ffe02f05ed29c32ceedc12c145fe1740.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Chapter 6 E-Business: Intra-Business E-Commerce

Internal Communication n Historically, paper n Updating a paper procedures manual n n B 2 Employee E-commerce n n Outdated material Numerous misunderstandings Some legal actions Maintain online – Web site E-business more general than B 2 E Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
Figure 6. 1 Miami University’s online publications and policies. Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

B 2 C vs. Intra-business E-commerce n Consumer oriented B 2 C n n Revolutionary Aggressive and risky First movers Intra-business and B 2 B n n n Evolutionary Methodical In business context Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Figure 6. 3 The value chain. The key to intra-business e-commerce is improving value chain efficiency. Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
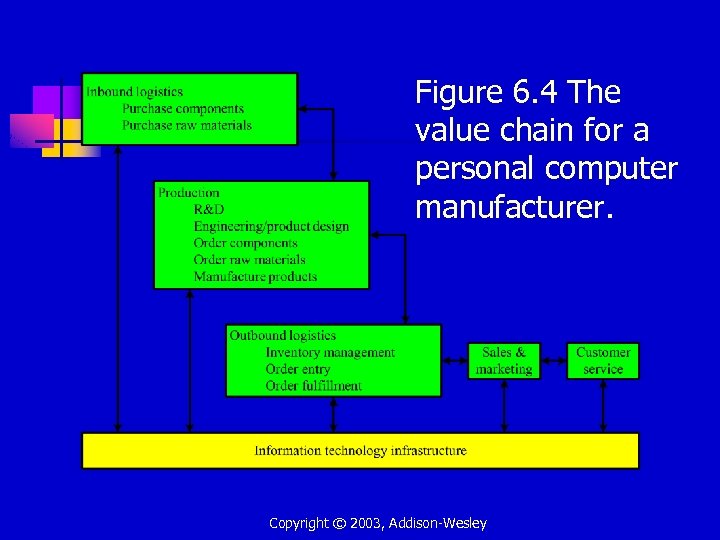
Figure 6. 4 The value chain for a personal computer manufacturer. Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
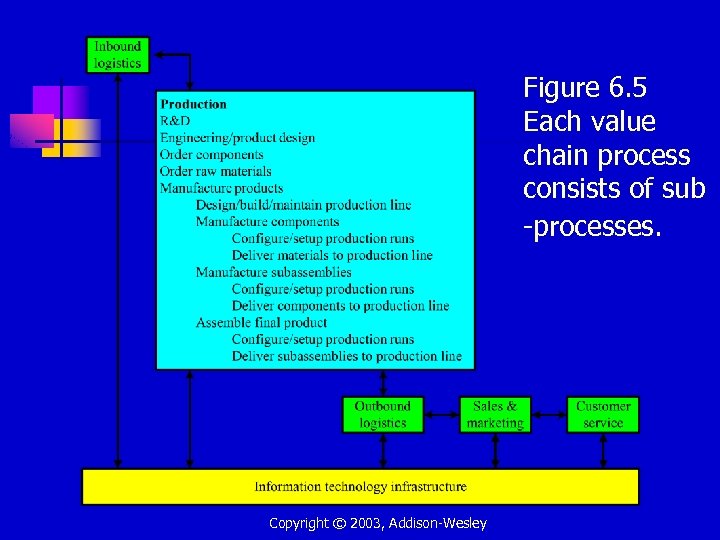
Figure 6. 5 Each value chain process consists of sub -processes. Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Efficiency and Effectiveness n Objective: reduce operating costs n Efficiency gains n n n Within individual processes Across the value chain Efficiency-based competitive advantage n n Hidden from public view Relatively easy to sustain Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Figure 6. 6 The organizational pyramid. n n n Before computers, companies organized along functional lines. Functional groups exchanged paperwork. Early computer applications supported a single function. Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Figure 6. 7 A manual payroll system. n Payroll was done manually until at least the late 1950 s. Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
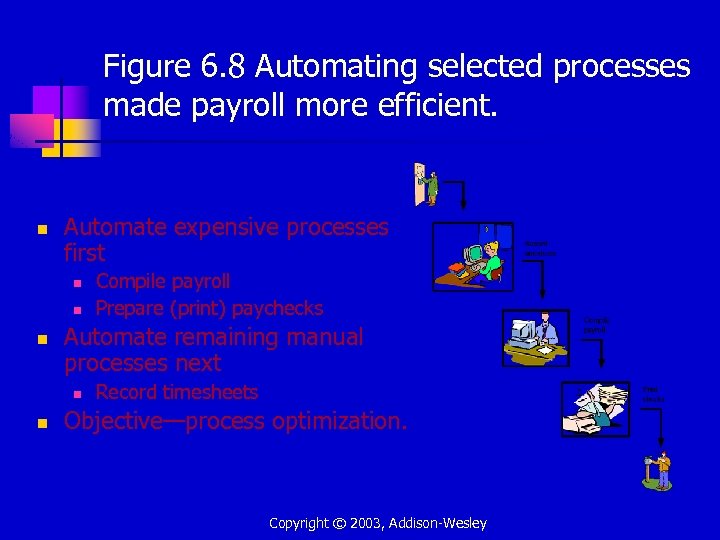
Figure 6. 8 Automating selected processes made payroll more efficient. n Automate expensive processes first n n n Automate remaining manual processes next n n Compile payroll Prepare (print) paychecks Record timesheets Objective—process optimization. Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
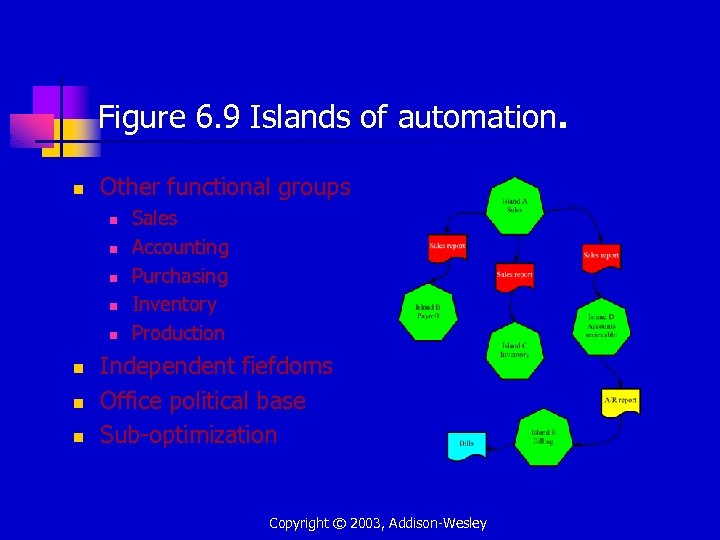
Figure 6. 9 Islands of automation. n Other functional groups n n n n Sales Accounting Purchasing Inventory Production Independent fiefdoms Office political base Sub-optimization Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
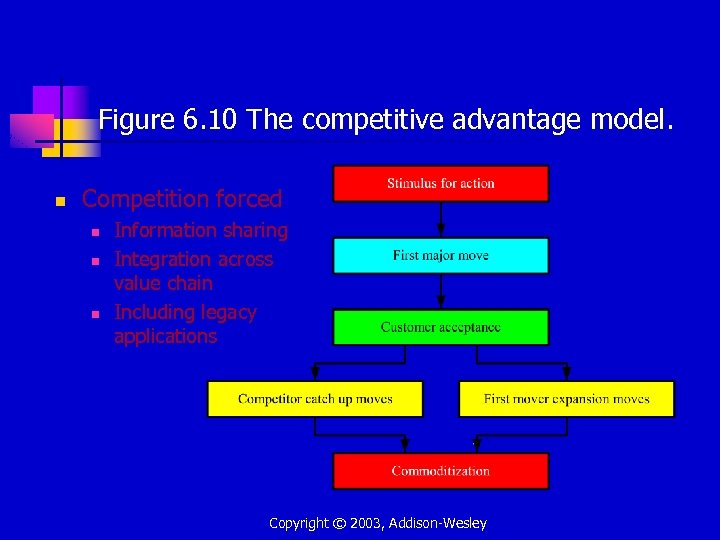
Figure 6. 10 The competitive advantage model. n Competition forced n n n Information sharing Integration across value chain Including legacy applications Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Incompatibilities n n Hardware, software, and data Data redundancy was a major problem n n n Same data value on multiple files Independently maintained Values differed Data formats differed Solution – central database Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

New Approaches to System Development n Information system planning n n Information technology infrastructure n n n Basic blueprint for technology integration Enterprise data model (EDM) Business process reengineering n n Elevated to strategic level Process improvements in context Problem – legacy applications Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Partitioning Order Entry n Client n n Display online order form Display order acknowledgement Error-check form data Server n n n Record order Read quantity on hand Access A/R Validate stock Check credit Either – Calculate taxes and total Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
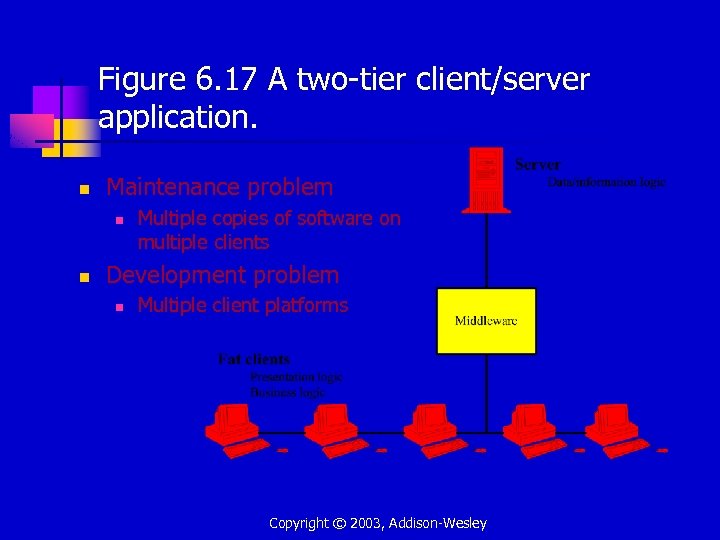
Figure 6. 17 A two-tier client/server application. n Maintenance problem n n Multiple copies of software on multiple clients Development problem n Multiple client platforms Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
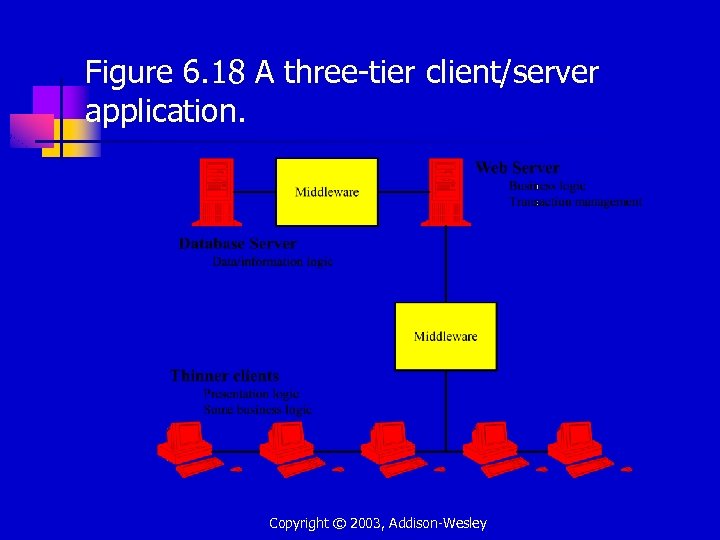
Figure 6. 18 A three-tier client/server application. Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
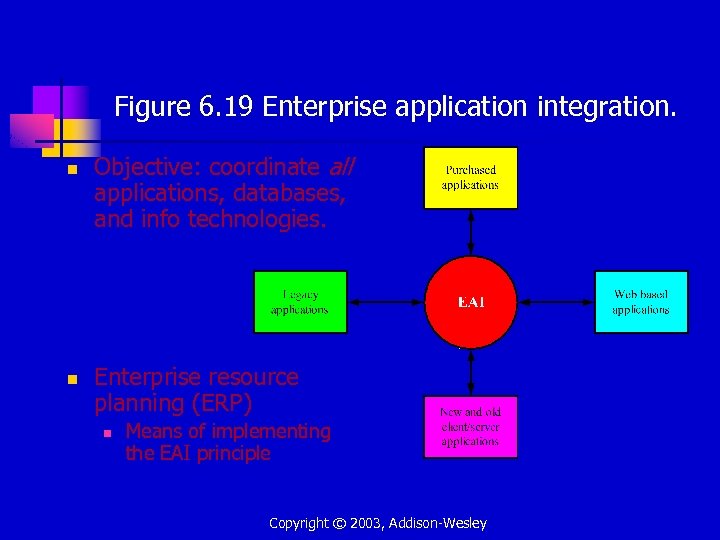
Figure 6. 19 Enterprise application integration. n n Objective: coordinate all applications, databases, and info technologies. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) n Means of implementing the EAI principle Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
Virtual Value Chain n Digital picture of value chain n Coordinate and monitor processes Organizational (not local) efficiency Applications n n n Fuel business process reengineering Mirror or replace physical processes Data mining Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Web Services n Application server software n n n Application service provider (ASP) n n n A server for middleware Scalable platform Intermediary that supplies applications Including mission-critical applications Management service provider (MSP) n Intermediary that manages IT services Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
Corporate Intranets n n Private corporate network Uses standard Internet protocols n n TCP/IP HTML and HTTP Browser and Web server Internet and intranet differences n n Intranet is smaller in scope Intranet limited to organization’s employees Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
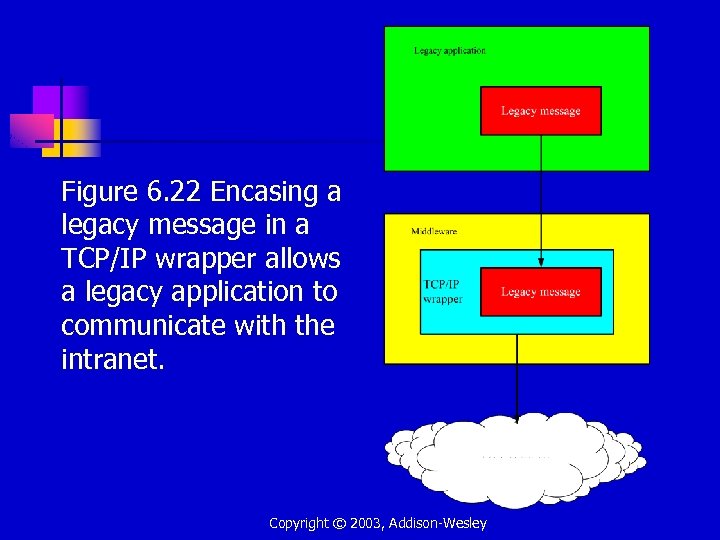
Figure 6. 22 Encasing a legacy message in a TCP/IP wrapper allows a legacy application to communicate with the intranet. Company intranet Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Figure 6. 23 Some examples of groupware. n n n n n E-mail Scheduling and calendars Whiteboarding Chat rooms and bulletin boards Video conferencing Electronic meetings Document management Workflow management Collaborative writing Group decision support systems Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
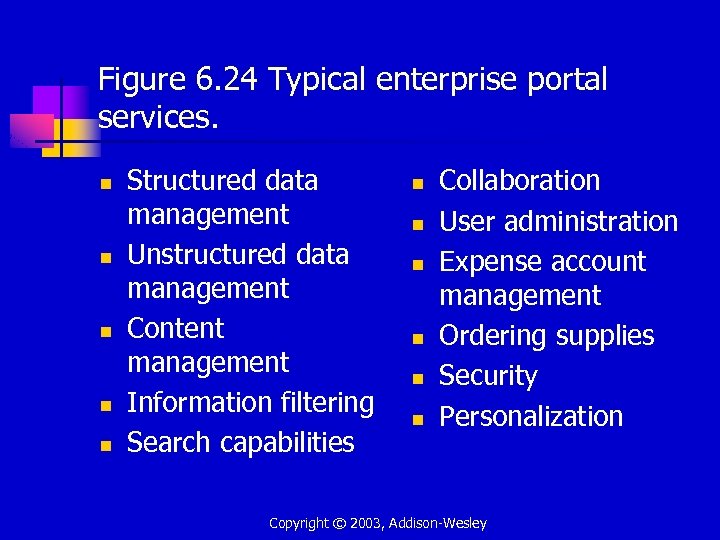
Figure 6. 24 Typical enterprise portal services. n n n Structured data management Unstructured data management Content management Information filtering Search capabilities n n n Collaboration User administration Expense account management Ordering supplies Security Personalization Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley

Geographically Dispersed Value Chains n n Value chain more complex Options n n n Secure private network Value added network Public network (e. g. , Internet) Virtual private network Security n n n Firewalls User identification Authentication Copyright © 2003, Addison-Wesley
ffe02f05ed29c32ceedc12c145fe1740.ppt