44e6e69f708296e8b02c4dfd5c8f95f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Chapter 6 The Internet
Chapter 6 The Internet
 6 Chapter Contents ïSection A: Internet Technology ïSection B: Fixed Internet Access ïSection C: Portable and Mobile Internet Access ïSection D: Internet Services ïSection E: Internet Security Chapter 6: The Internet 2
6 Chapter Contents ïSection A: Internet Technology ïSection B: Fixed Internet Access ïSection C: Portable and Mobile Internet Access ïSection D: Internet Services ïSection E: Internet Security Chapter 6: The Internet 2
 6 A SECTION Internet Technology ïBackground ïInternet Infrastructure ïInternet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains ïConnection Speed Chapter 6: The Internet 3
6 A SECTION Internet Technology ïBackground ïInternet Infrastructure ïInternet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains ïConnection Speed Chapter 6: The Internet 3
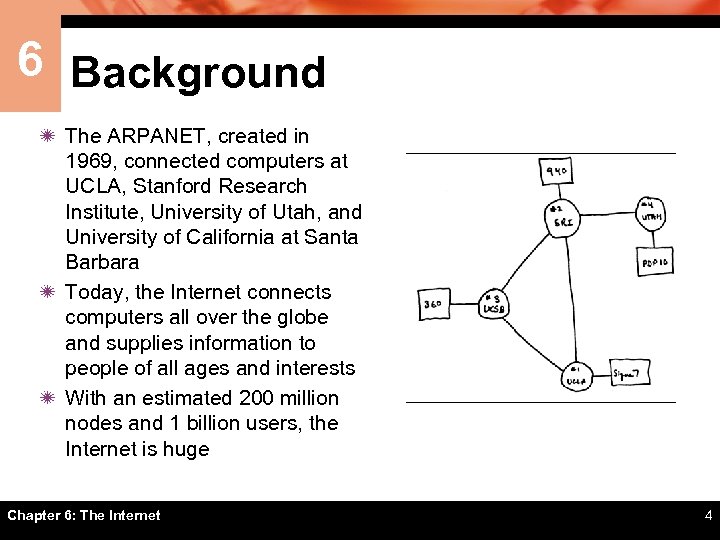 6 Background ï The ARPANET, created in 1969, connected computers at UCLA, Stanford Research Institute, University of Utah, and University of California at Santa Barbara ï Today, the Internet connects computers all over the globe and supplies information to people of all ages and interests ï With an estimated 200 million nodes and 1 billion users, the Internet is huge Chapter 6: The Internet 4
6 Background ï The ARPANET, created in 1969, connected computers at UCLA, Stanford Research Institute, University of Utah, and University of California at Santa Barbara ï Today, the Internet connects computers all over the globe and supplies information to people of all ages and interests ï With an estimated 200 million nodes and 1 billion users, the Internet is huge Chapter 6: The Internet 4
 6 Internet Infrastructure ï The Internet is not owned or operated by any single corporation or government ï The Internet backbone is a network of high-capacity communications links that provides the main routes for data traffic across the Internet ï Backbone links and routers are maintained by network service providers (NSPs) ï NSP equipment and links are tied together by network access points (NAPs) ï An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that offers Internet access to individuals, businesses, and smaller ISPs Chapter 6: The Internet 5
6 Internet Infrastructure ï The Internet is not owned or operated by any single corporation or government ï The Internet backbone is a network of high-capacity communications links that provides the main routes for data traffic across the Internet ï Backbone links and routers are maintained by network service providers (NSPs) ï NSP equipment and links are tied together by network access points (NAPs) ï An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that offers Internet access to individuals, businesses, and smaller ISPs Chapter 6: The Internet 5
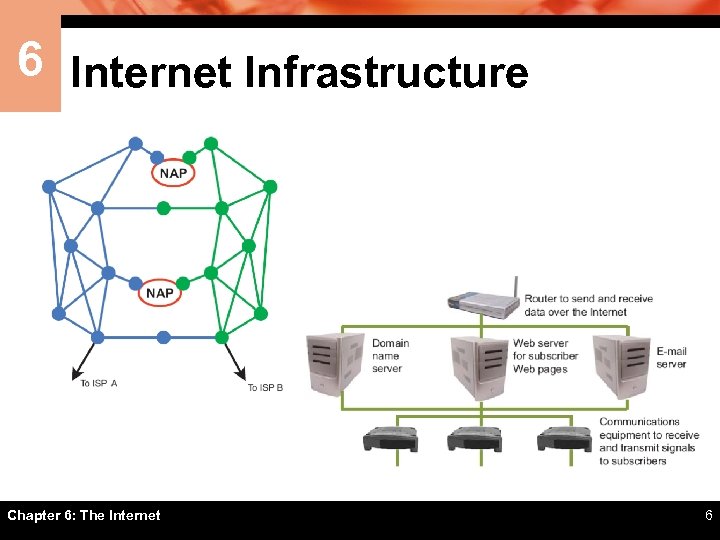 6 Internet Infrastructure Chapter 6: The Internet 6
6 Internet Infrastructure Chapter 6: The Internet 6
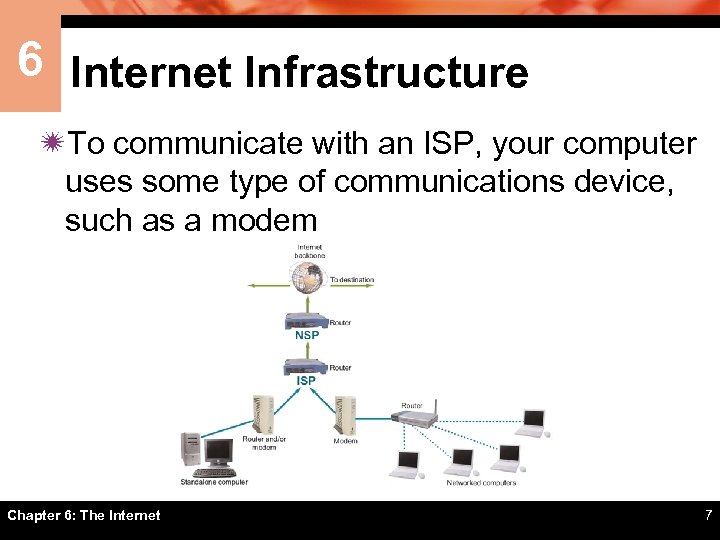 6 Internet Infrastructure ïTo communicate with an ISP, your computer uses some type of communications device, such as a modem Chapter 6: The Internet 7
6 Internet Infrastructure ïTo communicate with an ISP, your computer uses some type of communications device, such as a modem Chapter 6: The Internet 7
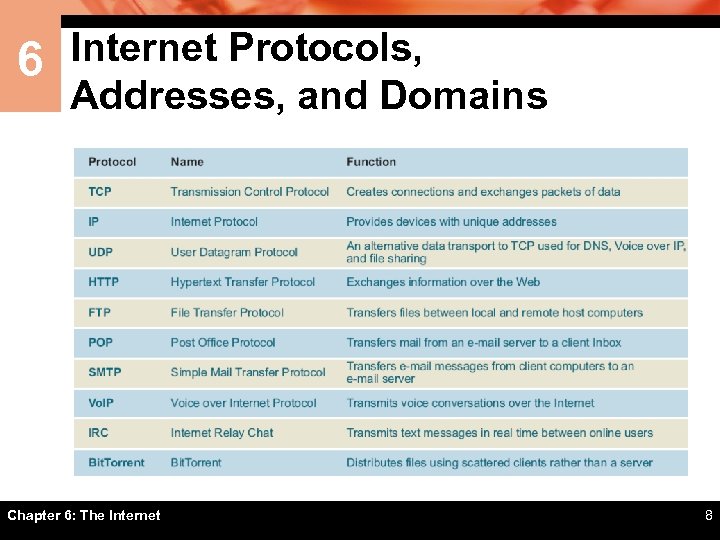 6 Internet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains Chapter 6: The Internet 8
6 Internet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains Chapter 6: The Internet 8
 6 Internet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains ïA domain name is a key component of Web addresses, e-mail addresses, and addresses on the Web called URLs Chapter 6: The Internet 9
6 Internet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains ïA domain name is a key component of Web addresses, e-mail addresses, and addresses on the Web called URLs Chapter 6: The Internet 9
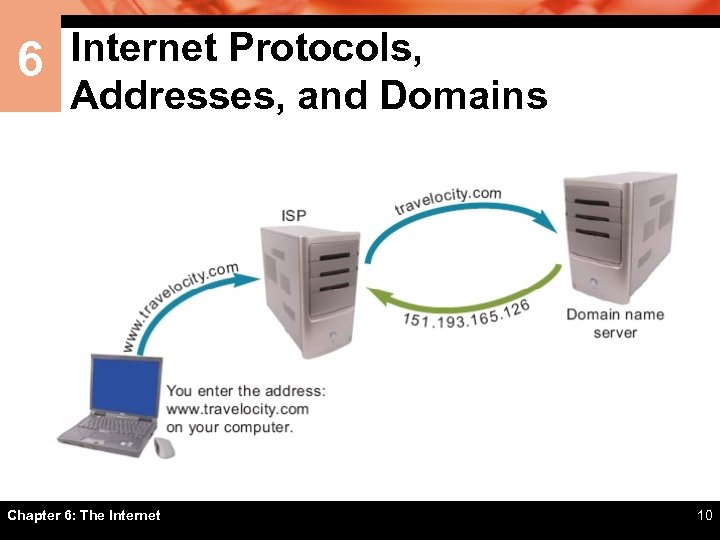 6 Internet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains Chapter 6: The Internet 10
6 Internet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains Chapter 6: The Internet 10
 6 Internet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains The first step in registering a domain name is to find out whether the name is currently in use or reserved for future use. If a domain name is not available, consider using a different top-level domain, such as biz instead of com. After you’ve found an available domain name, you can continue the registration process by filling out a simple online form. Chapter 6: The Internet 11
6 Internet Protocols, Addresses, and Domains The first step in registering a domain name is to find out whether the name is currently in use or reserved for future use. If a domain name is not available, consider using a different top-level domain, such as biz instead of com. After you’ve found an available domain name, you can continue the registration process by filling out a simple online form. Chapter 6: The Internet 11
 6 Connection Speed ïData travels over the Internet at an incredible speed ïThe elapsed time for data to make a round trip from point A to point B and back to point A is referred to as latency – Ping – Traceroute ïUpstream vs. downstream speed Chapter 6: The Internet 12
6 Connection Speed ïData travels over the Internet at an incredible speed ïThe elapsed time for data to make a round trip from point A to point B and back to point A is referred to as latency – Ping – Traceroute ïUpstream vs. downstream speed Chapter 6: The Internet 12
 6 Connection Speed ï When upstream speeds differ from downstream speeds, you have an asymmetric Internet connection ï When upstream and downstream speeds are the same, you have a symmetric Internet connection ï Internet connection options – Fixed Internet access – Portable Internet access – Mobile Internet access Chapter 6: The Internet 13
6 Connection Speed ï When upstream speeds differ from downstream speeds, you have an asymmetric Internet connection ï When upstream and downstream speeds are the same, you have a symmetric Internet connection ï Internet connection options – Fixed Internet access – Portable Internet access – Mobile Internet access Chapter 6: The Internet 13
 6 B SECTION Fixed Internet Access ïDial-up Connections ïDSL, ISDN, and Dedicated Lines ïCable Internet Service ïSatellite Internet Service ïFixed Wireless Service ïFixed Internet Connection Roundup Chapter 6: The Internet 14
6 B SECTION Fixed Internet Access ïDial-up Connections ïDSL, ISDN, and Dedicated Lines ïCable Internet Service ïSatellite Internet Service ïFixed Wireless Service ïFixed Internet Connection Roundup Chapter 6: The Internet 14
 6 Dial-up Connections ïA dial-up connection is a fixed Internet connection that uses a voiceband modem and telephone lines to transport data between your computer and your ISP Chapter 6: The Internet 15
6 Dial-up Connections ïA dial-up connection is a fixed Internet connection that uses a voiceband modem and telephone lines to transport data between your computer and your ISP Chapter 6: The Internet 15
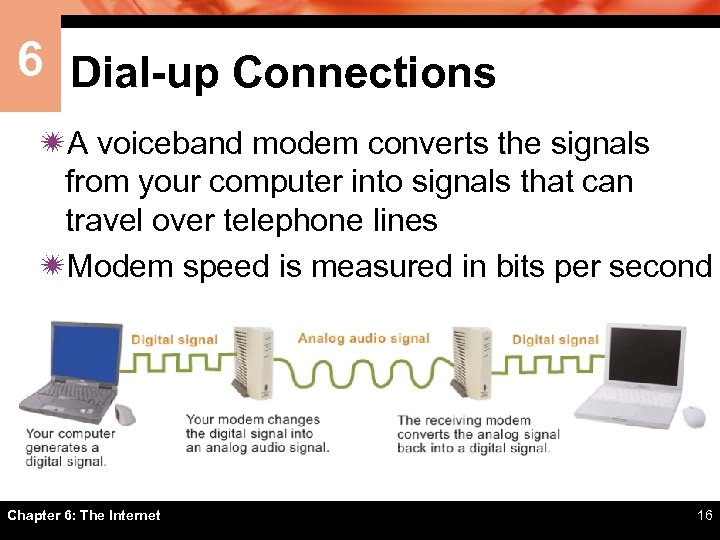 6 Dial-up Connections ïA voiceband modem converts the signals from your computer into signals that can travel over telephone lines ïModem speed is measured in bits per second Chapter 6: The Internet 16
6 Dial-up Connections ïA voiceband modem converts the signals from your computer into signals that can travel over telephone lines ïModem speed is measured in bits per second Chapter 6: The Internet 16
 6 DSL, ISDN, and Dedicated Lines ïT 1, T 3, and T 4 lines are leased from the telephone company, and offer fast, highcapacity data transmission ïISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) is a type of fixed Internet connection that moves data at speeds of 64 Kbps or 128 Kbps over ordinary telephone lines – ISDN terminal adapter connects a computer to a telephone wall jack and converts signals to travel over ISDN connection Chapter 6: The Internet 17
6 DSL, ISDN, and Dedicated Lines ïT 1, T 3, and T 4 lines are leased from the telephone company, and offer fast, highcapacity data transmission ïISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) is a type of fixed Internet connection that moves data at speeds of 64 Kbps or 128 Kbps over ordinary telephone lines – ISDN terminal adapter connects a computer to a telephone wall jack and converts signals to travel over ISDN connection Chapter 6: The Internet 17
 6 DSL, ISDN, and Dedicated Lines ïDSL is a high-speed, digital, always-on Internet access technology that runs over standard phone lines – Most DSL installations require service technicians • DSL modem Chapter 6: The Internet 18
6 DSL, ISDN, and Dedicated Lines ïDSL is a high-speed, digital, always-on Internet access technology that runs over standard phone lines – Most DSL installations require service technicians • DSL modem Chapter 6: The Internet 18
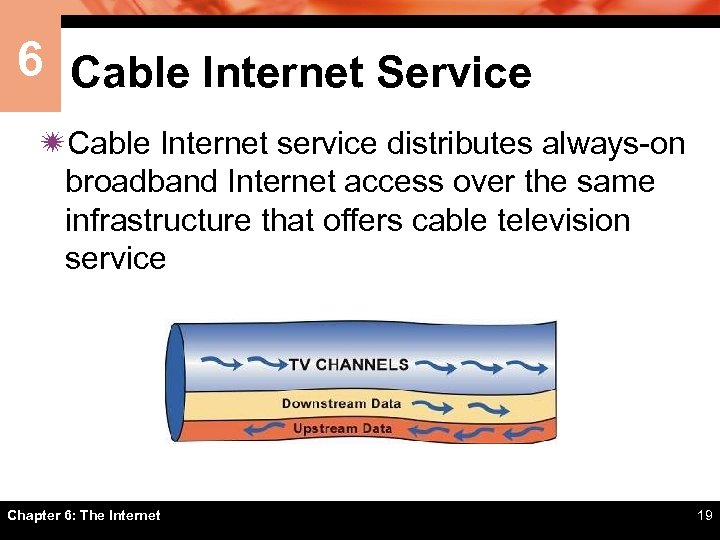 6 Cable Internet Service ïCable Internet service distributes always-on broadband Internet access over the same infrastructure that offers cable television service Chapter 6: The Internet 19
6 Cable Internet Service ïCable Internet service distributes always-on broadband Internet access over the same infrastructure that offers cable television service Chapter 6: The Internet 19
 6 Cable Internet Service ïCable modems convert your computer’s signal into one that can travel over the CATV network ïAlways-on connection ïDOCSIS-compliant cable modems Chapter 6: The Internet 20
6 Cable Internet Service ïCable modems convert your computer’s signal into one that can travel over the CATV network ïAlways-on connection ïDOCSIS-compliant cable modems Chapter 6: The Internet 20
 6 Satellite Internet Service ïSatellite Internet service distributes alwayson, high-speed asymmetric Internet access by broadcasting signals to and from a personal satellite dish ïA satellite modem is a device that modulates data signals from a computer into a frequency band that can be carried to the satellite dish where it is converted to another frequency, amplified, and transmitted Chapter 6: The Internet 21
6 Satellite Internet Service ïSatellite Internet service distributes alwayson, high-speed asymmetric Internet access by broadcasting signals to and from a personal satellite dish ïA satellite modem is a device that modulates data signals from a computer into a frequency band that can be carried to the satellite dish where it is converted to another frequency, amplified, and transmitted Chapter 6: The Internet 21
 6 Satellite Internet Service Chapter 6: The Internet 22
6 Satellite Internet Service Chapter 6: The Internet 22
 6 Fixed Wireless Service ïFixed wireless Internet service broadcasts RF signals in order to offer Internet access to large areas – Wi. MAX – AWi. MAX system transmits data to and from Wi. MAX antennas mounted on towers – Under ideal conditions, Wi. MAX can transmit data at 70 Mbps Chapter 6: The Internet 23
6 Fixed Wireless Service ïFixed wireless Internet service broadcasts RF signals in order to offer Internet access to large areas – Wi. MAX – AWi. MAX system transmits data to and from Wi. MAX antennas mounted on towers – Under ideal conditions, Wi. MAX can transmit data at 70 Mbps Chapter 6: The Internet 23
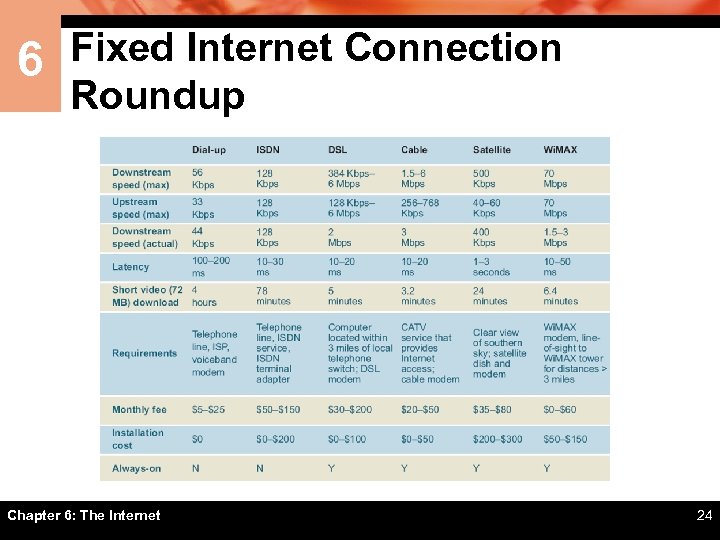 6 Fixed Internet Connection Roundup Chapter 6: The Internet 24
6 Fixed Internet Connection Roundup Chapter 6: The Internet 24
 6 C SECTION Portable and Mobile Internet Access ïInternet to Go ïWi-Fi Hotspots ïPortable and Mobile Wi. MAX ïPortable Satellite Service ïCellular Data Service Chapter 6: The Internet 25
6 C SECTION Portable and Mobile Internet Access ïInternet to Go ïWi-Fi Hotspots ïPortable and Mobile Wi. MAX ïPortable Satellite Service ïCellular Data Service Chapter 6: The Internet 25
 6 Internet To Go ï Portable Internet access can be defined as the ability to easily move your Internet service from one location to another ï Mobile Internet access offers a continuous Internet connection as you are walking or riding in a bus, car, train, or plane Chapter 6: The Internet 26
6 Internet To Go ï Portable Internet access can be defined as the ability to easily move your Internet service from one location to another ï Mobile Internet access offers a continuous Internet connection as you are walking or riding in a bus, car, train, or plane Chapter 6: The Internet 26
 6 Wi-Fi Hotspots ï A Wi-Fi hotspot is an area in which the public can access a Wi-Fi network that offers Internet service ï Wi-Fi does not typically provide acceptable mobile Internet access because you can only remain connected within range of the network’s hotspot Chapter 6: The Internet 27
6 Wi-Fi Hotspots ï A Wi-Fi hotspot is an area in which the public can access a Wi-Fi network that offers Internet service ï Wi-Fi does not typically provide acceptable mobile Internet access because you can only remain connected within range of the network’s hotspot Chapter 6: The Internet 27
 6 Portable and Mobile Wi. MAX ïWi. MAX can be used as a portable technology because Internet access is available to subscribers anywhere within a tower’s coverage area ïYou use the same Internet service provider whether you are at home or on the road. ïMobile Wi. MAX Chapter 6: The Internet 28
6 Portable and Mobile Wi. MAX ïWi. MAX can be used as a portable technology because Internet access is available to subscribers anywhere within a tower’s coverage area ïYou use the same Internet service provider whether you are at home or on the road. ïMobile Wi. MAX Chapter 6: The Internet 28
 6 Portable Satellite Service Chapter 6: The Internet 29
6 Portable Satellite Service Chapter 6: The Internet 29
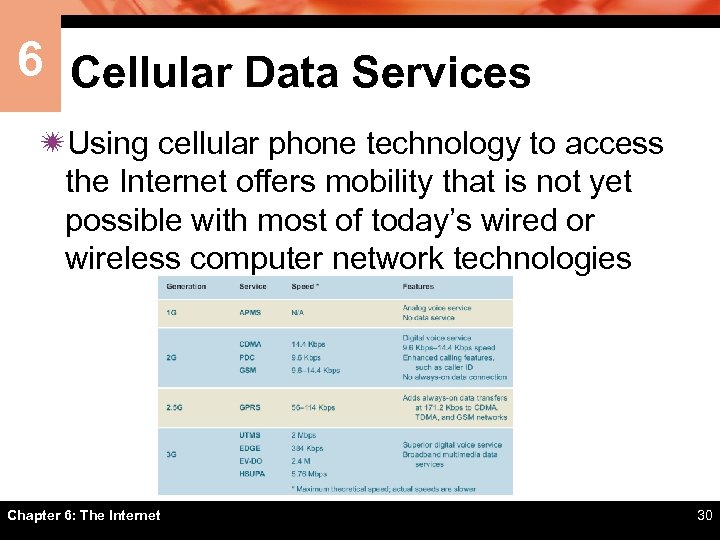 6 Cellular Data Services ïUsing cellular phone technology to access the Internet offers mobility that is not yet possible with most of today’s wired or wireless computer network technologies Chapter 6: The Internet 30
6 Cellular Data Services ïUsing cellular phone technology to access the Internet offers mobility that is not yet possible with most of today’s wired or wireless computer network technologies Chapter 6: The Internet 30
 6 Cellular Data Services ï The fastest cellular technologies for Internet access are EDGE, EV -DO, and HSUPA ï Most cellular service providers offer a data service plan for accessing the Internet ï You can use a cellular-ready PDA, such as Palm Treo, Blackberry, HP i. PAQ, or Dell Axim to directly access the Internet Chapter 6: The Internet 31
6 Cellular Data Services ï The fastest cellular technologies for Internet access are EDGE, EV -DO, and HSUPA ï Most cellular service providers offer a data service plan for accessing the Internet ï You can use a cellular-ready PDA, such as Palm Treo, Blackberry, HP i. PAQ, or Dell Axim to directly access the Internet Chapter 6: The Internet 31
 6 D SECTION Internet Services ïReal-Time Messaging ïVoice over IP ïGrid Computing ïFTP ïFile sharing Chapter 6: The Internet 32
6 D SECTION Internet Services ïReal-Time Messaging ïVoice over IP ïGrid Computing ïFTP ïFile sharing Chapter 6: The Internet 32
 6 Real-Time Messaging ïA networked-based real-time messaging system allows people to exchange short messages while they are online – Instant messaging (IM) – Chat Chapter 6: The Internet 33
6 Real-Time Messaging ïA networked-based real-time messaging system allows people to exchange short messages while they are online – Instant messaging (IM) – Chat Chapter 6: The Internet 33
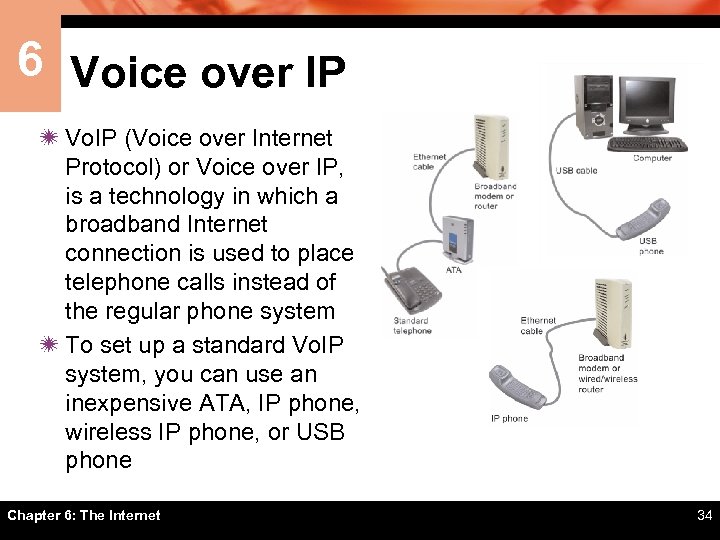 6 Voice over IP ï Vo. IP (Voice over Internet Protocol) or Voice over IP, is a technology in which a broadband Internet connection is used to place telephone calls instead of the regular phone system ï To set up a standard Vo. IP system, you can use an inexpensive ATA, IP phone, wireless IP phone, or USB phone Chapter 6: The Internet 34
6 Voice over IP ï Vo. IP (Voice over Internet Protocol) or Voice over IP, is a technology in which a broadband Internet connection is used to place telephone calls instead of the regular phone system ï To set up a standard Vo. IP system, you can use an inexpensive ATA, IP phone, wireless IP phone, or USB phone Chapter 6: The Internet 34
 6 Voice over IP ïAdvantages – Low cost – Flexibility – Phone number moves with you ïDisadvantages – Quality can vary – Must have power to work Chapter 6: The Internet 35
6 Voice over IP ïAdvantages – Low cost – Flexibility – Phone number moves with you ïDisadvantages – Quality can vary – Must have power to work Chapter 6: The Internet 35
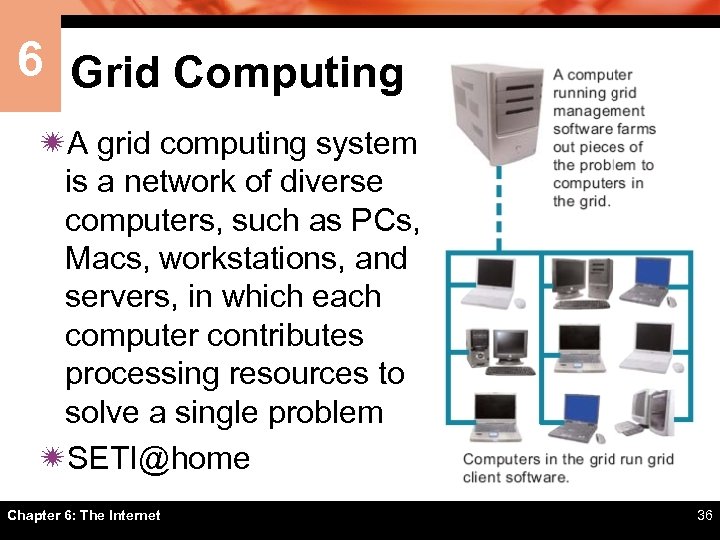 6 Grid Computing ïA grid computing system is a network of diverse computers, such as PCs, Macs, workstations, and servers, in which each computer contributes processing resources to solve a single problem ïSETI@home Chapter 6: The Internet 36
6 Grid Computing ïA grid computing system is a network of diverse computers, such as PCs, Macs, workstations, and servers, in which each computer contributes processing resources to solve a single problem ïSETI@home Chapter 6: The Internet 36
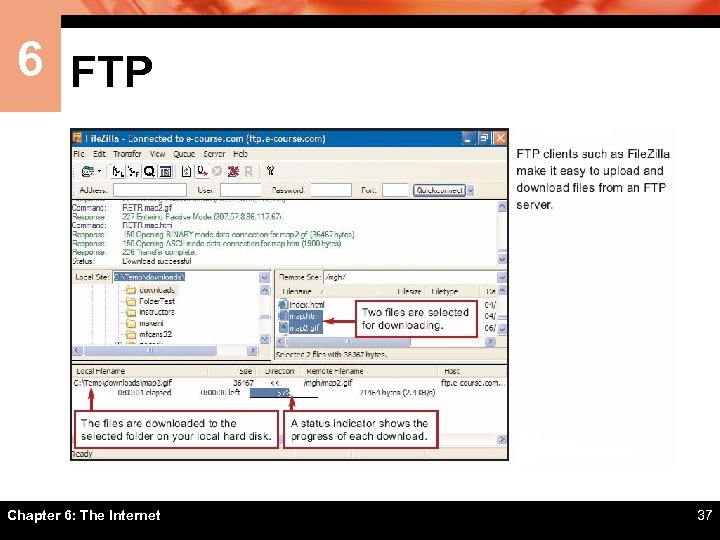 6 FTP Chapter 6: The Internet 37
6 FTP Chapter 6: The Internet 37
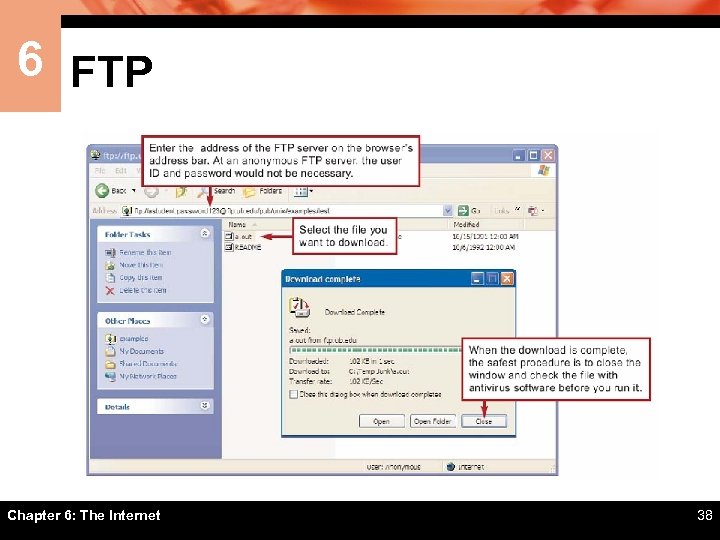 6 FTP Chapter 6: The Internet 38
6 FTP Chapter 6: The Internet 38
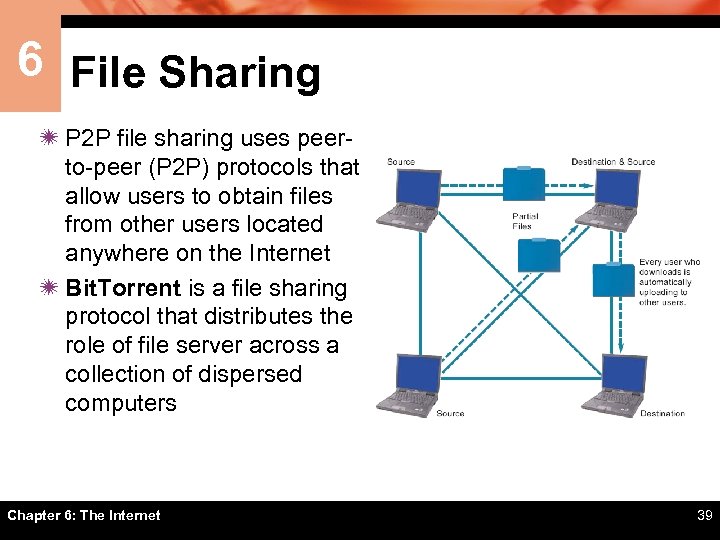 6 File Sharing ï P 2 P file sharing uses peerto-peer (P 2 P) protocols that allow users to obtain files from other users located anywhere on the Internet ï Bit. Torrent is a file sharing protocol that distributes the role of file server across a collection of dispersed computers Chapter 6: The Internet 39
6 File Sharing ï P 2 P file sharing uses peerto-peer (P 2 P) protocols that allow users to obtain files from other users located anywhere on the Internet ï Bit. Torrent is a file sharing protocol that distributes the role of file server across a collection of dispersed computers Chapter 6: The Internet 39
 6 E SECTION Internet Security ïIntrusion Attempts ïSecuring Ports ïRouters and NAT ïVirtual Private Networks Chapter 6: The Internet 40
6 E SECTION Internet Security ïIntrusion Attempts ïSecuring Ports ïRouters and NAT ïVirtual Private Networks Chapter 6: The Internet 40
 6 Intrusion Attempts ïAn intrusion is any access to data or programs by hackers, criminals, or other unauthorized persons ïLooking for open ports is one of the most common ways of gaining unauthorized access to a network-based computer ïA port probe (or port scan) uses automated software to locate computers that have open ports and are vulnerable to unauthorized access Chapter 6: The Internet 41
6 Intrusion Attempts ïAn intrusion is any access to data or programs by hackers, criminals, or other unauthorized persons ïLooking for open ports is one of the most common ways of gaining unauthorized access to a network-based computer ïA port probe (or port scan) uses automated software to locate computers that have open ports and are vulnerable to unauthorized access Chapter 6: The Internet 41
 6 Intrusion Attempts Chapter 6: The Internet 42
6 Intrusion Attempts Chapter 6: The Internet 42
 6 Securing Ports ï One of the easiest steps to enhance your computer’s security is to turn it off when you aren’t using it ï A firewall is software or hardware designed to filter out suspicious packets attempting to enter or leave a computer Chapter 6: The Internet 43
6 Securing Ports ï One of the easiest steps to enhance your computer’s security is to turn it off when you aren’t using it ï A firewall is software or hardware designed to filter out suspicious packets attempting to enter or leave a computer Chapter 6: The Internet 43
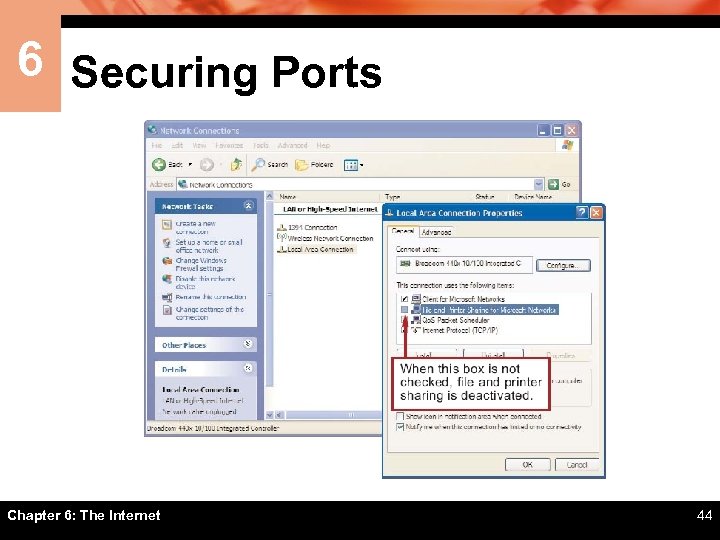 6 Securing Ports Chapter 6: The Internet 44
6 Securing Ports Chapter 6: The Internet 44
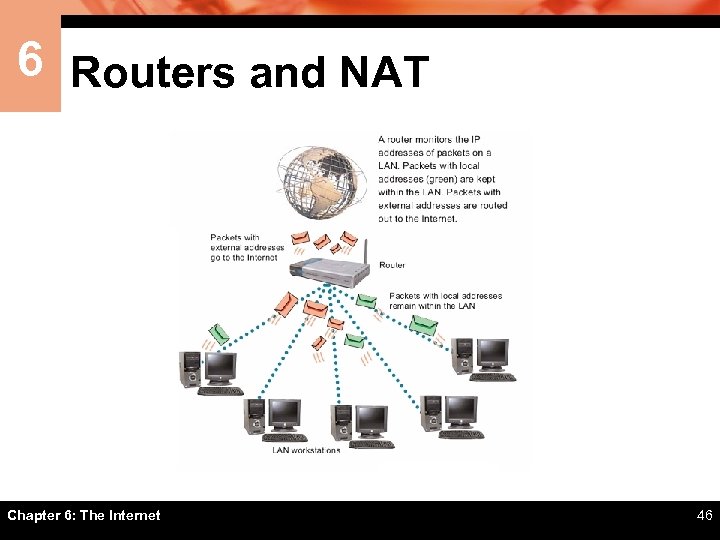
 6 Routers and NAT ïRouters are intended to work on LANs to monitor and direct packets being transported from one device to another ïA routable IP address is one which can be accessed by packets on the Internet ïA private IP address is a non-routable IP address that can be used within a LAN, but not for Internet data transport Chapter 6: The Internet 45
6 Routers and NAT ïRouters are intended to work on LANs to monitor and direct packets being transported from one device to another ïA routable IP address is one which can be accessed by packets on the Internet ïA private IP address is a non-routable IP address that can be used within a LAN, but not for Internet data transport Chapter 6: The Internet 45
 6 Routers and NAT Chapter 6: The Internet 46
6 Routers and NAT Chapter 6: The Internet 46
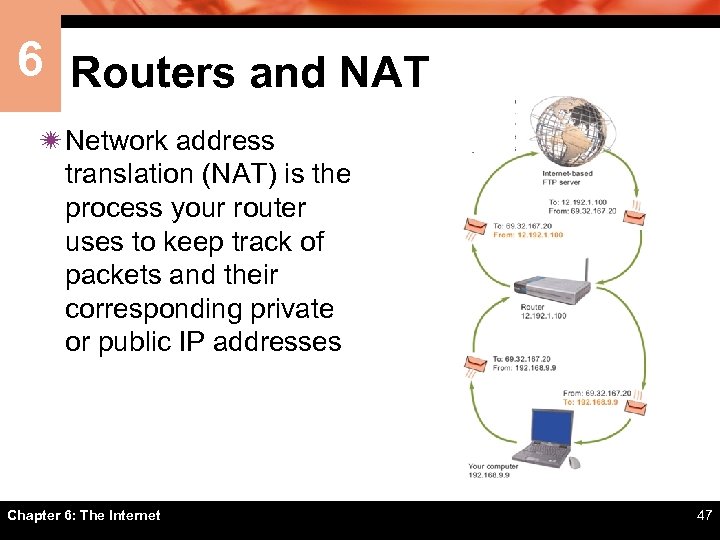 6 Routers and NAT ï Network address translation (NAT) is the process your router uses to keep track of packets and their corresponding private or public IP addresses Chapter 6: The Internet 47
6 Routers and NAT ï Network address translation (NAT) is the process your router uses to keep track of packets and their corresponding private or public IP addresses Chapter 6: The Internet 47
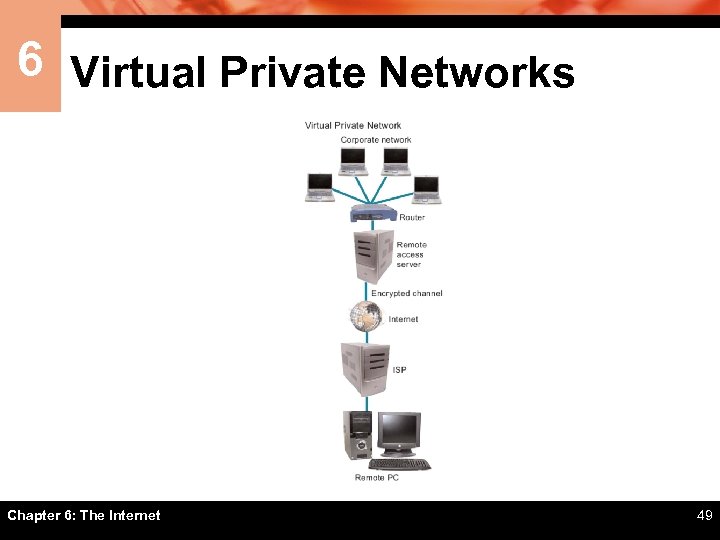
 6 Virtual Private Networks ïIt is possible to secure remote connections by setting up virtual private network (VPN) access to a remote access server in the corporate office ïAccess to a VPN is usually by invitation only. Employees who need to access a VPN are given the necessary instructions, addresses, and passwords to make connections Chapter 6: The Internet 48
6 Virtual Private Networks ïIt is possible to secure remote connections by setting up virtual private network (VPN) access to a remote access server in the corporate office ïAccess to a VPN is usually by invitation only. Employees who need to access a VPN are given the necessary instructions, addresses, and passwords to make connections Chapter 6: The Internet 48
 6 Virtual Private Networks Chapter 6: The Internet 49
6 Virtual Private Networks Chapter 6: The Internet 49
 Chapter 6 Complete The Internet
Chapter 6 Complete The Internet


