00d7b1f15bc483c36392a189f35abc29.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 CHAPTER 7 SECTION 1 FIRST EMPIRES OF INDIA
CHAPTER 7 SECTION 1 FIRST EMPIRES OF INDIA
 Vocab Epiphany: A sudden understanding (usually religious in nature) Infrastructure: system of public works that tie an area together. (examples? ) Asoka: Greatest ruler of the Gupta Empire. Mahayana: New form of Buddhism that worships Buddha as a god. Theravada: Traditional Buddhism.
Vocab Epiphany: A sudden understanding (usually religious in nature) Infrastructure: system of public works that tie an area together. (examples? ) Asoka: Greatest ruler of the Gupta Empire. Mahayana: New form of Buddhism that worships Buddha as a god. Theravada: Traditional Buddhism.
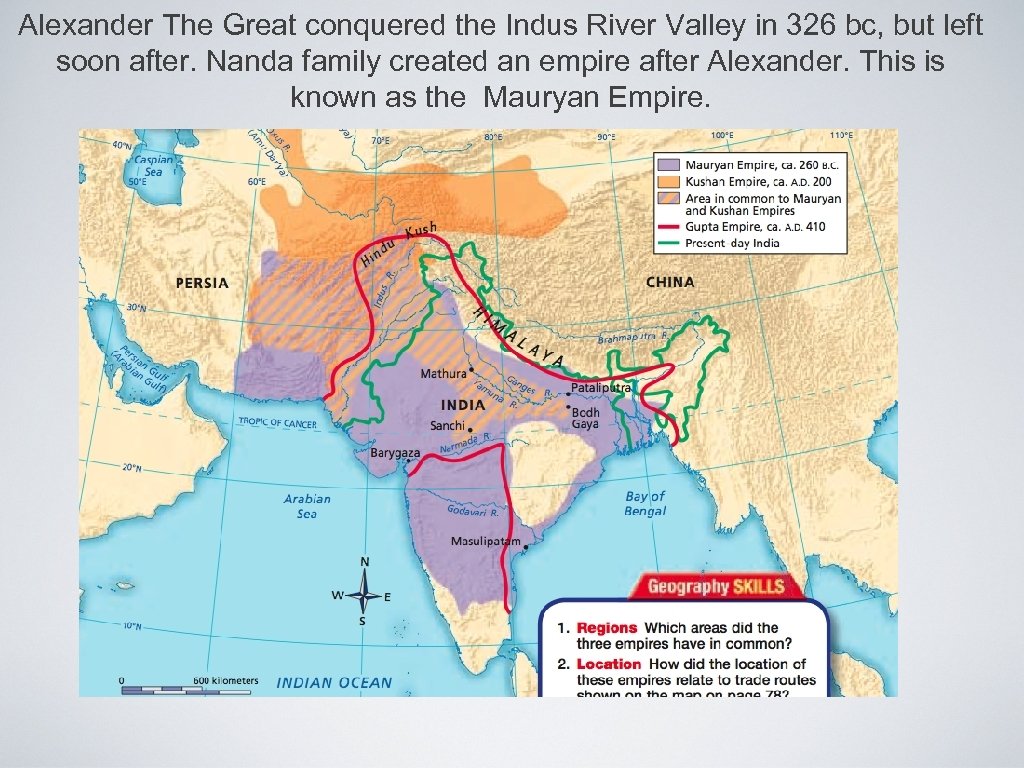 Alexander The Great conquered the Indus River Valley in 326 bc, but left soon after. Nanda family created an empire after Alexander. This is known as the Mauryan Empire.
Alexander The Great conquered the Indus River Valley in 326 bc, but left soon after. Nanda family created an empire after Alexander. This is known as the Mauryan Empire.
 Asoka was the greatest emperor. He fought devastating wars, which brought him a religious epiphany. He studied Buddhism and ruled thru its teachings. Asoka improved the empire. • He standardized laws • created roads • built infrastructure • (water wells, trees, watering holes)
Asoka was the greatest emperor. He fought devastating wars, which brought him a religious epiphany. He studied Buddhism and ruled thru its teachings. Asoka improved the empire. • He standardized laws • created roads • built infrastructure • (water wells, trees, watering holes)
 Asoka & War Elephants
Asoka & War Elephants
 So what happens when he dies? Empire fell into turmoil. • Regions broke off the empire. • Greek/Persian immigrants flooded in, brining new customs and culture.
So what happens when he dies? Empire fell into turmoil. • Regions broke off the empire. • Greek/Persian immigrants flooded in, brining new customs and culture.
 Asoka’s use of non-violence can be a very powerful, who else used a non-violent approach to achieve change? ____
Asoka’s use of non-violence can be a very powerful, who else used a non-violent approach to achieve change? ____
 The Gupta Empire resulted from a marriage of 2 powerful families.
The Gupta Empire resulted from a marriage of 2 powerful families.
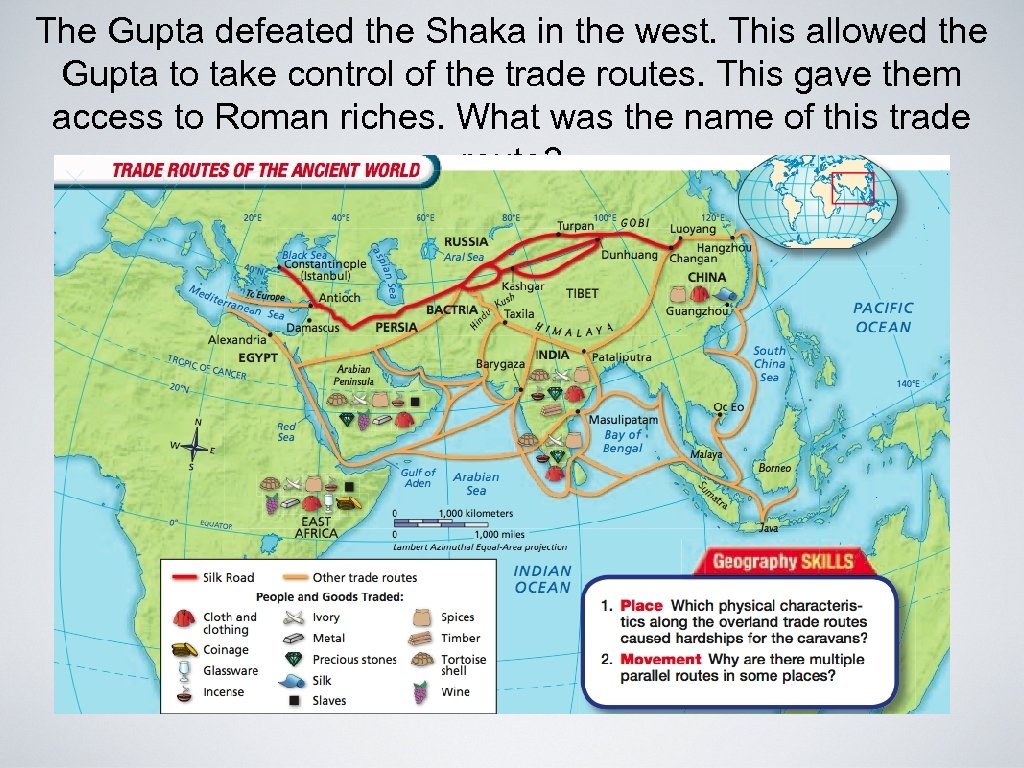 The Gupta defeated the Shaka in the west. This allowed the Gupta to take control of the trade routes. This gave them access to Roman riches. What was the name of this trade route?
The Gupta defeated the Shaka in the west. This allowed the Gupta to take control of the trade routes. This gave them access to Roman riches. What was the name of this trade route?
 So what happened to the gupta? The Gupta will eventual fall to the Hunas (cousins of the Huns who caused the collapse of Rome)
So what happened to the gupta? The Gupta will eventual fall to the Hunas (cousins of the Huns who caused the collapse of Rome)
 CHAPTER 7 SECTION 2 TRADE SPREADS INDIAN RELIGIONS & CULTURE
CHAPTER 7 SECTION 2 TRADE SPREADS INDIAN RELIGIONS & CULTURE
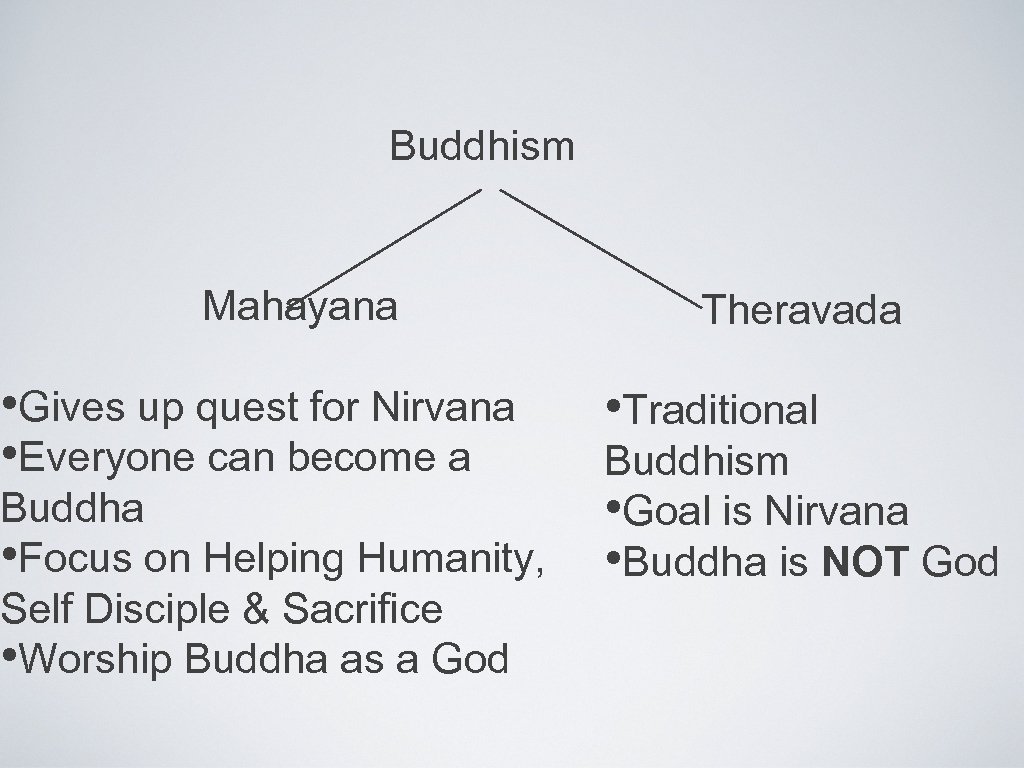 Buddhism Mahayana • Gives up quest for Nirvana • Everyone can become a Buddha • Focus on Helping Humanity, Self Disciple & Sacrifice • Worship Buddha as a God Theravada • Traditional Buddhism • Goal is Nirvana • Buddha is NOT God
Buddhism Mahayana • Gives up quest for Nirvana • Everyone can become a Buddha • Focus on Helping Humanity, Self Disciple & Sacrifice • Worship Buddha as a God Theravada • Traditional Buddhism • Goal is Nirvana • Buddha is NOT God
 CHANGES TO HINDUISM: Wait. Hinduism? Buddhism? What’s the difference?
CHANGES TO HINDUISM: Wait. Hinduism? Buddhism? What’s the difference?
 Hinduism Moved toward Monotheism. Thought of the world as having 1 driving force. The three most important gods became Brahma (creator) Vishnu (preserver) and Shiva (destroyer). These changes led to an increased interest in the religion. SHIVA - THE DESTROYER BRAHMA - THE CREATOR VISHNU - THE PROTECTOR
Hinduism Moved toward Monotheism. Thought of the world as having 1 driving force. The three most important gods became Brahma (creator) Vishnu (preserver) and Shiva (destroyer). These changes led to an increased interest in the religion. SHIVA - THE DESTROYER BRAHMA - THE CREATOR VISHNU - THE PROTECTOR
 Advances many cultural developments (especially math & astronomy) • the idea of zero • modern numbers • the decimal system • the value of pi to 4 places • the length of the year as 365. 3586805 Days
Advances many cultural developments (especially math & astronomy) • the idea of zero • modern numbers • the decimal system • the value of pi to 4 places • the length of the year as 365. 3586805 Days
 Spread of Trade: Trade with Mediterranean Region and African grew • when the invaders (Hunas) told indians of the silk road, Guptas realized there was profit in being a middleman. India also built a trading fleet to transport goods by waterways
Spread of Trade: Trade with Mediterranean Region and African grew • when the invaders (Hunas) told indians of the silk road, Guptas realized there was profit in being a middleman. India also built a trading fleet to transport goods by waterways
 Effects of Indian Trade • Rise of Banking (lending money and charging interest) • Indian traders brought their culture to South East Asia (especially Java, Thailand, Cambodia) • Buddhism spreads to Sri Lanka, Nepal, and eventually China - Korea and Japan.
Effects of Indian Trade • Rise of Banking (lending money and charging interest) • Indian traders brought their culture to South East Asia (especially Java, Thailand, Cambodia) • Buddhism spreads to Sri Lanka, Nepal, and eventually China - Korea and Japan.
 CHAPTER 7 SECTION 3 HAN EMPIRE IN CHINA
CHAPTER 7 SECTION 3 HAN EMPIRE IN CHINA
 Vocab Centralize Government: Central authority controls state Civil Service: Hiring gov’t workers who passed tests. The Han used confucianism to test workers. (Who died 400 yrs. Before!) Monopoly: When 1 group has total control over production and distribution of certain goods Assimilation: Process of making different people part of the same culture
Vocab Centralize Government: Central authority controls state Civil Service: Hiring gov’t workers who passed tests. The Han used confucianism to test workers. (Who died 400 yrs. Before!) Monopoly: When 1 group has total control over production and distribution of certain goods Assimilation: Process of making different people part of the same culture
 Shi Hungdi’s (remember? legalist) son could not maintain empire. • The peasants revolted against harsh legalist policies. • Soon warlords were fighting for control. • Which vocabulary words would the Chinese use to explain these events?
Shi Hungdi’s (remember? legalist) son could not maintain empire. • The peasants revolted against harsh legalist policies. • Soon warlords were fighting for control. • Which vocabulary words would the Chinese use to explain these events?
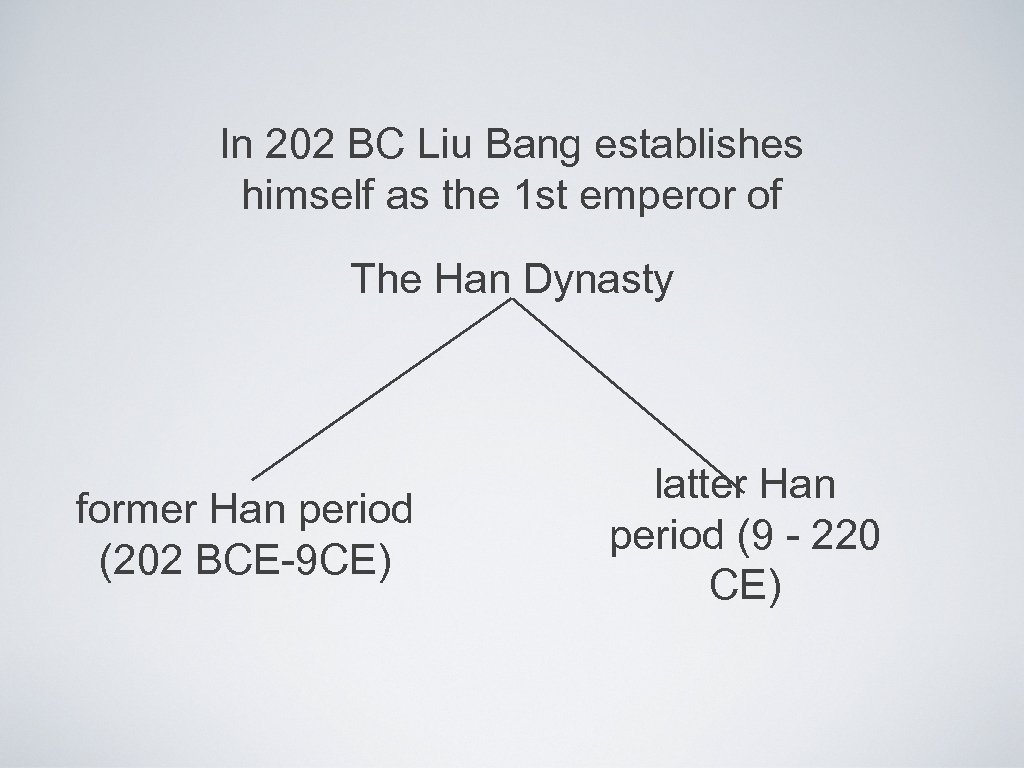 In 202 BC Liu Bang establishes himself as the 1 st emperor of The Han Dynasty former Han period (202 BCE-9 CE) latter Han period (9 - 220 CE)
In 202 BC Liu Bang establishes himself as the 1 st emperor of The Han Dynasty former Han period (202 BCE-9 CE) latter Han period (9 - 220 CE)
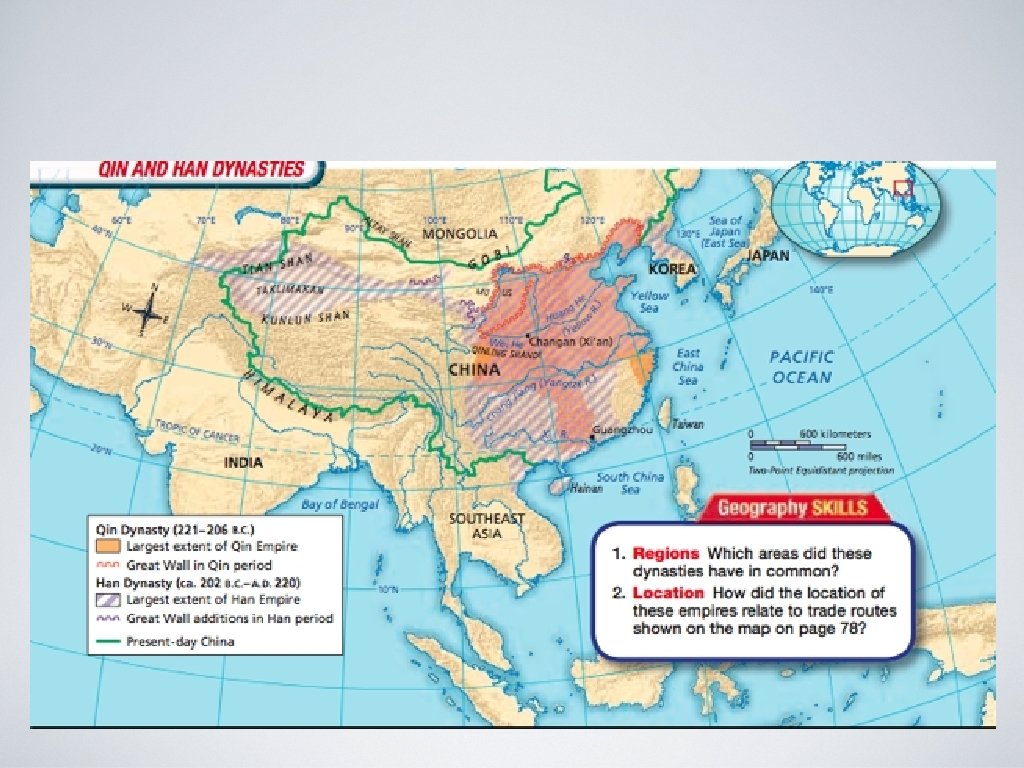
 Liu Bang maintained the centralized gov’t of the Qin Dynasty. Lowered taxes and softened punishments to end revolts. Who will take over when he dies? When Liu Bang died his son became emperor in name only, the real power was one of his wives, Lu. She ruled until he death in 180 BCE. Bang’s family then forced Lu’s out of power, HOW? by killing them
Liu Bang maintained the centralized gov’t of the Qin Dynasty. Lowered taxes and softened punishments to end revolts. Who will take over when he dies? When Liu Bang died his son became emperor in name only, the real power was one of his wives, Lu. She ruled until he death in 180 BCE. Bang’s family then forced Lu’s out of power, HOW? by killing them
 The Martial Emperor: Liu Bang’s grandson Wudi (woo-dee) expanded the empire. He conquer the nomadic raiders, Xiongnu (shee-ung-noo) in the North. After pushing them to Central Asia. He also took the northeast areas of what is today Manchuria and Korea, and to the South, in what is today vietnam. What effect does this have on Rome?
The Martial Emperor: Liu Bang’s grandson Wudi (woo-dee) expanded the empire. He conquer the nomadic raiders, Xiongnu (shee-ung-noo) in the North. After pushing them to Central Asia. He also took the northeast areas of what is today Manchuria and Korea, and to the South, in what is today vietnam. What effect does this have on Rome?
 Emperors had the Mandate of Heaven, what is that? _____What is the Dynasty Cycle? __________________
Emperors had the Mandate of Heaven, what is that? _____What is the Dynasty Cycle? __________________
 Highly Structured Gov’t: The Emperor could not rule alone. He taxed people to improve the land. Every farmer had to work 1/12 of the year for the emperor. This is how the Great Wall was expanded, and how the army was manned. Wudi had over 130, 000 gov’t workers. He wanted his workers to be “reverent, generous, truthful, diligent, and kind” since this is what Confucianism taught, he set up schools around China for those studying for government jobs. This system continued until 1912!
Highly Structured Gov’t: The Emperor could not rule alone. He taxed people to improve the land. Every farmer had to work 1/12 of the year for the emperor. This is how the Great Wall was expanded, and how the army was manned. Wudi had over 130, 000 gov’t workers. He wanted his workers to be “reverent, generous, truthful, diligent, and kind” since this is what Confucianism taught, he set up schools around China for those studying for government jobs. This system continued until 1912!
 • Han technology, commerce, & culture: During the time China invented: papera double bladed plowthe wheelbarrow started watermills to grind grain. What do most of these inventions deal with? During this time the # of Chinese grew to over 60, 000. With all these mouth to fed agriculture was prioritized. Manufacturing and commerce (______) were less important.
• Han technology, commerce, & culture: During the time China invented: papera double bladed plowthe wheelbarrow started watermills to grind grain. What do most of these inventions deal with? During this time the # of Chinese grew to over 60, 000. With all these mouth to fed agriculture was prioritized. Manufacturing and commerce (______) were less important.
 Wanting to keep the profits of trade the Han set up monopolies for salt, iron alcohol & minting of coinswith all this growing & conquering the Han tried to assimilate the different groups by sending farmers to the colonies, encouraging intermarriage, est. Schoolswriting & learning was encouraged why? _________
Wanting to keep the profits of trade the Han set up monopolies for salt, iron alcohol & minting of coinswith all this growing & conquering the Han tried to assimilate the different groups by sending farmers to the colonies, encouraging intermarriage, est. Schoolswriting & learning was encouraged why? _________

 Rebellion & Restoration: Land was given to sons, so as time goes on people are trying to grow food on not enough land. Families go into debt to buy ore land – if they can’t pay – they lose their land. Who wins who losses? ________ Political instability follows economic instability (loss of Mandate of Heaven) Wang Man (wahng mahng) decided a strong leader was need and the he should be it! this ends 1 st Han
Rebellion & Restoration: Land was given to sons, so as time goes on people are trying to grow food on not enough land. Families go into debt to buy ore land – if they can’t pay – they lose their land. Who wins who losses? ________ Political instability follows economic instability (loss of Mandate of Heaven) Wang Man (wahng mahng) decided a strong leader was need and the he should be it! this ends 1 st Han
 China in the latter Han Dynasty: Wang man: Minte who wins who losses? ______________
China in the latter Han Dynasty: Wang man: Minte who wins who losses? ______________
 In 11 CE a huge flood leaves 1, 000 s homeless and hungry. When they revolt the rich join them (why? ____) Wang is assassinated and replaced by a member of the old imperial family – latter Han dynasty begins So What Happened to the Han Empire? Although the latter Han reclaim some glory it declines and by 220 has split into 3 rival kingdoms.
In 11 CE a huge flood leaves 1, 000 s homeless and hungry. When they revolt the rich join them (why? ____) Wang is assassinated and replaced by a member of the old imperial family – latter Han dynasty begins So What Happened to the Han Empire? Although the latter Han reclaim some glory it declines and by 220 has split into 3 rival kingdoms.


