fd588dfddf55a2da93f4b085d25fb187.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

 Chapter 7 Network integration Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Chapter 7 Network integration Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Contents • Introduction • Network integration and supply chain design • Supply chain configuration and functional requirements • Stages of supply chain design and implementation • Factors to take into account in supply chain design • Modelling approaches • Concluding remarks Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Contents • Introduction • Network integration and supply chain design • Supply chain configuration and functional requirements • Stages of supply chain design and implementation • Factors to take into account in supply chain design • Modelling approaches • Concluding remarks Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Learning outcomes • Understand how supply chain design facilitates network integration. • Explain why and when network redesign is required. • Know what the different stages in network design and implementation entail. • Apply the main network design and implementation steps. • Identify the major factors to be taken into account during network design and in locating facilities. • Apply the centre-of-gravity method for single-facility locations. • Know which modelling approaches and techniques are applicable for network design. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Learning outcomes • Understand how supply chain design facilitates network integration. • Explain why and when network redesign is required. • Know what the different stages in network design and implementation entail. • Apply the main network design and implementation steps. • Identify the major factors to be taken into account during network design and in locating facilities. • Apply the centre-of-gravity method for single-facility locations. • Know which modelling approaches and techniques are applicable for network design. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Introduction • Supply chain network design can have a major impact an organisation’s competitiveness. • Network provides the veins, or channels, through which inventory flows. • Main network activities are movement, storage and transformation. Extends from the supply sources to the consumers of final products. • Decisions relating to the supply chain network have a significant effect for a relatively long period of time. • 80 per cent of a supply chain’s cost structure is determined by network design. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Introduction • Supply chain network design can have a major impact an organisation’s competitiveness. • Network provides the veins, or channels, through which inventory flows. • Main network activities are movement, storage and transformation. Extends from the supply sources to the consumers of final products. • Decisions relating to the supply chain network have a significant effect for a relatively long period of time. • 80 per cent of a supply chain’s cost structure is determined by network design. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
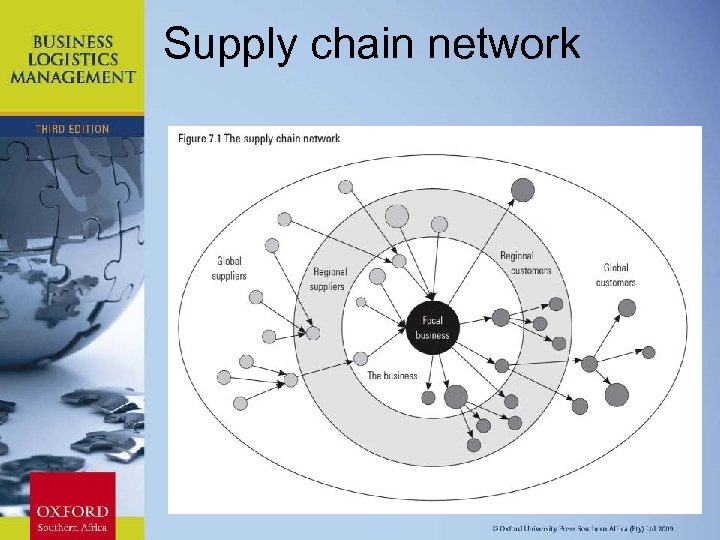 Supply chain network Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Supply chain network Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Network integration and supply chain design • Network integration requires the right design and configuration. • Involves the structural dimensions of the network as well as the careful selection of the members in the supply chain. • Relates to decisions regarding customer service; inventory policy; transportation modes; and the location and size of stocking points. • Key considerations include availability of sources of supply, manufacturing facilities and where the target markets are located. • Consider and evaluate a number of alternative supply chain networks (cost benefit trade-offs). Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Network integration and supply chain design • Network integration requires the right design and configuration. • Involves the structural dimensions of the network as well as the careful selection of the members in the supply chain. • Relates to decisions regarding customer service; inventory policy; transportation modes; and the location and size of stocking points. • Key considerations include availability of sources of supply, manufacturing facilities and where the target markets are located. • Consider and evaluate a number of alternative supply chain networks (cost benefit trade-offs). Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
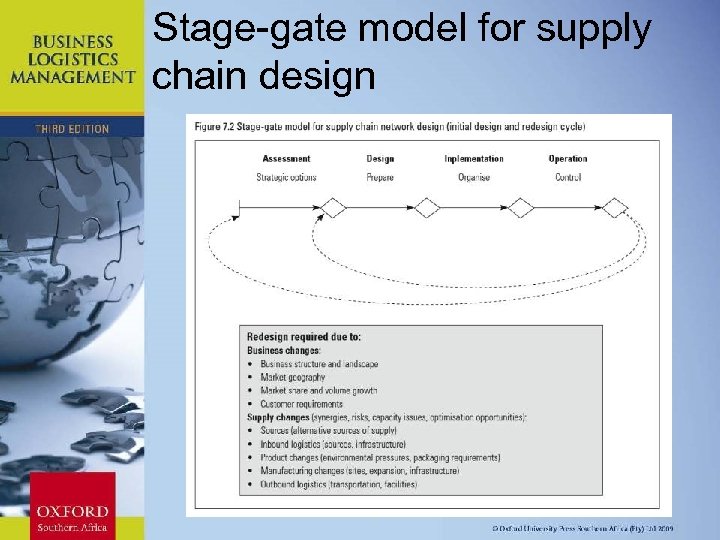 Stage-gate model for supply chain design Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Stage-gate model for supply chain design Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Supply chain design • Supply chain network may be relatively simple or very complex. • Supply chain attributes that determine supply chain complexity: customer base; product portfolio; supplier base; manufacturing (process, scale and variety); logistics scope (inbound and outbound); and systems/applications used. • Supply chain network design is generally not a regular activity (carried out every few years). • Capacity utilisation, throughput and inventory turnover: indicators used to evaluate how effective supply chain design is. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Supply chain design • Supply chain network may be relatively simple or very complex. • Supply chain attributes that determine supply chain complexity: customer base; product portfolio; supplier base; manufacturing (process, scale and variety); logistics scope (inbound and outbound); and systems/applications used. • Supply chain network design is generally not a regular activity (carried out every few years). • Capacity utilisation, throughput and inventory turnover: indicators used to evaluate how effective supply chain design is. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Supply chain design (continued) Key determinants of supply chain network structure: Markets • Marketing strategy and competitive requirements • Market segments, customers targeted, anticipated demand Facilities • Number, size and location • Geographic placement of production facilities, stocking points and transfer facilities Sources of supply • Location and number of sources of material, goods and services • Standardisation of major equipment, spare parts Transport • Physical link between customers and suppliers • Enabling the flow of materials and resources • Transport decision’s major impact Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Supply chain design (continued) Key determinants of supply chain network structure: Markets • Marketing strategy and competitive requirements • Market segments, customers targeted, anticipated demand Facilities • Number, size and location • Geographic placement of production facilities, stocking points and transfer facilities Sources of supply • Location and number of sources of material, goods and services • Standardisation of major equipment, spare parts Transport • Physical link between customers and suppliers • Enabling the flow of materials and resources • Transport decision’s major impact Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Supply chain configuration and functional requirements Design decision areas: • Network design and optimisation • Network operations analysis • Policy formulations and optimisation • Design for robustness (preparedness for risk) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Supply chain configuration and functional requirements Design decision areas: • Network design and optimisation • Network operations analysis • Policy formulations and optimisation • Design for robustness (preparedness for risk) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
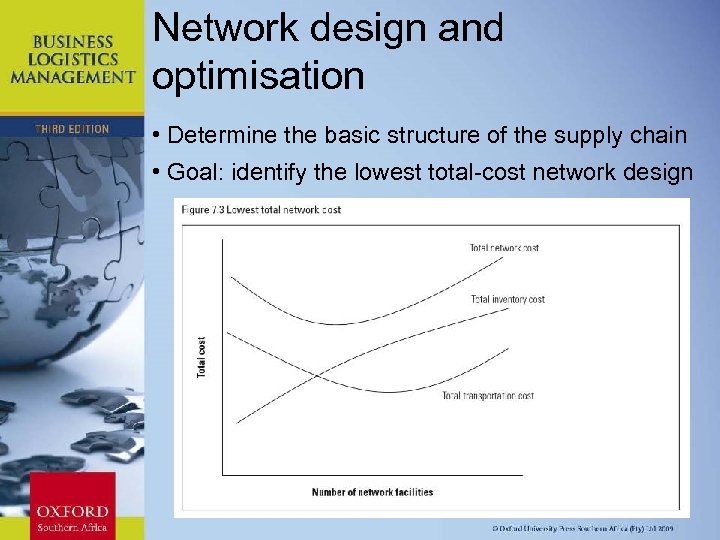 Network design and optimisation • Determine the basic structure of the supply chain • Goal: identify the lowest total-cost network design Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Network design and optimisation • Determine the basic structure of the supply chain • Goal: identify the lowest total-cost network design Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
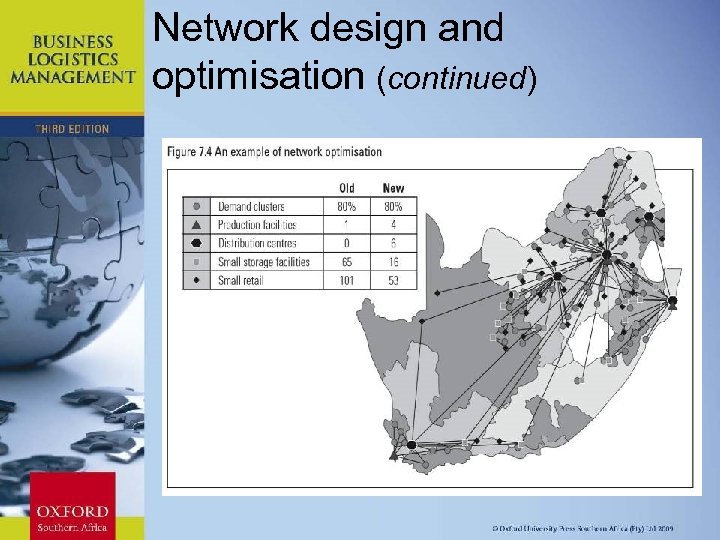 Network design and optimisation (continued) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Network design and optimisation (continued) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Network operations analysis • How will the supply chain operate in the real world with all its variability (variability in demand, supply and transportation)? • Network simulation is used. • Supply chain activities are evaluated for capacity, operation philosophy and some basic functional requirements. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Network operations analysis • How will the supply chain operate in the real world with all its variability (variability in demand, supply and transportation)? • Network simulation is used. • Supply chain activities are evaluated for capacity, operation philosophy and some basic functional requirements. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Policy formulations and optimisation • Establish best operating rules (policies). • Rules about whether or not inventory should be kept for various products, and how much and where inventory should be kept. • Other examples: will full truckload shipments suffice or are less than truckload shipments needed? Whether to make or buy components/sub-assemblies. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Policy formulations and optimisation • Establish best operating rules (policies). • Rules about whether or not inventory should be kept for various products, and how much and where inventory should be kept. • Other examples: will full truckload shipments suffice or are less than truckload shipments needed? Whether to make or buy components/sub-assemblies. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Design for robustness • Supply chains encounter some unforeseen disruptions, unplanned events or things that might go wrong (e. g. strikes, breakdowns and storms). • Risk assessment and contingency planning; methods to deal with such eventualities. • Ensure that the network does not perform poorly under other-than-expected conditions. • Some deviations from the original assumptions: • What if marketing was wrong about demand? • What if the cost of supply doubles? • What seemed like a good idea given forecasted conditions may kill the company under other conditions. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Design for robustness • Supply chains encounter some unforeseen disruptions, unplanned events or things that might go wrong (e. g. strikes, breakdowns and storms). • Risk assessment and contingency planning; methods to deal with such eventualities. • Ensure that the network does not perform poorly under other-than-expected conditions. • Some deviations from the original assumptions: • What if marketing was wrong about demand? • What if the cost of supply doubles? • What seemed like a good idea given forecasted conditions may kill the company under other conditions. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
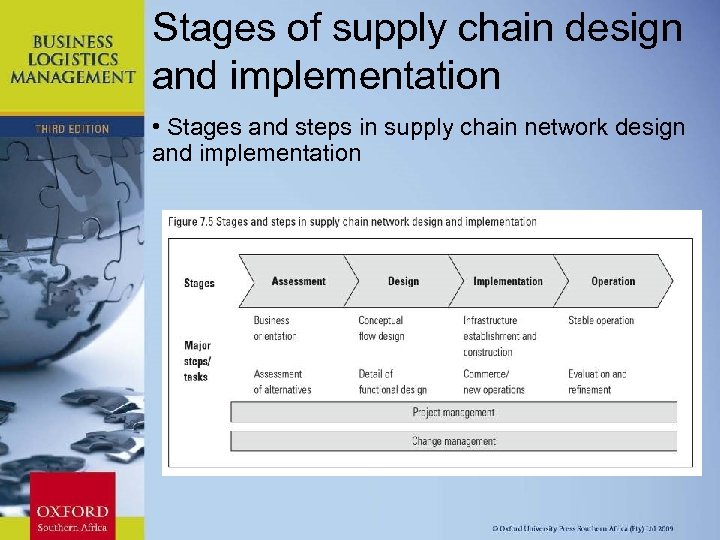 Stages of supply chain design and implementation • Stages and steps in supply chain network design and implementation Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Stages of supply chain design and implementation • Stages and steps in supply chain network design and implementation Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Assessment stage • Business orientation: • Business strategy, ownership, value-chain structure. • Alternatives business scenarios being considered. • Existing supply chain strategies and philosophy. • Product and market information. • Supply chain network alternatives: • Supply chain alternatives are developed and proposed. • Primary focus is on possible supply chain networks (inbound and outbound), basic configuration and assessing key supply chain role players. • Structured from a variety of the following available elements: storage and production facility locations; transport lanes and modes, etc. • First-order trade-offs between cost and service levels. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Assessment stage • Business orientation: • Business strategy, ownership, value-chain structure. • Alternatives business scenarios being considered. • Existing supply chain strategies and philosophy. • Product and market information. • Supply chain network alternatives: • Supply chain alternatives are developed and proposed. • Primary focus is on possible supply chain networks (inbound and outbound), basic configuration and assessing key supply chain role players. • Structured from a variety of the following available elements: storage and production facility locations; transport lanes and modes, etc. • First-order trade-offs between cost and service levels. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Design stage • Conceptual supply chain flow design: • Most feasible and effective supply chain alternatives are developed and refined; conceptual design proposal. • Prime focus is on inventory flow, buffer locations, infrastructure required and first-order functional and operational requirements (each elements or activities). • Aim to balance the capacity across all activities. • Risk assessment • Detailed functional design of the supply chain: • Detailed functional and/or operations design are refined and finalised for the supply chain proposed. • Focus on: finalising the supply chain configuration; functional and operations design; clarification with potential external suppliers, customers and internal departments. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Design stage • Conceptual supply chain flow design: • Most feasible and effective supply chain alternatives are developed and refined; conceptual design proposal. • Prime focus is on inventory flow, buffer locations, infrastructure required and first-order functional and operational requirements (each elements or activities). • Aim to balance the capacity across all activities. • Risk assessment • Detailed functional design of the supply chain: • Detailed functional and/or operations design are refined and finalised for the supply chain proposed. • Focus on: finalising the supply chain configuration; functional and operations design; clarification with potential external suppliers, customers and internal departments. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Implementation stage • Infrastructure establishment and construction: • Detailed supply chain functional design put into operation • Channels are prepared for commencing operations • Communication plays a vital role (alignment) • Operating procedures established • Commercial, operations and service-level agreements • Commence new operation: • Commencement of activities along the supply chain • Sales and operations planning (S&OP) fulfils key role • Sound communication plan (status, ramp-up, etc. ) • Conduct a pre-operation audit Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Implementation stage • Infrastructure establishment and construction: • Detailed supply chain functional design put into operation • Channels are prepared for commencing operations • Communication plays a vital role (alignment) • Operating procedures established • Commercial, operations and service-level agreements • Commence new operation: • Commencement of activities along the supply chain • Sales and operations planning (S&OP) fulfils key role • Sound communication plan (status, ramp-up, etc. ) • Conduct a pre-operation audit Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Operation stage • Post-implementation evaluation • Compare the actual configuration and performance with what was originally intended • Operations assessment and benchmarking • Customer-satisfaction survey • Philosophy of continuous improvement Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Operation stage • Post-implementation evaluation • Compare the actual configuration and performance with what was originally intended • Operations assessment and benchmarking • Customer-satisfaction survey • Philosophy of continuous improvement Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Factors to take into account in supply chain design • Understanding a specific business’s context • Interdependencies with other related supply chains • Master agreements within an organisation • Country-specific logistics infrastructure • Factors that influence location decisions. . . (next slide) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Factors to take into account in supply chain design • Understanding a specific business’s context • Interdependencies with other related supply chains • Master agreements within an organisation • Country-specific logistics infrastructure • Factors that influence location decisions. . . (next slide) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
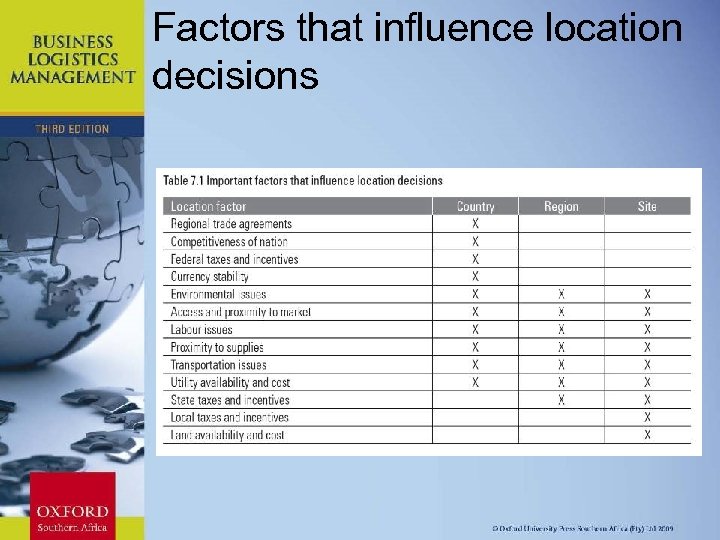 Factors that influence location decisions Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Factors that influence location decisions Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Modelling approaches • Approximate methods • Mathematical optimisation • Simulation • Heuristics Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Modelling approaches • Approximate methods • Mathematical optimisation • Simulation • Heuristics Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Weighted-factor rating method A popular approximate method used to compare the attractiveness of several alternatives against a number of quantitative and qualitative dimensions. The main steps to follow include: • identifying the factors; • assigning weights to each factor (0, 00– 1, 00; all weights add to 1); • subjectively rating each alternative against each factor (0– 100; 100 being the best); • multiplying the factor rating by the weight, then adding the weighted scores; and • selecting the alternative with the highest total weighted score. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Weighted-factor rating method A popular approximate method used to compare the attractiveness of several alternatives against a number of quantitative and qualitative dimensions. The main steps to follow include: • identifying the factors; • assigning weights to each factor (0, 00– 1, 00; all weights add to 1); • subjectively rating each alternative against each factor (0– 100; 100 being the best); • multiplying the factor rating by the weight, then adding the weighted scores; and • selecting the alternative with the highest total weighted score. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
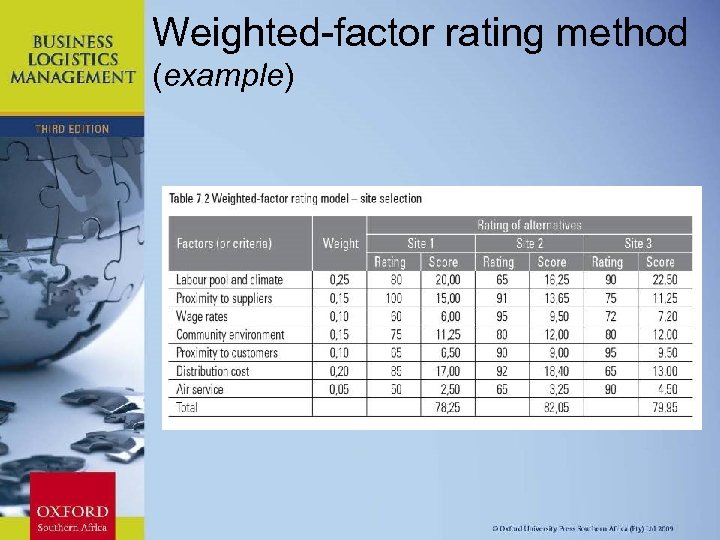 Weighted-factor rating method (example) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Weighted-factor rating method (example) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Centre-of-gravity method • Involves mapping a number of locations on an x-, y- coordinate grid and then finding a central location closest to all. • x-coordinate = sum of (each location’s x-coordinate x weight) total weight • y-coordinate = sum of (each location’s y-coordinate x weight) total weight Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Centre-of-gravity method • Involves mapping a number of locations on an x-, y- coordinate grid and then finding a central location closest to all. • x-coordinate = sum of (each location’s x-coordinate x weight) total weight • y-coordinate = sum of (each location’s y-coordinate x weight) total weight Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
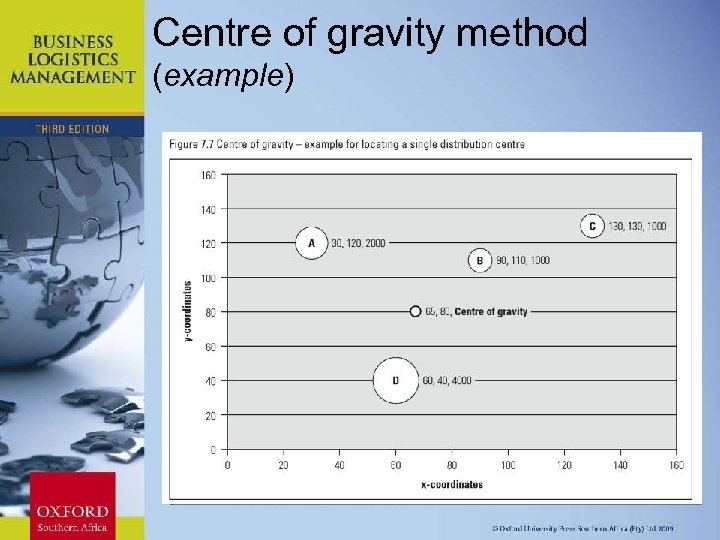 Centre of gravity method (example) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Centre of gravity method (example) Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
 Concluding remarks • Designing an optimal supply chain network is one of the cornerstones of competitive world-class organisations. • Network integration focuses on: physical structure and arrangement of supply chain activities; right interfacing; and balancing of capacity. • Many supply chains networks have purely evolved over time, making then less efficient and effective. • Design and implementation goes through stages to ensure sound decision making. • Many factors that influence design should be taken into account. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership
Concluding remarks • Designing an optimal supply chain network is one of the cornerstones of competitive world-class organisations. • Network integration focuses on: physical structure and arrangement of supply chain activities; right interfacing; and balancing of capacity. • Many supply chains networks have purely evolved over time, making then less efficient and effective. • Design and implementation goes through stages to ensure sound decision making. • Many factors that influence design should be taken into account. Chapter 11: Strategic Leadership


