4f7ba835127e2857c148ef760564cb78.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Chapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice
Chapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice
 Strategic Analysis & Choice n Re-visit the Mission u Revise, create, or maintain mission Set Long-Term Objectives n Generate feasible alternatives n Evaluate alternatives n Choose courses of action n
Strategic Analysis & Choice n Re-visit the Mission u Revise, create, or maintain mission Set Long-Term Objectives n Generate feasible alternatives n Evaluate alternatives n Choose courses of action n
 The Strategy Formulation Analytical Framework (Figure 6 -2) Stage 1: The Input Stage External Analysis SWOT Analysis Internal Analysis Stage 2: The Matching Stage Re-visit Mission and Set Long Term Objectives Generate feasible alternative Corporate Strategies Stage 3: The Decision Stage Evaluate and Choose Corporate Strategies
The Strategy Formulation Analytical Framework (Figure 6 -2) Stage 1: The Input Stage External Analysis SWOT Analysis Internal Analysis Stage 2: The Matching Stage Re-visit Mission and Set Long Term Objectives Generate feasible alternative Corporate Strategies Stage 3: The Decision Stage Evaluate and Choose Corporate Strategies
 Create, revise Mission Statement of the purpose of the organization n Describes the organization in terms of: n u Customers u Products or services u Markets u Basic beliefs about growth, public image, n employees Remember Hershey’s evolving Mission Statement n Purpose of Mission: u Communication Tool u Decision-Making Tool
Create, revise Mission Statement of the purpose of the organization n Describes the organization in terms of: n u Customers u Products or services u Markets u Basic beliefs about growth, public image, n employees Remember Hershey’s evolving Mission Statement n Purpose of Mission: u Communication Tool u Decision-Making Tool
 Quantitative Areas n Profitability u Net profit margin; ROI; ROE n Productivity u Lower costs (% of sales CGS, S&A) u Activity ratios n Growth u Increases in sales, assets, net income n Competitive Position u Market Share
Quantitative Areas n Profitability u Net profit margin; ROI; ROE n Productivity u Lower costs (% of sales CGS, S&A) u Activity ratios n Growth u Increases in sales, assets, net income n Competitive Position u Market Share
 Technological Leadership n Shareholder Wealth u. EPS; Dividends; Shareholder Value (stock) n Industry specific metrics n
Technological Leadership n Shareholder Wealth u. EPS; Dividends; Shareholder Value (stock) n Industry specific metrics n
 Qualitative Areas Employee Relations n Social Responsibility n Reputation n n These areas have long term objectives that can be measured.
Qualitative Areas Employee Relations n Social Responsibility n Reputation n n These areas have long term objectives that can be measured.
 Corporate Strategies n. The overall managerial game plan. n. How management plans to achieve mission and objectives.
Corporate Strategies n. The overall managerial game plan. n. How management plans to achieve mission and objectives.
 Alternatives for Growth Market Penetration Market Development Product Development Expansion of existing Businesses Alternatives for Growth Diversification into new Businesses Vertical Integration Forward & Backward Related Unrelated
Alternatives for Growth Market Penetration Market Development Product Development Expansion of existing Businesses Alternatives for Growth Diversification into new Businesses Vertical Integration Forward & Backward Related Unrelated
 Modes of Growth Internal development n Acquiring firms/businesses n Collaborative arrangements n u Strategic Alliances u Joint Ventures u Licensing
Modes of Growth Internal development n Acquiring firms/businesses n Collaborative arrangements n u Strategic Alliances u Joint Ventures u Licensing
 Repositioning Strategies n Retrenchment u Assets and/or costs Divestiture n Spin-offs n
Repositioning Strategies n Retrenchment u Assets and/or costs Divestiture n Spin-offs n
 Termination Strategies Liquidation n Merger n Being acquired n
Termination Strategies Liquidation n Merger n Being acquired n
 Tools for Formulating and Choosing Corporate Strategies 1. Portfolio Analysis
Tools for Formulating and Choosing Corporate Strategies 1. Portfolio Analysis
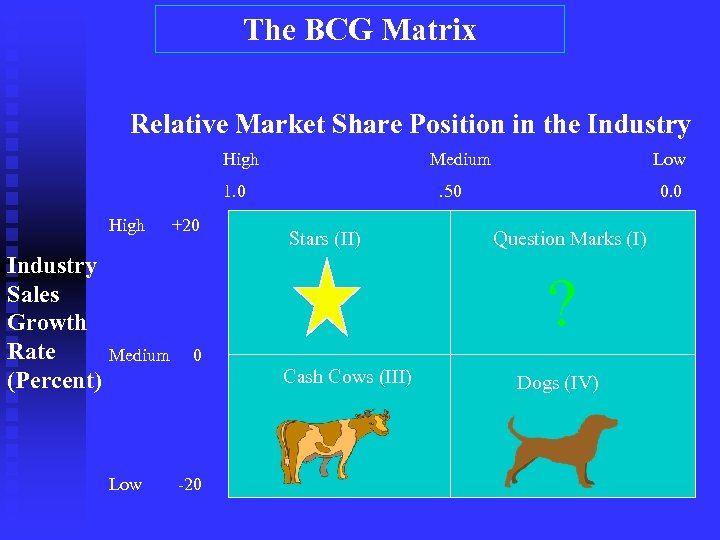 The BCG Matrix Relative Market Share Position in the Industry High Medium 1. 0 High Industry Sales Growth Rate (Percent) +20 Low . 50 Stars (II) 0. 0 Question Marks (I) ? Medium 0 Cash Cows (III) Low -20 Dogs (IV)
The BCG Matrix Relative Market Share Position in the Industry High Medium 1. 0 High Industry Sales Growth Rate (Percent) +20 Low . 50 Stars (II) 0. 0 Question Marks (I) ? Medium 0 Cash Cows (III) Low -20 Dogs (IV)
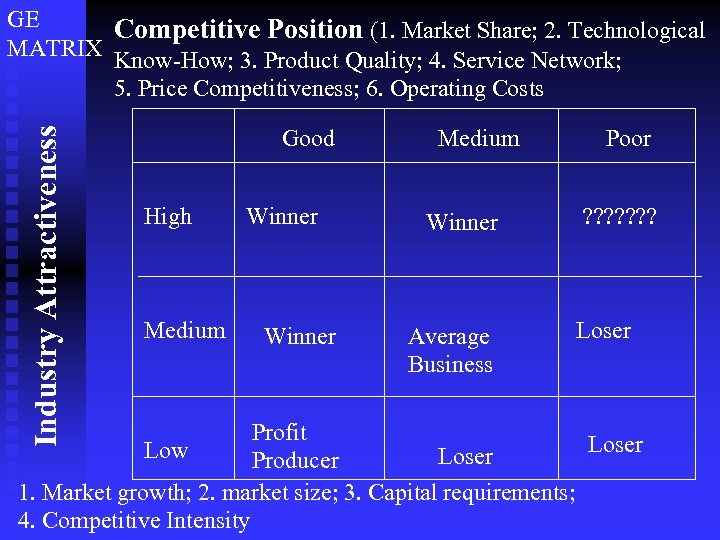 Industry Attractiveness GE Competitive Position (1. Market Share; 2. Technological MATRIX Know-How; 3. Product Quality; 4. Service Network; 5. Price Competitiveness; 6. Operating Costs Good High Medium Winner Average Business Poor ? ? ? ? Loser Profit Loser Low Loser Producer 1. Market growth; 2. market size; 3. Capital requirements; 4. Competitive Intensity
Industry Attractiveness GE Competitive Position (1. Market Share; 2. Technological MATRIX Know-How; 3. Product Quality; 4. Service Network; 5. Price Competitiveness; 6. Operating Costs Good High Medium Winner Average Business Poor ? ? ? ? Loser Profit Loser Low Loser Producer 1. Market growth; 2. market size; 3. Capital requirements; 4. Competitive Intensity
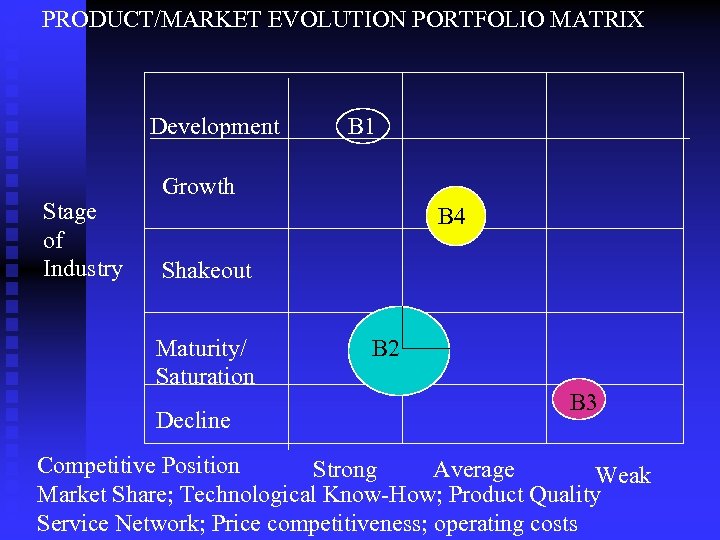 PRODUCT/MARKET EVOLUTION PORTFOLIO MATRIX Development Stage of Industry B 1 Growth B 4 Shakeout Maturity/ Saturation Decline B 2 B 3 Competitive Position Strong Average Weak Market Share; Technological Know-How; Product Quality Service Network; Price competitiveness; operating costs
PRODUCT/MARKET EVOLUTION PORTFOLIO MATRIX Development Stage of Industry B 1 Growth B 4 Shakeout Maturity/ Saturation Decline B 2 B 3 Competitive Position Strong Average Weak Market Share; Technological Know-How; Product Quality Service Network; Price competitiveness; operating costs
 Advantages of Portfolio Analyses Encourages top management to evaluate each business individually; to set objectives; and consider resources. n It stimulates use of external data to supplement management’s judgment. n Its graphic representation makes interpretation and communication easier. n
Advantages of Portfolio Analyses Encourages top management to evaluate each business individually; to set objectives; and consider resources. n It stimulates use of external data to supplement management’s judgment. n Its graphic representation makes interpretation and communication easier. n
 Limitations of Portfolio Analyses Defining product/market segments isn’t easy. n Using standard strategies may miss opportunities or be impractical. n Providing an illusion of scientific rigor masks the reality that positions are based on subjective judgments. n Determining what makes an industry attractive isn’t always possible. n
Limitations of Portfolio Analyses Defining product/market segments isn’t easy. n Using standard strategies may miss opportunities or be impractical. n Providing an illusion of scientific rigor masks the reality that positions are based on subjective judgments. n Determining what makes an industry attractive isn’t always possible. n
 More Tools u 2. Past Performance u % increase in sales u Contribution Margin F Sales or profit (gross, operating, net) u Continue to do what doing u 3. Mission and Long Term Objectives
More Tools u 2. Past Performance u % increase in sales u Contribution Margin F Sales or profit (gross, operating, net) u Continue to do what doing u 3. Mission and Long Term Objectives
 More Tools 4. Matrices
More Tools 4. Matrices
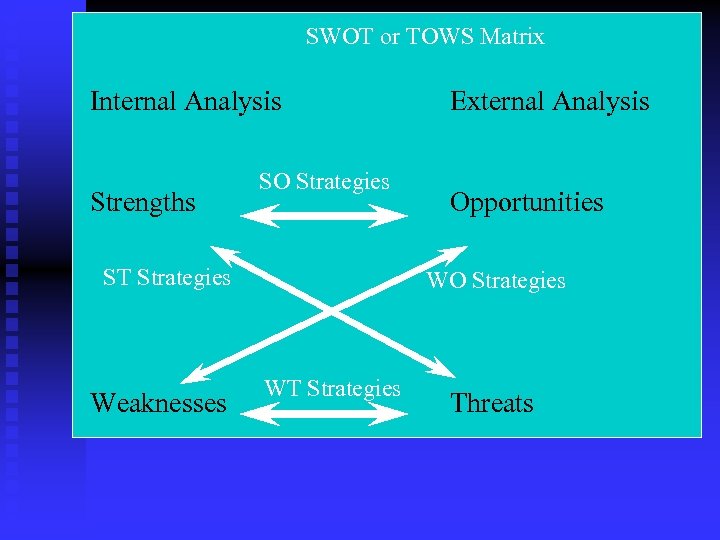 SWOT or TOWS Matrix Internal Analysis Strengths SO Strategies ST Strategies Weaknesses External Analysis Opportunities WO Strategies WT Strategies Threats
SWOT or TOWS Matrix Internal Analysis Strengths SO Strategies ST Strategies Weaknesses External Analysis Opportunities WO Strategies WT Strategies Threats
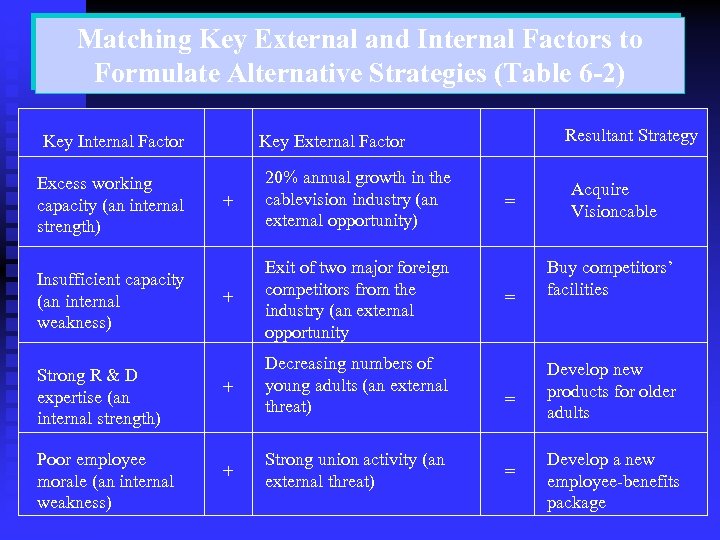 Matching Key External and Internal Factors to Formulate Alternative Strategies (Table 6 -2) Key Internal Factor Excess working capacity (an internal strength) Insufficient capacity (an internal weakness) Strong R & D expertise (an internal strength) Poor employee morale (an internal weakness) Resultant Strategy Key External Factor + 20% annual growth in the cablevision industry (an external opportunity) + Exit of two major foreign competitors from the industry (an external opportunity + Decreasing numbers of young adults (an external threat) + Strong union activity (an external threat) = = Acquire Visioncable Buy competitors’ facilities Develop new products for older adults Develop a new employee-benefits package
Matching Key External and Internal Factors to Formulate Alternative Strategies (Table 6 -2) Key Internal Factor Excess working capacity (an internal strength) Insufficient capacity (an internal weakness) Strong R & D expertise (an internal strength) Poor employee morale (an internal weakness) Resultant Strategy Key External Factor + 20% annual growth in the cablevision industry (an external opportunity) + Exit of two major foreign competitors from the industry (an external opportunity + Decreasing numbers of young adults (an external threat) + Strong union activity (an external threat) = = Acquire Visioncable Buy competitors’ facilities Develop new products for older adults Develop a new employee-benefits package
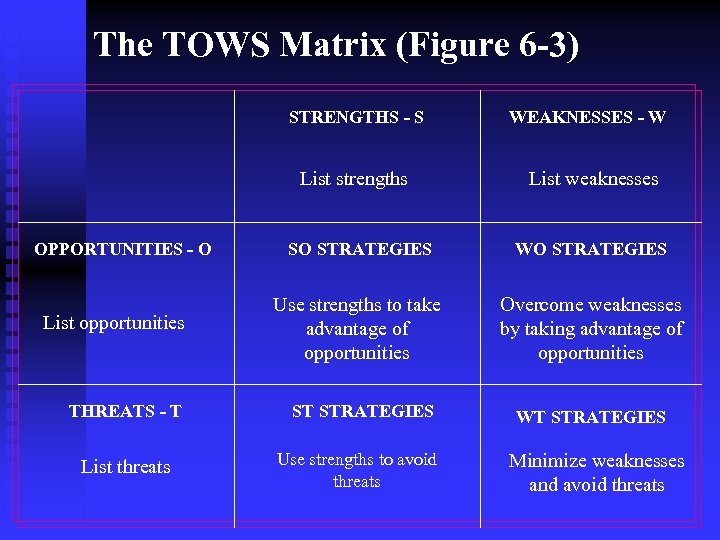 The TOWS Matrix (Figure 6 -3) STRENGTHS - S List strengths OPPORTUNITIES - O List opportunities THREATS - T List threats WEAKNESSES - W List weaknesses SO STRATEGIES WO STRATEGIES Use strengths to take advantage of opportunities Overcome weaknesses by taking advantage of opportunities ST STRATEGIES Use strengths to avoid threats WT STRATEGIES Minimize weaknesses and avoid threats
The TOWS Matrix (Figure 6 -3) STRENGTHS - S List strengths OPPORTUNITIES - O List opportunities THREATS - T List threats WEAKNESSES - W List weaknesses SO STRATEGIES WO STRATEGIES Use strengths to take advantage of opportunities Overcome weaknesses by taking advantage of opportunities ST STRATEGIES Use strengths to avoid threats WT STRATEGIES Minimize weaknesses and avoid threats
 Other Matrices Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) p. 165 n External Factor Evaluation (EFE) p. 130 n Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) p. 131 n Strategic Position and Action Evaluation (SPACE) p. 184 n Internal-External p. 190 n Grand Strategy p. 192 n
Other Matrices Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) p. 165 n External Factor Evaluation (EFE) p. 130 n Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) p. 131 n Strategic Position and Action Evaluation (SPACE) p. 184 n Internal-External p. 190 n Grand Strategy p. 192 n
 Other Tools Con’t 5. n 6. n 7. n 8. n Economic Value Added (EVA) Scenario Analysis Game Theory Quantitative Decision Techniques u Linear Programming, etc. n 9. Computer Assisted u Decision Support Systems (DSS) u Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Other Tools Con’t 5. n 6. n 7. n 8. n Economic Value Added (EVA) Scenario Analysis Game Theory Quantitative Decision Techniques u Linear Programming, etc. n 9. Computer Assisted u Decision Support Systems (DSS) u Artificial Intelligence (AI)
 Behavioral Aspects/Tools Propensity for risk n Personal Agendas n Personalities n Time Pressures n Reputation/Integrity n Imagination/Conceptualizations n Support/Coalitions n
Behavioral Aspects/Tools Propensity for risk n Personal Agendas n Personalities n Time Pressures n Reputation/Integrity n Imagination/Conceptualizations n Support/Coalitions n
 Core Competencies
Core Competencies
 Core Competencies of the Corporation Real sources of advantage - not based on businesses. n Core competencies are collective learning in the organization, especially: n u how to coordinate diverse production skills by integrating multiple streams of technologies.
Core Competencies of the Corporation Real sources of advantage - not based on businesses. n Core competencies are collective learning in the organization, especially: n u how to coordinate diverse production skills by integrating multiple streams of technologies.
 Tests to identify core competencies Provide potential access to a wide variety of markets/products/services. n Are difficult to imitate. n Are driven by knowledge and learning. n
Tests to identify core competencies Provide potential access to a wide variety of markets/products/services. n Are difficult to imitate. n Are driven by knowledge and learning. n
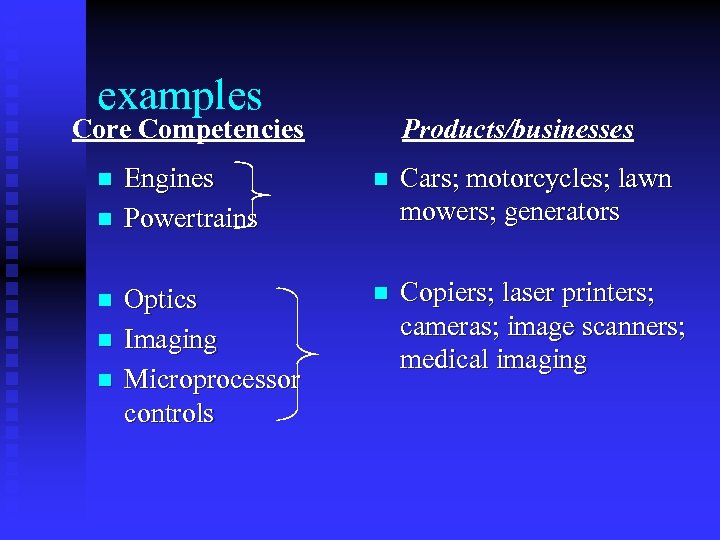 examples Core Competencies n n n Products/businesses Engines Powertrains n Cars; motorcycles; lawn mowers; generators Optics Imaging Microprocessor controls n Copiers; laser printers; cameras; image scanners; medical imaging
examples Core Competencies n n n Products/businesses Engines Powertrains n Cars; motorcycles; lawn mowers; generators Optics Imaging Microprocessor controls n Copiers; laser printers; cameras; image scanners; medical imaging
 More kinds of core competencies: Systems Integration n Virtual reality n Bioengineering n Delighting the customer n
More kinds of core competencies: Systems Integration n Virtual reality n Bioengineering n Delighting the customer n
 Strategic Analysis and Choice Summary Making subjective decisions based on objective information, and subjective interpretation
Strategic Analysis and Choice Summary Making subjective decisions based on objective information, and subjective interpretation


