5f7194be76ba823482e219cad38bf3d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64
 CHAPTER 8 A thin layer of gold covering a lot of corruption
CHAPTER 8 A thin layer of gold covering a lot of corruption
 Chapter 6 Need to Know § § Thomas Edison Electricity Alexander Graham Bell Transcontinental Railroad
Chapter 6 Need to Know § § Thomas Edison Electricity Alexander Graham Bell Transcontinental Railroad
 More Chapter 6 § Andrew Carnegie- Industrialist who made a fortune in steel § John D. Rockefeller- formed Standard Oil Company § J. P. Morgan- Financer, mainly railroad industry
More Chapter 6 § Andrew Carnegie- Industrialist who made a fortune in steel § John D. Rockefeller- formed Standard Oil Company § J. P. Morgan- Financer, mainly railroad industry
 MARK TWAIN • "Clothes make the man. Naked people have little or no influence on society. " • “Denial ain't just a river in Egypt. ” • Gilded Age coined by Twain
MARK TWAIN • "Clothes make the man. Naked people have little or no influence on society. " • “Denial ain't just a river in Egypt. ” • Gilded Age coined by Twain
 section 1 - business of Politics A. Laissez-Faire Policies Created by? -Adam Smith who wrote The Wealth of Nations in 1776 Subsidy? -Payment made by Gov to encourage the development of certain key industries, such as railroads
section 1 - business of Politics A. Laissez-Faire Policies Created by? -Adam Smith who wrote The Wealth of Nations in 1776 Subsidy? -Payment made by Gov to encourage the development of certain key industries, such as railroads
 C. Spoils System=Bribery DEFINITION RESULT
C. Spoils System=Bribery DEFINITION RESULT
 D. Opposing Political Parties republicans appealed to: • Industrialists, bankers, and eastern farmers • Strongest in the North and Midwest • Weakest in the South platform: §Favored tight money supply backed by gold §High tariffs to protect American business §Gov aid to railroads §Enforce Blue Laws -regulations that prohibited certain private activities that some people considered immoral- drinking alcohol on Sunday
D. Opposing Political Parties republicans appealed to: • Industrialists, bankers, and eastern farmers • Strongest in the North and Midwest • Weakest in the South platform: §Favored tight money supply backed by gold §High tariffs to protect American business §Gov aid to railroads §Enforce Blue Laws -regulations that prohibited certain private activities that some people considered immoral- drinking alcohol on Sunday
 2. DEMOCRATS APPEALED TO: ØNorthern urban immigrants, laborers, southern planters, and western farmers PLATFORM: o. Increased money supply backed by silver o. Lower tariffs on imported goods o. Less Gov aid to big business o. Fewer blue laws
2. DEMOCRATS APPEALED TO: ØNorthern urban immigrants, laborers, southern planters, and western farmers PLATFORM: o. Increased money supply backed by silver o. Lower tariffs on imported goods o. Less Gov aid to big business o. Fewer blue laws
 Rutherford Hayes • Against Spoils System • He began to reform the Civil Service- Gov non-elected workers • He strengthened the Gov and weakened the Republicans
Rutherford Hayes • Against Spoils System • He began to reform the Civil Service- Gov non-elected workers • He strengthened the Gov and weakened the Republicans
 James Garfield • 1880 Election: James Garfield v Winfield Hancock Republicans split into 3 parties -Stalwarts: defended spoils system -Half-Breeds: reform spoils system -Independents: against spoils system • Garfield a Half-Breed while VP Arthur was a Stalwart
James Garfield • 1880 Election: James Garfield v Winfield Hancock Republicans split into 3 parties -Stalwarts: defended spoils system -Half-Breeds: reform spoils system -Independents: against spoils system • Garfield a Half-Breed while VP Arthur was a Stalwart
 • July 2, 1881 - Charles Guiteau Shot Garfield. He shouted out “I am a Stalwart and Arthur is President now”. • A public outcry began against the spoils system
• July 2, 1881 - Charles Guiteau Shot Garfield. He shouted out “I am a Stalwart and Arthur is President now”. • A public outcry began against the spoils system
 v. Vice President Chester Arthur becomes President v. Reform of spoils system v. Pendleton Civil Service Act- 1883 *ENDED SPOILS SYSTEM
v. Vice President Chester Arthur becomes President v. Reform of spoils system v. Pendleton Civil Service Act- 1883 *ENDED SPOILS SYSTEM
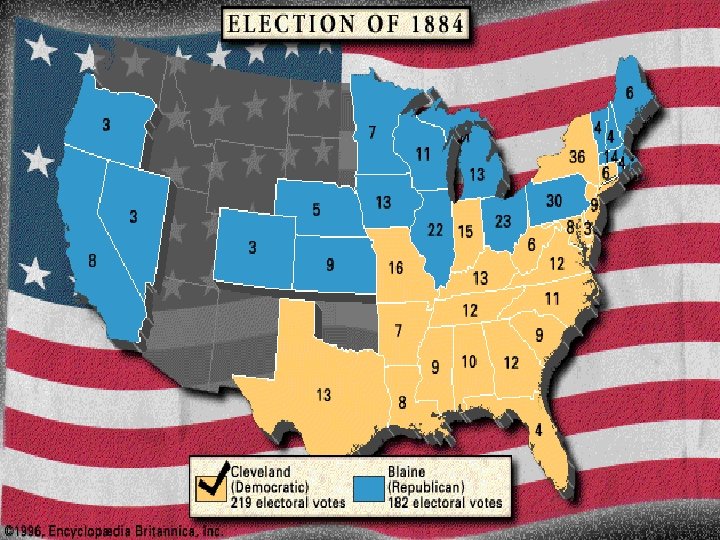
 Election 1884 Grover Cleveland- Democrat James Blaine- Republican
Election 1884 Grover Cleveland- Democrat James Blaine- Republican
 Issues of the Election, 1884 • High Tariffs, unfair business practices, and unregulated railroads • Scandals -Blaine receive stock options from railroad in return for votes? Did not admit and no one could prove it -Cleveland have a child out of wedlock (not married)? Admitted to this q Republicans repeated “Ma, where’s my Pa” q Democrats in response “Going to the White House, ha, ha”
Issues of the Election, 1884 • High Tariffs, unfair business practices, and unregulated railroads • Scandals -Blaine receive stock options from railroad in return for votes? Did not admit and no one could prove it -Cleveland have a child out of wedlock (not married)? Admitted to this q Republicans repeated “Ma, where’s my Pa” q Democrats in response “Going to the White House, ha, ha”
 Regulating Railroads What is charging? -charging more for a short haul than a long haul What are rebates? -partial refunds or discounts to favored customers
Regulating Railroads What is charging? -charging more for a short haul than a long haul What are rebates? -partial refunds or discounts to favored customers
 Munn vs. Illinois- 1877 -Case allowed states to regulate railroad business within their borders Wabash Case- 1886 -Interstate railroads were not regulated Congress Responds -Interstate Commerce Act Rates should be set according to distance traveled Rates should be made public. No rebates should be given
Munn vs. Illinois- 1877 -Case allowed states to regulate railroad business within their borders Wabash Case- 1886 -Interstate railroads were not regulated Congress Responds -Interstate Commerce Act Rates should be set according to distance traveled Rates should be made public. No rebates should be given
 Benjamin Harrison- 1888 • Harrison wanted increase in tariffs, Cleveland wanted minor reduction in tariffs • Signed Sherman Anti-Trust Act 1890 -outlawed companies that restrained interstate trade • Reached into the Treasury to give $$ to Civil War Vets dependents • His actions hurt the economy and eventually the country went into a long depression
Benjamin Harrison- 1888 • Harrison wanted increase in tariffs, Cleveland wanted minor reduction in tariffs • Signed Sherman Anti-Trust Act 1890 -outlawed companies that restrained interstate trade • Reached into the Treasury to give $$ to Civil War Vets dependents • His actions hurt the economy and eventually the country went into a long depression
 Cleveland’s 2 nd Term • Easily defeated Harrison- ran on lower tariffs again • Depression started after his term started- 1893 • Gov offered no help, many lost their jobs and wages cut
Cleveland’s 2 nd Term • Easily defeated Harrison- ran on lower tariffs again • Depression started after his term started- 1893 • Gov offered no help, many lost their jobs and wages cut
 Jacob Coxey and his Army § Wealthy Ohio quarry owner § Wanted Gov to make jobs for unemployed workers § Gathered many unemployed to march on Washington “We will send a petition to Washington with boots on” -Coxey-
Jacob Coxey and his Army § Wealthy Ohio quarry owner § Wanted Gov to make jobs for unemployed workers § Gathered many unemployed to march on Washington “We will send a petition to Washington with boots on” -Coxey-
 Cleveland Angers All • Farmers upset after he repealed Sherman Silver Purchase Act • Unions upset when Cleveland sent federal troops during the Pullman Strike of 1894 • Unemployed upset due to no Gov help • Most Democrats turned against him
Cleveland Angers All • Farmers upset after he repealed Sherman Silver Purchase Act • Unions upset when Cleveland sent federal troops during the Pullman Strike of 1894 • Unemployed upset due to no Gov help • Most Democrats turned against him
 William Mckinley Wins- 1896 • Defeated William Jennings Bryan (was for bimetallism) • Strong gold standard • “A full dinner pail”
William Mckinley Wins- 1896 • Defeated William Jennings Bryan (was for bimetallism) • Strong gold standard • “A full dinner pail”
 • Sept. 6, 1901 Mckinley shot by Leon Czolgosz who was thought to be mentally ill • Anarchist • Mckinley died 8 days later • "I killed the President because he was the enemy of the good people —the good working people. I am not sorry for my crime. "
• Sept. 6, 1901 Mckinley shot by Leon Czolgosz who was thought to be mentally ill • Anarchist • Mckinley died 8 days later • "I killed the President because he was the enemy of the good people —the good working people. I am not sorry for my crime. "
 Section 2 - People on the Move
Section 2 - People on the Move
 Why did people immigrate… -from homeland? -to the US? What were Pogroms? -violent massacres of Jews in Russia -could only live and work in certain places
Why did people immigrate… -from homeland? -to the US? What were Pogroms? -violent massacres of Jews in Russia -could only live and work in certain places
 Most immigrants traveled in Steerage -no comfort -no privacy -poor food -tickets were cheap -took 1 week to arrive at…. .
Most immigrants traveled in Steerage -no comfort -no privacy -poor food -tickets were cheap -took 1 week to arrive at…. .
 ELLIS ISLAND NEW YORK- most immigrants came through here
ELLIS ISLAND NEW YORK- most immigrants came through here
 • Physical Exams -anyone who had a disease faced quarantine -some were even deported -”It was harrowing to see families separated”
• Physical Exams -anyone who had a disease faced quarantine -some were even deported -”It was harrowing to see families separated”
 Where did they settle? • New York, Boston, Chicago, Cleveland, Detroit • Employers loved immigrants, Why? • Tried to settle with same kind of people -lived with same ethnic groups, this formed Ghettos
Where did they settle? • New York, Boston, Chicago, Cleveland, Detroit • Employers loved immigrants, Why? • Tried to settle with same kind of people -lived with same ethnic groups, this formed Ghettos
 RESTRICTIVE COVENANTS? -created a gap between the rich and poor
RESTRICTIVE COVENANTS? -created a gap between the rich and poor
 Angel Island 1910 -1940 • “Guardian of the Western Gate” • San Francisco Bay • Used to enforce Gov legislation on immigrants • Chinese and Japanese largest groups • Fire destroyed Admin building 1940 - shut down
Angel Island 1910 -1940 • “Guardian of the Western Gate” • San Francisco Bay • Used to enforce Gov legislation on immigrants • Chinese and Japanese largest groups • Fire destroyed Admin building 1940 - shut down
 Chinese Immigrants • Railroads • Lower wages, Unions upset • Chinese Exclusion Act 1882?
Chinese Immigrants • Railroads • Lower wages, Unions upset • Chinese Exclusion Act 1882?
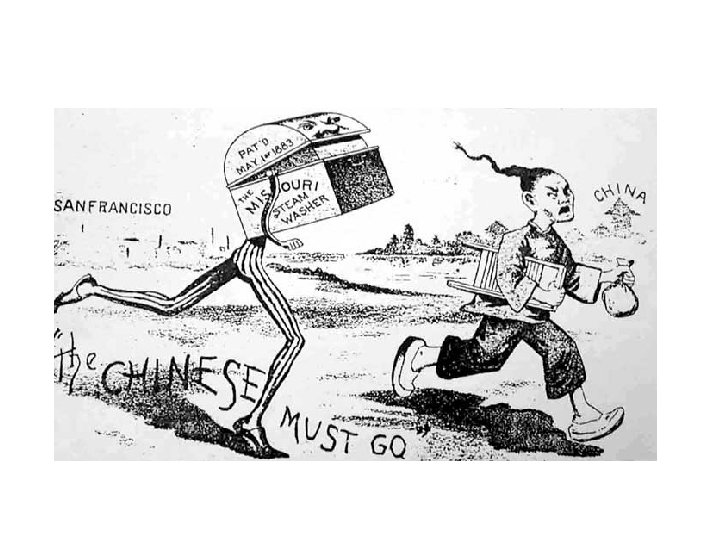


 Japanese Restriction Ends • 1906 Chinese, Japanese, and Korean not allowed in white schools • Japanese Gov upset so Teddy Roosevelt reached a compromise • 1907 Gentlemen’s Agreement • Asians were most discriminated against during this time
Japanese Restriction Ends • 1906 Chinese, Japanese, and Korean not allowed in white schools • Japanese Gov upset so Teddy Roosevelt reached a compromise • 1907 Gentlemen’s Agreement • Asians were most discriminated against during this time
 Immigration from Mexico • • Where did they work in the South? Pull Factor- new opportunities Push Factor- Turmoil in Homeland Mexican Revolution and civil war
Immigration from Mexico • • Where did they work in the South? Pull Factor- new opportunities Push Factor- Turmoil in Homeland Mexican Revolution and civil war
 Section 3 - The Cities • Expanding Cities- 1880 -1920 11 million left farms and headed to the cities along with many immigrants. • New York, Philly, Chicago, St. Louis • Farm labor decreased, why?
Section 3 - The Cities • Expanding Cities- 1880 -1920 11 million left farms and headed to the cities along with many immigrants. • New York, Philly, Chicago, St. Louis • Farm labor decreased, why?
 • After Reconstruction, segregation and racial violence increased against African Americans • 1910 boll weevil (beetle) destroyed cotton crops and floods ruined farmlands • African Americans went where?
• After Reconstruction, segregation and racial violence increased against African Americans • 1910 boll weevil (beetle) destroyed cotton crops and floods ruined farmlands • African Americans went where?
 How Cities Grew • Modes of transportation- If you had money you could afford this • People who could moved outside the city forming suburbs- ? • Modes of transportation….
How Cities Grew • Modes of transportation- If you had money you could afford this • People who could moved outside the city forming suburbs- ? • Modes of transportation….
 Horse Carriage
Horse Carriage
 Elevated Trains and Cable Cars (Trolleys)
Elevated Trains and Cable Cars (Trolleys)
 Subways
Subways
 1896 Ford
1896 Ford
 Elisha Otis • Invented safety device that made elevators possible in case a cable broke • Set the stage for skyscrapers, helped advance cities • 1 st one, Chicago- Home Insurance Company building 1885 • 10 stories tall, iron and steel, 4 passenger elevators
Elisha Otis • Invented safety device that made elevators possible in case a cable broke • Set the stage for skyscrapers, helped advance cities • 1 st one, Chicago- Home Insurance Company building 1885 • 10 stories tall, iron and steel, 4 passenger elevators
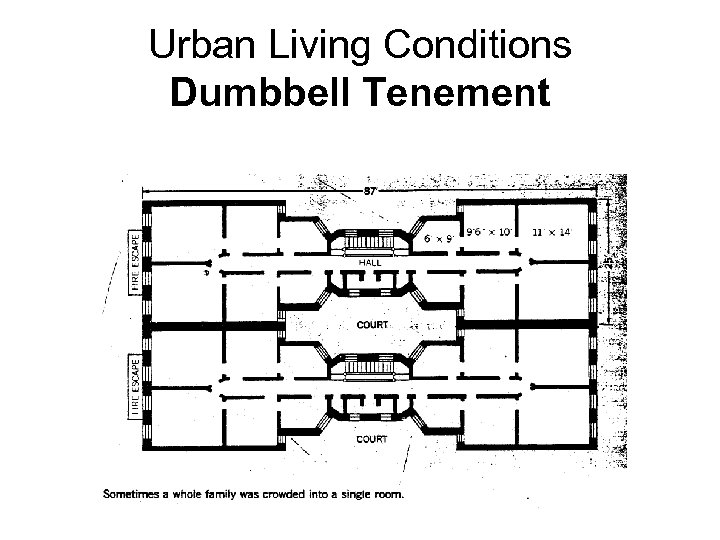 Urban Living Conditions Dumbbell Tenement
Urban Living Conditions Dumbbell Tenement
 • Housed many, low cost • Conditions: Air- lack of good ventilation caused disease to spread • Urban areas were slums at this time Water- contaminated, linked to cholera and typhoid Problems fixed Built reservoirs, had a filtration system, hallway bathrooms replaced outhouses, and bathroom sinks and tubs installed
• Housed many, low cost • Conditions: Air- lack of good ventilation caused disease to spread • Urban areas were slums at this time Water- contaminated, linked to cholera and typhoid Problems fixed Built reservoirs, had a filtration system, hallway bathrooms replaced outhouses, and bathroom sinks and tubs installed
 Jacob Riis • How the Other Half Lives • “the gang is the ripe fruit of tenement house growth”-? • “gangs are made up of the American-born sons of English, Irish, and German parents”-?
Jacob Riis • How the Other Half Lives • “the gang is the ripe fruit of tenement house growth”-? • “gangs are made up of the American-born sons of English, Irish, and German parents”-?
 Result of City Growth • Widened the gap between rich and poor • Cities raised taxes to form police and fire protection, sewage, electric and water service, etc. • Increased revenue gave Gov more power • Groups competed for control of City Gov
Result of City Growth • Widened the gap between rich and poor • Cities raised taxes to form police and fire protection, sewage, electric and water service, etc. • Increased revenue gave Gov more power • Groups competed for control of City Gov
 Political Machines • Unofficial city organization designed to keep a particular party or group in power. Headed by a single powerful “Boss” • They formed out of competition for control of city Gov • The boss would hand pick people to run for office then help them win or they would run themselves
Political Machines • Unofficial city organization designed to keep a particular party or group in power. Headed by a single powerful “Boss” • They formed out of competition for control of city Gov • The boss would hand pick people to run for office then help them win or they would run themselves
 • Handed out jobs and had other favors done by people they were representing in return for their vote • Willam “Boss” Tweed • Controlled Tammany Hall- political club that ran New York City’s Democratic Party • Gained millions through Fraud and Graft-?
• Handed out jobs and had other favors done by people they were representing in return for their vote • Willam “Boss” Tweed • Controlled Tammany Hall- political club that ran New York City’s Democratic Party • Gained millions through Fraud and Graft-?
 Thomas Nast v Helped bring Tweed down with his political cartoons by exposing his methods v Tweed was convicted in 1873, died in jail years later
Thomas Nast v Helped bring Tweed down with his political cartoons by exposing his methods v Tweed was convicted in 1873, died in jail years later


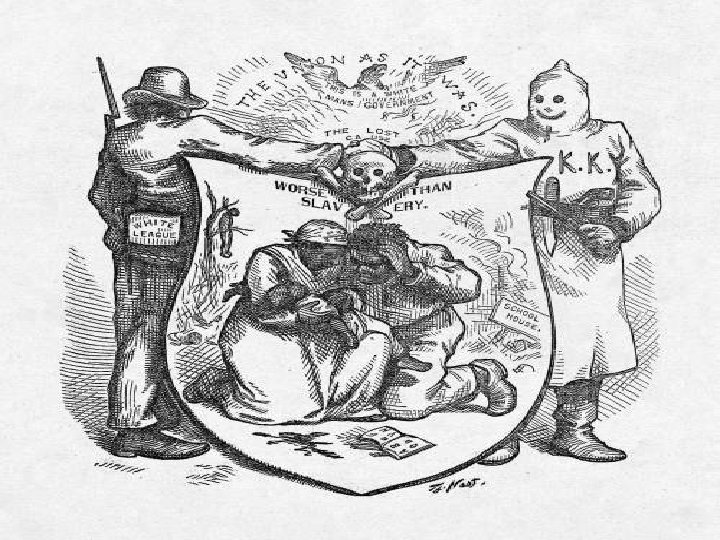
 Ideas for Reform • Helping the needy- Charity Organization Movement • 1882, Josephine Shaw Lowell • Wanted immigrants to adopt middle class standards for raising kids, cooking, cleaning, etc. • Some were upset others were grateful
Ideas for Reform • Helping the needy- Charity Organization Movement • 1882, Josephine Shaw Lowell • Wanted immigrants to adopt middle class standards for raising kids, cooking, cleaning, etc. • Some were upset others were grateful
 Social Gospel Movement • Social reform movement developed within religious institutions • Looked to apply Gospel of Jesus directly to society
Social Gospel Movement • Social reform movement developed within religious institutions • Looked to apply Gospel of Jesus directly to society
 Settlement Movement • Many educated men and women put social gospel movement into practice and formed settlement houses, what were they? • Began in Britain, people wanted to witness poverty 1 st hand to know how to fix living conditions • Jane Addams- Hull House 1 st settlement house • People attended cultural events and took classes
Settlement Movement • Many educated men and women put social gospel movement into practice and formed settlement houses, what were they? • Began in Britain, people wanted to witness poverty 1 st hand to know how to fix living conditions • Jane Addams- Hull House 1 st settlement house • People attended cultural events and took classes
 • Settlements houses set up Social Services: child-care centers, playgrounds, clubs, summer camps, offices to help people find jobs, and health care clinics • By 1910, 400 settlement houses were across the nation
• Settlements houses set up Social Services: child-care centers, playgrounds, clubs, summer camps, offices to help people find jobs, and health care clinics • By 1910, 400 settlement houses were across the nation
 Auguste Comte • Coined the word sociology, which is?
Auguste Comte • Coined the word sociology, which is?
 Controlling Immigration and Behavior • Nativism- ? • Wanted tighter rules on immigration • Wanted only American Culture and English taught in schools
Controlling Immigration and Behavior • Nativism- ? • Wanted tighter rules on immigration • Wanted only American Culture and English taught in schools
 Prohibition • Temperance Movement- organized campaign to eliminate alcohol consumption • Drinking led to personal tragedies • Supported 18 th Amendment?
Prohibition • Temperance Movement- organized campaign to eliminate alcohol consumption • Drinking led to personal tragedies • Supported 18 th Amendment?
 Carrie Nation • Smashed illegal saloons with a hatchet in Kansas • Branch off of social gospel movement • Saloons making the world un-Christian • Saloons undermined public morals
Carrie Nation • Smashed illegal saloons with a hatchet in Kansas • Branch off of social gospel movement • Saloons making the world un-Christian • Saloons undermined public morals
 Purity Crusaders • Vice- ? • Drugs, gambling, prostitution became big • People were upset so they became “purity crusaders”
Purity Crusaders • Vice- ? • Drugs, gambling, prostitution became big • People were upset so they became “purity crusaders”
 Anthony Comstock • 1873, founded New York Society for the suppression of Vice • Comstock Law- prohibited sending obscene materials through the mail, mainly descriptions of methods to prevent unwanted pregnancy • This law slowed distribution of info on birth control
Anthony Comstock • 1873, founded New York Society for the suppression of Vice • Comstock Law- prohibited sending obscene materials through the mail, mainly descriptions of methods to prevent unwanted pregnancy • This law slowed distribution of info on birth control


