c5e0355dfa4b91c1a0d7d75f1c61b297.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

Chapter 6 Computer Networks

OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, the reader should be able to: Understand the rationale for the existence of networks. Distinguish between the three types of networks: LANs, MANs, and WANs. Understand the OSI model and TCP/IP. List different connecting devices and the OSI layers in which each device operates. Understand client-server models.

6. 1 NETWORKS, LARGE AND SMALL

Network n Computer network – A combination of computers connected through transmission media. ¨ LAN (Local Area Network) ¨ MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) ¨ WAN (Wide Area Network) n Internetwork – (e. g. Internet) Networks can be connected using connecting device.
Model and Protocol Model – the specification set by a standards organization as a guideline for designing networks. n Protocol – a set of rules that controls the interaction of different devices in a network/internetwork. n

6. 2 OSI MODEL
Note: The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a theoretical model that shows how any two different systems can communicate with each other. n OSI Model – is a framework of 7 layers that gives network designers an idea of the functionality of each separate but related layer.
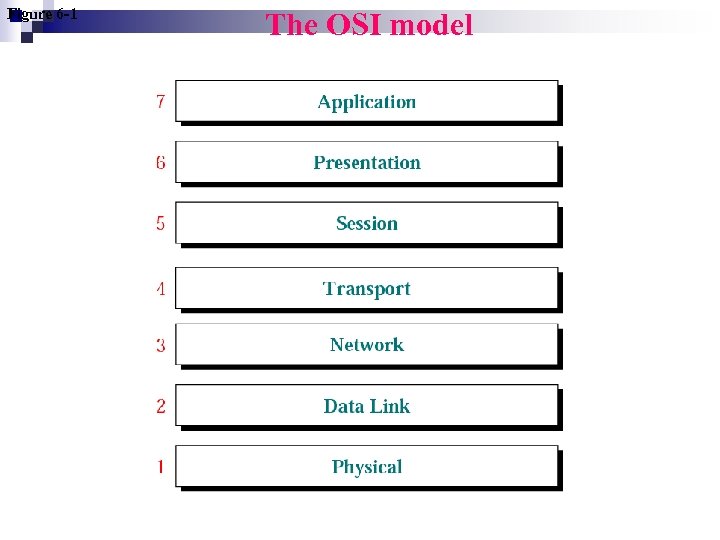
Figure 6 -1 The OSI model
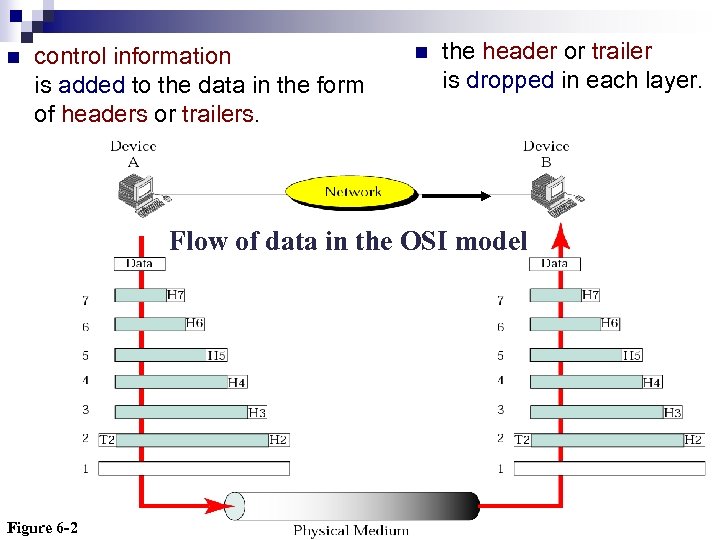
n control information is added to the data in the form of headers or trailers. n the header or trailer is dropped in each layer. Flow of data in the OSI model Figure 6 -2
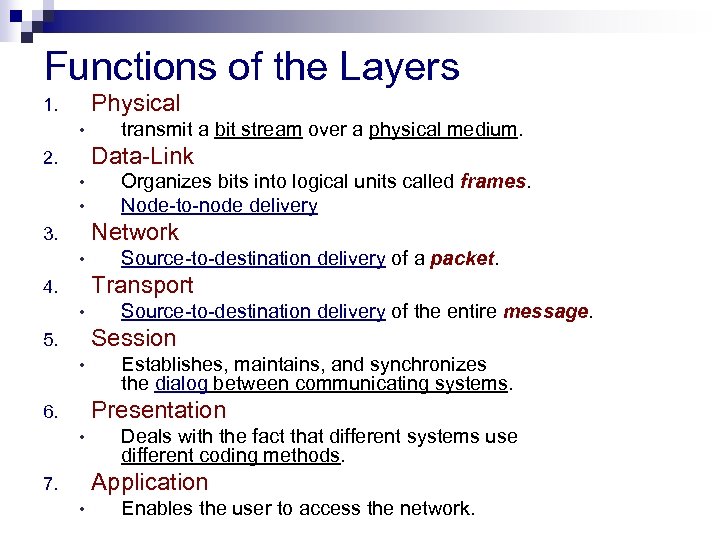
Functions of the Layers Physical 1. • transmit a bit stream over a physical medium. Data-Link 2. • • Organizes bits into logical units called frames. Node-to-node delivery Network 3. • Source-to-destination delivery of a packet. Transport 4. • Source-to-destination delivery of the entire message. Session 5. • Establishes, maintains, and synchronizes the dialog between communicating systems. Presentation 6. • Deals with the fact that different systems use different coding methods. Application 7. • Enables the user to access the network.
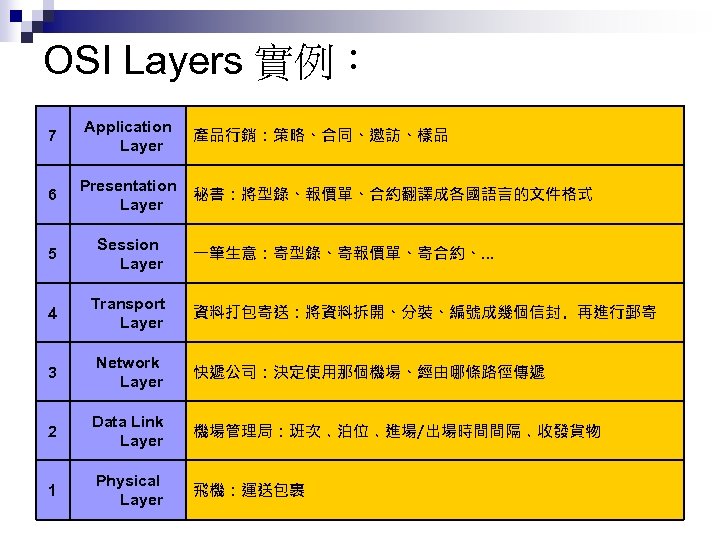
OSI Layers 實例: 7 Application Layer 6 Presentation Layer 5 Session Layer 4 Transport Layer 3 Network Layer 快遞公司:決定使用那個機場、經由哪條路徑傳遞 2 Data Link Layer 機場管理局:班次﹑泊位﹑進場/出場時間間隔﹑收發貨物 1 Physical Layer 飛機:運送包裹 產品行銷:策略、合同、邀訪、樣品 秘書:將型錄、報價單、合約翻譯成各國語言的文件格式 一筆生意:寄型錄、寄報價單、寄合約、… 資料打包寄送:將資料拆開、分裝、編號成幾個信封﹐再進行郵寄

6. 3 CATEGORIES OF NETWORKS
Categories of networks Figure 6 -3

LAN (Local Area Network) n Allow resource sharing between computers. ¨ Computers ¨ Peripheral devices ¨ Transmission medium (e. g. cable) n 3 types of topology ¨ Bus topology ¨ Star topology ¨ Ring topology
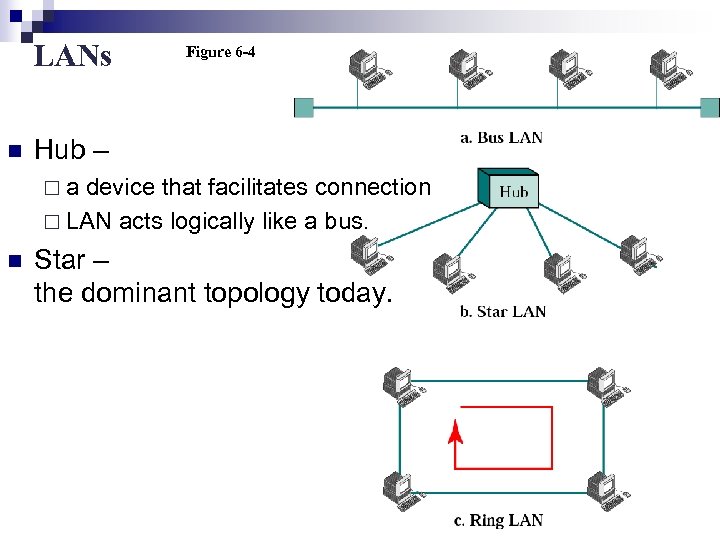
LANs n Figure 6 -4 Hub – ¨a device that facilitates connection ¨ LAN acts logically like a bus. n Star – the dominant topology today.
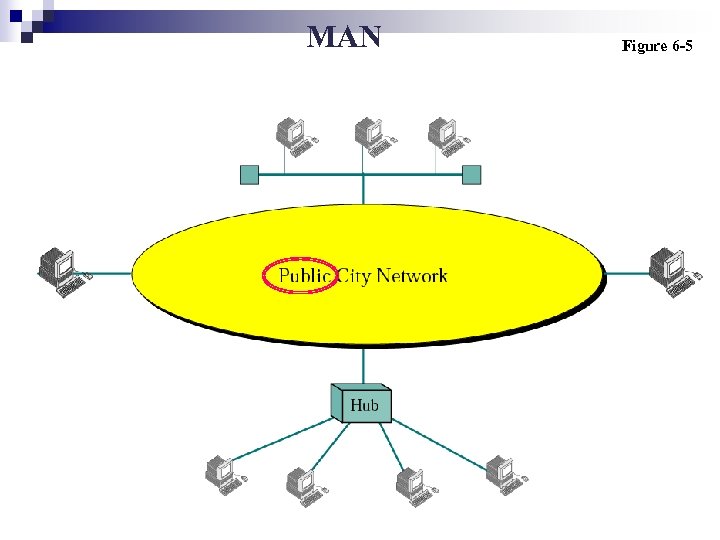
MAN Figure 6 -5

MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) n Uses services provided by a network service provider. (Tel. Company) ¨ Individual users’ computers ¨ Organizations’ LANs n Many Tel. Company provide a popular MAN service called SMDS (Switched Multimegabit Data Services) ¨ Prior to SMDS's arrival in 1995, the only way to connect LANs was through a dedicated private line.
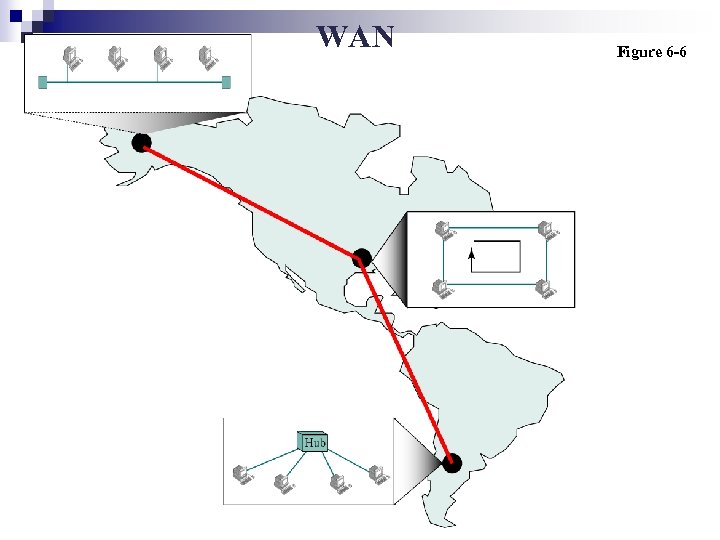
WAN Figure 6 -6

WAN (Wide Area Network) n The connection of individual computers or LANs over a large area (country, world). n User using a telephone line to connect to an ISP (Internet Service Provider) is using a WAN. ¨ Negotiates n n fee ISP Tel. company

6. 4 CONNECTING DEVICES
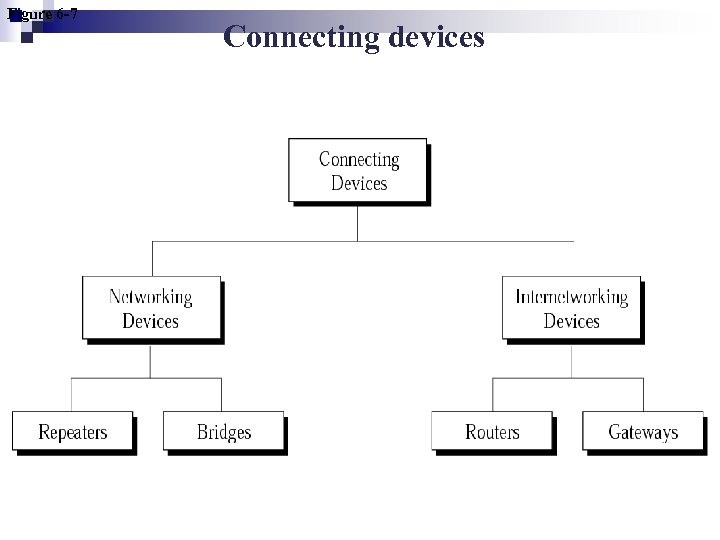
Figure 6 -7 Connecting devices
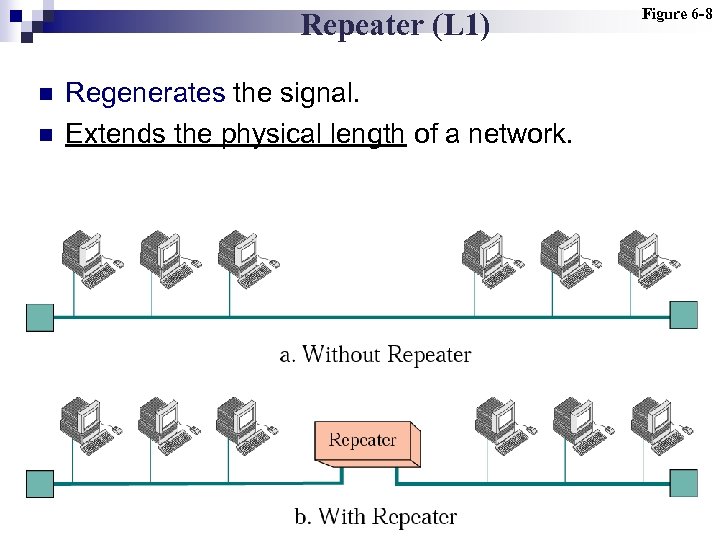
Repeater (L 1) n n Regenerates the signal. Extends the physical length of a network. Figure 6 -8

Note: Repeaters operate at the first layer of the OSI model.
Bridge/Switch n Bridge ¨A traffic controller ¨ Divide a long bus into smaller segments so that each segment is independent trafficwise. ¨ Regenerate data n Switch ¨A sophisticated bridge with multiple interfaces. ¨ A station that needs to send a frame sends it directly to the switch.
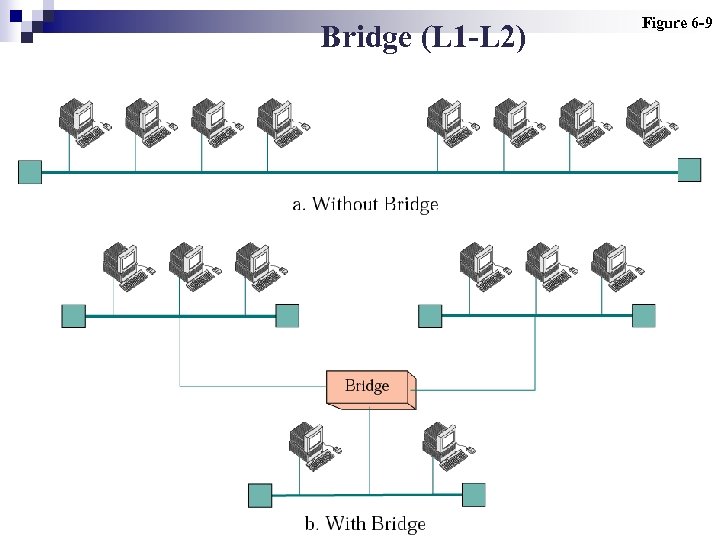
Bridge (L 1 -L 2) Figure 6 -9

Note: Bridges operate at the first two layers of the OSI model.
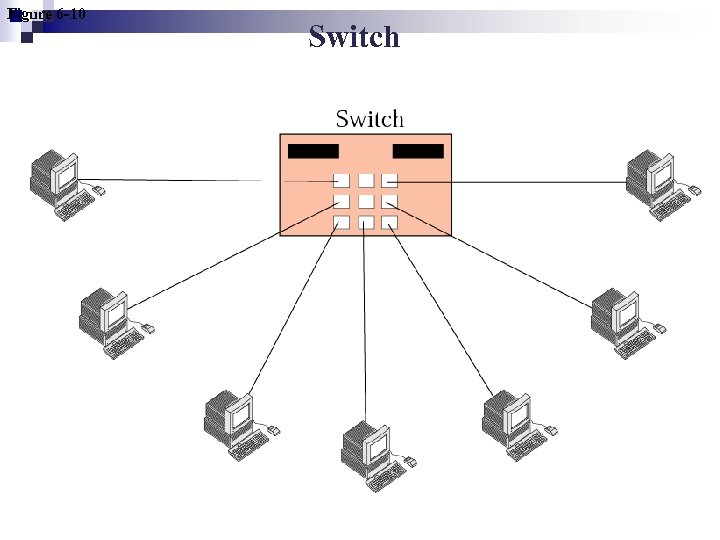
Figure 6 -10 Switch

Router Connect LANs, MANs, and WANs. n Routes a packet based on the logical address (network layer) of the packet. n Connect two independent networks: LAN-WAN, LAN-MAN, WAN-WAN… V. S. n Bridge n ¨ filters a frame based on the physical address (datalink layer) of the frame. ¨ Connect two segments of a LAN or two LANs belonging to the same organization.
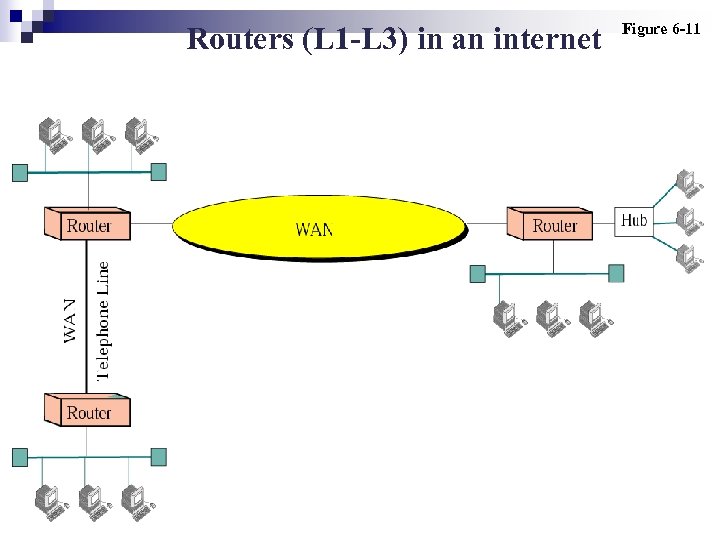
Routers (L 1 -L 3) in an internet Figure 6 -11

Note: Routers operate at the first three layers of the OSI model.

Gateway (L 1 -L 7) A protocol converter. n Understands the protocols used by each connected network and is able to translate from one to another. n
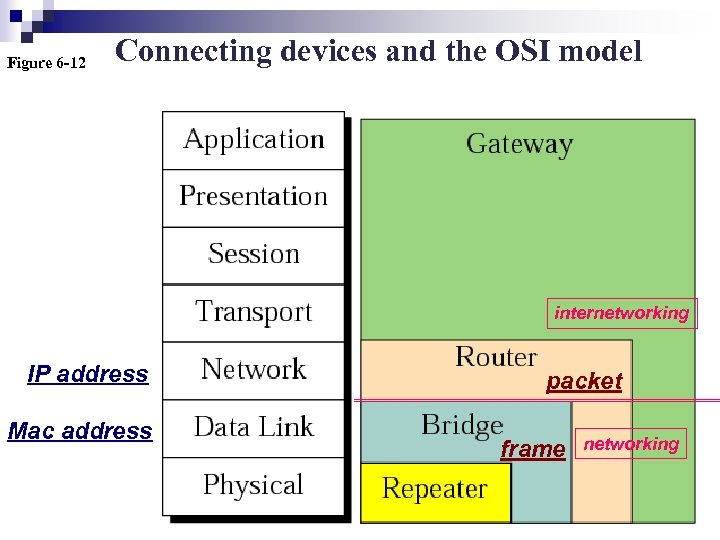
Figure 6 -12 Connecting devices and the OSI model internetworking IP address Mac address packet frame networking

n ISP (Internet Service Provider) a company that provides access to the Internet. For a monthly fee, the service provider gives you a software package, username, password and access phone number. Equipped with a modem, you can then log on to the Internet and browse the World Wide Web, and send and receive e-mail. n ICP (Internet Content Provider) 網際網路內容提供者。指的是在網際網路上提供各種服務內容的廠商。 如Yahoo雅虎、AOL美國線上等,都是屬於ICP的一種。任何人只要 有網路的空間放置網頁,都可以成為ICP。而ICP的收入大都來自廣 告收入。 n Web portal A Web site or service that offers a broad array of resources and services, such as e-mail, forums, search engines, and on-line shopping malls. n ASP (Application Service Provider) ASP 業者向軟體公司購買應用程式,然後將此程式放在 ASP 業者的 機房內,然後供企業或個人以存取網路的方式連接到機房來使用應用 程式,並依據使用方式與規定向客戶收取費用。

6. 5 THE INTERNET AND TCP/IP

Internet n internetwork (internet) ¨A network of networks ¨ Connect individual LANs, MANs, and WANs. n Internet – the most famous one
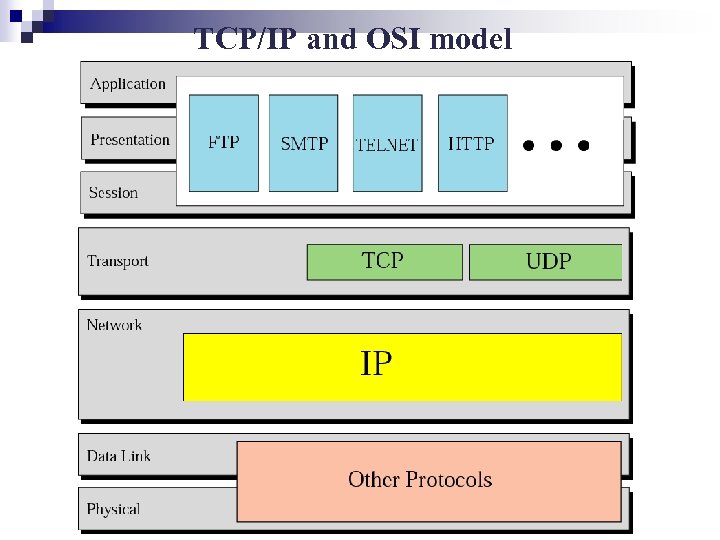
TCP/IP and OSI model
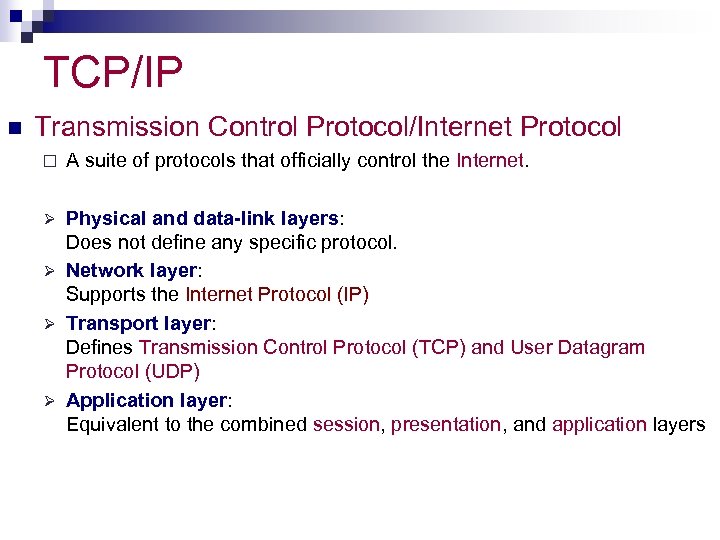
TCP/IP n Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol ¨ A suite of protocols that officially control the Internet. Physical and data-link layers: Does not define any specific protocol. Ø Network layer: Supports the Internet Protocol (IP) Ø Transport layer: Defines Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Ø Application layer: Equivalent to the combined session, presentation, and application layers Ø
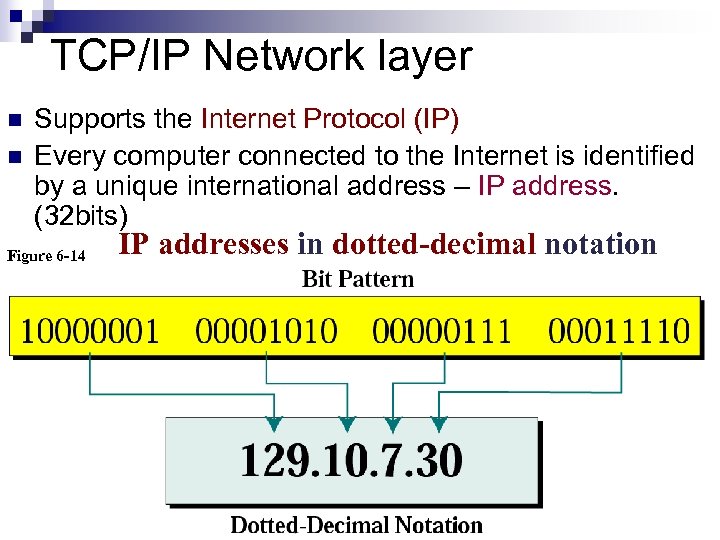
TCP/IP Network layer n n Supports the Internet Protocol (IP) Every computer connected to the Internet is identified by a unique international address – IP address. (32 bits) Figure 6 -14 IP addresses in dotted-decimal notation
TCP/IP Transport layer n Defines Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) n TCP is a reliable transport protocol. It divides a message into a sequence of segments that are numbered sequentially. ¨ If one segment is lost, it is sent again. ¨ If a segment is received out of order, it is ordered with the help of the sequence numbering mechanism.
TCP/IP Application layer n Equivalent to the combined session, presentation, and application layers of OSI model. n Communication on the Internet uses the client-server model. ¨ Client – an AP running on a local machine. ¨ Server – an AP running on a remote machine.
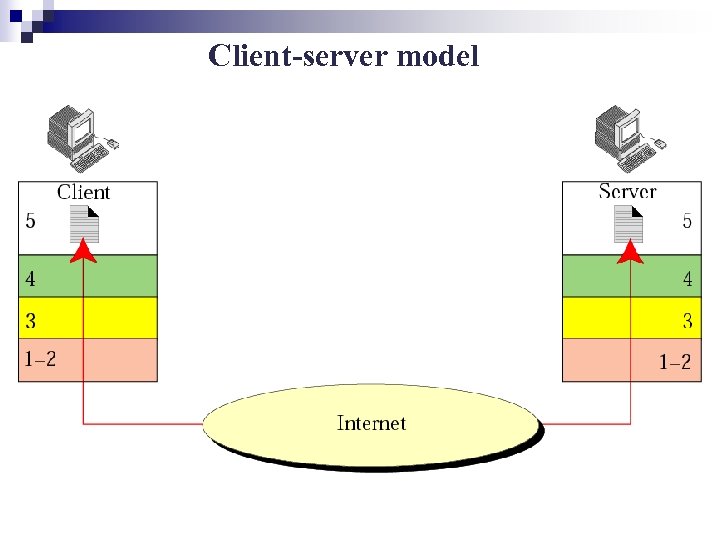
Client-server model
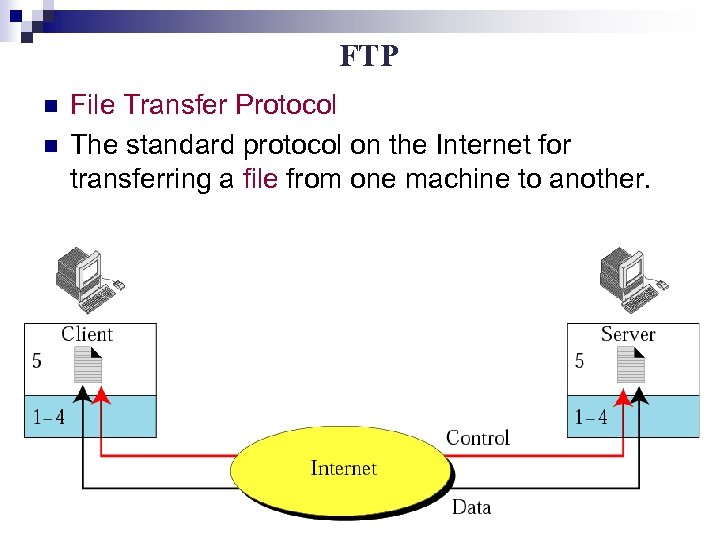
FTP n n File Transfer Protocol The standard protocol on the Internet for transferring a file from one machine to another.
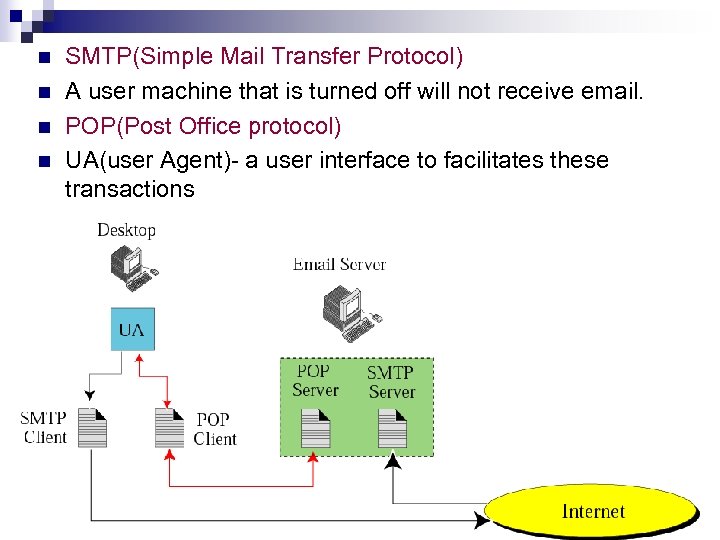
n n SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) A user machine that is turned off will not receive email. POP(Post Office protocol) UA(user Agent)- a user interface to facilitates these transactions

Email address n n Local part – user mailbox Domain name – the computer that serves as the SMTP server
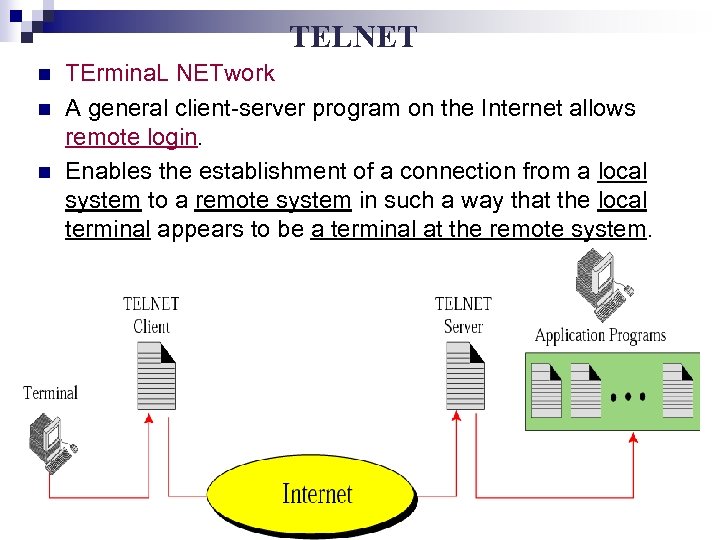
TELNET n n n TErmina. L NETwork A general client-server program on the Internet allows remote login. Enables the establishment of a connection from a local system to a remote system in such a way that the local terminal appears to be a terminal at the remote system.

HTTP Hyper. Text Transfer Protocol n the underlying protocol used by the World Wide Web. n use a special kind of addressing called URL(Uniform Resource Locator). n

URL Method – the client-server program used for transferring the documents. n Host – the computer where the information is located. n Port – the port number of server. n Path – the path of the file where the information is located. n

WWW n n World Wide Web Hypertext – a document containing special text, words, and phrases that can create a link to other documents. Page – a document of hypertext available on the web. Home page
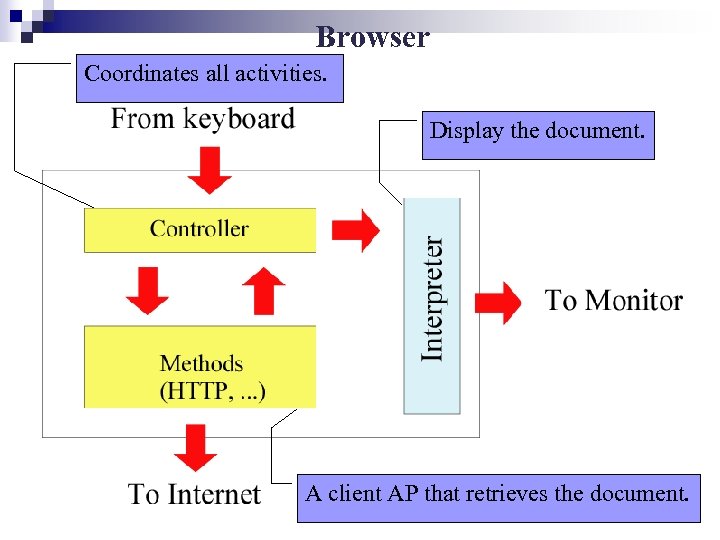
Browser Coordinates all activities. Display the document. A client AP that retrieves the document.
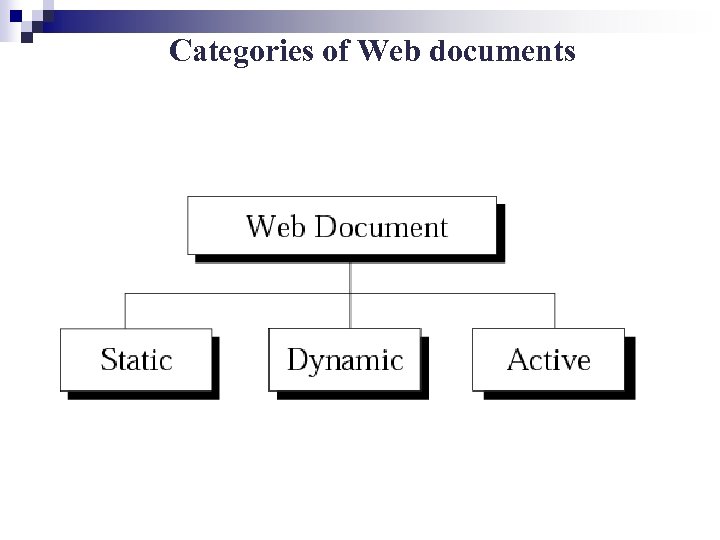
Categories of Web documents

Document types: n Static documents ¨ Have fixed contents ¨ HTML n Dynamic documents ¨ Programs residing at the server site. ¨ Use CGI(Common Gateway Interface) technology includes Perl and HTML to handle the document creation and interpretation. n Active documents ¨ The browser requests the transfer of the program. After transfer, it is run at the browser site. ¨ Java

n 台灣網路資訊中心(TWNIC) 國家級財團法人機構,以非營利為目的,是由 交通部電信總局及中華民國電腦學會共同捐助 設立,宗旨是以超然中立及互助共享網路資源 之精神,提供IP address分配、網域名稱 (Domain Name)註冊等服務。 n 網路蟑螂 ¨ 1999年底,登記使用business. com的權利,以 750 萬美金的天價在拍賣網站電子海灣(e. Bay. com)賣出。 ¨ china. com、ibm. com ¨ apple. com ¨ whitehouse. com

即時傳訊 (Instant Messenger) n 它支援在 Internet 上聊天、發送消息和文件等,另更有語音 聊天、網路攝影機等功能 1. ICQ 2. AIM﹙ AOL Instant Messenger﹚ 3. QQ 4. MSN即時通 全球最早出現的即時傳訊軟體,在 1998年 6月被AOL以 2. 87億美元所收購 由AOL所開發出來、類似ICQ的即時傳訊軟體 中國騰訊公司產品,佔中國95%使用人口(1億500 萬) 由微軟所開發出來的即時傳訊軟體 5. Yahoo!奇摩即時通 由全球入口網站領導品牌Yahoo!所開發的即時傳訊軟體 6. Yam. QQ 蕃薯藤 +QQ
c5e0355dfa4b91c1a0d7d75f1c61b297.ppt