dd5e4de55346ea856c77cf7f66749f7b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Chapter 6 Business-to-Business (B 2 B) Markets: How and Why Organizations Buy

Chapter Objectives 1. Explain each of the components of the business market. 2. Describe the major approaches to segmenting business-to-business (B 2 B) markets. 3. Identify the major ways the business market differs from the consumer market. 4. Classify organizational buying situations. 5. Discuss the Pro’s and Con’s of making products in-house versus Outsourcing 6 -2

B 2 B MARKETING B 2 B Marketing - Marketing of products either for use in producing a product or for usage in conducting business to: 1. Companies (ex: Paper to Office Depot or Winthrop University) 2. Government Organizations (ex: The Navy) 3. Institutions (ex: CMC Hospitals) 4. Non-Profit Organizations (ex: American Red Cross) 5. Retailers and Wholesalers (ex: Polo shirts) 6 -3

n Firm specializing in the B 2 B market 6 -4

HOW BUSINESS TO BUSINESS (B 2 B) DIFFERS FROM BUSINESS TO CONSUMER (B 2 C) 1. Customers are Other Businesses, rather than consumers 2. A much smaller number of Larger customers 3. Stronger Buyer-seller Relationships (personal selling) ü THE MOST important aspect of B 2 B Marketing 4. Stricter performance standards for products demanded by businesses – the stakes are often higher! (ex: Software for airplanes vs. software for Madden 2010) 6 -5

HOW BUSINESS TO BUSINESS (B 2 B) DIFFERS FROM BUSINESS TO CONSUMER (B 2 C) 5. More complicated purchasing decisions – large # of buyers involved & longer time to make decisions 6. Success is dependent upon other companies’ ability to market (ex: Lucky Brand Jeans) 7. The demand for a company’s products comes from the demand for their customer’s products = “Derived Demand” ØSony can’t sell Sony TV’s to Best Buy if customers don’t want to buy their TV’s from Best Buy! 6 -6
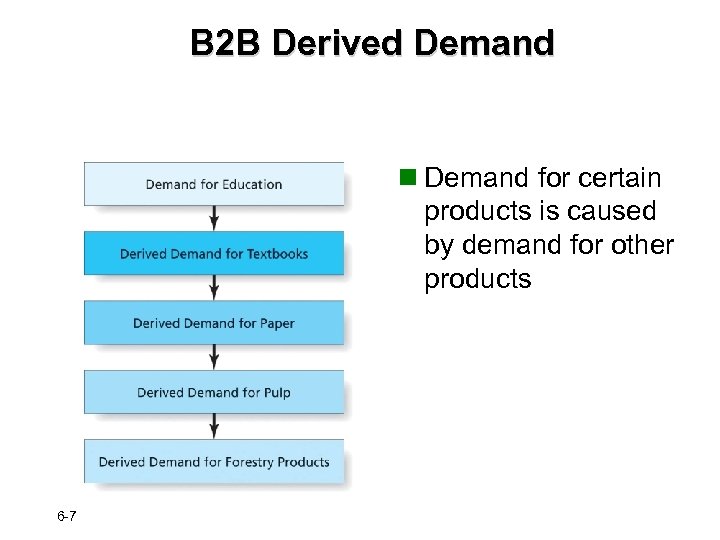
B 2 B Derived Demand n Demand for certain products is caused by demand for other products 6 -7

Advertising Aimed Mainly at Business Buyers May Often Appear to Be Consumer Advertising 6 -8

TYPICAL BUSINESS TO BUSINESS GOODS AND SERVICES INCLUDE: ü ü ü RAW MATERIALS COMPONENT OR OEM PARTS (Part of a completed product) ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT (Tools) CAPITAL EQUIPMENT (Machinery) MRO ITEMS (Operating supplies) FINISHED GOODS Q. Provide an Example for each of these 6 -9
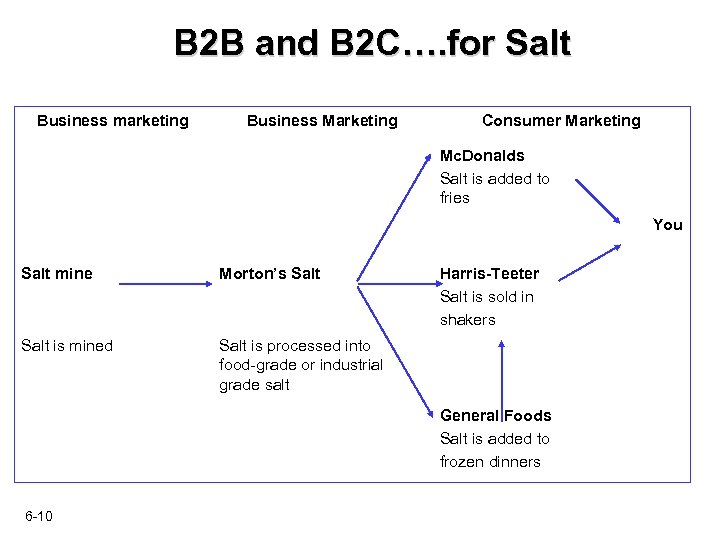
B 2 B and B 2 C…. for Salt Business marketing Business Marketing Consumer Marketing Mc. Donalds Salt is added to fries You Salt mine Morton’s Salt is mined Harris-Teeter Salt is sold in shakers Salt is processed into food-grade or industrial grade salt General Foods Salt is added to frozen dinners 6 -10

Business to Business (B 2 B) Marketing in YOUR WORLD For the last Food restaurant you ate in…. Q 1. Who was the Business to Consumer (B 2 C) marketer? Q 2. Who was the B 2 C Consumer? Q 3. What Business to Business (B 2 B) marketing may have taken place? Q 4. Who were the B 2 B customers? 6 -11

Business to Business (B 2 B) Marketing in YOUR WORLD For the shirt you are wearing today…. Q 1. Who was the Business to Consumer (B 2 C) marketer? Q 2. Who was the B 2 C Consumer? Q 3. What Business to Business (B 2 B) marketing may have taken place? Q 4. Who were the B 2 B customers? 6 -12

Business to Business (B 2 B) Marketing in YOUR WORLD For the textbook you (hopefully) have sitting on your desk…. Q 1. Who was the Business to Consumer (B 2 C) marketer? Q 2. Who was the B 2 C Consumer? Q 3. What Business to Business (B 2 B) marketing may have taken place? Q 4. Who were the B 2 B customers? 6 -13

Business to Business (B 2 B) Marketing in YOUR WORLD For the car you or someone you know bought…. Q 1. Who was the Business to Consumer (B 2 C) marketer? Q 2. Who was the B 2 C Consumer? Q 3. What Business to Business (B 2 B) marketing may have taken place? Q 4. Who were the B 2 B customers? 6 -14

One More Big Reason to Care about B 2 B Marketing College students generally land jobs in B 2 C marketing while…. College GRADUATES generally land jobs in B 2 B marketing… üGreater skill requirements (marketing, analytical, and people skills) + Greater responsibility ($/sale and total sales) = Greater challenge and Greater PAY! 6 -15
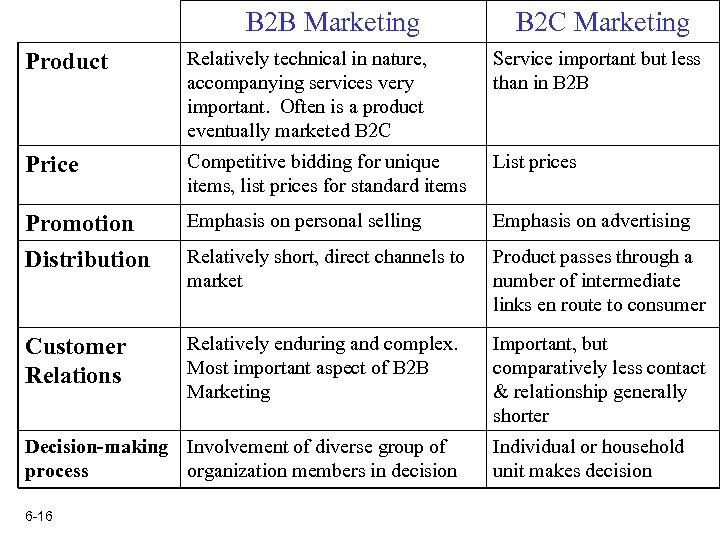
B 2 B Marketing B 2 C Marketing Product Relatively technical in nature, accompanying services very important. Often is a product eventually marketed B 2 C Service important but less than in B 2 B Price Competitive bidding for unique items, list prices for standard items List prices Promotion Distribution Emphasis on personal selling Emphasis on advertising Relatively short, direct channels to market Product passes through a number of intermediate links en route to consumer Customer Relations Relatively enduring and complex. Most important aspect of B 2 B Marketing Important, but comparatively less contact & relationship generally shorter Decision-making Involvement of diverse group of process organization members in decision 6 -16 Individual or household unit makes decision

Figure 6. 1 Differences Between Organizational and Consumer Markets 6 -17

North American Industry Classification System n Marketers use the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) to identify their customers and to find new customers üNAICS is a numerical coding of industries in the United States, Canada, and Mexico 6 -18
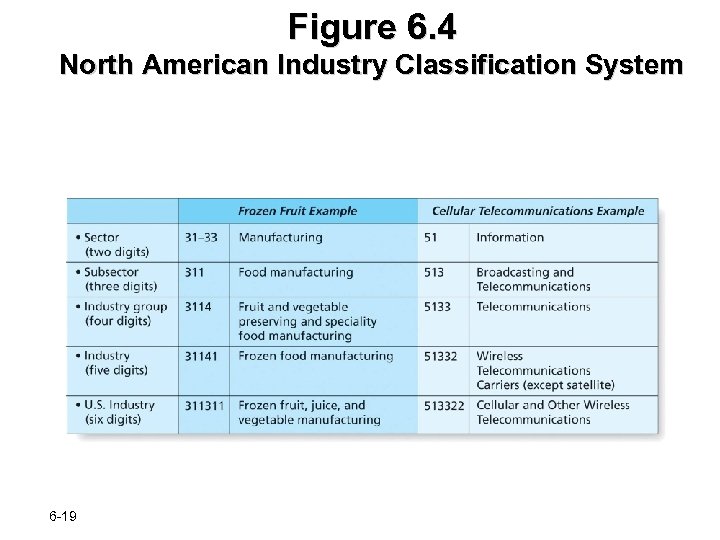
Figure 6. 4 North American Industry Classification System 6 -19

Classifying Business Buying Situations 1. Straight Rebuy - Recurring purchase decision in which a customer repurchases a good or service that has performed satisfactorily in the past 2. Modified Rebuy- purchase decision in which a purchaser is willing to reevaluate available options for repurchasing a good or service (the competition is given another shot) Bidding 3. New-Task Buying - first-time or unique f purchase situation that requires considerable effort by the decision Makers Bidding 6 -20

n Office. Max. com Promoting a straight rebuy 6 -21

n Purchasing a business jet: a new task buy 6 -22

It’s Debatable Class Discussion Question Suppose that the price of a key component used in your product has unexpectedly tripled. Think about the pros and cons of each of the following potential actions. Where do you stand? 1) Pass the price increase onto the customer 2) Absorb the price increase 3) Change vendors and purchase a lowerpriced alternative part instead 6 -23
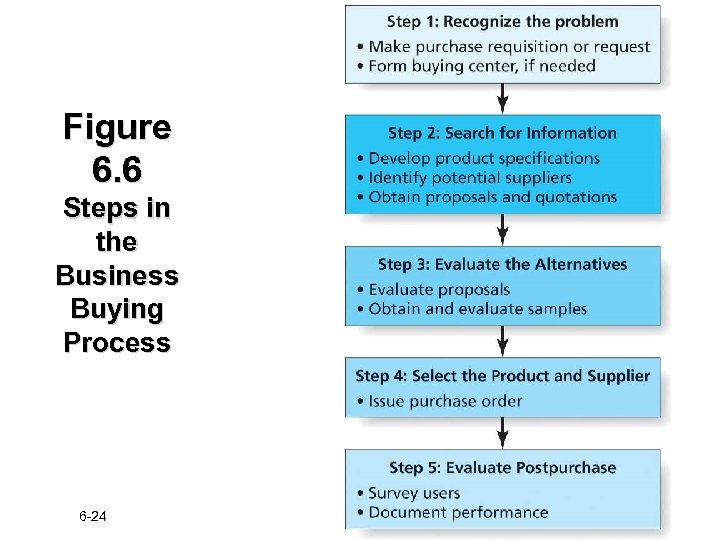
Figure 6. 6 Steps in the Business Buying Process 6 -24

Business Buying Decision Process Step 1: Recognize the Problem n Recognition often stems from üA need to replace outdated equipment üChanges in technology üMarketing communications spur action 6 -25

Business Buying Decision Process Step 2: Search for Information n In this stage, buyers: üSearch for information about products and suppliers üDevelop product specifications - Written descriptions of the quality, size, weight, color of the item to be purchased üIdentify potential suppliers and obtain proposals 6 -26

Business Buying Decision Process Step 3: Evaluate the Alternatives n Price is a primary consideration üEvaluations include discount policies, returnedgoods policies, cost of repair, terms of maintenance, and cost of financing n Other factors may be considered, such as extra services or other perks n Customer reference programs, product demos, and presentations can help sell the marketer’s products to firms 6 -27

Business Buying Decision Process Step 4: Select the Product & Supplier ü Single sourcing: Business practice of buying a particular product from only one supplier ü Multiple sourcing: Buying from several different suppliers ü Reciprocity: Trading partnership in which two firms agree to buy from one another ü Produce In-House or Outsource? ? 6 -28

In-House or Outsource? Outsourcing: using outside vendors to produce Outsourcing goods and services rather than produce them inhouse Q. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of making products yourself vs. outsourcing? Q. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of outsourcing? 6 -29

Advantages of Outsourcing üMay be cost effective üAllows a firm to obtain specialized technological expertise üFrees up the company to focus on its core competencies 6 -30

Disadvantages of Outsourcing üMany companies discover their cost savings to be less than half the figure promised by vendors üPotential problems with suppliers who fail to deliver goods properly or provide required services üRisk of losing touch with customers 6 -31

Business Buying Decision Process Step 5: Evaluate Postpurchase n Organizational buyers assess whether the performance of the product and the supplier live up to expectations üUsers are surveyed to determine satisfaction üProducers may also research end-user satisfaction with the final product üChanges in demand are analyzed 6 -32
dd5e4de55346ea856c77cf7f66749f7b.ppt