fd4f41122892405daa3625ed9dcb2c4d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Chapter 6 Personal Risk Management
Chapter 6 Personal Risk Management
 Chapter 6 Objectives Explain the concepts of risk and list the 3 types of consumer risk Describe risk assessment and list 4 risk strategies Explain the need for insurances protecting income and the types of plans available for each: Health Insurance Disability Insurance Life Insurance Explain the needs and types of insurance protecting property: • • Homeowners/Renters Insurance Auto Insurance Slide 2
Chapter 6 Objectives Explain the concepts of risk and list the 3 types of consumer risk Describe risk assessment and list 4 risk strategies Explain the need for insurances protecting income and the types of plans available for each: Health Insurance Disability Insurance Life Insurance Explain the needs and types of insurance protecting property: • • Homeowners/Renters Insurance Auto Insurance Slide 2
 What Is Risk? • Risk is the chance of injury, damage, or economic loss. • Probability is the likelihood of a risk. • A loss refers to physical injury, damage to property, or disappearance of assets. 6 -1 Risk Assessment and Strategies 3 Slide
What Is Risk? • Risk is the chance of injury, damage, or economic loss. • Probability is the likelihood of a risk. • A loss refers to physical injury, damage to property, or disappearance of assets. 6 -1 Risk Assessment and Strategies 3 Slide
 What Are the Types of Consumer Risk? Personal risk means you could lose something of personal value. o Example: breaking a leg missing fun activity Some risks result in a financial loss. o Example: driving without insurance paying a lot of money to repair car Some risks jeopardize financial resources. o Example: getting sued for causing an injury to another having your wages garnished to pay for judgment against you – this affects future assets and is serious 6 -1 Risk Assessment and Strategies Slide 4
What Are the Types of Consumer Risk? Personal risk means you could lose something of personal value. o Example: breaking a leg missing fun activity Some risks result in a financial loss. o Example: driving without insurance paying a lot of money to repair car Some risks jeopardize financial resources. o Example: getting sued for causing an injury to another having your wages garnished to pay for judgment against you – this affects future assets and is serious 6 -1 Risk Assessment and Strategies Slide 4
 How Can You Manage Risk Using Risk Strategies? Pg 188 -189 • Risk assessment involves identifying risks and deciding how serious they are. • Use risk strategies to protect yourself against loss. o o Reduce risk (change your actions) Avoid risk (stop a certain behavior) Transfer risk (buy insurance) Assume risk (self-insure) 6 -1 Risk Assessment and Strategies Slide 5
How Can You Manage Risk Using Risk Strategies? Pg 188 -189 • Risk assessment involves identifying risks and deciding how serious they are. • Use risk strategies to protect yourself against loss. o o Reduce risk (change your actions) Avoid risk (stop a certain behavior) Transfer risk (buy insurance) Assume risk (self-insure) 6 -1 Risk Assessment and Strategies Slide 5
 Risk Assessment Risk Probability of Occurrence Seriousness Possible Rating* Consequences Losing my job Medium 10 Getting in a car accident Unknown 10 Suffering physical injury from snowboarding Medium 3 Missed work time Medical bills Having bike stolen Low 2 New/used bike purchase * 1 is low risk; 5 is medium risk; 10 is high risk 6 -1 Risk Assessment and Strategies 6 Slide Missed payments Lower credit rating Personal injury Lawsuit
Risk Assessment Risk Probability of Occurrence Seriousness Possible Rating* Consequences Losing my job Medium 10 Getting in a car accident Unknown 10 Suffering physical injury from snowboarding Medium 3 Missed work time Medical bills Having bike stolen Low 2 New/used bike purchase * 1 is low risk; 5 is medium risk; 10 is high risk 6 -1 Risk Assessment and Strategies 6 Slide Missed payments Lower credit rating Personal injury Lawsuit
 Why Do You Need Health Insurance? • Health insurance is a plan for sharing the risk of medical costs. • There are three basic types of plans. o Fee-for-service(Unmanaged Care) o PPO (MANAGED CARE) o HMO(MANAGED CARE) • Medicare and Medicaid are government-sponsored insurance. Slide 7
Why Do You Need Health Insurance? • Health insurance is a plan for sharing the risk of medical costs. • There are three basic types of plans. o Fee-for-service(Unmanaged Care) o PPO (MANAGED CARE) o HMO(MANAGED CARE) • Medicare and Medicaid are government-sponsored insurance. Slide 7
 Health Care Types Managing Costs Deductibles and Copays- the part Basic Health Caremedical, hospital, surgery Major Medical- very serious injury or illness Dental and Vision you pay. If lower, then insurance premium is higher Stop-Loss Provisions- after you pay a certain amount, insurance pays 100% Health Spending Accounts FSA-flexible spending account HSA- health savings account Long-term care – for nursing homes and assisted living Slide 8
Health Care Types Managing Costs Deductibles and Copays- the part Basic Health Caremedical, hospital, surgery Major Medical- very serious injury or illness Dental and Vision you pay. If lower, then insurance premium is higher Stop-Loss Provisions- after you pay a certain amount, insurance pays 100% Health Spending Accounts FSA-flexible spending account HSA- health savings account Long-term care – for nursing homes and assisted living Slide 8
 What Is the Purpose of Disability Insurance? • Disability insurance provides income when the insured cannot work due to nonwork-related injury or illness. • It replaces a portion of normal earnings. • Short-term, long-term, and social security disability insurance are all options. 6 -2 Protecting Income Slide 9
What Is the Purpose of Disability Insurance? • Disability insurance provides income when the insured cannot work due to nonwork-related injury or illness. • It replaces a portion of normal earnings. • Short-term, long-term, and social security disability insurance are all options. 6 -2 Protecting Income Slide 9
 What is Life Insurance? • Life insurance pays money to a beneficiary upon the death of the insured person. • Temporary or Term insurance provides a death benefit only. • Permanent insurance provides a death benefit and builds cash value. • Group life insurance is available through employers. Ø See page 199 in textbook for list of reasons people buy life insurance: 6 -2 Protecting Income Slide 10
What is Life Insurance? • Life insurance pays money to a beneficiary upon the death of the insured person. • Temporary or Term insurance provides a death benefit only. • Permanent insurance provides a death benefit and builds cash value. • Group life insurance is available through employers. Ø See page 199 in textbook for list of reasons people buy life insurance: 6 -2 Protecting Income Slide 10
 Focus On. . . Health Care Reform • Most Americans will have insurance by 2020. • Purchasing health insurance will be mandatory. • Citizens cannot be denied coverage for pre-existing conditions. • Tax increases will pay for health care reform. • A major omission from the reform is a control on health care costs. 6 -2 Protecting Income Slide 11
Focus On. . . Health Care Reform • Most Americans will have insurance by 2020. • Purchasing health insurance will be mandatory. • Citizens cannot be denied coverage for pre-existing conditions. • Tax increases will pay for health care reform. • A major omission from the reform is a control on health care costs. 6 -2 Protecting Income Slide 11
 Success Skills Dealing With Health Care Fraud • Health care fraud is false billing for medical services. o Examples: falsifying a diagnosis to justify unneeded tests, upcoding, unbundling • Ten cents of every dollar goes toward fraudulent health care claims. • Consumers can help prevent fraud. o Examples: ask questions about services and charges, audit bills, report suspected fraud 6 -2 Protecting Income Slide 12
Success Skills Dealing With Health Care Fraud • Health care fraud is false billing for medical services. o Examples: falsifying a diagnosis to justify unneeded tests, upcoding, unbundling • Ten cents of every dollar goes toward fraudulent health care claims. • Consumers can help prevent fraud. o Examples: ask questions about services and charges, audit bills, report suspected fraud 6 -2 Protecting Income Slide 12
 What Is Homeowner’s Insurance? • Homeowner’s insurance protects the policyholder from risk of loss to a home and its contents. • It covers three types of risk. o Fire and other hazards o Criminal activity o Personal Liability(when others are injured on your property) • Acts of nature may not be covered. 6 -3 Protecting Property Slide 13
What Is Homeowner’s Insurance? • Homeowner’s insurance protects the policyholder from risk of loss to a home and its contents. • It covers three types of risk. o Fire and other hazards o Criminal activity o Personal Liability(when others are injured on your property) • Acts of nature may not be covered. 6 -3 Protecting Property Slide 13
 What if I rent, not own? . . . **Buy Renter’s Insurance A renter (tenant) cannot insure the building BUT you can insure your contents. Always purchase renter’s insurance to protect against risk of loss of personal property. Just like a homeowners policy, cover things like fire, theft, and other hazards. Includes personal liability coverage for what happens inside your residence. Renter’s insurance even covers your property in your car or at work! **A LOW COST way to protect your stuff!
What if I rent, not own? . . . **Buy Renter’s Insurance A renter (tenant) cannot insure the building BUT you can insure your contents. Always purchase renter’s insurance to protect against risk of loss of personal property. Just like a homeowners policy, cover things like fire, theft, and other hazards. Includes personal liability coverage for what happens inside your residence. Renter’s insurance even covers your property in your car or at work! **A LOW COST way to protect your stuff!
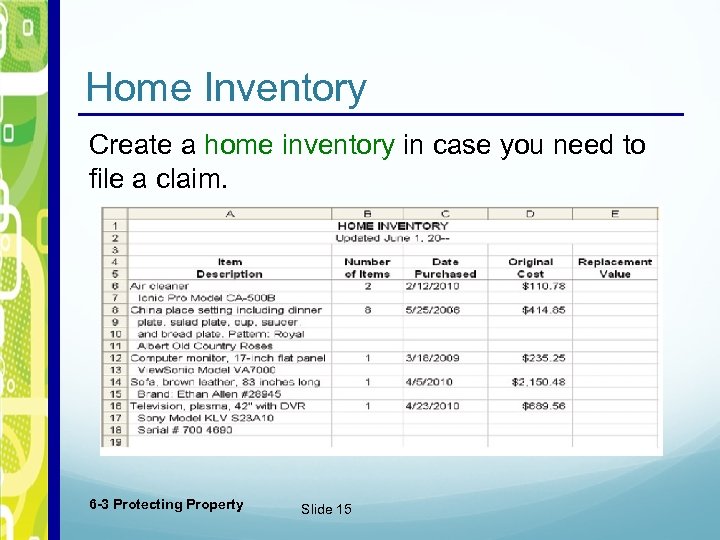 Home Inventory Create a home inventory in case you need to file a claim. 6 -3 Protecting Property Slide 15
Home Inventory Create a home inventory in case you need to file a claim. 6 -3 Protecting Property Slide 15
 How Does Insurance Protect Car Owners? • Automobile insurance protects a car owner from losses as a result of accidents and other events. • Cost depends on • model and style of car, • age (and gender) • driving record of driver. 6 -3 Protecting Property Slide 16
How Does Insurance Protect Car Owners? • Automobile insurance protects a car owner from losses as a result of accidents and other events. • Cost depends on • model and style of car, • age (and gender) • driving record of driver. 6 -3 Protecting Property Slide 16
 Types of Auto Insurance Coverage • Full coverage is required if you have a car loan. It includes: o o o Liability Collision Comprehensive Personal injury protection Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Towing/Rental Car Ø Go to pages 208 -209 in textbook for descriptions
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage • Full coverage is required if you have a car loan. It includes: o o o Liability Collision Comprehensive Personal injury protection Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Towing/Rental Car Ø Go to pages 208 -209 in textbook for descriptions
 Types of Auto Insurance Coverage o Liability: covers injury or damage to another person’s property (when you are at fault) o Collision: covers damage to your own vehicle if you hit someone, or lose control (when you’re at fault) o Comprehensive: covers losses other than collision like falling objects, theft, vandalism, hail, fire o Personal injury protection: covers medical, hospital costs of the insured and others in your car o Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist: covers you if someone doesn’t have insurance and they are at fault o Towing/Rental Car: optional but good to have
Types of Auto Insurance Coverage o Liability: covers injury or damage to another person’s property (when you are at fault) o Collision: covers damage to your own vehicle if you hit someone, or lose control (when you’re at fault) o Comprehensive: covers losses other than collision like falling objects, theft, vandalism, hail, fire o Personal injury protection: covers medical, hospital costs of the insured and others in your car o Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist: covers you if someone doesn’t have insurance and they are at fault o Towing/Rental Car: optional but good to have
 How Can You Reduce Auto Insurance Costs and Maximize Benefits? • Reducing costs can raise your overall risk but it can help you manage your budget. • Lower your costs using these strategies: ü choose higher deductibles ü change your driving habits* ü buy online ü comparison shop • Maximize benefits by reviewing your policy or getting umbrella coverage. 6 -3 Protecting Property Slide 19
How Can You Reduce Auto Insurance Costs and Maximize Benefits? • Reducing costs can raise your overall risk but it can help you manage your budget. • Lower your costs using these strategies: ü choose higher deductibles ü change your driving habits* ü buy online ü comparison shop • Maximize benefits by reviewing your policy or getting umbrella coverage. 6 -3 Protecting Property Slide 19
 *Change your driving habits Lower your premium costs Reduce risk of accidents ü Take driving training class ü Maintain good driving record ü Get good grades in school ü Choose a car with high safety rating ü Drive while rested instead of when tired ü Keep your car properly serviced ü Avoid heavy traffic or bad weather ü Install security devices on your ü Drive defensively; be aware of other drivers car ü Park in garage or protected area Slide 20 ü Avoid using cell phones, eating or other distractions
*Change your driving habits Lower your premium costs Reduce risk of accidents ü Take driving training class ü Maintain good driving record ü Get good grades in school ü Choose a car with high safety rating ü Drive while rested instead of when tired ü Keep your car properly serviced ü Avoid heavy traffic or bad weather ü Install security devices on your ü Drive defensively; be aware of other drivers car ü Park in garage or protected area Slide 20 ü Avoid using cell phones, eating or other distractions
 TODAY in Fin Lit: Book Q&A : Pg. 192: 17, 24 Pg. 213: 16, 23 Finish Key Terms Slide 21
TODAY in Fin Lit: Book Q&A : Pg. 192: 17, 24 Pg. 213: 16, 23 Finish Key Terms Slide 21
 Unit 2 Test*: Wed, 4/23 – Blocks C and G Thurs, 4/24 – Blocks D and F *Notebook check also Unit 2 Test Covers: § Chapter 4 – Budget and Financial Planning § Chapter 5 – Banking System § Chapter 6 – Risk Strategies and Insurance Be ready for Jeopardy 1 st day back from break Slide
Unit 2 Test*: Wed, 4/23 – Blocks C and G Thurs, 4/24 – Blocks D and F *Notebook check also Unit 2 Test Covers: § Chapter 4 – Budget and Financial Planning § Chapter 5 – Banking System § Chapter 6 – Risk Strategies and Insurance Be ready for Jeopardy 1 st day back from break Slide


