1d43a287e1bc43f5c5bf842179c33d96.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Chapter 5: Monetary Theory and Policy
Chapter 5: Monetary Theory and Policy
 Chapter 5: Monetary Theory and Policy Chapter Outline: • Monetary Theory. • Economic Indicators Monitored by the Fed. • Lags in Monetary Policy. • Integrating Monetary and Fiscal Policies. • Global Effects of Monetary Policy. 1 -
Chapter 5: Monetary Theory and Policy Chapter Outline: • Monetary Theory. • Economic Indicators Monitored by the Fed. • Lags in Monetary Policy. • Integrating Monetary and Fiscal Policies. • Global Effects of Monetary Policy. 1 -
 Monetary Theory • Keynesian Theory. • Quantity Theory and the Monetarist Approach. • Theory of Rational Expectation.
Monetary Theory • Keynesian Theory. • Quantity Theory and the Monetarist Approach. • Theory of Rational Expectation.
 Keynesian Theory John Maynard Keynes was a British economist whose theories were popular during the 1930 s and beyond. • Keynes believed that a market-driven economy is inherently unstable. Changes in output, prices, or unemployment would be magnified by the invisible hand. • Keynes believed that an economy can’t rely upon the market mechanism to correct the problem.
Keynesian Theory John Maynard Keynes was a British economist whose theories were popular during the 1930 s and beyond. • Keynes believed that a market-driven economy is inherently unstable. Changes in output, prices, or unemployment would be magnified by the invisible hand. • Keynes believed that an economy can’t rely upon the market mechanism to correct the problem.
 Keynesian Theory Keynes believed that government intervention was needed to control the instability of a market economy. If the economy slows down, the government should buy more output, employ more people, increase income transfers, and make more money available. If the economy overheats, then the role of government is to slow the economy down by increasing taxes, reducing government spending, and by making money less available.
Keynesian Theory Keynes believed that government intervention was needed to control the instability of a market economy. If the economy slows down, the government should buy more output, employ more people, increase income transfers, and make more money available. If the economy overheats, then the role of government is to slow the economy down by increasing taxes, reducing government spending, and by making money less available.
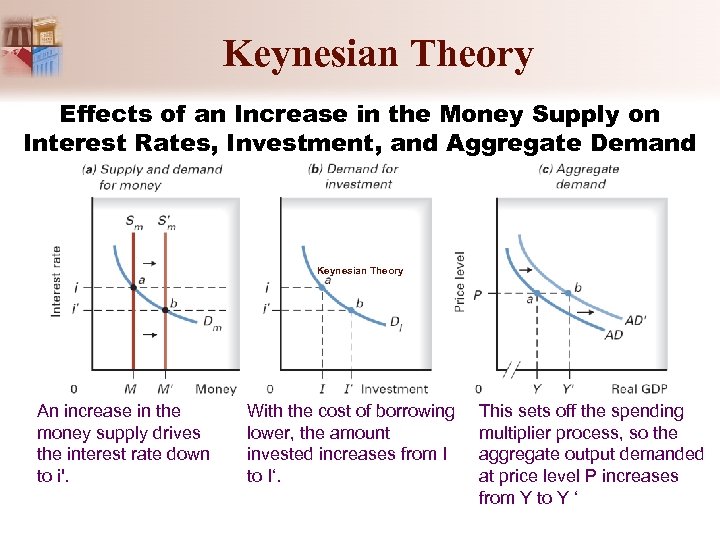 Keynesian Theory Effects of an Increase in the Money Supply on Interest Rates, Investment, and Aggregate Demand Keynesian Theory An increase in the money supply drives the interest rate down to i'. With the cost of borrowing lower, the amount invested increases from I to I‘. This sets off the spending multiplier process, so the aggregate output demanded at price level P increases from Y to Y ‘
Keynesian Theory Effects of an Increase in the Money Supply on Interest Rates, Investment, and Aggregate Demand Keynesian Theory An increase in the money supply drives the interest rate down to i'. With the cost of borrowing lower, the amount invested increases from I to I‘. This sets off the spending multiplier process, so the aggregate output demanded at price level P increases from Y to Y ‘
 Quantity Theory and the Monetarist Approach • It suggests a particular relationship between the money supply and the degree of the economic activity. • It is based on the equation of exchange: MV= P*Q M= Amount of money in the economy. V= Velocity of money. P= Weighted price level of goods and services in the economy. Q= Quantity of goods and services sold.
Quantity Theory and the Monetarist Approach • It suggests a particular relationship between the money supply and the degree of the economic activity. • It is based on the equation of exchange: MV= P*Q M= Amount of money in the economy. V= Velocity of money. P= Weighted price level of goods and services in the economy. Q= Quantity of goods and services sold.
 Comparison of the Monetarist and Keynesian Theories • Monetarists are passive. • Time required to improve the economy. • Accepting a natural rate of unemployment. • Relative importance for inflation and unemployment.
Comparison of the Monetarist and Keynesian Theories • Monetarists are passive. • Time required to improve the economy. • Accepting a natural rate of unemployment. • Relative importance for inflation and unemployment.
 Theory of Rational Expectations • The public accounts for all existing information when forming its expectations. • The public will use this information to forecast the impact of an existing policy and act accordingly.
Theory of Rational Expectations • The public accounts for all existing information when forming its expectations. • The public will use this information to forecast the impact of an existing policy and act accordingly.
 The Tradeoff Faced by the Fed. • Inflation. • Unemployment. • Gross domestic product.
The Tradeoff Faced by the Fed. • Inflation. • Unemployment. • Gross domestic product.
 Economic Indicators Monitored by the Fed. • Indicators of Economic Growth. • Indicators of Inflation. • Index of Leading Economic Indicators.
Economic Indicators Monitored by the Fed. • Indicators of Economic Growth. • Indicators of Inflation. • Index of Leading Economic Indicators.
 Indicators of Economic Growth • GDP • Level of Production • National Income • Unemployment rate • Industrial production index • Retail sales index • Home sales index • Consumer confidence survey
Indicators of Economic Growth • GDP • Level of Production • National Income • Unemployment rate • Industrial production index • Retail sales index • Home sales index • Consumer confidence survey
 Indicators of Inflation • Producer price index • Consumer price index • Housing price index. • Other indicators. • Oil Prices. • Price of Gold.
Indicators of Inflation • Producer price index • Consumer price index • Housing price index. • Other indicators. • Oil Prices. • Price of Gold.
 Index of Leading Economic Indicators • Leading index. • Coincident index. • Lagging index.
Index of Leading Economic Indicators • Leading index. • Coincident index. • Lagging index.
 Lags in Monetary Policy • Recognition Lag. • Implementation Lag. • Impact Lag.
Lags in Monetary Policy • Recognition Lag. • Implementation Lag. • Impact Lag.
 Assessing the Impact of Monetary Policy • Forecasting Money Supply Movements. • Improved Communication from the Fed. • Impact of Monetary Policy across Financial Markets.
Assessing the Impact of Monetary Policy • Forecasting Money Supply Movements. • Improved Communication from the Fed. • Impact of Monetary Policy across Financial Markets.
 Integrating Monetary and Fiscal Policies • History. • Monetizing the Debt. • Market Assessment of Integrated Policies.
Integrating Monetary and Fiscal Policies • History. • Monetizing the Debt. • Market Assessment of Integrated Policies.
 Global Effects of Monetary Policy • Impact of the Dollar. • Impact of Global Economic Conditions. • Transmission of Interest Rates.
Global Effects of Monetary Policy • Impact of the Dollar. • Impact of Global Economic Conditions. • Transmission of Interest Rates.
 End of Chapter 5
End of Chapter 5


