46d55b2cc458a9dd85e05b3f55e1e61d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 Chapter 6 Lecture Outline The Acquisition of Memories and the Working-Memory System © 2016 by W. W. Norton & Company
Chapter 6 Lecture Outline The Acquisition of Memories and the Working-Memory System © 2016 by W. W. Norton & Company
 Chapter 6: Working Memory n Lecture Outline ¨ The Modal Model ¨ Working Memory ¨ Entering Long-term Storage ¨ Elaborate Encoding ¨ Organizing and Memorizing ¨ Links Among Acquisition, Storage, and Retrieval ¨ Implications for Successful Studying © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Chapter 6: Working Memory n Lecture Outline ¨ The Modal Model ¨ Working Memory ¨ Entering Long-term Storage ¨ Elaborate Encoding ¨ Organizing and Memorizing ¨ Links Among Acquisition, Storage, and Retrieval ¨ Implications for Successful Studying © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Chapter 6: Working Memory n One way to frame learning and memory ¨ Acquisition ¨ Storage ¨ Retrieval n Analogy to creating, storing, and opening a computer file © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Chapter 6: Working Memory n One way to frame learning and memory ¨ Acquisition ¨ Storage ¨ Retrieval n Analogy to creating, storing, and opening a computer file © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Chapter 6: Working Memory n This view is problematic for at least two reasons. ¨ New learning is grounded in previously learned (stored) knowledge. ¨ Effective learning depends on how the information will be later retrieved. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Chapter 6: Working Memory n This view is problematic for at least two reasons. ¨ New learning is grounded in previously learned (stored) knowledge. ¨ Effective learning depends on how the information will be later retrieved. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
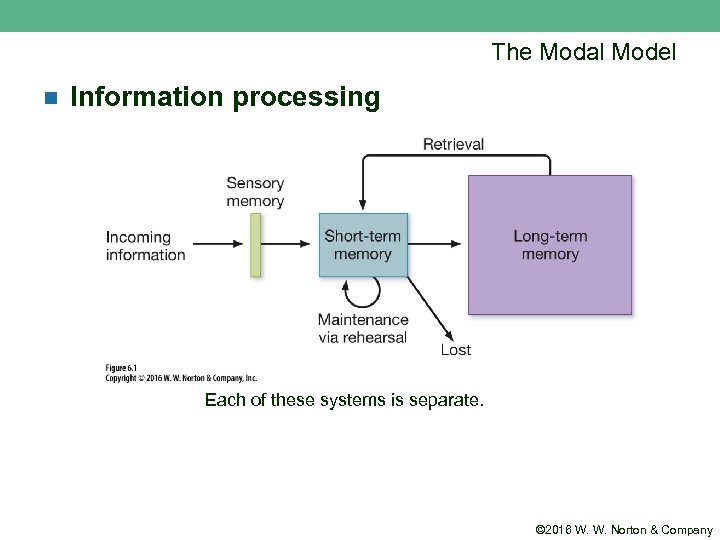 The Modal Model n Information processing Each of these systems is separate. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model n Information processing Each of these systems is separate. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 The Modal Model n The modal model (Atkinson & Shiffrin, 1968; Waugh & Norman, 1965) ¨ Sensory memory (iconic or echoic) ¨ Short-term memory (STM) ¨ Long-term memory (LTM) © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model n The modal model (Atkinson & Shiffrin, 1968; Waugh & Norman, 1965) ¨ Sensory memory (iconic or echoic) ¨ Short-term memory (STM) ¨ Long-term memory (LTM) © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 The Modal Model n Working memory (WM)—a dynamic form of short-term memory ¨ Less like a storage place and more like a status © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model n Working memory (WM)—a dynamic form of short-term memory ¨ Less like a storage place and more like a status © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
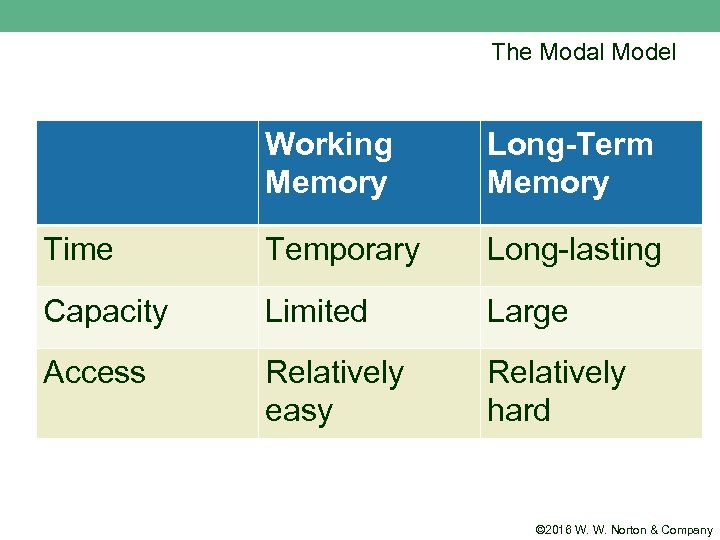 The Modal Model Working Memory Long-Term Memory Time Temporary Long-lasting Capacity Limited Large Access Relatively easy Relatively hard © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model Working Memory Long-Term Memory Time Temporary Long-lasting Capacity Limited Large Access Relatively easy Relatively hard © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 The Modal Model n Experiments supporting the modal model ¨ Presented with a long series of words (e. g. , 30) ¨ Perform free-recall afterward ¨ Look at the position in the list (serial recall) © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model n Experiments supporting the modal model ¨ Presented with a long series of words (e. g. , 30) ¨ Perform free-recall afterward ¨ Look at the position in the list (serial recall) © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
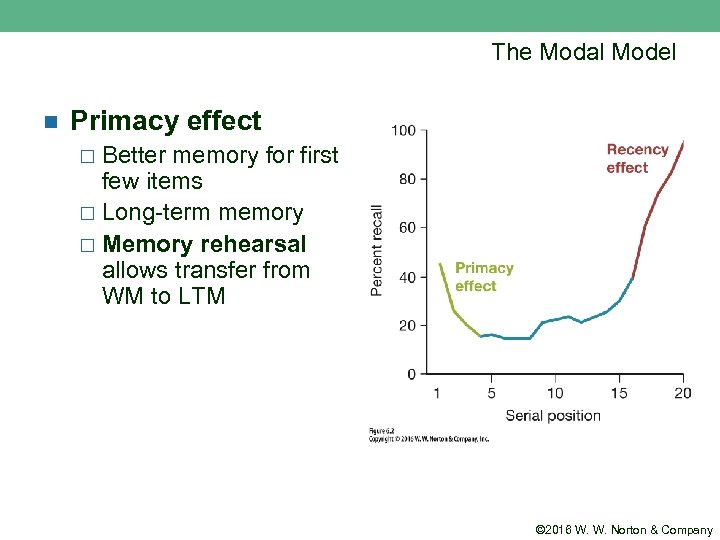 The Modal Model n Primacy effect Better memory for first few items ¨ Long-term memory ¨ Memory rehearsal allows transfer from WM to LTM ¨ © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model n Primacy effect Better memory for first few items ¨ Long-term memory ¨ Memory rehearsal allows transfer from WM to LTM ¨ © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
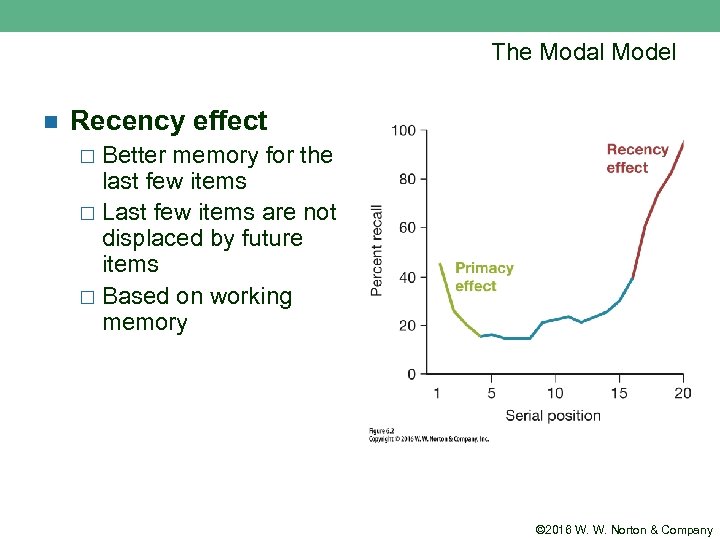 The Modal Model n Recency effect Better memory for the last few items ¨ Last few items are not displaced by future items ¨ Based on working memory ¨ © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model n Recency effect Better memory for the last few items ¨ Last few items are not displaced by future items ¨ Based on working memory ¨ © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
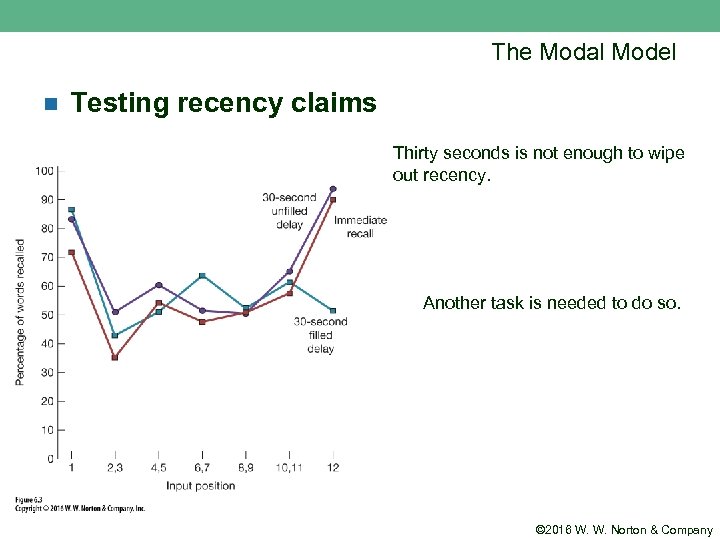 The Modal Model n Testing recency claims Thirty seconds is not enough to wipe out recency. Another task is needed to do so. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model n Testing recency claims Thirty seconds is not enough to wipe out recency. Another task is needed to do so. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
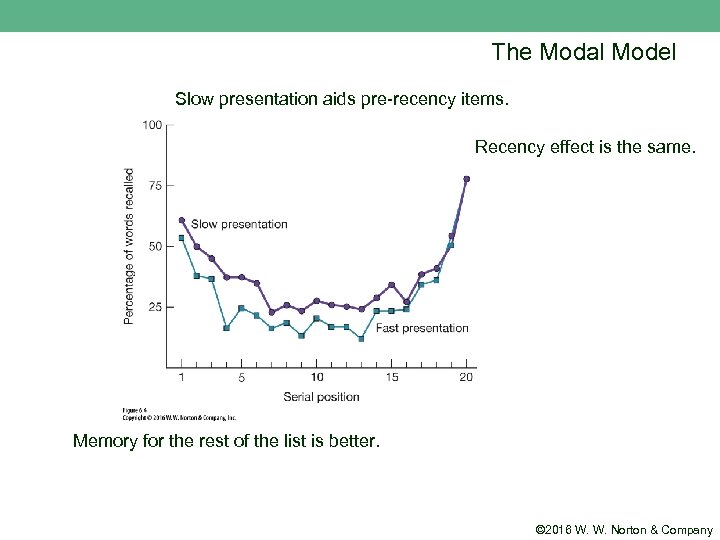 The Modal Model Slow presentation aids pre-recency items. Recency effect is the same. Memory for the rest of the list is better. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model Slow presentation aids pre-recency items. Recency effect is the same. Memory for the rest of the list is better. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
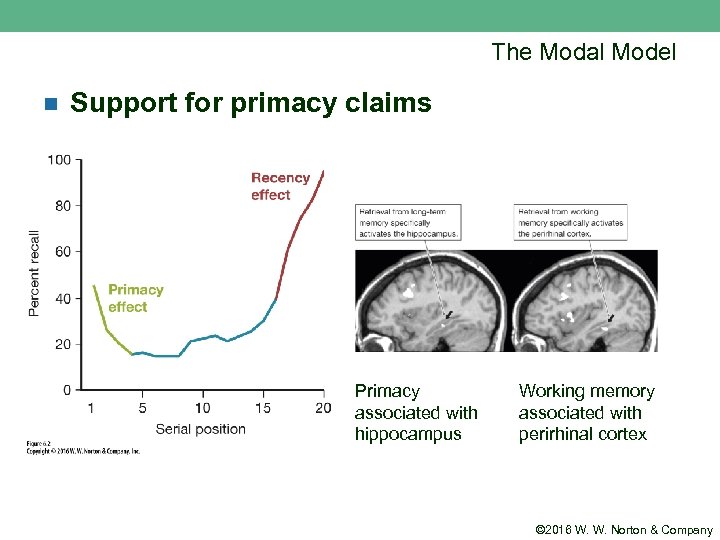 The Modal Model n Support for primacy claims Primacy associated with hippocampus Working memory associated with perirhinal cortex © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
The Modal Model n Support for primacy claims Primacy associated with hippocampus Working memory associated with perirhinal cortex © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Working Memory n Virtually all mental activities require working memory (WM). ¨ Reading ¨ Goal-driven behavior Some tasks demand more WM resources than others. n Individual differences in WM capacity predict some cognitive abilities. n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Working Memory n Virtually all mental activities require working memory (WM). ¨ Reading ¨ Goal-driven behavior Some tasks demand more WM resources than others. n Individual differences in WM capacity predict some cognitive abilities. n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Working Memory n Digit-span task ¨ The participant is asked to remember digits. n The list is increased until memory fails. n The maximum number is the digit span. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Working Memory n Digit-span task ¨ The participant is asked to remember digits. n The list is increased until memory fails. n The maximum number is the digit span. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Working Memory n Chunking ¨ The ability to condense information ¨ Requires effort ¨ Reduces load ¨ Does not increase WM © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Working Memory n Chunking ¨ The ability to condense information ¨ Requires effort ¨ Reduces load ¨ Does not increase WM © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
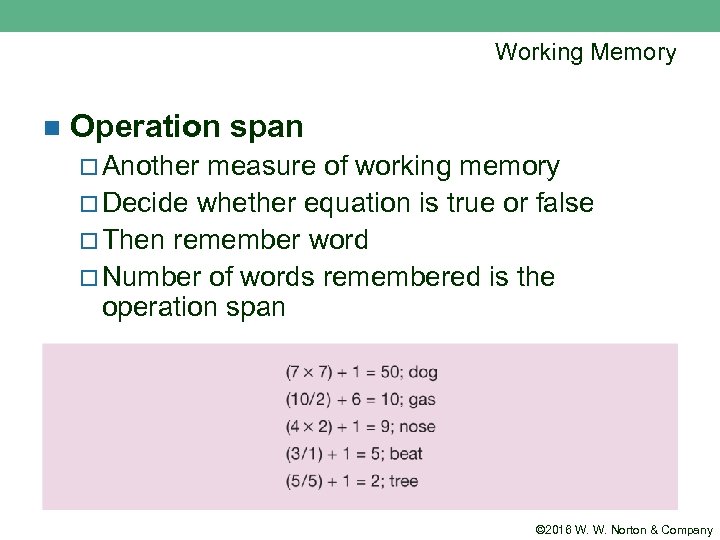 Working Memory n Operation span ¨ Another measure of working memory ¨ Decide whether equation is true or false ¨ Then remember word ¨ Number of words remembered is the operation span © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Working Memory n Operation span ¨ Another measure of working memory ¨ Decide whether equation is true or false ¨ Then remember word ¨ Number of words remembered is the operation span © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Working Memory n Reading span ¨ ¨ Captures active nature of working memory Participant reads sentences and remembers the last word in each sentence Number of sentences is increased to failure Number of words remembered is the reading span © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Working Memory n Reading span ¨ ¨ Captures active nature of working memory Participant reads sentences and remembers the last word in each sentence Number of sentences is increased to failure Number of words remembered is the reading span © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Working Memory n Reading span and operation span correlate strongly with ¨ ¨ ¨ Standardized test performance Reasoning Reading comprehension © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Working Memory n Reading span and operation span correlate strongly with ¨ ¨ ¨ Standardized test performance Reasoning Reading comprehension © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Working Memory n Working memory is often divided into three components ¨ Central executive ¨ Visuospatial buffer ¨ Articulatory rehearsal loop © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Working Memory n Working memory is often divided into three components ¨ Central executive ¨ Visuospatial buffer ¨ Articulatory rehearsal loop © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Working Memory n WM is an update to the modal model ¨A dynamic form of STM ¨ But still fragile © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Working Memory n WM is an update to the modal model ¨A dynamic form of STM ¨ But still fragile © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Entering Long-Term Storage n Two types of rehearsal ¨ Maintenance rehearsal—reciting ¨ Relational or elaborative rehearsal—linking © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Entering Long-Term Storage n Two types of rehearsal ¨ Maintenance rehearsal—reciting ¨ Relational or elaborative rehearsal—linking © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Entering Long-Term Storage Relational, or elaborative, rehearsal is superior. n Repeated exposure does not guarantee memory. n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Entering Long-Term Storage Relational, or elaborative, rehearsal is superior. n Repeated exposure does not guarantee memory. n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
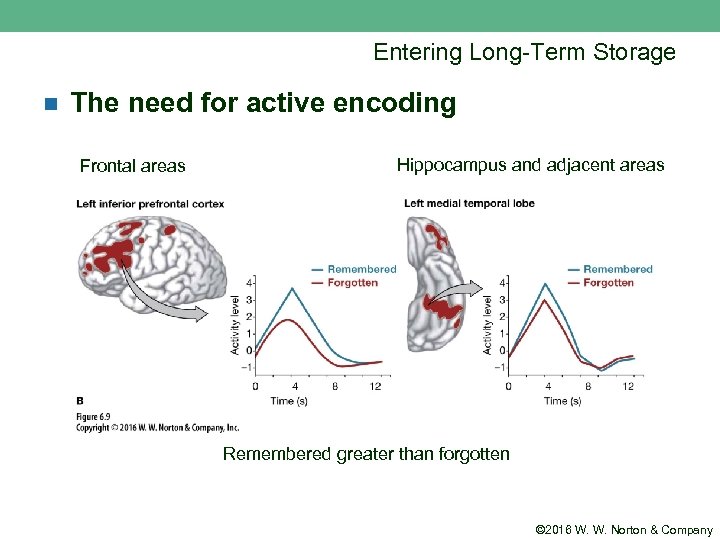 Entering Long-Term Storage n The need for active encoding Frontal areas Hippocampus and adjacent areas Remembered greater than forgotten © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Entering Long-Term Storage n The need for active encoding Frontal areas Hippocampus and adjacent areas Remembered greater than forgotten © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Entering Long-Term Storage Incidental learning—unintentional n Intentional learning—intentional n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Entering Long-Term Storage Incidental learning—unintentional n Intentional learning—intentional n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Entering Long-Term Storage Shallow processing—superficial n Deep processing—meaningful n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Entering Long-Term Storage Shallow processing—superficial n Deep processing—meaningful n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
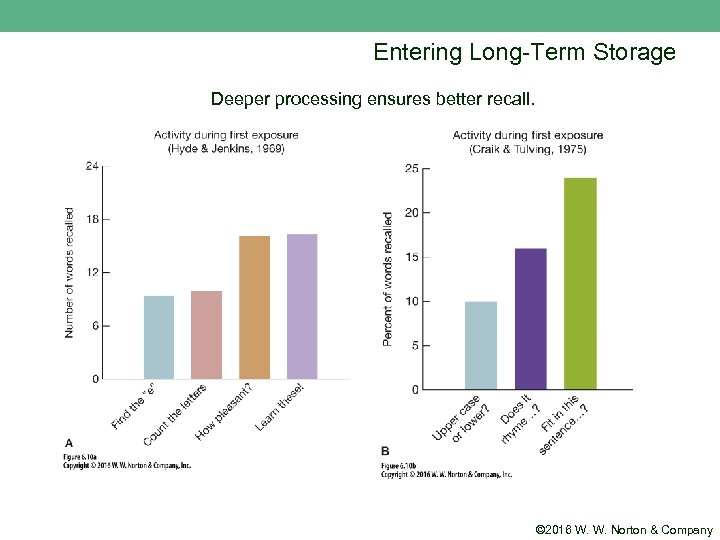 Entering Long-Term Storage Deeper processing ensures better recall. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Entering Long-Term Storage Deeper processing ensures better recall. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Entering Long-Term Storage n Imagine an experiment in which you cross depth of processing (three levels) ¨ Typeface task (shallow) ¨ Phonological task (intermediate) ¨ Semantic task (deep) n And intention to learn (two levels) ¨ Incidental learning ¨ Intentional learning © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Entering Long-Term Storage n Imagine an experiment in which you cross depth of processing (three levels) ¨ Typeface task (shallow) ¨ Phonological task (intermediate) ¨ Semantic task (deep) n And intention to learn (two levels) ¨ Incidental learning ¨ Intentional learning © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Entering Long-Term Storage Depth of processing is strong. n Intention to learn has no effect. n Intention to learn can lead you to choose a deeper strategy. n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Entering Long-Term Storage Depth of processing is strong. n Intention to learn has no effect. n Intention to learn can lead you to choose a deeper strategy. n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Elaborate Encoding n Very hard to find info n Very easy to find info © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Elaborate Encoding n Very hard to find info n Very easy to find info © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Elaborate Encoding n Depth of processing promotes recall by facilitating later retrieval. ¨ Consider learning as a way to establish indexing, a path to the information. ¨ Connections between items to be remembered facilitates retrieval. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Elaborate Encoding n Depth of processing promotes recall by facilitating later retrieval. ¨ Consider learning as a way to establish indexing, a path to the information. ¨ Connections between items to be remembered facilitates retrieval. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Elaborate Encoding n Memory connections facilitate retrieval. ¨ We can use this to help retrieval. “What words are related in meaning to the word I’m now considering? ” “What words have contrasting meaning? ” “What is the relationship between the start of this story and the way the story turned out? ” © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Elaborate Encoding n Memory connections facilitate retrieval. ¨ We can use this to help retrieval. “What words are related in meaning to the word I’m now considering? ” “What words have contrasting meaning? ” “What is the relationship between the start of this story and the way the story turned out? ” © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
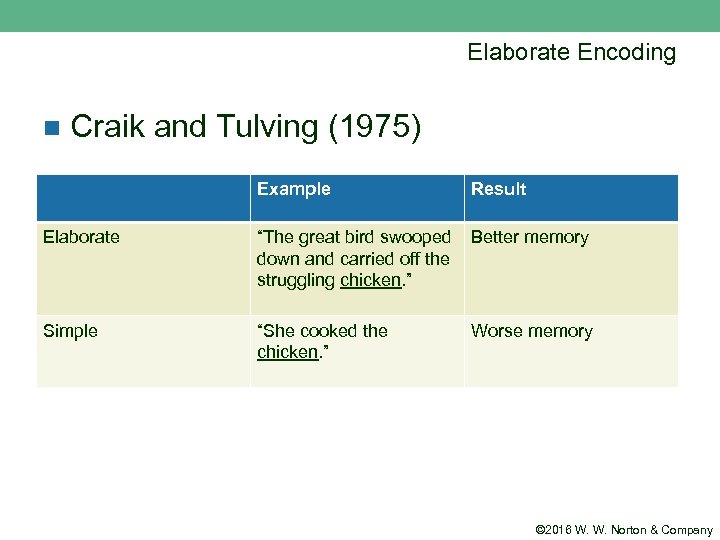 Elaborate Encoding n Craik and Tulving (1975) Example Result Elaborate “The great bird swooped down and carried off the struggling chicken. ” Better memory Simple “She cooked the chicken. ” Worse memory © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Elaborate Encoding n Craik and Tulving (1975) Example Result Elaborate “The great bird swooped down and carried off the struggling chicken. ” Better memory Simple “She cooked the chicken. ” Worse memory © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
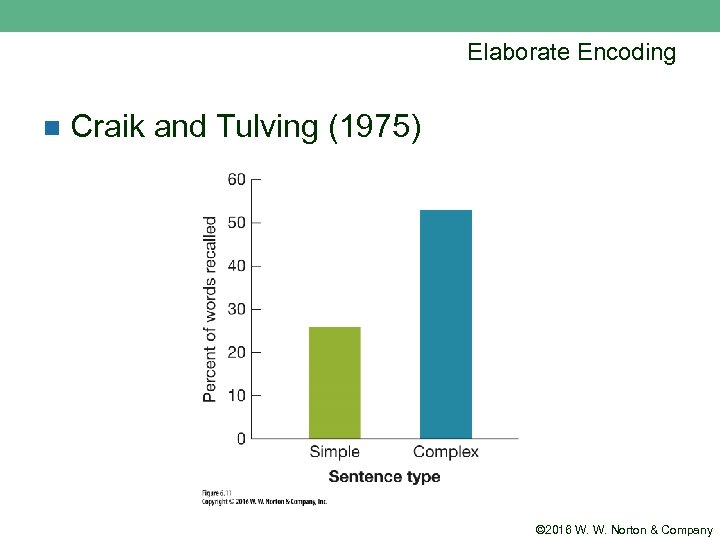 Elaborate Encoding n Craik and Tulving (1975) © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Elaborate Encoding n Craik and Tulving (1975) © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Elaborate Encoding n Elaborate sentences result in richer retrieval paths. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Elaborate Encoding n Elaborate sentences result in richer retrieval paths. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Organizing and Memorizing Katona (1940) argued that the key to creating connections in the material to be remembered is organization. n We memorize well when we find order in the material. n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Organizing and Memorizing Katona (1940) argued that the key to creating connections in the material to be remembered is organization. n We memorize well when we find order in the material. n © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
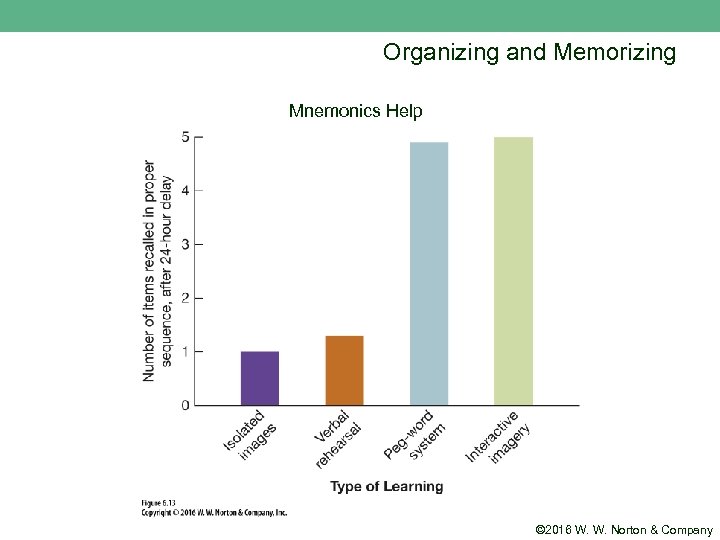
 Organizing and Memorizing n Mnemonics improve memory through organization. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Organizing and Memorizing n Mnemonics improve memory through organization. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Organizing and Memorizing n Peg-word systems: items are “hung” on a system of already well known “pegs” ¨ “One n is a bun, two is a shoe. . . ” First-letter mnemonics ¨ Roy G. Biv ¨ King Phillip Crossed the Ocean to Find Gold and Silver © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Organizing and Memorizing n Peg-word systems: items are “hung” on a system of already well known “pegs” ¨ “One n is a bun, two is a shoe. . . ” First-letter mnemonics ¨ Roy G. Biv ¨ King Phillip Crossed the Ocean to Find Gold and Silver © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Organizing and Memorizing Mnemonics Help © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Organizing and Memorizing Mnemonics Help © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Organizing and Memorizing The procedure is actually quite simple. First you arrange items into different groups. Of course one pile may be sufficient depending on how much there is to do. If you have to go somewhere else due to lack of facilities that is the next step; otherwise you are pretty well set. It is important not to overdo things. That is, it is better to do too few things at once than too many. In the short run, this may not seem important but complications can easily arise. A mistake can be expensive as well. At first, the whole procedure will seem complicated. Soon, however, it will become just another facet of life. It is difficult to foresee any end to the necessity for this task in the immediate future, but then, one never can tell. After the procedure is completed one arranges the materials into different groups again. Then they can be put into their appropriate places. Eventually they will be used once more and the whole cycle will then have to be repeated. However, that is part of life. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Organizing and Memorizing The procedure is actually quite simple. First you arrange items into different groups. Of course one pile may be sufficient depending on how much there is to do. If you have to go somewhere else due to lack of facilities that is the next step; otherwise you are pretty well set. It is important not to overdo things. That is, it is better to do too few things at once than too many. In the short run, this may not seem important but complications can easily arise. A mistake can be expensive as well. At first, the whole procedure will seem complicated. Soon, however, it will become just another facet of life. It is difficult to foresee any end to the necessity for this task in the immediate future, but then, one never can tell. After the procedure is completed one arranges the materials into different groups again. Then they can be put into their appropriate places. Eventually they will be used once more and the whole cycle will then have to be repeated. However, that is part of life. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Organizing and Memorizing n What is the pattern? © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Organizing and Memorizing n What is the pattern? © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Organizing and Memorizing n Ambiguous pictures are understood and remembered better if they are identified (Wiseman & Neisser, 1974) © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Organizing and Memorizing n Ambiguous pictures are understood and remembered better if they are identified (Wiseman & Neisser, 1974) © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Links Among Acquisition, Storage, and Retrieval n Memory is facilitated by organizing and understanding. ¨ What the memorizer was doing at the time of exposure matters. ¨ The background knowledge of the memorizer matters. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Links Among Acquisition, Storage, and Retrieval n Memory is facilitated by organizing and understanding. ¨ What the memorizer was doing at the time of exposure matters. ¨ The background knowledge of the memorizer matters. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Links Among Acquisition, Storage, and Retrieval n Acquisition, storage, and retrieval are not easily separable. ¨ New learning is grounded in previously learned (stored) knowledge. ¨ Effective learning depends on how the information will later be retrieved. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Links Among Acquisition, Storage, and Retrieval n Acquisition, storage, and retrieval are not easily separable. ¨ New learning is grounded in previously learned (stored) knowledge. ¨ Effective learning depends on how the information will later be retrieved. © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Links Among Acquisition, Storage, and Retrieval n Implications for studying ¨ Understand through self-questioning ¨ Actively engage ¨ Form connections ¨ Spaced learning © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Links Among Acquisition, Storage, and Retrieval n Implications for studying ¨ Understand through self-questioning ¨ Actively engage ¨ Form connections ¨ Spaced learning © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Chapter 6 Questions © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
Chapter 6 Questions © 2016 W. W. Norton & Company
 Which group would perform the WORST on a memory test? a) Participants engaged in shallow processing without previous warning of a memory test. b) Participants engaged in medium processing with previous warning of a memory test. c) Participants engaged in deep processing without previous warning of a memory test. d) Participants engaged in deep processing with previous warning of a memory test.
Which group would perform the WORST on a memory test? a) Participants engaged in shallow processing without previous warning of a memory test. b) Participants engaged in medium processing with previous warning of a memory test. c) Participants engaged in deep processing without previous warning of a memory test. d) Participants engaged in deep processing with previous warning of a memory test.
 Someone with a larger working-memory capacity is likely to perform better than someone with a smaller working-memory capacity on which of the following tasks? a) following directions b) efficient reading c) learning a computer language d) all of the above
Someone with a larger working-memory capacity is likely to perform better than someone with a smaller working-memory capacity on which of the following tasks? a) following directions b) efficient reading c) learning a computer language d) all of the above
 Which statement about working memory is TRUE? a) It has unlimited storage capacity. b) It functions as a storage container. c) Information in it is fragile and easily lost. d) It refers mainly to the resources that are retained over long intervals.
Which statement about working memory is TRUE? a) It has unlimited storage capacity. b) It functions as a storage container. c) Information in it is fragile and easily lost. d) It refers mainly to the resources that are retained over long intervals.
 Which of the following would be the LEAST help in improving recall of a difficult-tounderstand paragraph? a) quizzing yourself in order to improve comprehension of the paragraph b) chunking the sentences in the paragraph into smaller, meaningful groups c) repeating the paragraph aloud many times d) giving the paragraph a meaningful title
Which of the following would be the LEAST help in improving recall of a difficult-tounderstand paragraph? a) quizzing yourself in order to improve comprehension of the paragraph b) chunking the sentences in the paragraph into smaller, meaningful groups c) repeating the paragraph aloud many times d) giving the paragraph a meaningful title
 Veronica wanted to go to the grocery store but was out of paper for writing a shopping list. She came up with several possible ways to remember what she needed to buy (listed below). Which of her ideas is a simple mnemonic strategy? a) Using the peg-word system to associate different items on the shopping list with words in an easy-to-remember rhyme. b) Imagining what she can cook with all of the items on the list and imagining what all the food would taste like. c) Composing a long story with all the items on her list. d) Repeating all the items on her list multiple times.
Veronica wanted to go to the grocery store but was out of paper for writing a shopping list. She came up with several possible ways to remember what she needed to buy (listed below). Which of her ideas is a simple mnemonic strategy? a) Using the peg-word system to associate different items on the shopping list with words in an easy-to-remember rhyme. b) Imagining what she can cook with all of the items on the list and imagining what all the food would taste like. c) Composing a long story with all the items on her list. d) Repeating all the items on her list multiple times.
 What causes the recency effect? a) The last words heard are still in working memory at testing. b) The first words heard are also the first words to leave working memory. c) Words that get more attention are better encoded into long-term memory. d) Experimenters tend to provide easier words first as warm-up.
What causes the recency effect? a) The last words heard are still in working memory at testing. b) The first words heard are also the first words to leave working memory. c) Words that get more attention are better encoded into long-term memory. d) Experimenters tend to provide easier words first as warm-up.


