2a26e72f5b046812ee18b85c5ab69ff5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70
 Chapter 5 Innovative EC Systems: From Egovernment to E-learning, Collaborative Commerce, and C 2 C Commerce
Chapter 5 Innovative EC Systems: From Egovernment to E-learning, Collaborative Commerce, and C 2 C Commerce
 E-Government: An Overview § E-government l The use of IT and e-commerce to provide convenient access to government information and efficiently and effectively delivery of public services to citizens and business partners § Government-to-citizens (G 2 C) l E-government category that includes all the interactions between a government and its citizens that can take place electronically 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 1
E-Government: An Overview § E-government l The use of IT and e-commerce to provide convenient access to government information and efficiently and effectively delivery of public services to citizens and business partners § Government-to-citizens (G 2 C) l E-government category that includes all the interactions between a government and its citizens that can take place electronically 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 1
 Government to Citizens § Ask questions of government agencies and receive answers § Pay taxes § Receive payments and documents § Renew driver’s licenses, pay traffic tickets, make appointment for vehicle emission inspections, driving tests, … § Receive training and educational courses §… 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 2
Government to Citizens § Ask questions of government agencies and receive answers § Pay taxes § Receive payments and documents § Renew driver’s licenses, pay traffic tickets, make appointment for vehicle emission inspections, driving tests, … § Receive training and educational courses §… 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 2
 Electronic Voting § Voting processes require extraordinary integrity as well as honesty and experience among the people involved in administering elections § Vulnerabilities: l l Proprietary nature of software, weakness of the certification criteria, inability of black-box testing to provide full assurances of correctness Lack any mechanism whereby independent recounting of ballots and auditing of the vote totals can be performed § From a technology point of view, voting machines make electronic fraud unprecedentedly simple; therefore, security and auditing measures are key to the success of e-voting 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 3
Electronic Voting § Voting processes require extraordinary integrity as well as honesty and experience among the people involved in administering elections § Vulnerabilities: l l Proprietary nature of software, weakness of the certification criteria, inability of black-box testing to provide full assurances of correctness Lack any mechanism whereby independent recounting of ballots and auditing of the vote totals can be performed § From a technology point of view, voting machines make electronic fraud unprecedentedly simple; therefore, security and auditing measures are key to the success of e-voting 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 3
 Electronic Benefits Transfer § Electronic benefits transfer to l l Bank account Smart card § Advantages: l l Reduction in processing cost • 50 cents per paper check • 2 cents for electronic payment Reduction of fraud by using biometrics in smart cards and PCs 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 4
Electronic Benefits Transfer § Electronic benefits transfer to l l Bank account Smart card § Advantages: l l Reduction in processing cost • 50 cents per paper check • 2 cents for electronic payment Reduction of fraud by using biometrics in smart cards and PCs 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 4
 Government-to-Business § E-government category that includes interactions (providing services and selling products) between governments and businesses l l Government E-Procurement (Reverse Auction) of MRO (maintenance, repair, operation) and other materials Group Purchasing: e. g. hospitals and public schools Forward E-Auctions of government surpluses Tax Collection and Management 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 5
Government-to-Business § E-government category that includes interactions (providing services and selling products) between governments and businesses l l Government E-Procurement (Reverse Auction) of MRO (maintenance, repair, operation) and other materials Group Purchasing: e. g. hospitals and public schools Forward E-Auctions of government surpluses Tax Collection and Management 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 5
 E-Government: An Overview § Government-to-government (G 2 G) l l E-government category that includes activities within government units and those between governments Aim at improving the efficiency or effectiveness of the government § Government-to-employees (G 2 E) l l E-government category that includes activities and services between government units and their employees Aim at enabling efficient communication 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 6
E-Government: An Overview § Government-to-government (G 2 G) l l E-government category that includes activities within government units and those between governments Aim at improving the efficiency or effectiveness of the government § Government-to-employees (G 2 E) l l E-government category that includes activities and services between government units and their employees Aim at enabling efficient communication 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 6
 E-Government: An Overview § Government-to-employees and internal efficiency and effectiveness l l l l E-payroll E-records management E-training Enterprise case management Integrated acquisition Integrated human resources Recruitment one-stop 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 7
E-Government: An Overview § Government-to-employees and internal efficiency and effectiveness l l l l E-payroll E-records management E-training Enterprise case management Integrated acquisition Integrated human resources Recruitment one-stop 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 7
 Transformation to E-Government (I) 1. Information publishing/dissemination l Online resources help reduce paperwork and the number of help-line employees needed 2. “Official” two-way transactions with one department at a time l Customers are able to submit personal information to and conduct monetary transactions with single government department 3. Multipurpose portals l Allow customers to use a single point of entry to send and receive information and to process monetary transactions across multiple departments 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 8
Transformation to E-Government (I) 1. Information publishing/dissemination l Online resources help reduce paperwork and the number of help-line employees needed 2. “Official” two-way transactions with one department at a time l Customers are able to submit personal information to and conduct monetary transactions with single government department 3. Multipurpose portals l Allow customers to use a single point of entry to send and receive information and to process monetary transactions across multiple departments 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 8
 Transformation to E-Government (II) 4. Portal personalization l Allow customers to customize portals with their desired features 5. Clustering of common services l l Governments will cluster services along common lines to accelerate the delivery of shared services Customers view once-disparate services as a unified package through the portal, their perception of departments as distinct entities will begin to blur; business restructuring will take place 6. Full integration and enterprise transformation l Offer a full-service center, personalized to each customer’s needs and preferences 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 9
Transformation to E-Government (II) 4. Portal personalization l Allow customers to customize portals with their desired features 5. Clustering of common services l l Governments will cluster services along common lines to accelerate the delivery of shared services Customers view once-disparate services as a unified package through the portal, their perception of departments as distinct entities will begin to blur; business restructuring will take place 6. Full integration and enterprise transformation l Offer a full-service center, personalized to each customer’s needs and preferences 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 9
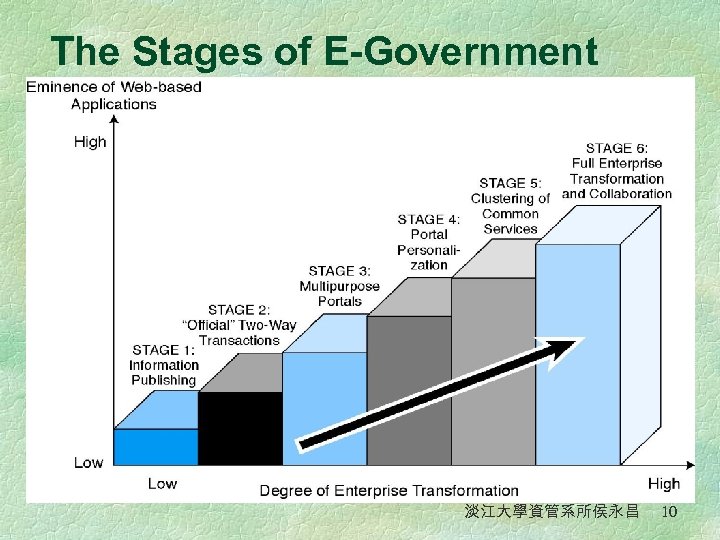 The Stages of E-Government 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 10
The Stages of E-Government 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 10
 Implementation Issues of E-Government § Transformation speed depends on l l Degree of resistance to change by government employees Rate at which citizens adopt the new applications Available budget Legal environment § G 2 B implementation is easier than G 2 C l G 2 B services have the potential for rapid cost saving, they can be a good way to begin an e-government initiative § Security and privacy issues are primary concern l Deciding on how much security to provide is an important managerial issue § Wireless applications must be included l Especially suitable for field employees 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 11
Implementation Issues of E-Government § Transformation speed depends on l l Degree of resistance to change by government employees Rate at which citizens adopt the new applications Available budget Legal environment § G 2 B implementation is easier than G 2 C l G 2 B services have the potential for rapid cost saving, they can be a good way to begin an e-government initiative § Security and privacy issues are primary concern l Deciding on how much security to provide is an important managerial issue § Wireless applications must be included l Especially suitable for field employees 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 11
 M-Government § Mobile government is the wireless implementation (mobile platform) of egovernment applications mostly to citizens, but also to business 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 12
M-Government § Mobile government is the wireless implementation (mobile platform) of egovernment applications mostly to citizens, but also to business 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 12
 The benefits of M-Government § Cost reduction § Increase efficiency § Transformation/modernization of public sector organization § Added convenience and flexibility for users § Better services to the citizens § Ability to reach a larger number of people through mobile devices than would be possible using wired Internet only 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 13
The benefits of M-Government § Cost reduction § Increase efficiency § Transformation/modernization of public sector organization § Added convenience and flexibility for users § Better services to the citizens § Ability to reach a larger number of people through mobile devices than would be possible using wired Internet only 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 13
 Some Implementation Issues § Wireless and mobile networks and related infrastructure, sufficient to support the increasing demand as well as software, must be developed § To increase citizen participation and provide citizenoriented services, governments need to offer easy access to m-government information in several forms § Mobile phone numbers and devices are relatively easy to hack, and wireless networks are vulnerable because they use public airwaves to send signals § Many countries have not yet adopted legislation for data and information practices that spell out the rights of citizens and the responsibilities of the data holders 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 14
Some Implementation Issues § Wireless and mobile networks and related infrastructure, sufficient to support the increasing demand as well as software, must be developed § To increase citizen participation and provide citizenoriented services, governments need to offer easy access to m-government information in several forms § Mobile phone numbers and devices are relatively easy to hack, and wireless networks are vulnerable because they use public airwaves to send signals § Many countries have not yet adopted legislation for data and information practices that spell out the rights of citizens and the responsibilities of the data holders 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 14
 E-Learning § E-learning l The online delivery of information for purposes of education, training, or knowledge management § Distance learning l Formal education that takes place off campus, usually, but not always, through online resources § Virtual university l An online university from which students take classes from home or other off-site locations, usually via the Internet 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 15
E-Learning § E-learning l The online delivery of information for purposes of education, training, or knowledge management § Distance learning l Formal education that takes place off campus, usually, but not always, through online resources § Virtual university l An online university from which students take classes from home or other off-site locations, usually via the Internet 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 15
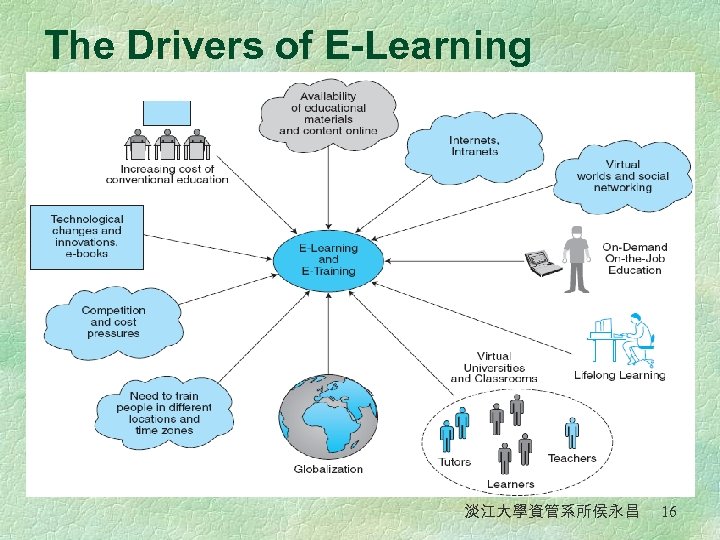 The Drivers of E-Learning 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 16
The Drivers of E-Learning 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 16
 Benefits of E-Learning (I) § E-learning can save money, reduce travel time increase access to experts, enable large numbers of students to take classes simultaneously, provide on-demand education, enable self-paced learning, and make less frustrating by making it more interactive and engaging § The better the match of the content and delivery vehicle to an individual’s learning style, the greater the content retention, and the better the learning results § Advanced e-learning support environments add value to traditional learning 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 17
Benefits of E-Learning (I) § E-learning can save money, reduce travel time increase access to experts, enable large numbers of students to take classes simultaneously, provide on-demand education, enable self-paced learning, and make less frustrating by making it more interactive and engaging § The better the match of the content and delivery vehicle to an individual’s learning style, the greater the content retention, and the better the learning results § Advanced e-learning support environments add value to traditional learning 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 17
 Benefits of E-Learning (II) § Time reduction l Training time may be reduced by 50% § Large volume and diversity l Provide training to a large number of people from diverse cultural backgrounds and educational levels even though they are at different locations in different time zones § Cost reduction l Cost may be reduced by 50 -70% § Higher content retention l Self-motivation results in 25 -60% higher content retention 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 18
Benefits of E-Learning (II) § Time reduction l Training time may be reduced by 50% § Large volume and diversity l Provide training to a large number of people from diverse cultural backgrounds and educational levels even though they are at different locations in different time zones § Cost reduction l Cost may be reduced by 50 -70% § Higher content retention l Self-motivation results in 25 -60% higher content retention 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 18
 Benefits of E-Learning (III) § Flexibility l Adjusting time, location, content, and speed of learning according to their own personal schedules § Updated and consistent material l l Offer just-in-time access to timely information 50 -60% more consistent because variations between teachers are eliminated § Fear-free and privacy-protected environment l Students can put forth any idea without fear of looking stupid 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 19
Benefits of E-Learning (III) § Flexibility l Adjusting time, location, content, and speed of learning according to their own personal schedules § Updated and consistent material l l Offer just-in-time access to timely information 50 -60% more consistent because variations between teachers are eliminated § Fear-free and privacy-protected environment l Students can put forth any idea without fear of looking stupid 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 19
 Drawbacks of E-Learning (I) § Need for instructor retraining l It costs money to provide such training § Equipment needs to support services l It needs additional funds to purchase tools to provide support services § Lack of face-to-face interaction and campus life l It can not fully be replicated the intellectual stimulation that takes places in a classroom with a “live” instructor § Assessment l It may not be able to adequately assess student’s work; there is no guarantee of who actually completed the assignment or exams 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 20
Drawbacks of E-Learning (I) § Need for instructor retraining l It costs money to provide such training § Equipment needs to support services l It needs additional funds to purchase tools to provide support services § Lack of face-to-face interaction and campus life l It can not fully be replicated the intellectual stimulation that takes places in a classroom with a “live” instructor § Assessment l It may not be able to adequately assess student’s work; there is no guarantee of who actually completed the assignment or exams 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 20
 Drawbacks of E-Learning (II) § Maintenance and updating l No online course can deliver real-time information and knowledge in a way a “live” instructor can § Protection of intellectual property l It is difficult and expensive to control the transmission of copyright works downloaded from e-learning platform § Computer literacy l E-learning cannot be extended to those students who are not computer literacy § Student retention l It may be difficult to keep students mentally engaged and enthusiastic over a long period of time 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 21
Drawbacks of E-Learning (II) § Maintenance and updating l No online course can deliver real-time information and knowledge in a way a “live” instructor can § Protection of intellectual property l It is difficult and expensive to control the transmission of copyright works downloaded from e-learning platform § Computer literacy l E-learning cannot be extended to those students who are not computer literacy § Student retention l It may be difficult to keep students mentally engaged and enthusiastic over a long period of time 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 21
 Challenges of E-Learning § Change the mind-set l l From the learner’s perspective, they must be willing to give up the idea of traditional classroom training; they must understand that continual, lifelong learning will be a part of normal work life From the teaching perspective, all learning objects must be converted (“tagged”) to a digital format; this task can really be challenging § Update the knowledge in e-learning systems l l l Who will do it? How often? How will the cost be covered? 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 22
Challenges of E-Learning § Change the mind-set l l From the learner’s perspective, they must be willing to give up the idea of traditional classroom training; they must understand that continual, lifelong learning will be a part of normal work life From the teaching perspective, all learning objects must be converted (“tagged”) to a digital format; this task can really be challenging § Update the knowledge in e-learning systems l l l Who will do it? How often? How will the cost be covered? 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 22
 Reasons of E-Learning Failures (I) § Believing that e-learning is always a cheaper learning or training alternative l E-learning can be less expensive than traditional instruction, however, if only a few students are to be served, e-leaning can be very expensive because of the high fixed costs § Overestimating what e-learning can accomplish l People sometimes do not understand the limitations of e-learning and therefore may expect too much § Overlooking the shortcomings of self-study l Some people cannot do self-study or do not want to; others may study incorrectly 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 23
Reasons of E-Learning Failures (I) § Believing that e-learning is always a cheaper learning or training alternative l E-learning can be less expensive than traditional instruction, however, if only a few students are to be served, e-leaning can be very expensive because of the high fixed costs § Overestimating what e-learning can accomplish l People sometimes do not understand the limitations of e-learning and therefore may expect too much § Overlooking the shortcomings of self-study l Some people cannot do self-study or do not want to; others may study incorrectly 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 23
 Reasons of E-Learning Failures (II) § Falling to look beyond the course paradigms l The instructor needs to look at the entire problem in the area of teaching, material creation and delivery § Viewing content as a commodity l This results in lack of attention to quality and delivery to individuals § Ignoring technology tools for e-learning or fixating too much on technology as a solution l A balanced approach is needed § Assuming that learned knowledge will be applied l This is difficult to accomplish successfully § Believing that because e-learning has been accomplished, employees and student will use it 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 24
Reasons of E-Learning Failures (II) § Falling to look beyond the course paradigms l The instructor needs to look at the entire problem in the area of teaching, material creation and delivery § Viewing content as a commodity l This results in lack of attention to quality and delivery to individuals § Ignoring technology tools for e-learning or fixating too much on technology as a solution l A balanced approach is needed § Assuming that learned knowledge will be applied l This is difficult to accomplish successfully § Believing that because e-learning has been accomplished, employees and student will use it 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 24
 Innovations in E-Learning § Since 2009, 29 robots developed by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology, each 3. 3 -feet tall, start to teach English in Korean elementary school § The robots which display a Caucasian face are wheeled around the classroom via remote control by teachers in Philippines, speaking to the students, reading books to them, and dancing to music by moving their head and arms § Cameras detect the Filipino teachers’ facial expressions and instantly reflect them on the robot’s avatar face 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 25
Innovations in E-Learning § Since 2009, 29 robots developed by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology, each 3. 3 -feet tall, start to teach English in Korean elementary school § The robots which display a Caucasian face are wheeled around the classroom via remote control by teachers in Philippines, speaking to the students, reading books to them, and dancing to music by moving their head and arms § Cameras detect the Filipino teachers’ facial expressions and instantly reflect them on the robot’s avatar face 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 25
 Social Learning § Learning, training, and knowledge sharing in social networks and by using social software tools for learning § Well-constructed social environments provide an excellent opportunity to share their experiences with others § Unfortunately the clutter and distractions found on these networks can make it difficult to focus on learning 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 26
Social Learning § Learning, training, and knowledge sharing in social networks and by using social software tools for learning § Well-constructed social environments provide an excellent opportunity to share their experiences with others § Unfortunately the clutter and distractions found on these networks can make it difficult to focus on learning 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 26
 Learning on-demand § Learning provided to an employee while the work is being done (in terms of troubleshooting or performance support) § In a learning on-demand environment, courses, references, help files, documents, Webcasts, audios, videos, books, and presentations are all made available when and where a worker needs them. 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 27
Learning on-demand § Learning provided to an employee while the work is being done (in terms of troubleshooting or performance support) § In a learning on-demand environment, courses, references, help files, documents, Webcasts, audios, videos, books, and presentations are all made available when and where a worker needs them. 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 27
 Learning Management System § Software applications for the administration, documentation, tracking, and reporting of training programs, classroom and online events, e-learning programs, and training content. It should be able to l l l Centralize and automate administration Use self-service and self-guided services Assemble and deliver learning content rapidly Consolidate training initiatives on a scalable Web-based platform Supportability and standards Personalize content and enable knowledge reuse 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 28
Learning Management System § Software applications for the administration, documentation, tracking, and reporting of training programs, classroom and online events, e-learning programs, and training content. It should be able to l l l Centralize and automate administration Use self-service and self-guided services Assemble and deliver learning content rapidly Consolidate training initiatives on a scalable Web-based platform Supportability and standards Personalize content and enable knowledge reuse 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 28
 E-Books § Electronic Books l A book in digital form that can be read on a computer screen or on a special device § E-books can be delivered and read via: l l l Web access; cannot be download Web download A dedicated reader A general-purpose reader A Web server; print-on-demand 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 29
E-Books § Electronic Books l A book in digital form that can be read on a computer screen or on a special device § E-books can be delivered and read via: l l l Web access; cannot be download Web download A dedicated reader A general-purpose reader A Web server; print-on-demand 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 29
 Advantages of E-Books § To readers l l l Portability; readers can carry hundreds of books, more when portable memory drivers are used, wherever they go Easy search capabilities and links Instant delivery via downloads from anywhere The ability to quickly and inexpensively copy material, including figures Easy integration of content with other text Reduce some physical burdens of traditional books 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 30
Advantages of E-Books § To readers l l l Portability; readers can carry hundreds of books, more when portable memory drivers are used, wherever they go Easy search capabilities and links Instant delivery via downloads from anywhere The ability to quickly and inexpensively copy material, including figures Easy integration of content with other text Reduce some physical burdens of traditional books 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 30
 Advantages of E-Books § To publishers l Lower production, marketing, and delivery costs l Lower updating and reproduction costs l Ability to reach many readers l Ease of combining several books; e. g. , professors can customize textbooks by using materials from different books l Easy to find out-of-print books 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 31
Advantages of E-Books § To publishers l Lower production, marketing, and delivery costs l Lower updating and reproduction costs l Ability to reach many readers l Ease of combining several books; e. g. , professors can customize textbooks by using materials from different books l Easy to find out-of-print books 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 31
 Limitations of E-Books § Require hardware and software that may be too expensive for some readers § Some people have difficulty reading large amounts of material on a screen § Batteries may run down § There are multiple and competing standards 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 32
Limitations of E-Books § Require hardware and software that may be too expensive for some readers § Some people have difficulty reading large amounts of material on a screen § Batteries may run down § There are multiple and competing standards 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 32
 Knowledge Management § Knowledge management (KM) l The process of capturing or creating knowledge, storing it, updating it constantly, interpreting it, and using it whenever necessary § KM and e-learning both use Knowledge l l E-learning: for the sake of individual learning KM: improve the functioning of an organization § Organizational knowledge base l l The repository for an enterprise’s accumulated knowledge; it allows for knowledge sharing To better perform EC tasks, organizations need knowledge, which is provided by KM 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 33
Knowledge Management § Knowledge management (KM) l The process of capturing or creating knowledge, storing it, updating it constantly, interpreting it, and using it whenever necessary § KM and e-learning both use Knowledge l l E-learning: for the sake of individual learning KM: improve the functioning of an organization § Organizational knowledge base l l The repository for an enterprise’s accumulated knowledge; it allows for knowledge sharing To better perform EC tasks, organizations need knowledge, which is provided by KM 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 33
 Knowledge Sharing § Knowledge is of limited value if it is not updated and shared § The ability to share knowledge decreases its cost per user and increases its effectiveness for greater competitive advantage § A major purpose of KM is to increase knowledge sharing. Shared knowledge can also decrease risk and uncertainty and facilitate problem solving § KM is about sharing a company’s knowledge repository, but increasingly it is also about sharing the information stored in people’s heads 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 34
Knowledge Sharing § Knowledge is of limited value if it is not updated and shared § The ability to share knowledge decreases its cost per user and increases its effectiveness for greater competitive advantage § A major purpose of KM is to increase knowledge sharing. Shared knowledge can also decrease risk and uncertainty and facilitate problem solving § KM is about sharing a company’s knowledge repository, but increasingly it is also about sharing the information stored in people’s heads 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 34
 Software Tools for Knowledge Sharing § Collaborative commerce tools § Expert and expertise location systems § Knowledge management systems § Social networks and Web 2. 0 tools l A major place of knowledge creation is in online communities. People post their problems on bulletin boards, forms, and blogs and wait for responses 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 35
Software Tools for Knowledge Sharing § Collaborative commerce tools § Expert and expertise location systems § Knowledge management systems § Social networks and Web 2. 0 tools l A major place of knowledge creation is in online communities. People post their problems on bulletin boards, forms, and blogs and wait for responses 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 35
 Knowledge Management Types § Organizational knowledge is embedded in these resources: l l l Human capital employee knowledge, competencies, and creativity Structured capital (organizational capital) organizational structure and culture, process, patents, and the capability to leverage knowledge through sharing and transferring Customer capital relationship between organizations and their customers and other partners 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 36
Knowledge Management Types § Organizational knowledge is embedded in these resources: l l l Human capital employee knowledge, competencies, and creativity Structured capital (organizational capital) organizational structure and culture, process, patents, and the capability to leverage knowledge through sharing and transferring Customer capital relationship between organizations and their customers and other partners 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 36
 Knowledge Management Activities § § § § Identification Creation Capture and Codification Classification Distribution Utilization Revolution 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 37
Knowledge Management Activities § § § § Identification Creation Capture and Codification Classification Distribution Utilization Revolution 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 37
 Online Advice and Consulting § § Medical advice Management consulting Legal advice Gurus (古魯; 印度教的導師) l Provide diversified expert services § Financial advice § Social networks § Other advisory services Cautions: it is not wise to risk your health, money, or legal status on free or even for-fee online advice; always seek more than one opinion, and carefully check the credentials for any advice provider 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 38
Online Advice and Consulting § § Medical advice Management consulting Legal advice Gurus (古魯; 印度教的導師) l Provide diversified expert services § Financial advice § Social networks § Other advisory services Cautions: it is not wise to risk your health, money, or legal status on free or even for-fee online advice; always seek more than one opinion, and carefully check the credentials for any advice provider 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 38
 Automated Question/Answer (QA) System § A system that locates, extracts, and provides specific answers to user questions expressed in natural language § Live chat with experts are becoming popular l l Moontoast: moontoast. com is an online knowledge marketplace, where experts exchange information with seekers via a live video chat session for a prearranged fee Search engines advice: answer. com and ask. com belong to a special category of search engines that has a huge collection of questions with appropriate answers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 39
Automated Question/Answer (QA) System § A system that locates, extracts, and provides specific answers to user questions expressed in natural language § Live chat with experts are becoming popular l l Moontoast: moontoast. com is an online knowledge marketplace, where experts exchange information with seekers via a live video chat session for a prearranged fee Search engines advice: answer. com and ask. com belong to a special category of search engines that has a huge collection of questions with appropriate answers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 39
 Expert Advice Within Organizations § Finding Experts Electronically l People who need help may post their problem on the corporate intranet and ask for help § Expert Location Systems l Interactive computerized systems that help employees find and connect with colleagues who have expertise required for specific problems—whether they are across the country or across the room—in order to solve specific, critical business problems in seconds 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 40
Expert Advice Within Organizations § Finding Experts Electronically l People who need help may post their problem on the corporate intranet and ask for help § Expert Location Systems l Interactive computerized systems that help employees find and connect with colleagues who have expertise required for specific problems—whether they are across the country or across the room—in order to solve specific, critical business problems in seconds 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 40
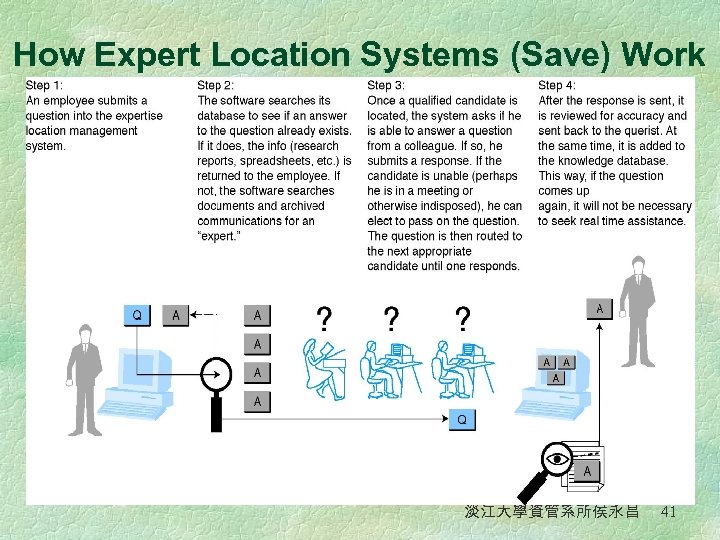 How Expert Location Systems (Save) Work 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 41
How Expert Location Systems (Save) Work 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 41
 Social networks and Web 2. 0 tools § A major place of knowledge creation is in online communities. § People post their problems on bulletin boards, forms, and blogs and wait for responses 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 42
Social networks and Web 2. 0 tools § A major place of knowledge creation is in online communities. § People post their problems on bulletin boards, forms, and blogs and wait for responses 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 42
 Collaborative Commerce § Collaborative Commerce (c-commerce) l The use of digital technologies that enable companies to collaboratively plan, design, develop, manage, and research products, services, and innovative EC applications. § Collaboration Hub (c-hub) l The central point of control for an e-market; a single c-hub, representing one e-market owner, can host multiple collaboration spaces (cspaces) in which trading partners use cenablers to exchange data with the c-hub 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 43
Collaborative Commerce § Collaborative Commerce (c-commerce) l The use of digital technologies that enable companies to collaboratively plan, design, develop, manage, and research products, services, and innovative EC applications. § Collaboration Hub (c-hub) l The central point of control for an e-market; a single c-hub, representing one e-market owner, can host multiple collaboration spaces (cspaces) in which trading partners use cenablers to exchange data with the c-hub 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 43
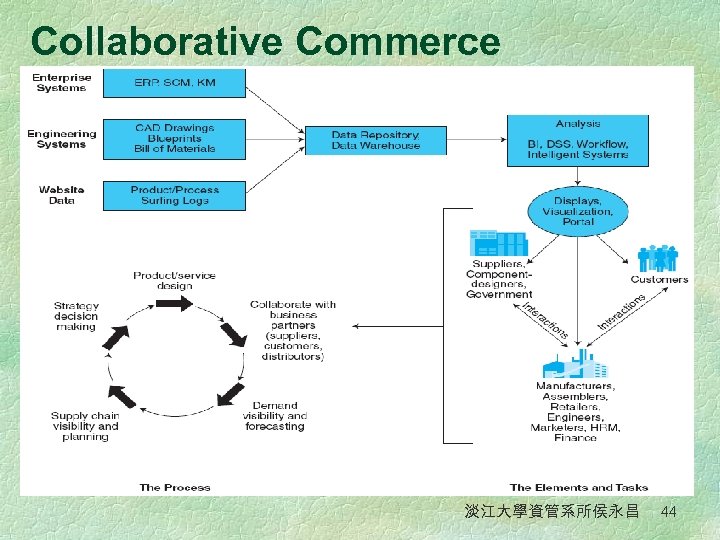 Collaborative Commerce 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 44
Collaborative Commerce 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 44
 Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) § A system in which retailers make their suppliers fully responsible for determining when to order and possibly how much to order § A third-party logistics provider(3 PL) can also be involved by organizing the shipment as needed § The retailer provides the supplier with realtime information, inventory levels, and the threshold below which orders are replenished 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 45
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) § A system in which retailers make their suppliers fully responsible for determining when to order and possibly how much to order § A third-party logistics provider(3 PL) can also be involved by organizing the shipment as needed § The retailer provides the supplier with realtime information, inventory levels, and the threshold below which orders are replenished 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 45
 Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) § With this approach, the retailer is no longer burdened with inventory management, demand forecasting becomes easier, the supplier can see the potential need for an item before the item is ordered, there are no purchase orders, inventories are keep low, and stock-outs become infrequent 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 46
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) § With this approach, the retailer is no longer burdened with inventory management, demand forecasting becomes easier, the supplier can see the potential need for an item before the item is ordered, there are no purchase orders, inventories are keep low, and stock-outs become infrequent 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 46
 Collaborative Commerce § Reducing Transportation and Inventory Costs § Reduction of Design Cycle Time § Reduction of Product Development Time § Elimination of Channel Conflict: Collaboration with Dealers and Retailers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 47
Collaborative Commerce § Reducing Transportation and Inventory Costs § Reduction of Design Cycle Time § Reduction of Product Development Time § Elimination of Channel Conflict: Collaboration with Dealers and Retailers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 47
 Implementing C-Commerce § Leading companies such as Dell, Cisco, and HP use collaborative commerce strategically, enabling sophisticated business models while transforming their value chains. § They also have implemented e-procurement and mature collaboration techniques to streamline operations, reduce overhead, and maintain or enhance margins in the face of intensive competition 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 48
Implementing C-Commerce § Leading companies such as Dell, Cisco, and HP use collaborative commerce strategically, enabling sophisticated business models while transforming their value chains. § They also have implemented e-procurement and mature collaboration techniques to streamline operations, reduce overhead, and maintain or enhance margins in the face of intensive competition 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 48
 Barriers to C-Commerce § Despite the many potential benefits, c-commerce is moving ahead fairly slowly in many companies except some very large ones l l l l Lack of internal integration, standards, and networks Security and privacy concerns Distrust over who has access to and control of information stored in a partner’s database Internal resistance to information sharing and to new approaches Lack of company skills to conduct c-commerce Gaining agreement on how to share costs and benefits Language incompatibility, cultural misunderstanding 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 49
Barriers to C-Commerce § Despite the many potential benefits, c-commerce is moving ahead fairly slowly in many companies except some very large ones l l l l Lack of internal integration, standards, and networks Security and privacy concerns Distrust over who has access to and control of information stored in a partner’s database Internal resistance to information sharing and to new approaches Lack of company skills to conduct c-commerce Gaining agreement on how to share costs and benefits Language incompatibility, cultural misunderstanding 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 49
 Customer-to-Customer E-Commerce § Customer-to-customer (C 2 C) E-commerce in which both the buyer and the seller are individuals, not businesses 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 50
Customer-to-Customer E-Commerce § Customer-to-customer (C 2 C) E-commerce in which both the buyer and the seller are individuals, not businesses 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 50
 C 2 C E-Commerce (I) § C 2 C Auctions l Most auctions are conducted by intermediaries, e. g. , e. Bay § Classified Ads l l They are available through most ISPs, portals, Internet directories, online newspapers They offer a national, rather than local audience; this greatly increase the supply of goods and services available and the number of potential buyers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 51
C 2 C E-Commerce (I) § C 2 C Auctions l Most auctions are conducted by intermediaries, e. g. , e. Bay § Classified Ads l l They are available through most ISPs, portals, Internet directories, online newspapers They offer a national, rather than local audience; this greatly increase the supply of goods and services available and the number of potential buyers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 51
 C 2 C E-Commerce (II) § Personal Services l l Numerous personal services are available on the Internet (lawyers, handy helpers, tax preparers, investment clubs, dating services) Some are free, some charge a fee § C 2 C Exchanges l l l Bartering exchange: goods and services are exchanged without monetary transactions Consumer exchange: help buyers and sellers find each other and negotiate deals Information exchange: consumers exchange information about products 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 52
C 2 C E-Commerce (II) § Personal Services l l Numerous personal services are available on the Internet (lawyers, handy helpers, tax preparers, investment clubs, dating services) Some are free, some charge a fee § C 2 C Exchanges l l l Bartering exchange: goods and services are exchanged without monetary transactions Consumer exchange: help buyers and sellers find each other and negotiate deals Information exchange: consumers exchange information about products 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 52
 C 2 C E-Commerce (III) § Selling Virtual Properties l l Millions of online game players in Asia are selling and buying online virtual properties IDC reported (2004) that 26. 7% of the 13. 8 million MMORPG players have bought or sold virtual property, for about US$ 120 million a year § Support Services for C 2 C l l When individuals buy products or services from other individuals online, they usually buy from strangers The issues of assuring quality, receiving payments, and preventing fraud are critical to the success of C 2 C 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 53
C 2 C E-Commerce (III) § Selling Virtual Properties l l Millions of online game players in Asia are selling and buying online virtual properties IDC reported (2004) that 26. 7% of the 13. 8 million MMORPG players have bought or sold virtual property, for about US$ 120 million a year § Support Services for C 2 C l l When individuals buy products or services from other individuals online, they usually buy from strangers The issues of assuring quality, receiving payments, and preventing fraud are critical to the success of C 2 C 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 53
 Peer-to-Peer Networks § Peer-to-peer (P 2 P) l A network architecture in which workstations (or PCs) share data (files) and computer resources (such as processing power) directly with each other rather than through a central server § Client-server l A network architecture in which some computers serve other computers via a central server 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 54
Peer-to-Peer Networks § Peer-to-peer (P 2 P) l A network architecture in which workstations (or PCs) share data (files) and computer resources (such as processing power) directly with each other rather than through a central server § Client-server l A network architecture in which some computers serve other computers via a central server 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 54
 Advantages of P 2 P Networks § Expand enormously the universe of information accessible from a PC or a mobile device § Offer better security, reliability, and availability of content § Other advantages over client-server l l No need for a network administrator The network is fast and inexpensive to set up and maintain Each PC can make a backup copy of its data to other PCs for security More productive because it enables direct connections between computers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 55
Advantages of P 2 P Networks § Expand enormously the universe of information accessible from a PC or a mobile device § Offer better security, reliability, and availability of content § Other advantages over client-server l l No need for a network administrator The network is fast and inexpensive to set up and maintain Each PC can make a backup copy of its data to other PCs for security More productive because it enables direct connections between computers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 55
 Characteristics of P 2 P Systems § Provide real-time access to other users through techniques such as instant messaging and multichannel collaboration applications § User computers can act as both clients and servers § The overall system is easy to use and is well integrated; devices can join the P 2 P network from any location with little effort § Maximize the use of physical attributes such as processor cycles, storage space, bandwidth, and location on the network § Employ user interfaces that load outside of a Web browser 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 56
Characteristics of P 2 P Systems § Provide real-time access to other users through techniques such as instant messaging and multichannel collaboration applications § User computers can act as both clients and servers § The overall system is easy to use and is well integrated; devices can join the P 2 P network from any location with little effort § Maximize the use of physical attributes such as processor cycles, storage space, bandwidth, and location on the network § Employ user interfaces that load outside of a Web browser 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 56
 Models of P 2 P Applications § Collaboration l Allow real-time direct interactions between people, including instant messaging and videoconferencing applications § Content distribution l Enable file sharing, made famous by Napster, Kazaa, and other music file-sharing services § Business process automation l Enhance existing business process applications § Distributed search l Enable the sending of search requests in real time to multiple information repositories rather than searching a centralized index 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 57
Models of P 2 P Applications § Collaboration l Allow real-time direct interactions between people, including instant messaging and videoconferencing applications § Content distribution l Enable file sharing, made famous by Napster, Kazaa, and other music file-sharing services § Business process automation l Enhance existing business process applications § Distributed search l Enable the sending of search requests in real time to multiple information repositories rather than searching a centralized index 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 57
 C 2 C P 2 P Applications (I) § Napster—the File-sharing utility l l Functioned as a directory that list the files being shared by other users Had more than 60 million members in 2002 U. S. federal court found Napster to be in violation of copyright law; Napster closed its free services in Mar. 2002 Roxio brought Napster’s intellectual property assets in Dec. 2002, relaunched Napster in 2004 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 58
C 2 C P 2 P Applications (I) § Napster—the File-sharing utility l l Functioned as a directory that list the files being shared by other users Had more than 60 million members in 2002 U. S. federal court found Napster to be in violation of copyright law; Napster closed its free services in Mar. 2002 Roxio brought Napster’s intellectual property assets in Dec. 2002, relaunched Napster in 2004 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 58
 C 2 C P 2 P Applications (II) § Other File-Sharing Programs l l Gnutella Kazaa § Other Commercial P 2 P Applications in C 2 C l Users can sell digital goods directly from their computers rather than going through centralized servers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 59
C 2 C P 2 P Applications (II) § Other File-Sharing Programs l l Gnutella Kazaa § Other Commercial P 2 P Applications in C 2 C l Users can sell digital goods directly from their computers rather than going through centralized servers 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 59
 Intrabusiness P 2 P Applications § Internal collaboration l l l In 1990, Intel wrote a file transfer program, Net. Batch, which allows chip designers to use the additional processing power of colleagues’ computers across sites in CA, AZ, and even foreign countries Under this arrangement, users were able to solve more complex problems that otherwise would have required the use of supercomputers Intel saved more than $500 million between 1992 and 2001 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 60
Intrabusiness P 2 P Applications § Internal collaboration l l l In 1990, Intel wrote a file transfer program, Net. Batch, which allows chip designers to use the additional processing power of colleagues’ computers across sites in CA, AZ, and even foreign countries Under this arrangement, users were able to solve more complex problems that otherwise would have required the use of supercomputers Intel saved more than $500 million between 1992 and 2001 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 60
 B 2 B P 2 P Applications § With P 2 P, people can share information, but they are not required to send it to an unknown server, as they do when using a regular exchange § Some companies fear that exchanges make it possible for unauthorized personnel to gain access to corporate data files § P 2 P applications enable such companies to store documents in-house instead of on an unknown, and possibly unsecured, server § P 2 P networks allow companies to avoid the fees charged by B 2 B exchanges and reduce the complexity and expense of the networking 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 61
B 2 B P 2 P Applications § With P 2 P, people can share information, but they are not required to send it to an unknown server, as they do when using a regular exchange § Some companies fear that exchanges make it possible for unauthorized personnel to gain access to corporate data files § P 2 P applications enable such companies to store documents in-house instead of on an unknown, and possibly unsecured, server § P 2 P networks allow companies to avoid the fees charged by B 2 B exchanges and reduce the complexity and expense of the networking 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 61
 B 2 C P 2 P Applications § Marketing § Advertising § B 2 C payments 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 62
B 2 C P 2 P Applications § Marketing § Advertising § B 2 C payments 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 62
 Managerial Issues (I) 1. What are the e-government opportunities? l If an organization is doing business with the government, eventually some or all of it may be moved online, because governments are getting serious about going online 2. Are there e-learning and e-training opportunities? l l l Adding an e-learning component to a company’s activities is useful when employees need to retrain themselves and keep up with new knowledge Organization can cut retraining cost and shorten the learning period Companies can help customers train their employees in new products 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 63
Managerial Issues (I) 1. What are the e-government opportunities? l If an organization is doing business with the government, eventually some or all of it may be moved online, because governments are getting serious about going online 2. Are there e-learning and e-training opportunities? l l l Adding an e-learning component to a company’s activities is useful when employees need to retrain themselves and keep up with new knowledge Organization can cut retraining cost and shorten the learning period Companies can help customers train their employees in new products 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 63
 Managerial Issues (II) 3. Can we capitalize on C 2 C? l l Businesses cannot capture much C 2 C activity unless they are providers of some innovative services, such as paypal Business may consider using P 2 P to support C 2 C 4. How well are we managing our knowledge? l l Connecting e-commerce initiatives with a KM program, if one exists, is a very viable strategy The knowledge is needed for the operation and implementation of EC projects as well as for e-training 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 64
Managerial Issues (II) 3. Can we capitalize on C 2 C? l l Businesses cannot capture much C 2 C activity unless they are providers of some innovative services, such as paypal Business may consider using P 2 P to support C 2 C 4. How well are we managing our knowledge? l l Connecting e-commerce initiatives with a KM program, if one exists, is a very viable strategy The knowledge is needed for the operation and implementation of EC projects as well as for e-training 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 64
 Managerial Issues (III) 5. Are there P 2 P applications? l l l Watch for new developments in P 2 P tools and applications Some experts say a major revolution is coming for faster and cheaper online communication and collaboration This technology could be very helpful in B 2 B applications 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 65
Managerial Issues (III) 5. Are there P 2 P applications? l l l Watch for new developments in P 2 P tools and applications Some experts say a major revolution is coming for faster and cheaper online communication and collaboration This technology could be very helpful in B 2 B applications 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 65
 Summary (I) 1. E-government to citizens, businesses, and others l l l Government worldwide are providing a variety of services to citizens over the Internet Such initiatives increase citizens’ satisfaction and decrease government expense Government are active in electronically trading with business; EC is done within and between governments 2. Other e-government activities l Notable applications are e-procurement using reverse auctions, e-payments to and from citizens and businesses, auctioning of surplus goods, and electronic travel management systems 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 66
Summary (I) 1. E-government to citizens, businesses, and others l l l Government worldwide are providing a variety of services to citizens over the Internet Such initiatives increase citizens’ satisfaction and decrease government expense Government are active in electronically trading with business; EC is done within and between governments 2. Other e-government activities l Notable applications are e-procurement using reverse auctions, e-payments to and from citizens and businesses, auctioning of surplus goods, and electronic travel management systems 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 66
 Summary (II) 3. Online publishing and e-books l l Online publishing of newspapers, magazines, books, software, music, games, movies, and other entertainment is growing rapidly Of special interest is blogging, the publishing of newsletter-like commentaries by individuals on the Internet 4. E-learning and virtual universities l l l E-learning is the delivery of educational content via electronic media, including the Internet and Intranet Degree programs, lifelong learning topics, and corporate training are delivered by thousands of organizations worldwide A growing area is distance learning via online university offerings; some are virtual, others are delivered both online and off-line 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 67
Summary (II) 3. Online publishing and e-books l l Online publishing of newspapers, magazines, books, software, music, games, movies, and other entertainment is growing rapidly Of special interest is blogging, the publishing of newsletter-like commentaries by individuals on the Internet 4. E-learning and virtual universities l l l E-learning is the delivery of educational content via electronic media, including the Internet and Intranet Degree programs, lifelong learning topics, and corporate training are delivered by thousands of organizations worldwide A growing area is distance learning via online university offerings; some are virtual, others are delivered both online and off-line 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 67
 Summary (III) 5. Knowledge management and dissemination as an e-business. l l Knowledge has been recognized as an important organizational assets; it is critical for many e-commerce tasks It needs to be properly captured, stored, managed, and shared 6. C 2 C activities. l l C 2 C consists of consumers conducting e-commerce with other consumers, mainly in auctions Buying and selling of goods and personal services can also take place through the use of online classified ads, exchanges, and special services 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 68
Summary (III) 5. Knowledge management and dissemination as an e-business. l l Knowledge has been recognized as an important organizational assets; it is critical for many e-commerce tasks It needs to be properly captured, stored, managed, and shared 6. C 2 C activities. l l C 2 C consists of consumers conducting e-commerce with other consumers, mainly in auctions Buying and selling of goods and personal services can also take place through the use of online classified ads, exchanges, and special services 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 68
 Summary (IV) 7. Peer-to-peer technology and applications l l P 2 P technology enables direct communication among client computers; it enables file sharing among individuals and between organizations P 2 P technology has tremendous potential for increased effectiveness and reduced cost of communication, information processing, and collaboration 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 69
Summary (IV) 7. Peer-to-peer technology and applications l l P 2 P technology enables direct communication among client computers; it enables file sharing among individuals and between organizations P 2 P technology has tremendous potential for increased effectiveness and reduced cost of communication, information processing, and collaboration 淡江大學資管系所侯永昌 69


