3e79d6e8ce45dc43d045378544e0b96c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Chapter 6 Systems Development: Phases, Tools, and Techniques SHEN Bo http: //shenbo. me
Chapter 6 Systems Development: Phases, Tools, and Techniques SHEN Bo http: //shenbo. me
 STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. Define the traditional systems development life cycle (SDLC) and describe the 7 major phases within it. 2. Compare and contrast the various componentbased development methodologies. 3. Describe the selfsourcing process as an alternative to the traditional SDLC. 4. Discuss the importance of prototyping and prototyping within any systems development methodology 5. Describe the outsourcing environment and how outsourcing works. Management Information Systems 6 -2
STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. Define the traditional systems development life cycle (SDLC) and describe the 7 major phases within it. 2. Compare and contrast the various componentbased development methodologies. 3. Describe the selfsourcing process as an alternative to the traditional SDLC. 4. Discuss the importance of prototyping and prototyping within any systems development methodology 5. Describe the outsourcing environment and how outsourcing works. Management Information Systems 6 -2
 INTRODUCTION • Information systems are the support structure for meeting the company’s strategies and goals • New systems are created because employees request them • New systems are created to obtain a competitive advantage Management Information Systems 6 -3
INTRODUCTION • Information systems are the support structure for meeting the company’s strategies and goals • New systems are created because employees request them • New systems are created to obtain a competitive advantage Management Information Systems 6 -3
 INTRODUCTION • When developing a new system, you have 3 “who” choices… 1. Insourcing – IT specialists inside your organization 2. Selfsourcing – do-it-yourself approach many end users take with little or no help from IT specialists 3. Outsourcing – a third-party organization (i. e. , let someone do the work and pay them for it) Management Information Systems 6 -4
INTRODUCTION • When developing a new system, you have 3 “who” choices… 1. Insourcing – IT specialists inside your organization 2. Selfsourcing – do-it-yourself approach many end users take with little or no help from IT specialists 3. Outsourcing – a third-party organization (i. e. , let someone do the work and pay them for it) Management Information Systems 6 -4
 INSOURCING AND THE SDLC • Insourcing: IT specialists inside your organization. Advantages: control over the time, resources and results of the work Management Information Systems 6 -5
INSOURCING AND THE SDLC • Insourcing: IT specialists inside your organization. Advantages: control over the time, resources and results of the work Management Information Systems 6 -5
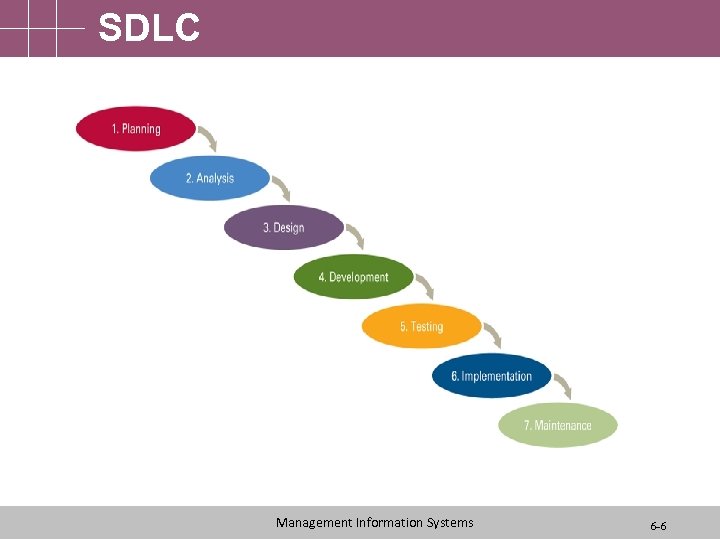 SDLC Management Information Systems 6 -6
SDLC Management Information Systems 6 -6
 SELFSOURCING • Selfsourcing (end-user development) – the development and support of IT systems by end users with little or no help from IT specialists • Do-it-yourself systems development approach • Can relieve IT specialists of the burden of developing many smaller systems Management Information Systems 6 -7
SELFSOURCING • Selfsourcing (end-user development) – the development and support of IT systems by end users with little or no help from IT specialists • Do-it-yourself systems development approach • Can relieve IT specialists of the burden of developing many smaller systems Management Information Systems 6 -7
 Selfsourcing Approach • Is similar to traditional SDLC • Big exception is that design, development, testing, and implementation are replaced by the process of prototyping • Prototyping is the process of building models, and – in this case – continually refining those models until they become the final system Management Information Systems 6 -8
Selfsourcing Approach • Is similar to traditional SDLC • Big exception is that design, development, testing, and implementation are replaced by the process of prototyping • Prototyping is the process of building models, and – in this case – continually refining those models until they become the final system Management Information Systems 6 -8
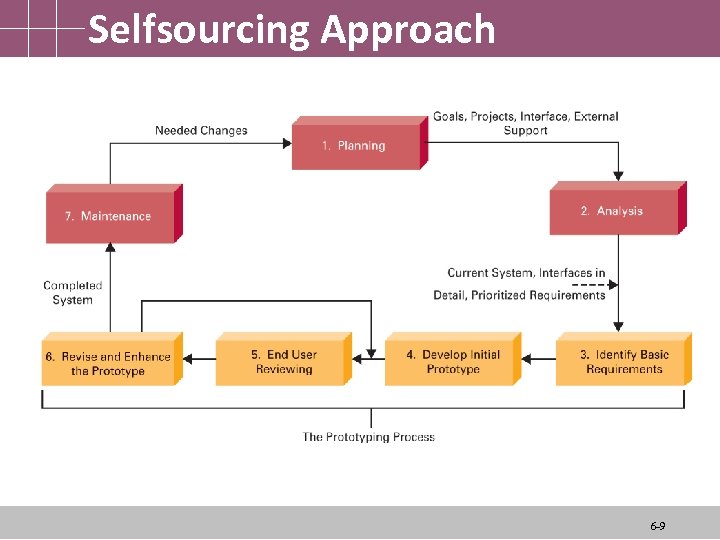 Selfsourcing Approach 6 -9
Selfsourcing Approach 6 -9
 Selfsourcing Advantages • Improves requirements determination • Increases end user participation and sense of ownership • Increases speed of systems development • Reduces invisible backlog – Invisible backlog – list of all systems that an organization needs to develop but – because of the prioritization of systems development needs – never get funded because of the lack of organizational resources Management Information Systems 6 -10
Selfsourcing Advantages • Improves requirements determination • Increases end user participation and sense of ownership • Increases speed of systems development • Reduces invisible backlog – Invisible backlog – list of all systems that an organization needs to develop but – because of the prioritization of systems development needs – never get funded because of the lack of organizational resources Management Information Systems 6 -10
 Selfsourcing Disadvantages • Inadequate end user expertise leads to inadequately developed systems • Lack of organizational focus creates “privatized” IT systems • Insufficient analysis of design alternatives leads to subpar( 低水平) IT systems • Lack of documentation and external support leads to short-lived systems Management Information Systems 6 -11
Selfsourcing Disadvantages • Inadequate end user expertise leads to inadequately developed systems • Lack of organizational focus creates “privatized” IT systems • Insufficient analysis of design alternatives leads to subpar( 低水平) IT systems • Lack of documentation and external support leads to short-lived systems Management Information Systems 6 -11
 The Right Tool for the Job • End users must have development tools that: – Are easy to use – Support multiple platforms – Offer low cost of ownership – Support a wide range of data types Management Information Systems 6 -12
The Right Tool for the Job • End users must have development tools that: – Are easy to use – Support multiple platforms – Offer low cost of ownership – Support a wide range of data types Management Information Systems 6 -12
 PROTOTYPING • Prototype – a model of a proposed product, service, or system • Prototyping - the process of building a model that demonstrates the features of a proposed product, service, or system – Proof-of-concept prototype - used to prove the technical feasibility of a proposed system – Selling prototype - used to convince people of the worth of a proposed system Management Information Systems 6 -13
PROTOTYPING • Prototype – a model of a proposed product, service, or system • Prototyping - the process of building a model that demonstrates the features of a proposed product, service, or system – Proof-of-concept prototype - used to prove the technical feasibility of a proposed system – Selling prototype - used to convince people of the worth of a proposed system Management Information Systems 6 -13
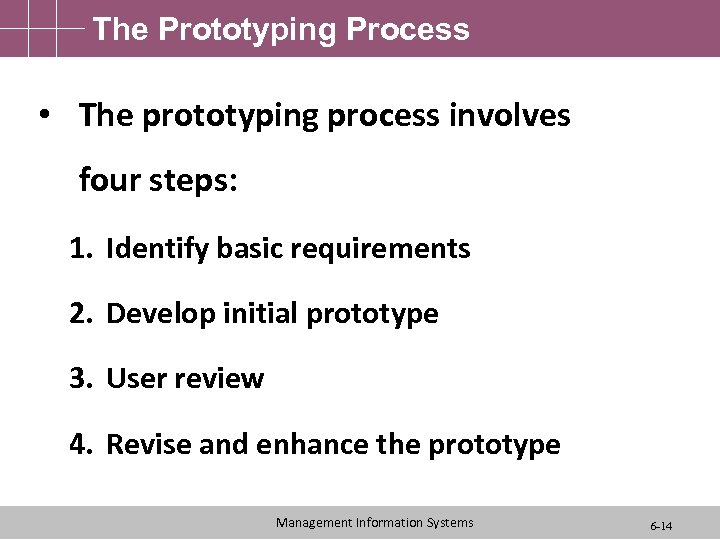 The Prototyping Process • The prototyping process involves four steps: 1. Identify basic requirements 2. Develop initial prototype 3. User review 4. Revise and enhance the prototype Management Information Systems 6 -14
The Prototyping Process • The prototyping process involves four steps: 1. Identify basic requirements 2. Develop initial prototype 3. User review 4. Revise and enhance the prototype Management Information Systems 6 -14
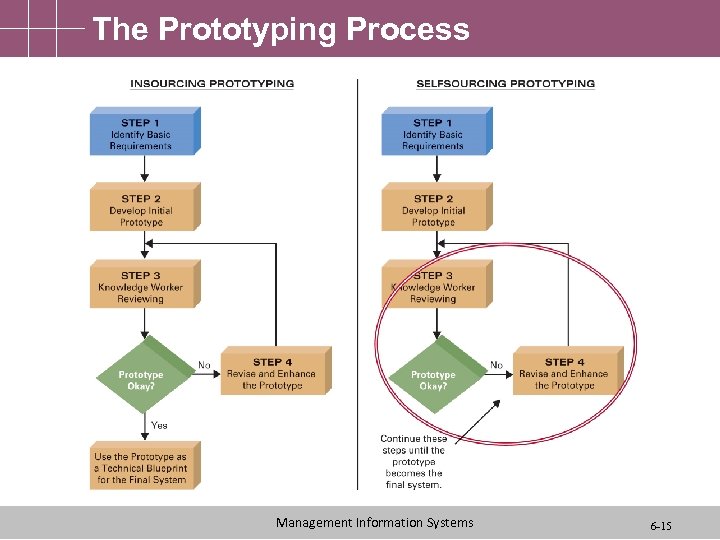 The Prototyping Process Management Information Systems 6 -15
The Prototyping Process Management Information Systems 6 -15
 Advantages of Prototyping • Encourages active user participation • Helps resolve discrepancies among users • Gives users a feel for the final system • Helps determine technical feasibility • Helps sell the idea of a proposed system Management Information Systems 6 -16
Advantages of Prototyping • Encourages active user participation • Helps resolve discrepancies among users • Gives users a feel for the final system • Helps determine technical feasibility • Helps sell the idea of a proposed system Management Information Systems 6 -16
 Disadvantages of Prototyping • Leads people to believe the final system will follow • Gives no indication of performance under operational conditions • Leads the project team to forgo proper testing and documentation Management Information Systems 6 -17
Disadvantages of Prototyping • Leads people to believe the final system will follow • Gives no indication of performance under operational conditions • Leads the project team to forgo proper testing and documentation Management Information Systems 6 -17
 OUTSOURCING • Outsourcing – the delegation of specified work to a third party for a specified length of time, at a specified cost, and at a specified level of service • The third “who” option of systems development, after insourcing and selfsourcing Management Information Systems 6 -18
OUTSOURCING • Outsourcing – the delegation of specified work to a third party for a specified length of time, at a specified cost, and at a specified level of service • The third “who” option of systems development, after insourcing and selfsourcing Management Information Systems 6 -18
 OUTSOURCING • The main reasons behind the rapid growth of the outsourcing industry include the following: – Globalization – The Internet – Growing economy and low unemployment rate – Technology – Deregulation Management Information Systems 6 -19
OUTSOURCING • The main reasons behind the rapid growth of the outsourcing industry include the following: – Globalization – The Internet – Growing economy and low unemployment rate – Technology – Deregulation Management Information Systems 6 -19
 Outsourcing Options • IT outsourcing for software development can take one of four forms: 1. Purchase existing software 2. Purchase existing software and pay the publisher to make certain modifications 3. Purchase existing software and pay the publisher for the right to make modifications yourself 4. Outsource the development of an entirely new and unique system for which no software Management Information Systems exists 6 -20
Outsourcing Options • IT outsourcing for software development can take one of four forms: 1. Purchase existing software 2. Purchase existing software and pay the publisher to make certain modifications 3. Purchase existing software and pay the publisher for the right to make modifications yourself 4. Outsource the development of an entirely new and unique system for which no software Management Information Systems exists 6 -20
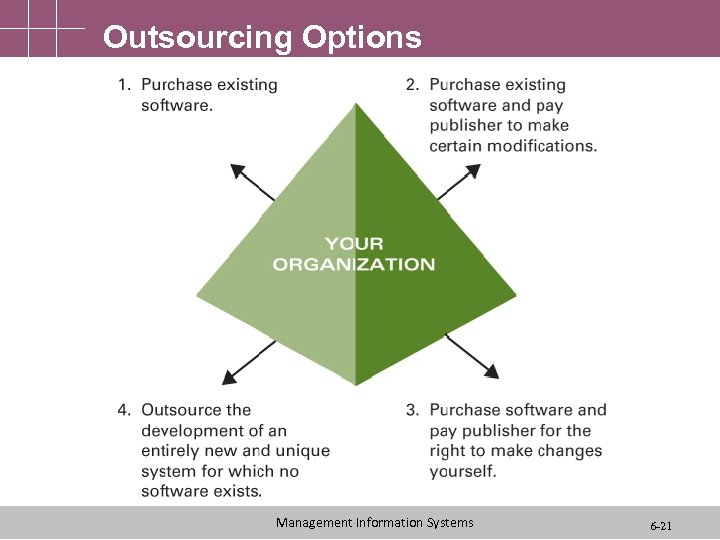 Outsourcing Options Management Information Systems 6 -21
Outsourcing Options Management Information Systems 6 -21
 Outsourcing Process • Like selfsourcing, the selfsourcing process looks similar to the traditional SDLC • Big exception here is that you “outsource” most of the work to another company Management Information Systems 6 -22
Outsourcing Process • Like selfsourcing, the selfsourcing process looks similar to the traditional SDLC • Big exception here is that you “outsource” most of the work to another company Management Information Systems 6 -22
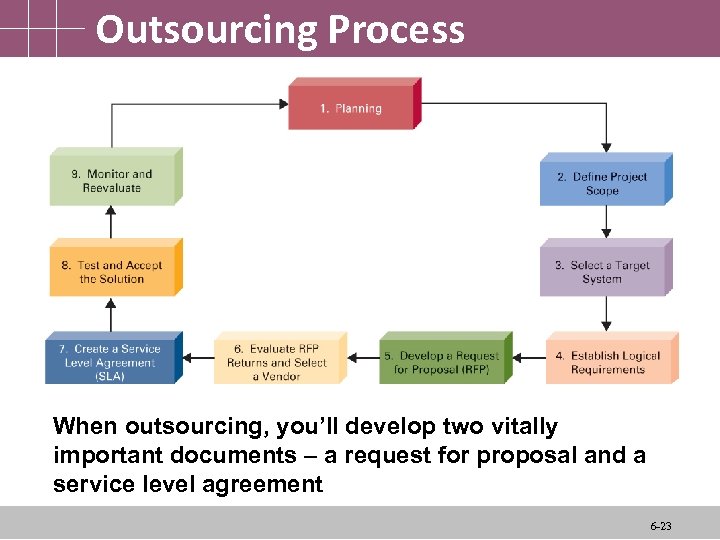 Outsourcing Process When outsourcing, you’ll develop two vitally important documents – a request for proposal and a service level agreement 6 -23
Outsourcing Process When outsourcing, you’ll develop two vitally important documents – a request for proposal and a service level agreement 6 -23
 Outsourcing – RFP • Request for proposal (RFP) – formal document that describes in excruciating detail your logical requirements for a proposed system and invites outsourcing organizations (vendors) to submit bids for its development • In outsourcing, you must tell another organization what you want developed; you do that with an RFP • Therefore, the RFP must be very detailed • Some RFPs can take years to develop Management Information Systems 6 -24
Outsourcing – RFP • Request for proposal (RFP) – formal document that describes in excruciating detail your logical requirements for a proposed system and invites outsourcing organizations (vendors) to submit bids for its development • In outsourcing, you must tell another organization what you want developed; you do that with an RFP • Therefore, the RFP must be very detailed • Some RFPs can take years to develop Management Information Systems 6 -24
 Outsourcing – SLA • Service level agreement (SLA) - formal contractually obligated agreement between two parties • In outsourcing, it is the legal agreement between you and the vendor and specifically identifies what the vendor is going to do (and by when) and how much you’re going to pay • Supporting SLA documents – service level specifications and service level objectives – contain very detailed numbers and metrics Management Information Systems 6 -25
Outsourcing – SLA • Service level agreement (SLA) - formal contractually obligated agreement between two parties • In outsourcing, it is the legal agreement between you and the vendor and specifically identifies what the vendor is going to do (and by when) and how much you’re going to pay • Supporting SLA documents – service level specifications and service level objectives – contain very detailed numbers and metrics Management Information Systems 6 -25
 Outsourcing Options • There are three different forms of outsourcing: 1. Onshore outsourcing (在岸外包) - the process of engaging another company within the same country for services 2. Nearshore outsourcing (近岸外包)- contracting an outsourcing arrangement with a company in a nearby country 3. Offshore outsourcing (离岸外包) - contracting with a company that is geographically far away Management Information Systems 6 -26
Outsourcing Options • There are three different forms of outsourcing: 1. Onshore outsourcing (在岸外包) - the process of engaging another company within the same country for services 2. Nearshore outsourcing (近岸外包)- contracting an outsourcing arrangement with a company in a nearby country 3. Offshore outsourcing (离岸外包) - contracting with a company that is geographically far away Management Information Systems 6 -26
 Offshore Outsourcing • Primary outsourcing countries are: – India – China – Eastern Europe (including Russia) – Ireland – Israel – Philippines Management Information Systems 6 -27
Offshore Outsourcing • Primary outsourcing countries are: – India – China – Eastern Europe (including Russia) – Ireland – Israel – Philippines Management Information Systems 6 -27
 The Advantages and Disadvantages of Outsourcing • Advantages: – Focus on unique core competencies – Exploit the intellect of another organization – Better predict future costs – Acquire leading-edge technology – Reduce costs – Improve performance accountability Management Information Systems 6 -28
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Outsourcing • Advantages: – Focus on unique core competencies – Exploit the intellect of another organization – Better predict future costs – Acquire leading-edge technology – Reduce costs – Improve performance accountability Management Information Systems 6 -28
 The Advantages and Disadvantages of Outsourcing • Disadvantages: – Reduces technical know-how for future innovation – Reduces degree of control – Increases vulnerability of your strategic information – Increases dependency on other organizations Management Information Systems 6 -29
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Outsourcing • Disadvantages: – Reduces technical know-how for future innovation – Reduces degree of control – Increases vulnerability of your strategic information – Increases dependency on other organizations Management Information Systems 6 -29
 Case Study • Getting on the Right Track at General Motors – P 186 -187 Management Information Systems 6 -30
Case Study • Getting on the Right Track at General Motors – P 186 -187 Management Information Systems 6 -30


