927706af70580eb64b70a48eec60e8cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Chapter 7 Congress at Work
Chapter 7 Congress at Work
 7. 1 What are the different types of bills & resolutions? n n n Private bills: indiv. people/places (e. g. claims against gov’t, immigration) Public bills: apply to entire nation (e. g. taxes, health care, security) Approx. 30% of total Resolutions ¨ Simple: one house, internal issue ¨ Joint: H&S, “law” w/Pres signature ¨ Concurrent: H&S, issues concerning Congress n Riders: unrelated provisions ¨ Used to “sneak” in a proposal or to “poison pill”
7. 1 What are the different types of bills & resolutions? n n n Private bills: indiv. people/places (e. g. claims against gov’t, immigration) Public bills: apply to entire nation (e. g. taxes, health care, security) Approx. 30% of total Resolutions ¨ Simple: one house, internal issue ¨ Joint: H&S, “law” w/Pres signature ¨ Concurrent: H&S, issues concerning Congress n Riders: unrelated provisions ¨ Used to “sneak” in a proposal or to “poison pill”
 7. 1 Why do most bills never become laws? n n Less than 5% become public laws Process is long and complicated (100+ steps) ¨ Advantage: opponents ¨ Proponents must compromise (and not tick off powerful interests) n Sometimes just for show
7. 1 Why do most bills never become laws? n n Less than 5% become public laws Process is long and complicated (100+ steps) ¨ Advantage: opponents ¨ Proponents must compromise (and not tick off powerful interests) n Sometimes just for show
 7. 1 What occurs before a bill is debated on the floor? n Introduction (either house, except $) ¨ Sometimes simultaneously in both houses ¨ Sponsors/co-sponsors ¨ 1 st Reading n Committee Action ¨ Hearings: testimony, debate ¨ Staff research ¨ Markup session ¨ Report, amend, kill, “pigeonhole”
7. 1 What occurs before a bill is debated on the floor? n Introduction (either house, except $) ¨ Sometimes simultaneously in both houses ¨ Sponsors/co-sponsors ¨ 1 st Reading n Committee Action ¨ Hearings: testimony, debate ¨ Staff research ¨ Markup session ¨ Report, amend, kill, “pigeonhole”
 7. 1 What happens during floor action? n Second reading ¨ Amendments offered after each section ¨ House can adopt “closed rule” n Debate ¨ Majority n approve any changes Voting (quorum needed) ¨ Third reading (with changes) ¨ Voice ¨ Standing/division ¨ Recorded/Roll-call
7. 1 What happens during floor action? n Second reading ¨ Amendments offered after each section ¨ House can adopt “closed rule” n Debate ¨ Majority n approve any changes Voting (quorum needed) ¨ Third reading (with changes) ¨ Voice ¨ Standing/division ¨ Recorded/Roll-call
 7. 1 What are the final steps in passing a bill? n Conference Committee Make identical version-typically experts ¨ Almost always issue conference report ¨ n Presidential Action ¨ n Sign, “pocket pass”, pocket veto, veto Congressional Override ¨ 2/3 vote of House and Senate-RARE
7. 1 What are the final steps in passing a bill? n Conference Committee Make identical version-typically experts ¨ Almost always issue conference report ¨ n Presidential Action ¨ n Sign, “pocket pass”, pocket veto, veto Congressional Override ¨ 2/3 vote of House and Senate-RARE
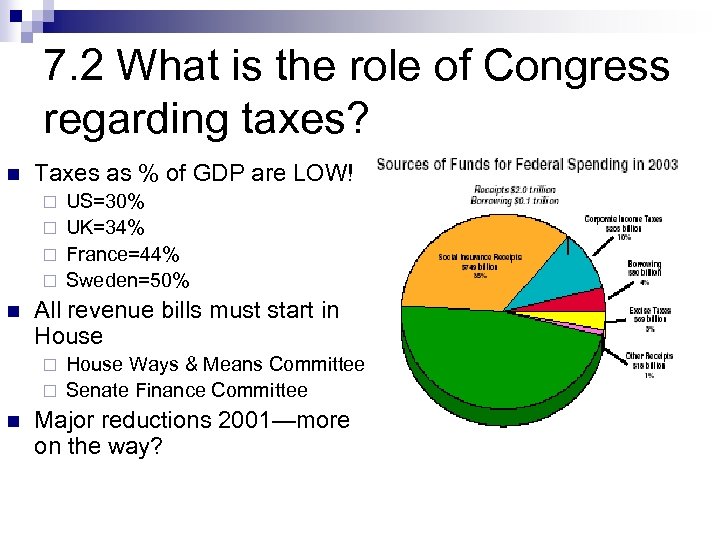 7. 2 What is the role of Congress regarding taxes? n Taxes as % of GDP are LOW! US=30% ¨ UK=34% ¨ France=44% ¨ Sweden=50% ¨ n All revenue bills must start in House Ways & Means Committee ¨ Senate Finance Committee ¨ n Major reductions 2001—more on the way?
7. 2 What is the role of Congress regarding taxes? n Taxes as % of GDP are LOW! US=30% ¨ UK=34% ¨ France=44% ¨ Sweden=50% ¨ n All revenue bills must start in House Ways & Means Committee ¨ Senate Finance Committee ¨ n Major reductions 2001—more on the way?
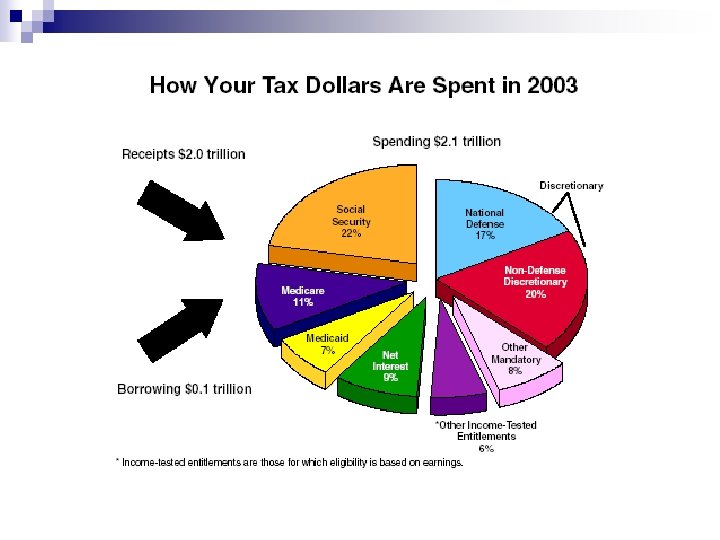
 7. 2 What is the role of Cong. regarding spending money? n n n U. S. spends over $2 trill/yr. (debt v. deficit) Congress appropriates—approves—government spending Authorization vs. Appropriation President submits a budget proposal H & S Appropriations Committees ¨ Hear n testimony on value of gov. programs Uncontrollables vs. Discretionary (2: 1) ¨ Entitlements: SS, Medicare, Medicaid, etc.
7. 2 What is the role of Cong. regarding spending money? n n n U. S. spends over $2 trill/yr. (debt v. deficit) Congress appropriates—approves—government spending Authorization vs. Appropriation President submits a budget proposal H & S Appropriations Committees ¨ Hear n testimony on value of gov. programs Uncontrollables vs. Discretionary (2: 1) ¨ Entitlements: SS, Medicare, Medicaid, etc.
 7. 3 How do voters influence Congress? n n Constituents: people one is elected to serve Needs of constituents vs. personal beliefs ¨ Daily n life=constituents, Other=personal Taking the Pulse: ¨ Visits home ¨ Letters/Calls/Emails/Visits ¨ Polls ¨ Big supporters’ wish lists n Voters are IGNORANT! ¨ Opponents enlighten, incumbents do the same
7. 3 How do voters influence Congress? n n Constituents: people one is elected to serve Needs of constituents vs. personal beliefs ¨ Daily n life=constituents, Other=personal Taking the Pulse: ¨ Visits home ¨ Letters/Calls/Emails/Visits ¨ Polls ¨ Big supporters’ wish lists n Voters are IGNORANT! ¨ Opponents enlighten, incumbents do the same
 7. 3 How do political parties influence Congress? n n n The more important the issue to the parties, the more partisan the vote Some issues aren’t clearly defined by parties Parties do mean something: ¨ R: less spending, local solutions, business and $$ ¨ D: social-welfare, tax help for ¢, regulate business n Sometimes Congress people are ignorant too! ¨ Vote with respected colleagues ¨ Vote how the people with big sticks tell you to
7. 3 How do political parties influence Congress? n n n The more important the issue to the parties, the more partisan the vote Some issues aren’t clearly defined by parties Parties do mean something: ¨ R: less spending, local solutions, business and $$ ¨ D: social-welfare, tax help for ¢, regulate business n Sometimes Congress people are ignorant too! ¨ Vote with respected colleagues ¨ Vote how the people with big sticks tell you to
 7. 3 What are the other influences on Congress? n President ¨ Proposals, n Interest Groups ¨ Lobbyists, n n n info, citizen action, testimony, $ Political Action Committees (PACs) ¨ Political n media pressure, favors/punish fundraising organizations Personality Nature of issue (personal vs. people) Congressional staff
7. 3 What are the other influences on Congress? n President ¨ Proposals, n Interest Groups ¨ Lobbyists, n n n info, citizen action, testimony, $ Political Action Committees (PACs) ¨ Political n media pressure, favors/punish fundraising organizations Personality Nature of issue (personal vs. people) Congressional staff
 7. 4 How do lawmakers help individual constituents? n Casework: helping people w/problems ¨ Caseworkers handle small problems ¨ Lawmakers handle big problems n Why bother? ¨ Votes, n oversight, it’s the nice thing to do Helping the folks back home ¨ Pork-barrel: n logrolling bring home the (bacon) public works ¨ Federal grants/contracts: get a return n Military contracts, federal projects, etc. on tax $
7. 4 How do lawmakers help individual constituents? n Casework: helping people w/problems ¨ Caseworkers handle small problems ¨ Lawmakers handle big problems n Why bother? ¨ Votes, n oversight, it’s the nice thing to do Helping the folks back home ¨ Pork-barrel: n logrolling bring home the (bacon) public works ¨ Federal grants/contracts: get a return n Military contracts, federal projects, etc. on tax $


