x * y – z Postfix xy 46
As another test case, we start with x*y-z. After moving ‘x’ to postfix, ‘*’ is temporarily saved, and then ‘y’ 被加到postfix. What happens when ‘-’ is accessed? Infix x * y – z Postfix xy 46
 47
47
 暫時儲存處是: Stack! Here is the strategy (pseudo-code) for maintaining the stack: 48
暫時儲存處是: Stack! Here is the strategy (pseudo-code) for maintaining the stack: 48
 49
49
 口 訣 : if Infix Greater, Push 50
口 訣 : if Infix Greater, Push 50
 Convert from infix to postfix: Infix a + b * c / d - e Postfix 51
Convert from infix to postfix: Infix a + b * c / d - e Postfix 51
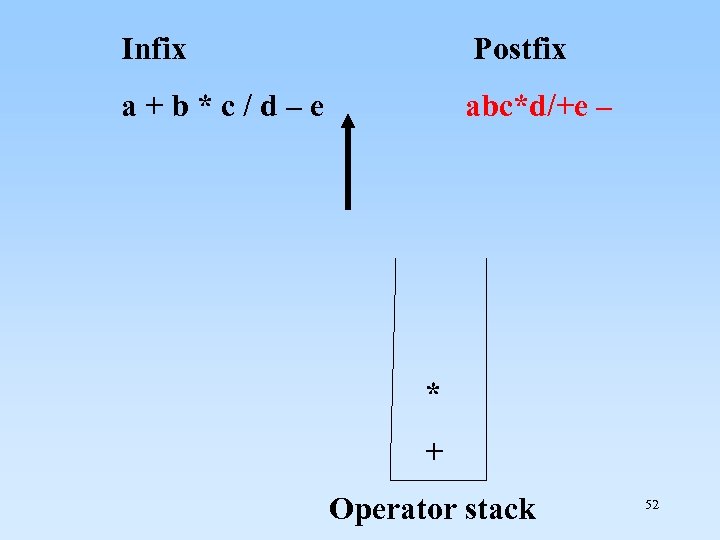 Infix Postfix a + b * c / d – e abc*d/+e – * + Operator stack 52
Infix Postfix a + b * c / d – e abc*d/+e – * + Operator stack 52
 53
53
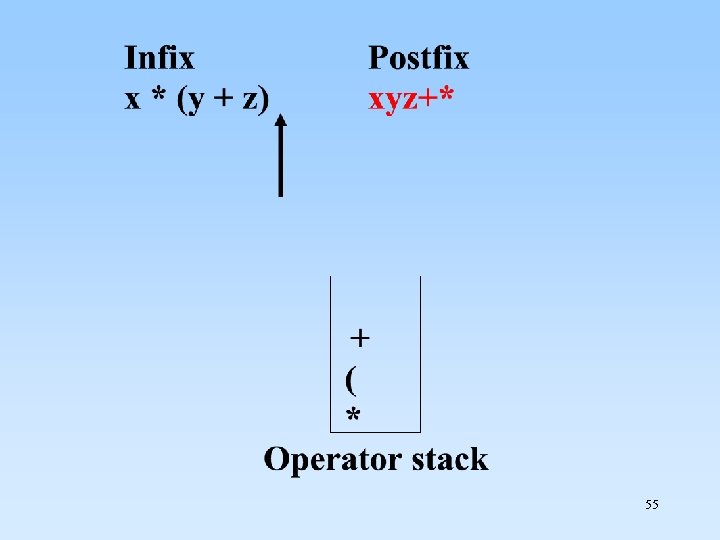
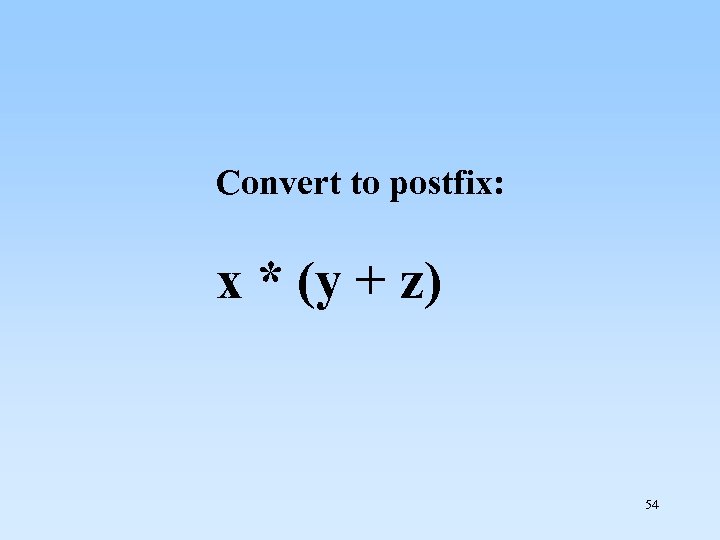 Convert to postfix: x * (y + z) 54
Convert to postfix: x * (y + z) 54
 55
55
 56
56
 57
57
 58
58
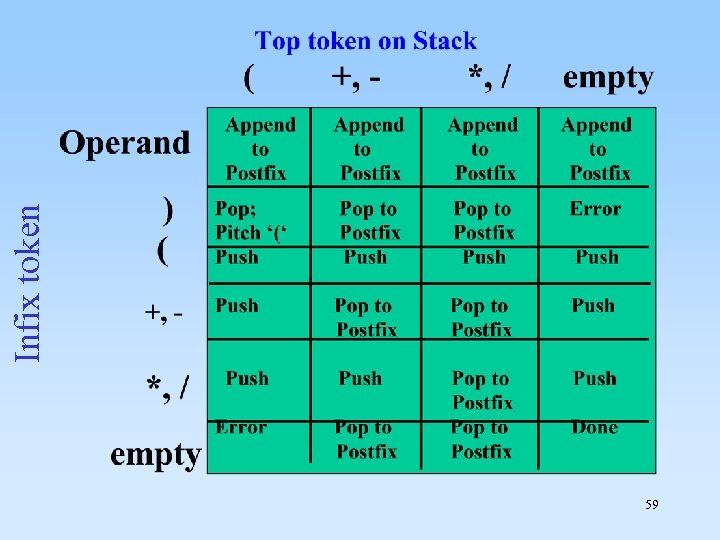 59 Infix token
59 Infix token
 Tokens 60
Tokens 60
 61
61
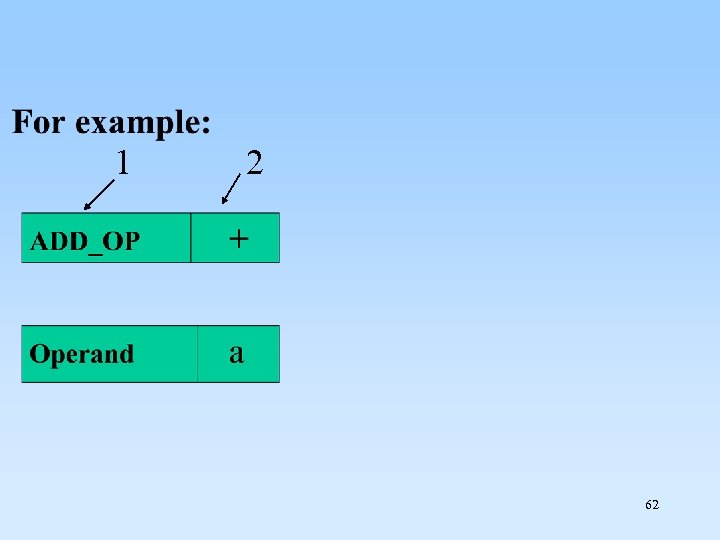 1 2 62
1 2 62
 8. 1. 5 Prefix(前置式) Notation 63
8. 1. 5 Prefix(前置式) Notation 63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
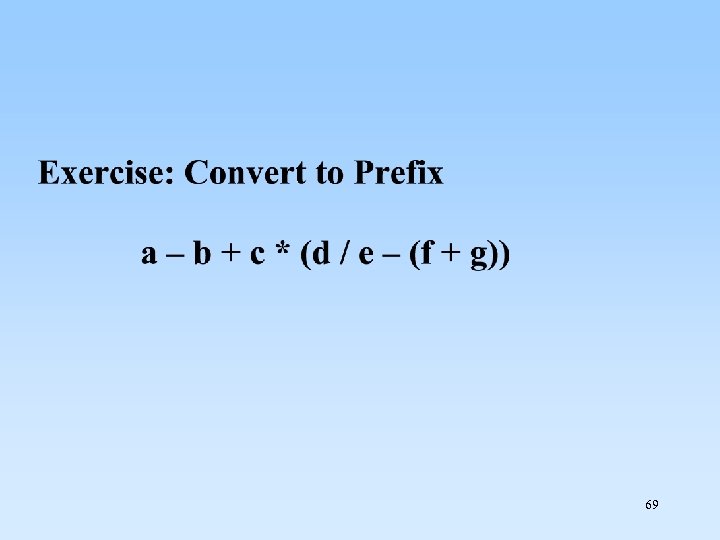 69
69
 8. 2 Queues 70
8. 2 Queues 70
 71
71
 回想一下; STACK: (Last-In-First-Out) LIFO 72
回想一下; STACK: (Last-In-First-Out) LIFO 72
 Enqueue “張三” 73
Enqueue “張三” 73
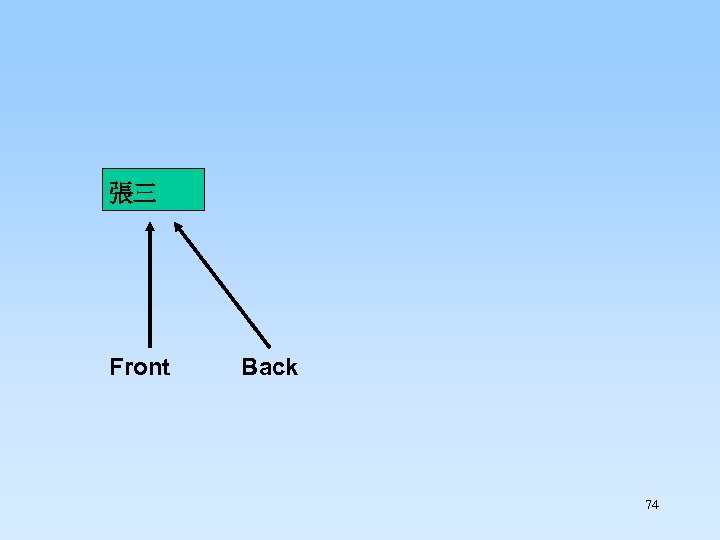 張三 Front Back 74
張三 Front Back 74
 Enqueue “李四” 75
Enqueue “李四” 75
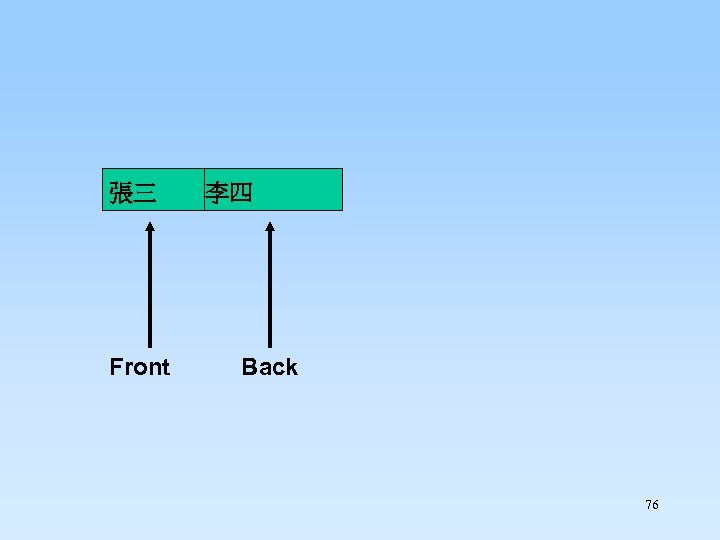 張三 Front 李四 Back 76
張三 Front 李四 Back 76
 Enqueue “王五” 77
Enqueue “王五” 77
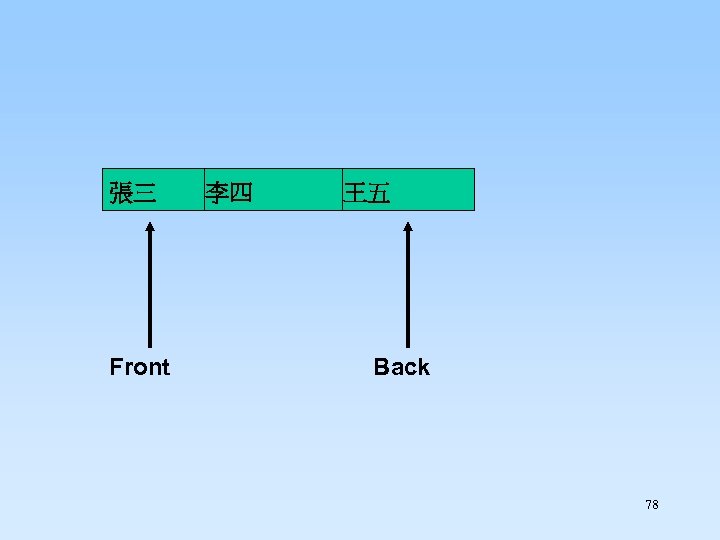 張三 Front 李四 王五 Back 78
張三 Front 李四 王五 Back 78
 Dequeue 79
Dequeue 79
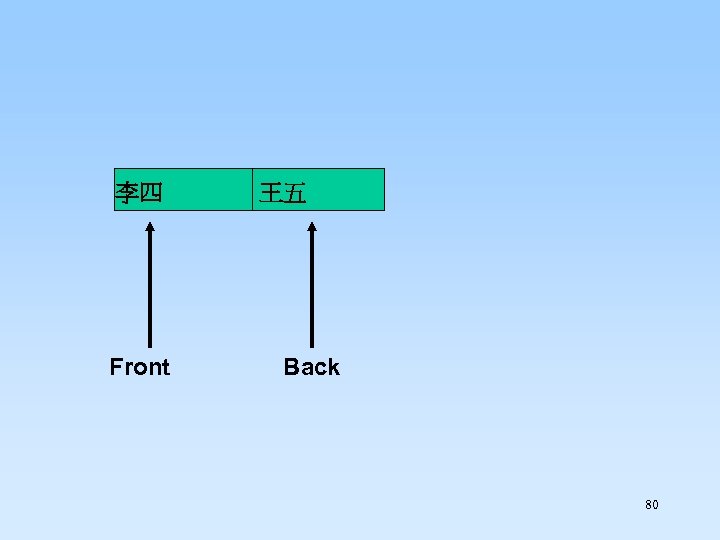 李四 Front 王五 Back 80
李四 Front 王五 Back 80
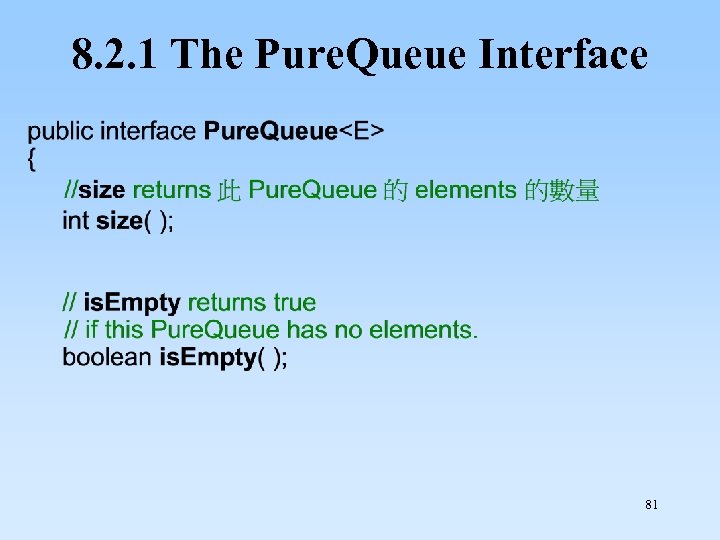 8. 2. 1 The Pure. Queue Interface 81
8. 2. 1 The Pure. Queue Interface 81
 82
82
 83
83
 84
84
 8. 2. 2 Implementations of the Pure. Queue Interface 85
8. 2. 2 Implementations of the Pure. Queue Interface 85
 86
86
 87
87
 Heavy Inheritance Tax 在 class reuse 實務上, 被reuse的class要有完整method description developers 清楚了解後, 再寫dummy code (如上述get) 來override 不能reuse的methods. 這是相當沉重的負擔,有如稅負,故叫 Inheritance Tax. 88
Heavy Inheritance Tax 在 class reuse 實務上, 被reuse的class要有完整method description developers 清楚了解後, 再寫dummy code (如上述get) 來override 不能reuse的methods. 這是相當沉重的負擔,有如稅負,故叫 Inheritance Tax. 88
 89
89
 90
90
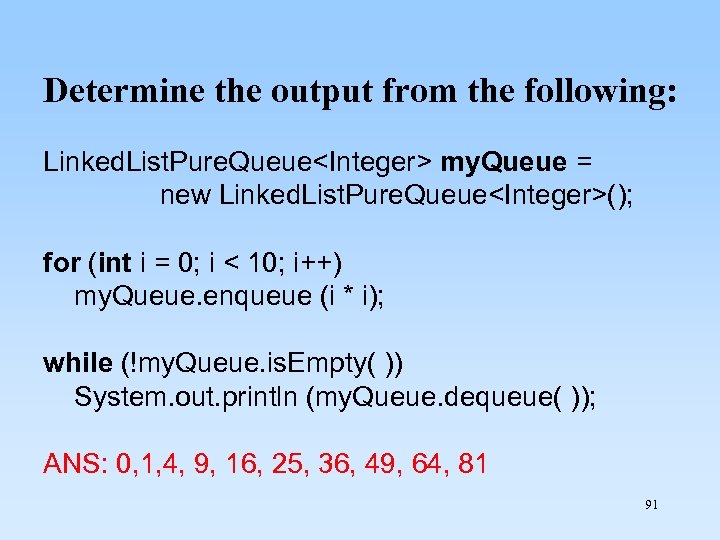 Determine the output from the following: Linked. List. Pure. Queue
Determine the output from the following: Linked. List. Pure. Queue
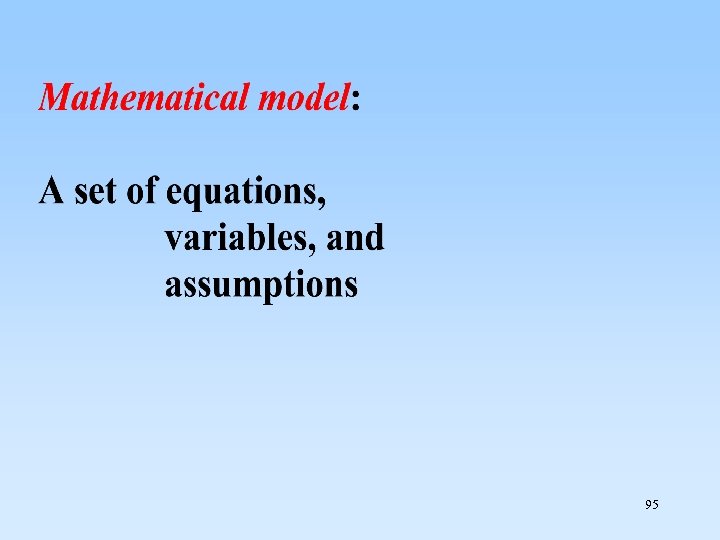
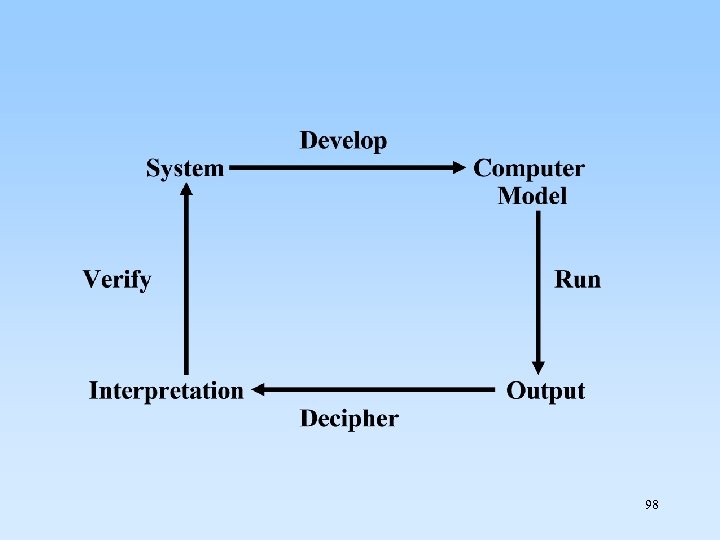
 8. 2. 3 Computer Simulation(模擬) SYSTEM 是由互動的部分 (interacting parts) 所組成 92
8. 2. 3 Computer Simulation(模擬) SYSTEM 是由互動的部分 (interacting parts) 所組成 92
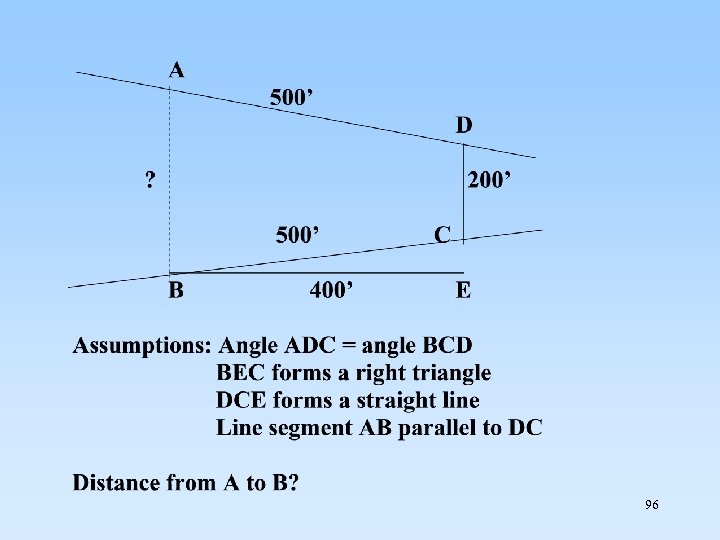
 model 是 system的簡化. 建構model 是為了研究 system 93
model 是 system的簡化. 建構model 是為了研究 system 93
 94
94
 95
95
 96
96
 97
97
 98
98
 99
99
 100
100
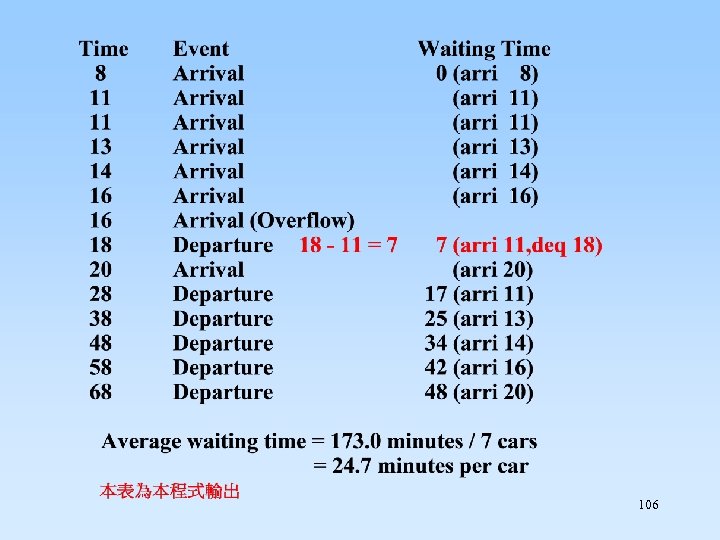
 8. 2. 4 Queue Application: A Simulated Car Wash 101
8. 2. 4 Queue Application: A Simulated Car Wash 101
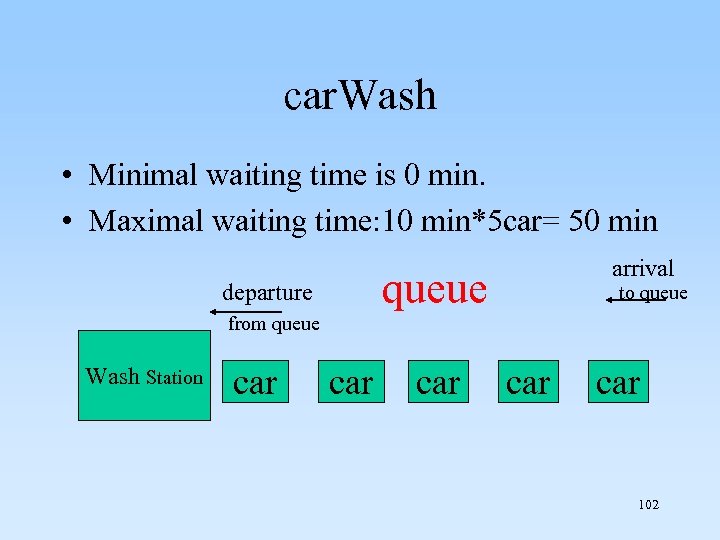 car. Wash • Minimal waiting time is 0 min. • Maximal waiting time: 10 min*5 car= 50 min arrival queue departure to queue from queue Wash Station car car car 102
car. Wash • Minimal waiting time is 0 min. • Maximal waiting time: 10 min*5 car= 50 min arrival queue departure to queue from queue Wash Station car car car 102
 103
103
 104
104
 105
105
 106
106
 107
107
 108
108
 109
109
 110
110
 111
111
 112
112
 113
113
 114
114
 115
115
 Car class • • • /* Car * 初始化 Car object * 為指定的下次到達時間 */ public Car (int next. Arrival. Time) /* get. Arrival. Time • /* 記錄 the just dequeued car 的 arrival time. • * @return the arrival time of this car • */ • public int get. Arrival. Time() 116
Car class • • • /* Car * 初始化 Car object * 為指定的下次到達時間 */ public Car (int next. Arrival. Time) /* get. Arrival. Time • /* 記錄 the just dequeued car 的 arrival time. • * @return the arrival time of this car • */ • public int get. Arrival. Time() 116
 117
117
 118
118
 119
119
 120
120
 121
121
 122
122
 123
123
 124
124
 125
125
 126
126
 127
127
 public class Car{ protected int arrival. Time; public Car(){}//default constructor, //for the sake of sub-classses of Car public Car (int next. Arrival. Time){ arrival. Time=next. Arrival. Time; }// constructor with int parameter public int get. Arrival. Time(){ return arrival. Time; }/*get. Arrival. Time*/ }/*Car*/ 128
public class Car{ protected int arrival. Time; public Car(){}//default constructor, //for the sake of sub-classses of Car public Car (int next. Arrival. Time){ arrival. Time=next. Arrival. Time; }// constructor with int parameter public int get. Arrival. Time(){ return arrival. Time; }/*get. Arrival. Time*/ }/*Car*/ 128
 129
129
 130
130
 131
131
 A Deque is a “double ended queue” (pronounced as “deck”) that allows inserting and removing from both ends. As a real-world example, a ticket purchasing line acts like a queue, but sometimes somebody who purchased the ticket suddenly comes back to ask something. Because he/she already purchased the ticket, he/she got the privilege to come to the front and ask further questions. Here we need a data structure to add data from front. Also, user can also leave the queue from rear. [edited from web site “stackoverflow”] 132
A Deque is a “double ended queue” (pronounced as “deck”) that allows inserting and removing from both ends. As a real-world example, a ticket purchasing line acts like a queue, but sometimes somebody who purchased the ticket suddenly comes back to ask something. Because he/she already purchased the ticket, he/she got the privilege to come to the front and ask further questions. Here we need a data structure to add data from front. Also, user can also leave the queue from rear. [edited from web site “stackoverflow”] 132
 Python List It is implemented as array, written in C. list 1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2015] list 2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ] print (list 1[0]) physics print (list 2[1: 5]) [2, 3, 4, 5] print (list 2[-1]) 7 133
Python List It is implemented as array, written in C. list 1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2015] list 2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ] print (list 1[0]) physics print (list 2[1: 5]) [2, 3, 4, 5] print (list 2[-1]) 7 133
 Python Tuple is a special list whose elements cannot be changed. tuple 1= (12, 26, 12, 54) print (tuple 1[0]) 12 print (tuple 1[1: 3]) 26 12 print (tuple 1[-1]) 54 tuple 1[0] = 15 Type Error: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment. 134
Python Tuple is a special list whose elements cannot be changed. tuple 1= (12, 26, 12, 54) print (tuple 1[0]) 12 print (tuple 1[1: 3]) 26 12 print (tuple 1[-1]) 54 tuple 1[0] = 15 Type Error: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment. 134
![Python Set set 1 = set ( [12, 26, 12, 54] ) print Python Set set 1 = set ( [12, 26, 12, 54] ) print](https://present5.com/presentation/668346b5cf3861b4495ab4d24487318c/image-135.jpg) Python Set set 1 = set ( [12, 26, 12, 54] ) print (set 1) set ([12, 26, 54]) set 1. add(32) set ([32, 12, 26, 54]) print (12 in set 1) True print (13 in set 1) False 135
Python Set set 1 = set ( [12, 26, 12, 54] ) print (set 1) set ([12, 26, 54]) set 1. add(32) set ([32, 12, 26, 54]) print (12 in set 1) True print (13 in set 1) False 135
 Python Dictionary It is similar to Java Map with key: value pairs. dict 1= { ‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2, ‘c’: 1} print (dict 1) { ‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2, ‘c’: 1} print (dict 1. get(‘a’) ) 1 del dict 1[‘c’] print (dict 1) { ‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2} 136
Python Dictionary It is similar to Java Map with key: value pairs. dict 1= { ‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2, ‘c’: 1} print (dict 1) { ‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2, ‘c’: 1} print (dict 1. get(‘a’) ) 1 del dict 1[‘c’] print (dict 1) { ‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 2} 136


