ae11dda0362a2925f727e3aef2a83878.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Chapter 7: Creating The Constitution How did the United States Constitution overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of confederation and provide for the organization of the new government?
Chapter 7: Creating The Constitution How did the United States Constitution overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of confederation and provide for the organization of the new government?
 Section 1: Governing A New Nation What were the major success and failures of the government under the Articles of Confederation?
Section 1: Governing A New Nation What were the major success and failures of the government under the Articles of Confederation?
 Government By the States • Eleven of 13 States write constitutions • Constitution is a document stating the rules under which a government will operate • New State Constitutions limited the powers of the governor • Most power went to the State legislatures elected by the people
Government By the States • Eleven of 13 States write constitutions • Constitution is a document stating the rules under which a government will operate • New State Constitutions limited the powers of the governor • Most power went to the State legislatures elected by the people
 George Clinton Governor’s Powers • Governor’s of NYS • Appointed Key state officials • Served as the State’s executive
George Clinton Governor’s Powers • Governor’s of NYS • Appointed Key state officials • Served as the State’s executive
 Articles of Confederation • • • POWER RESERVED FOR THE STATES!! 1 Branch- Congress Makes laws 1 vote per state Deal with foreign and Native American nations Borrow money from foreign powers Coin money Set taxes Declare war or peace
Articles of Confederation • • • POWER RESERVED FOR THE STATES!! 1 Branch- Congress Makes laws 1 vote per state Deal with foreign and Native American nations Borrow money from foreign powers Coin money Set taxes Declare war or peace
 Problems Under The Articles of Confederation • • Congress COULD NOT… Regulate trade Force states to pay taxes Control/regulate interstate trade (commerce) • LIMITED FEDERAL POWER
Problems Under The Articles of Confederation • • Congress COULD NOT… Regulate trade Force states to pay taxes Control/regulate interstate trade (commerce) • LIMITED FEDERAL POWER
 Western Lands • The United States extended to the Mississippi River • Congress wanted to settle the lands in the Ohio River Valley • Congress needed laws to settle the land
Western Lands • The United States extended to the Mississippi River • Congress wanted to settle the lands in the Ohio River Valley • Congress needed laws to settle the land
 Land Ordinance of 1785 • Surveyors divided the land into townships • 6 miles on each side • Each of the 36 sections would sell for not less than $1. 00 and acre • Within each township 1 acre was set aside for schools • The nation’s leaders believed that democracy depended on EDUCATION
Land Ordinance of 1785 • Surveyors divided the land into townships • 6 miles on each side • Each of the 36 sections would sell for not less than $1. 00 and acre • Within each township 1 acre was set aside for schools • The nation’s leaders believed that democracy depended on EDUCATION
 Northwest Ordinance of 1787 • 3 Step Process for this area to be divided into states • First, Congress would appoint a governor, secretary, and 3 judges • Second, when 5, 000 free adult males had settled the area they could elect a legislature • Third, once there were 60, 000 free settlers they could apply for statehood
Northwest Ordinance of 1787 • 3 Step Process for this area to be divided into states • First, Congress would appoint a governor, secretary, and 3 judges • Second, when 5, 000 free adult males had settled the area they could elect a legislature • Third, once there were 60, 000 free settlers they could apply for statehood
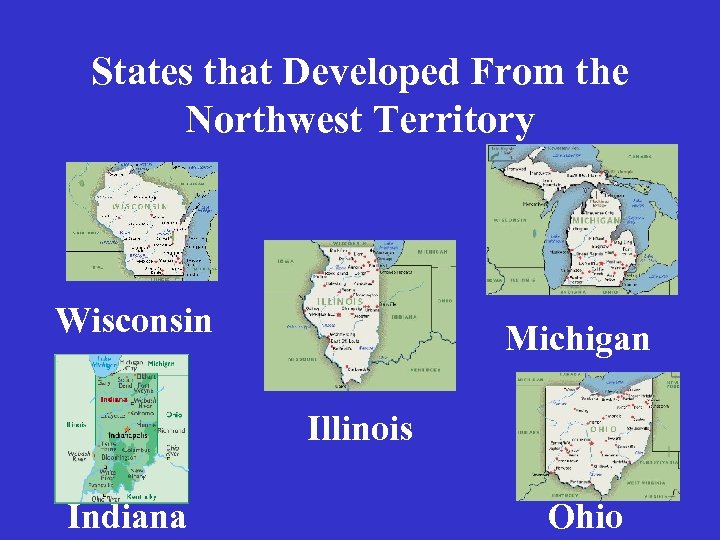 States that Developed From the Northwest Territory Wisconsin Michigan Illinois Indiana Ohio
States that Developed From the Northwest Territory Wisconsin Michigan Illinois Indiana Ohio
 Growing Problems • Economic problems led to Shay’s Rebellion • Foreign Affairs were week • Many nations felt that the US was week because Britain still occupied the Northwest Territory
Growing Problems • Economic problems led to Shay’s Rebellion • Foreign Affairs were week • Many nations felt that the US was week because Britain still occupied the Northwest Territory
 Shay’s Rebellion • Daniel Shays • 1786 • Economic depression hits and farmers in MA cannot pay taxes and money owed on farms • MA legislature decides to take the land from the farmers • Shays and about 1, 000 to 2, 000 farmers rebel • Rebellion does not last, but proves that the Federal Government is too week under the Articles of Confederation
Shay’s Rebellion • Daniel Shays • 1786 • Economic depression hits and farmers in MA cannot pay taxes and money owed on farms • MA legislature decides to take the land from the farmers • Shays and about 1, 000 to 2, 000 farmers rebel • Rebellion does not last, but proves that the Federal Government is too week under the Articles of Confederation
 Section 2: The Constitutional Convention What role did compromise play in the creation of the United States Constitution? Pictures from: http: //www. thecre. com/fedlaw/legal 9/bdsdhome. htm and http: //library. thinkquest. org/11572/media/meeting. jpeg
Section 2: The Constitutional Convention What role did compromise play in the creation of the United States Constitution? Pictures from: http: //www. thecre. com/fedlaw/legal 9/bdsdhome. htm and http: //library. thinkquest. org/11572/media/meeting. jpeg
 The Constitutional Convention • Meets in Philadelphia, PA • Summer 1787 • Members do NOT have the authority to “form some new system of government” • Congress was called to just REVISE the Articles of Confederation • Delegates realize this is not enough
The Constitutional Convention • Meets in Philadelphia, PA • Summer 1787 • Members do NOT have the authority to “form some new system of government” • Congress was called to just REVISE the Articles of Confederation • Delegates realize this is not enough
 Virginia Plan • • Edmund Randolph and James Madison, VA Plan promotes idea of STRONG Central Govt. 3 branches- Executive, Judicial, and Legislative branch – 2 Houses Lower House and Upper house • Representation in those branches based on States’ Population Pictures from: http: //www. visitingdc. com/president/james-madison-picture. htm and http: //memory. loc. gov/ammem/collections/continental/randolph. html
Virginia Plan • • Edmund Randolph and James Madison, VA Plan promotes idea of STRONG Central Govt. 3 branches- Executive, Judicial, and Legislative branch – 2 Houses Lower House and Upper house • Representation in those branches based on States’ Population Pictures from: http: //www. visitingdc. com/president/james-madison-picture. htm and http: //memory. loc. gov/ammem/collections/continental/randolph. html
 New Jersey Plan • William Paterson, NJ • 3 Banches of Govt. Executive, Judicial, and Legislative • Only 1 House within the Legislature and only 1 Vote Per State No matter the size Pictures From:
New Jersey Plan • William Paterson, NJ • 3 Banches of Govt. Executive, Judicial, and Legislative • Only 1 House within the Legislature and only 1 Vote Per State No matter the size Pictures From:
 The Great Compromise • Roger Sherman, CT • 3 Branches of Govt. - Executive, Judicial, and Legislative • 2 Houses for the legislative and Upper and Lower House • The Lower House- House of Representatives based on Population • The Upper house – 2 Representatives per state Pictures From: http: //www. cslib. org/gov/images/baldwinrs. jpg and http: //www. americanrevolution. com/images/Roger. Sherman 1. jpg
The Great Compromise • Roger Sherman, CT • 3 Branches of Govt. - Executive, Judicial, and Legislative • 2 Houses for the legislative and Upper and Lower House • The Lower House- House of Representatives based on Population • The Upper house – 2 Representatives per state Pictures From: http: //www. cslib. org/gov/images/baldwinrs. jpg and http: //www. americanrevolution. com/images/Roger. Sherman 1. jpg
 Question #13 During the Constitutional Convention how did the VA Plan and NJ Plan differ? The VA Plan called for a two house legislature with more representation for larger states; the NJ Plan called for a one house legislature with equal representation for all states
Question #13 During the Constitutional Convention how did the VA Plan and NJ Plan differ? The VA Plan called for a two house legislature with more representation for larger states; the NJ Plan called for a one house legislature with equal representation for all states
 Question #14 Why did NJ and other small states oppose the VA Plan? The small states felt it would give the large states too much power. They felt the large states would always be able to out vote them because they would have more representation in Congress.
Question #14 Why did NJ and other small states oppose the VA Plan? The small states felt it would give the large states too much power. They felt the large states would always be able to out vote them because they would have more representation in Congress.
 Question #15 How did the Great Compromise satisfy large and Small States? Large States: House of Representatives representation was based on population Small States: Representation in the Senate was 2 per state
Question #15 How did the Great Compromise satisfy large and Small States? Large States: House of Representatives representation was based on population Small States: Representation in the Senate was 2 per state
 3/5 ths Compromise • Now the problem was how was population to be counted? ? • Should slaves be counted in Southern Population to determine representation in the House of Rep. ? • Compromise: • 3/5 ths So, for every 5 slaves they would count as 3 people toward population count • Ex. 5, 000 slaves would count as 3, 000 toward population count
3/5 ths Compromise • Now the problem was how was population to be counted? ? • Should slaves be counted in Southern Population to determine representation in the House of Rep. ? • Compromise: • 3/5 ths So, for every 5 slaves they would count as 3 people toward population count • Ex. 5, 000 slaves would count as 3, 000 toward population count
 Question #16 What compromise did the North and South reach on the slave trade issue? Ships would be allowed to bring slaves in for 20 more years. After 1808 Congress would stop the Trans-Atlantic slave trade. However, Domestic Slave trade would continue
Question #16 What compromise did the North and South reach on the slave trade issue? Ships would be allowed to bring slaves in for 20 more years. After 1808 Congress would stop the Trans-Atlantic slave trade. However, Domestic Slave trade would continue
 Section 3: Debating the Constitution How did those in favor of the Constitution achieve its ratification? Pictures From: http: //www. historyteacher. net/AHAP/Web. Quests/WQ-Constitutional. Convention/WQ-Con. Conv-student-main_page. htm
Section 3: Debating the Constitution How did those in favor of the Constitution achieve its ratification? Pictures From: http: //www. historyteacher. net/AHAP/Web. Quests/WQ-Constitutional. Convention/WQ-Con. Conv-student-main_page. htm
 Federalists • John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, James Madison • STRONG CENTRAL GOVERNMENT!! Pictures From: http: //www. archives. gov/nhprc/annotation/march-2002/religion-founding-fathers. html and http: //www. explorepahistory. com/cms/pbfiles/Project 1/Scheme 34/Explore. PAHistory-a 0 h 9 q 5 -a_349. jpg and
Federalists • John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, James Madison • STRONG CENTRAL GOVERNMENT!! Pictures From: http: //www. archives. gov/nhprc/annotation/march-2002/religion-founding-fathers. html and http: //www. explorepahistory. com/cms/pbfiles/Project 1/Scheme 34/Explore. PAHistory-a 0 h 9 q 5 -a_349. jpg and
 Federalists • John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, James Madison • Wanted a STRONG CENTRAL GOVT • Thought the Constitution was fine the way it was • The National Govt. had to be strong and hold powers that it was not granted under the Articles of confederation
Federalists • John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, James Madison • Wanted a STRONG CENTRAL GOVT • Thought the Constitution was fine the way it was • The National Govt. had to be strong and hold powers that it was not granted under the Articles of confederation
 Federalist Papers • John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, James Madison • Series of 85 newspaper essays • Tried to get people to SUPPORT RATIFYING THE CONSTITUTION
Federalist Papers • John Jay, Alexander Hamilton, James Madison • Series of 85 newspaper essays • Tried to get people to SUPPORT RATIFYING THE CONSTITUTION
 Anti. Federalists • • Patrick Henry and George Mason Stronger State Power Needs a BILL of RIGHTS Says Constitution weakens the states, needs a Bill of Rights to protect the people from tyranny, would the president be too much like a King Under the Constitution Pictures From: http: //www. redhill. org/images. Rh/home_ph. jpg and http: //www. vahistorical. org/sva 2003/mason. htm
Anti. Federalists • • Patrick Henry and George Mason Stronger State Power Needs a BILL of RIGHTS Says Constitution weakens the states, needs a Bill of Rights to protect the people from tyranny, would the president be too much like a King Under the Constitution Pictures From: http: //www. redhill. org/images. Rh/home_ph. jpg and http: //www. vahistorical. org/sva 2003/mason. htm
 Bill of Rights • 1 st 10 Amendments to the Constitution • • • 1 st Amendment: Freedom of Speech, Religion Press, Assembly, Petition 2 nd Amendment: Right to Bear Arms 3 rd Amendment: No Quartering Troops 4 th Amendment: No Illegal Search and Seizures 5 th Amendment: Right to Due Process 6 th Amendment: Right to Trial By Jury 7 th Amendment: Civil Trials 8 th Amendment: No Excessive Bail 9 th Amendment: The Rights of the people are not limited to those listed in the Bill of Rights 10 th Amendment: Powers Reserved to the States
Bill of Rights • 1 st 10 Amendments to the Constitution • • • 1 st Amendment: Freedom of Speech, Religion Press, Assembly, Petition 2 nd Amendment: Right to Bear Arms 3 rd Amendment: No Quartering Troops 4 th Amendment: No Illegal Search and Seizures 5 th Amendment: Right to Due Process 6 th Amendment: Right to Trial By Jury 7 th Amendment: Civil Trials 8 th Amendment: No Excessive Bail 9 th Amendment: The Rights of the people are not limited to those listed in the Bill of Rights 10 th Amendment: Powers Reserved to the States


