5c81f46481b33a500b53df16a4e2c160.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Chapter 5 The Banking System

Ch. 5 Objectives • Explain the purpose and use of checking accounts and savings accounts • Prepare checks and deposit slips and maintain a checkbook register • Prepare a bank reconciliation between checkbook register and bank statement • Explain how you can grow your savings with compound interest Slide 2
Financial Planning Three main influences when considering financial planning: • Life Situation • Personal Values • Economic Factors Slide 3

Why Save and Invest Money? • • Allow your money to grow Keep up with inflation Earn interest on interest Make your money work for you Through: – Compounding interest – Investment growth Slide 4
Time Value of Money A dollar you receive in the future will be worth less than a dollar you receive today

Did You Know? Small amounts saved and invested can easily grow into larger sums – If a person saved a dollar each day by not having a candy bar or soda, they would save $365 per year, if the $365 was deposited into a certificate of deposit (CD) with 5% interest, the money could grow to nearly $400 in one year!

Cash Management The daily routine of handling money to take care of individual or family needs • Effective cash management includes having money available for: – Living expenses – Emergencies – Savings – Investing Slide 7
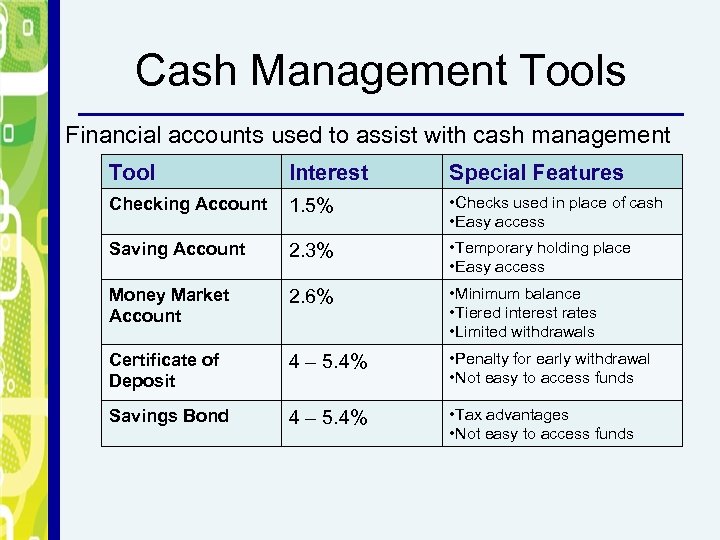
Cash Management Tools Financial accounts used to assist with cash management Tool Interest Special Features Checking Account 1. 5% • Checks used in place of cash • Easy access Saving Account 2. 3% • Temporary holding place • Easy access Money Market Account 2. 6% • Minimum balance • Tiered interest rates • Limited withdrawals Certificate of Deposit 4 – 5. 4% • Penalty for early withdrawal • Not easy to access funds Savings Bond 4 – 5. 4% • Tax advantages • Not easy to access funds

Why Have Checking Account? • Checking Account – A demand deposit account on which checks are drawn • Check - a written order to a bank to pay a person or business.

Checking Accounts Why open a checking account? – Safe place to keep money (Insured by the FDIC) – Easy to pay bills by mail (writing a check) – Easy access to money to make cash purchases • • Withdrawal money Write checks against the account Debit cards Internet Banking

Checking Account Features • May be interest earning • Minimum balance requirements – (Money Market Checking) • Charge transaction fees • Limited number of checks written monthly • Reduces the need to carry large amount of cash
Opening a Checking Account • What will I need? – – Money! ($50 or $100) Personal information Identification Provide an official signature • What will I be given? – Checkbook register – Debit card
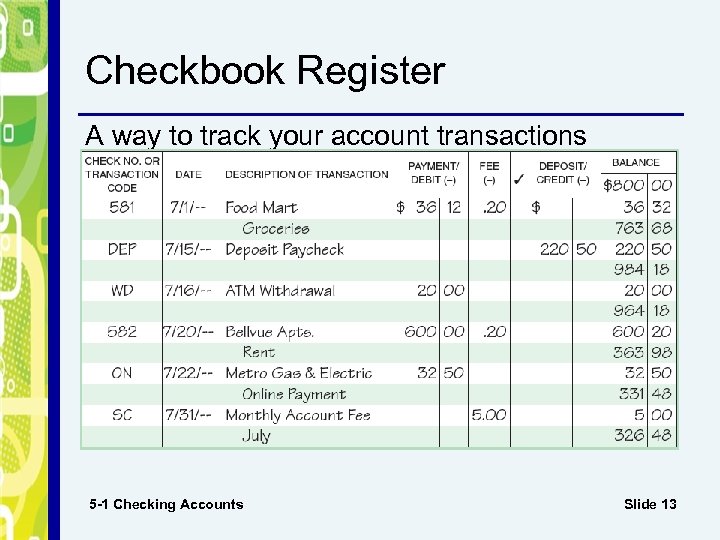
Checkbook Register A way to track your account transactions 5 -1 Checking Accounts Slide 13

Withdrawals and Deposits • A withdrawal involves taking money from your account. o Writing checks o Using debit cards • A deposit of money can be made to your account. o Endorsing checks o Direct deposit
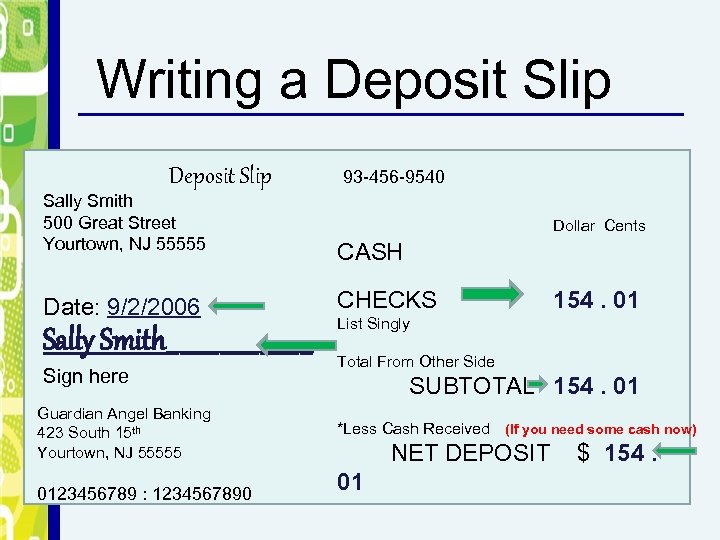
Writing a Deposit Slip Sally Smith 500 Great Street Yourtown, NJ 55555 Date: 9/2/2006 Sally Smith______ Sign here Guardian Angel Banking 423 South 15 th Yourtown, NJ 55555 0123456789 : 1234567890 93 -456 -9540 Dollar Cents CASH CHECKS 154. 01 List Singly Total From Other Side SUBTOTAL 154. 01 *Less Cash Received (If you need some cash now) NET DEPOSIT 01 $ 154.

Writing a Check Sally Smith 500 Great Street Yourtown, NJ 55555 93 -456 -9540 45086244786 503 Date: 9/6/2006 Pay to the Order Of The Pizza Place $ 9. 50 _Nine dollars_--------------------------------50/100_ Dollars Guardian Angel Banking 423 South 15 th Yourtown, NJ 55555 Memo __Pizza_ ___ 0123456789 : 1234567890 : 503 Sally Smith____
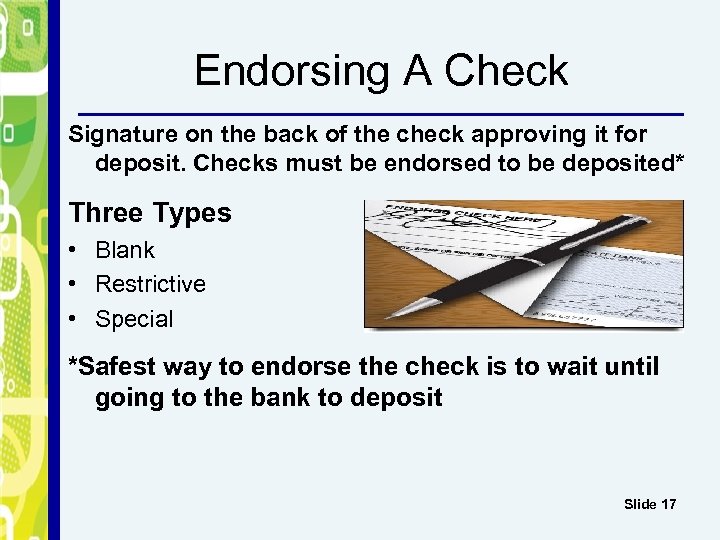
Endorsing A Check Signature on the back of the check approving it for deposit. Checks must be endorsed to be deposited* Three Types • Blank • Restrictive • Special *Safest way to endorse the check is to wait until going to the bank to deposit Slide 17
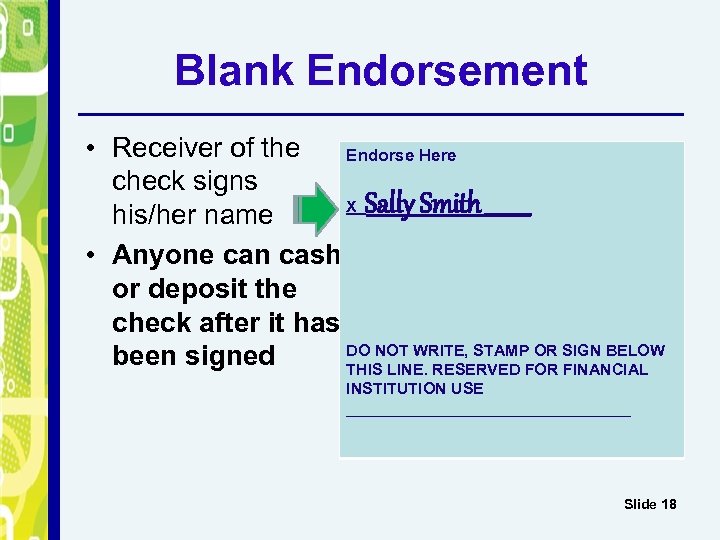
Blank Endorsement • Receiver of the Endorse Here check signs X Sally Smith_____ his/her name • Anyone can cash or deposit the check after it has DO NOT WRITE, STAMP OR SIGN BELOW been signed THIS LINE. RESERVED FOR FINANCIAL INSTITUTION USE ________________ Slide 18

Restrictive Endorsement • More secure than blank endorsement • Receiver writes “for deposit only” above his/her signature Endorse Here For Deposit Only – Acct. 654986 – Allows the check only to be deposited, not cashed X Sally Smith_____ Slide 19 DO NOT WRITE, STAMP OR

Special Endorsement • Receiver signs and writes “pay to the order of” (fill in person’s name) • Allows the check to be transferred to a second party – Also known as a third-party check Endorse Here Pay to the order of Mike Smith X Sally Smith_____ DO NOT WRITE, STAMP OR SIGN BELOW THIS LINE. RESERVED FOR FINANCIAL INSTITUTION USE ________________ Slide 20

Check 21 • Check clearing for the 21 st Century Act (check 21) – Current trend that changes how money is withdrawn and deposited into accounts
How Check 21 Works • Prior to Check 21 – Paper checks physically moved from place to place • After Check 21 – Paper checks scanned to computer to create a “substitute check” (truncated) – Substitute check is transferred electronically from place to place Slide 22
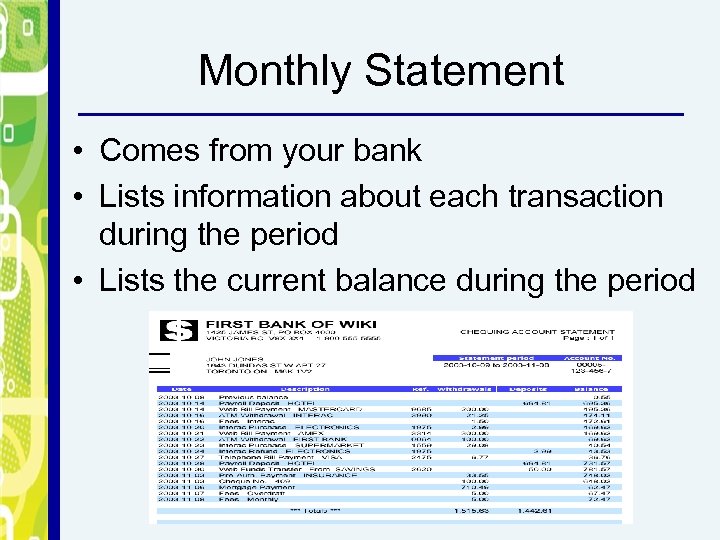
Monthly Statement • Comes from your bank • Lists information about each transaction during the period • Lists the current balance during the period

Reconcile a Bank Statement Bank reconciliation - the process of adjusting the checkbook register and bank statement so they agree • Consider the following: o deposits in transit o outstanding checks o transposition errors

What Is the Purpose of Savings? Savings Account - a demand deposit account for the accumulation of money • It is a safe place to hold money to meet future needs and wants • It pays interest at a low rate 5 -2 Savings Accounts

Liquidity How quickly and easily an asset can be converted into cash. Liquid assets are important for emergency situations Investors should - Invest in both liquid and non-liquid tools
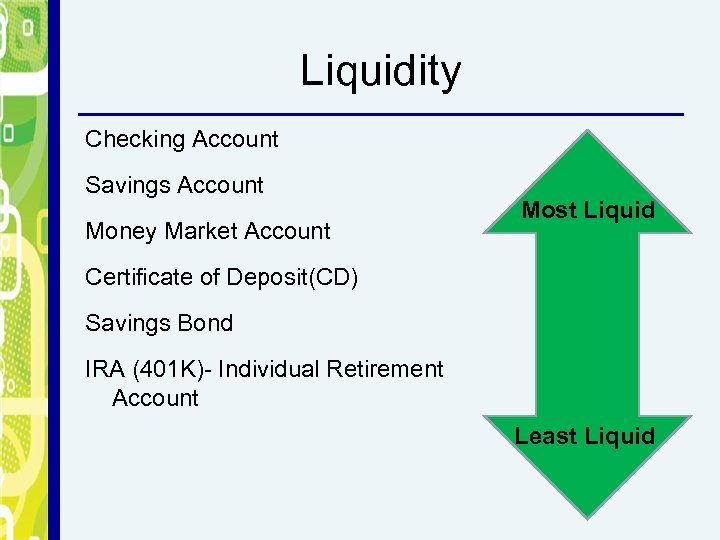
Liquidity Checking Account Savings Account Money Market Account Most Liquid Certificate of Deposit(CD) Savings Bond IRA (401 K)- Individual Retirement Account Least Liquid
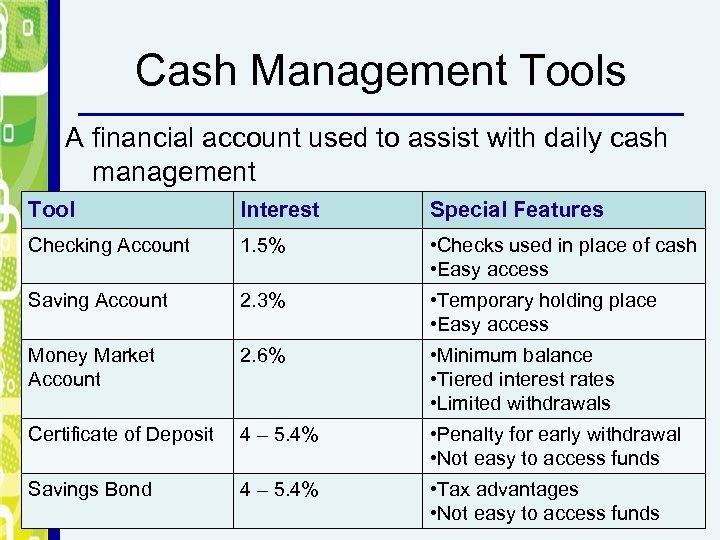
Cash Management Tools A financial account used to assist with daily cash management Tool Interest Special Features Checking Account 1. 5% • Checks used in place of cash • Easy access Saving Account 2. 3% • Temporary holding place • Easy access Money Market Account 2. 6% • Minimum balance • Tiered interest rates • Limited withdrawals Certificate of Deposit 4 – 5. 4% • Penalty for early withdrawal • Not easy to access funds Savings Bond 4 – 5. 4% • Tax advantages • Not easy to access funds

Watch Your Money Grow! How can you grow your savings? Through… • Principal • Simple interest • Compound interest 5 -2 Savings Accounts Slide 29
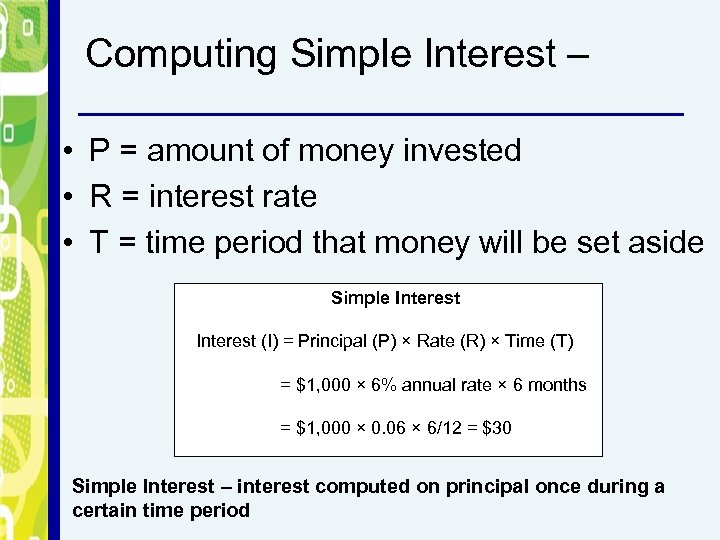
Computing Simple Interest – • P = amount of money invested • R = interest rate • T = time period that money will be set aside Simple Interest (I) = Principal (P) × Rate (R) × Time (T) = $1, 000 × 6% annual rate × 6 months = $1, 000 × 0. 06 × 6/12 = $30 Simple Interest – interest computed on principal once during a certain time period
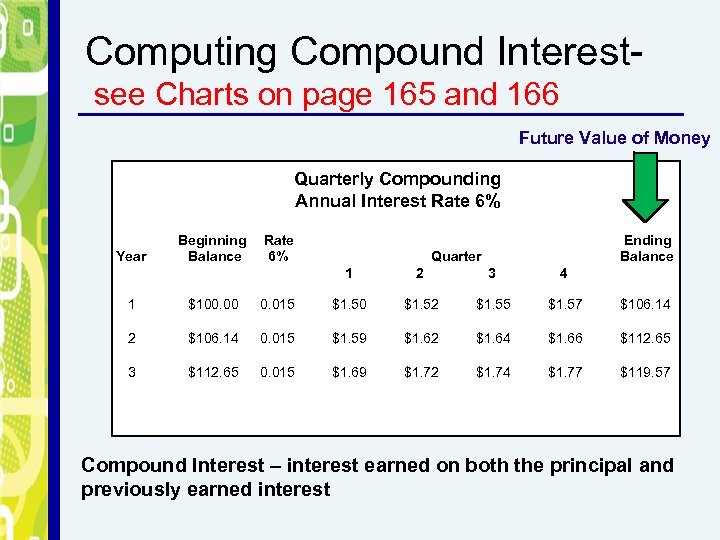
Computing Compound Interestsee Charts on page 165 and 166 Future Value of Money Quarterly Compounding Annual Interest Rate 6% Year Beginning Balance Rate 6% Ending Balance Quarter 1 2 3 4 1 $100. 00 0. 015 $1. 50 $1. 52 $1. 55 $1. 57 $106. 14 2 $106. 14 0. 015 $1. 59 $1. 62 $1. 64 $1. 66 $112. 65 3 $112. 65 0. 015 $1. 69 $1. 72 $1. 74 $1. 77 $119. 57 Compound Interest – interest earned on both the principal and previously earned interest

Rule of 72 How long will it take to double my money? • Divide annual interest rate into 72 Example: if you invest $50 at 6% interest, your money will grow to $100 in 12 years ( 72 ÷ 6 = 12 years)

Focus On. . . The FDIC • Protects depositors of insured U. S. banks against loss if the bank fails (up to $250 k per account • Covers all types of deposits • Covers principal and accrued interest • Does not insure some items o Examples: stocks, bonds, valuables • Insures deposits in different banks separately 5 -2 Savings Accounts Slide 33

Available Banking Services • • Safe deposit boxes Overdraft protection ATMs Cashier’s checks Financial advising Loans Internet banking Bank cards 5 -3 Banking Services and Fees Slide 34
Costs of Banking • • • Monthly account fees Nonsufficient fund fees Special service fees o Examples: stop payment, cashier’s check, money order ATM fees Inactive account fees

What Are Consumer Responsibilities? • Maintain your balance. o Avoid writing bad checks. o NSF means bounced check • Monitor your account. o Reconcile your bank account. • Know your rights. o Be aware of consumer protection laws.

Success Skills Negotiating It is the process of reaching an agreement that benefits both parties. • • Understand your position. Understand the other party’s position. Create a proposed solution. Identify what is important and what you are willing to give up. 5 -3 Banking Services and Fees Slide 37
5c81f46481b33a500b53df16a4e2c160.ppt