52828010ac276b2fbd848b67b2cb760b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70
 CHAPTER 6 Executive Decision Support Systems 1
CHAPTER 6 Executive Decision Support Systems 1
 Enterprise Decision Support Systems n DSS to provide enterprise-wide support n Executives n n Many decision makers in different locations Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems 2
Enterprise Decision Support Systems n DSS to provide enterprise-wide support n Executives n n Many decision makers in different locations Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems 2
 Enterprise Systems: Concepts and Definitions n Executive information systems (EIS) n Executive support systems (ESS) n Enterprise information systems (EIS) 3
Enterprise Systems: Concepts and Definitions n Executive information systems (EIS) n Executive support systems (ESS) n Enterprise information systems (EIS) 3
 Evolution of Executive and Enterprise Information Systems DSS and ODSS n 1980 s: Top execs get Executive Information Systems n 1995+’s: Move to everybody’s information systems and enterprise information systems n Definitions follow n 4
Evolution of Executive and Enterprise Information Systems DSS and ODSS n 1980 s: Top execs get Executive Information Systems n 1995+’s: Move to everybody’s information systems and enterprise information systems n Definitions follow n 4
 Executive Information System (EIS) n n n A computer-based system that serves the information needs of top executives Provides rapid access to timely information and direct access to management reports Very user-friendly, supported by graphics Provides exceptions reporting and "drill-down" capabilities Easily connected to the Internet Drill down 5
Executive Information System (EIS) n n n A computer-based system that serves the information needs of top executives Provides rapid access to timely information and direct access to management reports Very user-friendly, supported by graphics Provides exceptions reporting and "drill-down" capabilities Easily connected to the Internet Drill down 5
 Executive Support System (ESS) Comprehensive support system that goes beyond EIS to include n n Communications Office automation Analysis support Intelligence 6
Executive Support System (ESS) Comprehensive support system that goes beyond EIS to include n n Communications Office automation Analysis support Intelligence 6
 7
7
 Enterprise Information System n n n Corporate-wide system Provides holistic information From a corporate view Part of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems For business intelligence Leading up to enterprise information portals and knowledge management systems 8
Enterprise Information System n n n Corporate-wide system Provides holistic information From a corporate view Part of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems For business intelligence Leading up to enterprise information portals and knowledge management systems 8
 Executives’ Role and Their Information Needs n Decisional Executive Role (2 Phases) 1. Identification of problems and/or opportunities 2. The decision of what to do about them n n Flow chart and information flow (Figure 8. 1) Use phases to determine executives’ information needs 9
Executives’ Role and Their Information Needs n Decisional Executive Role (2 Phases) 1. Identification of problems and/or opportunities 2. The decision of what to do about them n n Flow chart and information flow (Figure 8. 1) Use phases to determine executives’ information needs 9
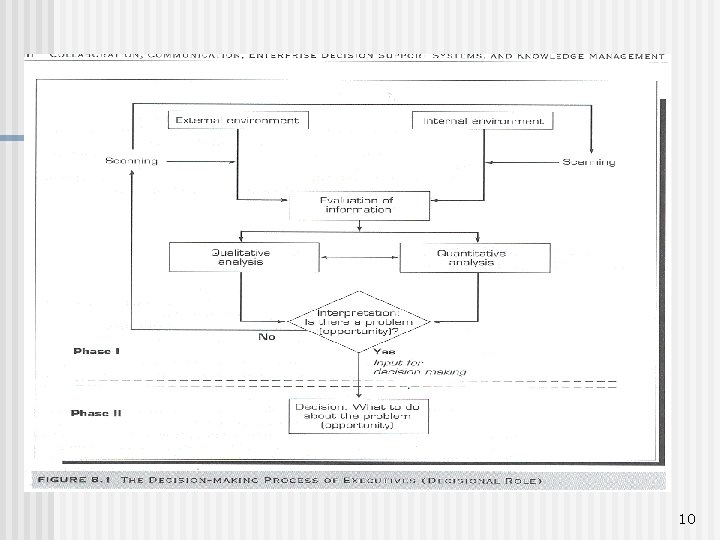 10
10
 Methods for Finding Information Needs n Wetherbe's Approach 1. Structured Interviews n n IBM's Business System Planning (BSP) Critical Success Factors (CSF) Ends/Means (E/M) Analysis 2. Prototyping Watson and Frolick's Approach n n Asking (interview approach) Deriving the needs from an existing information system Synthesis from characteristics of the systems Discovering (Prototyping) • Ten methods n Other Methods 11
Methods for Finding Information Needs n Wetherbe's Approach 1. Structured Interviews n n IBM's Business System Planning (BSP) Critical Success Factors (CSF) Ends/Means (E/M) Analysis 2. Prototyping Watson and Frolick's Approach n n Asking (interview approach) Deriving the needs from an existing information system Synthesis from characteristics of the systems Discovering (Prototyping) • Ten methods n Other Methods 11
 Characteristics of EIS Drill down n Critical success Factors (CSF) n Status access n Analysis n Colors and audio n Navigation of information n Communication n 12
Characteristics of EIS Drill down n Critical success Factors (CSF) n Status access n Analysis n Colors and audio n Navigation of information n Communication n 12
 Critical Success Factors (CSF) Monitored by five types of information 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Key problem narratives Highlight charts Top-level financials Key factors (key performance indicators (KPI)) Detailed KPI responsibility reports 13
Critical Success Factors (CSF) Monitored by five types of information 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Key problem narratives Highlight charts Top-level financials Key factors (key performance indicators (KPI)) Detailed KPI responsibility reports 13
 Critical Success Factors 14
Critical Success Factors 14
 Characteristics and Benefits of EIS (Table 8. 1) n n Quality of information User interface Technical capability provided Benefits 15
Characteristics and Benefits of EIS (Table 8. 1) n n Quality of information User interface Technical capability provided Benefits 15
 16
16
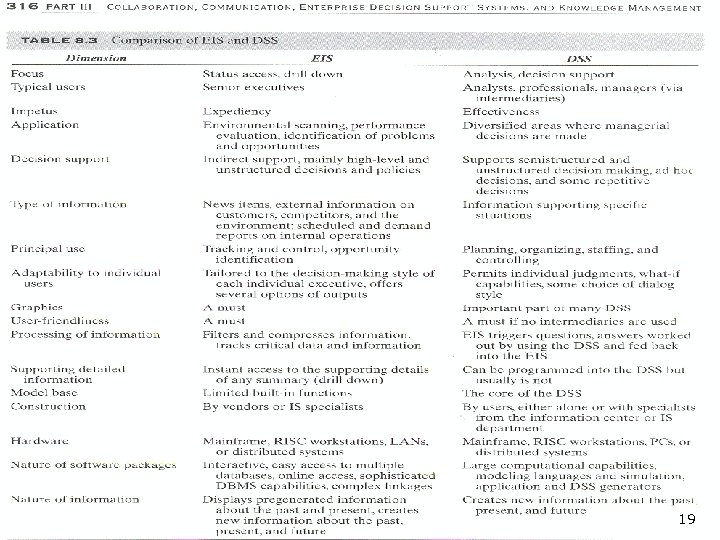
 Comparing and Integrating EIS and DSS n Tables 8. 2 and 8. 3 compare the two systems n n n Table 8. 2 - DSS definitions related to EIS Table 8. 3 - Comparison of EIS and DSS EIS is part of decision support 17
Comparing and Integrating EIS and DSS n Tables 8. 2 and 8. 3 compare the two systems n n n Table 8. 2 - DSS definitions related to EIS Table 8. 3 - Comparison of EIS and DSS EIS is part of decision support 17
 18
18
 19
19
 Integrating EIS and Group Support Systems n n n EIS vendors - easy interfaces with GSS Some EIS built in Lotus Domino / Notes Comshare Inc. and Pilot Software, Inc. - Lotus Domino/Notes-based enhancements and Web/Internet/Intranet links 20
Integrating EIS and Group Support Systems n n n EIS vendors - easy interfaces with GSS Some EIS built in Lotus Domino / Notes Comshare Inc. and Pilot Software, Inc. - Lotus Domino/Notes-based enhancements and Web/Internet/Intranet links 20
 Traditional EIS Software n Major Commercial EIS Software Vendors n n n Comshare Inc. (www. comshare. com) Pilot Software Inc. (www. pilotsw. com) Application Development Tools n n n In-house components Comshare Commander tools Pilot Software’s Command Center Plus and Pilot Decision Support Suite 21
Traditional EIS Software n Major Commercial EIS Software Vendors n n n Comshare Inc. (www. comshare. com) Pilot Software Inc. (www. pilotsw. com) Application Development Tools n n n In-house components Comshare Commander tools Pilot Software’s Command Center Plus and Pilot Decision Support Suite 21
 EIS n Data access n Data warehousing n OLAP n Multidimensional analysis n Presentations n Web n 22
EIS n Data access n Data warehousing n OLAP n Multidimensional analysis n Presentations n Web n 22
 Multidimensional Analysis n n Easy to develop an EIS in an OLAP system Most are Web-ready Can tap into data in a data warehouse via the Web Use advanced visualization tools 23
Multidimensional Analysis n n Easy to develop an EIS in an OLAP system Most are Web-ready Can tap into data in a data warehouse via the Web Use advanced visualization tools 23
 Representative OLAP / Multidimensional Analysis Packages n n n n n Brio. Query (Brio Technology Inc. ) Business Objects (Business Objects Inc. ) Decision Web (Comshare Inc. ) Data. Fountain (Dimensional Insight Inc. ) DSS Web (Micro. Strategy Inc. ) Focus Fusion (Information Builders Inc. ) Info. Beacon Web (Platinum Technology Inc. ) Oracle xpress Server (Oracle Corporation) Pilot Internet Publisher (Pilot Software Inc. ) 24
Representative OLAP / Multidimensional Analysis Packages n n n n n Brio. Query (Brio Technology Inc. ) Business Objects (Business Objects Inc. ) Decision Web (Comshare Inc. ) Data. Fountain (Dimensional Insight Inc. ) DSS Web (Micro. Strategy Inc. ) Focus Fusion (Information Builders Inc. ) Info. Beacon Web (Platinum Technology Inc. ) Oracle xpress Server (Oracle Corporation) Pilot Internet Publisher (Pilot Software Inc. ) 24
 Including Soft Information in EIS Soft information is fuzzy, unofficial, intuitive, subjective, nebulous, implied, and vague 25
Including Soft Information in EIS Soft information is fuzzy, unofficial, intuitive, subjective, nebulous, implied, and vague 25
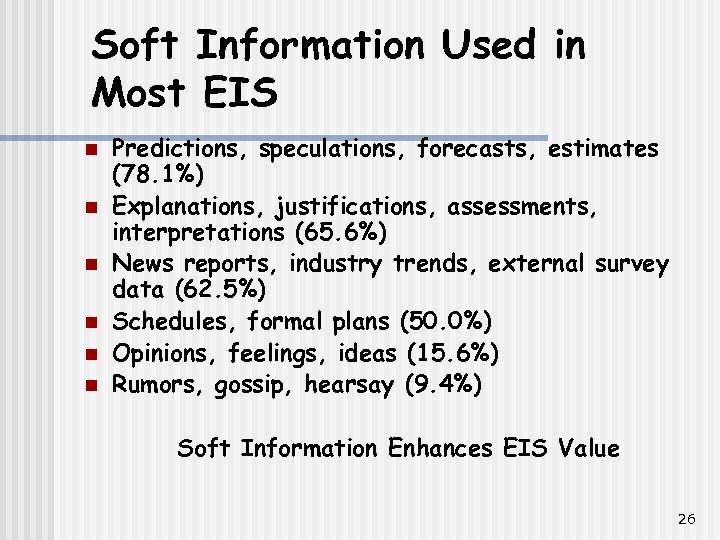 Soft Information Used in Most EIS n n n Predictions, speculations, forecasts, estimates (78. 1%) Explanations, justifications, assessments, interpretations (65. 6%) News reports, industry trends, external survey data (62. 5%) Schedules, formal plans (50. 0%) Opinions, feelings, ideas (15. 6%) Rumors, gossip, hearsay (9. 4%) Soft Information Enhances EIS Value 26
Soft Information Used in Most EIS n n n Predictions, speculations, forecasts, estimates (78. 1%) Explanations, justifications, assessments, interpretations (65. 6%) News reports, industry trends, external survey data (62. 5%) Schedules, formal plans (50. 0%) Opinions, feelings, ideas (15. 6%) Rumors, gossip, hearsay (9. 4%) Soft Information Enhances EIS Value 26
 Organizational DSS (ODSS) n Three Types of Decision Support n n n Individual Group Organizational Hackathorn and Keen (1981) 27
Organizational DSS (ODSS) n Three Types of Decision Support n n n Individual Group Organizational Hackathorn and Keen (1981) 27
 n n n Organizational decision support focuses on an organizational task or activity involving a sequence of operations and actors Each individual's activities must mesh closely with other people's work Computer support is for n n Improving communication and coordination Problem solving 28
n n n Organizational decision support focuses on an organizational task or activity involving a sequence of operations and actors Each individual's activities must mesh closely with other people's work Computer support is for n n Improving communication and coordination Problem solving 28
 Definitions of ODSS n n A combination of computer and communication technology designed to coordinate and disseminate decision-making across functional areas and hierarchical layers in order that decisions are congruent with organizational goals and management's shared interpretation of the competitive environment (R. T. Watson, 1990) A DSS that is used by individuals or groups at several workstations in more than one organizational unit who make varied (interrelated but autonomous) decisions using a common set of tools (Carter et al. , 1992) 29
Definitions of ODSS n n A combination of computer and communication technology designed to coordinate and disseminate decision-making across functional areas and hierarchical layers in order that decisions are congruent with organizational goals and management's shared interpretation of the competitive environment (R. T. Watson, 1990) A DSS that is used by individuals or groups at several workstations in more than one organizational unit who make varied (interrelated but autonomous) decisions using a common set of tools (Carter et al. , 1992) 29
 n n A distributed decision support system (DDSS). Not a manager's DSS, but supports the organization's division of labor in decision making (Swanson and Zmud, 1990) Apply the technologies of computers and communications to enhance the organizational decision-making process. Vision of technological support for group processes to the higher level of organizations (King and Star, 1990) 30
n n A distributed decision support system (DDSS). Not a manager's DSS, but supports the organization's division of labor in decision making (Swanson and Zmud, 1990) Apply the technologies of computers and communications to enhance the organizational decision-making process. Vision of technological support for group processes to the higher level of organizations (King and Star, 1990) 30
 Common Characteristics of ODSS (George, 1991) n n n Focus is on an organizational task or activity or a decision that affects several organizational units or corporate problems Cuts across organizational functions or hierarchical layers Almost always involves computer-based technologies, and may involve communication technologies Can Integrate ODSS with Group DSS and Executive Information Systems ODSS are an enterprise information system directly concerned with decision support 31
Common Characteristics of ODSS (George, 1991) n n n Focus is on an organizational task or activity or a decision that affects several organizational units or corporate problems Cuts across organizational functions or hierarchical layers Almost always involves computer-based technologies, and may involve communication technologies Can Integrate ODSS with Group DSS and Executive Information Systems ODSS are an enterprise information system directly concerned with decision support 31
 32
32
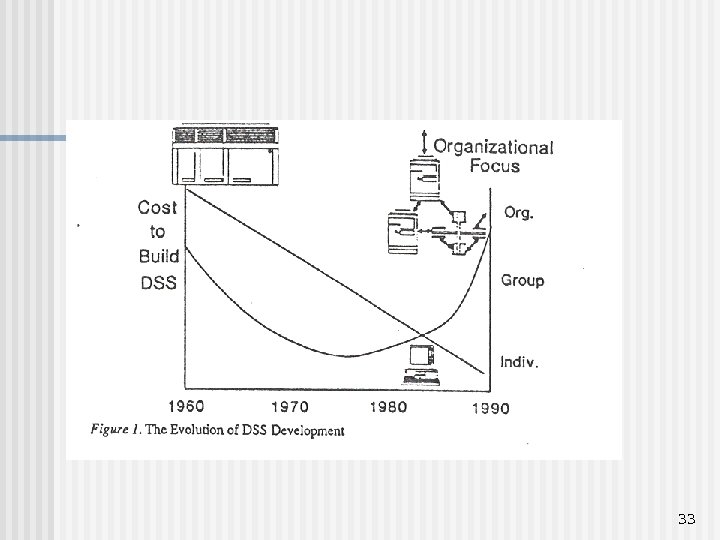 33
33
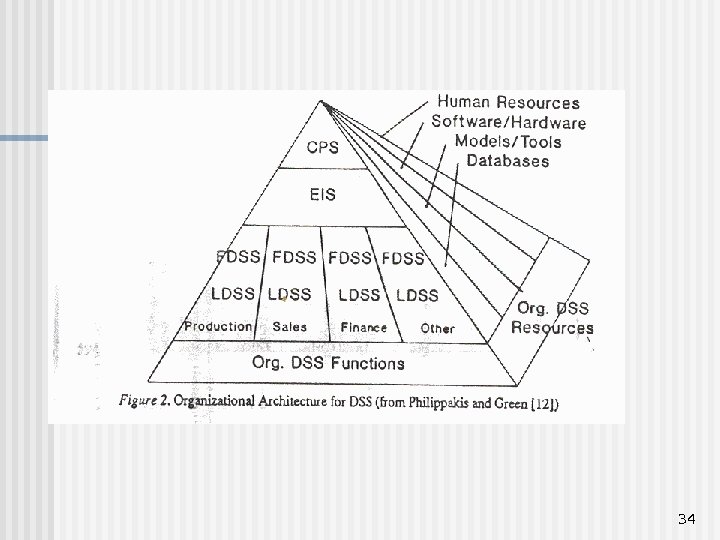 34
34
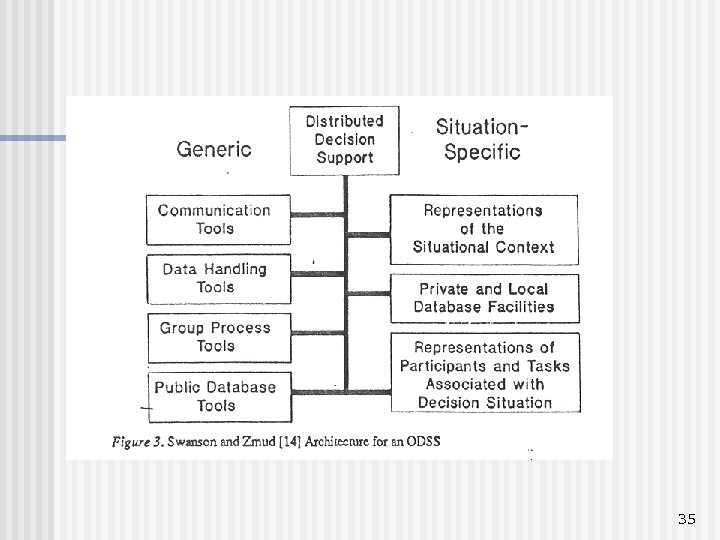 35
35
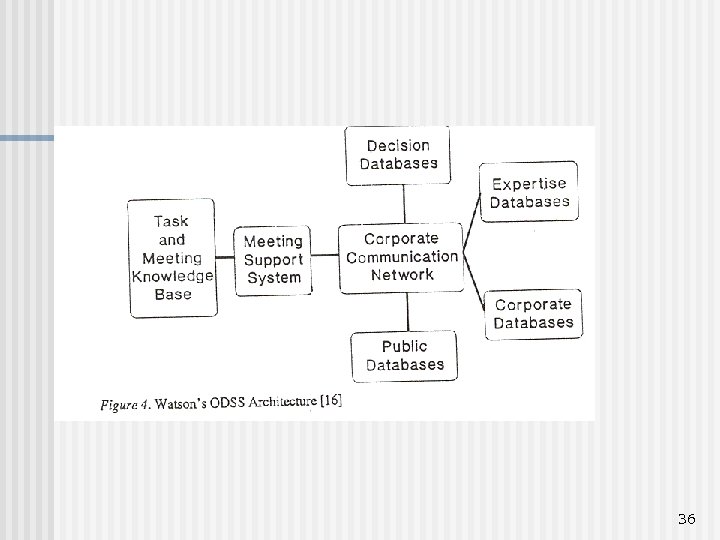 36
36
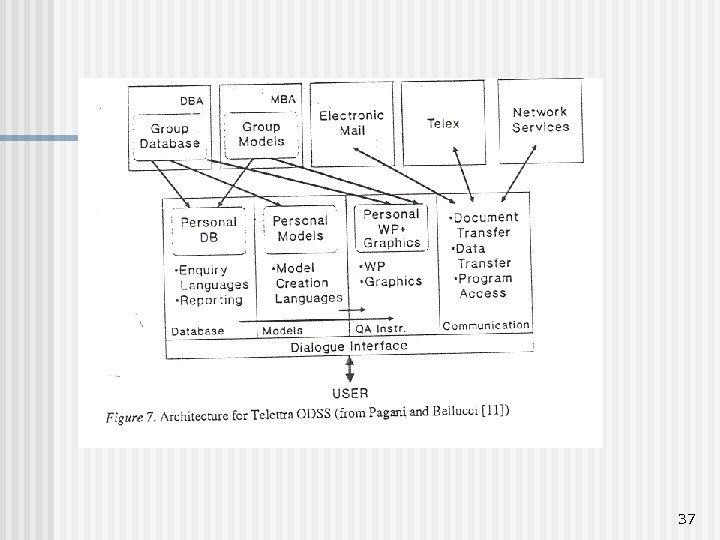 37
37
 38
38
 George, Nunamaker & Valacich, 1992: Classification of ODSS based on Key Issues n Downsizing: Reduction in the number of human resources and hierarchical layers- Keys to ODSS: n ODSS to act as knowledge filters and amplifiers n ODSS to handle increased communication caused by an increase in the span of control n ODSS to integrate the gaps created by the missing Management 39
George, Nunamaker & Valacich, 1992: Classification of ODSS based on Key Issues n Downsizing: Reduction in the number of human resources and hierarchical layers- Keys to ODSS: n ODSS to act as knowledge filters and amplifiers n ODSS to handle increased communication caused by an increase in the span of control n ODSS to integrate the gaps created by the missing Management 39
 George, Nunamaker & Valacich, 1992: Classification of ODSS based on Key Issues n Self-Managed Teams: This address the gaps. n Need increased coordination tools: Groupware n Need increased flexibility in decision making n Need different types of people (for discussion) 40
George, Nunamaker & Valacich, 1992: Classification of ODSS based on Key Issues n Self-Managed Teams: This address the gaps. n Need increased coordination tools: Groupware n Need increased flexibility in decision making n Need different types of people (for discussion) 40
 George, Nunamaker & Valacich, 1992: Classification of ODSS based on Key Issues n Outsourcing: • Strategic versus tactical issues • Coordination issues 41
George, Nunamaker & Valacich, 1992: Classification of ODSS based on Key Issues n Outsourcing: • Strategic versus tactical issues • Coordination issues 41
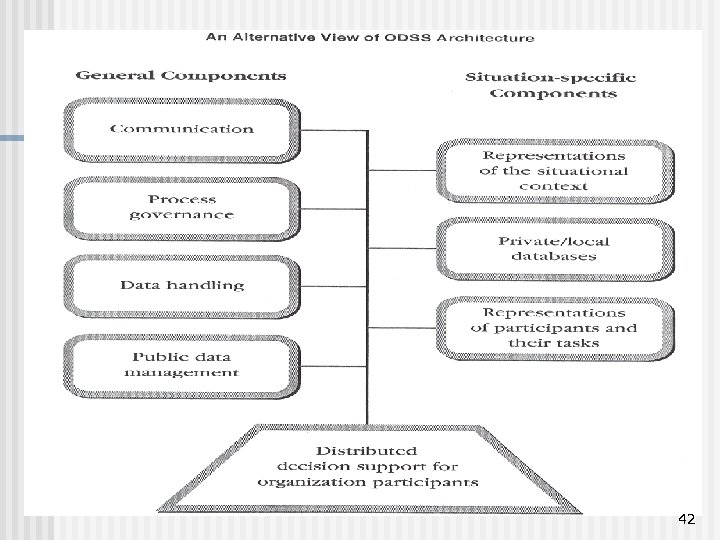 42
42
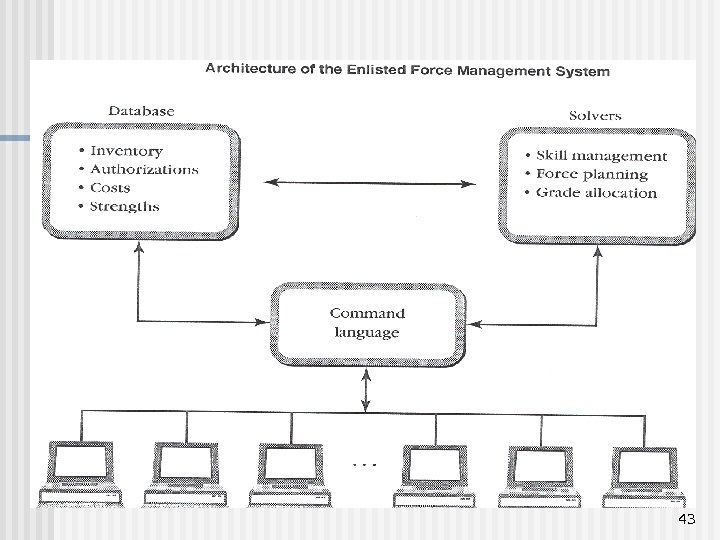 43
43
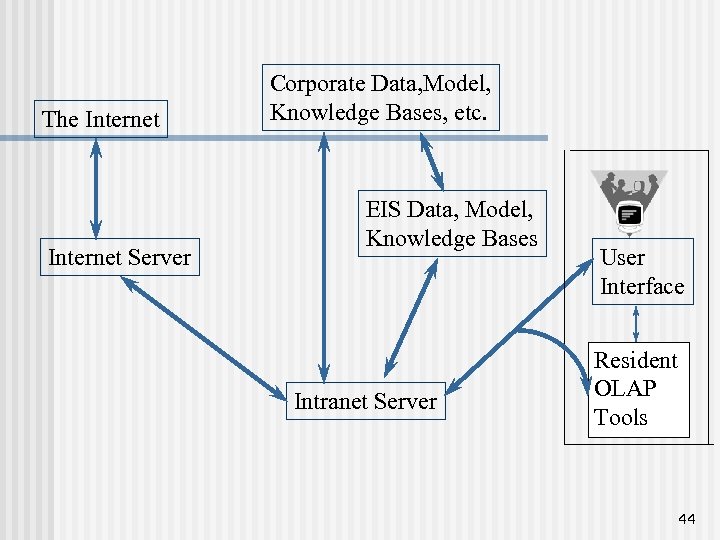 The Internet Server Corporate Data, Model, Knowledge Bases, etc. EIS Data, Model, Knowledge Bases Intranet Server User Interface Resident OLAP Tools 44
The Internet Server Corporate Data, Model, Knowledge Bases, etc. EIS Data, Model, Knowledge Bases Intranet Server User Interface Resident OLAP Tools 44
 45
45
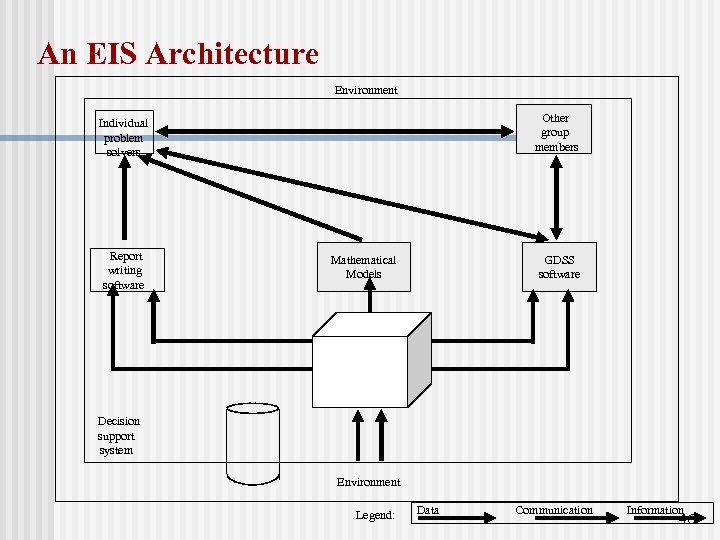 An EIS Architecture Environment Other group members Individual problem solvers Report writing software GDSS software Mathematical Models RDB Decision support system Environment Legend: Data Communication Information 46
An EIS Architecture Environment Other group members Individual problem solvers Report writing software GDSS software Mathematical Models RDB Decision support system Environment Legend: Data Communication Information 46
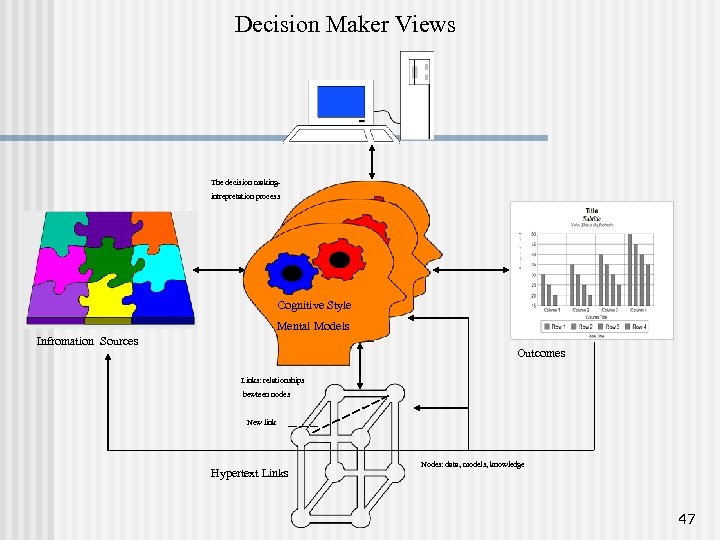 Decision Maker Views The decision makingintrepretation process Cognitive Style Mental Models Infromation Sources Outcomes Links: relationships bewteen nodes New link Hypertext Links Nodes: data, models, knowledge 47
Decision Maker Views The decision makingintrepretation process Cognitive Style Mental Models Infromation Sources Outcomes Links: relationships bewteen nodes New link Hypertext Links Nodes: data, models, knowledge 47
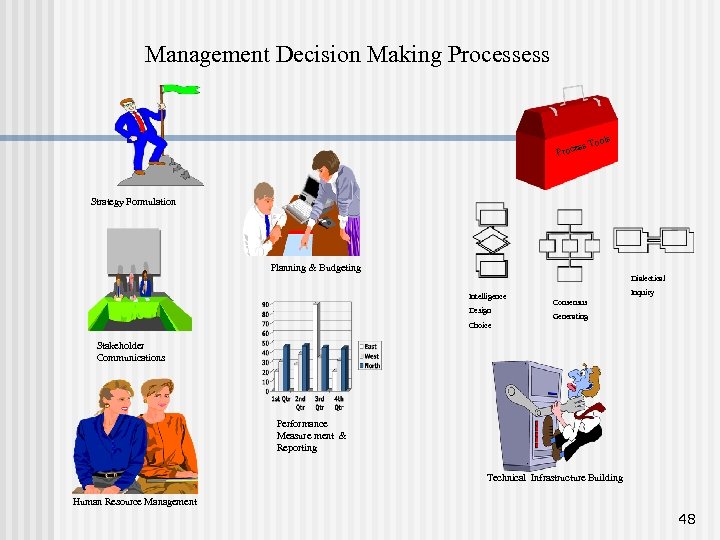 Management Decision Making Processess s Too es Proc ls Strategy Formulation Planning & Budgeting Dialectical Intelligence Design Choice Inquiry Consensus Generating Stakeholder Communications Performance Measure ment & Reporting Technical Infrastructure Building Human Resource Management 48
Management Decision Making Processess s Too es Proc ls Strategy Formulation Planning & Budgeting Dialectical Intelligence Design Choice Inquiry Consensus Generating Stakeholder Communications Performance Measure ment & Reporting Technical Infrastructure Building Human Resource Management 48
 49
49
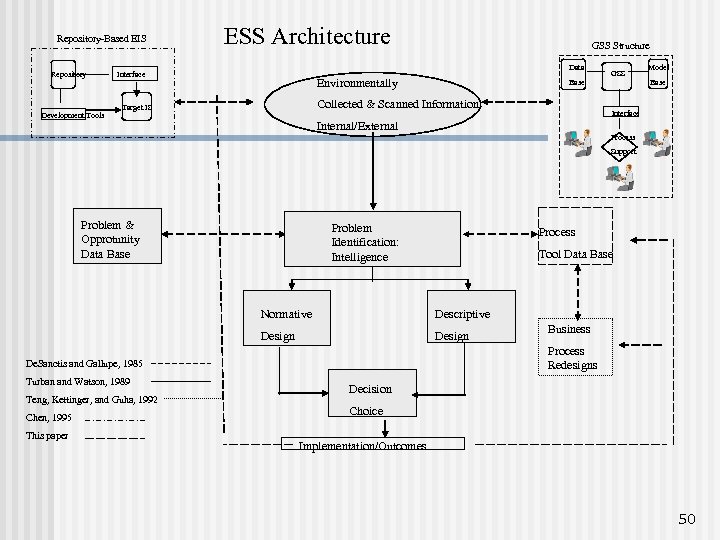 Repository-Based EIS Repository Development Tools ESS Architecture GSS Structure Data Interface Environmentally Base Collected & Scanned Information: Target IS GSS Model Base Interface Internal/External Process Support Problem & Opprotunity Data Base Problem Identification: Intelligence Process Tool Data Base Normative Descriptive Design Process Redesigns De. Sanctis and Gallupe, 1985 Turban and Watson, 1989 Teng, Kettinger, and Guha, 1992 Chen, 1995 This paper Business Decision Choice Implementation/Outcomes 50
Repository-Based EIS Repository Development Tools ESS Architecture GSS Structure Data Interface Environmentally Base Collected & Scanned Information: Target IS GSS Model Base Interface Internal/External Process Support Problem & Opprotunity Data Base Problem Identification: Intelligence Process Tool Data Base Normative Descriptive Design Process Redesigns De. Sanctis and Gallupe, 1985 Turban and Watson, 1989 Teng, Kettinger, and Guha, 1992 Chen, 1995 This paper Business Decision Choice Implementation/Outcomes 50
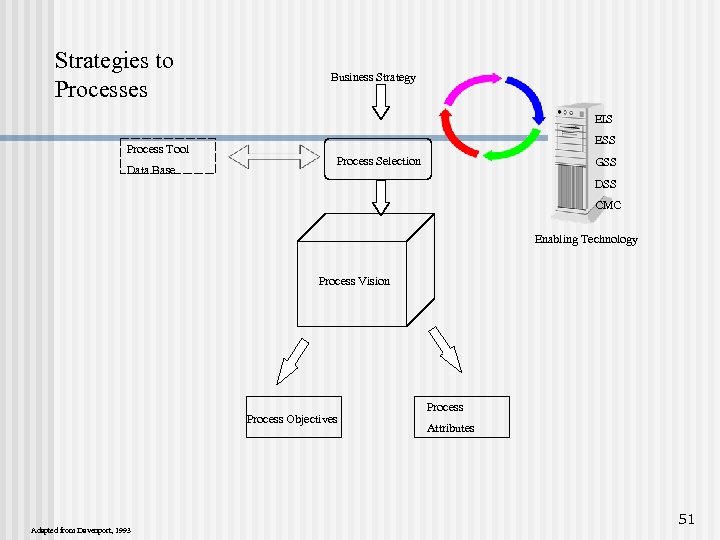 Strategies to Processes Business Strategy EIS Process Tool Data Base ESS Process Selection GSS DSS CMC Enabling Technology Process Vision Process Objectives Adapted from Davenport, 1993 Process Attributes 51
Strategies to Processes Business Strategy EIS Process Tool Data Base ESS Process Selection GSS DSS CMC Enabling Technology Process Vision Process Objectives Adapted from Davenport, 1993 Process Attributes 51
 Supply and Value Chains and Decision Support n n Supply chain: (originally) flow of materials from sources to internal use Demand chain: flow from inside to customers 52
Supply and Value Chains and Decision Support n n Supply chain: (originally) flow of materials from sources to internal use Demand chain: flow from inside to customers 52
 Supply Chain n n The flow of materials, information, and services from raw material suppliers through factories and warehouses to the end customers Includes the organizations and processes that create and deliver value to the end customers 53
Supply Chain n n The flow of materials, information, and services from raw material suppliers through factories and warehouses to the end customers Includes the organizations and processes that create and deliver value to the end customers 53
 Supply Chain Management (SCM) n n To deliver an effective supply chain and do it effectively To plan, organize, and coordinate the supply chain’s activities 54
Supply Chain Management (SCM) n n To deliver an effective supply chain and do it effectively To plan, organize, and coordinate the supply chain’s activities 54
 SCM Benefits Reduction in uncertainty and risks in the supply chain n Positively affect n inventory levels n cycle time n processes n customer service n n Increase profitability 55
SCM Benefits Reduction in uncertainty and risks in the supply chain n Positively affect n inventory levels n cycle time n processes n customer service n n Increase profitability 55
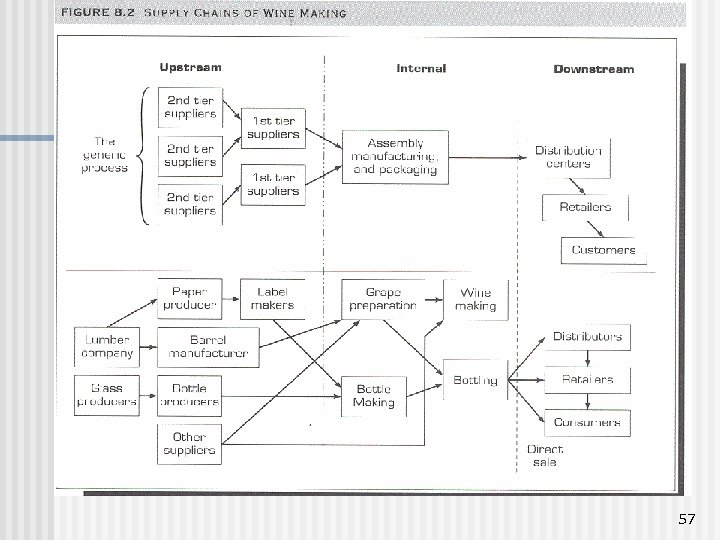
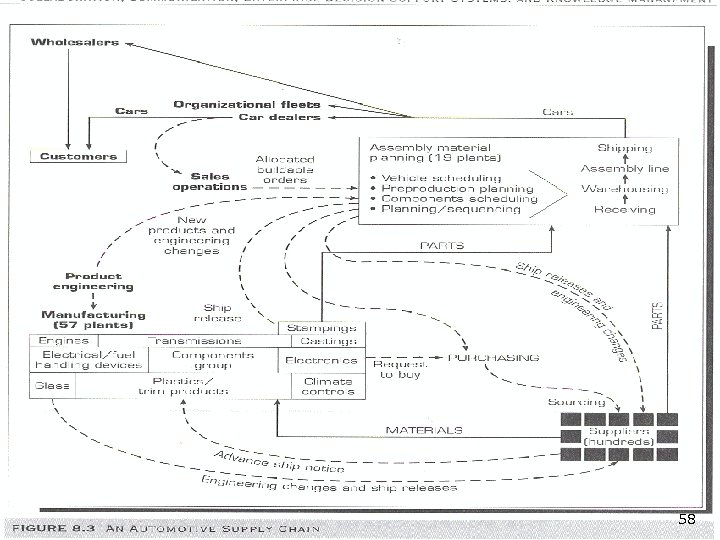
 Supply Chain Components Upstream n Internal supply chain n Downstream n Involves product life cycle activities Example (Figure 8. 2) 56
Supply Chain Components Upstream n Internal supply chain n Downstream n Involves product life cycle activities Example (Figure 8. 2) 56
 57
57
 58
58
 Supply Chain Related to Porter’s (1985)Value Chain 1. Inbound logistics (inputs) n 2. Operations (i. e manufacturing) n 3. Outbound logistics (i. e. storage, distribution) n 4. Marketing and Sales n 5. Service n 59
Supply Chain Related to Porter’s (1985)Value Chain 1. Inbound logistics (inputs) n 2. Operations (i. e manufacturing) n 3. Outbound logistics (i. e. storage, distribution) n 4. Marketing and Sales n 5. Service n 59
 Supply Chain Problems Uncertainty in the demand forecast n Uncertainty in delivery times n Quality problems n Poor customer service n High inventory costs n Low revenue n Extra costs n 60
Supply Chain Problems Uncertainty in the demand forecast n Uncertainty in delivery times n Quality problems n Poor customer service n High inventory costs n Low revenue n Extra costs n 60
 Solutions to Supply Chain Problems n n n Outsourcing Buy, not make Configure optimal shipping plans Optimize purchasing Strategic partnerships with suppliers Just-in-time delivery of purchases Reduce intermediaries Reduce lead times (EDI) Use fewer suppliers Improve the supplier-buyer relationships Build-to-order Accurate demand by working with suppliers 61
Solutions to Supply Chain Problems n n n Outsourcing Buy, not make Configure optimal shipping plans Optimize purchasing Strategic partnerships with suppliers Just-in-time delivery of purchases Reduce intermediaries Reduce lead times (EDI) Use fewer suppliers Improve the supplier-buyer relationships Build-to-order Accurate demand by working with suppliers 61
 Computerized Systems MRP n ERP n SCM n Integrating the supply chain 62
Computerized Systems MRP n ERP n SCM n Integrating the supply chain 62
 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) n Objective: integrate all departments and functions across an organization into a single computer system that can serve the entire enterprise’s needs 63
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) n Objective: integrate all departments and functions across an organization into a single computer system that can serve the entire enterprise’s needs 63
 ERP Software Vendors SAP n Baan n People. Soft n Oracle n J. D. Edwards n Computer Associates n 64
ERP Software Vendors SAP n Baan n People. Soft n Oracle n J. D. Edwards n Computer Associates n 64
 ERP Very (VERY!) expensive n 2 nd generation: doing better n Early 2000: moving to Web n Will fail if an organization’s business processes do not fit the ERP system’s model n 65
ERP Very (VERY!) expensive n 2 nd generation: doing better n Early 2000: moving to Web n Will fail if an organization’s business processes do not fit the ERP system’s model n 65
 Application Service Providers and ERP Outsourcing n ASP: software vendor who leases ERP -based applications n Outsourcing n Now via the Web 66
Application Service Providers and ERP Outsourcing n ASP: software vendor who leases ERP -based applications n Outsourcing n Now via the Web 66
 Corporate (Enterprise) Portals and EIS Integrates internal applications with external applications n Generally via the Web n Can include n n n n groupware technologies presentation and customization publishing and distribution search categorization integration 67
Corporate (Enterprise) Portals and EIS Integrates internal applications with external applications n Generally via the Web n Can include n n n n groupware technologies presentation and customization publishing and distribution search categorization integration 67
 Frontline Decision Support Systems n n Process of automating decision processes and pushing them down into the organization and even partners Includes empowering employees 68
Frontline Decision Support Systems n n Process of automating decision processes and pushing them down into the organization and even partners Includes empowering employees 68
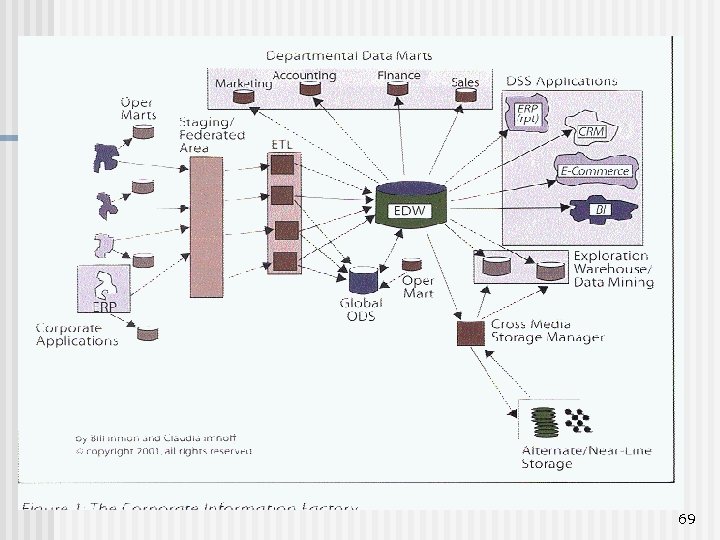 69
69
 Future of Executive and Enterprise Support Systems n n n Toolbox for customized systems Multimedia support Better access (via PDFs and cell phones) Virtual Reality and 3 -D Image Displays Merging of analytical systems (OLAP / multidimensional analysis)) with desktop publishing Client/server architecture Web-enabled EIS Automated support and intelligent assistance Integration of EIS and Group Support Systems Global EIS Integration and deployment with ERP products 70
Future of Executive and Enterprise Support Systems n n n Toolbox for customized systems Multimedia support Better access (via PDFs and cell phones) Virtual Reality and 3 -D Image Displays Merging of analytical systems (OLAP / multidimensional analysis)) with desktop publishing Client/server architecture Web-enabled EIS Automated support and intelligent assistance Integration of EIS and Group Support Systems Global EIS Integration and deployment with ERP products 70


