c07d35417622a6a1390436cf3f1932ce.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 CHAPTER 7: COMPUTER SOFTWARE
CHAPTER 7: COMPUTER SOFTWARE
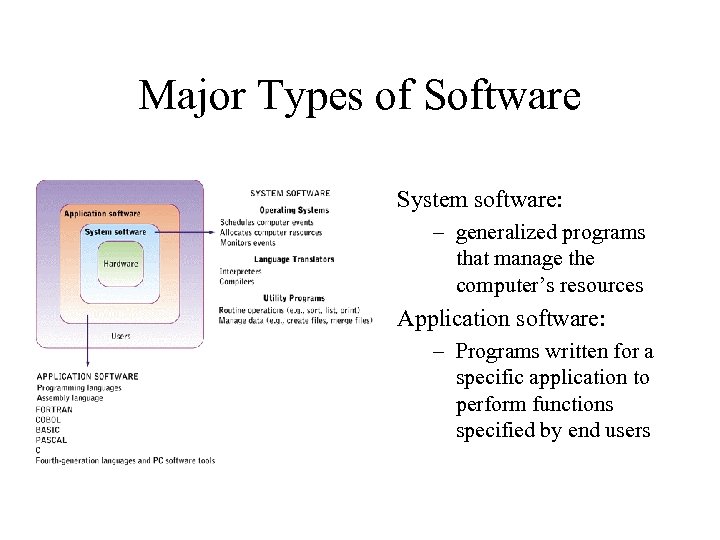 Major Types of Software System software: – generalized programs that manage the computer’s resources Application software: – Programs written for a specific application to perform functions specified by end users
Major Types of Software System software: – generalized programs that manage the computer’s resources Application software: – Programs written for a specific application to perform functions specified by end users
 Operating System Functions • Allocation and Assignment – Allocates resources to applications – Controls primary memory allocation • Scheduling – Scheduling processing, inputs and outputs • Monitoring – Keeps tracks of users and jobs
Operating System Functions • Allocation and Assignment – Allocates resources to applications – Controls primary memory allocation • Scheduling – Scheduling processing, inputs and outputs • Monitoring – Keeps tracks of users and jobs
 Managing Multiple Users (1) • Multiprogramming/Multitasking – Allows two or more programs to share resources of same computer – CPU executes one program while managing input and output of other program • Multithreading – The capability of an operating system to execute different parts of the same program (threads) at the same time
Managing Multiple Users (1) • Multiprogramming/Multitasking – Allows two or more programs to share resources of same computer – CPU executes one program while managing input and output of other program • Multithreading – The capability of an operating system to execute different parts of the same program (threads) at the same time
 Managing Multiple Users (2) • Virtual Memory – Creates efficiency by dividing the programs into small sections (pages) and reading them into memory only when needed • Timesharing – Allows computer resources to be shared by many users simultaneously by having the CPU spend a fixed amount of time on each user’s program • Multiprocessing – Allows computer to execute two or more instructions simultaneously in a single computer system by using multiple CPUs
Managing Multiple Users (2) • Virtual Memory – Creates efficiency by dividing the programs into small sections (pages) and reading them into memory only when needed • Timesharing – Allows computer resources to be shared by many users simultaneously by having the CPU spend a fixed amount of time on each user’s program • Multiprocessing – Allows computer to execute two or more instructions simultaneously in a single computer system by using multiple CPUs
 Language Translation • Compiler – Translates source code into object code all at one time • Interpreters – Translates source code one line at a time
Language Translation • Compiler – Translates source code into object code all at one time • Interpreters – Translates source code one line at a time
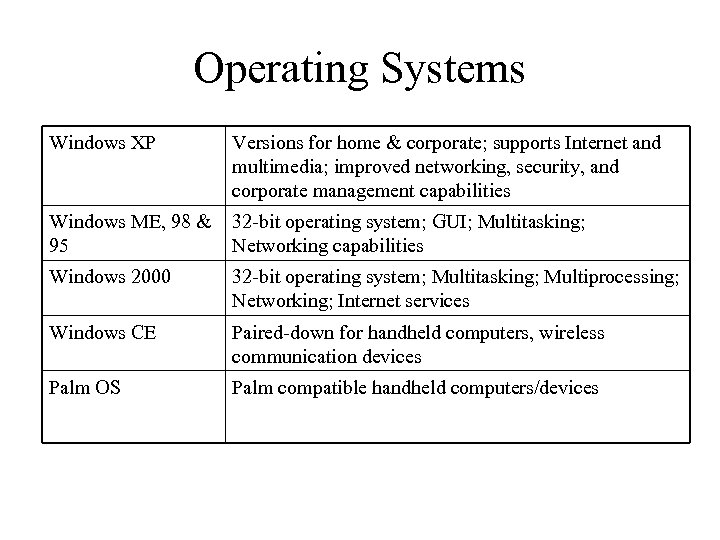 Operating Systems Windows XP Versions for home & corporate; supports Internet and multimedia; improved networking, security, and corporate management capabilities Windows ME, 98 & 95 32 -bit operating system; GUI; Multitasking; Networking capabilities Windows 2000 32 -bit operating system; Multitasking; Multiprocessing; Networking; Internet services Windows CE Paired-down for handheld computers, wireless communication devices Palm OS Palm compatible handheld computers/devices
Operating Systems Windows XP Versions for home & corporate; supports Internet and multimedia; improved networking, security, and corporate management capabilities Windows ME, 98 & 95 32 -bit operating system; GUI; Multitasking; Networking capabilities Windows 2000 32 -bit operating system; Multitasking; Multiprocessing; Networking; Internet services Windows CE Paired-down for handheld computers, wireless communication devices Palm OS Palm compatible handheld computers/devices
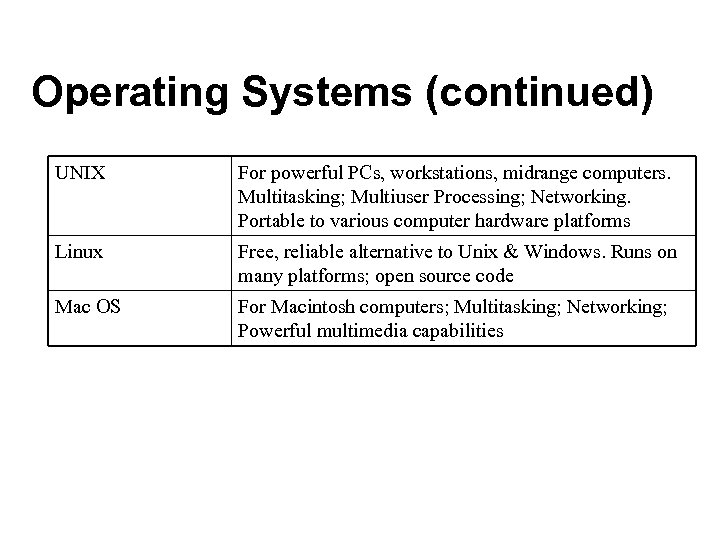 Operating Systems (continued) UNIX For powerful PCs, workstations, midrange computers. Multitasking; Multiuser Processing; Networking. Portable to various computer hardware platforms Linux Free, reliable alternative to Unix & Windows. Runs on many platforms; open source code Mac OS For Macintosh computers; Multitasking; Networking; Powerful multimedia capabilities
Operating Systems (continued) UNIX For powerful PCs, workstations, midrange computers. Multitasking; Multiuser Processing; Networking. Portable to various computer hardware platforms Linux Free, reliable alternative to Unix & Windows. Runs on many platforms; open source code Mac OS For Macintosh computers; Multitasking; Networking; Powerful multimedia capabilities
 Programming Languages • First Generation: Machine Language – All instructions written in binary (0 s and 1 s) • Second Generation: Assembly languages (1950 s) – Substitutes mnemonics for numeric codes • Third Generation: since mid 1950 s – Instructions more English-like • Fourth Generation: since late 1970 s – Application Specific Language
Programming Languages • First Generation: Machine Language – All instructions written in binary (0 s and 1 s) • Second Generation: Assembly languages (1950 s) – Substitutes mnemonics for numeric codes • Third Generation: since mid 1950 s – Instructions more English-like • Fourth Generation: since late 1970 s – Application Specific Language
 Third-Generation Languages • FORTRAN (FORmula TRANslator) – Scientific & Mathematical applications • COBOL (COmmon Business Oriented Language): – Business applications; Process large data files; alphanumerics • BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) & Pascal: – Used to teach programming; quite easy to use • C and C++ – Efficient and portable – C++ is object oriented version of C
Third-Generation Languages • FORTRAN (FORmula TRANslator) – Scientific & Mathematical applications • COBOL (COmmon Business Oriented Language): – Business applications; Process large data files; alphanumerics • BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) & Pascal: – Used to teach programming; quite easy to use • C and C++ – Efficient and portable – C++ is object oriented version of C
 Fourth-Generation Languages (1) • Query Languages – Structured Query Language (SQL) • Report Generators – Create customized reports • Graphics Languages – Retrieve data and display them graphically • Application Generators – Generator creates logic and code for application • Very high-level programming languages – Professional programmer productivity tool
Fourth-Generation Languages (1) • Query Languages – Structured Query Language (SQL) • Report Generators – Create customized reports • Graphics Languages – Retrieve data and display them graphically • Application Generators – Generator creates logic and code for application • Very high-level programming languages – Professional programmer productivity tool
 Fourth-Generation Languages (2) • Application software packages – Word processing, spreadsheets, data management, presentation graphics, web browsers, email, groupware – Integrated software packages and suites – Software for specific tasks (tax programs, accounting packages)
Fourth-Generation Languages (2) • Application software packages – Word processing, spreadsheets, data management, presentation graphics, web browsers, email, groupware – Integrated software packages and suites – Software for specific tasks (tax programs, accounting packages)
 Software for Enterprise Integration • Enterprise Software – Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) – Integrated modules (sales, accounting, production, etc. ) that allow data to be used by multiple functions and business processes • Middleware – Software to connect applications and allow them to share data • Enterprise Application Integration Software – Software that ties together multiple applications
Software for Enterprise Integration • Enterprise Software – Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) – Integrated modules (sales, accounting, production, etc. ) that allow data to be used by multiple functions and business processes • Middleware – Software to connect applications and allow them to share data • Enterprise Application Integration Software – Software that ties together multiple applications
 Tools for Software Development • Object-Oriented Programming • New Languages – JAVA, HTML, XML
Tools for Software Development • Object-Oriented Programming • New Languages – JAVA, HTML, XML
 Object-Oriented Programming • Combines data & procedures into a single object • Program sends message to object to perform embedded procedure • Object’s data encapsulated from rest of system • Creates reusable code
Object-Oriented Programming • Combines data & procedures into a single object • Program sends message to object to perform embedded procedure • Object’s data encapsulated from rest of system • Creates reusable code
 JAVA • Sun Microsystems object-oriented programming language • Platform independent • Use Java to create applets – tiny program to execute small function – Applets downloaded from centralized server
JAVA • Sun Microsystems object-oriented programming language • Platform independent • Use Java to create applets – tiny program to execute small function – Applets downloaded from centralized server
 HTML and XML • HTML • XML – e. Xtensibe Markup Language – Describes structure of document & its data • XBRL – e. Xtensible Business Reporting Language – Designed to make financial statements & reports easier to prepare and consistent • XHTML – e. Xtensible Hypertext Markup Language – Hybrid of HTML and XML
HTML and XML • HTML • XML – e. Xtensibe Markup Language – Describes structure of document & its data • XBRL – e. Xtensible Business Reporting Language – Designed to make financial statements & reports easier to prepare and consistent • XHTML – e. Xtensible Hypertext Markup Language – Hybrid of HTML and XML
 Managing Software Assets • Rent Versus Buy Versus Build – ASP (application service provider) • Company that provides software (and sometimes hardware) that is rented over the network • Maintenance • Selecting Software – Appropriateness, Efficiency, Compatibility and Support
Managing Software Assets • Rent Versus Buy Versus Build – ASP (application service provider) • Company that provides software (and sometimes hardware) that is rented over the network • Maintenance • Selecting Software – Appropriateness, Efficiency, Compatibility and Support


