a9633b5e14826ea462a9d1cbdd0a857c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Chapter 5 Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit Text Sources 1. Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3&4: 4 th Edition – Malpeli, Horton, Davey and Telford 2006. 2. Live It Up 2: 2 nd Edition – Smyth, Brown, Judge, Mc. Callum and Pritchard 2006. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Chapter 5 Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit Text Sources 1. Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3&4: 4 th Edition – Malpeli, Horton, Davey and Telford 2006. 2. Live It Up 2: 2 nd Edition – Smyth, Brown, Judge, Mc. Callum and Pritchard 2006. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Body Systems Revision Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Body Systems Revision Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
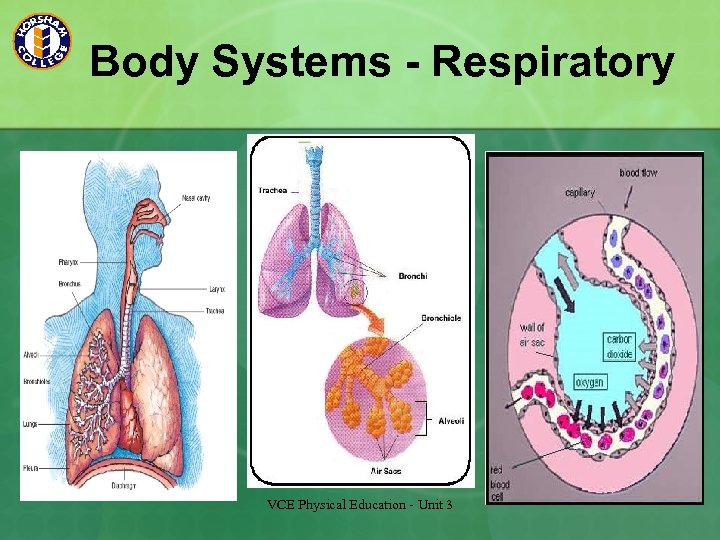 Body Systems - Respiratory VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Body Systems - Respiratory VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
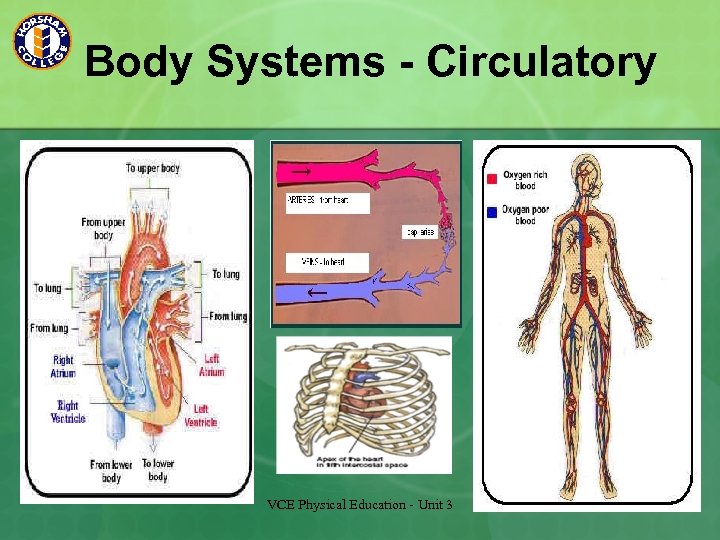 Body Systems - Circulatory VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Body Systems - Circulatory VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
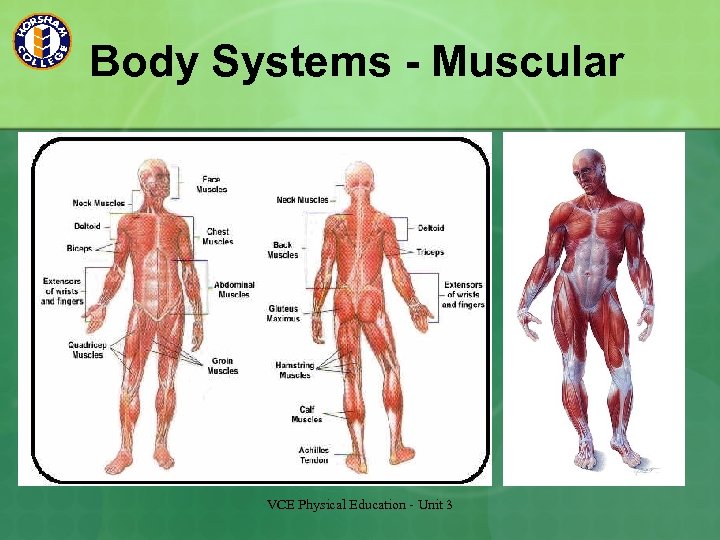 Body Systems - Muscular VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Body Systems - Muscular VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
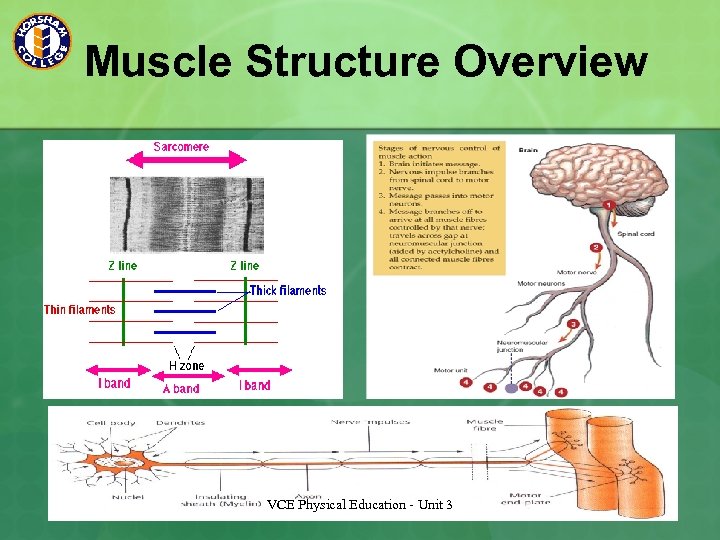 Muscle Structure Overview VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Muscle Structure Overview VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Oxygen Uptake Intake – Inspiration of atmospheric oxygen via pulmonary ventilation. n Transport – Oxygen is diffused from the lungs into the blood and is pumped to the body via the circulatory system. n Uptake – Skeletal muscle diffuses the oxygen into its cells with assistance from myoglobin. n Consumption – Occurs in the muscle cell by the mitochondria. Physical Education - Unit 3 VCE n
Oxygen Uptake Intake – Inspiration of atmospheric oxygen via pulmonary ventilation. n Transport – Oxygen is diffused from the lungs into the blood and is pumped to the body via the circulatory system. n Uptake – Skeletal muscle diffuses the oxygen into its cells with assistance from myoglobin. n Consumption – Occurs in the muscle cell by the mitochondria. Physical Education - Unit 3 VCE n
 Delivery of Oxygen to the Working Muscles The respiratory system is responsible for the extraction of oxygen from the atmosphere. This process is called ventilation. n Diffusion – Exchange of gases based on concentration levels (High to low). Occurs at a cellular level (In the lungs and in the muscle cell) n Cardiac output (Heart rate x stroke volume) - The heart pumps out oxygenated blood to the vascular system. n Oxygen combines with haemoglobin in the blood n Myoglobin, in the muscle attracts the oxygen from the blood and draws it into the mitochondria. n Waste produces of aerobic metabolism is removed from the muscle cell via diffusion. See fig 5. 2 p. 119 n VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Delivery of Oxygen to the Working Muscles The respiratory system is responsible for the extraction of oxygen from the atmosphere. This process is called ventilation. n Diffusion – Exchange of gases based on concentration levels (High to low). Occurs at a cellular level (In the lungs and in the muscle cell) n Cardiac output (Heart rate x stroke volume) - The heart pumps out oxygenated blood to the vascular system. n Oxygen combines with haemoglobin in the blood n Myoglobin, in the muscle attracts the oxygen from the blood and draws it into the mitochondria. n Waste produces of aerobic metabolism is removed from the muscle cell via diffusion. See fig 5. 2 p. 119 n VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Oxygen Uptake Limiting factors to oxygen uptake; n Respiratory system – ability to take in oxygen n Cardiovascular system – ability to transport and deliver oxygen n Muscular system – Utilisation of oxygen n Type of exercise performed, genetic inheritance, lifestyle, age and gender. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Oxygen Uptake Limiting factors to oxygen uptake; n Respiratory system – ability to take in oxygen n Cardiovascular system – ability to transport and deliver oxygen n Muscular system – Utilisation of oxygen n Type of exercise performed, genetic inheritance, lifestyle, age and gender. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
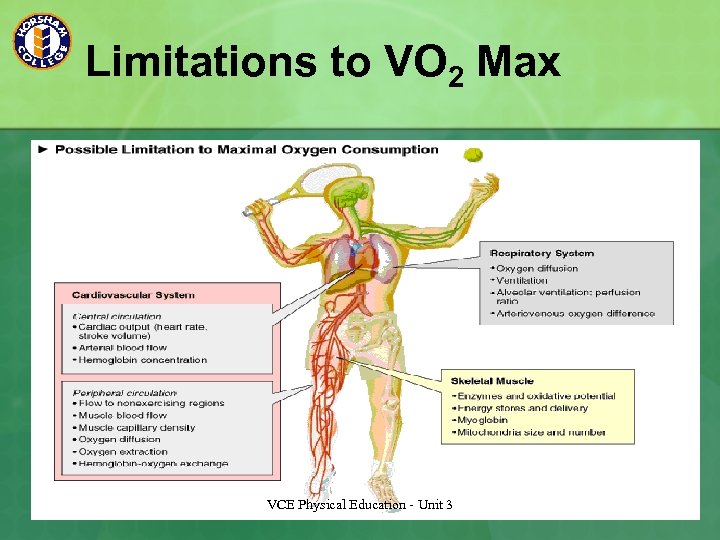 Limitations to VO 2 Max VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Limitations to VO 2 Max VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
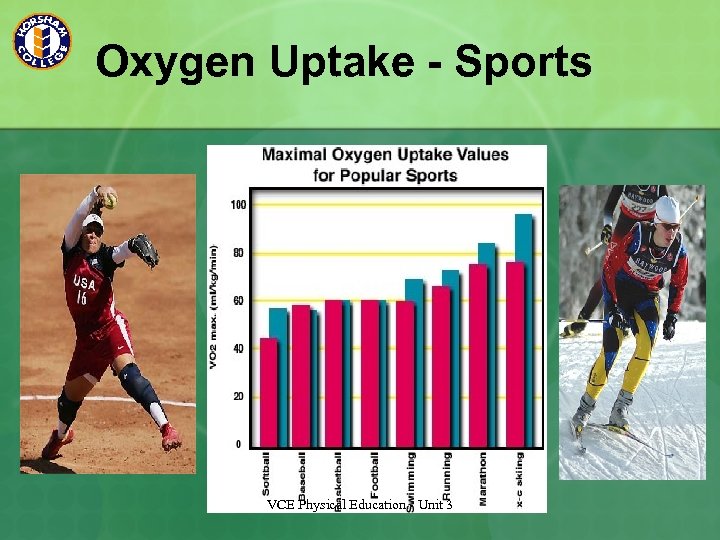 Oxygen Uptake - Sports VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Oxygen Uptake - Sports VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
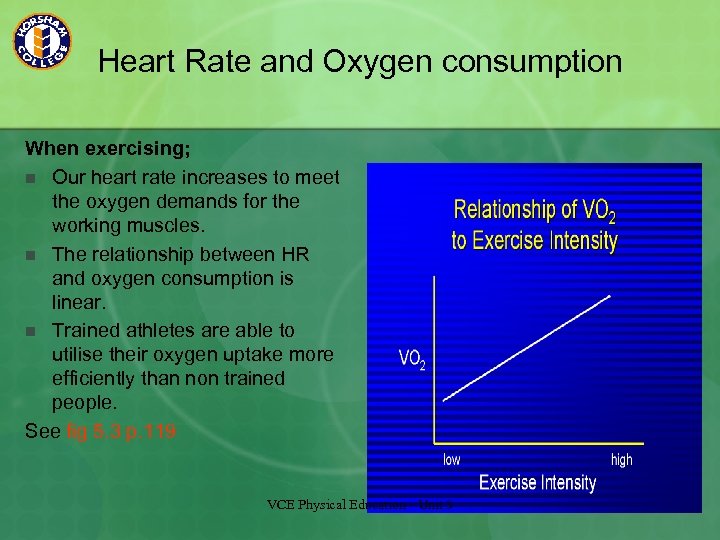 Heart Rate and Oxygen consumption When exercising; n Our heart rate increases to meet the oxygen demands for the working muscles. n The relationship between HR and oxygen consumption is linear. n Trained athletes are able to utilise their oxygen uptake more efficiently than non trained people. See fig 5. 3 p. 119 VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Heart Rate and Oxygen consumption When exercising; n Our heart rate increases to meet the oxygen demands for the working muscles. n The relationship between HR and oxygen consumption is linear. n Trained athletes are able to utilise their oxygen uptake more efficiently than non trained people. See fig 5. 3 p. 119 VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
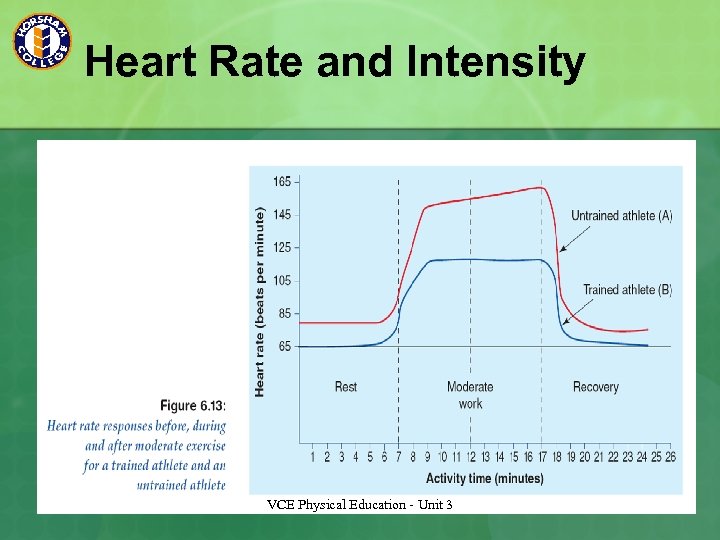 Heart Rate and Intensity VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Heart Rate and Intensity VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Checkpoints n Complete questions 1 -4 page 119 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Checkpoints n Complete questions 1 -4 page 119 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Oxygen Deficit Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Oxygen Deficit Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Oxygen Deficit Oxygen deficit occurs when the demand for oxygen exceeds the supply of oxygen available. The body therefore needs to obtain ATP through anaerobic pathways. Short duration/high intensity – Lactic acid is produced but is removed once oxygen demands are met. Performance is hindered due to the presence of lactic acid Once oxygen demands are met, the body reaches its steady state. Aerobic glycolysis assists in the removal of lactic acid. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Oxygen Deficit Oxygen deficit occurs when the demand for oxygen exceeds the supply of oxygen available. The body therefore needs to obtain ATP through anaerobic pathways. Short duration/high intensity – Lactic acid is produced but is removed once oxygen demands are met. Performance is hindered due to the presence of lactic acid Once oxygen demands are met, the body reaches its steady state. Aerobic glycolysis assists in the removal of lactic acid. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
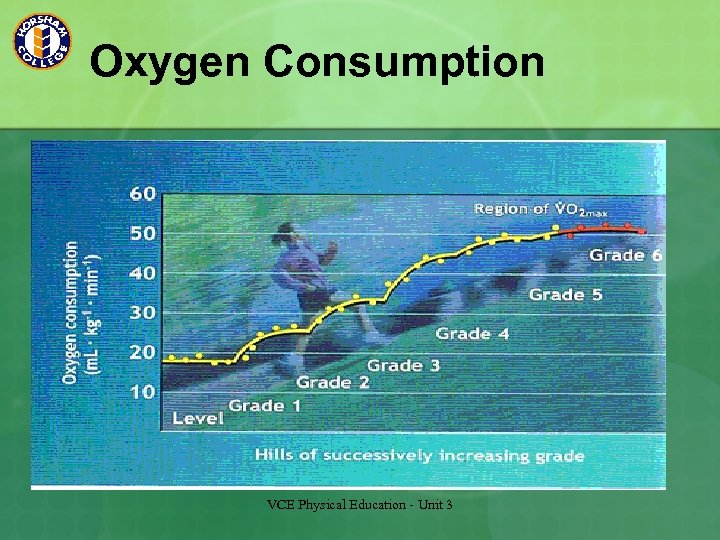 Oxygen Consumption VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Oxygen Consumption VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Checkpoints n Complete questions 1 -4 page 120 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Checkpoints n Complete questions 1 -4 page 120 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Acute Responses Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Acute Responses Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Acute Responses Acute responses occur to supply extra oxygen and nutrients to support ATP production. Acute responses include; n Reduction in creatine stores n Accumulation of lactic acid n Increase in epinephrine (Regulates BP and O 2 consumption levels) Reduction in glycogen stores n Increase in muscle temperature n Increase in cardiac output n Redistribution of blood to working muscles. Responses are dependent on intensity, duration, fitness levels and type of activity used. n VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Acute Responses Acute responses occur to supply extra oxygen and nutrients to support ATP production. Acute responses include; n Reduction in creatine stores n Accumulation of lactic acid n Increase in epinephrine (Regulates BP and O 2 consumption levels) Reduction in glycogen stores n Increase in muscle temperature n Increase in cardiac output n Redistribution of blood to working muscles. Responses are dependent on intensity, duration, fitness levels and type of activity used. n VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Acute Responses Acute responses to exercise. Increase in; n Oxygen intake n Transport of oxygen n Extraction of oxygen from the blood n Consumption of oxygen by working muscles n Continues until maximum uptake is met (VO 2 max) http: //www. bbc. co. uk/science/ humanbody/ VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Acute Responses Acute responses to exercise. Increase in; n Oxygen intake n Transport of oxygen n Extraction of oxygen from the blood n Consumption of oxygen by working muscles n Continues until maximum uptake is met (VO 2 max) http: //www. bbc. co. uk/science/ humanbody/ VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Checkpoints n Complete questions 1 -3 page 122 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Checkpoints n Complete questions 1 -3 page 122 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Oxygen Debt Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Oxygen Debt Oxygen Uptake, Oxygen Deficit and Oxygen Debit VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
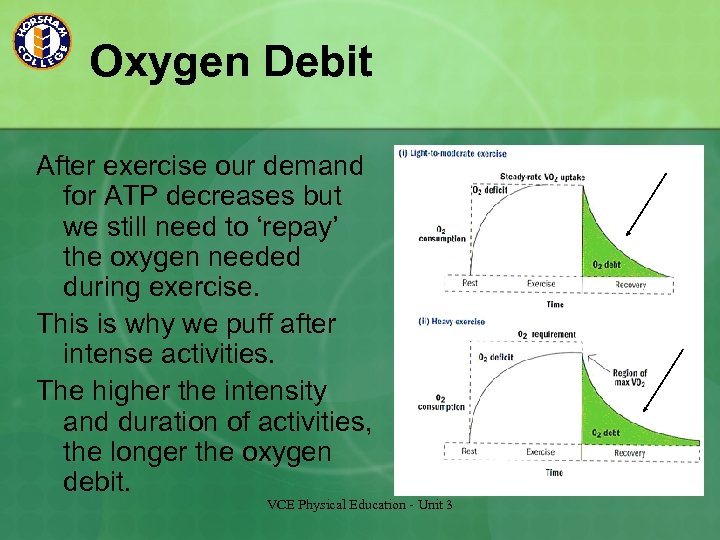 Oxygen Debit After exercise our demand for ATP decreases but we still need to ‘repay’ the oxygen needed during exercise. This is why we puff after intense activities. The higher the intensity and duration of activities, the longer the oxygen debit. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Oxygen Debit After exercise our demand for ATP decreases but we still need to ‘repay’ the oxygen needed during exercise. This is why we puff after intense activities. The higher the intensity and duration of activities, the longer the oxygen debit. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
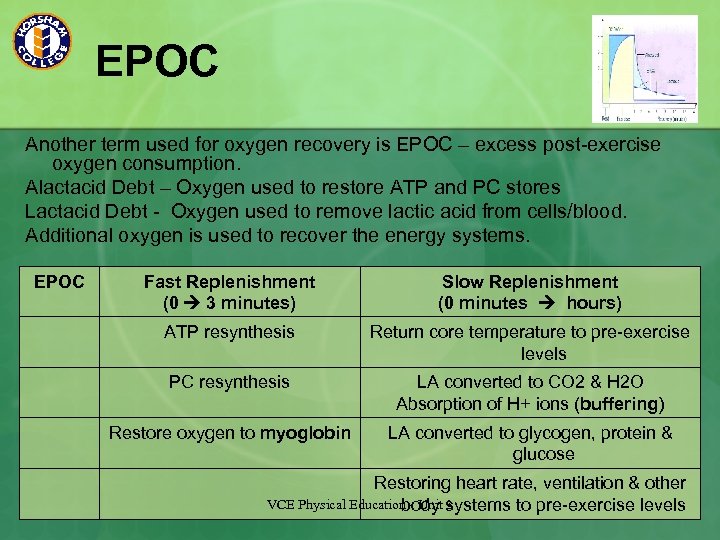 EPOC Another term used for oxygen recovery is EPOC – excess post-exercise oxygen consumption. Alactacid Debt – Oxygen used to restore ATP and PC stores Lactacid Debt - Oxygen used to remove lactic acid from cells/blood. Additional oxygen is used to recover the energy systems. EPOC Fast Replenishment (0 3 minutes) Slow Replenishment (0 minutes hours) ATP resynthesis Return core temperature to pre-exercise levels PC resynthesis LA converted to CO 2 & H 2 O Absorption of H+ ions (buffering) Restore oxygen to myoglobin LA converted to glycogen, protein & glucose Restoring heart rate, ventilation & other VCE Physical Education - Unit systems to pre-exercise levels body 3
EPOC Another term used for oxygen recovery is EPOC – excess post-exercise oxygen consumption. Alactacid Debt – Oxygen used to restore ATP and PC stores Lactacid Debt - Oxygen used to remove lactic acid from cells/blood. Additional oxygen is used to recover the energy systems. EPOC Fast Replenishment (0 3 minutes) Slow Replenishment (0 minutes hours) ATP resynthesis Return core temperature to pre-exercise levels PC resynthesis LA converted to CO 2 & H 2 O Absorption of H+ ions (buffering) Restore oxygen to myoglobin LA converted to glycogen, protein & glucose Restoring heart rate, ventilation & other VCE Physical Education - Unit systems to pre-exercise levels body 3
 Coursework 5. 1 and 5. 2 n Complete the data analysis tasks on page 124 and 125 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Coursework 5. 1 and 5. 2 n Complete the data analysis tasks on page 124 and 125 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Checkpoints n Complete questions 1 -3 page 127 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Checkpoints n Complete questions 1 -3 page 127 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Test Your Knowledge n Complete the review questions 1 -4 page 128 -9 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Test Your Knowledge n Complete the review questions 1 -4 page 128 -9 of Nelson Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Peak Performance n Complete the chapter questions on page 2939 of Nelson Peak Performance Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Peak Performance n Complete the chapter questions on page 2939 of Nelson Peak Performance Physical Education VCE Units 3 & 4. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 PHYS ED Notes n Read the summarised information of pages 47 -53 of PHYS ED Notes and complete the revision questions. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
PHYS ED Notes n Read the summarised information of pages 47 -53 of PHYS ED Notes and complete the revision questions. VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 VCAA Questions VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
VCAA Questions VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
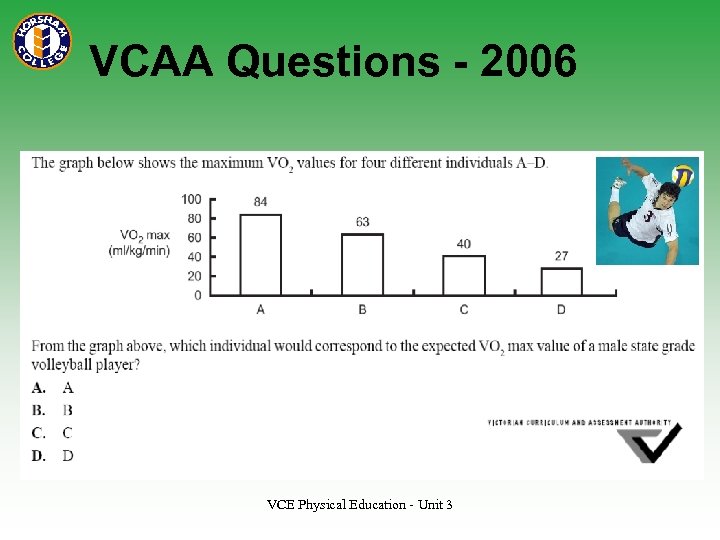 VCAA Questions - 2006 VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
VCAA Questions - 2006 VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
 Web Links – Chapter 5 • • Australian Sports Commission: http: //www. ausport. gov. au http: //www. find 30. com. au. UK: Interactive body and mind tests from the BBC • Find 30 promotion (Government of WA Department of Health): • Walking School Bus promotion (UK): http: //www. walkingbus. com http: //www. bbc. co. uk/science/humanbody • Ministry of Health (New Zealand) toolkits: http: //www. newhealth. govt. nz • • The 10, 000 Steps Rockhampton project: http: //www. 10000 steps. org. au/rockhampton/ Human anatomy: http: //www. innerbody. com • Travelsmart Australia: http: //www. travelsmart. gov. au • Health Organisation: • World Foundation Australia: http: //www. who. int and anatomy – Virtual Body: Information about the body • Heart http: //www. heartfoundation. com. au • Vic. Health (The Victorian Health Promotion Foundation): http: //www. vichealth. vic. gov. au http: //www. ehc. com/vbody. asp • Be Active promotion (Government of South Australia): http: //www. beactive. com. au • • Go For Your Life: Resources for Health Professionals – Measure of Anaerobicprevention – USA): Article – http: //www. goforyourlife. vic. gov. au Oxygen Deficit: A Introduction (Centre for disease control and Capacity: • Physical Activity http: //www. cdc. gov/nccdphp/dnpa/physical/health_professionals/index. htm http: //www. faccioni. com/Reviews/oxygendeficit. htm • Health Promotion (Public Health Agency of Canada): http: //www. phac-aspc. gc. ca/hp-ps/index. html • Inter-Governmental • Strategicyouth (Centre foron. Forum ontransport and Health (SIGPAH): in the blood, from the Australasian Society Information disease control and prevention (USA): http: //www. cdc. gov/Healthy. Youth/ the Physical Activity of oxygen http: //www. nphp. gov. au/workprog/sigpah/ • Healthy • America On The Move promotion: http: //www. americaonthemove. org of Cardio-Vascular of Behavioural Nutrition and Physical Activity: http: //www. ijbnpa. org/home Perfusionists: • Papers from the International Journal • Department of health and aging (Australian government): http: //www. health. gov. au/internet/wcms/publishing. nsf/content/home http: //www. perfusion. com. au/CCP/Physiology/Oxygen and carbon dioxide • Building a healthy, active Australia (Australian government): http: //www. healthyactive. gov. au • National Public Health Partnership: http: //www. nphp. gov. au transport. htm • Be Active promotion (Government of South Australia): http: //www. beactive. com. au • • Sport and Recreation Australia: http: //www. sport. vic. gov. au Nicholas Institute of Sports Medicine and Athletic Trauma – A primer on maximum oxygen consumption: http: //www. nismat. org/physcor/max_o 2. html • Australian Sports Commission: http: //www. ausport. gov. au • Sports Coach UK: http: //www. brianmac. demon. co. uk VCE Physical Education - Unit 3
Web Links – Chapter 5 • • Australian Sports Commission: http: //www. ausport. gov. au http: //www. find 30. com. au. UK: Interactive body and mind tests from the BBC • Find 30 promotion (Government of WA Department of Health): • Walking School Bus promotion (UK): http: //www. walkingbus. com http: //www. bbc. co. uk/science/humanbody • Ministry of Health (New Zealand) toolkits: http: //www. newhealth. govt. nz • • The 10, 000 Steps Rockhampton project: http: //www. 10000 steps. org. au/rockhampton/ Human anatomy: http: //www. innerbody. com • Travelsmart Australia: http: //www. travelsmart. gov. au • Health Organisation: • World Foundation Australia: http: //www. who. int and anatomy – Virtual Body: Information about the body • Heart http: //www. heartfoundation. com. au • Vic. Health (The Victorian Health Promotion Foundation): http: //www. vichealth. vic. gov. au http: //www. ehc. com/vbody. asp • Be Active promotion (Government of South Australia): http: //www. beactive. com. au • • Go For Your Life: Resources for Health Professionals – Measure of Anaerobicprevention – USA): Article – http: //www. goforyourlife. vic. gov. au Oxygen Deficit: A Introduction (Centre for disease control and Capacity: • Physical Activity http: //www. cdc. gov/nccdphp/dnpa/physical/health_professionals/index. htm http: //www. faccioni. com/Reviews/oxygendeficit. htm • Health Promotion (Public Health Agency of Canada): http: //www. phac-aspc. gc. ca/hp-ps/index. html • Inter-Governmental • Strategicyouth (Centre foron. Forum ontransport and Health (SIGPAH): in the blood, from the Australasian Society Information disease control and prevention (USA): http: //www. cdc. gov/Healthy. Youth/ the Physical Activity of oxygen http: //www. nphp. gov. au/workprog/sigpah/ • Healthy • America On The Move promotion: http: //www. americaonthemove. org of Cardio-Vascular of Behavioural Nutrition and Physical Activity: http: //www. ijbnpa. org/home Perfusionists: • Papers from the International Journal • Department of health and aging (Australian government): http: //www. health. gov. au/internet/wcms/publishing. nsf/content/home http: //www. perfusion. com. au/CCP/Physiology/Oxygen and carbon dioxide • Building a healthy, active Australia (Australian government): http: //www. healthyactive. gov. au • National Public Health Partnership: http: //www. nphp. gov. au transport. htm • Be Active promotion (Government of South Australia): http: //www. beactive. com. au • • Sport and Recreation Australia: http: //www. sport. vic. gov. au Nicholas Institute of Sports Medicine and Athletic Trauma – A primer on maximum oxygen consumption: http: //www. nismat. org/physcor/max_o 2. html • Australian Sports Commission: http: //www. ausport. gov. au • Sports Coach UK: http: //www. brianmac. demon. co. uk VCE Physical Education - Unit 3


