879c648ccafdd2df17171afa885e003f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Chapter 5 Marginal Utility & Consumer Choice 3/16/2018 © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 1
Chapter 5 Marginal Utility & Consumer Choice 3/16/2018 © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 1
 What is Utility? The satisfaction or enjoyment a person obtains from consuming a good © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 2
What is Utility? The satisfaction or enjoyment a person obtains from consuming a good © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 2
 What is a Util? A hypothetical unit used to measure how much utility a person obtains from consuming a good © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 3
What is a Util? A hypothetical unit used to measure how much utility a person obtains from consuming a good © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 3
 What is Marginal Utility? The change in total utility a person derives from consuming an additional unit of a good © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 4
What is Marginal Utility? The change in total utility a person derives from consuming an additional unit of a good © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 4
 What is Total Utility? The total number of utils a person derives from consuming a specific quantity of a good © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 5
What is Total Utility? The total number of utils a person derives from consuming a specific quantity of a good © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 5
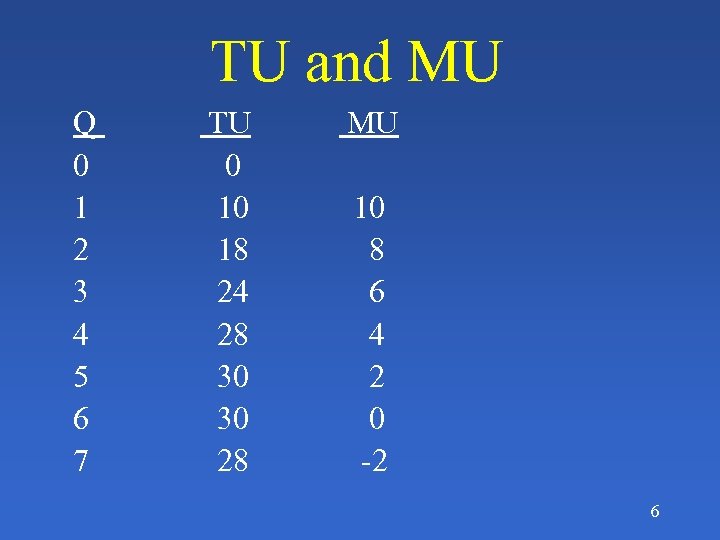 TU and MU Q 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 TU 0 10 18 24 28 30 30 28 MU 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 6
TU and MU Q 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 TU 0 10 18 24 28 30 30 28 MU 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 6
 What is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility? As more of a good is consumed, at some point, the marginal utility a person derives from each additional unit diminishes 7
What is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility? As more of a good is consumed, at some point, the marginal utility a person derives from each additional unit diminishes 7
 Does the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility apply to all goods consumed? YES © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 8
Does the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility apply to all goods consumed? YES © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 8
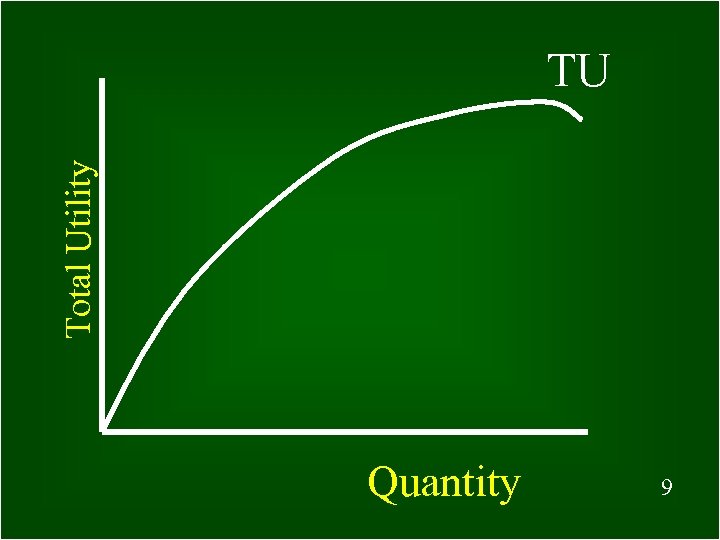 Total Utility TU Quantity 9 9
Total Utility TU Quantity 9 9
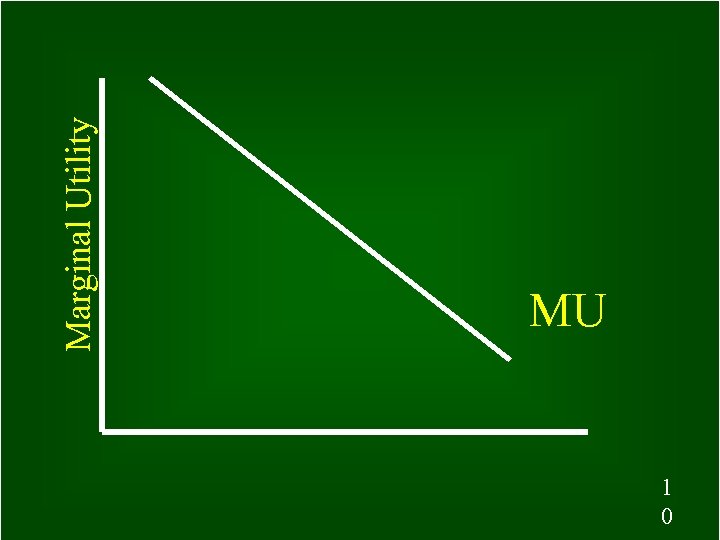 Marginal Utility MU 1 10 0
Marginal Utility MU 1 10 0
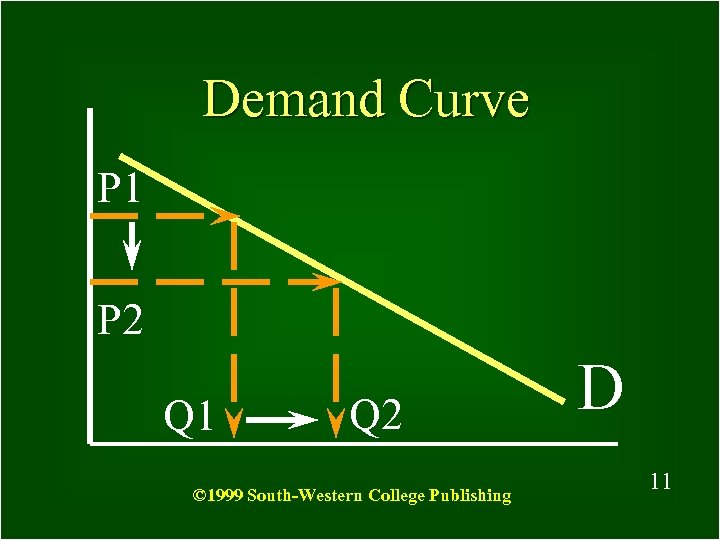 Demand Curve P 1 P 2 Q 1 Q 2 © 1999 South-Western College Publishing D 11 11
Demand Curve P 1 P 2 Q 1 Q 2 © 1999 South-Western College Publishing D 11 11
 Why does MU = P explain the downward sloping demand curve? © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 12
Why does MU = P explain the downward sloping demand curve? © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 12
 If you are hungry for a Shawarma, how many Shawarmas will you buy? Up to where your MU = P © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 13
If you are hungry for a Shawarma, how many Shawarmas will you buy? Up to where your MU = P © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 13
 Why? Because if MU > P you will buy another Shawarma If MU < P you will not buy that last Shawarma © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 14
Why? Because if MU > P you will buy another Shawarma If MU < P you will not buy that last Shawarma © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 14
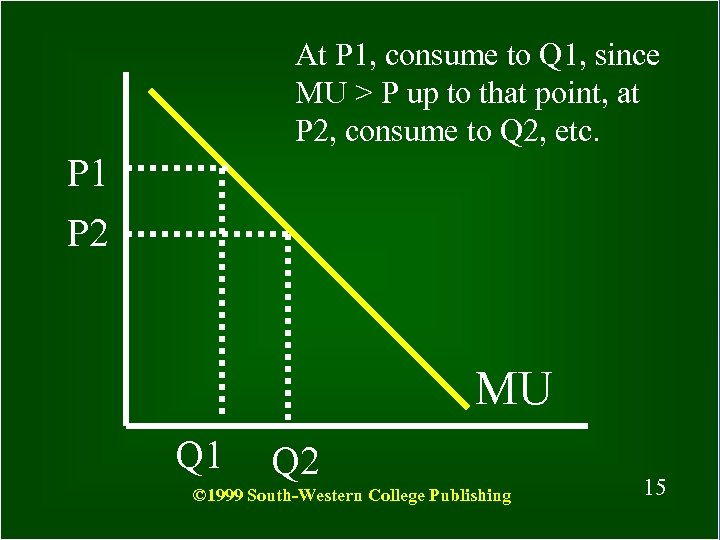 At P 1, consume to Q 1, since MU > P up to that point, at P 2, consume to Q 2, etc. P 1 P 2 MU Q 1 Q 2 © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 15 15
At P 1, consume to Q 1, since MU > P up to that point, at P 2, consume to Q 2, etc. P 1 P 2 MU Q 1 Q 2 © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 15 15
 Consumer equilibrium Now go from 1 good to 2 or more goods: have to take prices of good into account 16
Consumer equilibrium Now go from 1 good to 2 or more goods: have to take prices of good into account 16
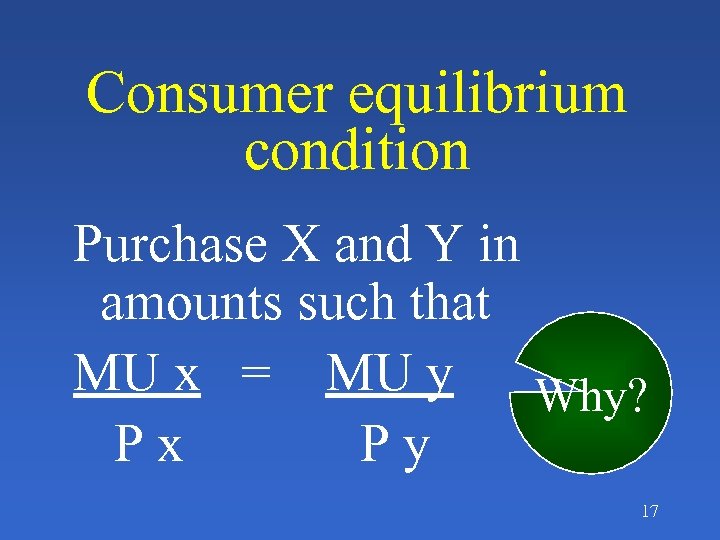 Consumer equilibrium condition Purchase X and Y in amounts such that MU x = MU y Why? Px Py 17
Consumer equilibrium condition Purchase X and Y in amounts such that MU x = MU y Why? Px Py 17
 Assume you are not in equilibrium… say that MU x > MU y Px Py What would you do? ? 18
Assume you are not in equilibrium… say that MU x > MU y Px Py What would you do? ? 18
 Purchase more of X (due to its greater satisfaction per dollar), and less of Y But more of X reduces MUX and less of Y increases MUY so we are heading back to equilibrium!! 19
Purchase more of X (due to its greater satisfaction per dollar), and less of Y But more of X reduces MUX and less of Y increases MUY so we are heading back to equilibrium!! 19
 For more than 2 goods, the equilibrium condition becomes…. . MUx/Px = Muy/Py = Muz/Pz = ……. for all goods 20
For more than 2 goods, the equilibrium condition becomes…. . MUx/Px = Muy/Py = Muz/Pz = ……. for all goods 20
 In other words, when is your Total Utility maximized? When the last dollar spent on each good yields the same marginal utility © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 21
In other words, when is your Total Utility maximized? When the last dollar spent on each good yields the same marginal utility © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 21
 Applications of Utility • The water-diamond paradox--why is water so cheap and diamonds so expensive? 22
Applications of Utility • The water-diamond paradox--why is water so cheap and diamonds so expensive? 22
 Water-high TU but low MU due to abundance, diamonds the opposite. Price reflects marginal valuation, not totals 23
Water-high TU but low MU due to abundance, diamonds the opposite. Price reflects marginal valuation, not totals 23
 What statement do these sites make about the marginal utility of diamonds? http: //www. rostar. com http: //www. usdiamond. com © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 24
What statement do these sites make about the marginal utility of diamonds? http: //www. rostar. com http: //www. usdiamond. com © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 24
 The marginal utility of money? • Does it diminish as with goods? 25
The marginal utility of money? • Does it diminish as with goods? 25
 Diminishing MU of money often used as an argument for progressive taxation. 26
Diminishing MU of money often used as an argument for progressive taxation. 26
 What is Interpersonal comparison of utility? A comparison of the marginal utility that different people derive from a good or a dollar © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 27
What is Interpersonal comparison of utility? A comparison of the marginal utility that different people derive from a good or a dollar © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 27
 Economists argue that we should avoid such interpersonal utility comparisons 28
Economists argue that we should avoid such interpersonal utility comparisons 28
 What is Consumer Surplus? The difference between the maximum amount that a consumer is willing to pay for something and what he actually pays © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 29
What is Consumer Surplus? The difference between the maximum amount that a consumer is willing to pay for something and what he actually pays © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 29
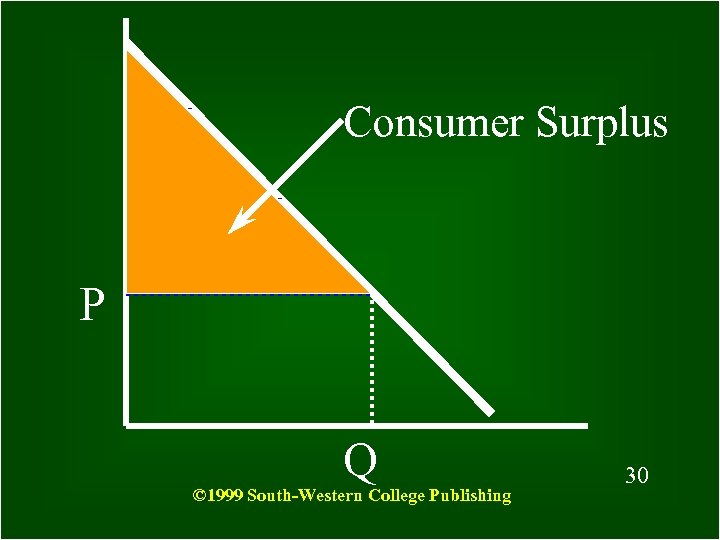 Consumer Surplus P Q © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 30 30
Consumer Surplus P Q © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 30 30
 What happens to Consumer Surplus as Market Price changes? It increases when price falls and falls when prices increase © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 31
What happens to Consumer Surplus as Market Price changes? It increases when price falls and falls when prices increase © 1999 South-Western College Publishing 31
 • What is a Util? • What is Utility? • What is Marginal Utility? • What is Total Utility? • What is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility? • What is a Demand Curve? 32
• What is a Util? • What is Utility? • What is Marginal Utility? • What is Total Utility? • What is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility? • What is a Demand Curve? 32


