7ce4daf086033cb9e1006dc151daf033.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

CHAPTER 7 Business Strategy: Innovation and Strategic Entrepreneurship Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Part 2 Strategy Formulation

LO 7 -1 Define innovation and describe its role in the competitive process. LO 7 -2 Describe the competitive implications of different stages in the industry life cycle. LO 7 -3 Apply strategic management concepts to entrepreneurship and innovation. LO 7 -4 Evaluate different types of innovation and derive their strategic implications. LO 7 -5 Describe the long-tail concept and derive strategic implications. LO 7 -6 Evaluate discontinuities and describe the dynamics of paradigm changes. LO 7 -7 Identify the process leading to hypercompetition, and explain why competitive advantage can often be sustained through continuous innovation.
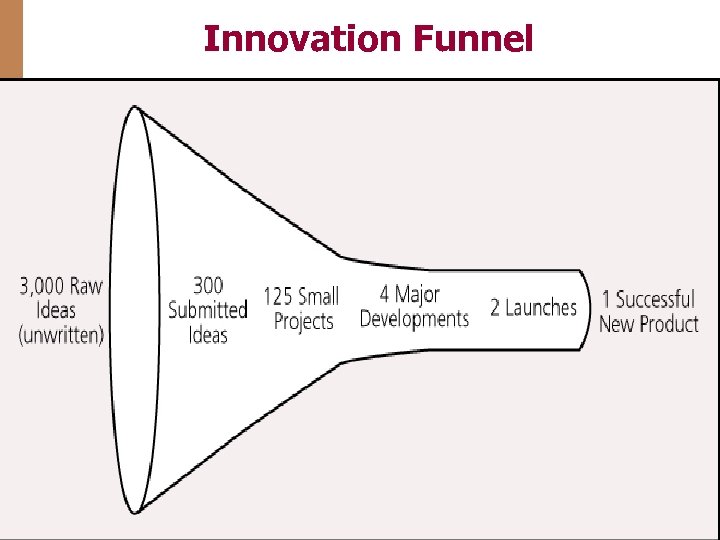
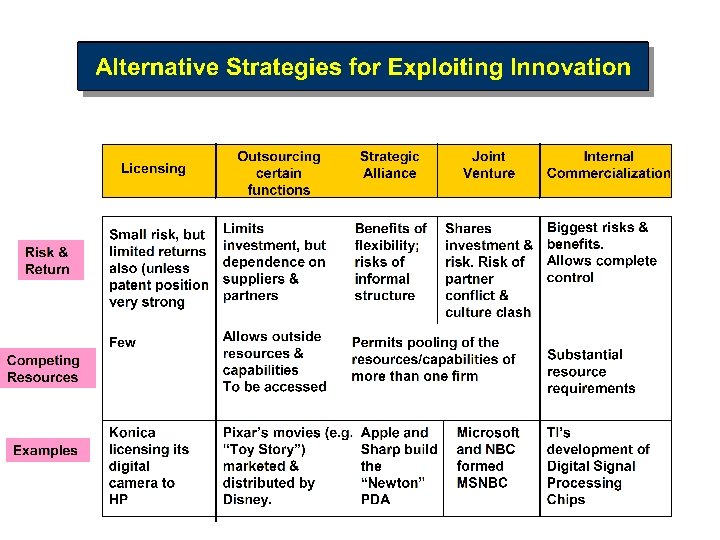
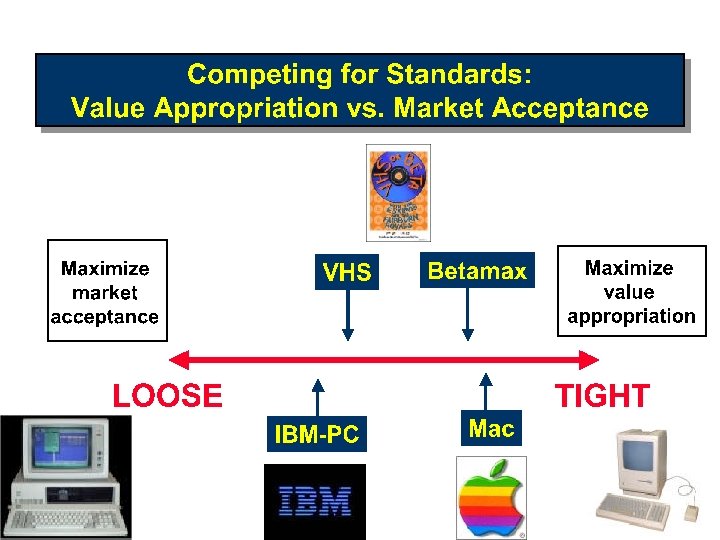
Innovation Funnel

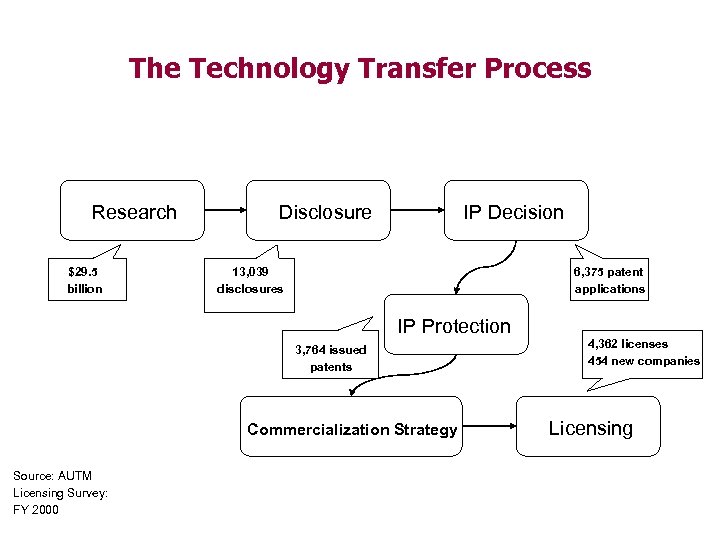
The Technology Transfer Process Research $29. 5 billion Disclosure IP Decision 13, 039 disclosures 6, 375 patent applications IP Protection 3, 764 issued patents Commercialization Strategy Source: AUTM Licensing Survey: FY 2000 4, 362 licenses 454 new companies Licensing


Chapter Case 7 From Encyclopedia Britannica to Encarta to Wikipedia • 18 th century Scottish Enlightenment creates Encyclopedia Britannica (E. B. ) Ø 65, 000 topics by 4, 000 scholars Ø In 1991, E. B. sales $650 M (market was $1. 2 billion annually) v Price ~$2, 000 per set of books • Microsoft launches Encarta in 1993 for $99 ea. Ø By 1996 Encarta U. S. sales over $100 M & E. B. ~$300 M • Mr. Wales launches Wikipedia in 2001 for $0 ea. Ø 3. 6 million articles in English ( 40 X E. B. !) v 18 million total in 281 languages Ø In ‘ 09 Microsoft shut down Encarta Ø Peer-reviewed study of 42 topics found 4 errors in Wiki… 3 in E. B.

Chapter Case 7 From Encyclopedia Britannica to Encarta to Wikipedia • The innovation of CD-based encyclopedia Ø Destroyed more than ½ the revenue of encyclopedias • Technology allowed Wikipedia to increase value and decrease costs • The innovative business model: Ø "Crowd wisdom" for big value v But NO revenue v Wikipedia is funded by donations of time and money

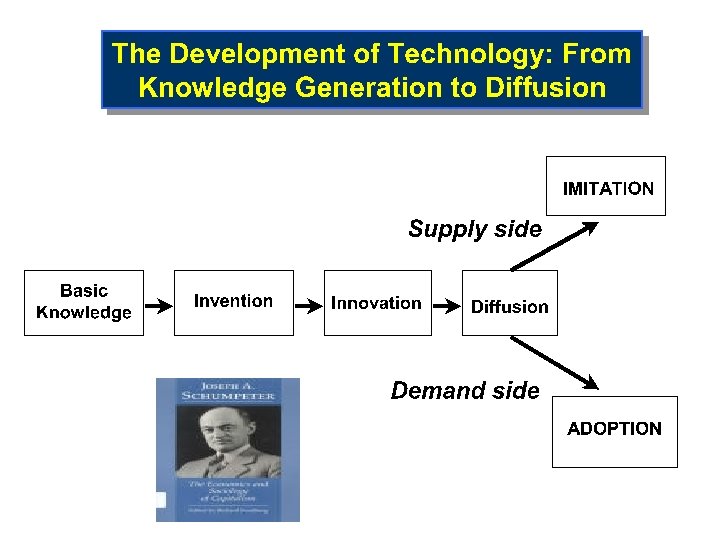
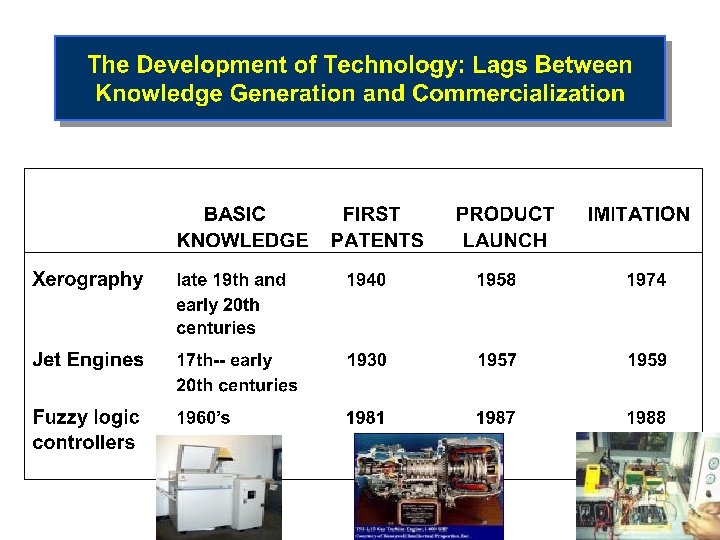
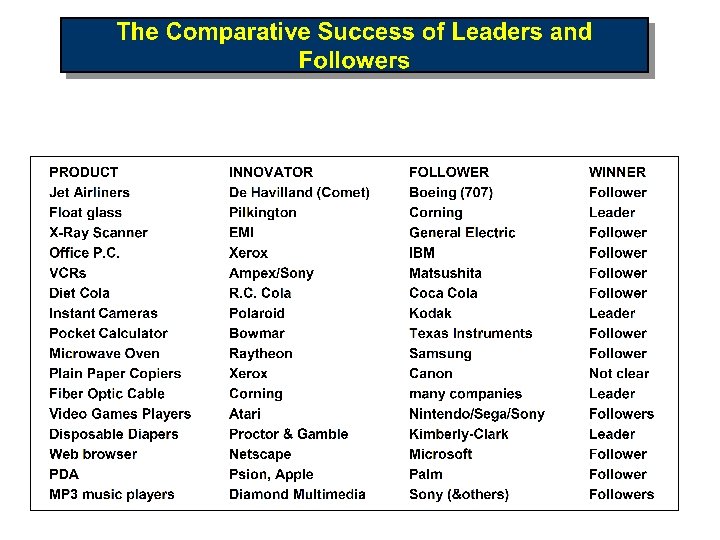
Competition Driven by Innovation • Invention is discovery of new ideas/products Ø Wright brothers – airplane flight • Innovation is the commercialization of invention Ø Boeing & Airbus – selling the airplanes • Schumpeter’s “gale of creative destruction” Ø Encyclopedias to Wikipedia… Ø Typewriters to PCs to ? ? ? Ø Pharmaceuticals to custom treatments (individualized medicine)
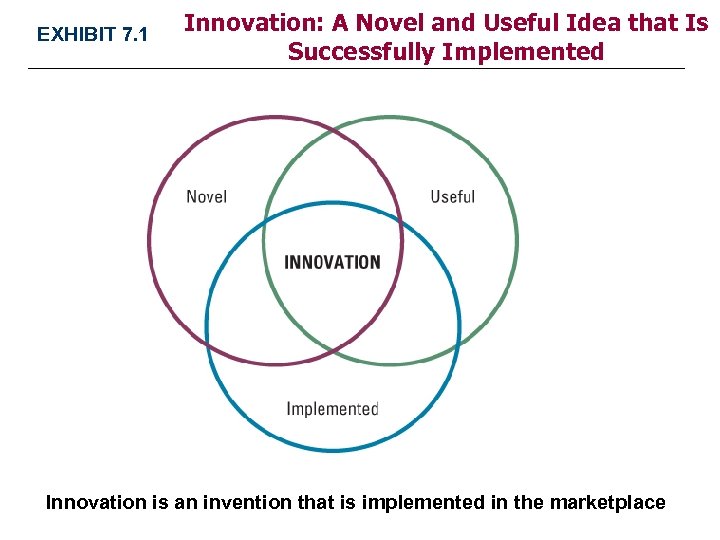
EXHIBIT 7. 1 Innovation: A Novel and Useful Idea that Is Successfully Implemented Innovation is an invention that is implemented in the marketplace
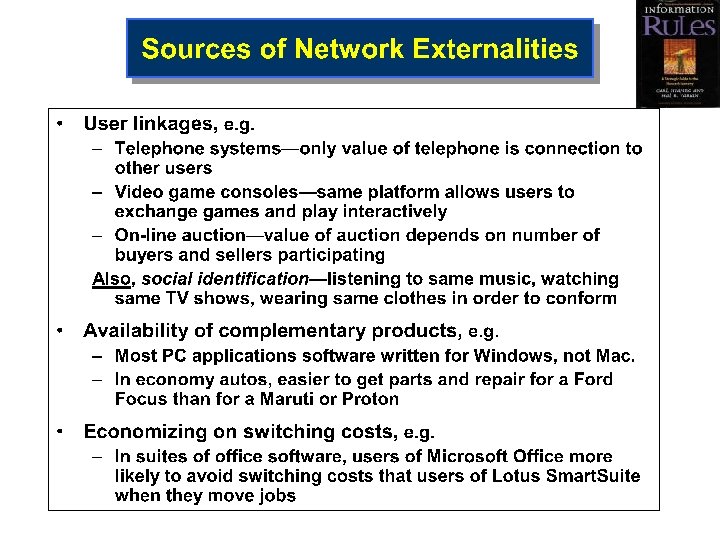
Innovation and the Industry Life Cycle • Innovations create new industries Ø Big box retailing Ø Express delivery Ø Nanotechnology still evolving • Four stages of industry development 1. Introduction Early adopters will pay a premium v Only a few innovators in the market – differentiated v Strategy here — market acceptance & seeds for growth – Network effects helpful v • Positive effects ONE user has for other users
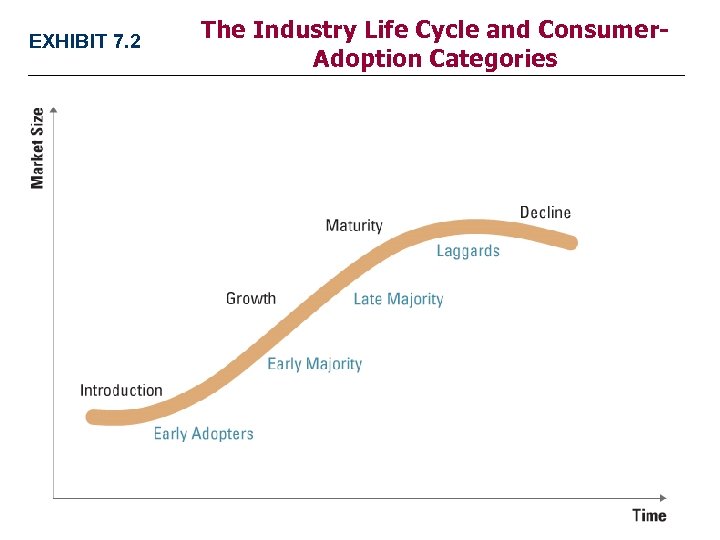
EXHIBIT 7. 2 The Industry Life Cycle and Consumer. Adoption Categories

STRATEGY HIGHLIGHT 7. 1 Apple Leverages Network Effects to Propel Growth • Apple launched i. Phone in summer ‘ 07 Ø Launched app store a year later v Small programs but BIG business! - Over $4 billion in 2012 Ø Virtuous cycle of 10 billion Apple apps downloaded by 2011 v Apps increase value of the i. Phone (& i. Pad too!) v More devices sold, incentivizes software developers v Recent i. Book store likely to grow the network effects still more 1– 25
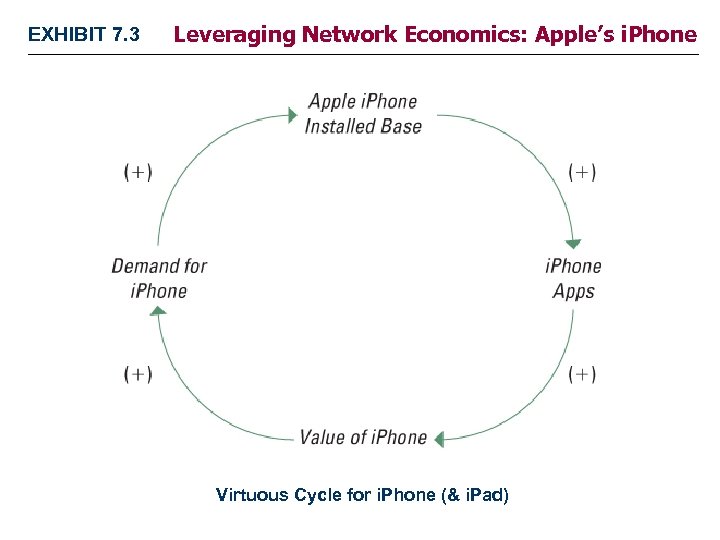
EXHIBIT 7. 3 Leveraging Network Economics: Apple’s i. Phone Virtuous Cycle for i. Phone (& i. Pad)
Innovation and the Industry Life Cycle • Four stages of industry development (cont'd) 2. Growth Stage Early majority buyers increase growth rapidly v Dominant design is set – IBM PC: Wintel – Government influence – GSM standard for mobile phones – QWERTY keyboards v Core competencies move to manufacturing & marketing v Ø An example of growth stage v Women’s shapeware industry – Spanx started in 1998 • Sold over 5 M units & over $750 million in sales by 2008 – Maidenform, Body Wrap, & Miraclesuit are competitors
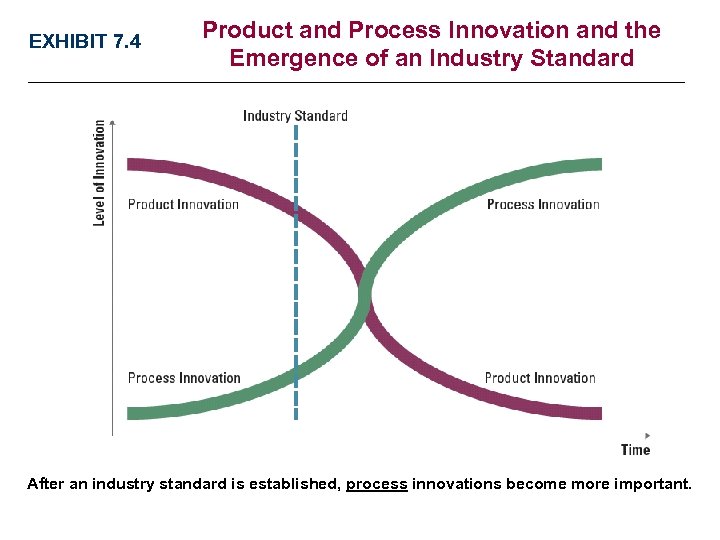
EXHIBIT 7. 4 Product and Process Innovation and the Emergence of an Industry Standard After an industry standard is established, process innovations become more important.

STRATEGY HIGHLIGHT 7. 2 Some Standards Die Hard: QWERTY vs. DSK • QWERTY introduced in 1870 s Ø Slowed down typing to avoid jamming keys • Dvorak introduced in 1930 s Ø Minimized finger reach to speed up typing
Innovation and the Industry Life-Cycle • Four stages of industry development (cont'd) 3. Maturity Late majority buyers & more limited market growth – Increased competitive rivalry v Cost leadership firms tend to drive industry – Weaker firms will exit v Oligopoly is dominant industry structure in this stage v 4. Decline v v Laggards are buyers and market size shrinks Four strategic options: – Exit – get out of the industry – Harvest – stay with limited investments (Olivetti) – Maintain – stay & continue marketing (Marlboro) – Consolidate – buy rivals, near monopoly (IBM mainframes)
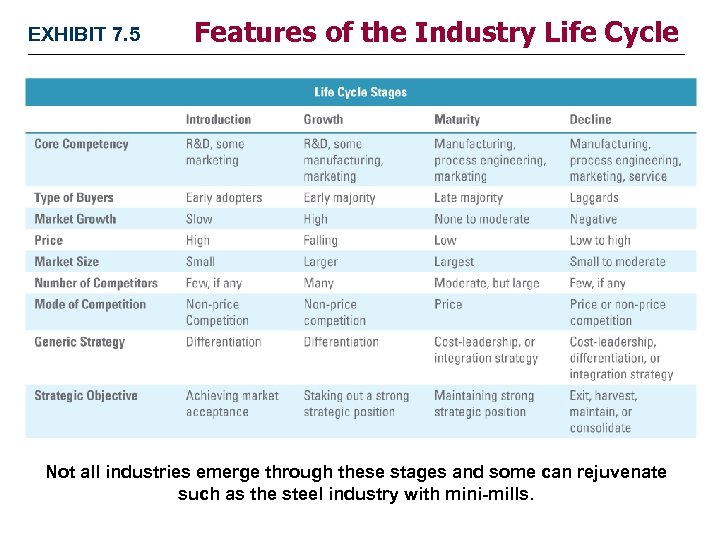
EXHIBIT 7. 5 Features of the Industry Life Cycle Not all industries emerge through these stages and some can rejuvenate such as the steel industry with mini-mills.

LO 7 -1 Define innovation and describe its role in the competitive process. LO 7 -2 Describe the competitive implications of different stages in the industry life cycle. LO 7 -3 Apply strategic management concepts to entrepreneurship and innovation. LO 7 -4 Evaluate different types of innovation and derive their strategic implications. LO 7 -5 Describe the long-tail concept and derive strategic implications. LO 7 -6 Evaluate discontinuities and describe the dynamics of paradigm changes. LO 7 -7 Identify the process leading to hypercompetition, and explain why competitive advantage can often be sustained through continuous innovation.

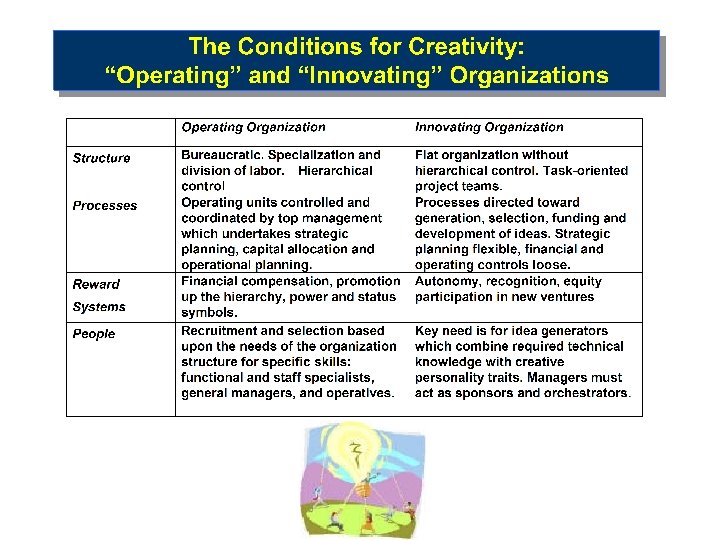
Strategic Entrepreneurship • Entrepreneurs are the change agents for creative destruction. Ø Create new opportunities and exploit them Jeff Bezos – Amazon. com – Saw growth of Internet in 1994 – Chose books as the first product for online sales v Oprah Winfrey – Harpo Productions – Rose from abuse & poverty to over $2 billion net worth – Ended talk show to devote time to OWN TV channel v Jeff Hawkins – Palm Computing (founded in 1992) – Palm. Pilot and Treo products v Ø How to combine entrepreneurial with strategic actions? v Example: P&G continued innovations in detergent
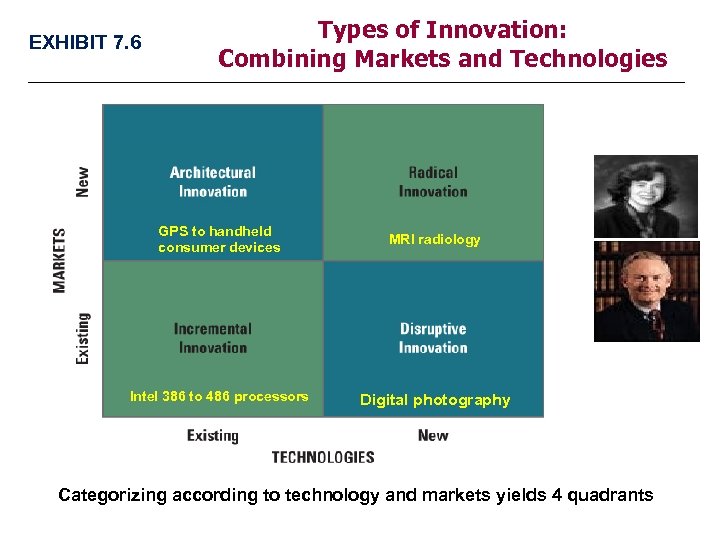
EXHIBIT 7. 6 Types of Innovation: Combining Markets and Technologies GPS to handheld consumer devices MRI radiology Intel 386 to 486 processors Digital photography Categorizing according to technology and markets yields 4 quadrants

STRATEGY HIGHLIGHT 7. 3 1930 s From King Gillette to King of Incremental Innovation 2011 1– 35

STRATEGY HIGHLIGHT 7. 3 From King Gillette to King of Incremental Innovation • Gillette invented the safety razor in 1903 Ø A radical innovation at the start Ø Innovative business model v Make money from the blades NOT the razors Ø Incremental innovation v Moved from 1 to six blades (so far…) Ø Top selling blades today! Over $1 billion in sales v Prices steady to higher for the blades! 1– 36
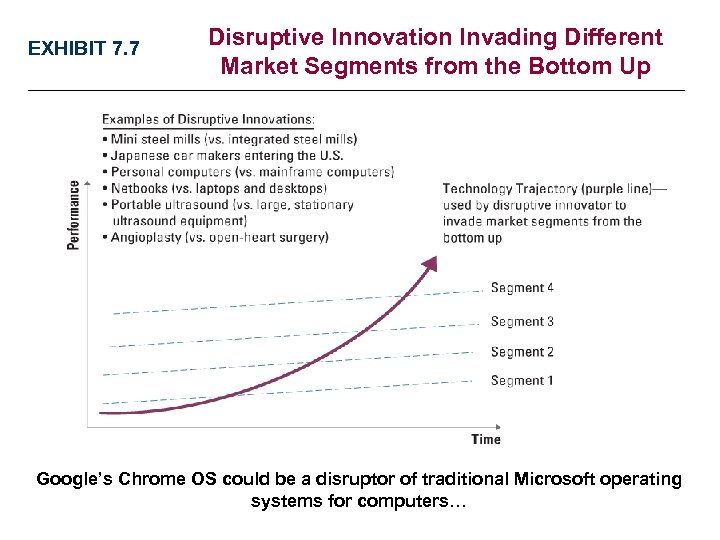
EXHIBIT 7. 7 Disruptive Innovation Invading Different Market Segments from the Bottom Up Google’s Chrome OS could be a disruptor of traditional Microsoft operating systems for computers…

STRATEGY HIGHLIGHT 7. 4 GE’s Reverse Innovation: Disrupt Yourself! • GE Healthcare – global leader in diagnostics Ø Ultrasound machine for research hospitals – $230, 000 v Limited market for these in developing countries Ø 2002 local team at GE China – developed portable US v Laptop-based technology – Under $30, 000 for U. S. rollout Ø 2009 introduced a handheld US – about $10, 000 v Vscan - large cell phone – shaped device GE Vscan Video 1– 38

LO 7 -1 Define innovation and describe its role in the competitive process. LO 7 -2 Describe the competitive implications of different stages in the industry life cycle. LO 7 -3 Apply strategic management concepts to entrepreneurship and innovation. LO 7 -4 Evaluate different types of innovation and derive their strategic implications. LO 7 -5 Describe the long-tail concept and derive strategic implications. LO 7 -6 Evaluate discontinuities and describe the dynamics of paradigm changes. LO 7 -7 Identify the process leading to hypercompetition, and explain why competitive advantage can often be sustained through continuous innovation.

The Internet as Disruptive Force: The Long Tail • Long tail in a digital world Ø Both opportunity and threat Ø 80% sales in a given category are NOT “hits” v Pareto principle Ø Technology enables easier access to the ‘tail’ Selling “less of more” v Online firms can gain a large share of revenue from selling a small number of nearly unlimited choices v • Short head is the mainstream Ø Available at brick & mortar stores v Significant inventory costs Ray Kurzwiel Video
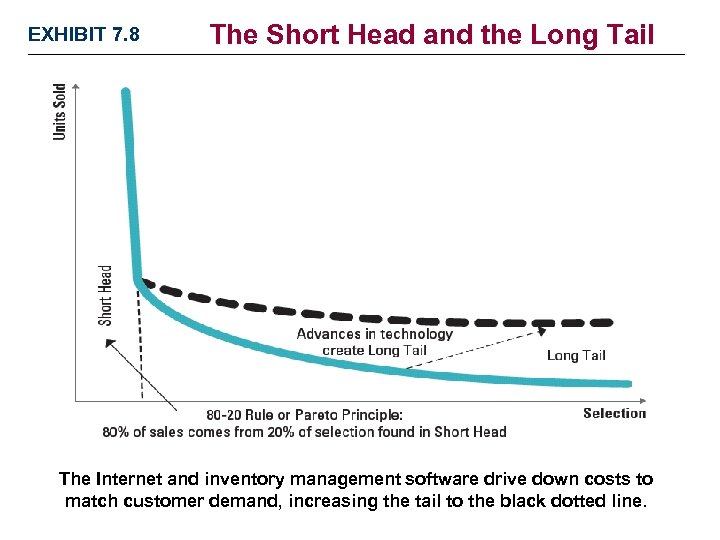
EXHIBIT 7. 8 The Short Head and the Long Tail The Internet and inventory management software drive down costs to match customer demand, increasing the tail to the black dotted line.
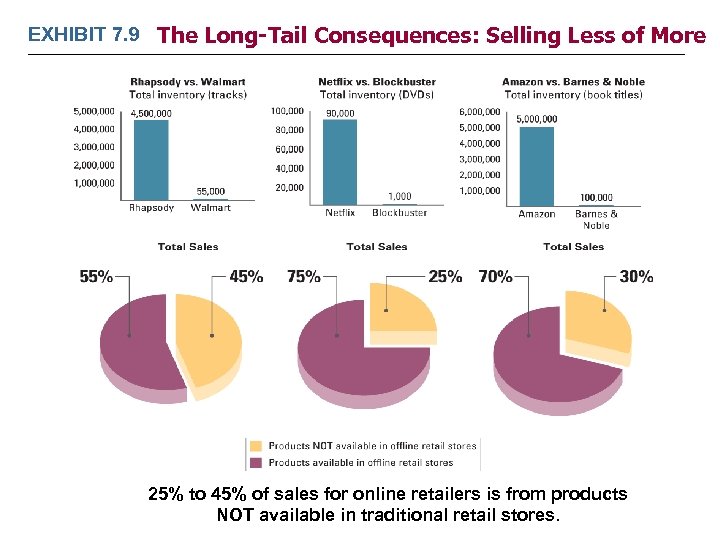
EXHIBIT 7. 9 The Long-Tail Consequences: Selling Less of More 25% to 45% of sales for online retailers is from products NOT available in traditional retail stores.

LO 7 -1 Define innovation and describe its role in the competitive process. LO 7 -2 Describe the competitive implications of different stages in the industry life cycle. LO 7 -3 Apply strategic management concepts to entrepreneurship and innovation. LO 7 -4 Evaluate different types of innovation and derive their strategic implications. LO 7 -5 Describe the long-tail concept and derive strategic implications. LO 7 -6 Evaluate discontinuities and describe the dynamics of paradigm changes. LO 7 -7 Identify the process leading to hypercompetition, and explain why competitive advantage can often be sustained through continuous innovation.
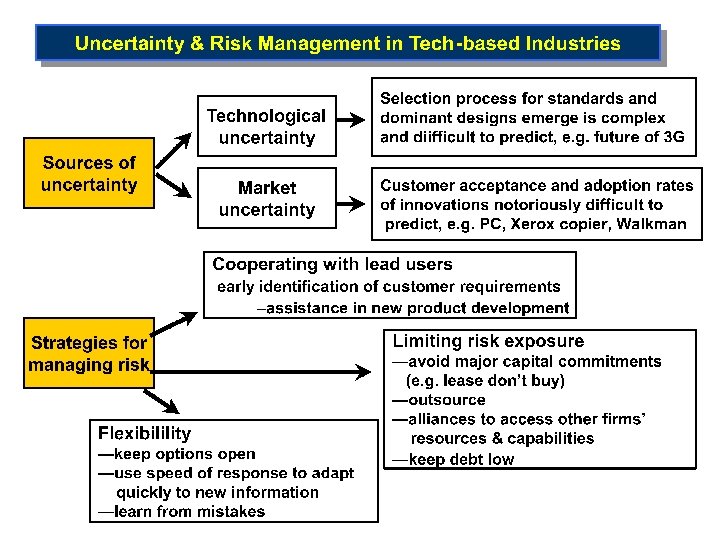
Discontinuities: Periods of Paradigm Change • Periods when underlying standard changes Ø Paradigm shift New technology revolutionizes existing industries – New standard is established v Technology “S-curve” – Physical limits nearing or reached v Ø Incumbents need absorptive capacity v Existing firms must place “good bets” on new technologies Ø Examples of Discontinuities Airplanes: propellers to jets v Cameras: film to digital v TV screens: vacuum tube to flat panel v Music storage: vinyl to CDs to MP 3 storage v Steven Chu Plant Energy Video
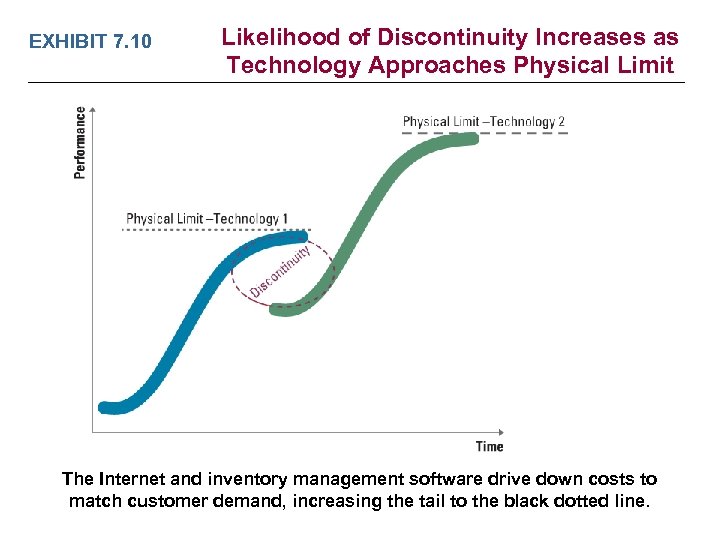
EXHIBIT 7. 10 Likelihood of Discontinuity Increases as Technology Approaches Physical Limit The Internet and inventory management software drive down costs to match customer demand, increasing the tail to the black dotted line.
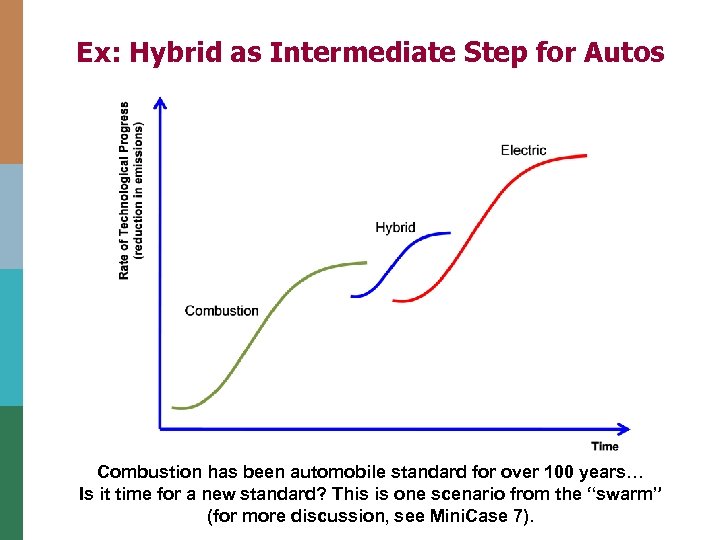
Ex: Hybrid as Intermediate Step for Autos Combustion has been automobile standard for over 100 years… Is it time for a new standard? This is one scenario from the “swarm” (for more discussion, see Mini. Case 7).
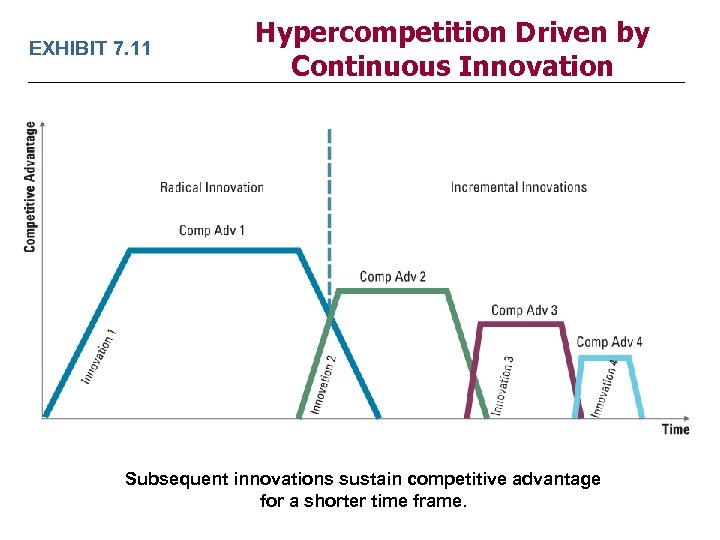
EXHIBIT 7. 11 Hypercompetition Driven by Continuous Innovation Subsequent innovations sustain competitive advantage for a shorter time frame.

Take-Away Concepts LO 7 -1 Define innovation and describe its role in the competitive process. ü Continuous innovation is the engine behind successful companies. ü Innovation is a potent competitive weapon; it enables firms to redefine the marketplace in their favor and achieve much-needed growth. ü The successful commercialization of a new product or service allows a firm to extract temporary monopoly profits. LO 7 -2 Describe the competitive implications of different stages in the industry life cycle. ü Innovations frequently lead to the birth of new industries. ü Industries generally follow a predictable industry life cycle, with four distinct stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. ü Different life-cycle stages have different consumer adoption rates and different competitive implications (see Exhibit 7. 4).

Take-Away Concepts LO 7 -3 Apply strategic management concepts to entrepreneurship and innovation. ü Strategic entrepreneurship focuses on generating integrated insights pertaining to innovation and change using the concepts available in strategic management. LO 7 -4 Evaluate different types of innovation and derive their strategic implications. ü Four types of innovation emerge when applying the existing versus new dimensions of technology and markets: incremental, radical, architectural, and disruptive innovations. LO 7 -5 Describe the long-tail concept and derive strategic implications. ü The Internet is a strongly disruptive force that digitizes any industry that can be digitized. ü The long tail describes a business model in which companies can obtain a significant part of their revenues by selling a small number of units from among almost unlimited choices.

Take-Away Concepts LO 7 -6 Evaluate discontinuities and describe the dynamics of paradigm changes. ü Discontinuities can lead to a paradigm shift, in which a new technology revolutionizes an existing industry and eventually establishes itself as the new standard. ü Technologies follow a predictable technology S-curve, improving in performance over time as a consequence of continued R&D effort. ü The probability of a discontinuity increases when a given technology approaches its physical limit.

Take-Away Concepts LO 7 -7 Identify the process leading to hypercompetition and explain why competitive advantage can be sustained through continuous innovation ü Competitive intensity has increased and periods of competitive advantage have shortened, especially in newer, technology-based industries. ü No single strategy can sustain competitive advantage over time. ü Any competitive advantage must be a string of short-lived advantages. This is achieved through a constant escalation of competition in the areas of price, quality, timing and know-how, capital commitments, and supply-chain management. ü Hypercompetition can result from a lack of strategic positioning.
7ce4daf086033cb9e1006dc151daf033.ppt