0807ac72f4408b69a472829426837d97.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 122

Chapter 6 Early India Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Early India Chapter Introduction Section 1 India’s First Civilizations Section 2 Hinduism and Buddhism Section 3 India’s First Empires Reading Review Chapter Assessment Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides.

Early India Chapter Objectives • Describe how climate and geography affected India, and how the Aryans changed India. • Summarize the main tenets of Hinduism and Buddhism. • Discuss the effects of the Mauryan and Gupta empires on India. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Early India Click the speaker button to play the audio.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Get Ready to Read Section Overview This section describes how geography and climate affected the Harappans and the changes to India’s civilization following the arrival of the Aryans.

India’s First Civilizations Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Focusing on the Main Ideas • Climate and geography influenced the rise of India’s first civilization. • The Aryans conquered India and introduced new ideas and technology. • The Aryans created a caste system that separated Indians into groups. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Locating Places • Himalaya (HIH·muh·LAY·uh) • Ganges River (GAN·JEEZ) • Indus River (IHN·duhs) • Harappa (huh·RA·puh) • Mohenjo-Daro (moh·HEHN·joh DAHR·oh) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Meeting People • Aryans (AR·ee·uhnz) • Brahmans (BRAH·muhns) Building Your Vocabulary • subcontinent (SUHB·KAHN·tuhn·uhnt) • monsoon (mahn·SOON) • Sanskrit (SAN·SKRIHT) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Building Your Vocabulary (cont. ) • raja (RAH·juh) • caste (KAST) • guru (GUR·oo) Reading Strategy Organizing Information Complete a diagram like the on page 194 of your textbook showing how the Aryans changed India. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations The Land of India • India is a subcontinent because it is separated from the rest of Asia by the Himalayas, the highest mountains in the world. • The Indian subcontinent contains five nations: India, Pakistan, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Nepal. • India has two fertile river valleys created by the Ganges River and the Indus River. (pages 195– 197) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations The Land of India (cont. ) • A monsoon is a strong wind that blows one direction in winter and the opposite direction in summer. • Monsoons bring rain in summer. • The first civilization in India arose near the Indus River after the river flooded and left fertile soil behind. • This civilization started about 3000 B. C. and lasted until about 1500 B. C. (pages 195– 197) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations The Land of India (cont. ) • Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro were large, well-planned cities in ancient India. • The cities had wells, drains for wastewater, garbage chutes, and organized governments. • The houses were made from baked mud bricks. • Most people were farmers. • They grew wheat, barley, peas, and (pages 195– 197) cotton. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations The Land of India (cont. ) • City dwellers were artisans, who made jewelry, pottery, tools, and cloth. • The Harappans traded their goods with people from other lands. (pages 195– 197) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Why do archaeologists think the Harappans were peaceful people? Scientists have found few weapons in the ruins of Harappa. This implies that the people were not warriors. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations The Aryans Invade • The Aryans were hunters who also raised and herded cattle. • Because they herded animals, Aryans were also nomads and expert warriors. • They had metal-tipped spears and wooden chariots. • The Aryans invaded Harappan civilization and destroyed it. (pages 198– 199) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations The Aryans Invade (cont. ) • They later conquered all of the Indian subcontinent except the southern tip of India. • After conquering India, the Aryans became farmers but continued to raise cattle. • The cattle were so important, the Aryans eventually declared them sacred. (pages 198– 199) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations The Aryans Invade (cont. ) • The Aryans invented an iron plow and built canals to improve farming. • The Aryans’ written language is called Sanskrit. • Aryan tribes were led by a raja, or prince. (pages 198– 199) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Why were nomads good warriors? Because nomads traveled, they often met up with other people whom they considered enemies. They also came upon villages they needed to plunder food. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations Society in Ancient India • A caste is a social group that someone is born into and cannot change. • The Aryans believed in four levels of society. • The top level included priests and warriors. • The next level was common people, such as merchants and farmers. (pages 199– 201) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Society in Ancient India (cont. ) • The third level included laborers and servants. • The lowest level was made up of the Untouchables. • These people did work others did not want to do. (pages 199– 201) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Society in Ancient India (cont. ) • Men’s lives were considered more important than women’s lives. • In most cases, only men could inherit property. • Only men were allowed to go to school or become priests. • Parents arranged marriages, and divorce was not allowed. (pages 199– 201) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Civilizations Under the caste system in India, what aspects of life are affected by a person’s caste? A person’s caste affects what job they will have, who they can marry, and who they can socialize with. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations Describe the cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro were planned cities with wide main streets and a wall around each neighborhood. Each mud brick house had a flat roof and was laid out around a courtyard. Each city had public wells, a sewage system, and garbage disposal. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations Why are monsoons important to Indian farmers? They cause soil-enriching floods. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations Cause and Effect What caused the collapse of Harappan civilization? earthquakes, floods, the Indus River changing its course, and the Aryan invasions Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations Contrast How did the Aryan and Harappan lifestyles differ? Harappans were city-dwellers; Aryans were war-like nomads. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations Explain How did the Aryans control the people they conquered? Possible answers: strong military, effects of caste system Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations Descriptive Writing Write a description of the city of Harappa or Mohenjo-Daro that could have been used to attract residents to that city in ancient India. Answers should demonstrate understanding of the text. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Civilizations Discuss the influence of geographic factors on the Harappans and the Aryans.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism Get Ready to Read Section Overview The religion of Hinduism is based on the beliefs of the Aryans. Buddhism, a new religion, was popular with many people in India and other areas of Asia.

Hinduism and Buddhism Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Focusing on the Main Ideas • Hinduism grew out of the ancient beliefs of the Aryans. • A new religion, Buddhism, appealed to many people in India and other parts of Asia. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Locating Places • Nepal (nuh·PAWL) • Tibet (tuh·BEHT) Meeting People • Siddhartha Gautama (sih·DAHR·tuh GOW·tuh·muh) • Dalai Lama (DAH·LY LAH·muh) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Building Your Vocabulary • Hinduism (HIHN·doo·IH·zuhm) • Brahman (BRAH·muhn) • reincarnation (REE·ihn·kahr·NAY·shuhn) • dharma (DAHR·muh) • karma (KAHR·muh) • Buddhism (BOO·DIH·zuhm) • nirvana (nihr·VAH·nuh) • theocracy (thee·AH·kruh·see) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Reading Strategy Summarizing Information Create a web diagram like the on page 202 of your textbook. In the ovals, identify major beliefs of Hinduism.

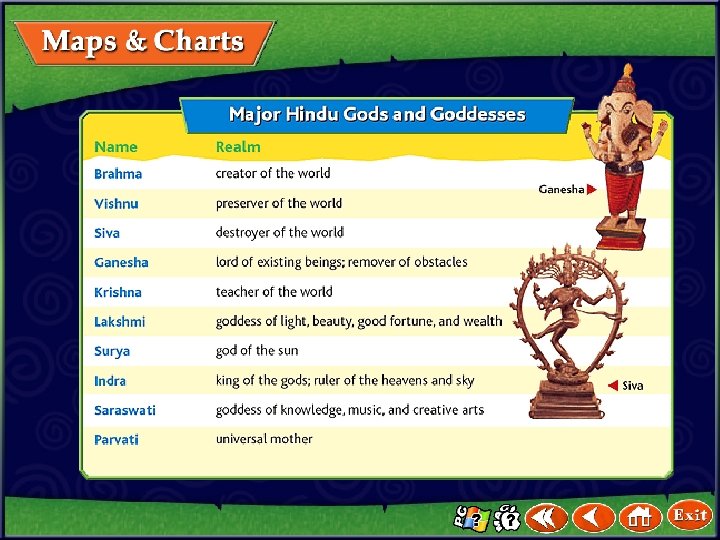
Hinduism and Buddhism Hinduism • Hinduism, the world’s third largest religion, is one of the oldest religions. • Hinduism’s roots are in the Aryan religion, which changed after borrowing ideas from conquered people of India. • The Brahman is the universal spirit made up of thousands of gods and goddesses. (pages 203– 204) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism Hinduism (cont. ) • The Upanishads are ancient religious writings that describe the search for Brahman. • Reincarnation is the idea of passing through many lives to reach the Brahman. • Dharma is the divine law of Hindus. (pages 203– 204) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism Hinduism (cont. ) • This law states that Hindus must perform the duties of their caste. • The consequences of how a person lives is called karma. (pages 203– 204) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism According to Hindus, what are the consequences of a good and a bad life? Hindus believe if a person lives a good life, then that person might be reborn into a higher caste. If the person lives a bad life, then the person might be reborn in a lower caste. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Hinduism and Buddhism • Buddhism is a religion founded by Siddhartha Gautama, the man who became known as the Buddha, or “Enlightened One. ” • Siddhartha Gautama was a prince who left his family and wealth to travel. • In his travels, he saw much suffering and questioned the need for suffering. (pages 205– 208) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism (cont. ) • Legend tells he meditated under a tree for 49 days, and then he understood. • For the rest of his life, Siddhartha traveled to tell people about his discovery. • Nirvana, a state of wisdom, occurs when a person gives up all desires. (pages 205– 208) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism (cont. ) • The core of Buddha’s teaching is called the Four Noble Truths. • The Eightfold Path describes the steps to eliminate suffering. • Buddhism divided into Theravada Buddhism and Mahayana Buddhism. • Theravada Buddhists believe the Buddha was a great teacher, not a god. (pages 205– 208) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism (cont. ) • Mahayana Buddhists believe the Buddha was a god who came to save people. • Tibet is a country in central Asia where Mahayana Buddhism mixed with traditional Tibetan religion and Hinduism to create a special kind of Mahayana Buddhism. • In Tibet, religious leaders, called lamas, headed the government. (pages 205– 208) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism (cont. ) • The Dalai Lama was the government leader, and the Panchen Lama was the religious leader. • A theocracy is a form of government in which religious leaders head the government. (pages 205– 208) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Hinduism and Buddhism Why was Buddhism popular with people of lower castes? The Buddha taught that a person’s life depended on the person, not the caste into which the person was born. He believed that a person could stop being reborn by following the Eightfold Path. This gave lower caste people hope. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Hinduism and Buddhism What are the Upanishads? The Upanishads are ancient religious writings that describe the search for a universal spirit. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Hinduism and Buddhism What is reincarnation? Reincarnation is a religious belief that a soul is reborn many times. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Hinduism and Buddhism Describe Explain the concept of karma. Karma is the consequences a soul faces in its next life for its actions in this life. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Hinduism and Buddhism Explain What is the importance of the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path? The Four Noble Truths explain why people suffer. The Eightfold Path describes behaviors that will end suffering. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Hinduism and Buddhism Analyze How did the belief in reincarnation both strengthen the divisions in Indian society and provide hope for the lower classes? One’s position in society results from past acts. Lower classes hoped to improve their position in a future life. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Hinduism and Buddhism Expository Writing Write a short essay describing Siddhartha Guatama’s journey to enlightenment. Answers should be based on the text. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Hinduism and Buddhism Hinduism is more than a religion; it is a whole way of life. Identify facts that support this statement.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires Get Ready to Read Section Overview The Mauryan and Gupta dynasties built empires in India, and they contributed greatly to literature, mathematics, and science.

India’s First Empires Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Focusing on the Main Ideas • The Mauryan dynasty built India’s first great empire. • The Gupta empire reunited much of northern India and became wealthy through trade. • The Mauryan and Gupta empires made important contributions in literature, mathematics, and science. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Locating Places • Pataliputra (PAH·tuh·lih·POO·truh) Meeting People • Chandragupta Maurya (CHUHN·druh·GUP·tuh MAH·oor·yuh) • Asoka (uh·SOH·kuh) • Kalidasa (KAH·lih·DAH·suh) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires Get Ready to Read (cont. ) Building Your Vocabulary • dynasty (DY·nuh·stee) • stupa (STOO·puh) • pilgrim (PIHL·gruhm) Reading Strategy Categorizing Information Complete a chart like the on page 209 of your textbook identifying the important dates, capital city, and government of the Mauryan empire. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires The Mauryan Dynasty • Chandragupta Maurya, an Indian prince, founded India’s first empire after Alexander the Great left India. • This empire was called the Mauryan dynasty. • A dynasty is a series of rulers from the same family. • Chandragupta controlled his dynasty by retaining a strong army and using spies. (pages 210– 211) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires The Mauryan Dynasty (cont. ) • Many historians consider Asoka the Mauryan dynasty’s greatest king. • After he was a strong military leader, Asoka turned away from violence. • He made a vow to live a peaceful life and follow Buddhism. • Asoka did many great things for his people. (pages 210– 211) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires The Mauryan Dynasty (cont. ) • For example, he built hospitals and new roads and sent teachers throughout India to teach Buddhism. • The empire grew weak after Asoka’s death. • The kings made poor decisions, and the Mauryan Empire fell. (pages 210– 211) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires What happened as a result of Alexander the Great’s invasion of northern India? Alexander the Great’s army weakened the people of India. After Alexander the Great and his men left, the people could not resist Chandragupta. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Empires The Gupta Empire • After 500 years of fighting, another Chandragupta took power and founded the Gupta dynasty. • After Chandragupta died, his son, Samudragupta, took over and expanded the empire. • The Guptas ruled for about 200 years. • They grew wealthy from trade with China and kingdoms in southeast Asia and the Mediterranean. (page 213) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires The Gupta Empire (cont. ) • Pilgrims were people who often used the trade routes to travel to a religious shrine or site. • Visiting pilgrims helped make cities wealthy just as tourists make cities wealthy today. • The Guptas were Hindus, and they made Hinduism the official religion. • The golden age of art and learning in India was during the Gupta empire. (page 213) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires What advantage did the Gupta rulers have that the Mauryan rulers did not? The kingdom had gotten smaller before the Gupta rulers took power. The smaller kingdom was easier to rule. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Empires Indian Literature and Science • The Vedas of India are hymns and prayers used in religious ceremonies. • The Vedas were recorded in Sanskrit after the Aryan people came to India. • The epics Mahabharata and Ramayana are two poems that are still famous in India today. • Both epics tell about warriors and their brave deeds. (pages 214– 216) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires Indian Literature and Science (cont. ) • Kalidasa was a writer who lived during the Gupta dynasty. • His poem The Cloud Messenger is one of the most popular Sanskrit poems. • Aryabhata was a mathematician who lived during the Gupta dynasty. • He was one of the first scientists to use algebra. (pages 214– 216) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires Indian Literature and Science (cont. ) • Mathematicians in the Gupta empire developed the symbols for the numbers 1 to 9 that we use today. • They also invented algorithms and the idea of zero. • Indians also developed ideas in astronomy and medicine. (pages 214– 216) Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

India’s First Empires What kinds of medical advances were made by Gupta doctors? Gupta doctors could set broken bones and perform surgeries. They also developed medical tools. One doctor even carried out an early form of plastic surgery. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Empires Describe trade during the Gupta empire? Indians traded salt, cloth, and iron with China, Southeast Asia, and the Mediterranean. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Empires What is the message of the Bhagavad Gita? It taught people to do their duty even when it was painful. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Empires Analyze How were Asoka’s Buddhist beliefs reflected in his accomplishments as king? His improvements were for the overall good. He built hospitals, roads, and rest stops for travelers; sent missionaries throughout India and Asia; carved Buddha’s principles on pillars; built stupas; and practiced religious tolerance. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Empires Expository Writing Which of the Indian emperors described in this section do you think was the greatest ruler? Write a short essay explaining your choice. Be sure to provide reasons for your choice of ruler. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Empires Math Link Why would the development of a number system be important in a civilization that depended on trade? to keep records of transactions and to monitor the exchange of money Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

India’s First Empires Summarize how religion affected the Gupta empire.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Early India Section 1: India’s First Civilizations Focusing on the Main Ideas • Climate and geography influenced the rise of India’s first civilization. • The Aryans conquered India and introduced new ideas and technology. • The Aryans created a caste system that separated Indians into groups. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Early India Section 2: Hinduism and Buddhism Focusing on the Main Ideas • Hinduism grew out of the ancient beliefs of the Aryans. • A new religion, Buddhism, appealed to many people in India and other parts of Asia. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Early India Section 3: India’s First Empires Focusing on the Main Ideas • The Mauryan dynasty built India’s first great empire. • The Gupta empire reunited much of northern India and became wealthy through trade. • The Mauryan and Gupta empires made important contributions in literature, mathematics, and science. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
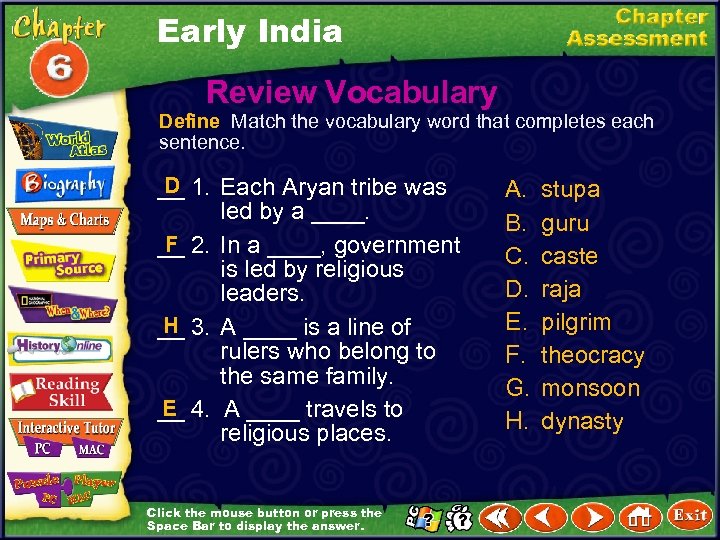
Early India Review Vocabulary Define Match the vocabulary word that completes each sentence. D __ 1. Each Aryan tribe was led by a ____. F __ 2. In a ____, government is led by religious leaders. H __ 3. A ____ is a line of rulers who belong to the same family. E __ 4. A ____ travels to religious places. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. stupa guru caste raja pilgrim theocracy monsoon dynasty

Early India Review Vocabulary Define Match the vocabulary word that completes each sentence. G __ 5. A ____ is a strong wind that blows one direction in winter and the opposite direction in summer. B __ 6. A ____, is a teacher. C __ 7. A ____ is a social group that someone is born into and cannot change. A __ 8. ____ are Buddhist shrines that have the shape of a dome or mound. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. stupa guru caste raja pilgrim theocracy monsoon dynasty

Early India Review Main Ideas Section 1 India’s First Civilizations What influenced the rise of India’s first civilizations? Geography and climate influenced the first civilizations. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Review Main Ideas Section 1 India’s First Civilizations What was the purpose of the caste system? No one is sure, but possibly to help Aryans stay in control. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Review Main Ideas Section 2 Hinduism and Buddhism From what did Hinduism form? Hinduism formed from the ancient beliefs of the Aryans. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Review Main Ideas Section 2 Hinduism and Buddhism Which religion appealed to people in India and other parts of Asia? Buddhism Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Review Main Ideas Section 3 India’s First Empires Which dynasty built India’s first great empire? the Mauryan dynasty Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Review Main Ideas Section 3 India’s First Empires Why was the Gupta empire important? It reunited much of India and became wealthy through trade. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Compare How do you think the Eightfold Path is similar to the Ten Commandments of Judaism? They both describe behaviors that believers must try to follow. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Analyze How does the Mahabharata reflect the ideals of ancient India? It stresses the importance of doing one’s duty. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Explain How did the monsoons affect the development of India’s first civilizations? The summer monsoon made the Indus River flood, fertilizing the soil and leading to good farming. Surplus food led to specialization and civilization. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Early India Predict What do you think might have happened if Asoka had approved of the slaughter on the battlefield during his wars of conquest? Answers might include that wars might have continued during the Mauryan empire; the empire might have been larger; Buddhism may not have spread so quickly. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Explore online information about the topics introduced in this chapter. Click on the Connect button to launch your browser and go to the Journey Across Time Web site. Click on Chapter 6 -Chapter Overviews to preview information about this chapter. When you finish exploring, exit the browser program to return to this presentation. If you experience difficulty connecting to the Web site, manually launch your Web browser and go to http: //www. jat. glencoe. com

Maps Geography of India Aryan Migration 2000– 500 B. C. Mauryan Empire c. 250 B. C. Gupta Empire c. A. D. 600 Charts Early India’s Social System Major Hindu Gods and Goddesses Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides.
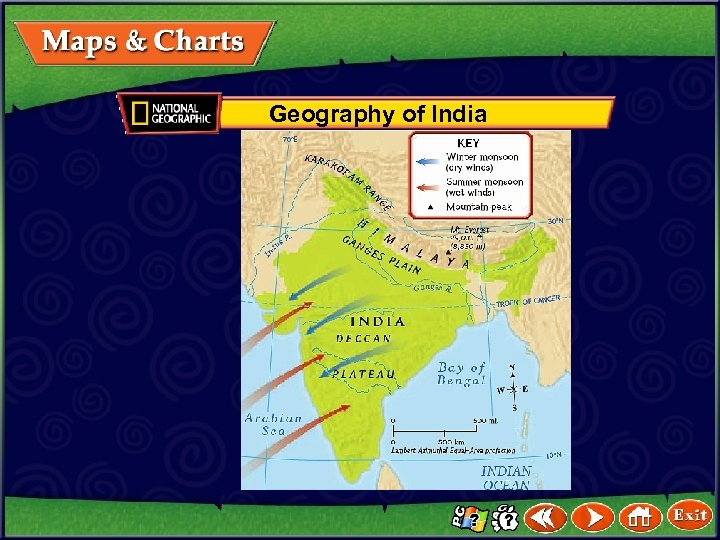
Geography of India
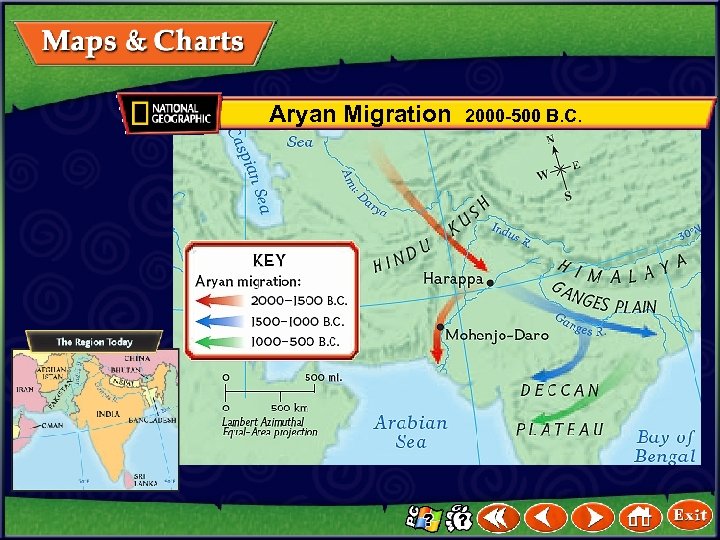
Aryan Migration 2000 -500 B. C.
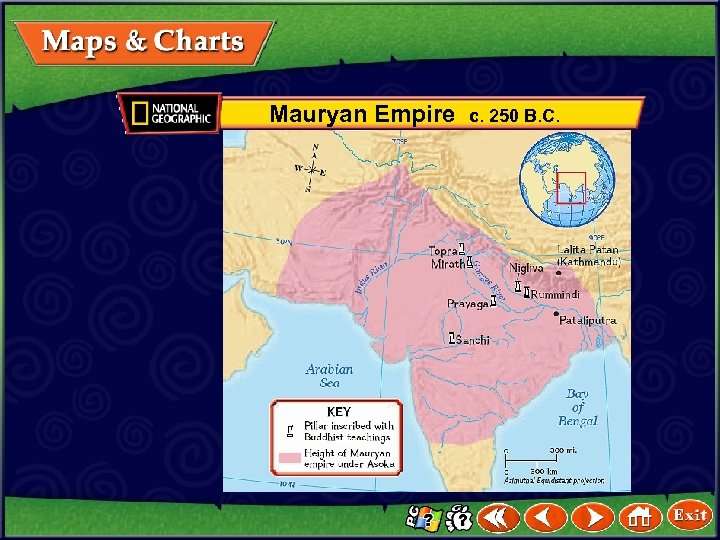
Mauryan Empire c. 250 B. C.
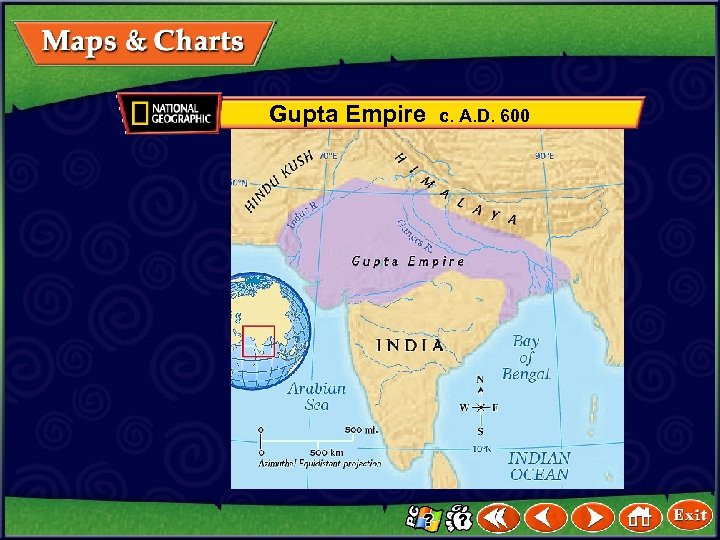
Gupta Empire c. A. D. 600


As dangerous as monsoon flooding can be, drought is much more devastating to the people of India. In 1770, the rains did not come, and a famine occurred because of the drought. About 10 million people died in Bengal, an Indian state.

In 1949, the country of Tibet was invaded by China still occupies Tibet and tries to expel Tibetan Buddhism. Tibetans who fail to denounce their religion or who possess an image of the Dalai Lama, their religious leader, are punished.

Following Buddhist ways, Asoka respected all life and even created hospitals for animals.

Reading Social Studies Learn It! Building Your Vocabulary What do you do when you are reading and come to a word you do not know? Here are some hints: • Use clues in the sentence (called context clues) to help you define it. • Look for prefixes, suffixes, or root words that you already know. • Look it up in the glossary or a dictionary. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Reading Social Studies Learn It! Building Your Vocabulary What do you do when you are reading and come to a word you do not know? Here are some hints: • Write it down and ask for help with the meaning. • Guess at its meaning. Look at the word Untouchables in the paragraph on the next slide. Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Reading Social Studies Context The “Untouchables” were a “group. ” They had a “low” rank in society. There was one group so low that it was not even part of the caste system. Its members were called Pariahs, or the Untouchables. They performed work other Indians thought was too dirty, such as collecting trash, skinning animals, or handling dead bodies. Context If you know what the caste system is, it will help you figure out the meaning of Untouchables. —from page 200 Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Reading Social Studies Prefixes and Suffixes You might know that the prefix unmeans “not” and the suffix –able means “to be able to. ” You might guess that the meaning of Untouchable is an Indian who was not to be touched by others. There was one group so low that it was not even part of the caste system. Its members were called Pariahs, or the Untouchables. They performed work other Indians thought was too dirty, such as collecting trash, skinning animals, or handling dead bodies. Context The fact that they performed the “dirty” work indicates how they were viewed by others in Indian society. —from page 200 Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Reading Social Studies There was one group so low that it was not even part of the caste system. Its members were called Pariahs, or the Untouchables. They performed work other Indians thought was too dirty, such as collecting trash, skinning animals, or handling dead bodies. —from page 200 Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Reading Social Studies Practice It! Defining Words Read the paragraph from Chapter 6 on page 193 of your textbook. • What are three things you could do to help you understand the meaning of the word subcontinent in this paragraph? Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

Early India Introduction
India’s First Civilizations

Hinduism and Buddhism
India’s First Empires

Morality in the Eightfold Path Click the speaker button to play the audio.

The Bhagavad Gita Click the speaker button to play the audio.

The Buddha 563– 483 B. C. Sculpture of the Buddha sitting on a cobra. Click the speaker button to play the audio. The Buddha

Emperor Asoka Carving from top of pillar created under Asoka. Click the speaker button to play the audio. Asoka

Chapter 6 Daily Focus Skills Transparency 6– 1 Click the mouse button or press the Space bar to display the answer. Click the speaker button to play the audio. Bar to display the information.
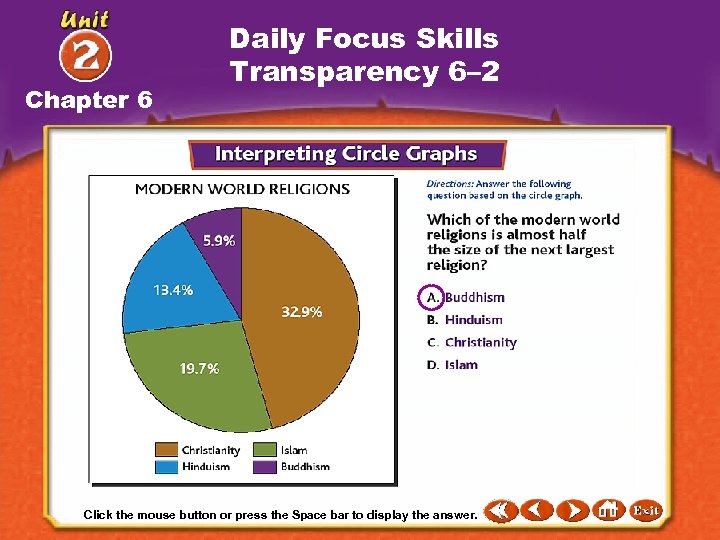
Chapter 6 Daily Focus Skills Transparency 6– 2 Click the mouse button or press the Space bar to display the answer. Click the speaker button to play the audio. Bar to display the information.

Chapter 6 Daily Focus Skills Transparency 6– 3 Click the mouse button or press the Space bar to display the answer. Click the speaker button to play the audio. Bar to display the information.

Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
0807ac72f4408b69a472829426837d97.ppt