919a084b9d0e6c05b9312be8500bdf0c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Chapter 8. 1 Royal Power Grows • Medieval monarchs struggled for power w/ nobles and churchmen. • They slowly built the framework for the nation-states of today
Chapter 8. 1 Royal Power Grows • Medieval monarchs struggled for power w/ nobles and churchmen. • They slowly built the framework for the nation-states of today
 Objective To learn about: üMonarchs (Kings) gain power from Nobles and the church üEngland becomes powerful, FR too üEnglish King has to share power w/ nobles—Magna Carta (1215)
Objective To learn about: üMonarchs (Kings) gain power from Nobles and the church üEngland becomes powerful, FR too üEnglish King has to share power w/ nobles—Magna Carta (1215)
 This is important b/c…. . The US legal system has many of the components of these early European systems: • Habeas corpus, due process of law • Congress • Juries, Grand Juries • Limited authority of govt. officials
This is important b/c…. . The US legal system has many of the components of these early European systems: • Habeas corpus, due process of law • Congress • Juries, Grand Juries • Limited authority of govt. officials
 Ch. 8 vocab King John 1 Lay investiture 2 Reconquista 3 Scholasticism 4 Vernacular 4 King Louis IX 1 Frederick Barbarossa 2 crusades 3 Illumination 4 Epidemic 5
Ch. 8 vocab King John 1 Lay investiture 2 Reconquista 3 Scholasticism 4 Vernacular 4 King Louis IX 1 Frederick Barbarossa 2 crusades 3 Illumination 4 Epidemic 5
 What we’ll learn üMonarchs (Kings) gain power from Nobles and the church üEngland becomes powerful, FR too üEnglish King has to share power w/ nobles Why? üWhere did countries come from? üWhy didn’t monarchs have unlimited power? Essential Q: how do Monarchs gain power from nobles and the Church?
What we’ll learn üMonarchs (Kings) gain power from Nobles and the church üEngland becomes powerful, FR too üEnglish King has to share power w/ nobles Why? üWhere did countries come from? üWhy didn’t monarchs have unlimited power? Essential Q: how do Monarchs gain power from nobles and the Church?
 FQ #1 Thursday, 10/10 Tell me about the Magna Carta üWho signed it? When? üWhy did he sign it? üWhat did it signify? üSee teacher tube video—from AIHE —titled Magna Carta, 6 min.
FQ #1 Thursday, 10/10 Tell me about the Magna Carta üWho signed it? When? üWhy did he sign it? üWhat did it signify? üSee teacher tube video—from AIHE —titled Magna Carta, 6 min.
 FQ: What’s your “currency? ” • What skills and abilities are required for you to be successful? There are many. • Think of the skills needed in a career, in society, in your family, in a relationship… • Mine include: patience, knowledge, mental toughness, fitness, high energy, sense of humor, etc.
FQ: What’s your “currency? ” • What skills and abilities are required for you to be successful? There are many. • Think of the skills needed in a career, in society, in your family, in a relationship… • Mine include: patience, knowledge, mental toughness, fitness, high energy, sense of humor, etc.
 Focus Q: • How much time do you spend thinking about conflict? How’s this make you feel? • Does thinking about conflict impact you positively or negatively? • How does this impact your thoughts? • How does this impact your actions? • If you could, would you think about conflict less?
Focus Q: • How much time do you spend thinking about conflict? How’s this make you feel? • Does thinking about conflict impact you positively or negatively? • How does this impact your thoughts? • How does this impact your actions? • If you could, would you think about conflict less?
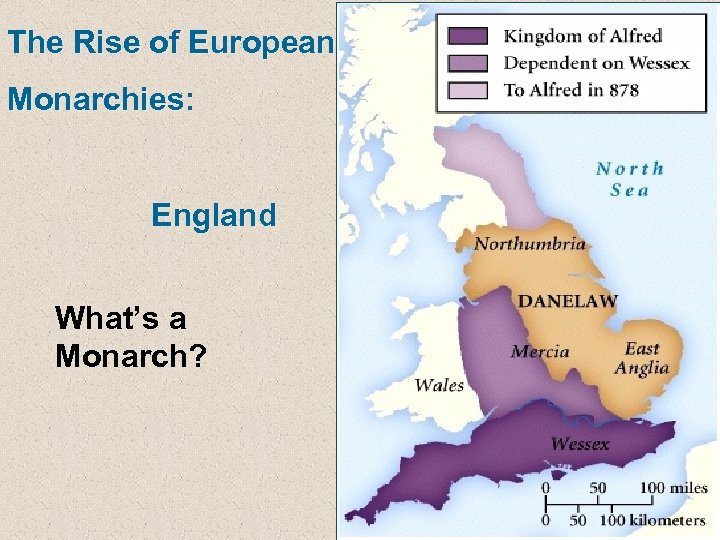 The Rise of European Monarchies: England What’s a Monarch?
The Rise of European Monarchies: England What’s a Monarch?
 Monarchs, Nobles, and the Church 1. In the early middle ages, monarchs are at the top of society, but had limited power. 2. Sometimes nobles or the church had more power 3. Nobles and the church: –Have armies, collect taxes, have their own courts
Monarchs, Nobles, and the Church 1. In the early middle ages, monarchs are at the top of society, but had limited power. 2. Sometimes nobles or the church had more power 3. Nobles and the church: –Have armies, collect taxes, have their own courts
 Monarchs, Nobles, and the Church Monarchs get more power by: – Set up royal courts – Organize govt. bureaucracies – Develop tax systems – Build armies – ***Strengthen ties w/ townspeople of the middle class—they support rulers who imposed peace needed for successful trade***
Monarchs, Nobles, and the Church Monarchs get more power by: – Set up royal courts – Organize govt. bureaucracies – Develop tax systems – Build armies – ***Strengthen ties w/ townspeople of the middle class—they support rulers who imposed peace needed for successful trade***
 English Kings Strengthen Their Power 1. In the 400 s and 500 s, Anglo-Saxons conquer most of the area of Britain 2. 1066, rule is contested—Harold vs. William (the Conqueror), Duke of Normandy 3. William the Conqueror wins at the Battle of Hastings (1066)
English Kings Strengthen Their Power 1. In the 400 s and 500 s, Anglo-Saxons conquer most of the area of Britain 2. 1066, rule is contested—Harold vs. William (the Conqueror), Duke of Normandy 3. William the Conqueror wins at the Battle of Hastings (1066)
 William the Conqueror expands power 1. Kept much land for himself—granted some fiefs to the church, nobles ***W the C Required each vassal to swear allegiance to him*** 1. 1086—census taken—published in Domesday Book –***Helped him develop tax system*** and later a royal treasury (exchequer)
William the Conqueror expands power 1. Kept much land for himself—granted some fiefs to the church, nobles ***W the C Required each vassal to swear allegiance to him*** 1. 1086—census taken—published in Domesday Book –***Helped him develop tax system*** and later a royal treasury (exchequer)
 William the Conqueror
William the Conqueror
 Review Q ØWhy did ties between rulers (kings) and the middle class get stronger?
Review Q ØWhy did ties between rulers (kings) and the middle class get stronger?
 I thought they were funny…. . Yogi Berra quotes • Baseball is 90% mental, the other half is physical. • Always go to other peoples funerals, otherwise they won’t go to yours. • We made too many wrong mistakes. • You better cut the pizza into 4 pieces, because I’m not hungry enough to eat 6.
I thought they were funny…. . Yogi Berra quotes • Baseball is 90% mental, the other half is physical. • Always go to other peoples funerals, otherwise they won’t go to yours. • We made too many wrong mistakes. • You better cut the pizza into 4 pieces, because I’m not hungry enough to eat 6.
 Henry II expands power 1. 1154, begins expanding customs into laws 2. Decisions of royal courts became foundation of English common law—legal system based on custom and court rulings ***English common law applied to all of England*** ***People began to bring grievances to royal courts rather than nobles or church courts*** 3. Also began an early jury system—like a grand jury
Henry II expands power 1. 1154, begins expanding customs into laws 2. Decisions of royal courts became foundation of English common law—legal system based on custom and court rulings ***English common law applied to all of England*** ***People began to bring grievances to royal courts rather than nobles or church courts*** 3. Also began an early jury system—like a grand jury
 v. Any idea how English common law and our legal system differ? v. English common law—legal system based on custom and court rulings v. Much is not written down
v. Any idea how English common law and our legal system differ? v. English common law—legal system based on custom and court rulings v. Much is not written down
 Henry II has conflict w/ the Church ***Henry II has conflict w/ the Church b/c Henry claimed the right to try clergy in royal courts*** 1. Archbishop of Canterbury, Thomas Beckett, vehemently opposed this 2. Beckett is murdered, later sainted
Henry II has conflict w/ the Church ***Henry II has conflict w/ the Church b/c Henry claimed the right to try clergy in royal courts*** 1. Archbishop of Canterbury, Thomas Beckett, vehemently opposed this 2. Beckett is murdered, later sainted
 Henry II of England
Henry II of England
 Evolving Traditions of Govt. • English rulers cont. to have trouble w/ nobles and the Church when they tried to raise taxes or impose their will on those traditional medieval authorities. • King John of England makes a historic decision………………
Evolving Traditions of Govt. • English rulers cont. to have trouble w/ nobles and the Church when they tried to raise taxes or impose their will on those traditional medieval authorities. • King John of England makes a historic decision………………
 King John makes enemies…. . 1. 1205, loses a war to Philip II of France and loses part of Anjou and Normandy 2. Battles Pope Innocent III over who the next Archbishop of Canterbury would be – Innocent placed the interdict (no church services) on England – John had to accept England as a fief of pope and pay yearly to Rome
King John makes enemies…. . 1. 1205, loses a war to Philip II of France and loses part of Anjou and Normandy 2. Battles Pope Innocent III over who the next Archbishop of Canterbury would be – Innocent placed the interdict (no church services) on England – John had to accept England as a fief of pope and pay yearly to Rome
 King John and the Magna Carta 1. 1215, the Great Charter— 63 articles ***His nobles are mad at high taxes and other abuses of power*** 2. Forced to sign the M. C. at Runnymeade 3. King gives up some of his power
King John and the Magna Carta 1. 1215, the Great Charter— 63 articles ***His nobles are mad at high taxes and other abuses of power*** 2. Forced to sign the M. C. at Runnymeade 3. King gives up some of his power
 Magna Carta 1. Nobles have certain rights (similar to Bill of Rights? ) 2. Monarchs must obey the law 3. No new taxes w/o consulting the Great Council (later Parliament) – American colonists would claim this meant no taxation w/o representation
Magna Carta 1. Nobles have certain rights (similar to Bill of Rights? ) 2. Monarchs must obey the law 3. No new taxes w/o consulting the Great Council (later Parliament) – American colonists would claim this meant no taxation w/o representation
 Magna Carta 4. Freemen protected from arbitrary arrest, imprisonment – Basis of due process of law – Monarch is not above the law – Basis for habeas corpus—can’t be imprisoned unless charged w/ a crime
Magna Carta 4. Freemen protected from arbitrary arrest, imprisonment – Basis of due process of law – Monarch is not above the law – Basis for habeas corpus—can’t be imprisoned unless charged w/ a crime
 Development of Parliament 1. Great Council develops into Parliament— England’s legislature ***Edward I approves a 2 -house body— House of Lords, House of Commons*** 2. Over time get the “power of the purse”— right to approve any new taxes—is a check on the power of the monarch 3. Similar political body in the U. S. ?
Development of Parliament 1. Great Council develops into Parliament— England’s legislature ***Edward I approves a 2 -house body— House of Lords, House of Commons*** 2. Over time get the “power of the purse”— right to approve any new taxes—is a check on the power of the monarch 3. Similar political body in the U. S. ?
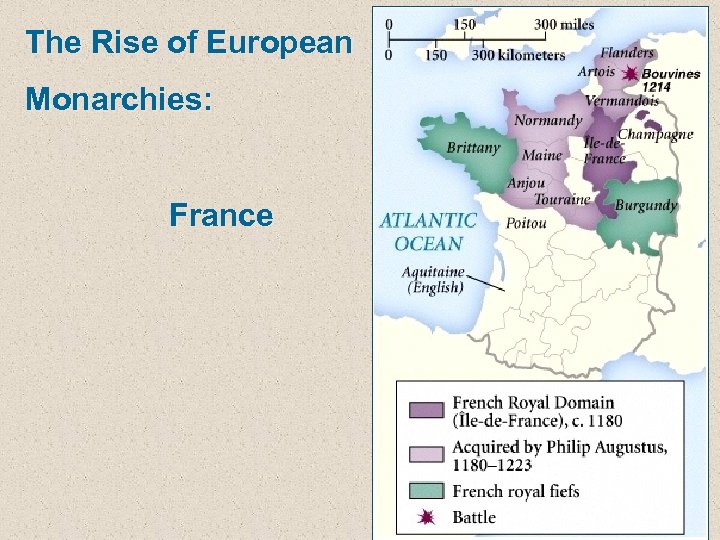 The Rise of European Monarchies: France
The Rise of European Monarchies: France
 Louis IX of France 1. Very religious, sainted 30 yrs. after death 2. Persecuted Jews, led Knights on 2 Crusades against Muslims ***Improved royal govt*** – Sent officials to check on local administrators – Expanded royal courts, outlawed private wars – Ended serfdom in his personal domain
Louis IX of France 1. Very religious, sainted 30 yrs. after death 2. Persecuted Jews, led Knights on 2 Crusades against Muslims ***Improved royal govt*** – Sent officials to check on local administrators – Expanded royal courts, outlawed private wars – Ended serfdom in his personal domain
 Clashing w/ the Pope 1. Philip IV (FR) tried to tax the clergy 2. Pope Boniface VIII forbade it 3. Philip sends troops to seize the pope, who escaped, but died soon afterward ***1305 French pope elected, Clement V – 1309, moved papal court to Avignon, where FR rulers could better control it***
Clashing w/ the Pope 1. Philip IV (FR) tried to tax the clergy 2. Pope Boniface VIII forbade it 3. Philip sends troops to seize the pope, who escaped, but died soon afterward ***1305 French pope elected, Clement V – 1309, moved papal court to Avignon, where FR rulers could better control it***
 Paris
Paris
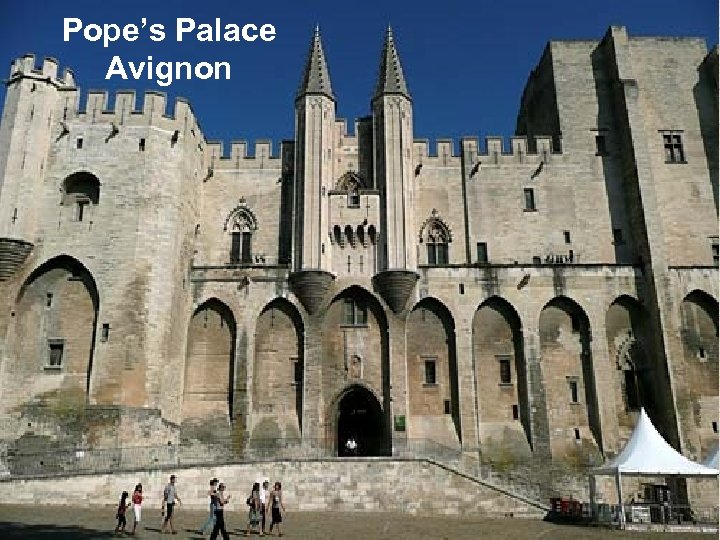 Pope’s Palace Avignon
Pope’s Palace Avignon
 Clashing w/ the Pope 1. Causes a crisis in the church 2. Another pope elected in Rome, as a result…… ***Power of the papacy is declining***
Clashing w/ the Pope 1. Causes a crisis in the church 2. Another pope elected in Rome, as a result…… ***Power of the papacy is declining***
 8. 1 Creative side: What was the essential idea? ØGive 2 examples of how Monarchs gained power from nobles and the church. ØGive 1 example of limitations on the power of Monarchs. ØDraw 1 picture w/ a caption of one of the above ideas.
8. 1 Creative side: What was the essential idea? ØGive 2 examples of how Monarchs gained power from nobles and the church. ØGive 1 example of limitations on the power of Monarchs. ØDraw 1 picture w/ a caption of one of the above ideas.


