aa2eac4d989f542215a18eda8e33f641.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 195
 Chapter 6 Multiplying and Dividing Decimals and Fractions Click the mouse or press the space bar to continue.
Chapter 6 Multiplying and Dividing Decimals and Fractions Click the mouse or press the space bar to continue.
 6 Multiplying and Dividing Decimals and Fractions Lesson 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Lesson 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Lesson 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Lesson 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Lesson 6 -5 Lesson 6 -6 Dividing by Decimals Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Lesson 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Lesson 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Lesson 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers Lesson 6 -10 Dividing Fractions
6 Multiplying and Dividing Decimals and Fractions Lesson 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Lesson 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Lesson 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Lesson 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Lesson 6 -5 Lesson 6 -6 Dividing by Decimals Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Lesson 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Lesson 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Lesson 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers Lesson 6 -10 Dividing Fractions
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Five-Minute Check (over Chapter 5) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Example 1: Multiply Decimals Example 2: Multiply Decimals Example 3: Annex Zeros in the Product Example 4: Annex Zeros in the Product Example 5: Scientific Notation
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Five-Minute Check (over Chapter 5) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Example 1: Multiply Decimals Example 2: Multiply Decimals Example 3: Annex Zeros in the Product Example 4: Annex Zeros in the Product Example 5: Scientific Notation
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Chapter 5) Find 6 1 3 – 2. 4 4 1 A. 3 2 B. 3 8 4 1 C. 4 2 D. 4
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Chapter 5) Find 6 1 3 – 2. 4 4 1 A. 3 2 B. 3 8 4 1 C. 4 2 D. 4
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Chapter 5) Find 5 1 5 – 3. 3 9 4 A. 2 9 B. 7 1 9 6 C. 8 9 D. 6 29
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Chapter 5) Find 5 1 5 – 3. 3 9 4 A. 2 9 B. 7 1 9 6 C. 8 9 D. 6 29
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Chapter 5) Find 5 2 4 – 3. 5 5 3 A. 1 5 B. 2 2 5 C. 2 3 5 D. 4 85
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Chapter 5) Find 5 2 4 – 3. 5 5 3 A. 1 5 B. 2 2 5 C. 2 3 5 D. 4 85
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Chapter 5) Find 15 1 7 – 9. 4 8 6 A. 6 8 B. 6 5 8 C. 5 3 8 D. 3 23 8
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Chapter 5) Find 15 1 7 – 9. 4 8 6 A. 6 8 B. 6 5 8 C. 5 3 8 D. 3 23 8
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers • I will estimate and find the product of decimals and whole numbers. • scientific notation
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers • I will estimate and find the product of decimals and whole numbers. • scientific notation
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results.
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results.
 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers 6 -1 Find 18. 9 × 4. One Way: Use estimation. Round 18. 9 to 19. 18. 9 × 4 19 × 4 or 76 33 18. 9 × 4 75. 6 Since the estimate is 76, place the decimal point after the 5.
Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers 6 -1 Find 18. 9 × 4. One Way: Use estimation. Round 18. 9 to 19. 18. 9 × 4 19 × 4 or 76 33 18. 9 × 4 75. 6 Since the estimate is 76, place the decimal point after the 5.
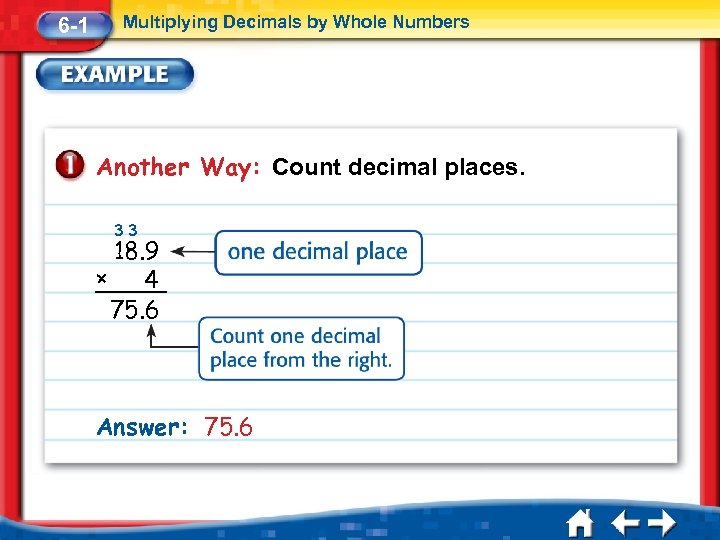 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Another Way: Count decimal places. 33 18. 9 × 4 75. 6 Answer: 75. 6
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Another Way: Count decimal places. 33 18. 9 × 4 75. 6 Answer: 75. 6
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 12. 7 × 5. A. 64 B. 63. 5 C. 60. 35 D. 63. 35
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 12. 7 × 5. A. 64 B. 63. 5 C. 60. 35 D. 63. 35
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 0. 56 × 7. One Way: Use estimation. Round 0. 56 to 1. 0. 56 × 7 1 × 7 or 7 3 4 0. 56 × 7 3. 92 Since the estimate is 7, place the decimal point after the 3.
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 0. 56 × 7. One Way: Use estimation. Round 0. 56 to 1. 0. 56 × 7 1 × 7 or 7 3 4 0. 56 × 7 3. 92 Since the estimate is 7, place the decimal point after the 3.
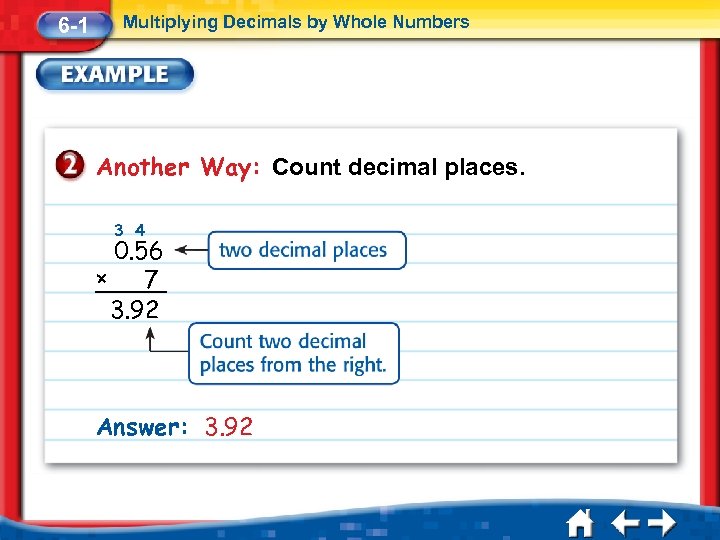 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Another Way: Count decimal places. 3 4 0. 56 × 7 3. 92 Answer: 3. 92
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Another Way: Count decimal places. 3 4 0. 56 × 7 3. 92 Answer: 3. 92
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 0. 47 × 8. A. 8 B. 5. 76 C. 3. 76 D. 0. 392
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 0. 47 × 8. A. 8 B. 5. 76 C. 3. 76 D. 0. 392
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 3 × 0. 016. 1 0. 016 × 3 0. 048 Answer: 0. 048
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 3 × 0. 016. 1 0. 016 × 3 0. 048 Answer: 0. 048
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 0. 026 × 2. A. 0. 052 B. 0. 52 C. 0. 0052 D. 0. 502
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 0. 026 × 2. A. 0. 052 B. 0. 52 C. 0. 0052 D. 0. 502
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers ALGEBRA Evaluate 5 g if g = 0. 0091. 5 g = 5 × 0. 0091 4 0. 0091 × 5 0. 0455 Answer: 0. 0455 Replace g with 0. 0091.
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers ALGEBRA Evaluate 5 g if g = 0. 0091. 5 g = 5 × 0. 0091 4 0. 0091 × 5 0. 0455 Answer: 0. 0455 Replace g with 0. 0091.
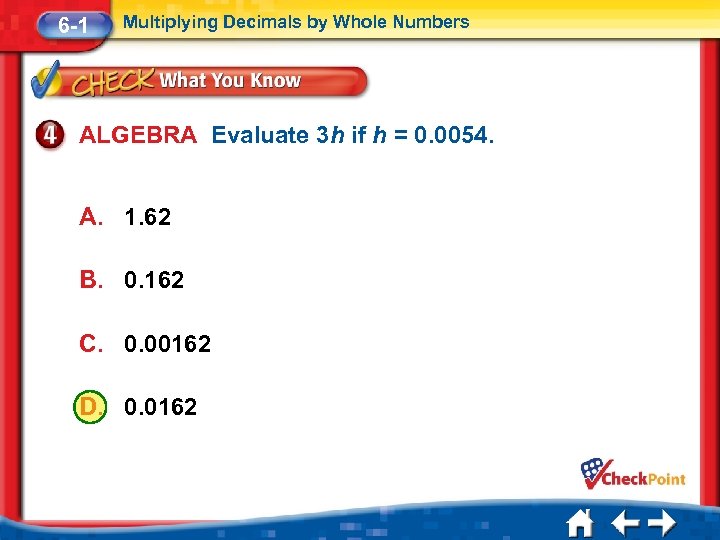 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers ALGEBRA Evaluate 3 h if h = 0. 0054. A. 1. 62 B. 0. 162 C. 0. 00162 D. 0. 0162
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers ALGEBRA Evaluate 3 h if h = 0. 0054. A. 1. 62 B. 0. 162 C. 0. 00162 D. 0. 0162
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers The average distance from Earth to the Sun is 1. 5 × 108 kilometers. Write the distance in standard form.
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers The average distance from Earth to the Sun is 1. 5 × 108 kilometers. Write the distance in standard form.
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers One Way: Use order of operations. Evaluate 108 first. Then multiply. 1. 5 × 108 = 1. 5 × 100, 000 = 150, 000 kilometers
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers One Way: Use order of operations. Evaluate 108 first. Then multiply. 1. 5 × 108 = 1. 5 × 100, 000 = 150, 000 kilometers
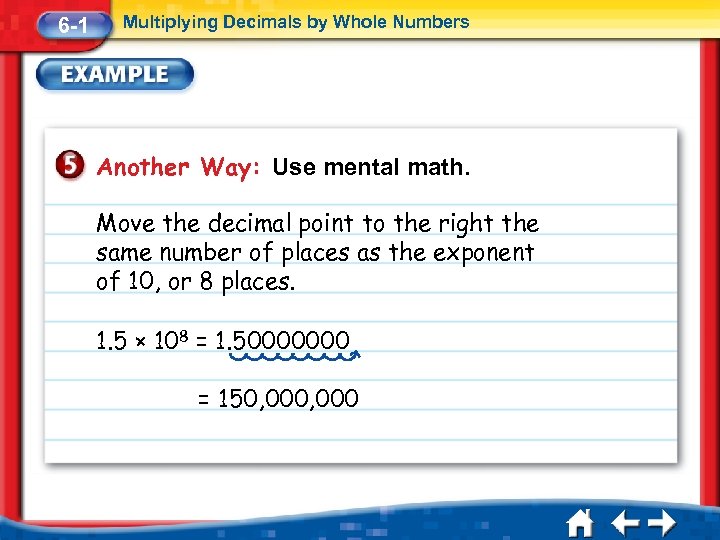 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Another Way: Use mental math. Move the decimal point to the right the same number of places as the exponent of 10, or 8 places. 1. 5 × 108 = 1. 50000000 = 150, 000
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Another Way: Use mental math. Move the decimal point to the right the same number of places as the exponent of 10, or 8 places. 1. 5 × 108 = 1. 50000000 = 150, 000
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Answer: The average distance from Earth to the Sun is 150, 000 kilometers.
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers Answer: The average distance from Earth to the Sun is 150, 000 kilometers.
 6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers The average distance from the Sun to the planet Jupiter is 5. 88 × 108 kilometers. Choose the answer showing the distance written in standard form. A. 588, 000 kilometers B. 58, 000 kilometers C. 5, 880, 000 kilometers D. 5, 800, 000 kilometers
6 -1 Multiplying Decimals by Whole Numbers The average distance from the Sun to the planet Jupiter is 5. 88 × 108 kilometers. Choose the answer showing the distance written in standard form. A. 588, 000 kilometers B. 58, 000 kilometers C. 5, 880, 000 kilometers D. 5, 800, 000 kilometers

 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -1) Main Idea California Standards Example 1: Multiply Decimals Example 2: Multiply Decimals Example 3: Evaluate an Expression Example 4: Real-World Example
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -1) Main Idea California Standards Example 1: Multiply Decimals Example 2: Multiply Decimals Example 3: Evaluate an Expression Example 4: Real-World Example
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Find 3. 8 × 2. A. 5. 8 B. 7. 6 C. 5. 6 D. 5
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Find 3. 8 × 2. A. 5. 8 B. 7. 6 C. 5. 6 D. 5
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Find 0. 6 × 25. A. 15 B. 25 C. 10 D. 4
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Find 0. 6 × 25. A. 15 B. 25 C. 10 D. 4
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Find 0. 038 × 15. A. 0. 63 B. 1. 35 C. 0. 57 D. 1
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Find 0. 038 × 15. A. 0. 63 B. 1. 35 C. 0. 57 D. 1
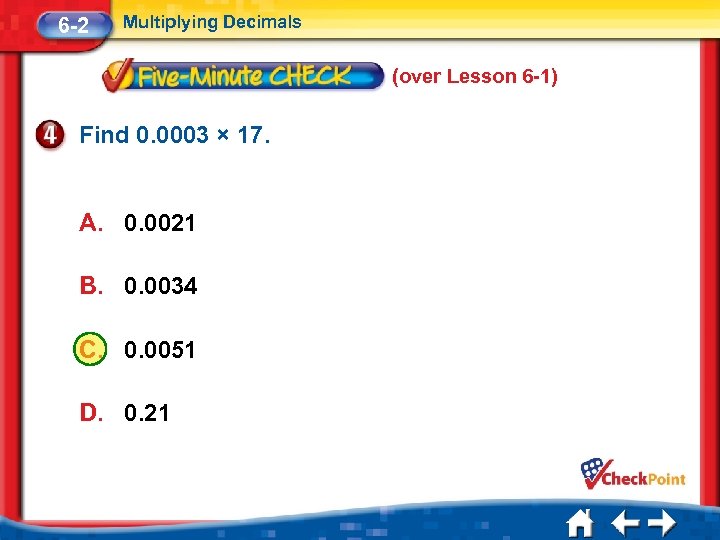 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Find 0. 0003 × 17. A. 0. 0021 B. 0. 0034 C. 0. 0051 D. 0. 21
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Find 0. 0003 × 17. A. 0. 0021 B. 0. 0034 C. 0. 0051 D. 0. 21
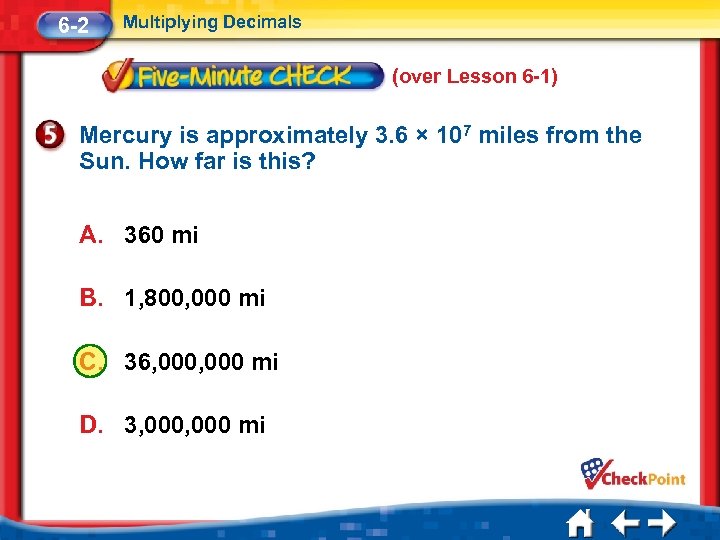 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Mercury is approximately 3. 6 × 107 miles from the Sun. How far is this? A. 360 mi B. 1, 800, 000 mi C. 36, 000 mi D. 3, 000 mi
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals (over Lesson 6 -1) Mercury is approximately 3. 6 × 107 miles from the Sun. How far is this? A. 360 mi B. 1, 800, 000 mi C. 36, 000 mi D. 3, 000 mi
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals • I will multiply decimals by decimals.
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals • I will multiply decimals by decimals.
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results. Standard 5 MR 2. 1 Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results.
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results. Standard 5 MR 2. 1 Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results.
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Find 8. 3 × 2. 9. Estimate 8. 3 × 2. 9 747 + 166 24. 07 8 × 3 or 24 one decimal place two decimal places Answer: So, the product is 24. 07.
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Find 8. 3 × 2. 9. Estimate 8. 3 × 2. 9 747 + 166 24. 07 8 × 3 or 24 one decimal place two decimal places Answer: So, the product is 24. 07.
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Check for Reasonableness Compare 24. 07 to the estimate. 24. 07 is about 24.
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Check for Reasonableness Compare 24. 07 to the estimate. 24. 07 is about 24.
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Find 4. 5 × 3. 9. A. 17. 55 B. 20 C. 18. 44 D. 19. 45
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Find 4. 5 × 3. 9. A. 17. 55 B. 20 C. 18. 44 D. 19. 45
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Find 0. 12 × 5. 3. Estimate 0. 12 × 5. 3 36 + 60 0. 636 0 × 5 or 0 two decimal places one decimal place three decimal places Answer: So, the product is 0. 636.
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Find 0. 12 × 5. 3. Estimate 0. 12 × 5. 3 36 + 60 0. 636 0 × 5 or 0 two decimal places one decimal place three decimal places Answer: So, the product is 0. 636.
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Check for Reasonableness Compare 0. 636 to the estimate. 0. 636 is about 0.
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Check for Reasonableness Compare 0. 636 to the estimate. 0. 636 is about 0.
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Find 0. 14 × 3. 3. A. 0. 636 B. 0. 543 C. 0. 462 D. 0. 723
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Find 0. 14 × 3. 3. A. 0. 636 B. 0. 543 C. 0. 462 D. 0. 723
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals ALGEBRA Evaluate 1. 8 r if r = 0. 029. 1. 8 r = 1. 8 × 0. 029 × 1. 8 232 + 29 0. 0522 Replace r with 0. 029. three decimal places one decimal place Annex a zero to make four decimal places. Answer: So, the product is 0. 0522.
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals ALGEBRA Evaluate 1. 8 r if r = 0. 029. 1. 8 r = 1. 8 × 0. 029 × 1. 8 232 + 29 0. 0522 Replace r with 0. 029. three decimal places one decimal place Annex a zero to make four decimal places. Answer: So, the product is 0. 0522.
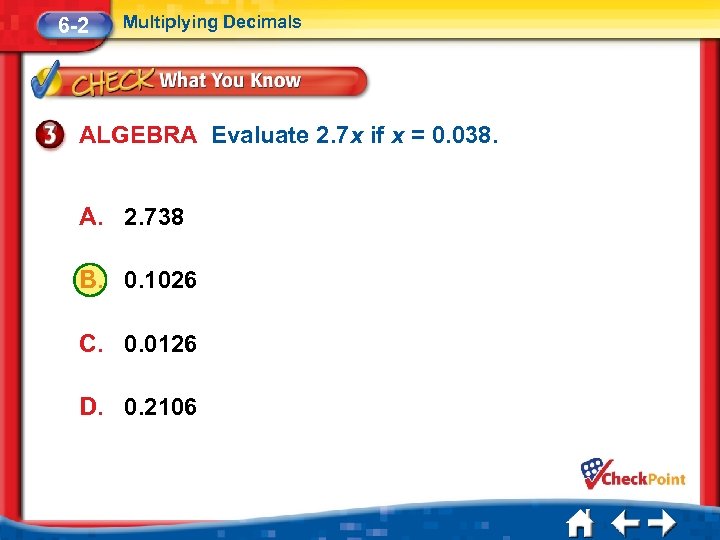 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals ALGEBRA Evaluate 2. 7 x if x = 0. 038. A. 2. 738 B. 0. 1026 C. 0. 0126 D. 0. 2106
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals ALGEBRA Evaluate 2. 7 x if x = 0. 038. A. 2. 738 B. 0. 1026 C. 0. 0126 D. 0. 2106
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Carmen earns $14. 60 per hour as a painter’s helper. She worked a total of 15. 75 hours one week. How much money did she earn? Estimate 14. 60 × 15. 75 $14. 60 × 15. 75 7300 10220 7300 + 1460 229. 9500 15 × 16 or 240 two decimal places
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Carmen earns $14. 60 per hour as a painter’s helper. She worked a total of 15. 75 hours one week. How much money did she earn? Estimate 14. 60 × 15. 75 $14. 60 × 15. 75 7300 10220 7300 + 1460 229. 9500 15 × 16 or 240 two decimal places
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Answer: So, Carmen earned $229. 95. Check for Reasonableness Compare $229. 95 to the estimate. $229. 95 is about $240.
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Answer: So, Carmen earned $229. 95. Check for Reasonableness Compare $229. 95 to the estimate. $229. 95 is about $240.
 6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Alex went shopping for 6. 5 hours and spent $32. 50 per hour. How much did she spend? A. $211. 25 B. $225 C. $250. 25 D. $211. 50
6 -2 Multiplying Decimals Alex went shopping for 6. 5 hours and spent $32. 50 per hour. How much did she spend? A. $211. 25 B. $225 C. $250. 25 D. $211. 50

 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -2) Main Idea California Standards Example 1: Problem-Solving Strategy
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -2) Main Idea California Standards Example 1: Problem-Solving Strategy
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers (over Lesson 6 -2) Find 75. 4 × 2. 9. A. 150. 36 B. 77. 36 C. 125 D. 218. 66
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers (over Lesson 6 -2) Find 75. 4 × 2. 9. A. 150. 36 B. 77. 36 C. 125 D. 218. 66
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers (over Lesson 6 -2) Find 0. 05 × 0. 123. A. 0. 15 B. 0. 00615 C. 0. 00506 D. 1
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers (over Lesson 6 -2) Find 0. 05 × 0. 123. A. 0. 15 B. 0. 00615 C. 0. 00506 D. 1
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers (over Lesson 6 -2) Evaluate 2. 5 y if y = 4. 8. A. 4. 8 B. 10. 48 C. 8. 5 D. 12
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers (over Lesson 6 -2) Evaluate 2. 5 y if y = 4. 8. A. 4. 8 B. 10. 48 C. 8. 5 D. 12
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers (over Lesson 6 -2) Selam makes $6. 75 an hour. Last week, she worked 12. 4 hours. How much did she earn? A. $36. 75 B. $48. 55 C. $48. 50 D. $83. 70
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers (over Lesson 6 -2) Selam makes $6. 75 an hour. Last week, she worked 12. 4 hours. How much did she earn? A. $36. 75 B. $48. 55 C. $48. 50 D. $83. 70
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers • I will solve problems by determining reasonable answers.
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers • I will solve problems by determining reasonable answers.
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Standard 5 MR 3. 1 Evaluate the reasonableness of the solution in the context of the original situation. Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results.
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Standard 5 MR 3. 1 Evaluate the reasonableness of the solution in the context of the original situation. Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results.
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers For their science project, Stephanie and Angel need to know about how much more a blue whale weighs in pounds than a humpback whale. They have learned that there are 2, 000 pounds in one ton. While doing research, they found a table that shows the weights of whales in tons.
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers For their science project, Stephanie and Angel need to know about how much more a blue whale weighs in pounds than a humpback whale. They have learned that there are 2, 000 pounds in one ton. While doing research, they found a table that shows the weights of whales in tons.
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Understand What facts do you know? • There are 2, 000 pounds in one ton. • A blue whale weighs 151. 0 tons. • A humpback whale weighs 38. 1 tons. What do you need to find? • A reasonable estimate of the difference in the weight of a blue whale and a humpback whale.
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Understand What facts do you know? • There are 2, 000 pounds in one ton. • A blue whale weighs 151. 0 tons. • A humpback whale weighs 38. 1 tons. What do you need to find? • A reasonable estimate of the difference in the weight of a blue whale and a humpback whale.
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Plan Estimate to find the weight of each whale in pounds and then subtract to find a reasonable estimate of the difference.
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Plan Estimate to find the weight of each whale in pounds and then subtract to find a reasonable estimate of the difference.
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Solve Blue whale: 2, 000 × 150 × 151 300, 000 Humpback whale: 2, 000 × 38. 1 × 40 80, 000 300, 000 – 80, 000 = 220, 000 Answer: A reasonable estimate for the difference in the weight of a blue whale and a humpback whale is 220, 000 pounds.
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Solve Blue whale: 2, 000 × 150 × 151 300, 000 Humpback whale: 2, 000 × 38. 1 × 40 80, 000 300, 000 – 80, 000 = 220, 000 Answer: A reasonable estimate for the difference in the weight of a blue whale and a humpback whale is 220, 000 pounds.
 6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Check Look back at the problem. A blue whale weighs about 150 – 40 or 110 more tons than a humpback whale. This is equal to 110 × 2, 000 or 220, 000 pounds. So the answer is reasonable.
6 -3 Problem-Solving Strategy: Reasonable Answers Check Look back at the problem. A blue whale weighs about 150 – 40 or 110 more tons than a humpback whale. This is equal to 110 × 2, 000 or 220, 000 pounds. So the answer is reasonable.

 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -3) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Example 1: Divide a Decimal by a 1 -Digit Number Example 2: Divide a Decimal by a 2 -Digit Number Example 3: Real-World Example
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -3) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Example 1: Divide a Decimal by a 1 -Digit Number Example 2: Divide a Decimal by a 2 -Digit Number Example 3: Real-World Example
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Lesson 6 -3) Determine a reasonable answer. Mr. Nieto has 63. 75 yards of fencing. How many feet of fencing is that? A. 127. 50 ft B. 191. 25 ft C. 255 ft D. 33. 75 ft
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Lesson 6 -3) Determine a reasonable answer. Mr. Nieto has 63. 75 yards of fencing. How many feet of fencing is that? A. 127. 50 ft B. 191. 25 ft C. 255 ft D. 33. 75 ft
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Lesson 6 -3) Cafeteria workers made 23. 5 gallons of punch for an awards banquet. They are serving the punch in 1 -quart pitchers. How many containers do they need for all the punch? (1 gal = 4 qt) A. 11. 75 pitchers B. 40 pitchers C. 4 pitchers D. 94 pitchers
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers (over Lesson 6 -3) Cafeteria workers made 23. 5 gallons of punch for an awards banquet. They are serving the punch in 1 -quart pitchers. How many containers do they need for all the punch? (1 gal = 4 qt) A. 11. 75 pitchers B. 40 pitchers C. 4 pitchers D. 94 pitchers
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers • I will divide decimals by whole numbers. • quotient
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers • I will divide decimals by whole numbers. • quotient
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results.
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results.
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 2 Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multidigit divisors.
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 2 Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multidigit divisors.
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 7. 2 ÷ 3. Estimate 7. 2 ÷ 3 2. 4 3 7. 2 – 6 12 – 1 2 0 6 ÷ 3 or about 2
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 7. 2 ÷ 3. Estimate 7. 2 ÷ 3 2. 4 3 7. 2 – 6 12 – 1 2 0 6 ÷ 3 or about 2
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Answer: 7. 2 ÷ 3 = 2. 4 Check Compared to the estimate, the quotient is reasonable.
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Answer: 7. 2 ÷ 3 = 2. 4 Check Compared to the estimate, the quotient is reasonable.
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 6. 4 ÷ 4. A. 8 B. 16 C. 1. 6 D. 0. 8
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 6. 4 ÷ 4. A. 8 B. 16 C. 1. 6 D. 0. 8
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 6. 6 ÷ 15. Estimate 6. 6 ÷ 15 0. 44 15 6. 60 – 0 66 – 6 0 60 – 60 0 8 ÷ 16 or about 0. 5
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 6. 6 ÷ 15. Estimate 6. 6 ÷ 15 0. 44 15 6. 60 – 0 66 – 6 0 60 – 60 0 8 ÷ 16 or about 0. 5
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Answer: 6. 6 ÷ 15 = 0. 44 Check Compared to the estimate, the quotient is reasonable.
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Answer: 6. 6 ÷ 15 = 0. 44 Check Compared to the estimate, the quotient is reasonable.
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 8. 8 ÷ 16. A. 5. 5 B. 0. 55 C. 0. 22 D. 2. 2
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Find 8. 8 ÷ 16. A. 5. 5 B. 0. 55 C. 0. 22 D. 2. 2
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers During a science experiment, Nita measured the mass of four unknown samples. Her data is shown below. What is the mean mass in grams of the four samples?
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers During a science experiment, Nita measured the mass of four unknown samples. Her data is shown below. What is the mean mass in grams of the four samples?
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers First, add all the data together. 6. 23 5. 81 5. 93 + 6. 47 24. 44 Divide by the number of addends to find the mean mass. 6. 11 4 24. 44 Answer: So, the mean mass of Nita’s samples is 6. 11 grams.
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers First, add all the data together. 6. 23 5. 81 5. 93 + 6. 47 24. 44 Divide by the number of addends to find the mean mass. 6. 11 4 24. 44 Answer: So, the mean mass of Nita’s samples is 6. 11 grams.
 6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Greta bought 4 pairs of socks for $25. 36. If each pair of socks costs the same amount, how much was each pair? A. $6. 34 B. $6. 00 C. $4. 63 D. $3. 64
6 -4 Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Greta bought 4 pairs of socks for $25. 36. If each pair of socks costs the same amount, how much was each pair? A. $6. 34 B. $6. 00 C. $4. 63 D. $3. 64

 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -4) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Example 1: Divide by Decimals Example 2: Zeros in the Quotient and Dividend Example 3: Zeros in the Quotient and Dividend Example 4: Round Quotients
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -4) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Example 1: Divide by Decimals Example 2: Zeros in the Quotient and Dividend Example 3: Zeros in the Quotient and Dividend Example 4: Round Quotients
 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals (over Lesson 6 -4) Find 27. 09 ÷ 9. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. A. 7. 1 B. 4 C. 3 D. 7
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals (over Lesson 6 -4) Find 27. 09 ÷ 9. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. A. 7. 1 B. 4 C. 3 D. 7
 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals (over Lesson 6 -4) Find 378. 5 ÷ 5. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. A. 75. 7 B. 75 C. 35. 5 D. 102
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals (over Lesson 6 -4) Find 378. 5 ÷ 5. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. A. 75. 7 B. 75 C. 35. 5 D. 102
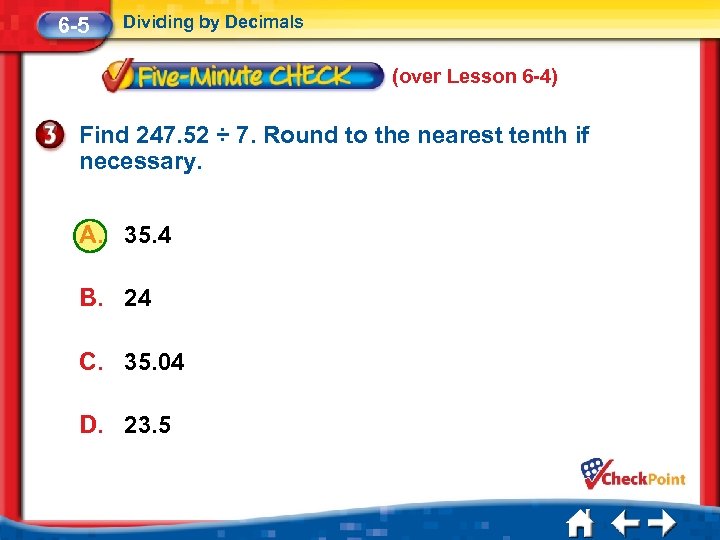 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals (over Lesson 6 -4) Find 247. 52 ÷ 7. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. A. 35. 4 B. 24 C. 35. 04 D. 23. 5
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals (over Lesson 6 -4) Find 247. 52 ÷ 7. Round to the nearest tenth if necessary. A. 35. 4 B. 24 C. 35. 04 D. 23. 5
 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals (over Lesson 6 -4) Find the mean for the following set of data: 7. 8, 9. 02, 2. 62. A. 4. 5 B. 4. 45 C. 6. 48 D. 5. 55
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals (over Lesson 6 -4) Find the mean for the following set of data: 7. 8, 9. 02, 2. 62. A. 4. 5 B. 4. 45 C. 6. 48 D. 5. 55
 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals • I will divide decimals by decimals. • power
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals • I will divide decimals by decimals. • power
 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results.
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; add with negative integers; subtract positive integers from negative integers; and verify the reasonableness of results.
 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Standard 5 NS 2. 2 Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multidigit divisors.
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Standard 5 NS 2. 2 Demonstrate proficiency with division, including division with positive decimals and long division with multidigit divisors.
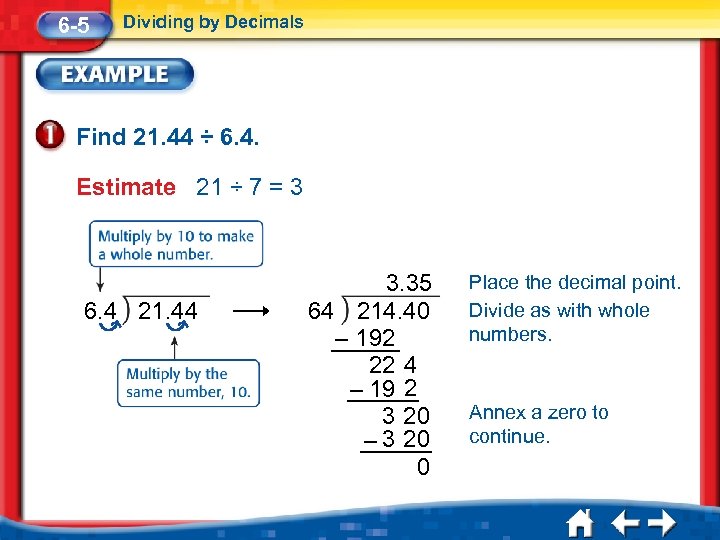 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 21. 44 ÷ 6. 4. Estimate 21 ÷ 7 = 3 6. 4 21. 44 3. 35 64 214. 40 – 192 22 4 – 19 2 3 20 – 3 20 0 Place the decimal point. Divide as with whole numbers. Annex a zero to continue.
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 21. 44 ÷ 6. 4. Estimate 21 ÷ 7 = 3 6. 4 21. 44 3. 35 64 214. 40 – 192 22 4 – 19 2 3 20 – 3 20 0 Place the decimal point. Divide as with whole numbers. Annex a zero to continue.
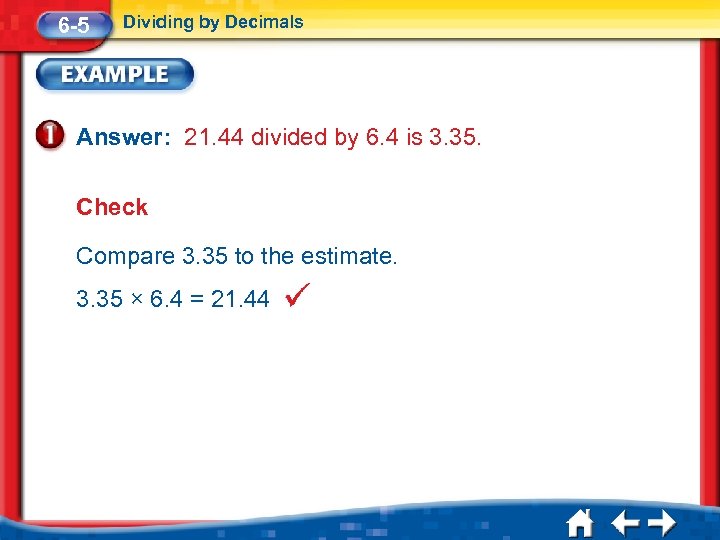 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Answer: 21. 44 divided by 6. 4 is 3. 35. Check Compare 3. 35 to the estimate. 3. 35 × 6. 4 = 21. 44
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Answer: 21. 44 divided by 6. 4 is 3. 35. Check Compare 3. 35 to the estimate. 3. 35 × 6. 4 = 21. 44
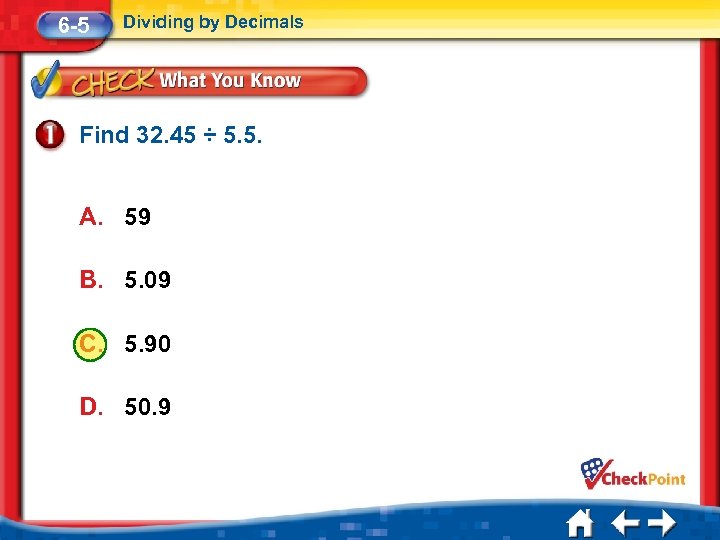 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 32. 45 ÷ 5. 5. A. 59 B. 5. 09 C. 5. 90 D. 50. 9
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 32. 45 ÷ 5. 5. A. 59 B. 5. 09 C. 5. 90 D. 50. 9
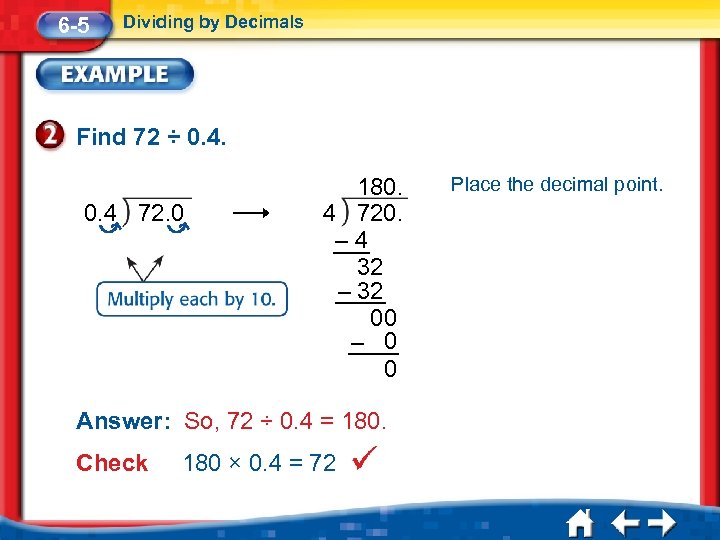 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 72 ÷ 0. 4 72. 0 180. 4 720. – 4 32 – 32 00 – 0 0 Answer: So, 72 ÷ 0. 4 = 180. Check 180 × 0. 4 = 72 Place the decimal point.
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 72 ÷ 0. 4 72. 0 180. 4 720. – 4 32 – 32 00 – 0 0 Answer: So, 72 ÷ 0. 4 = 180. Check 180 × 0. 4 = 72 Place the decimal point.
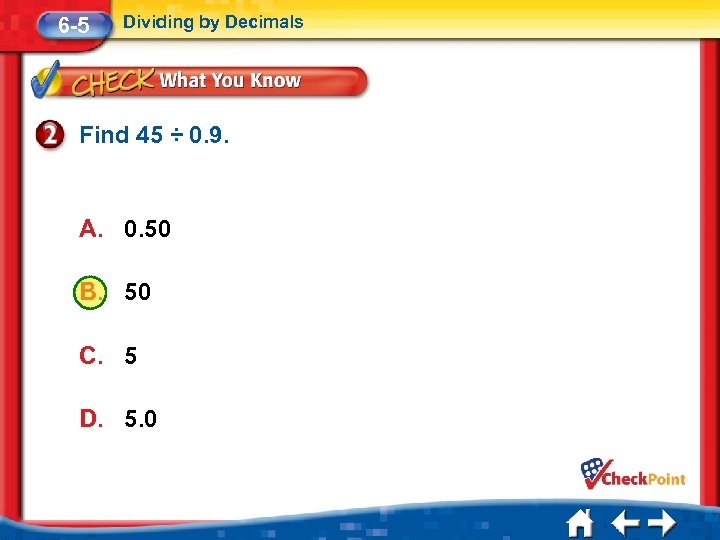 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 45 ÷ 0. 9. A. 0. 50 B. 50 C. 5 D. 5. 0
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 45 ÷ 0. 9. A. 0. 50 B. 50 C. 5 D. 5. 0
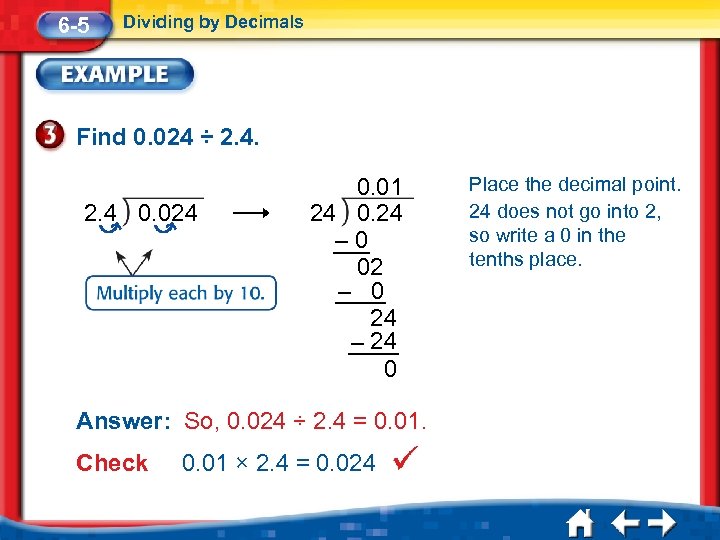 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 0. 024 ÷ 2. 4 0. 024 0. 01 24 0. 24 – 0 02 – 0 24 – 24 0 Answer: So, 0. 024 ÷ 2. 4 = 0. 01. Check 0. 01 × 2. 4 = 0. 024 Place the decimal point. 24 does not go into 2, so write a 0 in the tenths place.
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 0. 024 ÷ 2. 4 0. 024 0. 01 24 0. 24 – 0 02 – 0 24 – 24 0 Answer: So, 0. 024 ÷ 2. 4 = 0. 01. Check 0. 01 × 2. 4 = 0. 024 Place the decimal point. 24 does not go into 2, so write a 0 in the tenths place.
 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 0. 036 ÷ 1. 2. A. 0. 03 B. 3 C. 0. 3 D. 1. 2
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Find 0. 036 ÷ 1. 2. A. 0. 03 B. 3 C. 0. 3 D. 1. 2
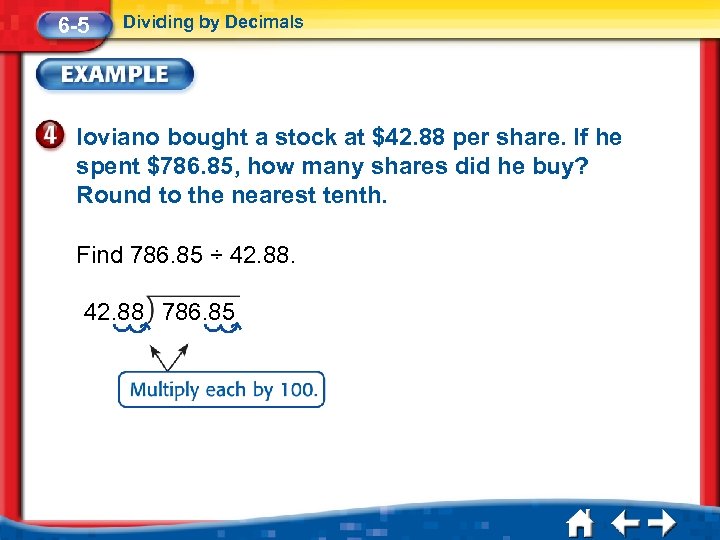 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Ioviano bought a stock at $42. 88 per share. If he spent $786. 85, how many shares did he buy? Round to the nearest tenth. Find 786. 85 ÷ 42. 88 786. 85
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals Ioviano bought a stock at $42. 88 per share. If he spent $786. 85, how many shares did he buy? Round to the nearest tenth. Find 786. 85 ÷ 42. 88 786. 85
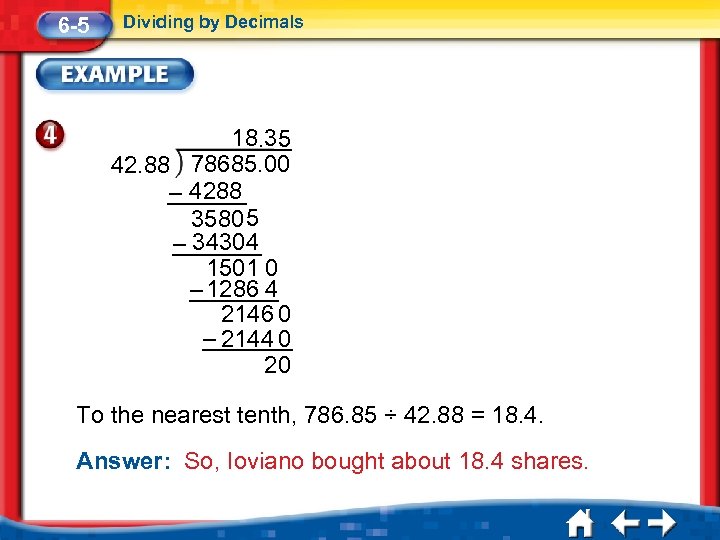 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals 18. 35 42. 88 78685. 00 – 4288 35805 – 34304 1501 0 – 1286 4 2146 0 – 2144 0 20 To the nearest tenth, 786. 85 ÷ 42. 88 = 18. 4. Answer: So, Ioviano bought about 18. 4 shares.
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals 18. 35 42. 88 78685. 00 – 4288 35805 – 34304 1501 0 – 1286 4 2146 0 – 2144 0 20 To the nearest tenth, 786. 85 ÷ 42. 88 = 18. 4. Answer: So, Ioviano bought about 18. 4 shares.
 6 -5 Dividing by Decimals The Martin family drove 354. 5 miles for a camping trip and used 12. 3 gallons of gas. How many miles did they get per gallon of gas? Round to the nearest tenth. A. 2. 8 miles per gallon B. 28. 2 miles per gallon C. 28. 8 miles per gallon D. 288. 2 miles per gallon
6 -5 Dividing by Decimals The Martin family drove 354. 5 miles for a camping trip and used 12. 3 gallons of gas. How many miles did they get per gallon of gas? Round to the nearest tenth. A. 2. 8 miles per gallon B. 28. 2 miles per gallon C. 28. 8 miles per gallon D. 288. 2 miles per gallon

 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -5) Main Idea California Standards Example 1: Problem-Solving Investigation
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -5) Main Idea California Standards Example 1: Problem-Solving Investigation
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy (over Lesson 6 -5) Find 24. 36 ÷ 4. 2. A. 5. 8 B. 5. 66 C. 4 D. 6. 18
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy (over Lesson 6 -5) Find 24. 36 ÷ 4. 2. A. 5. 8 B. 5. 66 C. 4 D. 6. 18
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy (over Lesson 6 -5) Find 15. 39 ÷ 0. 05. A. 128. 5 B. 3 C. 12 D. 307. 8
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy (over Lesson 6 -5) Find 15. 39 ÷ 0. 05. A. 128. 5 B. 3 C. 12 D. 307. 8
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy (over Lesson 6 -5) Find 0. 648 ÷ 0. 12. A. 0. 85 B. 1. 48 C. 5. 4 D. 5. 6
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy (over Lesson 6 -5) Find 0. 648 ÷ 0. 12. A. 0. 85 B. 1. 48 C. 5. 4 D. 5. 6
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy (over Lesson 6 -5) Find 0. 782 ÷ 3. 4. A. 0. 23 B. 0. 015 C. 4 D. 12
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy (over Lesson 6 -5) Find 0. 782 ÷ 3. 4. A. 0. 23 B. 0. 015 C. 4 D. 12
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy • I will choose the best strategy to solve a problem.
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy • I will choose the best strategy to solve a problem.
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Standard 5 MR 1. 1 Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; . . . and verify the reasonableness of results.
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Standard 5 MR 1. 1 Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing patterns. Standard 5 NS 2. 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide with decimals; . . . and verify the reasonableness of results.
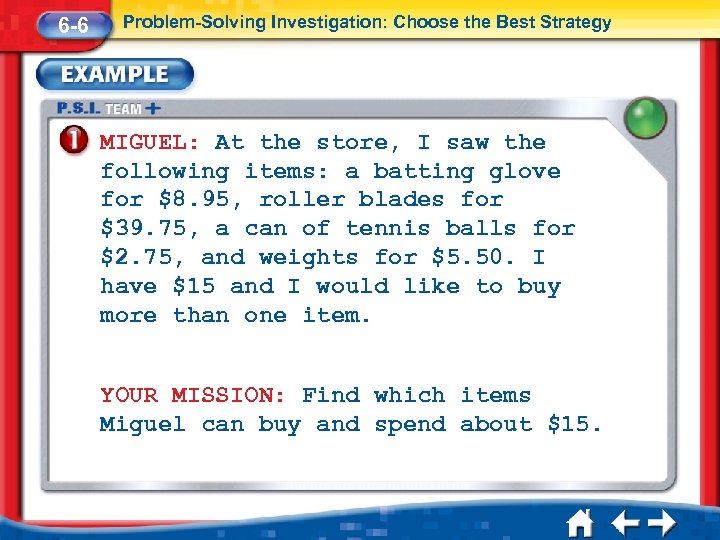 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy MIGUEL: At the store, I saw the following items: a batting glove for $8. 95, roller blades for $39. 75, a can of tennis balls for $2. 75, and weights for $5. 50. I have $15 and I would like to buy more than one item. YOUR MISSION: Find which items Miguel can buy and spend about $15.
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy MIGUEL: At the store, I saw the following items: a batting glove for $8. 95, roller blades for $39. 75, a can of tennis balls for $2. 75, and weights for $5. 50. I have $15 and I would like to buy more than one item. YOUR MISSION: Find which items Miguel can buy and spend about $15.
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Understand What facts do you know? • You know the cost of the items and that Miguel has $15 to spend. What do you need to find? • You need to find which items Miguel can buy.
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Understand What facts do you know? • You know the cost of the items and that Miguel has $15 to spend. What do you need to find? • You need to find which items Miguel can buy.
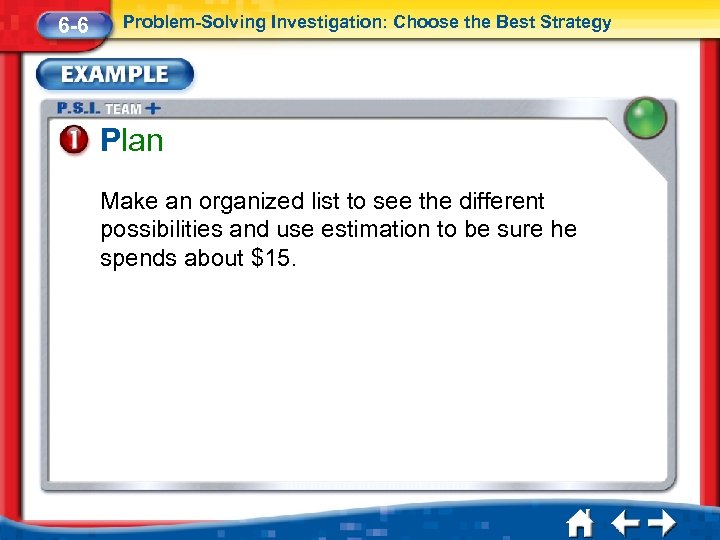 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Plan Make an organized list to see the different possibilities and use estimation to be sure he spends about $15.
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Plan Make an organized list to see the different possibilities and use estimation to be sure he spends about $15.
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Solve Since the roller blades cost more than $15, you can eliminate the roller blades. The batting glove is about $9, the weights are about $6, and the can of tennis balls is about $3. Start with the batting glove: • 1 glove + 1 weights ≈ $9 + $6 or $15 • 1 glove + 2 cans of tennis balls ≈ $9 + $6 or $15
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Solve Since the roller blades cost more than $15, you can eliminate the roller blades. The batting glove is about $9, the weights are about $6, and the can of tennis balls is about $3. Start with the batting glove: • 1 glove + 1 weights ≈ $9 + $6 or $15 • 1 glove + 2 cans of tennis balls ≈ $9 + $6 or $15
 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Solve List other combinations that contain the weights: • 2 weights + 1 can of tennis balls ≈ $12 + $3 or $15 • 1 weights + 3 cans of tennis balls ≈ $6 + $9 or $15 List the remaining combinations that contain only tennis balls: • 5 cans of tennis balls ≈ $15
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Solve List other combinations that contain the weights: • 2 weights + 1 can of tennis balls ≈ $12 + $3 or $15 • 1 weights + 3 cans of tennis balls ≈ $6 + $9 or $15 List the remaining combinations that contain only tennis balls: • 5 cans of tennis balls ≈ $15
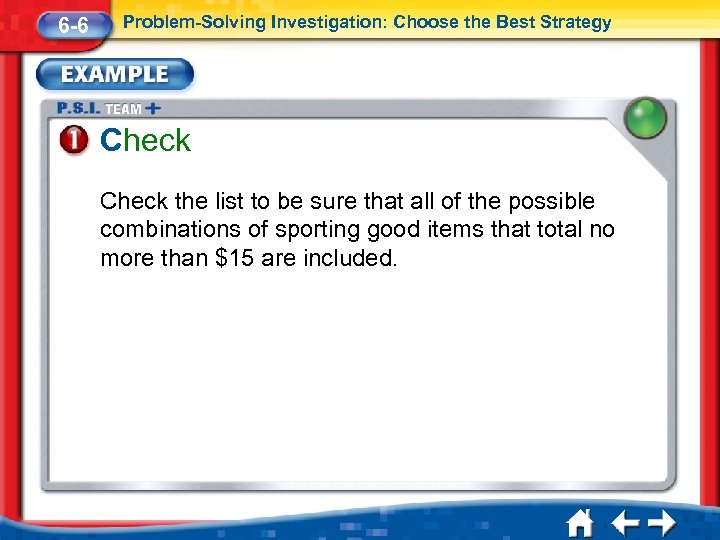 6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Check the list to be sure that all of the possible combinations of sporting good items that total no more than $15 are included.
6 -6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Choose the Best Strategy Check the list to be sure that all of the possible combinations of sporting good items that total no more than $15 are included.

 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -6) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Example 1: Estimate Using Compatible Numbers Example 2: Estimate Using Compatible Numbers 1 Example 3: Estimate by Rounding to 0, 2 , or 1 Example 4: Estimate With Mixed Numbers
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -6) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Example 1: Estimate Using Compatible Numbers Example 2: Estimate Using Compatible Numbers 1 Example 3: Estimate by Rounding to 0, 2 , or 1 Example 4: Estimate With Mixed Numbers
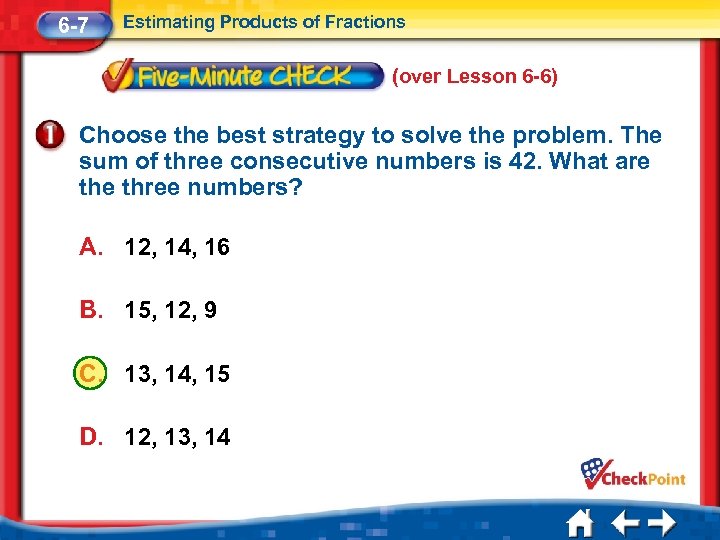 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions (over Lesson 6 -6) Choose the best strategy to solve the problem. The sum of three consecutive numbers is 42. What are three numbers? A. 12, 14, 16 B. 15, 12, 9 C. 13, 14, 15 D. 12, 13, 14
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions (over Lesson 6 -6) Choose the best strategy to solve the problem. The sum of three consecutive numbers is 42. What are three numbers? A. 12, 14, 16 B. 15, 12, 9 C. 13, 14, 15 D. 12, 13, 14
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions • I will estimate products of fractions using compatible numbers and rounding. • compatible numbers
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions • I will estimate products of fractions using compatible numbers and rounding. • compatible numbers
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Standard 5 MR 2. 5 Indicate the relative advantages of exact and approximate solutions to problems and give answers to a specified degree of accuracy. Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Standard 5 MR 2. 5 Indicate the relative advantages of exact and approximate solutions to problems and give answers to a specified degree of accuracy. Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate 1 × 16. 5 1 × 16 means 1 of 16. 5 5 Find a multiple of 5 that is close to 16. 1 × 16 5 1 × 15 = 3 5 Answer: So, 1 × 15 5 15 and 5 are compatible numbers since 15 ÷ 5 = 3 1 × 16 is about 3. 5
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate 1 × 16. 5 1 × 16 means 1 of 16. 5 5 Find a multiple of 5 that is close to 16. 1 × 16 5 1 × 15 = 3 5 Answer: So, 1 × 15 5 15 and 5 are compatible numbers since 15 ÷ 5 = 3 1 × 16 is about 3. 5
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate A. 2 B. 3 C. D. 1 22 1 24 1 × 19. 9
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate A. 2 B. 3 C. D. 1 22 1 24 1 × 19. 9
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate 3 × 23. 4 Estimate 1 × 23 first. 4 Find a multiple of 4 that is close to 23. 1 × 23 4 1 × 24 = 6 4 1 × 24 4 Use 24 since 24 and 4 are compatible numbers. 24 ÷ 4 = 6
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate 3 × 23. 4 Estimate 1 × 23 first. 4 Find a multiple of 4 that is close to 23. 1 × 23 4 1 × 24 = 6 4 1 × 24 4 Use 24 since 24 and 4 are compatible numbers. 24 ÷ 4 = 6
 6 -7 If Estimating Products of Fractions 1 3 of 24 is 6, then of 24 is 6 × 3 or 18. 4 4 Answer: So, 3 of 23 is about 18. 4
6 -7 If Estimating Products of Fractions 1 3 of 24 is 6, then of 24 is 6 × 3 or 18. 4 4 Answer: So, 3 of 23 is about 18. 4
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate A. 17 B. 18 C. 17 D. 20 2 5 3 × 29. 5
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate A. 17 B. 18 C. 17 D. 20 2 5 3 × 29. 5
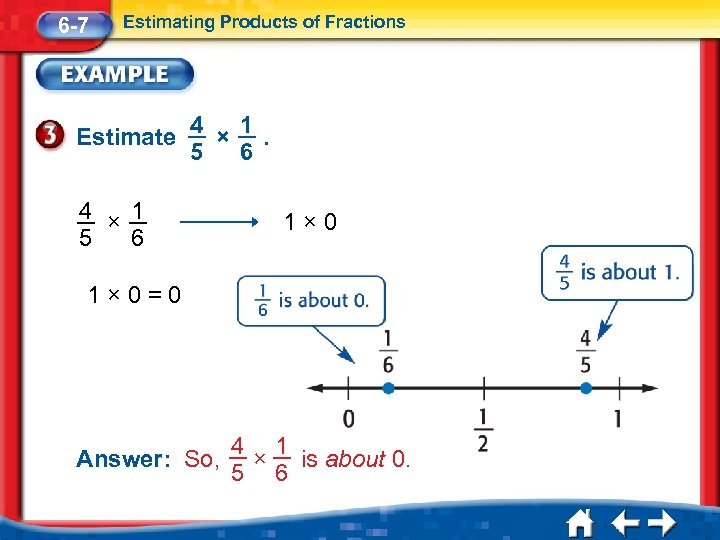 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate 4 1 ×. 5 6 4 × 1 6 5 1× 0=0 Answer: So, 4 1 × is about 0. 5 6
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate 4 1 ×. 5 6 4 × 1 6 5 1× 0=0 Answer: So, 4 1 × is about 0. 5 6
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate A. 1 3 8 B. 2 C. 1 2 D. 1 26 5 3 ×. 6 8
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate A. 1 3 8 B. 2 C. 1 2 D. 1 26 5 3 ×. 6 8
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate the area of the rectangle. Round each mixed number to the nearest whole number.
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate the area of the rectangle. Round each mixed number to the nearest whole number.
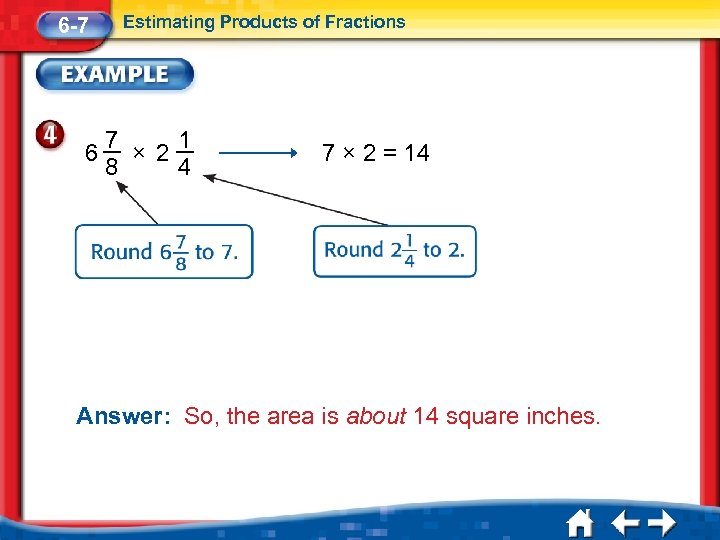 6 -7 6 Estimating Products of Fractions 1 7 × 2 4 8 7 × 2 = 14 Answer: So, the area is about 14 square inches.
6 -7 6 Estimating Products of Fractions 1 7 × 2 4 8 7 × 2 = 14 Answer: So, the area is about 14 square inches.
 6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate the area of a rectangle with a width of 1 4 9 in. and a length of 3 in. 8 5 A. 30 in 2 B. 27 in 2 C. 40 in 2 D. 36 in 2
6 -7 Estimating Products of Fractions Estimate the area of a rectangle with a width of 1 4 9 in. and a length of 3 in. 8 5 A. 30 in 2 B. 27 in 2 C. 40 in 2 D. 36 in 2

 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -7) Main Idea California Standards Key Concept: Multiply Fractions Click here to continue the Lesson Menu
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -7) Main Idea California Standards Key Concept: Multiply Fractions Click here to continue the Lesson Menu
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Example 1: Multiply Fractions Example 2: Multiply Fractions and Whole Numbers Example 3: Simplify Before Multiplying Example 4: Evaluate Expressions
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Example 1: Multiply Fractions Example 2: Multiply Fractions and Whole Numbers Example 3: Simplify Before Multiplying Example 4: Evaluate Expressions
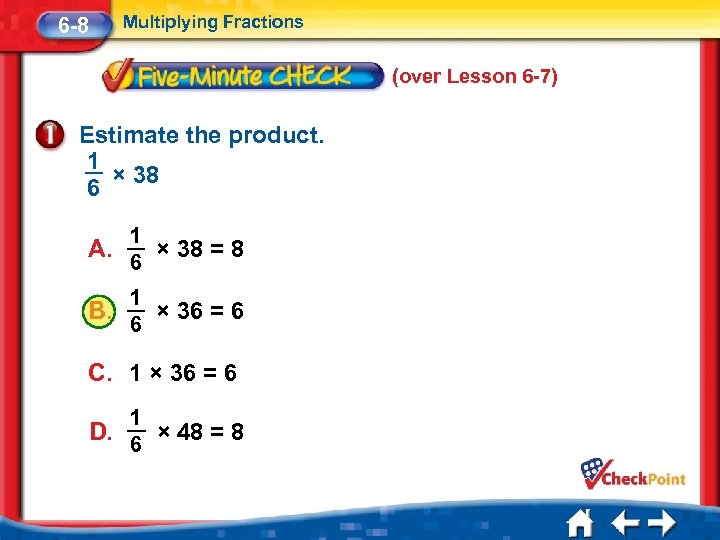 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions (over Lesson 6 -7) Estimate the product. 1 × 38 6 1 A. × 38 = 8 6 B. 1 × 36 = 6 6 C. 1 × 36 = 6 D. 1 × 48 = 8 6
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions (over Lesson 6 -7) Estimate the product. 1 × 38 6 1 A. × 38 = 8 6 B. 1 × 36 = 6 6 C. 1 × 36 = 6 D. 1 × 48 = 8 6
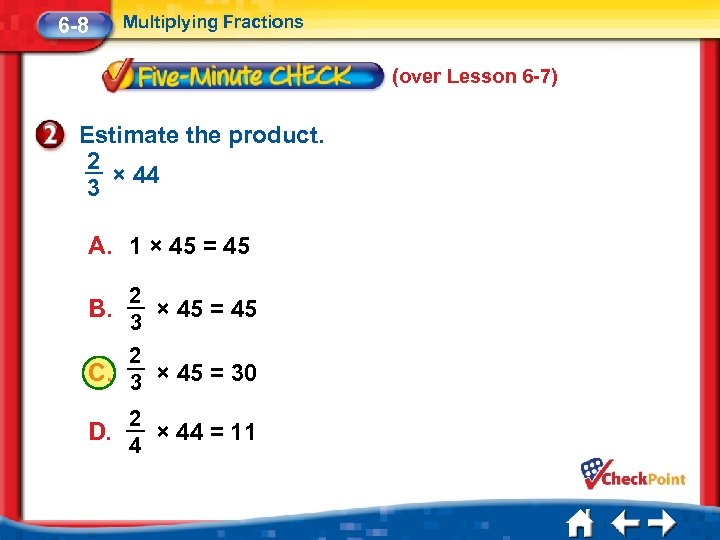 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions (over Lesson 6 -7) Estimate the product. 2 × 44 3 A. 1 × 45 = 45 2 B. × 45 = 45 3 2 C. 3 × 45 = 30 D. 2 × 44 = 11 4
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions (over Lesson 6 -7) Estimate the product. 2 × 44 3 A. 1 × 45 = 45 2 B. × 45 = 45 3 2 C. 3 × 45 = 30 D. 2 × 44 = 11 4
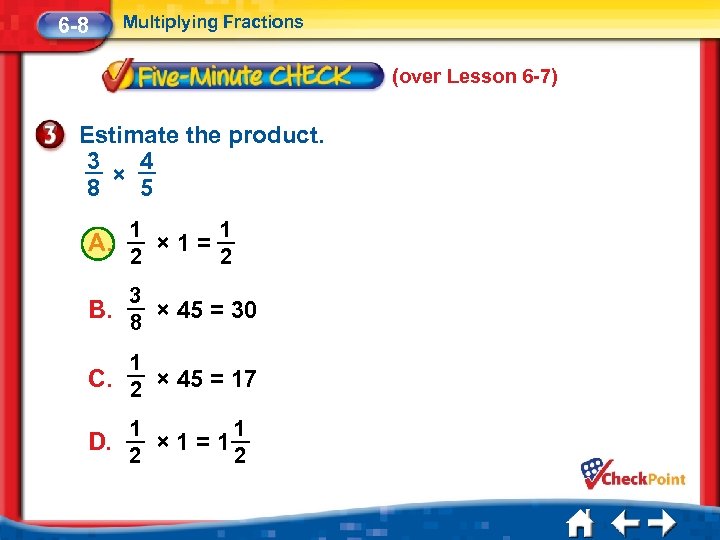 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions (over Lesson 6 -7) Estimate the product. 3 4 × 8 5 A. 1 1 × 1= 2 2 3 B. × 45 = 30 8 1 C. 2 × 45 = 17 D. 1 1 × 1=1 2 2
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions (over Lesson 6 -7) Estimate the product. 3 4 × 8 5 A. 1 1 × 1= 2 2 3 B. × 45 = 30 8 1 C. 2 × 45 = 17 D. 1 1 × 1=1 2 2
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions (over Lesson 6 -7) 1 5 A pool is 25 4 feet wide and 39 6 feet long. Estimate the area. A. 25 × 40 = 975 ft 2 B. 25 × 40 = 1, 000 ft 2 C. 26 × 40 = 1, 040 ft 2 D. 25 × 4 = 100 ft 2
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions (over Lesson 6 -7) 1 5 A pool is 25 4 feet wide and 39 6 feet long. Estimate the area. A. 25 × 40 = 975 ft 2 B. 25 × 40 = 1, 000 ft 2 C. 26 × 40 = 1, 040 ft 2 D. 25 × 4 = 100 ft 2
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions • I will multiply fractions.
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions • I will multiply fractions.
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Find 1 1 ×. 5 6 1 × 1 6 5 = 1× 1 5× 6 1 = 30 Answer: 1 30 Multiply the numerators. Multiply the denominators. Simplify.
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Find 1 1 ×. 5 6 1 × 1 6 5 = 1× 1 5× 6 1 = 30 Answer: 1 30 Multiply the numerators. Multiply the denominators. Simplify.
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Find 1 1 ×. 7 2 2 14 1 B. 7 A. C. 1 2 1 D. 14
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Find 1 1 ×. 7 2 2 14 1 B. 7 A. C. 1 2 1 D. 14
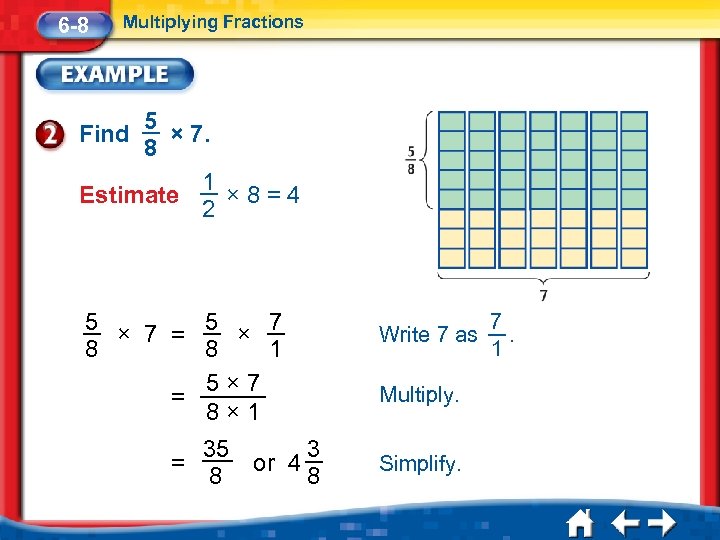 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions 5 × 7. 8 1 Estimate × 8=4 2 Find 5 × 7 = 1 8 8 5× 7 = 8× 1 = 35 3 or 4 8 8 Write 7 as Multiply. Simplify. 7. 1
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions 5 × 7. 8 1 Estimate × 8=4 2 Find 5 × 7 = 1 8 8 5× 7 = 8× 1 = 35 3 or 4 8 8 Write 7 as Multiply. Simplify. 7. 1
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Answer: 4 3 8 Check for Reasonableness 4 3 is about 4. 8
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Answer: 4 3 8 Check for Reasonableness 4 3 is about 4. 8
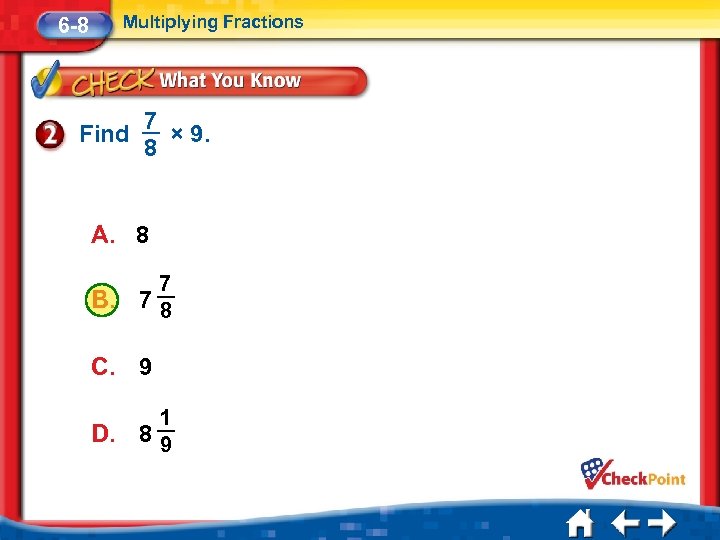 Multiplying Fractions 6 -8 Find 7 × 9. 8 A. 8 B. 7 78 C. 9 D. 1 89
Multiplying Fractions 6 -8 Find 7 × 9. 8 A. 8 B. 7 78 C. 9 D. 1 89
 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions 3 2 ×. 7 9 1 Estimate × 0=0 2 Find 1 3× 2 3 × 2 = 9 7 7× 9 Divide both the numerator and denominator by 3. 3 The numerator and denominator have a common factor, 3. Answer: 2 21 2 = 21 Simplify.
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions 3 2 ×. 7 9 1 Estimate × 0=0 2 Find 1 3× 2 3 × 2 = 9 7 7× 9 Divide both the numerator and denominator by 3. 3 The numerator and denominator have a common factor, 3. Answer: 2 21 2 = 21 Simplify.
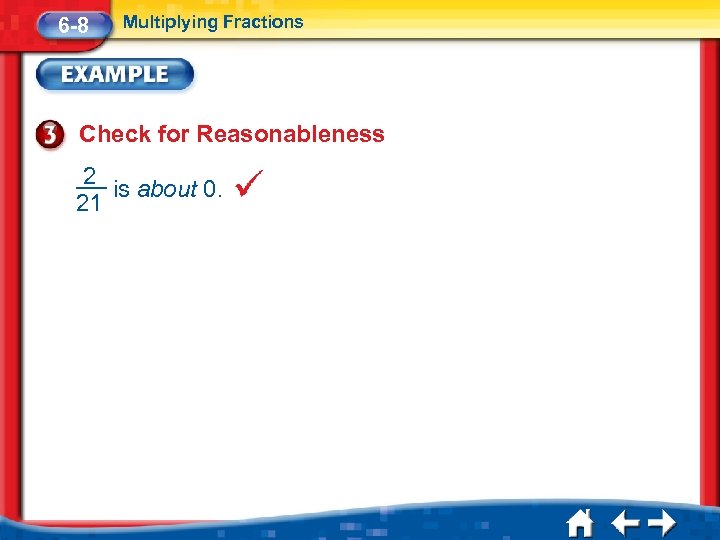 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Check for Reasonableness 2 is about 0. 21
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Check for Reasonableness 2 is about 0. 21
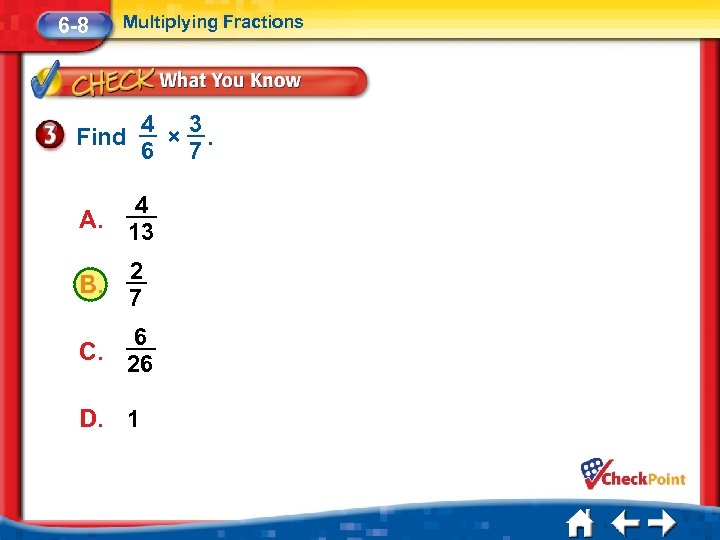 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Find 4 3 ×. 6 7 4 A. 13 B. 2 7 C. 6 26 D. 1
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions Find 4 3 ×. 6 7 4 A. 13 B. 2 7 C. 6 26 D. 1
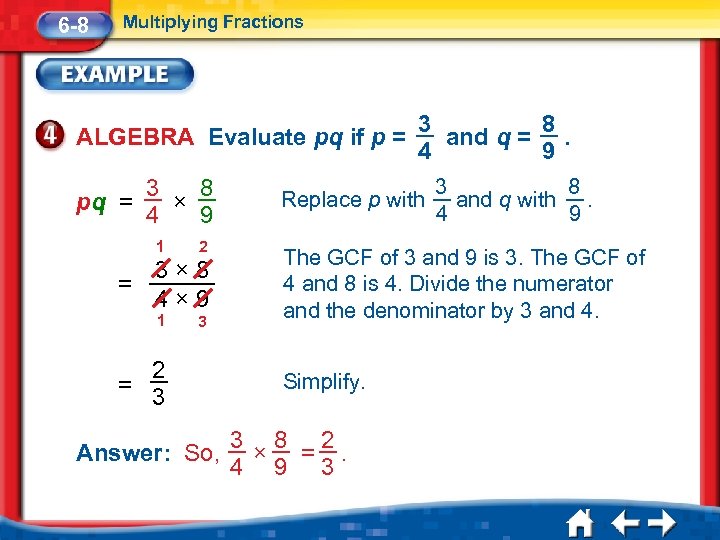 6 -8 Multiplying Fractions ALGEBRA Evaluate pq if p = 3 8 pq = × 4 9 1 2 3 8 and q =. 4 9 Replace p with 3 8 and q with. 4 9 3× 8 = 4× 9 The GCF of 3 and 9 is 3. The GCF of 4 and 8 is 4. Divide the numerator and the denominator by 3 and 4. 2 = 3 Simplify. 1 3 Answer: So, 3 8 2 × =. 4 9 3
6 -8 Multiplying Fractions ALGEBRA Evaluate pq if p = 3 8 pq = × 4 9 1 2 3 8 and q =. 4 9 Replace p with 3 8 and q with. 4 9 3× 8 = 4× 9 The GCF of 3 and 9 is 3. The GCF of 4 and 8 is 4. Divide the numerator and the denominator by 3 and 4. 2 = 3 Simplify. 1 3 Answer: So, 3 8 2 × =. 4 9 3
 Multiplying Fractions 6 -8 ALGEBRA Evaluate gh if g = A. 1 2 B. 1 5 C. 10 50 D. 5 50 2 5 and h =. 5 10
Multiplying Fractions 6 -8 ALGEBRA Evaluate gh if g = A. 1 2 B. 1 5 C. 10 50 D. 5 50 2 5 and h =. 5 10

 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -8) Main Idea California Standards Key Concept: Multiply Mixed Numbers Example 1: Multiply a Fraction and a Mixed Number Example 2: Multiply Mixed Numbers Example 3: Evaluate Expressions
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -8) Main Idea California Standards Key Concept: Multiply Mixed Numbers Example 1: Multiply a Fraction and a Mixed Number Example 2: Multiply Mixed Numbers Example 3: Evaluate Expressions
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -8) Multiply. Write in simplest form. 9 2 × 10 3 A. 4 5 B. 1 3 C. 9 10 D. 3 5
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -8) Multiply. Write in simplest form. 9 2 × 10 3 A. 4 5 B. 1 3 C. 9 10 D. 3 5
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -8) Multiply. Write in simplest form. 4 5 × 5 6 A. 2 3 B. 4 5 C. 1 D. 1 3 2 5
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -8) Multiply. Write in simplest form. 4 5 × 5 6 A. 2 3 B. 4 5 C. 1 D. 1 3 2 5
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -8) Evaluate A. 4 5 B. 1 3 C. 2 3 D. 3 9 3 8 n if n =. Write in simplest form. 4 9
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -8) Evaluate A. 4 5 B. 1 3 C. 2 3 D. 3 9 3 8 n if n =. Write in simplest form. 4 9
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -8) Evaluate 10 n if n = 1 A. 7 2 B. 2 43 C. 7 9 D. 1 3 3. Write in simplest form. 4
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -8) Evaluate 10 n if n = 1 A. 7 2 B. 2 43 C. 7 9 D. 1 3 3. Write in simplest form. 4
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers • I will multiply mixed numbers.
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers • I will multiply mixed numbers.
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 3 1 × 3. 8 3 1 1 Estimate × 3=1 2 2 Find 3 × 10 3 × 31 = 3 3 8 8 1 5 3 × 10 = 8× 3 4 = 1 Answer: 1 4 1 10 Write 3 3 as. 3 Divide 10 and 8 by their GCF, 2. Divide 3 and 3 by their GCF, 3. 1 5 or 1 1 4 4 Simplify. Compare to the estimate.
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 3 1 × 3. 8 3 1 1 Estimate × 3=1 2 2 Find 3 × 10 3 × 31 = 3 3 8 8 1 5 3 × 10 = 8× 3 4 = 1 Answer: 1 4 1 10 Write 3 3 as. 3 Divide 10 and 8 by their GCF, 2. Divide 3 and 3 by their GCF, 3. 1 5 or 1 1 4 4 Simplify. Compare to the estimate.
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 4 2 Find × 2. 5 3 A. 2 B. 2 15 1 22 C. 3 D. 1 32
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 4 2 Find × 2. 5 3 A. 2 B. 2 15 1 22 C. 3 D. 1 32
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 1 times farther from school than 2 1 Elena does. If Elena lives 4 miles from school, 5 how far from school does Belinda live? Belinda lives 1 Elena lives 4 1 1 1 miles from school. Multiply 4 × 1. 5 2 5
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 1 times farther from school than 2 1 Elena does. If Elena lives 4 miles from school, 5 how far from school does Belinda live? Belinda lives 1 Elena lives 4 1 1 1 miles from school. Multiply 4 × 1. 5 2 5
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 1 1 4 × 1 = 21 × 3 2 5 5 2 21 × 3 = 5× 2 = 63 or 6 3 10 10 First, write mixed numbers as improper fractions. Then, multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators. Simplify. Answer: So, Belinda lives 6 3 miles from school. 10
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 1 1 4 × 1 = 21 × 3 2 5 5 2 21 × 3 = 5× 2 = 63 or 6 3 10 10 First, write mixed numbers as improper fractions. Then, multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators. Simplify. Answer: So, Belinda lives 6 3 miles from school. 10
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 1 times the recipe for crispy 4 1 treats. If the recipe calls for 1 cups of butter, how 4 much butter will she need? Mariah is making 4 A. B. C. D. 85 cups 16 1 5 5 cups 16 25 cups 16
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 1 times the recipe for crispy 4 1 treats. If the recipe calls for 1 cups of butter, how 4 much butter will she need? Mariah is making 4 A. B. C. D. 85 cups 16 1 5 5 cups 16 25 cups 16
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers ALGEBRA If y = 3 4 3 and w = 2 , what is the value 5 4 of wy? wy = 2 4 × 3 3 4 5 7 4 3 and y with 3. 5 4 3 15 14 × = 4 5 1 = Replace w with 2 2 21 or 10 1 2 2 1 Answer: 10 2 Divide the numerator and denominator by 2 and 5. Simplify.
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers ALGEBRA If y = 3 4 3 and w = 2 , what is the value 5 4 of wy? wy = 2 4 × 3 3 4 5 7 4 3 and y with 3. 5 4 3 15 14 × = 4 5 1 = Replace w with 2 2 21 or 10 1 2 2 1 Answer: 10 2 Divide the numerator and denominator by 2 and 5. Simplify.
 6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 5 6 ALGEBRA If m = 4 and n = 2 , what is the value 8 7 of mn? A. 185 14 B. 180 14 3 C. 13 14 D. 13
6 -9 Multiplying Mixed Numbers 5 6 ALGEBRA If m = 4 and n = 2 , what is the value 8 7 of mn? A. 185 14 B. 180 14 3 C. 13 14 D. 13

 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -9) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Key Concept: Divide Fractions Example 1: Find Reciprocals Example 2: Find Reciprocals Example 3: Divide by a Fraction Example 4: Divide by a Fraction Example 5: Real-World Example
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -9) Main Idea and Vocabulary California Standards Key Concept: Divide Fractions Example 1: Find Reciprocals Example 2: Find Reciprocals Example 3: Divide by a Fraction Example 4: Divide by a Fraction Example 5: Real-World Example
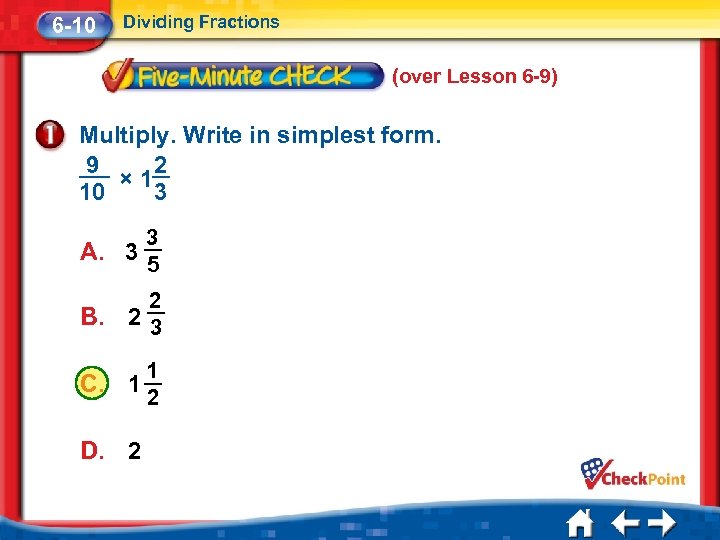 6 -10 Dividing Fractions (over Lesson 6 -9) Multiply. Write in simplest form. 9 2 × 1 10 3 3 A. 3 5 B. 2 23 C. 1 D. 2 1 2
6 -10 Dividing Fractions (over Lesson 6 -9) Multiply. Write in simplest form. 9 2 × 1 10 3 3 A. 3 5 B. 2 23 C. 1 D. 2 1 2
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions (over Lesson 6 -9) Multiply. Write in simplest form. 1 5 5 × 45 6 1 A. 10 5 B. 1 24 2 C. 21 1 2 D. 31 1 2
6 -10 Dividing Fractions (over Lesson 6 -9) Multiply. Write in simplest form. 1 5 5 × 45 6 1 A. 10 5 B. 1 24 2 C. 21 1 2 D. 31 1 2
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions (over Lesson 6 -9) The length of a square sandbox is 4 the area of the sandbox? 7 2 A. 21 9 ft 5 2 B. 23 9 ft 5 2 ft 9 1 2 9 ft 3 C. 21 D. 2 feet. What is 3
6 -10 Dividing Fractions (over Lesson 6 -9) The length of a square sandbox is 4 the area of the sandbox? 7 2 A. 21 9 ft 5 2 B. 23 9 ft 5 2 ft 9 1 2 9 ft 3 C. 21 D. 2 feet. What is 3
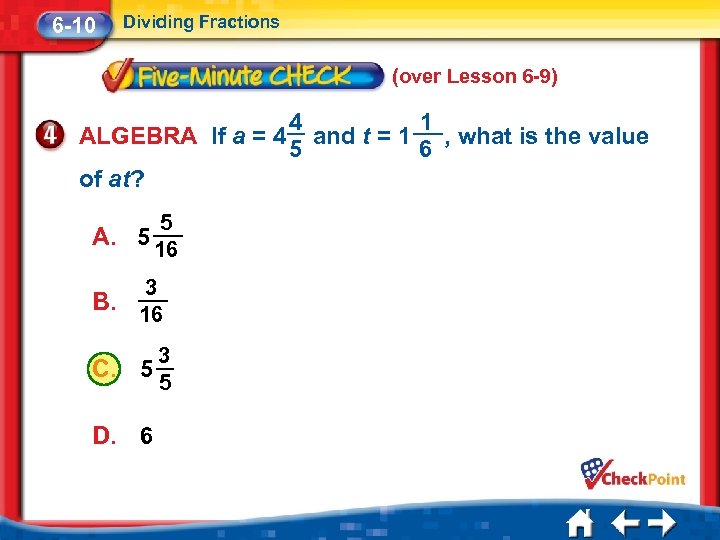 6 -10 Dividing Fractions (over Lesson 6 -9) ALGEBRA If a = 4 of at? 5 A. 5 16 3 B. 16 C. 3 5 5 D. 6 4 1 and t = 1 , what is the value 5 6
6 -10 Dividing Fractions (over Lesson 6 -9) ALGEBRA If a = 4 of at? 5 A. 5 16 3 B. 16 C. 3 5 5 D. 6 4 1 and t = 1 , what is the value 5 6
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions • I will divide fractions. • reciprocal
6 -10 Dividing Fractions • I will divide fractions. • reciprocal
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions
6 -10 Dividing Fractions
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find the reciprocal of 8. Answer: Since, 8 × 1 1 = 1, the reciprocal of 8 is. 8 8
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find the reciprocal of 8. Answer: Since, 8 × 1 1 = 1, the reciprocal of 8 is. 8 8
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find the reciprocal of 6. A. 6 B. 0. 6 C. 6 1 D. 1 6
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find the reciprocal of 6. A. 6 B. 0. 6 C. 6 1 D. 1 6
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions 3 Find the reciprocal of. 5 5 3 Answer: Since, × = 1, the reciprocal 3 5 5 3 of 5 is 3.
6 -10 Dividing Fractions 3 Find the reciprocal of. 5 5 3 Answer: Since, × = 1, the reciprocal 3 5 5 3 of 5 is 3.
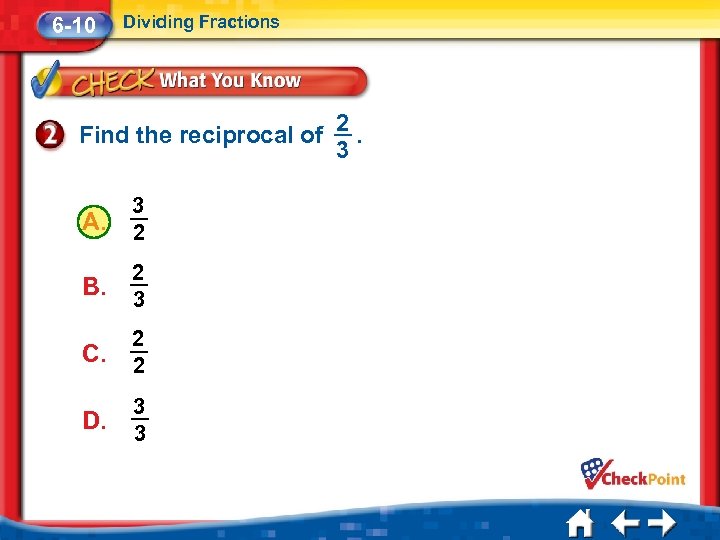 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find the reciprocal of A. 3 2 B. 2 3 C. 2 2 D. 3 3 2. 3
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find the reciprocal of A. 3 2 B. 2 3 C. 2 2 D. 3 3 2. 3
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find 1 5 ÷. 3 6 1 ÷ 5 1 × 6 = 6 5 3 3 Multiply by the reciprocal 6. 5 2 = 1× 6 3× 5 Divide 3 and 6 by the GCF, 3. 1 2 = 5 Answer: 2 5 Multiply numerators. Multiply denominators.
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find 1 5 ÷. 3 6 1 ÷ 5 1 × 6 = 6 5 3 3 Multiply by the reciprocal 6. 5 2 = 1× 6 3× 5 Divide 3 and 6 by the GCF, 3. 1 2 = 5 Answer: 2 5 Multiply numerators. Multiply denominators.
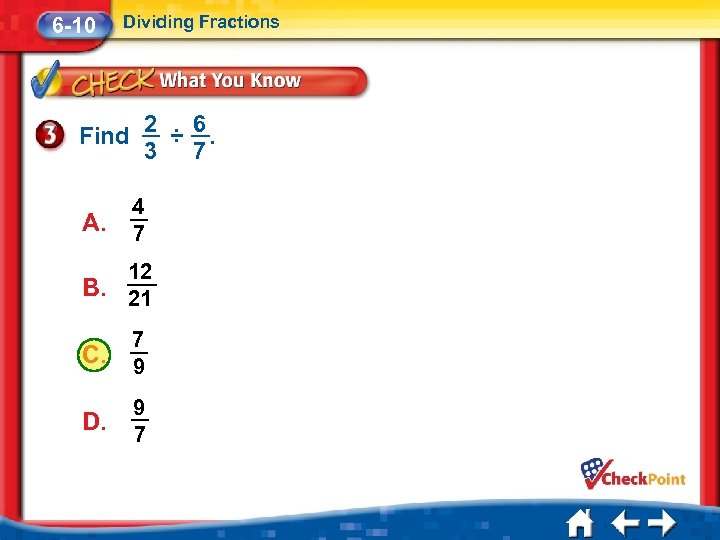 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find A. 2 6 ÷. 3 7 4 7 12 B. 21 C. 7 9 D. 9 7
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find A. 2 6 ÷. 3 7 4 7 12 B. 21 C. 7 9 D. 9 7
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find 5 ÷ 1. 6 5 ÷ 1 = 5 × 6 1 = 30 or 30 1 Answer: 30 6 Multiply by the reciprocal. 1 Simplify.
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find 5 ÷ 1. 6 5 ÷ 1 = 5 × 6 1 = 30 or 30 1 Answer: 30 6 Multiply by the reciprocal. 1 Simplify.
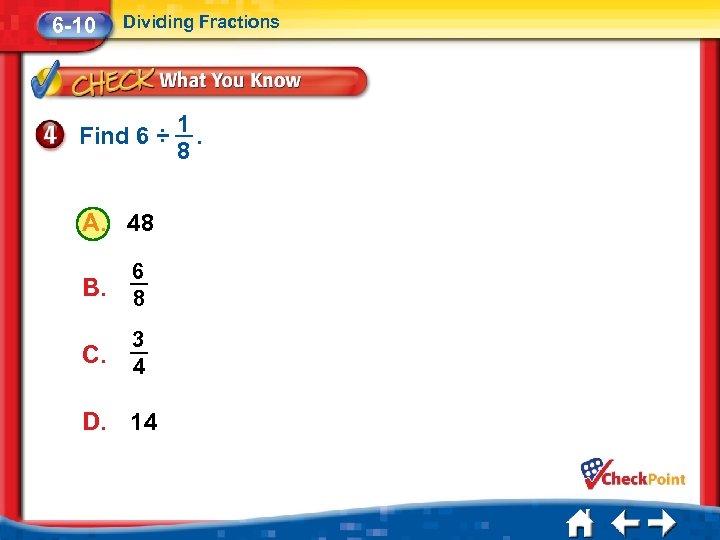 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find 6 ÷ A. 48 B. 6 8 C. 3 4 D. 14 1. 8
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Find 6 ÷ A. 48 B. 6 8 C. 3 4 D. 14 1. 8
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions 3 of a mile long. There are 4 runners 4 in the race. What portion of a mile will each racer A relay race is run? Divide 3 into 4 equal parts. 4
6 -10 Dividing Fractions 3 of a mile long. There are 4 runners 4 in the race. What portion of a mile will each racer A relay race is run? Divide 3 into 4 equal parts. 4
 6 -10 Dividing Fractions 3 ÷ 4 3 × 1 = 4 4 4 = 3 16 Multiply by the reciprocal. Simplify. Answer: So, each runner ran 3 of a mile. 16
6 -10 Dividing Fractions 3 ÷ 4 3 × 1 = 4 4 4 = 3 16 Multiply by the reciprocal. Simplify. Answer: So, each runner ran 3 of a mile. 16
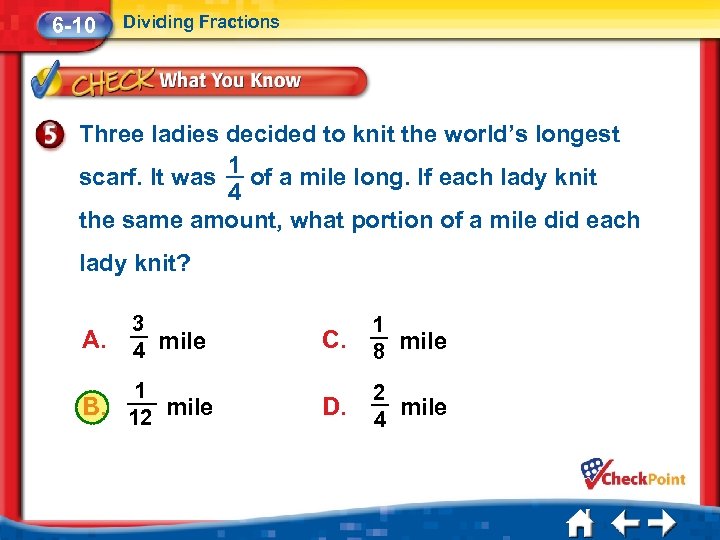 6 -10 Dividing Fractions Three ladies decided to knit the world’s longest scarf. It was 1 of a mile long. If each lady knit 4 the same amount, what portion of a mile did each lady knit? A. 3 4 mile 1 B. 12 mile C. 1 8 mile D. 2 mile 4
6 -10 Dividing Fractions Three ladies decided to knit the world’s longest scarf. It was 1 of a mile long. If each lady knit 4 the same amount, what portion of a mile did each lady knit? A. 3 4 mile 1 B. 12 mile C. 1 8 mile D. 2 mile 4

 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -10) Main Idea California Standards Key Concept: Dividing by Mixed Numbers Example 1: Divide by a Mixed Number Example 2: Evaluate Expressions Example 3: Real-World Example
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 6 -10) Main Idea California Standards Key Concept: Dividing by Mixed Numbers Example 1: Divide by a Mixed Number Example 2: Evaluate Expressions Example 3: Real-World Example
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -10) Divide. Write in simplest form. 4 1 ÷ 5 10 5 A. 10 B. 1 2 C. 4 D. 8
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -10) Divide. Write in simplest form. 4 1 ÷ 5 10 5 A. 10 B. 1 2 C. 4 D. 8
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -10) Divide. Write in simplest form. 1 7 ÷ 4 8 1 A. 3 2 B. 4 C. 3 D. 2
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -10) Divide. Write in simplest form. 1 7 ÷ 4 8 1 A. 3 2 B. 4 C. 3 D. 2
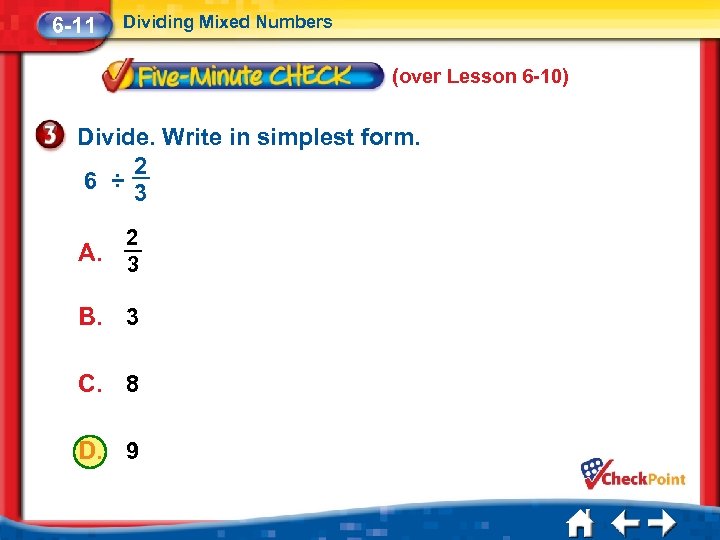 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -10) Divide. Write in simplest form. 2 6 ÷ 3 A. 2 3 B. 3 C. 8 D. 9
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -10) Divide. Write in simplest form. 2 6 ÷ 3 A. 2 3 B. 3 C. 8 D. 9
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -10) Divide. Write in simplest form. 3 1 ÷ 4 2 A. 2 3 B. 1 2 C. 1 D. 1 3
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers (over Lesson 6 -10) Divide. Write in simplest form. 3 1 ÷ 4 2 A. 2 3 B. 1 2 C. 1 D. 1 3
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers • I will divide mixed numbers.
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers • I will divide mixed numbers.
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers Standard 5 NS 2. 5 Compute and perform simple multiplication and division of fractions and apply these procedures to solving problems.
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers
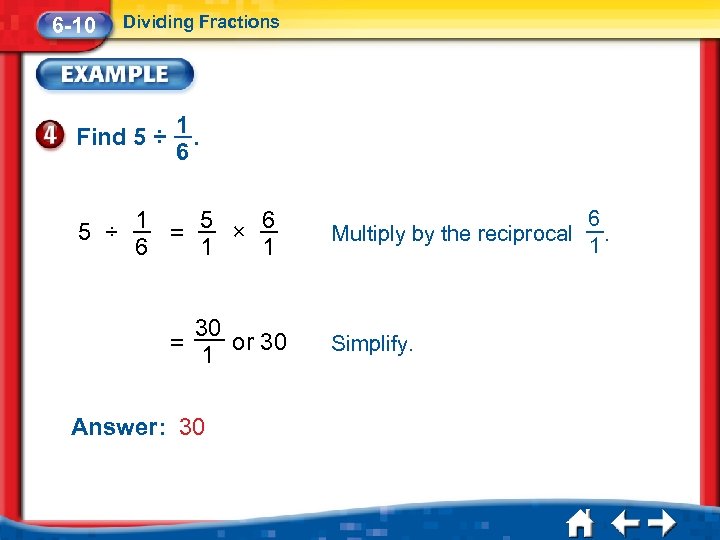
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers Find 6 1 1 ÷ 2. 4 2 Estimate 6 ÷ 3 = 2 6 1 ÷ 2 1 = 25 ÷ 5 2 4 25 × 2 = 4 5 Write mixed numbers as improper fractions. Multiply by the reciprocal.
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers Find 6 1 1 ÷ 2. 4 2 Estimate 6 ÷ 3 = 2 6 1 ÷ 2 1 = 25 ÷ 5 2 4 25 × 2 = 4 5 Write mixed numbers as improper fractions. Multiply by the reciprocal.
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 5 1 25 × 2 = 4 5 2 Answer: 2 1 5 or 2 1 2 2 = Divide 2 and 4 by the GCF, 2, and 25 and 5 by the GCF, 5. Simplify. 1 2 Check for Reasonableness 2 1 is about 2. 2
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 5 1 25 × 2 = 4 5 2 Answer: 2 1 5 or 2 1 2 2 = Divide 2 and 4 by the GCF, 2, and 25 and 5 by the GCF, 5. Simplify. 1 2 Check for Reasonableness 2 1 is about 2. 2
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers Find 3 A. 2 3 1 ÷ 1. 4 2 6 12 1 B. 2 2 C. 2 D. 3 2 4
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers Find 3 A. 2 3 1 ÷ 1. 4 2 6 12 1 B. 2 2 C. 2 D. 3 2 4
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 5 2 ALGEBRA Find a ÷ b if a = 2 8 and b = 3. a ÷ b = 25 ÷ 2 8 3 Replace a with 2 5 2 and b with. 8 3 = 21 ÷ 2 8 3 Write the mixed number as an improper fraction. = 21 × 3 8 2 Multiply by the reciprocal. 63 or 3 15 16 16 Answer: 3 15 16 = Simplify.
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 5 2 ALGEBRA Find a ÷ b if a = 2 8 and b = 3. a ÷ b = 25 ÷ 2 8 3 Replace a with 2 5 2 and b with. 8 3 = 21 ÷ 2 8 3 Write the mixed number as an improper fraction. = 21 × 3 8 2 Multiply by the reciprocal. 63 or 3 15 16 16 Answer: 3 15 16 = Simplify.
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 2 5 ALGEBRA Find f ÷ g if f = 3 3 and g = 8. A. 5 3 5 B. 7 2 24 C. 13 5 15 D. 1 2 6
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 2 5 ALGEBRA Find f ÷ g if f = 3 3 and g = 8. A. 5 3 5 B. 7 2 24 C. 13 5 15 D. 1 2 6
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 3 A team took 3 days to complete 180 miles of an 4 adventure race consisting of hiking, biking, and river rafting. How many miles did they average each day? Estimate 200 ÷ 4 = 50 180 ÷ 3 3 4 180 ÷ 15 = 4 1 Write mixed numbers as improper fractions.
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 3 A team took 3 days to complete 180 miles of an 4 adventure race consisting of hiking, biking, and river rafting. How many miles did they average each day? Estimate 200 ÷ 4 = 50 180 ÷ 3 3 4 180 ÷ 15 = 4 1 Write mixed numbers as improper fractions.
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 180 × 4 15 1 = Multiply by the reciprocal. 180 × 4 15 1 Divide 15 and 180 by the GCF, 15. 12 = = 48 1 Simplify. Compare to the estimate. Answer: So, the team averaged 48 miles each day.
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 180 × 4 15 1 = Multiply by the reciprocal. 180 × 4 15 1 Divide 15 and 180 by the GCF, 15. 12 = = 48 1 Simplify. Compare to the estimate. Answer: So, the team averaged 48 miles each day.
 6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 2 A cross country skier took 4 days to travel 3 240 miles. How many miles did he average each day? 3 A. 51 miles 7 6 B. 51 14 miles C. 3 50 4 miles D. 52 1 miles 2
6 -11 Dividing Mixed Numbers 2 A cross country skier took 4 days to travel 3 240 miles. How many miles did he average each day? 3 A. 51 miles 7 6 B. 51 14 miles C. 3 50 4 miles D. 52 1 miles 2



