c531eb6efbc607237106a5b9c813c3b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Chapter 8 Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 1
Chapter 8 Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 1
 Learning Objectives • Introduce the concepts of aggregate demand aggregate supply. • Distinguish between short-run and long- run aggregate supply. • Discuss the relationship that exists between the aggregate expenditures model and the aggregate demand curve. Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 2
Learning Objectives • Introduce the concepts of aggregate demand aggregate supply. • Distinguish between short-run and long- run aggregate supply. • Discuss the relationship that exists between the aggregate expenditures model and the aggregate demand curve. Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 2
 Learning Objectives (cont. ) • Combine the aggregate demand aggregate supply curves to provide a model of macroeconomic equilibrium. • Discuss how the aggregate demand– aggregate supply model may be used to analyse the circumstances outlined in Chapter 5. • Contrast demand-pull and cost-push inflation. Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 3
Learning Objectives (cont. ) • Combine the aggregate demand aggregate supply curves to provide a model of macroeconomic equilibrium. • Discuss how the aggregate demand– aggregate supply model may be used to analyse the circumstances outlined in Chapter 5. • Contrast demand-pull and cost-push inflation. Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 3
 Learning Objectives (cont. ) • Discuss the reasons why the general level of prices is downwards ‘sticky’— the ratchet effect. • Explain the impact of price-level changes on the size of the multiplier. Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 4
Learning Objectives (cont. ) • Discuss the reasons why the general level of prices is downwards ‘sticky’— the ratchet effect. • Explain the impact of price-level changes on the size of the multiplier. Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 4
 Aggregate Demand (AD) • Represents the amount of goods and services that consumers, businesses, government and foreign buyers are willing and able to buy at various price levels Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 5
Aggregate Demand (AD) • Represents the amount of goods and services that consumers, businesses, government and foreign buyers are willing and able to buy at various price levels Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 5
 AD Curve The AD curve is downsloping due to: • Interest-rate effect • Real-balances effect (wealth effect) • Foreign-purchases effect Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 6
AD Curve The AD curve is downsloping due to: • Interest-rate effect • Real-balances effect (wealth effect) • Foreign-purchases effect Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 6
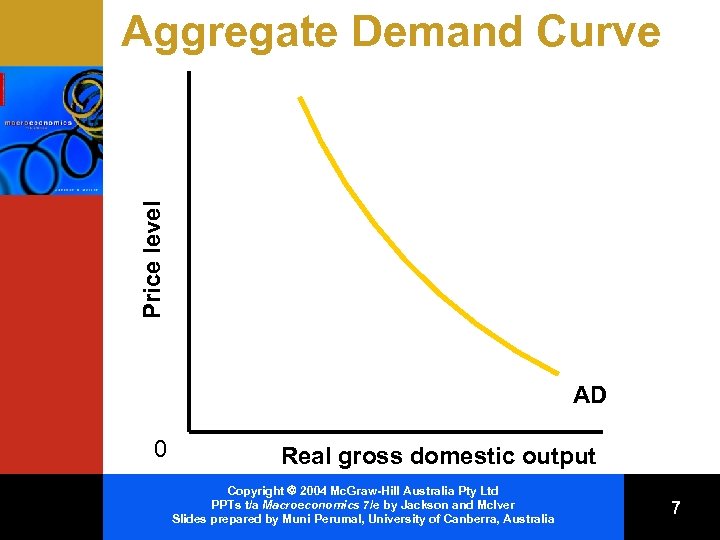 Price level Aggregate Demand Curve AD 0 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 7
Price level Aggregate Demand Curve AD 0 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 7
 Interest-Rate Effect • Rising price level causes higher nominal interest rates, which causes reduction in certain kinds of consumption and investment spending —most importantly, investment spending Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 8
Interest-Rate Effect • Rising price level causes higher nominal interest rates, which causes reduction in certain kinds of consumption and investment spending —most importantly, investment spending Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 8
 Real-Balances Effect • Also known as ‘wealth effect’ • At a higher price level, the real value or purchasing power of the accumulated financial assets held by the public falls (real wealth falls), leading to a fall in consumption spending Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 9
Real-Balances Effect • Also known as ‘wealth effect’ • At a higher price level, the real value or purchasing power of the accumulated financial assets held by the public falls (real wealth falls), leading to a fall in consumption spending Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 9
 Foreign-Purchases Effect • Higher domestic prices cause the relative price of foreign goods (local goods) to decrease (increase) • This causes increased imports and decreased exports, resulting in a fall in net exports Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 10
Foreign-Purchases Effect • Higher domestic prices cause the relative price of foreign goods (local goods) to decrease (increase) • This causes increased imports and decreased exports, resulting in a fall in net exports Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 10
 Deriving the AD Curve • Aggregate expenditure model – drawn at a constant price level • Aggregate demand model – real GDP at various price levels Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 11
Deriving the AD Curve • Aggregate expenditure model – drawn at a constant price level • Aggregate demand model – real GDP at various price levels Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 11
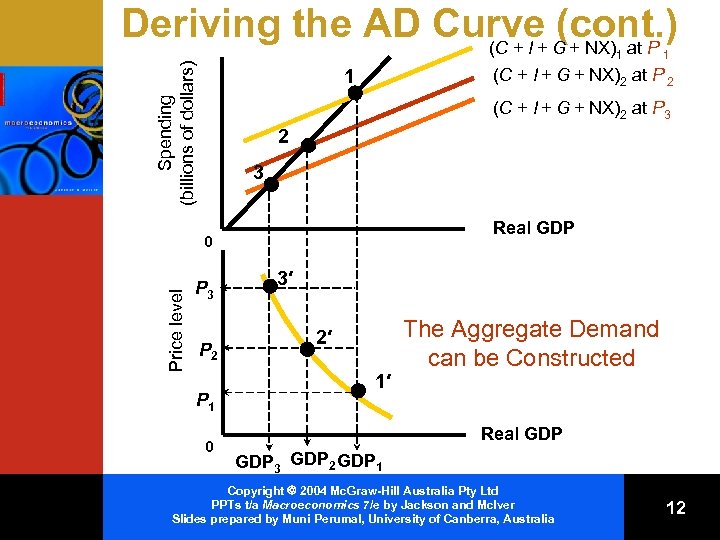 Deriving the AD Curve G + NX) at P (cont. ) (C + I + Spending (billions of dollars) 1 (C + I + G + NX)2 at P 2 1 (C + I + G + NX)2 at P 3 2 3 Real GDP 0 Price level 1 P 3 P 2 P 1 0 3′ 2′ 1′ The Aggregate Demand can be Constructed Real GDP 3 GDP 2 GDP 1 Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 12
Deriving the AD Curve G + NX) at P (cont. ) (C + I + Spending (billions of dollars) 1 (C + I + G + NX)2 at P 2 1 (C + I + G + NX)2 at P 3 2 3 Real GDP 0 Price level 1 P 3 P 2 P 1 0 3′ 2′ 1′ The Aggregate Demand can be Constructed Real GDP 3 GDP 2 GDP 1 Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 12
 Non-Price Determinants of Aggregate Demand • Results in shift in the AD curve • Changes in consumer spending – Consumer wealth – Consumer expectations – Consumer indebtedness – Taxes Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 13
Non-Price Determinants of Aggregate Demand • Results in shift in the AD curve • Changes in consumer spending – Consumer wealth – Consumer expectations – Consumer indebtedness – Taxes Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 13
 Non-Price Determinants of Aggregate Demand (cont. ) • Changes in investment spending – Interest rates – Profit expectation on investment projects – Business taxes – Technology – Degree of excess capacity • Changes in Government spending Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 14
Non-Price Determinants of Aggregate Demand (cont. ) • Changes in investment spending – Interest rates – Profit expectation on investment projects – Business taxes – Technology – Degree of excess capacity • Changes in Government spending Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 14
 Non-Price Determinants of Aggregate Demand (cont. ) Changes in net export spending: • Growth in foreign GDP • The level of the exchange rates Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 15
Non-Price Determinants of Aggregate Demand (cont. ) Changes in net export spending: • Growth in foreign GDP • The level of the exchange rates Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 15
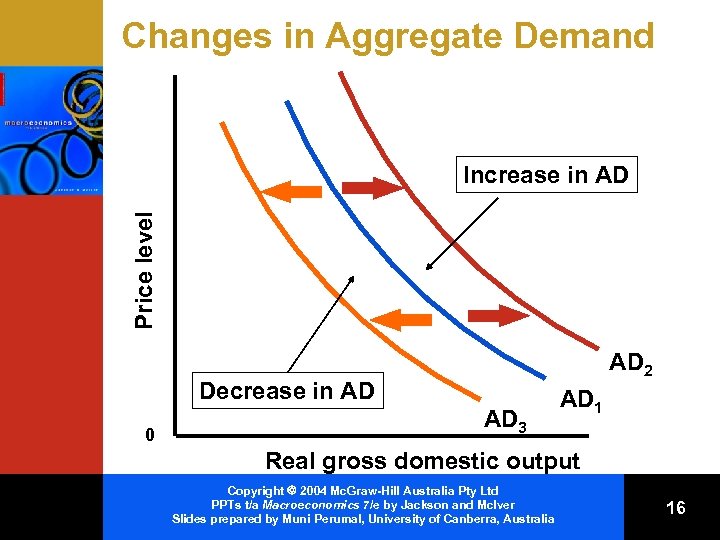 Changes in Aggregate Demand Price level Increase in AD AD 2 Decrease in AD 0 AD 3 AD 1 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 16
Changes in Aggregate Demand Price level Increase in AD AD 2 Decrease in AD 0 AD 3 AD 1 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 16
 Shifts of AD • Caused by changes of non-price determinants • Movements left or right • Degree of shift affected by the multiplier • Shift in AD = change in spending times the multiplier Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 17
Shifts of AD • Caused by changes of non-price determinants • Movements left or right • Degree of shift affected by the multiplier • Shift in AD = change in spending times the multiplier Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 17
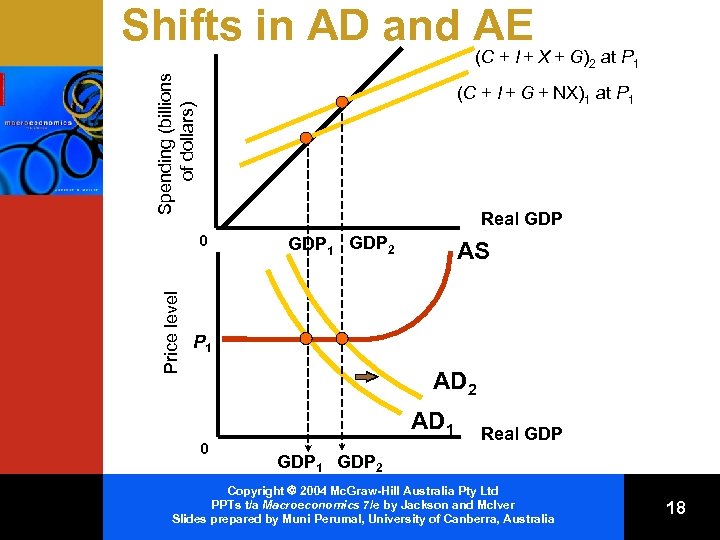 Shifts in AD and AE Spending (billions of dollars) (C + I + X + G)2 at P 1 (C + I + G + NX)1 at P 1 Real GDP Price level 0 GDP 1 GDP 2 AS P 1 AD 2 AD 1 0 Real GDP 1 GDP 2 Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 18
Shifts in AD and AE Spending (billions of dollars) (C + I + X + G)2 at P 1 (C + I + G + NX)1 at P 1 Real GDP Price level 0 GDP 1 GDP 2 AS P 1 AD 2 AD 1 0 Real GDP 1 GDP 2 Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 18
 Aggregate Supply (AS) • Indicates the level of real GDP that will be produced at each possible price level Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 19
Aggregate Supply (AS) • Indicates the level of real GDP that will be produced at each possible price level Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 19
 Short-Run Period • Short run is a period in which input prices, particularly nominal wages remain fixed while other prices change • Input prices are fixed due to: workers not being aware of higher or lower prices – existence of fixed wage contracts – Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 20
Short-Run Period • Short run is a period in which input prices, particularly nominal wages remain fixed while other prices change • Input prices are fixed due to: workers not being aware of higher or lower prices – existence of fixed wage contracts – Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 20
 Long-Run Period • This is a period in which input prices— wages etc. , are fully responsive to changes in the price level • Workers are freed from existing wage contracts and can negotiate new nominal wages and salaries Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 21
Long-Run Period • This is a period in which input prices— wages etc. , are fully responsive to changes in the price level • Workers are freed from existing wage contracts and can negotiate new nominal wages and salaries Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 21
 Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve • Upward sloping and is constructed on the basis of two assumptions: – a given price level – nominal wages have been established on the expectations that the given price level will persist Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 22
Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve • Upward sloping and is constructed on the basis of two assumptions: – a given price level – nominal wages have been established on the expectations that the given price level will persist Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 22
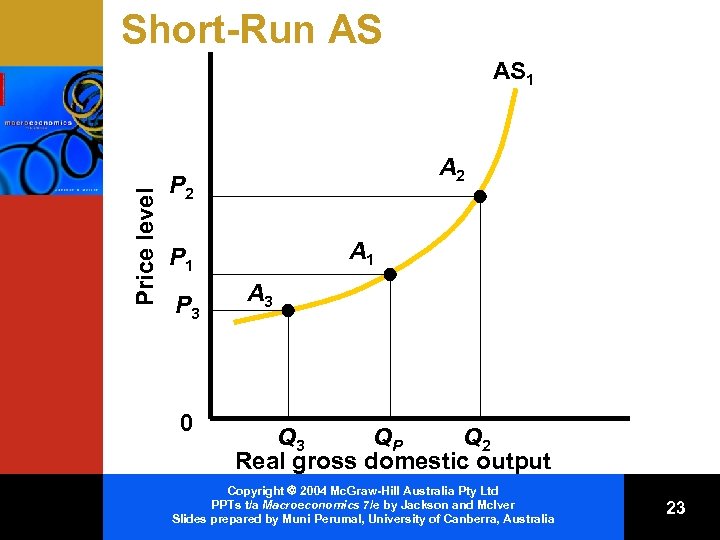 Short-Run AS Price level AS 1 A 2 P 2 A 1 P 3 0 A 3 QP Q 2 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 23
Short-Run AS Price level AS 1 A 2 P 2 A 1 P 3 0 A 3 QP Q 2 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 23
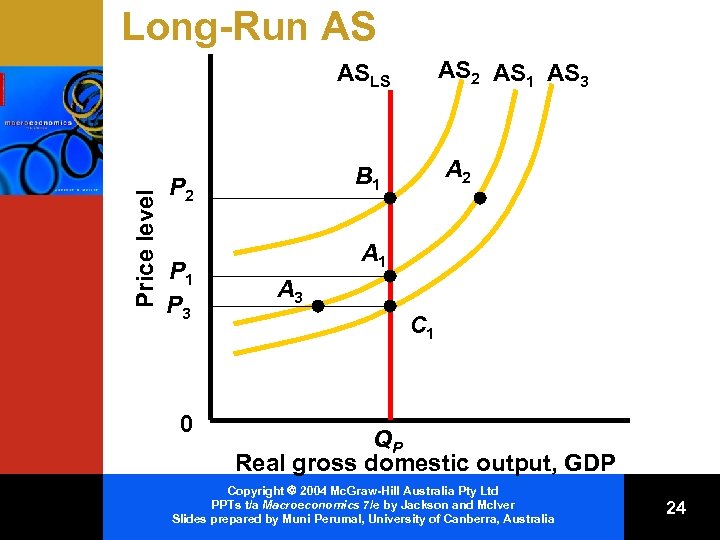 Long-Run AS AS 2 AS 1 AS 3 Price level ASLS P 2 P 1 P 3 0 A 2 B 1 A 3 C 1 QP Real gross domestic output, GDP Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 24
Long-Run AS AS 2 AS 1 AS 3 Price level ASLS P 2 P 1 P 3 0 A 2 B 1 A 3 C 1 QP Real gross domestic output, GDP Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 24
 Non-Price Determinants of AS • Shift the AS curve • Changes in input prices – Domestic resource availability < < land labour capital entrepreneurial ability Imported resource prices – Market power – Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 25
Non-Price Determinants of AS • Shift the AS curve • Changes in input prices – Domestic resource availability < < land labour capital entrepreneurial ability Imported resource prices – Market power – Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 25
 Non-Price Determinants of AS (cont. ) • Changes in productivity • Changes in the legal and institutional environment – Business taxes & subsidies – Government regulation Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 26
Non-Price Determinants of AS (cont. ) • Changes in productivity • Changes in the legal and institutional environment – Business taxes & subsidies – Government regulation Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 26
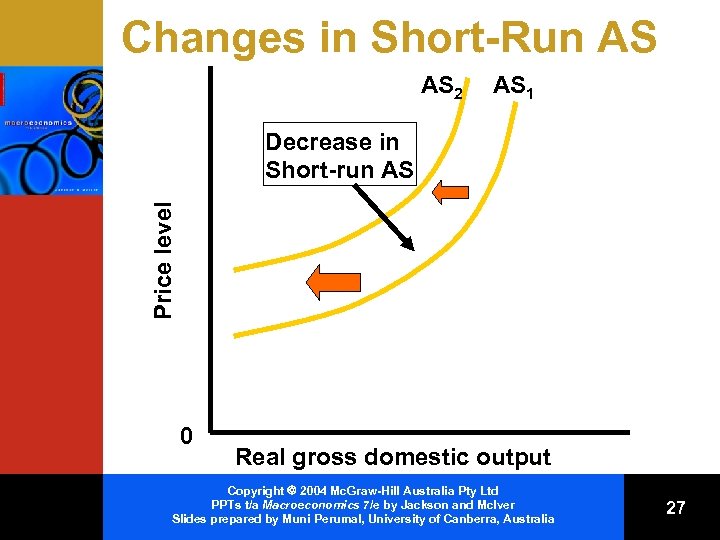 Changes in Short-Run AS AS 2 AS 1 Price level Decrease in Short-run AS 0 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 27
Changes in Short-Run AS AS 2 AS 1 Price level Decrease in Short-run AS 0 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 27
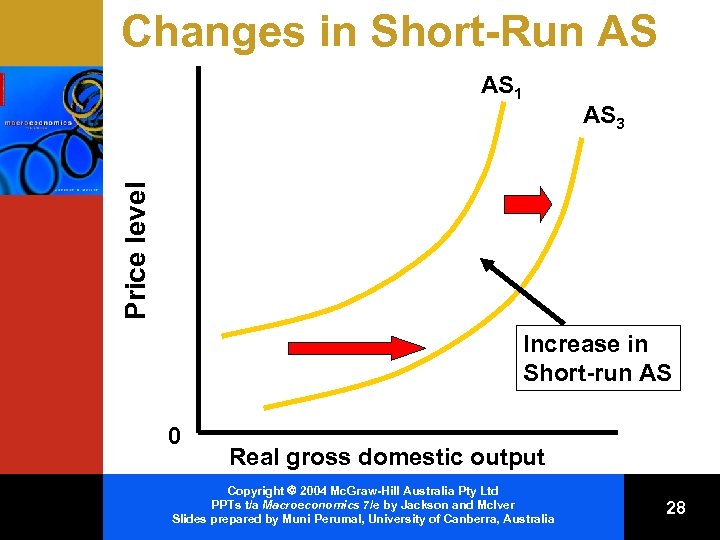 Changes in Short-Run AS AS 3 Price level AS 1 Increase in Short-run AS 0 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 28
Changes in Short-Run AS AS 3 Price level AS 1 Increase in Short-run AS 0 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 28
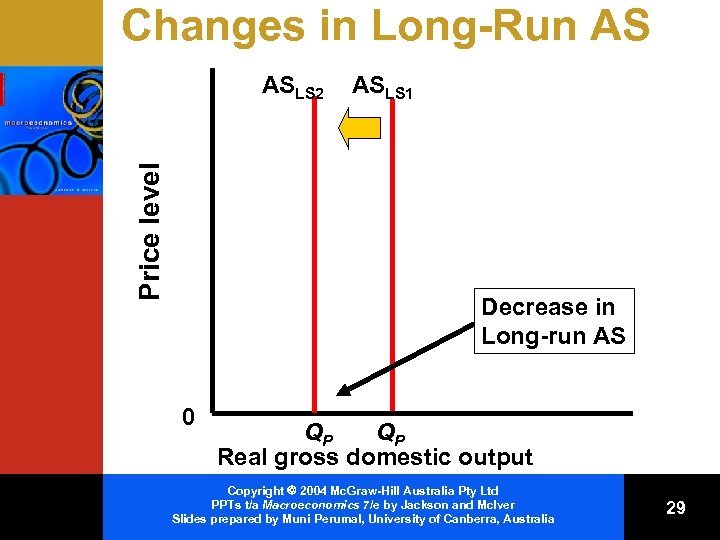 Changes in Long-Run AS Price level ASLS 2 ASLS 1 Decrease in Long-run AS 0 QP QP Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 29
Changes in Long-Run AS Price level ASLS 2 ASLS 1 Decrease in Long-run AS 0 QP QP Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 29
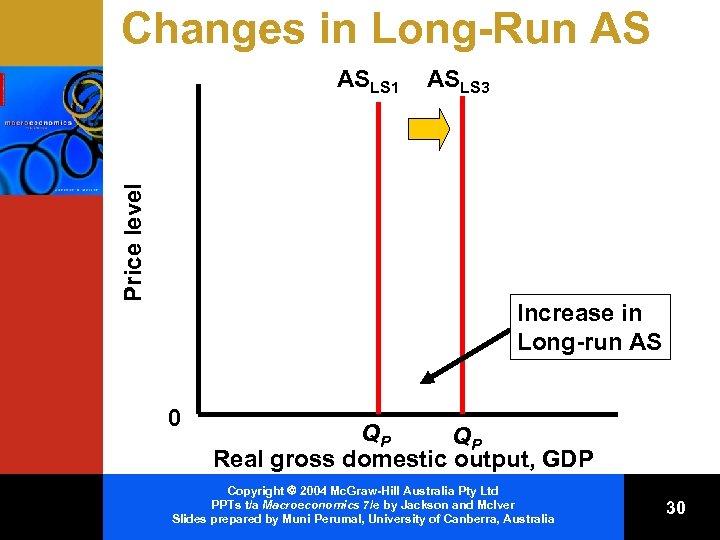 Changes in Long-Run AS Price level ASLS 1 ASLS 3 Increase in Long-run AS 0 QP QP Real gross domestic output, GDP Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 30
Changes in Long-Run AS Price level ASLS 1 ASLS 3 Increase in Long-run AS 0 QP QP Real gross domestic output, GDP Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 30
 Equilibrium • Intersection of AS and AD determines equilibrium real GDP and the price level • At all other points there will be pressure on real GDP and/or prices to change Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 31
Equilibrium • Intersection of AS and AD determines equilibrium real GDP and the price level • At all other points there will be pressure on real GDP and/or prices to change Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 31
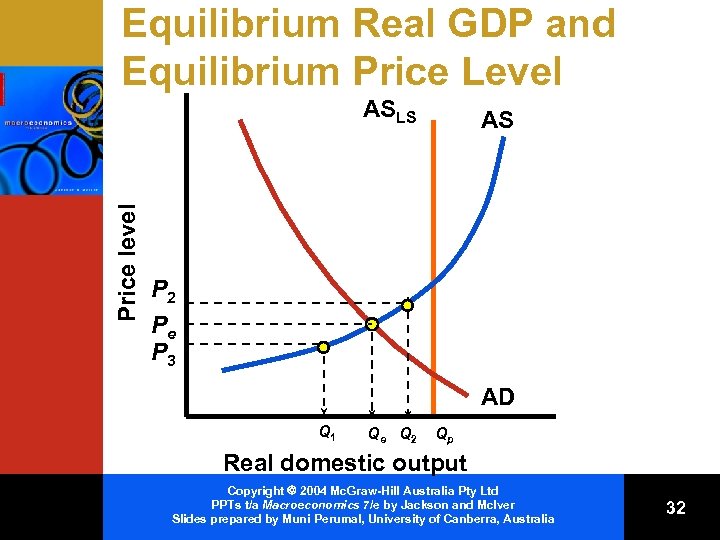 Equilibrium Real GDP and Equilibrium Price Level Price level ASLS AS P 2 Pe P 3 AD Q 1 Qe Q 2 Qp Real domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 32
Equilibrium Real GDP and Equilibrium Price Level Price level ASLS AS P 2 Pe P 3 AD Q 1 Qe Q 2 Qp Real domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 32
 Shift in Aggregate Demand the Price Level • The effects of an increase in aggregate demand on the price level depend upon the position of the shortrun aggregate supply in which it occurs • Demand-pull inflation is a situation of rising prices due to shift in AD Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 33
Shift in Aggregate Demand the Price Level • The effects of an increase in aggregate demand on the price level depend upon the position of the shortrun aggregate supply in which it occurs • Demand-pull inflation is a situation of rising prices due to shift in AD Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 33
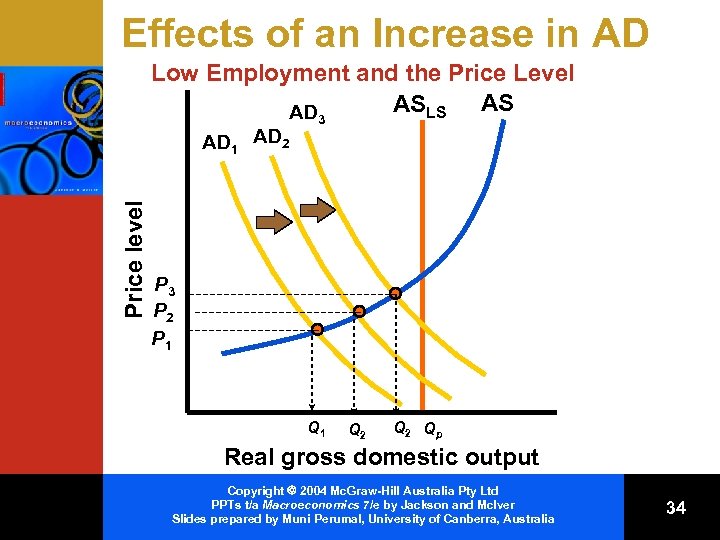 Effects of an Increase in AD Low Employment and the Price Level ASLS AS AD 3 Price level AD 1 AD 2 P 3 P 2 P 1 Q 2 Qp Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 34
Effects of an Increase in AD Low Employment and the Price Level ASLS AS AD 3 Price level AD 1 AD 2 P 3 P 2 P 1 Q 2 Qp Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 34
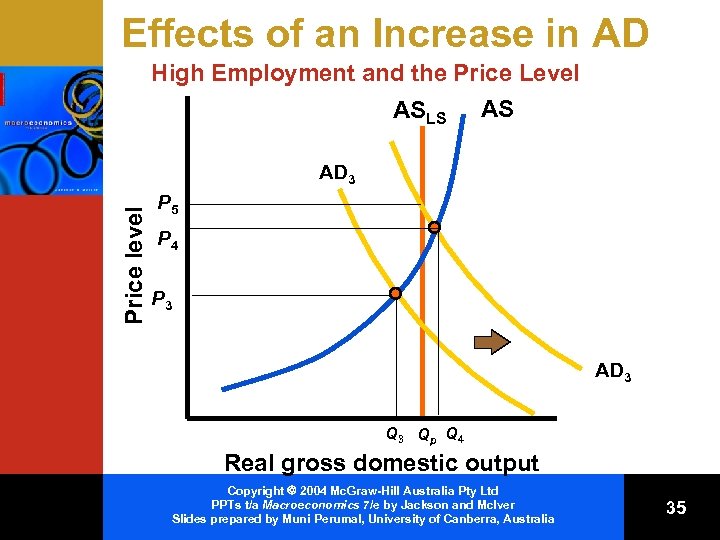 Effects of an Increase in AD High Employment and the Price Level ASLS AS Price level AD 3 P 5 P 4 P 3 AD 3 Qp Q 4 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 35
Effects of an Increase in AD High Employment and the Price Level ASLS AS Price level AD 3 P 5 P 4 P 3 AD 3 Qp Q 4 Real gross domestic output Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 35
 Ratchet Effect • The result of the tendency for prices of both products and resources to be individually ‘sticky’ or inflexible in a downward direction, leading to a loss in downward flexibility of the general level of prices Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 36
Ratchet Effect • The result of the tendency for prices of both products and resources to be individually ‘sticky’ or inflexible in a downward direction, leading to a loss in downward flexibility of the general level of prices Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 36
 Price Inflexibility Causes: • Wage inflexibility • Employers’ interests • Monopoly power • Menu costs Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 37
Price Inflexibility Causes: • Wage inflexibility • Employers’ interests • Monopoly power • Menu costs Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 37
 Shift in Aggregate Supply and the Price Level Causes • Higher production costs shift the AS leftwards, resulting in higher prices and lower real GDP • Leads to cost-push inflation • Adverse shifts in the aggregate supply result in stagflation, a situation of higher prices and higher unemployment Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 38
Shift in Aggregate Supply and the Price Level Causes • Higher production costs shift the AS leftwards, resulting in higher prices and lower real GDP • Leads to cost-push inflation • Adverse shifts in the aggregate supply result in stagflation, a situation of higher prices and higher unemployment Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 38
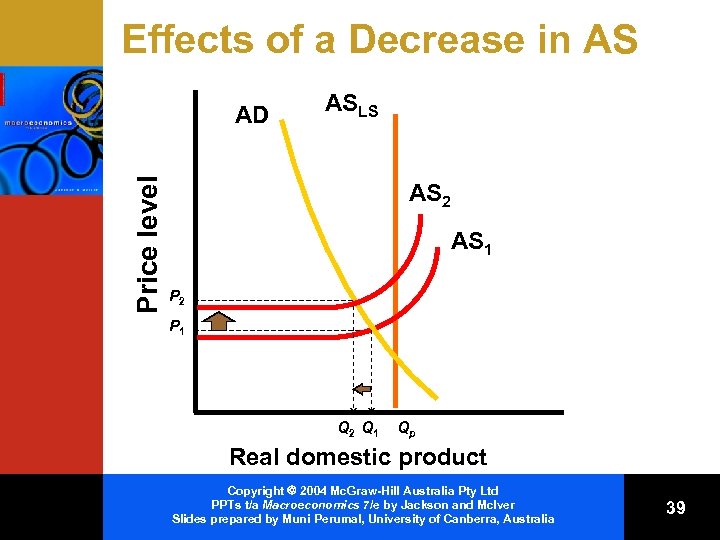 Effects of a Decrease in AS Price level AD ASLS AS 2 AS 1 P 2 P 1 Q 2 Q 1 Qp Real domestic product Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 39
Effects of a Decrease in AS Price level AD ASLS AS 2 AS 1 P 2 P 1 Q 2 Q 1 Qp Real domestic product Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 39
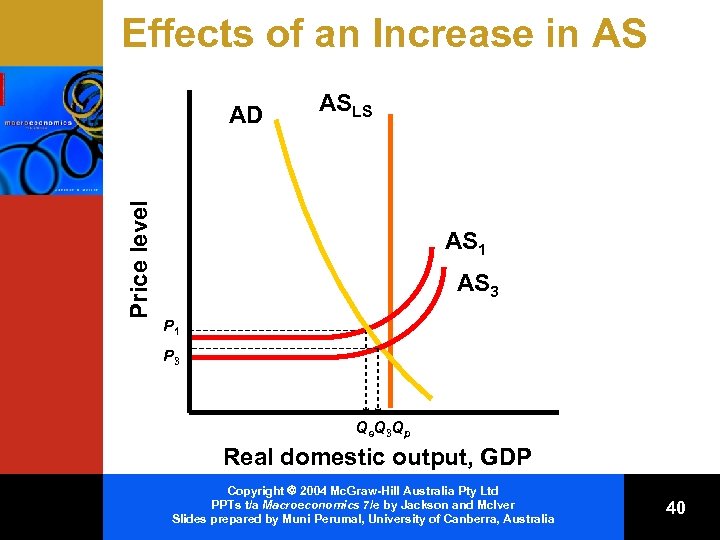 Effects of an Increase in AS Price level AD ASLS AS 1 AS 3 P 1 P 3 Qe. Q 3 Qp Real domestic output, GDP Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 40
Effects of an Increase in AS Price level AD ASLS AS 1 AS 3 P 1 P 3 Qe. Q 3 Qp Real domestic output, GDP Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 40
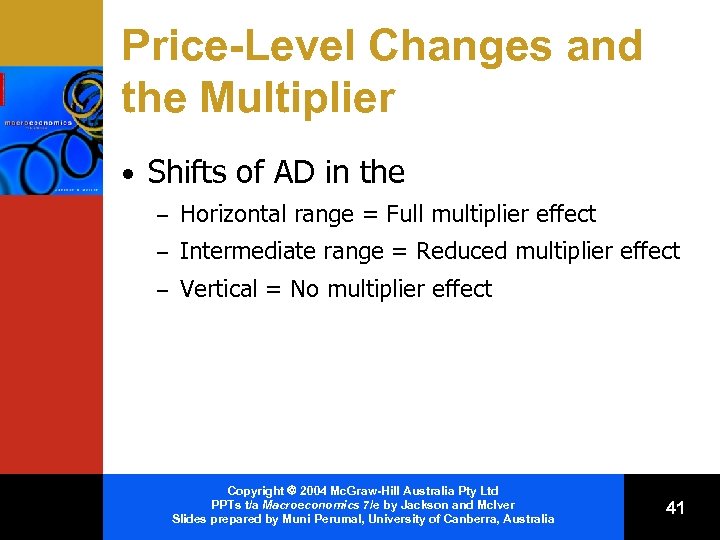 Price-Level Changes and the Multiplier • Shifts of AD in the – Horizontal range = Full multiplier effect – Intermediate range = Reduced multiplier effect – Vertical = No multiplier effect Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 41
Price-Level Changes and the Multiplier • Shifts of AD in the – Horizontal range = Full multiplier effect – Intermediate range = Reduced multiplier effect – Vertical = No multiplier effect Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 41
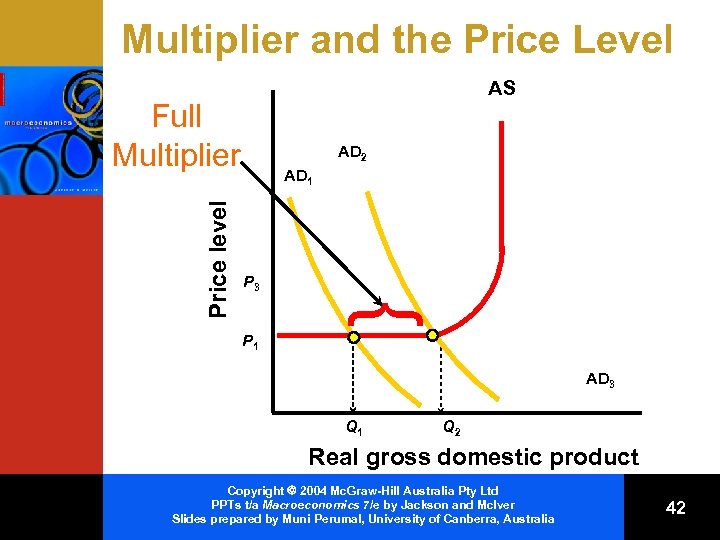 Multiplier and the Price Level AS AD 2 AD 1 P 3 } Price level Full Multiplier P 1 AD 3 Q 1 Q 2 Real gross domestic product Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 42
Multiplier and the Price Level AS AD 2 AD 1 P 3 } Price level Full Multiplier P 1 AD 3 Q 1 Q 2 Real gross domestic product Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 42
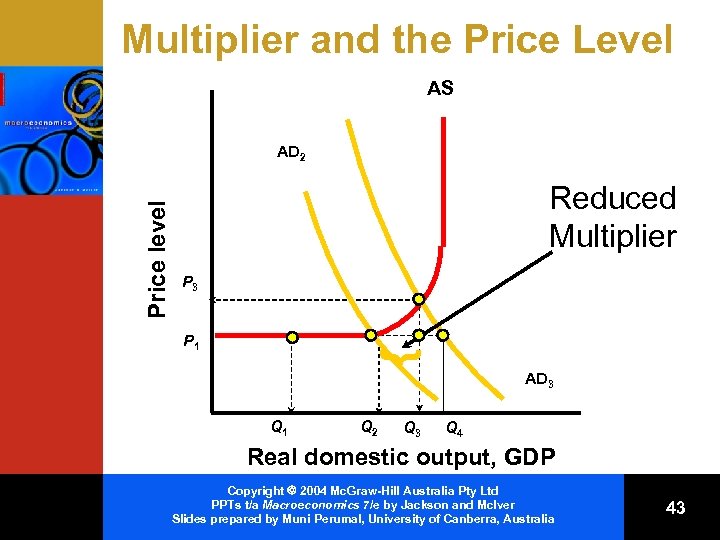 Multiplier and the Price Level AS Price level AD 2 Reduced Multiplier P 3 } P 1 AD 3 Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Real domestic output, GDP Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 43
Multiplier and the Price Level AS Price level AD 2 Reduced Multiplier P 3 } P 1 AD 3 Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 Q 4 Real domestic output, GDP Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 43
 Next Chapter: Fiscal Policy and the Public Debt Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 44
Next Chapter: Fiscal Policy and the Public Debt Copyright 2004 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Macroeconomics 7/e by Jackson and Mc. Iver Slides prepared by Muni Perumal, University of Canberra, Australia 44


