4efe494b5d1dddde2aec41c1c43361e6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Chapter 6 Understanding and Assessing Hardware: Evaluating Your System • To buy or upgrade? Evaluating your system: – CPU – RAM – Storage devices – Video output – Sound systems © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1
Chapter 6 Understanding and Assessing Hardware: Evaluating Your System • To buy or upgrade? Evaluating your system: – CPU – RAM – Storage devices – Video output – Sound systems © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1
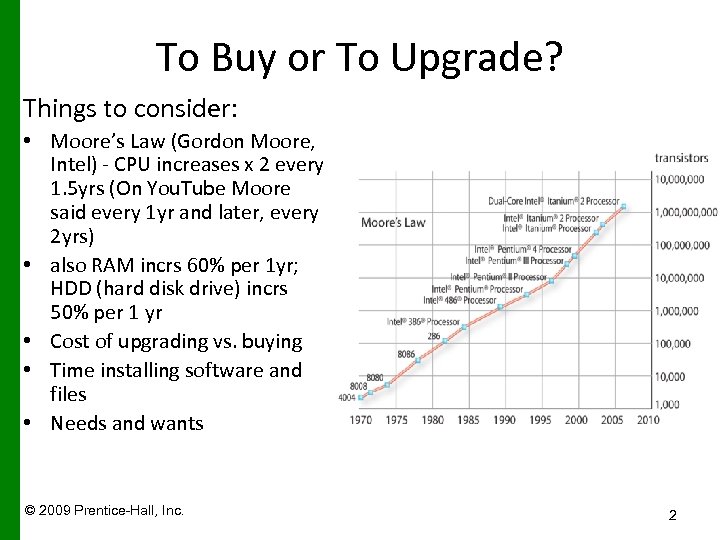 To Buy or To Upgrade? Things to consider: • Moore’s Law (Gordon Moore, Intel) - CPU increases x 2 every 1. 5 yrs (On You. Tube Moore said every 1 yr and later, every 2 yrs) • also RAM incrs 60% per 1 yr; HDD (hard disk drive) incrs 50% per 1 yr • Cost of upgrading vs. buying • Time installing software and files • Needs and wants © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2
To Buy or To Upgrade? Things to consider: • Moore’s Law (Gordon Moore, Intel) - CPU increases x 2 every 1. 5 yrs (On You. Tube Moore said every 1 yr and later, every 2 yrs) • also RAM incrs 60% per 1 yr; HDD (hard disk drive) incrs 50% per 1 yr • Cost of upgrading vs. buying • Time installing software and files • Needs and wants © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2
 Evaluating the CPU • How does the CPU work? (works together with RAM) – 2 parts: – Control unit – Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) – Machine cycle (4 steps): • Fetch – Decode – Execute – Store – (Fetch from and store to RAM) – Common speeds: desktop: 2 - 4 GHz – Ex: 3. 8 GHz = 3. 8 giga Hertz = 3. 8 billion cycles per second (clock cycles ~ instructions per sec) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3
Evaluating the CPU • How does the CPU work? (works together with RAM) – 2 parts: – Control unit – Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) – Machine cycle (4 steps): • Fetch – Decode – Execute – Store – (Fetch from and store to RAM) – Common speeds: desktop: 2 - 4 GHz – Ex: 3. 8 GHz = 3. 8 giga Hertz = 3. 8 billion cycles per second (clock cycles ~ instructions per sec) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3
 Differentiating CPUs’ power • Clock speed (previous slide) • Number of cores (next slide) – Core: A complete processing section from a CPU embedded into the same physical chip – Number of threads – hyperthreading: a secondary set of instructions can start in CPU before the last set is finished • Cache memory – small amounts of high speed expensive memory on/near CPU that it to execute instructions better: Levels 1, 2, 3. • Overclock the CPU – techies do! They manipulate their CPU to make it run faster that manufacturer’s recommended speed. It voids warranty. • Omit - FSB – front side bus (think bus route b/c it is the route for signals between CPU and RAM). Not listed on newest CPU spec list © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 4
Differentiating CPUs’ power • Clock speed (previous slide) • Number of cores (next slide) – Core: A complete processing section from a CPU embedded into the same physical chip – Number of threads – hyperthreading: a secondary set of instructions can start in CPU before the last set is finished • Cache memory – small amounts of high speed expensive memory on/near CPU that it to execute instructions better: Levels 1, 2, 3. • Overclock the CPU – techies do! They manipulate their CPU to make it run faster that manufacturer’s recommended speed. It voids warranty. • Omit - FSB – front side bus (think bus route b/c it is the route for signals between CPU and RAM). Not listed on newest CPU spec list © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 4
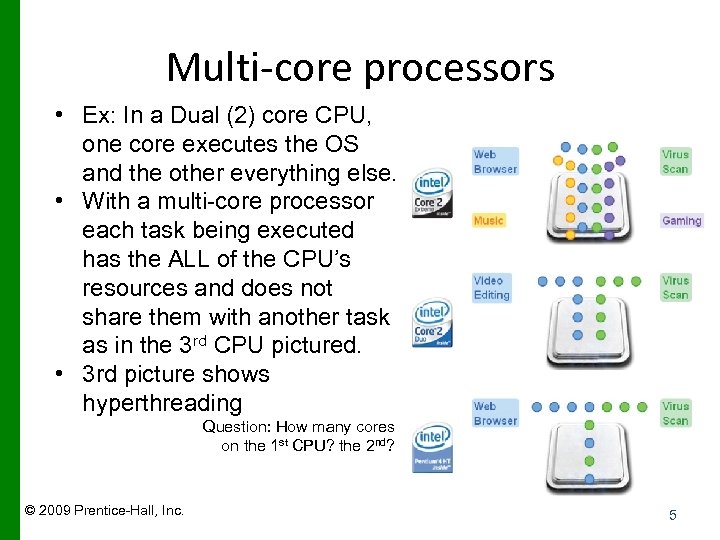 Multi-core processors • Ex: In a Dual (2) core CPU, one core executes the OS and the other everything else. • With a multi-core processor each task being executed has the ALL of the CPU’s resources and does not share them with another task as in the 3 rd CPU pictured. • 3 rd picture shows hyperthreading Question: How many cores on the 1 st CPU? the 2 nd? © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 5
Multi-core processors • Ex: In a Dual (2) core CPU, one core executes the OS and the other everything else. • With a multi-core processor each task being executed has the ALL of the CPU’s resources and does not share them with another task as in the 3 rd CPU pictured. • 3 rd picture shows hyperthreading Question: How many cores on the 1 st CPU? the 2 nd? © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 5
 Evaluating the CPU – id your system’s parts • Identify your CPU in Windows 8: – In File Explorer “folder” icon, go to the “This PC” and then the Computer tab will appear. Click it and System button – Right click Windows icon, lower left of screen, select System In Win 7, right-click Computer folder, select Properties (or click Sys Props button in Computer) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
Evaluating the CPU – id your system’s parts • Identify your CPU in Windows 8: – In File Explorer “folder” icon, go to the “This PC” and then the Computer tab will appear. Click it and System button – Right click Windows icon, lower left of screen, select System In Win 7, right-click Computer folder, select Properties (or click Sys Props button in Computer) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
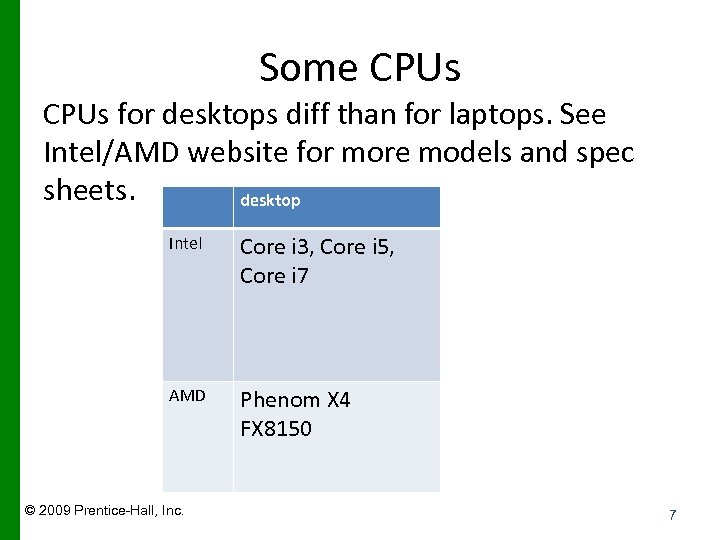 Some CPUs for desktops diff than for laptops. See Intel/AMD website for more models and spec sheets. desktop Intel Core i 3, Core i 5, Core i 7 AMD Phenom X 4 FX 8150 © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 7
Some CPUs for desktops diff than for laptops. See Intel/AMD website for more models and spec sheets. desktop Intel Core i 3, Core i 5, Core i 7 AMD Phenom X 4 FX 8150 © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 7
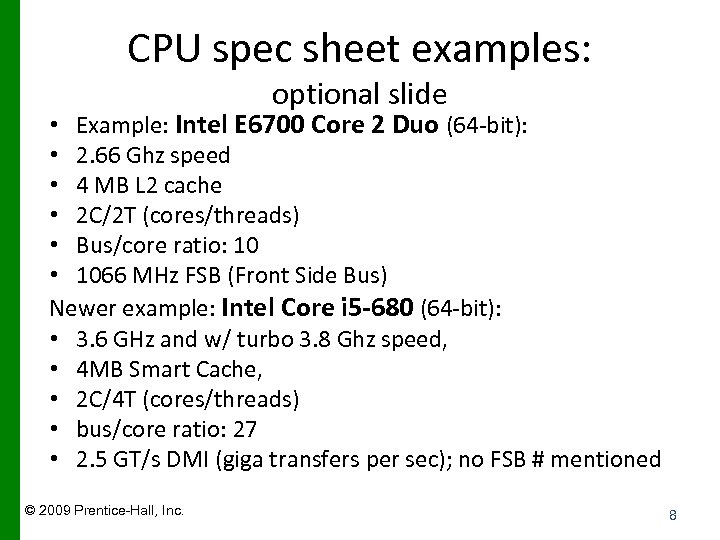 CPU spec sheet examples: optional slide • Example: Intel E 6700 Core 2 Duo (64 -bit): • 2. 66 Ghz speed • 4 MB L 2 cache • 2 C/2 T (cores/threads) • Bus/core ratio: 10 • 1066 MHz FSB (Front Side Bus) Newer example: Intel Core i 5 -680 (64 -bit): • 3. 6 GHz and w/ turbo 3. 8 Ghz speed, • 4 MB Smart Cache, • 2 C/4 T (cores/threads) • bus/core ratio: 27 • 2. 5 GT/s DMI (giga transfers per sec); no FSB # mentioned © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 8
CPU spec sheet examples: optional slide • Example: Intel E 6700 Core 2 Duo (64 -bit): • 2. 66 Ghz speed • 4 MB L 2 cache • 2 C/2 T (cores/threads) • Bus/core ratio: 10 • 1066 MHz FSB (Front Side Bus) Newer example: Intel Core i 5 -680 (64 -bit): • 3. 6 GHz and w/ turbo 3. 8 Ghz speed, • 4 MB Smart Cache, • 2 C/4 T (cores/threads) • bus/core ratio: 27 • 2. 5 GT/s DMI (giga transfers per sec); no FSB # mentioned © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 8
 RAM (names for) • Random access memory (RAM): – Temporary storage (memory) also called Volatile • Physical memory • Memory modules fit on motherboard into memory banks (slots) • Module also called dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) – DDR 2, DDR 3 • DDR 3 current version for most PCs still DDR == double data rate © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
RAM (names for) • Random access memory (RAM): – Temporary storage (memory) also called Volatile • Physical memory • Memory modules fit on motherboard into memory banks (slots) • Module also called dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) – DDR 2, DDR 3 • DDR 3 current version for most PCs still DDR == double data rate © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
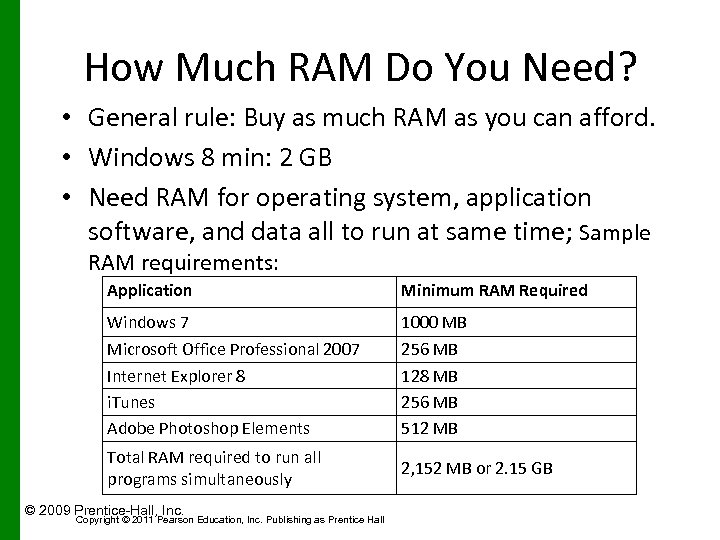 How Much RAM Do You Need? • General rule: Buy as much RAM as you can afford. • Windows 8 min: 2 GB • Need RAM for operating system, application software, and data all to run at same time; Sample RAM requirements: Application Minimum RAM Required Windows 7 1000 MB Microsoft Office Professional 2007 Internet Explorer 8 i. Tunes Adobe Photoshop Elements 256 MB 128 MB 256 MB 512 MB Total RAM required to run all programs simultaneously 2, 152 MB or 2. 15 GB © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
How Much RAM Do You Need? • General rule: Buy as much RAM as you can afford. • Windows 8 min: 2 GB • Need RAM for operating system, application software, and data all to run at same time; Sample RAM requirements: Application Minimum RAM Required Windows 7 1000 MB Microsoft Office Professional 2007 Internet Explorer 8 i. Tunes Adobe Photoshop Elements 256 MB 128 MB 256 MB 512 MB Total RAM required to run all programs simultaneously 2, 152 MB or 2. 15 GB © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Adding RAM • Easy to do and reasonably priced • Increases system performance (May need to add more if your system is slower over the years) • Check your RAM amount: go to Computer Tab in File Explorer, in This PC window • To upgrade, look up your RAM type and requirements in documents at your computer’s manufacturer support page online. Or try www. crucial. com look up tool using your computer’s model – Type of module (i. e. DDR 3) – Maximum total limit, maximum limit per slot – Maximum limit for your operating system • Common size: 4 -24 GB (expandable to 24 GB) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 11
Adding RAM • Easy to do and reasonably priced • Increases system performance (May need to add more if your system is slower over the years) • Check your RAM amount: go to Computer Tab in File Explorer, in This PC window • To upgrade, look up your RAM type and requirements in documents at your computer’s manufacturer support page online. Or try www. crucial. com look up tool using your computer’s model – Type of module (i. e. DDR 3) – Maximum total limit, maximum limit per slot – Maximum limit for your operating system • Common size: 4 -24 GB (expandable to 24 GB) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 11
 Omit: Virtual Memory Virtual memory was covered in chapter 5! • Memory bound (sys that runs out of RAM space) • Virtual memory (also page file)– When system runs out of RAM, hard drive space is resorted to. • Drawback = speed is slowed. That is, RAM operates in nanosecs (1/billion= 1/1, 000, 000) and Hard Disk Drive operates in millisecs (1/1000) • Increasing RAM can avoid this problem © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 12
Omit: Virtual Memory Virtual memory was covered in chapter 5! • Memory bound (sys that runs out of RAM space) • Virtual memory (also page file)– When system runs out of RAM, hard drive space is resorted to. • Drawback = speed is slowed. That is, RAM operates in nanosecs (1/billion= 1/1, 000, 000) and Hard Disk Drive operates in millisecs (1/1000) • Increasing RAM can avoid this problem © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 12
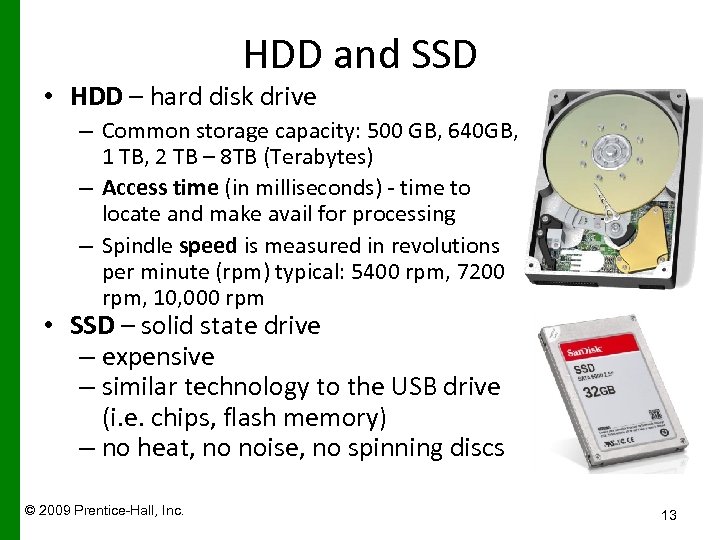 HDD and SSD • HDD – hard disk drive – Common storage capacity: 500 GB, 640 GB, 1 TB, 2 TB – 8 TB (Terabytes) – Access time (in milliseconds) - time to locate and make avail for processing – Spindle speed is measured in revolutions per minute (rpm) typical: 5400 rpm, 7200 rpm, 10, 000 rpm • SSD – solid state drive – expensive – similar technology to the USB drive (i. e. chips, flash memory) – no heat, no noise, no spinning discs © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 13
HDD and SSD • HDD – hard disk drive – Common storage capacity: 500 GB, 640 GB, 1 TB, 2 TB – 8 TB (Terabytes) – Access time (in milliseconds) - time to locate and make avail for processing – Spindle speed is measured in revolutions per minute (rpm) typical: 5400 rpm, 7200 rpm, 10, 000 rpm • SSD – solid state drive – expensive – similar technology to the USB drive (i. e. chips, flash memory) – no heat, no noise, no spinning discs © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 13
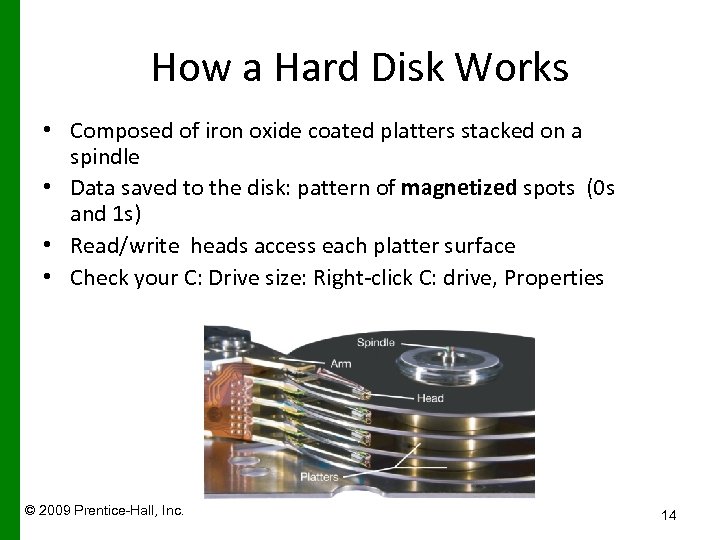 How a Hard Disk Works • Composed of iron oxide coated platters stacked on a spindle • Data saved to the disk: pattern of magnetized spots (0 s and 1 s) • Read/write heads access each platter surface • Check your C: Drive size: Right-click C: drive, Properties Access arms © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 14
How a Hard Disk Works • Composed of iron oxide coated platters stacked on a spindle • Data saved to the disk: pattern of magnetized spots (0 s and 1 s) • Read/write heads access each platter surface • Check your C: Drive size: Right-click C: drive, Properties Access arms © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 14
 Optical Storage • Optical media: Store data as tiny pits burned into a disc by a laser; nonpits=lands – Prerecorded • CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, BD-ROM – Recordable • CD-R, DVD-R, BD-R – Rewritable (rewrite again and again) • CD-RW, DVD-RW, BD-RE • A DVD-RW burner will burn CDs and DVDs; • A Blu-ray burner will most likely burn CDs and DVDs © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
Optical Storage • Optical media: Store data as tiny pits burned into a disc by a laser; nonpits=lands – Prerecorded • CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, BD-ROM – Recordable • CD-R, DVD-R, BD-R – Rewritable (rewrite again and again) • CD-RW, DVD-RW, BD-RE • A DVD-RW burner will burn CDs and DVDs; • A Blu-ray burner will most likely burn CDs and DVDs © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
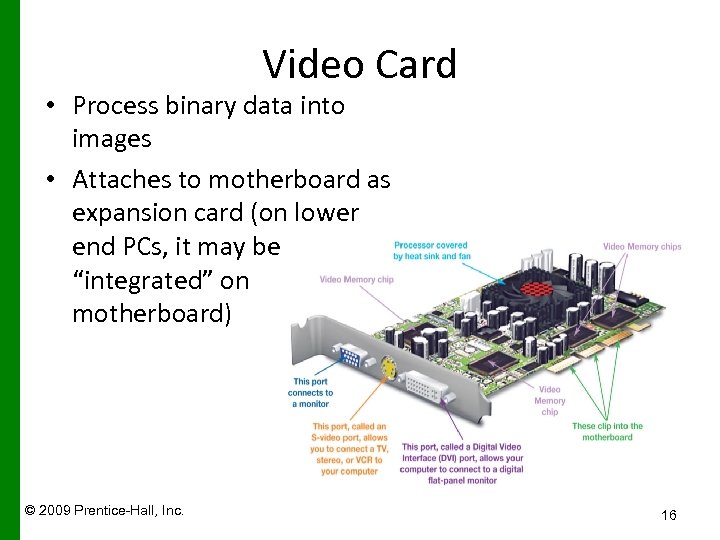 Video Card • Process binary data into images • Attaches to motherboard as expansion card (on lower end PCs, it may be “integrated” on motherboard) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 16
Video Card • Process binary data into images • Attaches to motherboard as expansion card (on lower end PCs, it may be “integrated” on motherboard) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 16
 Video Card Contains its own RAM, video RAM or VRAM types: GDDR 3, GDDR 5 Serious gamers use cards with more VRAM Contains its own graphics processor (GPU) To determine specs of your video card (graphics card) -- go to screen resolution settings screen in Control Panel, click Advanced button • Ports on video card: DVI (LCD monitor) and HDMI (TVs etc) • • • © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 17
Video Card Contains its own RAM, video RAM or VRAM types: GDDR 3, GDDR 5 Serious gamers use cards with more VRAM Contains its own graphics processor (GPU) To determine specs of your video card (graphics card) -- go to screen resolution settings screen in Control Panel, click Advanced button • Ports on video card: DVI (LCD monitor) and HDMI (TVs etc) • • • © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 17
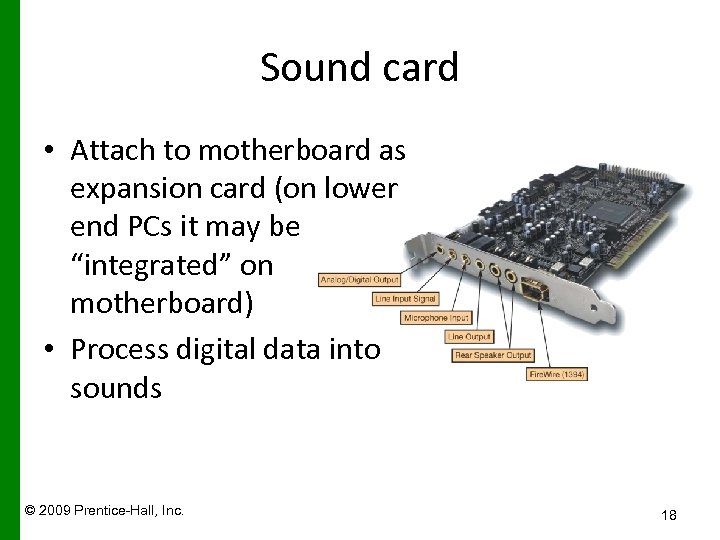 Sound card • Attach to motherboard as expansion card (on lower end PCs it may be “integrated” on motherboard) • Process digital data into sounds © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 18
Sound card • Attach to motherboard as expansion card (on lower end PCs it may be “integrated” on motherboard) • Process digital data into sounds © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 18
 Evaluating System Reliability • Performance: – Is slow – Freezes – Crashes • Upkeep and maintenance: – System tools – Control panel – Update software, and hardware drivers (Windows update can include Microsoft’s other software) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 19
Evaluating System Reliability • Performance: – Is slow – Freezes – Crashes • Upkeep and maintenance: – System tools – Control panel – Update software, and hardware drivers (Windows update can include Microsoft’s other software) © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 19
 Upkeep and Maintenance • System tools: – Disk defragmenter – Disk cleanup – Add/remove programs – Run anti-virus and anti-spyware scans – Updates Windows – Update programs © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 20
Upkeep and Maintenance • System tools: – Disk defragmenter – Disk cleanup – Add/remove programs – Run anti-virus and anti-spyware scans – Updates Windows – Update programs © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 20
 The Last Resort • If problems persist: First… – Try reinstalling the software application that is the probable cause – Create a restore point • Drastic measures… – Reinstall (“recover”) the operating system. Or take it into to shop! In Windows 8 this can be done with the “Windows Refresh” tool. It is imilar to the nondestructive recovery we talked about in the Windows Unit. See “Maintain your PC” notes on Windows Unit page of perel website. © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 21
The Last Resort • If problems persist: First… – Try reinstalling the software application that is the probable cause – Create a restore point • Drastic measures… – Reinstall (“recover”) the operating system. Or take it into to shop! In Windows 8 this can be done with the “Windows Refresh” tool. It is imilar to the nondestructive recovery we talked about in the Windows Unit. See “Maintain your PC” notes on Windows Unit page of perel website. © 2009 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 21


