c31664f3322a6aba1f659bf563f67ff6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Chapter 7 A More Perfect Union
Chapter 7 A More Perfect Union
 Section 1 The Articles of Confederation
Section 1 The Articles of Confederation
 Thirteen Independent States u u In May 1776 the Continental Congress asked the states to organize their governments. Each state quickly adopted state constitutions, or plans of government. Colonists experience with British rule made Americans cautious about giving too much power to a single ruler. Most states greatly limited the power of the governor.
Thirteen Independent States u u In May 1776 the Continental Congress asked the states to organize their governments. Each state quickly adopted state constitutions, or plans of government. Colonists experience with British rule made Americans cautious about giving too much power to a single ruler. Most states greatly limited the power of the governor.
 Thirteen Independent States cont. u u The states took other measures to prevent a concentration of power. They divided government functions between the governor and the legislature. Most states established a two-house, or bicameral, legislatures to divide power further. They not only wanted to prevent abuses of power but also keep the power in the hands of the people.
Thirteen Independent States cont. u u The states took other measures to prevent a concentration of power. They divided government functions between the governor and the legislature. Most states established a two-house, or bicameral, legislatures to divide power further. They not only wanted to prevent abuses of power but also keep the power in the hands of the people.
 Forming a Republic u u The continental congress agreed that the country should be a republic, a government in which citizens rule through elected representatives. At first most Americans wanted a weak central govt. In 1776 the second continental congress appointed a committee to draw up a national constitution. In November 1777 the Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation. This was America's first constitution.
Forming a Republic u u The continental congress agreed that the country should be a republic, a government in which citizens rule through elected representatives. At first most Americans wanted a weak central govt. In 1776 the second continental congress appointed a committee to draw up a national constitution. In November 1777 the Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation. This was America's first constitution.

 New Land Policies u u By the 1790’s more than 120, 000 Americans lived west of the Appalachian Mts. These western settlers hoped to organize their lands to eventually become states. However, under the Articles of Confederation their was no provision for statehood. In 1784 the Congress established self-governing districts. When these districts reached the population of the smallest existing state they could petition, or apply for statehood.
New Land Policies u u By the 1790’s more than 120, 000 Americans lived west of the Appalachian Mts. These western settlers hoped to organize their lands to eventually become states. However, under the Articles of Confederation their was no provision for statehood. In 1784 the Congress established self-governing districts. When these districts reached the population of the smallest existing state they could petition, or apply for statehood.
 New Land Policies cont. u In 1785 the Congress passed an ordinance, or law, that established a procedure for surveying and selling the western lands north of the Ohio River.
New Land Policies cont. u In 1785 the Congress passed an ordinance, or law, that established a procedure for surveying and selling the western lands north of the Ohio River.
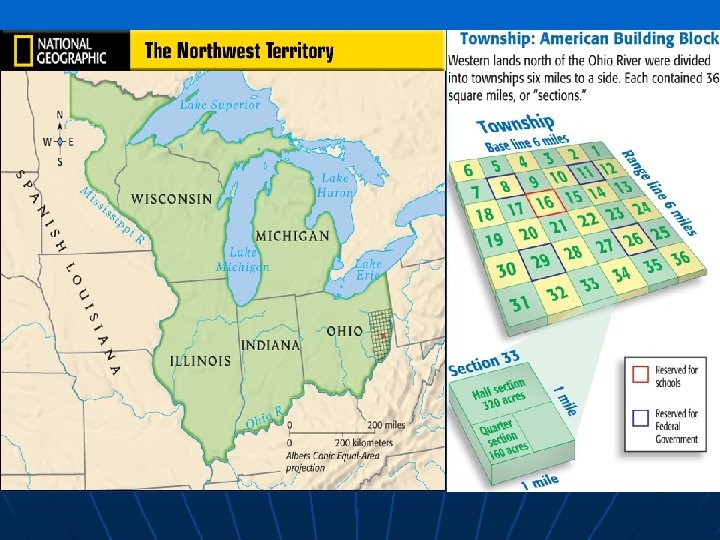
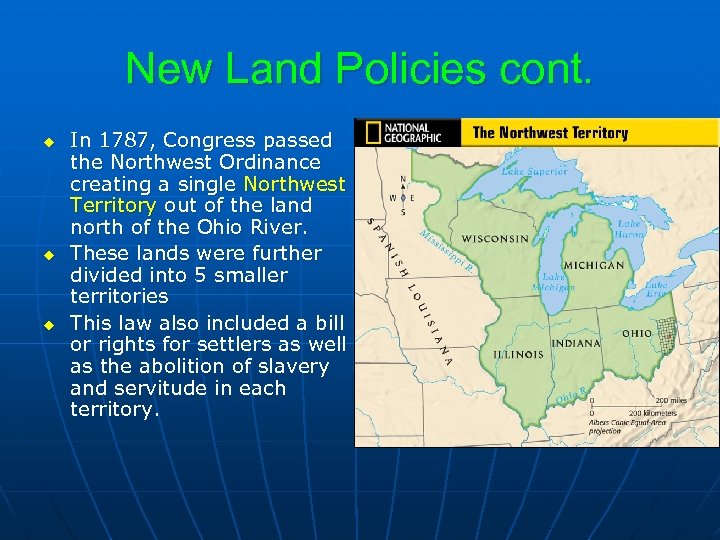 New Land Policies cont. u u u In 1787, Congress passed the Northwest Ordinance creating a single Northwest Territory out of the land north of the Ohio River. These lands were further divided into 5 smaller territories This law also included a bill or rights for settlers as well as the abolition of slavery and servitude in each territory.
New Land Policies cont. u u u In 1787, Congress passed the Northwest Ordinance creating a single Northwest Territory out of the land north of the Ohio River. These lands were further divided into 5 smaller territories This law also included a bill or rights for settlers as well as the abolition of slavery and servitude in each territory.
 Trouble on Two Fronts u u After the Revolutionary War, the U. S. had severe money troubles. The Confederation Congress had little power to resolve the money problems. Continental dollars value had depreciated, or fallen in value while prices for food soared. Also the Congress had a huge war debt that needed to be paid.
Trouble on Two Fronts u u After the Revolutionary War, the U. S. had severe money troubles. The Confederation Congress had little power to resolve the money problems. Continental dollars value had depreciated, or fallen in value while prices for food soared. Also the Congress had a huge war debt that needed to be paid.
 Trouble on Two Fronts cont. u u In 1781, faced with a total collapse of the country’s finances, Congress created a dept. of finance under Robert Morris. Weakness in the new American gov’t created problems with other countries. American merchants had trouble with trade in British markets. John Adams was sent to London to try and deal with these issues. The Spanish closed the lower Mississippi River to American shipping which was the lifeblood for to western settlers.
Trouble on Two Fronts cont. u u In 1781, faced with a total collapse of the country’s finances, Congress created a dept. of finance under Robert Morris. Weakness in the new American gov’t created problems with other countries. American merchants had trouble with trade in British markets. John Adams was sent to London to try and deal with these issues. The Spanish closed the lower Mississippi River to American shipping which was the lifeblood for to western settlers.
 Convention and Compromise Section 2
Convention and Compromise Section 2
 Economic Depression u u Many Americans believed that the Confederation gov’t was too weak to deal with many growing problems. After the Revolutionary War ended the U. S. went into a depression, a period when economic activity slowed and unemployment rises. Farmers were unable to pay their debts and began to lose their land. In 1786 angry farmers led by Daniel Shays attacked Massachusetts courts and a federal arsenal in Springfield, Mass. Shay’s Rebellion was put down but it did worry many Americans that our gov’t couldn’t deal with unrest.
Economic Depression u u Many Americans believed that the Confederation gov’t was too weak to deal with many growing problems. After the Revolutionary War ended the U. S. went into a depression, a period when economic activity slowed and unemployment rises. Farmers were unable to pay their debts and began to lose their land. In 1786 angry farmers led by Daniel Shays attacked Massachusetts courts and a federal arsenal in Springfield, Mass. Shay’s Rebellion was put down but it did worry many Americans that our gov’t couldn’t deal with unrest.
 The Issue of Slavery u u The struggle for liberty during the Revolutionary War brought the contradiction of slavery to the forefront for many Americans. Many states had outlawed or heavily taxed the importation of slaves but not the institution itself. By 1804 all states south of Pennsylvania still had slavery. In Virginia, a law was passed that encouraged manumission, the freeing of individual slaves.
The Issue of Slavery u u The struggle for liberty during the Revolutionary War brought the contradiction of slavery to the forefront for many Americans. Many states had outlawed or heavily taxed the importation of slaves but not the institution itself. By 1804 all states south of Pennsylvania still had slavery. In Virginia, a law was passed that encouraged manumission, the freeing of individual slaves.
 A Call for Change u u The American Revolution had led to a union of 13 states but had not created a nation. Many saw a strong national gov’t as the solution to America’s problems. Many demanded reform of the Articles of Confederation. Two Americans active in the movement were James Madison and Alexander Hamilton. Once George Washington agreed to attend the convention, the meeting took on greater significance.
A Call for Change u u The American Revolution had led to a union of 13 states but had not created a nation. Many saw a strong national gov’t as the solution to America’s problems. Many demanded reform of the Articles of Confederation. Two Americans active in the movement were James Madison and Alexander Hamilton. Once George Washington agreed to attend the convention, the meeting took on greater significance.
 The Constitutional Convention u u The Convention began in May 1787 and continued through the summer. 55 delegates attended, all from varying backgrounds. The presence of George Washington and Benjamin Franklin ensured that many people would trust the Convention’s work. A Virginian, James Madison will be called the Father of the Constitution because he was the author of the basic plan of government the Convention adopted.
The Constitutional Convention u u The Convention began in May 1787 and continued through the summer. 55 delegates attended, all from varying backgrounds. The presence of George Washington and Benjamin Franklin ensured that many people would trust the Convention’s work. A Virginian, James Madison will be called the Father of the Constitution because he was the author of the basic plan of government the Convention adopted.
 The Virginia Plan u u Another Virginian named Edmund Randolph opened the convention proposing a new constitution instead of revising the articles. He introduced the Virginia Plan, which was largely the work of James Madison.
The Virginia Plan u u Another Virginian named Edmund Randolph opened the convention proposing a new constitution instead of revising the articles. He introduced the Virginia Plan, which was largely the work of James Madison.
 The Virginia Plan cont. u u u The plan called for a two-house legislature. A chief executive (President) chosen by the legislature. Also their would be a court system established. The members of the lower house (House of Representatives) would be elected by the people. The members of the upper house (Senate) would chosen by the lower house. In both houses the number of representatives would be proportional, or corresponding in size, to the population of each state.
The Virginia Plan cont. u u u The plan called for a two-house legislature. A chief executive (President) chosen by the legislature. Also their would be a court system established. The members of the lower house (House of Representatives) would be elected by the people. The members of the upper house (Senate) would chosen by the lower house. In both houses the number of representatives would be proportional, or corresponding in size, to the population of each state.
 The New Jersey Plan u u u On June 15, 1787 William Paterson of New Jersey proposed an alternative called the New Jersey Plan. His plan had just a single house legislature, with one vote for each state and could set taxes along with regulating trade. This congress would elect a weak executive branch. This plan simply amended the Articles of Confederation.
The New Jersey Plan u u u On June 15, 1787 William Paterson of New Jersey proposed an alternative called the New Jersey Plan. His plan had just a single house legislature, with one vote for each state and could set taxes along with regulating trade. This congress would elect a weak executive branch. This plan simply amended the Articles of Confederation.
 Compromise Wins Out u u u Under Ben Franklin’s leadership, the convention appointed a “grand committee” to try to resolve the disagreements between large and small populated states. Roger Sherman of Connecticut suggested what came to be known as the Great Compromise. A compromise is an agreement between two or more sides in which each gives up something it wants. Sherman proposed a twohouse legislature. The number of members in the lower house would be determined by the population of each state, while the upper house would have two members per state.
Compromise Wins Out u u u Under Ben Franklin’s leadership, the convention appointed a “grand committee” to try to resolve the disagreements between large and small populated states. Roger Sherman of Connecticut suggested what came to be known as the Great Compromise. A compromise is an agreement between two or more sides in which each gives up something it wants. Sherman proposed a twohouse legislature. The number of members in the lower house would be determined by the population of each state, while the upper house would have two members per state.
 The Three-Fifths Compromise u u The issue of slavery was another sticking point at the convention. The southern states wanted to count their slaves to gain representatives in the House of Representatives. The Northern states argued that slaves were legal property and therefore should be counted for purposes of taxation not representation. The solution became known as the Three. Fifths Compromise.
The Three-Fifths Compromise u u The issue of slavery was another sticking point at the convention. The southern states wanted to count their slaves to gain representatives in the House of Representatives. The Northern states argued that slaves were legal property and therefore should be counted for purposes of taxation not representation. The solution became known as the Three. Fifths Compromise.
 The Three-Fifths Compromise cont. This compromise was to count each enslaved person as 3/5 ths of a free person for both taxation and representation. u Every five enslaved persons would equal 3 free persons. u The convention also agreed to put off the issue of slavery and the slave trade till 1808. u
The Three-Fifths Compromise cont. This compromise was to count each enslaved person as 3/5 ths of a free person for both taxation and representation. u Every five enslaved persons would equal 3 free persons. u The convention also agreed to put off the issue of slavery and the slave trade till 1808. u
 A New Plan of Government Section 3
A New Plan of Government Section 3
 Roots of the Constitution u u u Even though the U. S. Constitution is a uniquely American document, its roots came from many other civilizations from history. The hope was to avoid the mistakes of the past. Much of what is in the Constitution comes from many British institutions and traditions. The Magna Carta (1215) had placed limits on the power of the monarch. Many of the framers of the Constitution got many ideas on the nature of people and gov’t from European writers of the Enlightenment. The Enlightenment was a movement in the 1700’s that promoted knowledge, reason, and science as a way to improve society.
Roots of the Constitution u u u Even though the U. S. Constitution is a uniquely American document, its roots came from many other civilizations from history. The hope was to avoid the mistakes of the past. Much of what is in the Constitution comes from many British institutions and traditions. The Magna Carta (1215) had placed limits on the power of the monarch. Many of the framers of the Constitution got many ideas on the nature of people and gov’t from European writers of the Enlightenment. The Enlightenment was a movement in the 1700’s that promoted knowledge, reason, and science as a way to improve society.
 Roots of the Constitution cont. u u u James Madison studied the works of Enlightenment thinkers such as John Locke and Baron de Montesquieu. John Locke believed that all people had natural rights of life, liberty, and property. Montesquieu believed that the powers of gov’t should be separated and balanced against each other.
Roots of the Constitution cont. u u u James Madison studied the works of Enlightenment thinkers such as John Locke and Baron de Montesquieu. John Locke believed that all people had natural rights of life, liberty, and property. Montesquieu believed that the powers of gov’t should be separated and balanced against each other.
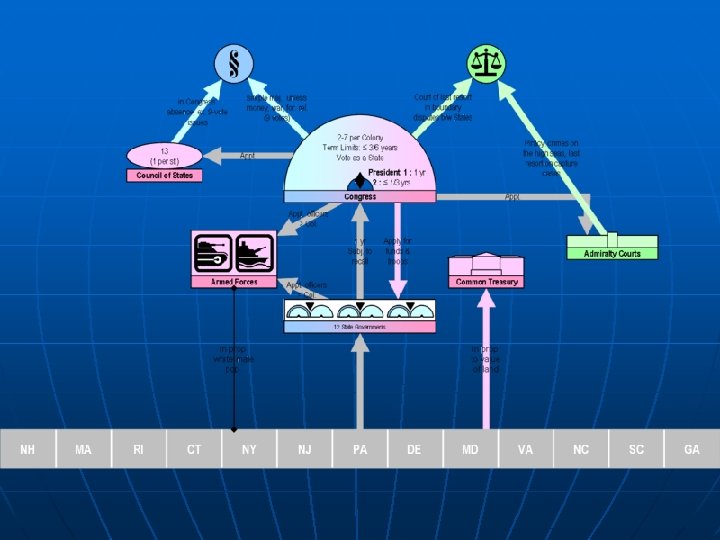
 The Organization of Government u u The Constitution created a system that divided powers between the national gov’t and the state gov’t. This system called Federalism, or sharing power between the federal and state gov’t is a unique aspect of our gov’t. The framers of the Constitution divided the gov’t into three branches—legislative, executive and judicial. The first three articles or parts, of the Constitution describe the powers and responsibilities of each branch. P. 232
The Organization of Government u u The Constitution created a system that divided powers between the national gov’t and the state gov’t. This system called Federalism, or sharing power between the federal and state gov’t is a unique aspect of our gov’t. The framers of the Constitution divided the gov’t into three branches—legislative, executive and judicial. The first three articles or parts, of the Constitution describe the powers and responsibilities of each branch. P. 232
 The Organization of Government cont. u u The gov’t as described by the Constitution is broken down into 3 branches. Each branch has specific responsibilities to the law. The Legislative branch, or lawmaking branch, makes the Law. The Executive branch, headed by the president, enforces the law. The Judicial branch, or court system, makes sure the laws are constitutional.
The Organization of Government cont. u u The gov’t as described by the Constitution is broken down into 3 branches. Each branch has specific responsibilities to the law. The Legislative branch, or lawmaking branch, makes the Law. The Executive branch, headed by the president, enforces the law. The Judicial branch, or court system, makes sure the laws are constitutional.
 System of Checks and Balances One of the main features of our gov’t is that its powers are separated. u To keep any one branch from gaining too much power, the framers built in a system of checks and balances. u The three branches of gov’t have roles that check, or limit, the others so no single branch can dominate the gov’t. u
System of Checks and Balances One of the main features of our gov’t is that its powers are separated. u To keep any one branch from gaining too much power, the framers built in a system of checks and balances. u The three branches of gov’t have roles that check, or limit, the others so no single branch can dominate the gov’t. u
 The Constitutional Debate u u u A great debate would take place throughout the U. S. on whether to support the new constitution or not. Before it could go into effect nine states needed to ratify, or approve, it. Ratifying conventions were set-up with Rhode Island not participating because they opposed the Constitution. Supporters of the new Constitution were called Federalists. Those who were against the new Constitution were called Antifederalists.
The Constitutional Debate u u u A great debate would take place throughout the U. S. on whether to support the new constitution or not. Before it could go into effect nine states needed to ratify, or approve, it. Ratifying conventions were set-up with Rhode Island not participating because they opposed the Constitution. Supporters of the new Constitution were called Federalists. Those who were against the new Constitution were called Antifederalists.
 Adopting the Constitution u u On Dec. 7 th, 1787, Delaware became the first state to approve the Constitution. New Hampshire would be the ninth state to ratify. Once their was an assurance that a bill of rights amendment would be included others states followed. An amendment is something added to a document.
Adopting the Constitution u u On Dec. 7 th, 1787, Delaware became the first state to approve the Constitution. New Hampshire would be the ninth state to ratify. Once their was an assurance that a bill of rights amendment would be included others states followed. An amendment is something added to a document.


