e8b2ad659a17057530996a13541cd819.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Chapter 6 Strategy Analysis & Choice STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 1
Chapter 6 Strategy Analysis & Choice STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 1
 Strategy Analysis and Selection 1) SWOT Matrix 2) SPACE Matrix 3) BCG Matrix 4) IE Matrix 5) Grand Strategy Matrix STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 2
Strategy Analysis and Selection 1) SWOT Matrix 2) SPACE Matrix 3) BCG Matrix 4) IE Matrix 5) Grand Strategy Matrix STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 2
 SWOT Matrix Ø Strengths: "A strength is defined as anything internal to the company that may lead to an advantage relative to competitors and a benefit to customers. " Ø Weaknesses: "A weakness is defined as anything internal that may lead to a disadvantage relative to competitors and customers“ Ø Opportunities: "An opportunity is anything in the external environment that may help a firm reach its goals. " Ø Threats: "A threat is anything in the external environment that may prevent a firm from reaching its goals. " STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 3
SWOT Matrix Ø Strengths: "A strength is defined as anything internal to the company that may lead to an advantage relative to competitors and a benefit to customers. " Ø Weaknesses: "A weakness is defined as anything internal that may lead to a disadvantage relative to competitors and customers“ Ø Opportunities: "An opportunity is anything in the external environment that may help a firm reach its goals. " Ø Threats: "A threat is anything in the external environment that may prevent a firm from reaching its goals. " STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 3
 Steps to construct a SWOT Matrix 1. List the firm’s key external opportunities. 2. List the firm’s key external threats. 3. List the firm’s key internal strengths. 4. List the firm’s key internal weaknesses. 5. Match internal strengths with external opportunities and record the resulting SO strategies in the appropriate cell. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 4
Steps to construct a SWOT Matrix 1. List the firm’s key external opportunities. 2. List the firm’s key external threats. 3. List the firm’s key internal strengths. 4. List the firm’s key internal weaknesses. 5. Match internal strengths with external opportunities and record the resulting SO strategies in the appropriate cell. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 4
 Steps to construct a SWOT Matrix 6. Match internal weaknesses with external opportunities and record the resulting WO strategies. 7. Match internal strengths with external threats and record the resultant ST strategies. 8. Match internal weaknesses with external threats and record the resulting WT strategies. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 5
Steps to construct a SWOT Matrix 6. Match internal weaknesses with external opportunities and record the resulting WO strategies. 7. Match internal strengths with external threats and record the resultant ST strategies. 8. Match internal weaknesses with external threats and record the resulting WT strategies. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 5
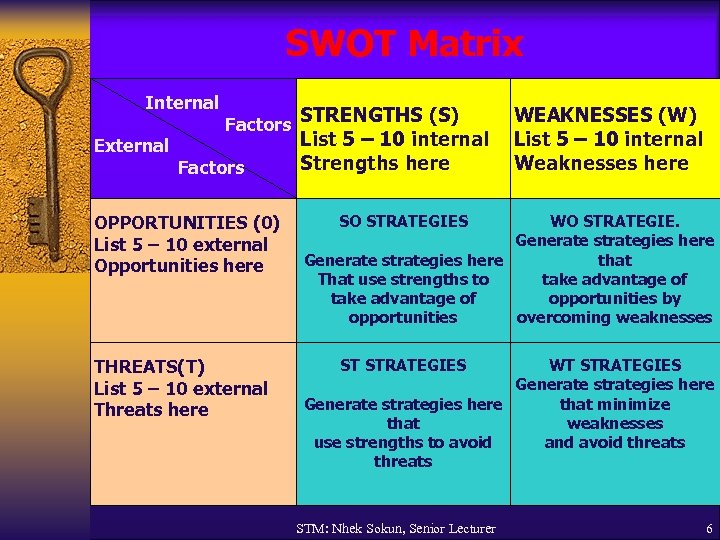 SWOT Matrix Internal External Factors STRENGTHS (S) Factors OPPORTUNITIES (0) List 5 – 10 external Opportunities here THREATS(T) List 5 – 10 external Threats here List 5 – 10 internal Strengths here WEAKNESSES (W) List 5 – 10 internal Weaknesses here SO STRATEGIES WO STRATEGIE. Generate strategies here that That use strengths to take advantage of opportunities by opportunities overcoming weaknesses ST STRATEGIES WT STRATEGIES Generate strategies here that minimize that weaknesses use strengths to avoid and avoid threats STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 6
SWOT Matrix Internal External Factors STRENGTHS (S) Factors OPPORTUNITIES (0) List 5 – 10 external Opportunities here THREATS(T) List 5 – 10 external Threats here List 5 – 10 internal Strengths here WEAKNESSES (W) List 5 – 10 internal Weaknesses here SO STRATEGIES WO STRATEGIE. Generate strategies here that That use strengths to take advantage of opportunities by opportunities overcoming weaknesses ST STRATEGIES WT STRATEGIES Generate strategies here that minimize that weaknesses use strengths to avoid and avoid threats STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 6
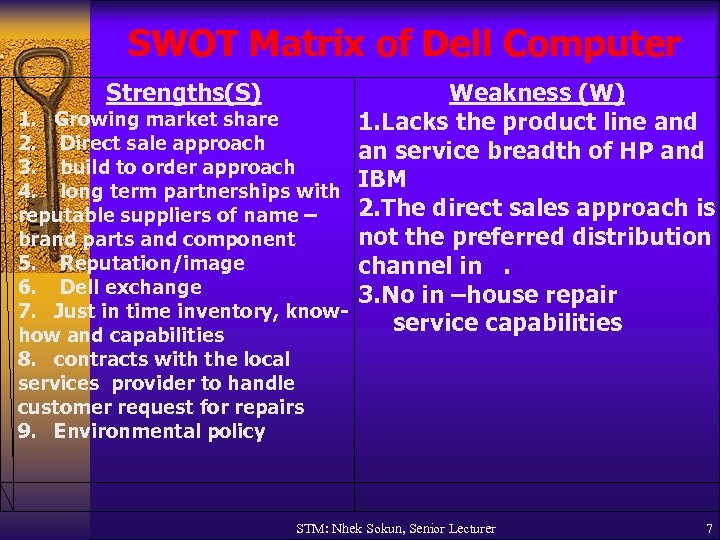 SWOT Matrix of Dell Computer Strengths(S) Weakness (W) 1. Growing market share 1. Lacks the product line and 2. Direct sale approach an service breadth of HP and 3. build to order approach IBM 4. long term partnerships with 2. The direct sales approach is reputable suppliers of name – not the preferred distribution brand parts and component 5. Reputation/image channel in. 6. Dell exchange 3. No in –house repair 7. Just in time inventory, knowservice capabilities how and capabilities 8. contracts with the local services provider to handle customer request for repairs 9. Environmental policy STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 7
SWOT Matrix of Dell Computer Strengths(S) Weakness (W) 1. Growing market share 1. Lacks the product line and 2. Direct sale approach an service breadth of HP and 3. build to order approach IBM 4. long term partnerships with 2. The direct sales approach is reputable suppliers of name – not the preferred distribution brand parts and component 5. Reputation/image channel in. 6. Dell exchange 3. No in –house repair 7. Just in time inventory, knowservice capabilities how and capabilities 8. contracts with the local services provider to handle customer request for repairs 9. Environmental policy STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 7
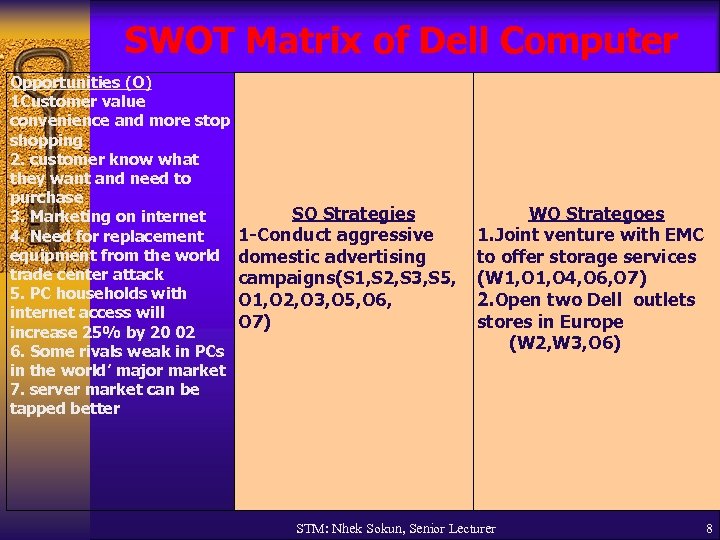 SWOT Matrix of Dell Computer Opportunities (O) 1 Customer value convenience and more stop shopping 2. customer know what they want and need to purchase 3. Marketing on internet 4. Need for replacement equipment from the world trade center attack 5. PC households with internet access will increase 25% by 20 02 6. Some rivals weak in PCs in the world’ major market 7. server market can be tapped better SO Strategies 1 -Conduct aggressive domestic advertising campaigns(S 1, S 2, S 3, S 5, O 1, O 2, O 3, O 5, O 6, O 7) WO Strategoes 1. Joint venture with EMC to offer storage services (W 1, O 4, O 6, O 7) 2. Open two Dell outlets stores in Europe (W 2, W 3, O 6) STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 8
SWOT Matrix of Dell Computer Opportunities (O) 1 Customer value convenience and more stop shopping 2. customer know what they want and need to purchase 3. Marketing on internet 4. Need for replacement equipment from the world trade center attack 5. PC households with internet access will increase 25% by 20 02 6. Some rivals weak in PCs in the world’ major market 7. server market can be tapped better SO Strategies 1 -Conduct aggressive domestic advertising campaigns(S 1, S 2, S 3, S 5, O 1, O 2, O 3, O 5, O 6, O 7) WO Strategoes 1. Joint venture with EMC to offer storage services (W 1, O 4, O 6, O 7) 2. Open two Dell outlets stores in Europe (W 2, W 3, O 6) STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 8
 SWOT Matrix of Dell Computer Threats 1. Global economic recession 2. Aggressive pricing war 3. Continuously changing consumer demand 4. Strong brand name of competitor(IBM, HP) 5. Rapid technological advancement 6. A long term slow down in global sales of PC and servers 7. Corporate customers relying more & more heavily on the systems and service capabilities ST Strategies 1. Produce low price standardizes PC (T 2, S 1, S 2, S 4, S 5, S 7) 2. Reduce workforce by employees to cut costs (T 1, T 2, T 6, S 2, S 3, S 4, S 7) WT Strategies 1. Conduct aggressive European ad campaign to promote Dell Direct selling(W 2, T 3, T 2) STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 9
SWOT Matrix of Dell Computer Threats 1. Global economic recession 2. Aggressive pricing war 3. Continuously changing consumer demand 4. Strong brand name of competitor(IBM, HP) 5. Rapid technological advancement 6. A long term slow down in global sales of PC and servers 7. Corporate customers relying more & more heavily on the systems and service capabilities ST Strategies 1. Produce low price standardizes PC (T 2, S 1, S 2, S 4, S 5, S 7) 2. Reduce workforce by employees to cut costs (T 1, T 2, T 6, S 2, S 3, S 4, S 7) WT Strategies 1. Conduct aggressive European ad campaign to promote Dell Direct selling(W 2, T 3, T 2) STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 9
 SPACE Matrix (Strategic Position & Action Evaluation Matrix) ¨ The SPACE Matrix evaluates the organization in terms of 4 dimensions: Ø Financial Strength (FS) Ø Competitive Advantage (CA) Ø Environmental Stability (ES) Ø Industry Strength (IS) ¨ The first 2 dimensions are internal (FS & CA), while the last 2 dimensions are external (ES & IS). STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 10
SPACE Matrix (Strategic Position & Action Evaluation Matrix) ¨ The SPACE Matrix evaluates the organization in terms of 4 dimensions: Ø Financial Strength (FS) Ø Competitive Advantage (CA) Ø Environmental Stability (ES) Ø Industry Strength (IS) ¨ The first 2 dimensions are internal (FS & CA), while the last 2 dimensions are external (ES & IS). STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 10
 SPACE Matrix (Strategic Position & Action Evaluation Matrix) ¨ Financial Strength (FS): Refer to financial strength of the organization or company in terms of financial ratios (Liquidity Ratios, Activity Ratios, Leverage Ratios, and Profitability Ratios) ¨ Competitive Advantages (CA): Refer to the advantages which organization or company has compared to its competitors. ¨ Environmental Stability (ES): Refer to the level of the stability in general and task environments (Political Stability, Economic Stability, Inflation Rate…etc. ). ¨ Industry Strength (IS): Refer to the strength of particular industry in which the organization or company competes. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 11
SPACE Matrix (Strategic Position & Action Evaluation Matrix) ¨ Financial Strength (FS): Refer to financial strength of the organization or company in terms of financial ratios (Liquidity Ratios, Activity Ratios, Leverage Ratios, and Profitability Ratios) ¨ Competitive Advantages (CA): Refer to the advantages which organization or company has compared to its competitors. ¨ Environmental Stability (ES): Refer to the level of the stability in general and task environments (Political Stability, Economic Stability, Inflation Rate…etc. ). ¨ Industry Strength (IS): Refer to the strength of particular industry in which the organization or company competes. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 11
 The steps to develop a SPACE Matrix 1. Select a set of variables to define financial strength (FS), competitive advantage (CA), environmental stability (ES), and industry strength (IS). 2. Assign a numerical value ranging from 1 (worst) to 6 (best) for the variables that make up the FS and IS dimensions. Assign a number between – 1 (best) to – 6 (worst) for variables that make up the ES and CA dimensions. On the FS and CA axes, make comparison to competitors. On the IS and ES axes, make comparison to other industries. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 12
The steps to develop a SPACE Matrix 1. Select a set of variables to define financial strength (FS), competitive advantage (CA), environmental stability (ES), and industry strength (IS). 2. Assign a numerical value ranging from 1 (worst) to 6 (best) for the variables that make up the FS and IS dimensions. Assign a number between – 1 (best) to – 6 (worst) for variables that make up the ES and CA dimensions. On the FS and CA axes, make comparison to competitors. On the IS and ES axes, make comparison to other industries. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 12
 The steps to develop a SPACE Matrix 3. Compute an average score for FS, CA, IS, and ES by summing the values given to the variables and dividing by the number of variables included in each dimension. 4. Plot the average scores for FS, IS, ES, and CA on the appropriate axis in the SPACE Matrix. 5. Add the two scores on the x-axis and plot the resultant point on X. 6. Add the two scores on the y-axis and plot the resultant point on Y. Plot the intersection of the new XY point. 7. Draw a directional vector from the origin of the SPACE matrix through the new intersection point. This vector reveals the type of strategies recommended for the organization. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 13
The steps to develop a SPACE Matrix 3. Compute an average score for FS, CA, IS, and ES by summing the values given to the variables and dividing by the number of variables included in each dimension. 4. Plot the average scores for FS, IS, ES, and CA on the appropriate axis in the SPACE Matrix. 5. Add the two scores on the x-axis and plot the resultant point on X. 6. Add the two scores on the y-axis and plot the resultant point on Y. Plot the intersection of the new XY point. 7. Draw a directional vector from the origin of the SPACE matrix through the new intersection point. This vector reveals the type of strategies recommended for the organization. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 13
 Æ Aggressive: concentration, vertical and horizontal integration, concentric and conglomerate diversification or combination strategies. Æ Competitive: vertical and horizontal integration, concentration and joint venture. Æ Defensive: turnaround, divest, liquidation and concentric diversification Æ Conservative: concentration and concentric diversification STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 14
Æ Aggressive: concentration, vertical and horizontal integration, concentric and conglomerate diversification or combination strategies. Æ Competitive: vertical and horizontal integration, concentration and joint venture. Æ Defensive: turnaround, divest, liquidation and concentric diversification Æ Conservative: concentration and concentric diversification STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 14
 BCG Matrix §Ratio of a division’s own market share in an industry to the market share held by the largest rival firm in that industry. §The BCG Matrix graphically portrays differences among divisions (of a firm) in terms of relative market share position and industry growth rate. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 15
BCG Matrix §Ratio of a division’s own market share in an industry to the market share held by the largest rival firm in that industry. §The BCG Matrix graphically portrays differences among divisions (of a firm) in terms of relative market share position and industry growth rate. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 15
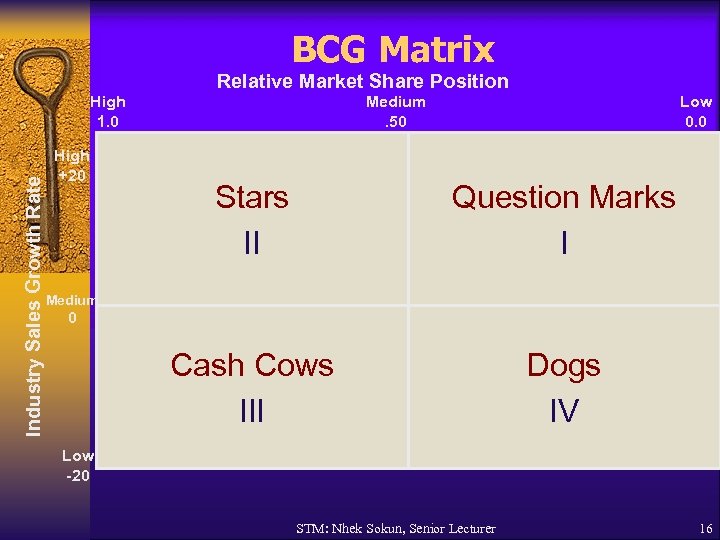 BCG Matrix Relative Market Share Position Industry Sales Growth Rate High 1. 0 High +20 Medium. 50 Low 0. 0 Stars II Question Marks I Cash Cows III Dogs IV Medium 0 Low -20 STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 16
BCG Matrix Relative Market Share Position Industry Sales Growth Rate High 1. 0 High +20 Medium. 50 Low 0. 0 Stars II Question Marks I Cash Cows III Dogs IV Medium 0 Low -20 STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 16
 BCG Matrix (Question Marks) §Low relative market share – compete in high-growth industry §Cash needs are high §Case generation is low §Decision to strengthen (intensive strategies) or divest STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 17
BCG Matrix (Question Marks) §Low relative market share – compete in high-growth industry §Cash needs are high §Case generation is low §Decision to strengthen (intensive strategies) or divest STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 17
 BCG Matrix (Stars) §High relative market share and high growth rate §Best long-run opportunities for growth & profitability §Substantial investment to maintain or strengthen dominant position §Integration strategies, intensive strategies, joint ventures STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 18
BCG Matrix (Stars) §High relative market share and high growth rate §Best long-run opportunities for growth & profitability §Substantial investment to maintain or strengthen dominant position §Integration strategies, intensive strategies, joint ventures STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 18
 BCG Matrix (Cash Cows) §High relative market share, competes in lowgrowth industry §Generate cash in excess of their needs §Milked for other purposes §Maintain strong position as long as possible §Product development, concentric diversification §If weakens—retrenchment or divestiture STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 19
BCG Matrix (Cash Cows) §High relative market share, competes in lowgrowth industry §Generate cash in excess of their needs §Milked for other purposes §Maintain strong position as long as possible §Product development, concentric diversification §If weakens—retrenchment or divestiture STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 19
 BCG Matrix (Dogs) §Low relative market share & compete in slow or no market growth §Weak internal & external position §Liquidation, divestiture, retrenchment STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 20
BCG Matrix (Dogs) §Low relative market share & compete in slow or no market growth §Weak internal & external position §Liquidation, divestiture, retrenchment STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 20
 The IE Matrix ØThe IE Matrix positions an organization’s various divisions in a nine-cell display ØThe IE Matrix is similar to the BCG Matrix in that both tools involve plotting organization divisions in a schematic diagram; this is why they are called portfolio matrices. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 21
The IE Matrix ØThe IE Matrix positions an organization’s various divisions in a nine-cell display ØThe IE Matrix is similar to the BCG Matrix in that both tools involve plotting organization divisions in a schematic diagram; this is why they are called portfolio matrices. STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 21
 Steps to develop IE Matrix 1. Record your organization's IFE Total Score on the X axis. If your organization has several divisions (different businesses / product), then calculate a separate IFE score for each business and plot the total for each product on the X axis. 2. Record your organization's EFE Total Score on the Y axis. If your organization has several divisions, then calculate a separate EFE score for each business and plot the total for each business / product on the Y axis. 3. Plot the location of your company (or divisions) in the appropriate sector (from I to IX). STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 22
Steps to develop IE Matrix 1. Record your organization's IFE Total Score on the X axis. If your organization has several divisions (different businesses / product), then calculate a separate IFE score for each business and plot the total for each product on the X axis. 2. Record your organization's EFE Total Score on the Y axis. If your organization has several divisions, then calculate a separate EFE score for each business and plot the total for each business / product on the Y axis. 3. Plot the location of your company (or divisions) in the appropriate sector (from I to IX). STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 22
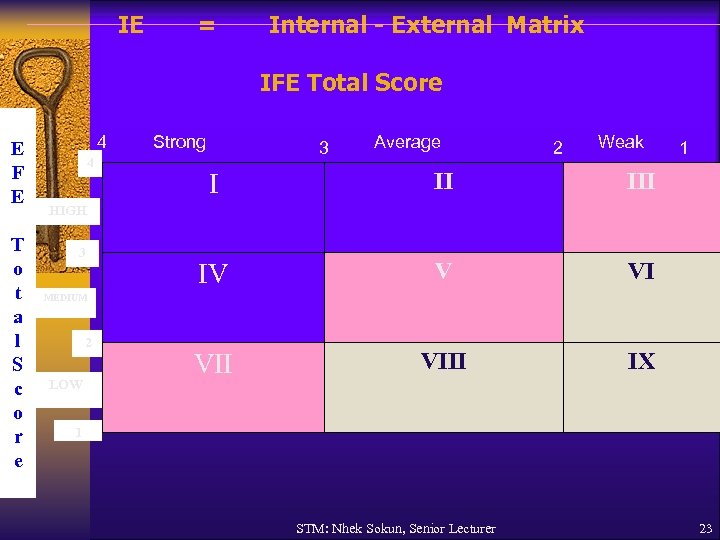 IE = Internal - External Matrix IFE Total Score E F E T o t a l S c o r e 4 4 Strong 3 Average 2 Weak I II IV V VI VIII 1 IX HIGH 3 MEDIUM 2 LOW 1 STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 23
IE = Internal - External Matrix IFE Total Score E F E T o t a l S c o r e 4 4 Strong 3 Average 2 Weak I II IV V VI VIII 1 IX HIGH 3 MEDIUM 2 LOW 1 STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 23
 IE Matrix: (Recommended Strategies) – Sectors I, IV : Recommended strategies: ¨ Grow and Build (concentration, integration) – Sectors III, V, VII: Recommended strategies: ¨ Hold and Maintain (concentration) – Sectors VI, VIII, IX: Recommended strategies: ¨ Harvest or Divest (restructuring ) STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 24
IE Matrix: (Recommended Strategies) – Sectors I, IV : Recommended strategies: ¨ Grow and Build (concentration, integration) – Sectors III, V, VII: Recommended strategies: ¨ Hold and Maintain (concentration) – Sectors VI, VIII, IX: Recommended strategies: ¨ Harvest or Divest (restructuring ) STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 24
 Grand Strategy Matrix §Tool formulating alternative strategies §Based on two dimensions §Competitive position §Market growth STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 25
Grand Strategy Matrix §Tool formulating alternative strategies §Based on two dimensions §Competitive position §Market growth STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 25
 RAPID MARKET GROWTH 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. WEAK COMPETITIVE POSITION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Quadrant II Market development Market penetration Product development Horizontal integration Divestiture Liquidation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Quadrant I Market development Market penetration Product development Forward integration Backward integration Horizontal integration Concentric diversification STRONG COMPETITIVE POSITION Quadrant III Quadrant IV Retrenchment 1. Concentric diversification 2. Horizontal diversification 3. Conglomerate diversification 4. Joint ventures Liquidation SLOW MARKET GROWTH STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 26
RAPID MARKET GROWTH 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. WEAK COMPETITIVE POSITION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Quadrant II Market development Market penetration Product development Horizontal integration Divestiture Liquidation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Quadrant I Market development Market penetration Product development Forward integration Backward integration Horizontal integration Concentric diversification STRONG COMPETITIVE POSITION Quadrant III Quadrant IV Retrenchment 1. Concentric diversification 2. Horizontal diversification 3. Conglomerate diversification 4. Joint ventures Liquidation SLOW MARKET GROWTH STM: Nhek Sokun, Senior Lecturer 26


