43b0a0d36f56610bb670ad8af2fac2df.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Chapter 8 Political Parties Develop

Vocabulary Sections 1 & 2 Cabinet Tariff Neutral

The Big Idea As the county’s first President, George Washington worked to earn respect for the new government of the United States.

George Washington had been elected the first President in 1789. Following his inauguration, the official swearing in ceremony, he selected his Cabinet (unwritten constitution), officials to head departments of the executive branch. Two crucial posts were filled by Alexander Hamilton, as Secretary of the Treasury and Thomas Jefferson, Secretary of State.

Jefferson was more concerned with domestic affairs, a nations internal matters, than with foreign affairs. He did not fully trust the government, resigned in 1793, and eventually became a harsh critic of Washington.

Hamilton was a staunch Federalist who believed in strong government power to get things done. Hamilton created a financial plan to get the country out of debt. The plan was a success.

During his first administration, or term of office, Washington and his officials established precedents, or rules, examples, or traditions to be followed by others. Aware he would be doing this, Washington worked to establish a tone of dignity, and even though he was often surrounded by elaborate ceremonies, he remained a very popular president.

Big Idea During the 1790 s, Americas became divided over how much power should be held by the federal government.

When Secretary of Treasury Alexander Hamilton persuaded Congress to assume the war debts of the states, he strengthened the power of the national government. To raise money, Hamilton placed a tariff, or tax on imported goods, on whiskey.

Opponents, such as Thomas Jefferson, favored a less active central government. Jefferson believed in strict construction of the Constitution-that the national government could not do anything unless it was specifically stated in the Constitution.

Hamilton favored loose construction of the Constitution-that the government could not do anything not specifically forbidden in the Constitution.

Hamilton vs. Jefferson *Strict Construction- Government should NOT do anything that the Constitution did not specially say it could do. (Jefferson) *Loose Construction- The government could do anything that the Constitution did NOT say it could do. (Hamilton)

Americans' idea on foreign policy were also split. Some people supported the radical French Revolution. Others opposed it as too violent. When France and Britain went to war, the United States remained neutral, not taking either side. Washington felt the United States needed time to gain economic and military strength.

However, to remain friendly with Britain, Washington sent John Jay to England, and he negotiated Jay’s Treaty. The treaty called for British to leave forts in the Northwest Territory in exchange for expanded trade. Many Americans felt it was a betrayal of revolutionary ideals.

Meanwhile, in western Pennsylvania, a group of farmers revolted in protest of the whiskey tariff. Washington sent an army (state militia) to put down the Whiskey Rebellion, showing the American citizens and the world that the national government was committed to enforcing its laws.

Critics, including Jefferson, formed a new political party, a group of people who seek to be elected to office. These Jeffersonian Republicans made Jefferson their presidential candidate in the 1796 election. Jefferson lost to the Federalist candidate, John Adams.

Federalist versus Jeffersonian Republicans Federalists Jeffersonian Republicans Led by Washington and Hamilton Led by Jefferson Favor strong central government Favor weak central government Support new taxes and tariffs Oppose new taxes and tariffs Support more powerful army and Against large army and navy Pro-British Pro-French Pro-business Pro-agriculture

Quiz Alexander Hamilton supported – A. Declaring tariffs illegal – B. Establishing the nation's capital in Philadelphia – C. Having the federal government take on the states’ debts – D. Ending the tax on whiskey The creation of the presidential cabinet and political parties are examples of – – A. B. C. D. The unwritten constitution Separation of Powers The elastic clause Judicial review

An example of the use of the unwritten constitution is the creation of the – A. – B. – C. – D. Presidential veto United States Navy Federal postal system President’s cabinet

President George Washington pursued a foreign policy of neutrality during his administration primarily because he believed that – A. The United States needed time to gain economic and military strength – B. Treaties were prohibited by the Constitution – C. The United States should not expand by force – D. Alliances should be established with both France and England

The decision of President George Washington to use the state militia to put down the Whiskey Rebellion in 1794 demonstrated that the – A. States were still the dominant power in the new nation – B. President was becoming a military dictator – C. Federal Government had no authority to impose an excise tax – D. New National Government intended to enforce Federal laws

Section 3 Vocabulary and Important Terms XYZ affair Alien and Sedition Acts Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions

Big Idea Jefferson’s election in 1800 represented the nation’ first transition of power from one political party to another.

Like Washington, John Adams was a Federalist, and he faced the challenge to leading a nation that was politically divided. Conflicts with France, such as the XYZ affair (when the French government tried to bribe United States officials) pg 161, helped the Federalists expand the power of the government.

They increased the size of the army and imposed higher taxes. They also passed the Alien and Sedition Acts in 1798, under which the President could imprison or deport aliens and fine or imprison Americans who criticized the government.

Jeffersonian Republicans declared these acts unconstitutional, claiming that he acts violated freedom of speech. They promoted their views in the Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions, which said that the states, not the federal government, could decide what laws were unconstitutional.

Virginia and Kentucky proposed that idea of nullification, that if a state declared a federal as unconstitutional, they could also declare that law as “null and void” within the state.

As tensions increased, President Adams became unpopular with his own party for making peace with France. Many people also viewed the Alien and Sedition Acts as unjustifiable. The election of 1800 was a smear campaign in which each party brutally insulated the oppositions candidate.

The outcome was the Jefferson defeated the Adams. More important, however, was that fact that power was peacefully transferred from one political party to another.

Section 4 and 5 Vocabulary Embargo Judicial review Bureaucracy

Court Cases – Marbury v. Madison = This decision established the principle of judicial review, that is, the power of the Supreme Court to decided whether laws passed by Congress are constitutional. – Flecher v. Peck = established the right of the Supreme Court to strike down state laws that disagreed with the federal Constitution. – Mc. Culloch v. Maryland = the Supreme Court of the United States, in which the Court determined the separate states could not tax the federal government.

As President, Jefferson set out to limit the power of the government. He reduced the size of the bureaucracy, the departments and workers that make of the federal government, and reduced taxes.
He also supported the Supreme Court decision in the case of Marbury v. Madison. This decision established the principle of judicial review, that is, the power of the Supreme Court to decided whether laws passed by Congress are constitutional.

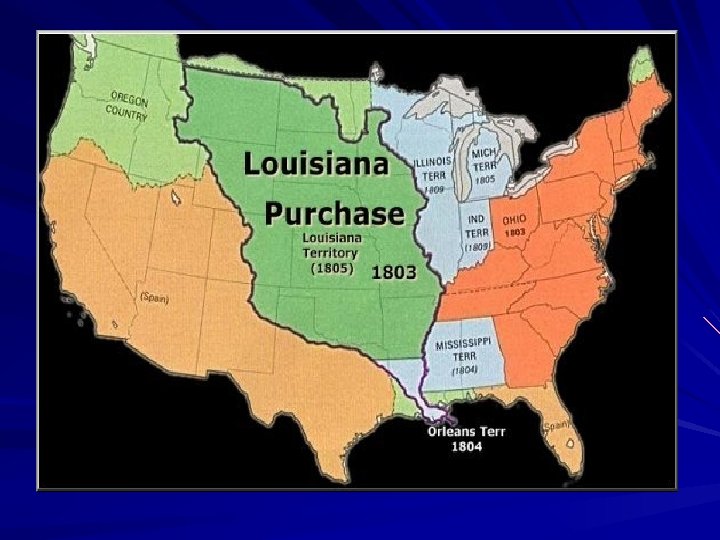
Although Jefferson opposed the development of a strong central government, he used the government's power and money to further his policies. He encouraged Americans to buy land in the West, and he approved a western land deal with France call the Louisiana Purchase, which dramatically increased the size of the United States. And more importantly allowed the United States to control the port of New Orleans.
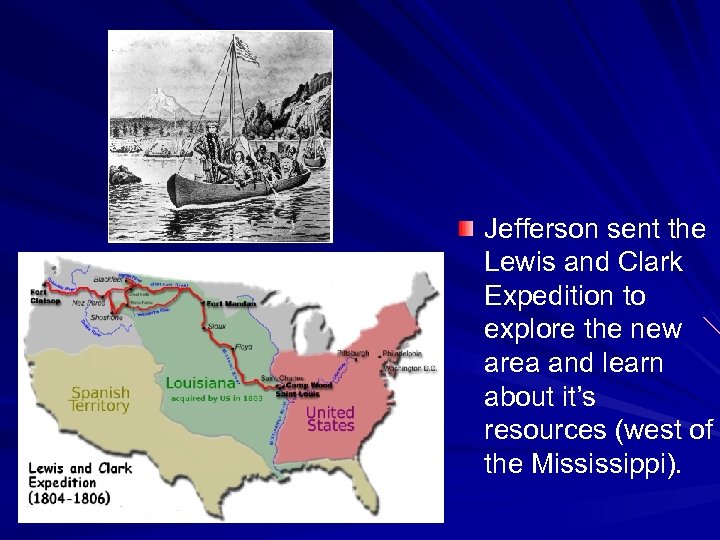
Jefferson sent the Lewis and Clark Expedition to explore the new area and learn about it’s resources (west of the Mississippi).

Jefferson’s policies were popular, and he had kept peace with Europe. In the 1804 election, Jefferson’s only true rival, Alexander Hamilton, was killed in a duel and Jefferson won a landslide victory.

In his second term, however, he faced growing conflict with Britain and France over their seizure of American ships. In 1807 Jefferson imposed an embargo, or restriction of trade with Britain and France. The embargo did not hurt those nations, but it did hurt American merchants and traders. In the 1808 election James Madison, a Jeffersonian Republican, became President, and Jefferson retired as an unpopular figure.

A geographic and economic motivation for the Louisiana Purchase (1803) was the desire to – A. – B. – C. – D. Annex California Secure land for Erie Canal Control the port of New Orleans Own all of the Great Lakes

A major goal of the Lewis and Clark expedition was to – A. Gather information about natural resources west of the Mississippi. – B. Gain control over the Native Americans living west of the Mississippi – C. Drive the Spanish out of the lands of the Southwest – D. Drive the French out of fur trading forts along the Mississippi.

Jefferson’s main goal as President was to – A. Increase the power and size of government – B. Raise taxes and tariffs. – C. Decrease the power and size of government. – D. Increase the size of the United States.
43b0a0d36f56610bb670ad8af2fac2df.ppt