b8e90d70249371345043d4a43bc6e73e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Chapter 6
Chapter 6
 Venipuncture Equipment Includes: • Vacuum tubes and safety-engineered needle collection devices • Tourniquet • Supplies to cleanse the puncture site Labeling supplies • Gloves • Special trays to transport blood specimens
Venipuncture Equipment Includes: • Vacuum tubes and safety-engineered needle collection devices • Tourniquet • Supplies to cleanse the puncture site Labeling supplies • Gloves • Special trays to transport blood specimens
 Vacuum (Evacuated) Tube System • Requires an evacuated tube, a special needle, and a special safety plastic holder (adapter) that covers the needle after blood collection • One end of the double-pointed needle enters the vein, the other end pierces the top of the tube, and the vacuum aspirates the blood
Vacuum (Evacuated) Tube System • Requires an evacuated tube, a special needle, and a special safety plastic holder (adapter) that covers the needle after blood collection • One end of the double-pointed needle enters the vein, the other end pierces the top of the tube, and the vacuum aspirates the blood
 Two Criteria used to Describe Vacuum Tube Size • External tube diameter and length • The maximum amount of specimen to be drawn into the vacuum tube
Two Criteria used to Describe Vacuum Tube Size • External tube diameter and length • The maximum amount of specimen to be drawn into the vacuum tube
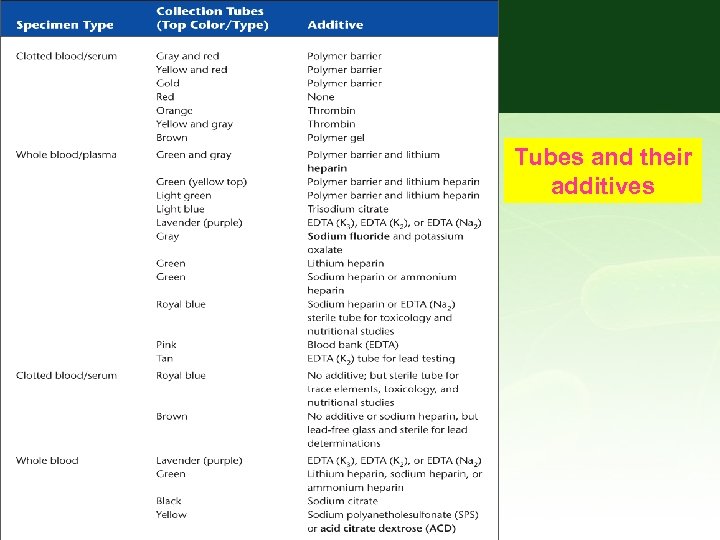
 Additives in Tubes • Additives- substances (gels, clotting activators or anti coagulants) that are added in small amounts to tubes to alter the specimen to make it appropriate for analysis • EDTA- ethyleneadiamine tetra acetic acid- anti coagulant** • Oxalates, citrates and EDTA prevent coagulation by removing calcium and forming insoluble salts**
Additives in Tubes • Additives- substances (gels, clotting activators or anti coagulants) that are added in small amounts to tubes to alter the specimen to make it appropriate for analysis • EDTA- ethyleneadiamine tetra acetic acid- anti coagulant** • Oxalates, citrates and EDTA prevent coagulation by removing calcium and forming insoluble salts**
 Tubes and their additives
Tubes and their additives
 • Tube tops are color-coded according to the additive • Serum, plasma, or whole blood for various assays • Many coagulation factors are involved in blood clotting, and coagulation can be prevented by the addition of different types of anticoagulants. • These anticoagulants often contain preservatives that can extend the metabolism and life span of the red blood cells (RBCs) after blood collection
• Tube tops are color-coded according to the additive • Serum, plasma, or whole blood for various assays • Many coagulation factors are involved in blood clotting, and coagulation can be prevented by the addition of different types of anticoagulants. • These anticoagulants often contain preservatives that can extend the metabolism and life span of the red blood cells (RBCs) after blood collection
 Green-Topped Tubes • Contain the anticoagulants sodium heparin, ammonium heparin, and lithium heparin. • These tubes are used in various laboratory assays requiring plasma or whole blood. • Should not be used for collections for blood smears. • Used for most chemistry tests (electrolytes) • BUN- Blood Urea Nitrogen*** kidney function • Creatinine- kidney function • Glucose • Calcium • CK- Creatine kinase-** heart damage
Green-Topped Tubes • Contain the anticoagulants sodium heparin, ammonium heparin, and lithium heparin. • These tubes are used in various laboratory assays requiring plasma or whole blood. • Should not be used for collections for blood smears. • Used for most chemistry tests (electrolytes) • BUN- Blood Urea Nitrogen*** kidney function • Creatinine- kidney function • Glucose • Calcium • CK- Creatine kinase-** heart damage
 Purple (Lavender)-Topped Tubes • • • Contain EDTA Typically used for CBC(complete blood count)** Hematological procedures Blood-banking procedures Molecular diagnostic testing Under filled purple topsinaccurate cell counts inaccurate hematocrit
Purple (Lavender)-Topped Tubes • • • Contain EDTA Typically used for CBC(complete blood count)** Hematological procedures Blood-banking procedures Molecular diagnostic testing Under filled purple topsinaccurate cell counts inaccurate hematocrit
 Light Blue–Topped Tubes • Contain sodium citrate • Many coagulation procedures, such as PT and APTT** are done on blood collected in light blue– topped vacuum tubes. • If a light blue–topped tube is under filled, coagulation results will be inaccurate must be filled to the line
Light Blue–Topped Tubes • Contain sodium citrate • Many coagulation procedures, such as PT and APTT** are done on blood collected in light blue– topped vacuum tubes. • If a light blue–topped tube is under filled, coagulation results will be inaccurate must be filled to the line
 Red-Topped, Royal Blue–Topped, Brown-Topped Tubes and Tan-Topped Tubes • Red-topped tubes are tubes without anticoagulant for the collection of serum. • Royal blue –topped tubes are used to collect samples for nutritional studies, therapeutic drug studies monitoring, and toxicology. ** • Royal blue–topped tube is the trace element tube.
Red-Topped, Royal Blue–Topped, Brown-Topped Tubes and Tan-Topped Tubes • Red-topped tubes are tubes without anticoagulant for the collection of serum. • Royal blue –topped tubes are used to collect samples for nutritional studies, therapeutic drug studies monitoring, and toxicology. ** • Royal blue–topped tube is the trace element tube.
 • The brown-topped tube contains heparin or no additive and is used for blood lead values. • The tan-topped tube is used for lead testing and contains EDTA** • Grey topped tubes contain sodium flouride used for glucose and lactic acid has glycolitic inhibitor- prevents glucose breakdown***
• The brown-topped tube contains heparin or no additive and is used for blood lead values. • The tan-topped tube is used for lead testing and contains EDTA** • Grey topped tubes contain sodium flouride used for glucose and lactic acid has glycolitic inhibitor- prevents glucose breakdown***
 Yellow-Topped Tubes • Contains sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS). • Used for blood culture specimen collections in microbiology. • Tubes containing ACD additive are use for specialty blood banking
Yellow-Topped Tubes • Contains sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS). • Used for blood culture specimen collections in microbiology. • Tubes containing ACD additive are use for specialty blood banking
 Mottled-Topped, Speckled. Topped, and Gold-Topped Tubes • AKA: Serum Separation Tubes • These tubes contain a polymer barrier in the bottom of the tube. • During centrifugation, the polymer barrier forms a barrier between the serum and blood cells
Mottled-Topped, Speckled. Topped, and Gold-Topped Tubes • AKA: Serum Separation Tubes • These tubes contain a polymer barrier in the bottom of the tube. • During centrifugation, the polymer barrier forms a barrier between the serum and blood cells
 Pink-Topped Tubes • Contain EDTA and are used for blood bank collections • Type and Cross for blood transfusions
Pink-Topped Tubes • Contain EDTA and are used for blood bank collections • Type and Cross for blood transfusions
 Black Topped tubes • Contains sodium citrate additive • Used for testing ESR (sed rate)**
Black Topped tubes • Contains sodium citrate additive • Used for testing ESR (sed rate)**
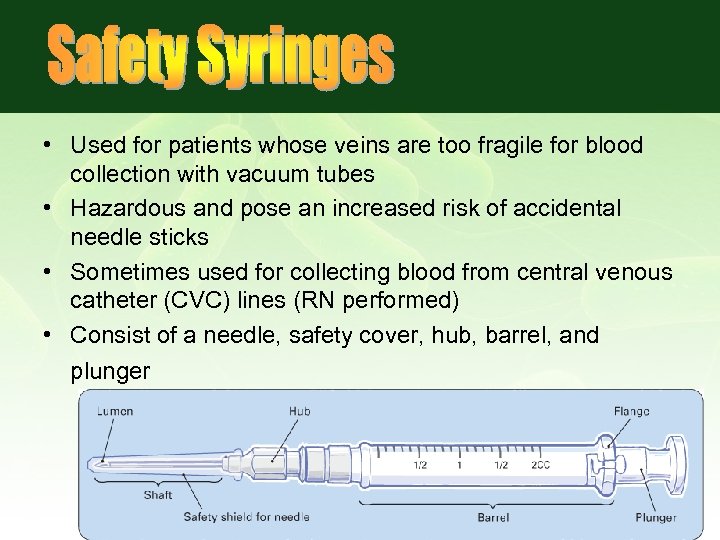 • Used for patients whose veins are too fragile for blood collection with vacuum tubes • Hazardous and pose an increased risk of accidental needle sticks • Sometimes used for collecting blood from central venous catheter (CVC) lines (RN performed) • Consist of a needle, safety cover, hub, barrel, and plunger
• Used for patients whose veins are too fragile for blood collection with vacuum tubes • Hazardous and pose an increased risk of accidental needle sticks • Sometimes used for collecting blood from central venous catheter (CVC) lines (RN performed) • Consist of a needle, safety cover, hub, barrel, and plunger
 Safety Syringes • The syringe needle should be shielded after blood collection, removed, and discarded in a sharps disposal container. • The BD blood-transfer device is attached to the syringe, and a vacuum tube is inserted into the transfer device. • The blood is transferred from the syringe to the tube using the tube’s vacuum
Safety Syringes • The syringe needle should be shielded after blood collection, removed, and discarded in a sharps disposal container. • The BD blood-transfer device is attached to the syringe, and a vacuum tube is inserted into the transfer device. • The blood is transferred from the syringe to the tube using the tube’s vacuum
 Gauge and Length of a Needle • The gauge number indicates the diameter of the needle; the smaller the gauge number, the larger the needle diameter **and higher the flow rate. • Larger (16 - to 18 -gauge) needles are used for collecting donor units of blood (450 m. L or less) • Smaller (21 - and 22 -gauge) needles are used for collecting specimens for laboratory assays. (this is typically what you will be using) • Color coding of needles indicates gauge size**
Gauge and Length of a Needle • The gauge number indicates the diameter of the needle; the smaller the gauge number, the larger the needle diameter **and higher the flow rate. • Larger (16 - to 18 -gauge) needles are used for collecting donor units of blood (450 m. L or less) • Smaller (21 - and 22 -gauge) needles are used for collecting specimens for laboratory assays. (this is typically what you will be using) • Color coding of needles indicates gauge size**
 • There are many manufacturers of venipuncture equipment. The type of equipment depends on the facility. • Essentially, they are all the same • Familiarize yourself with the equipment that your facility uses
• There are many manufacturers of venipuncture equipment. The type of equipment depends on the facility. • Essentially, they are all the same • Familiarize yourself with the equipment that your facility uses
 • Sterilized and packaged by vendors in sealed shields that maintain sterility. • Check the tip of each needle for damage. • Multiple-sample needles are used with vacuum collection tubes and the holder to allow for multiple tube changes without blood leakage within the plastic holder
• Sterilized and packaged by vendors in sealed shields that maintain sterility. • Check the tip of each needle for damage. • Multiple-sample needles are used with vacuum collection tubes and the holder to allow for multiple tube changes without blood leakage within the plastic holder
 The Butterfly Needle (Blood Collection Set) • Also called a blood collection set or winged infusion set • The most commonly used intravenous device • The most common butterfly needle sizes are 21 and 23 gauge and the length of these needles range from ½ to ¾ inches long. • These safety needles each have a shield that automatically covers the contaminated needle point upon withdrawal from the patient’s vein • Highest rate of needle stick injuries**.
The Butterfly Needle (Blood Collection Set) • Also called a blood collection set or winged infusion set • The most commonly used intravenous device • The most common butterfly needle sizes are 21 and 23 gauge and the length of these needles range from ½ to ¾ inches long. • These safety needles each have a shield that automatically covers the contaminated needle point upon withdrawal from the patient’s vein • Highest rate of needle stick injuries**.
 Needle and Other Sharps Disposal • Must be discarded in rigid, leak-proof, plastic containers. • Each unit is usually orange or red. • Disposable as biohazardous waste
Needle and Other Sharps Disposal • Must be discarded in rigid, leak-proof, plastic containers. • Each unit is usually orange or red. • Disposable as biohazardous waste
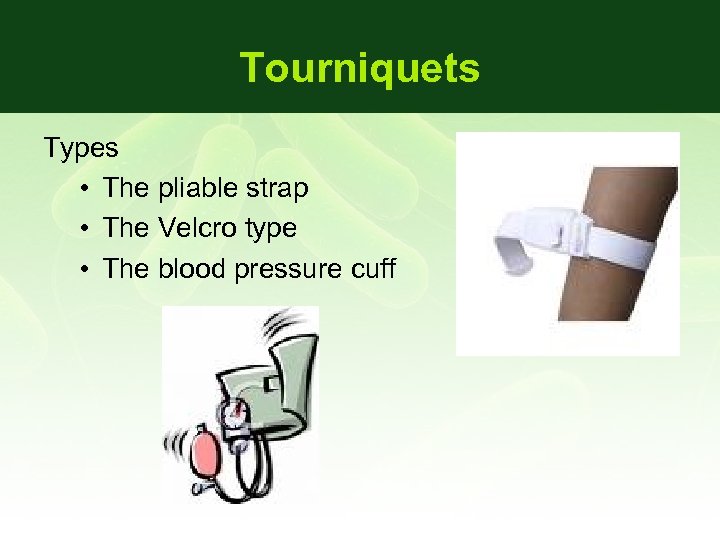 Tourniquets Types • The pliable strap • The Velcro type • The blood pressure cuff
Tourniquets Types • The pliable strap • The Velcro type • The blood pressure cuff
 • Non-latex disposable tourniquets are now available. • If the tourniquets used in the health care facility are not disposable, they must be wiped frequently with 70 percent isopropyl alcohol and disinfected with a chlorine bleach dilution of 1: 10 if contaminated with blood or other body fluids. • Provide a barrier to slow down venous flow
• Non-latex disposable tourniquets are now available. • If the tourniquets used in the health care facility are not disposable, they must be wiped frequently with 70 percent isopropyl alcohol and disinfected with a chlorine bleach dilution of 1: 10 if contaminated with blood or other body fluids. • Provide a barrier to slow down venous flow
 Gloves for Blood Collection • Use non-latex gloves • Do not use gloves with talcum powder • Change gloves after each patients’ blood collection • Do not wash, disinfect, or reuse gloves.
Gloves for Blood Collection • Use non-latex gloves • Do not use gloves with talcum powder • Change gloves after each patients’ blood collection • Do not wash, disinfect, or reuse gloves.
 Other items needed for blood collection • . Antiseptics, Sterile Gauze Pads and Bandages • 70% isopropyl alcohol preparation • iodine swab sticks or pads** (for blood cultures) are essential for blood collection
Other items needed for blood collection • . Antiseptics, Sterile Gauze Pads and Bandages • 70% isopropyl alcohol preparation • iodine swab sticks or pads** (for blood cultures) are essential for blood collection
 Micro collection Equipment • Usually, skin puncture blood-collecting techniques are used on infants, because venipuncture is excessively hazardous. • For infants, the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute recommends a penetration depth of less than 2. 0 mm on heelsticks to avoid penetrating bone. ***
Micro collection Equipment • Usually, skin puncture blood-collecting techniques are used on infants, because venipuncture is excessively hazardous. • For infants, the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute recommends a penetration depth of less than 2. 0 mm on heelsticks to avoid penetrating bone. ***
 Lancets and Tubes • Different facilities use different manufacturers Examples • BD Quikheel Lancet • BD Genie Lancet • Tenderlett Automated Skin Incision Device • Monoject Monoletter Safety Lancet • Greiner Bio-One Lancets
Lancets and Tubes • Different facilities use different manufacturers Examples • BD Quikheel Lancet • BD Genie Lancet • Tenderlett Automated Skin Incision Device • Monoject Monoletter Safety Lancet • Greiner Bio-One Lancets
 Microcontainers • For dermal sticks two additional equipment is required-Plastic micro hematocrit capillary tubes -Disposable narrow-bore pipettes that are used for packed red cell volume in microcentrifugation
Microcontainers • For dermal sticks two additional equipment is required-Plastic micro hematocrit capillary tubes -Disposable narrow-bore pipettes that are used for packed red cell volume in microcentrifugation
 Micro collection tubes • Have colored bands; a red band indicates a heparin-coated tube, and a blue band indicates no anticoagulant • Usually color coded according to the established protocol for blood collection vacuum tube tops
Micro collection tubes • Have colored bands; a red band indicates a heparin-coated tube, and a blue band indicates no anticoagulant • Usually color coded according to the established protocol for blood collection vacuum tube tops
 Different manufacturers • • Samplette micro blood collector BD Microtainer tube Microvette capillary blood collection system SAFE-T-FILL capillary blood collection system
Different manufacturers • • Samplette micro blood collector BD Microtainer tube Microvette capillary blood collection system SAFE-T-FILL capillary blood collection system
 Specimen Collection Trays • Taken on blood-collecting rounds • Made of plastic (preferably latex free) that can be sterilized • Includes all necessary collection equipment • Prior to rounds- ensure that your tray is fully stocked
Specimen Collection Trays • Taken on blood-collecting rounds • Made of plastic (preferably latex free) that can be sterilized • Includes all necessary collection equipment • Prior to rounds- ensure that your tray is fully stocked
 Specimen Collection Trays For Home Health Care Providers • Carry an enclosed container with the biohazard symbol visible on the outside • Lockable, to protect the contents from tampering or accidental contamination • With a tight seal to reduce the risk of infection from bloodborne pathogens due to spills or accidents
Specimen Collection Trays For Home Health Care Providers • Carry an enclosed container with the biohazard symbol visible on the outside • Lockable, to protect the contents from tampering or accidental contamination • With a tight seal to reduce the risk of infection from bloodborne pathogens due to spills or accidents


