5bd4dcdac713882b51b7a37c182f1549.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Chapter 5 Information Systems in Business: Software Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 1

Learning Objectives • Explain why professionals must keep abreast of software developments • Enumerate the different generations of programming languages and explain how they differ • Explain the difference between application software and system software Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 2

Learning Objectives (Cont. ) • Compare the strengths and weaknesses of tailored software versus off-the shelf software • Cite the latest major developments in application and system software • List characteristics that are important in evaluating packaged software applications for business use Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 3

Software: Instructions to the Computer • A computer program is a series of instructions to a computer to execute any and all processes • Computers only “understand” instructions consisting of electrical signals alternating between two states Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 4

Software: Instructions to the Computer (Cont. ) • Application software enables users to complete a particular task, such as word processing • System software enables application software to run on a computer and manages the interaction between hardware devices Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 5

Programming Languages • Abbreviated forms of instructions that translate into machine language • New programming languages make programming easier for people who are not necessarily hardware experts Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 6
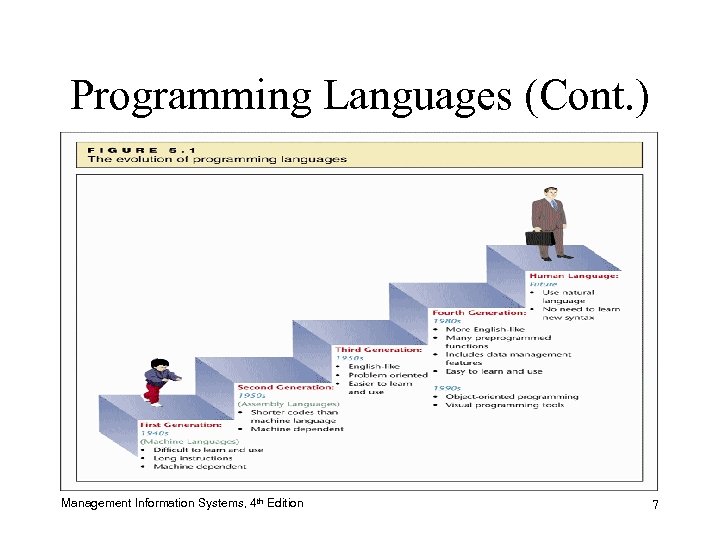
Programming Languages (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 7
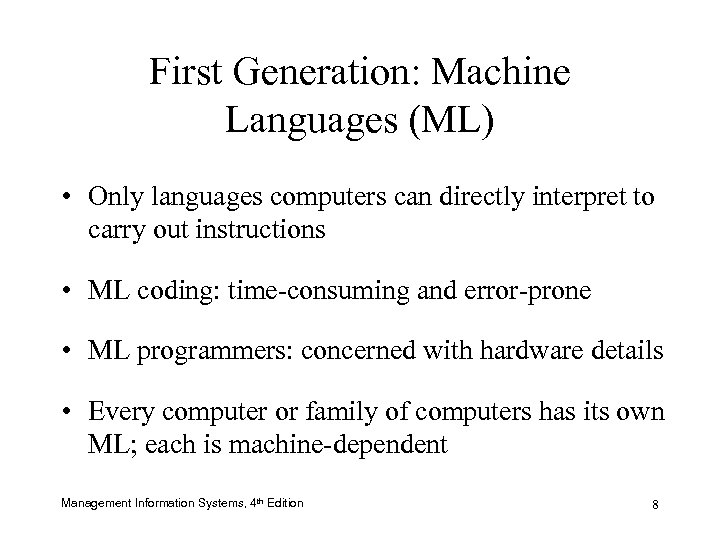
First Generation: Machine Languages (ML) • Only languages computers can directly interpret to carry out instructions • ML coding: time-consuming and error-prone • ML programmers: concerned with hardware details • Every computer or family of computers has its own ML; each is machine-dependent Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 8
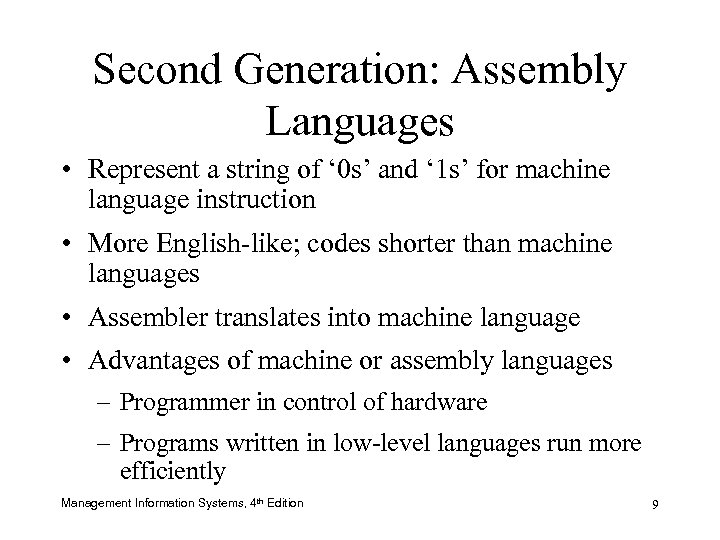
Second Generation: Assembly Languages • Represent a string of ‘ 0 s’ and ‘ 1 s’ for machine language instruction • More English-like; codes shorter than machine languages • Assembler translates into machine language • Advantages of machine or assembly languages – Programmer in control of hardware – Programs written in low-level languages run more efficiently Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 9

Third Generation: Procedural Languages • Third-generation (procedural) languages are more English-like than assembly languages • Programmers focus on the procedure of the application problem at hand • Some languages are standardized or portable • Relatively easy to learn, write, and debug • FORTRAN, COBOL, BASIC Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 10

Fourth Generation Languages (4 GL) • 4 GLs are more English-like than procedural languages • Programmer only has to select an action without having to specify the action’s formula or procedure • Easy to learn and use; shorter application development time • Power. Builder, FOCUS, NOMAD, and RAMIS Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 11
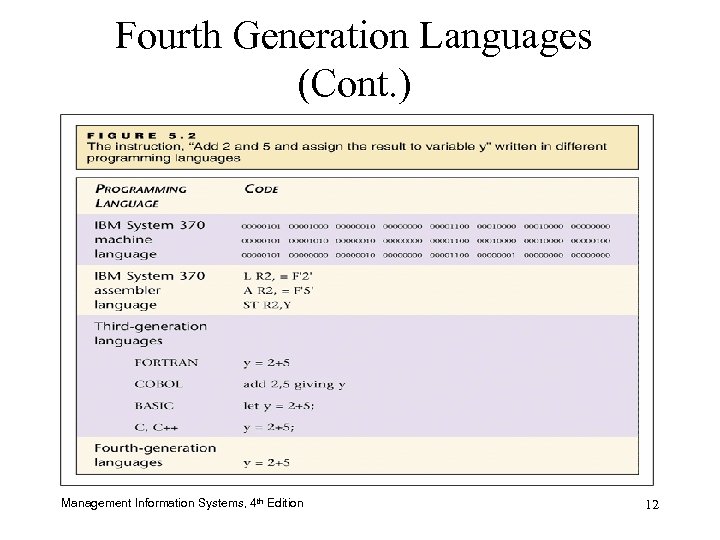
Fourth Generation Languages (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 12
Visual Programming • Languages that let programmers create field windows, scroll-down menus, click buttons, etc. , by choosing from a palette • Appropriate code written automatically • Accelerates work • Microsoft’s Visual Basic Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 13
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) • Emphasis on the objects involved in the task, not on the procedure • An object encapsulates a data set with the code that is used to operate on it • Standardized programming modules can be reused • Applications can be rapidly developed with appropriate objects from an object library Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 14

Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 15

The object EMPLOYEE Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 16
Application Software vs. System Software • Application: – Program developed to address a specific business need; software for development of such programs • System: – Programs designed to carry out general routine operations, such as loading, copying, or deleting a file Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 17
Programming Languages (Cont. ) – Levels of Programming Languages: Pluses and Minuses – Language Translation: Compilers and Interpreters • Source code • Object code • Compiler • Interpreter Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 18
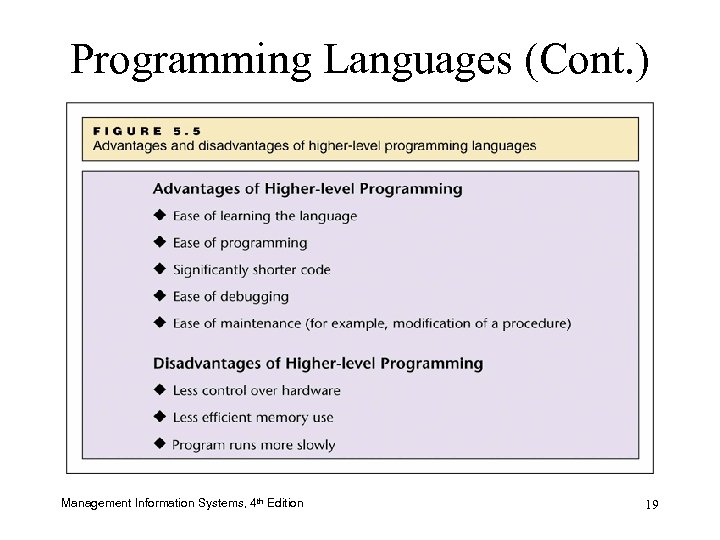
Programming Languages (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 19
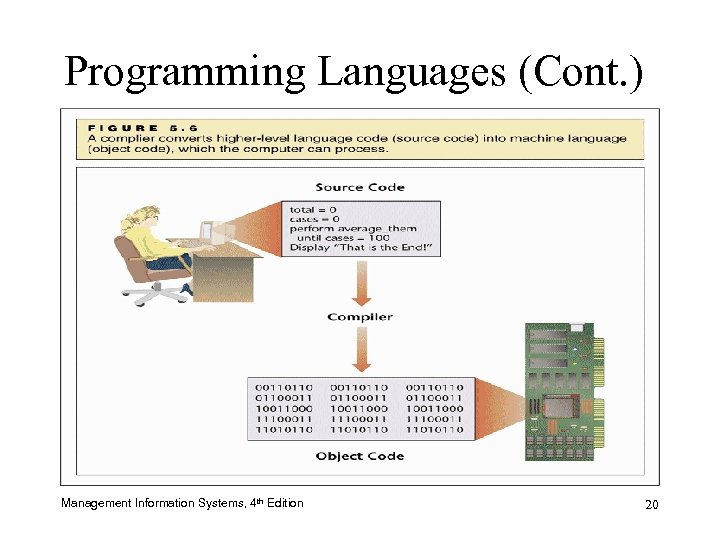
Programming Languages (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 20

Bugs • Errors in a program to be eliminated before it runs smoothly • Occur when a certain operation cannot be carried out • Logic errors are most difficult to spot Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 21

Application Software • Application-specific programs – Programs designed to perform specific jobs • General-purpose programs – Usable for different purposes Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 22

Custom-Designed Application Advantages • Meeting the organization’s needs exactly • In-house developers are sensitive to the organizational culture Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 23

Custom-Designed Application Disadvantages • High cost • Production schedule subject to long delays • Incompatible with other organizations’ systems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 24
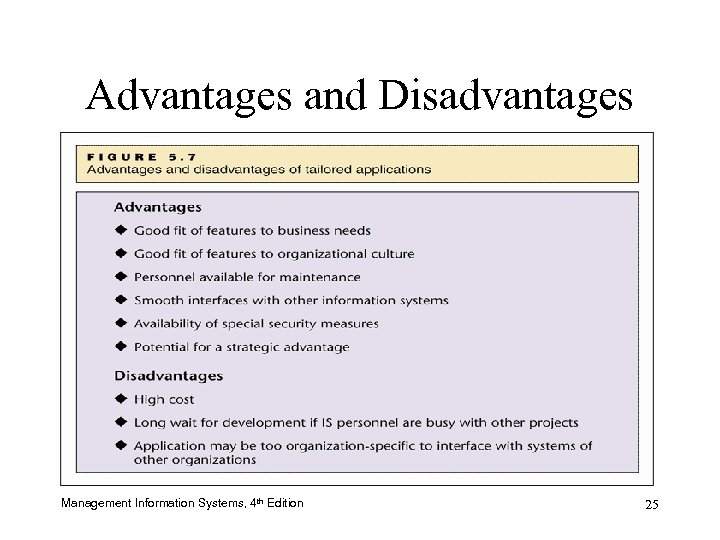
Advantages and Disadvantages Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 25

Packaged Software • Advantages: – Low cost – High quality – Vendor support – Immediate availability • Often tested at user sites (alpha sites and beta sites) before the final version is released Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 26
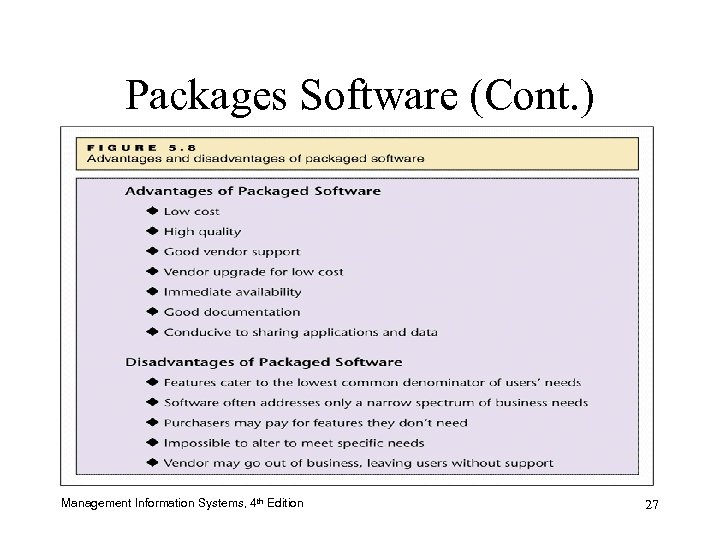
Packages Software (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 27
Packaged Software (Cont. ) • Word processors • Electronic spreadsheets • Database management systems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 28
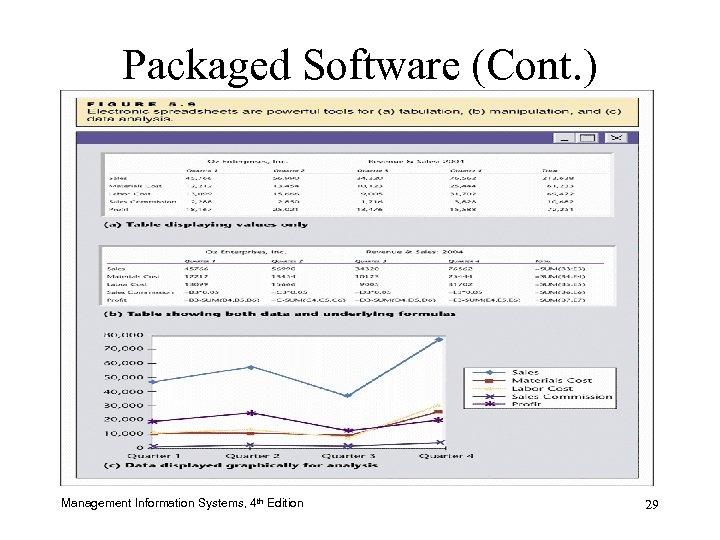
Packaged Software (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 29

Multimedia • Can handle many different types of data such as text, voice, and image • Powerful means of communicating • Uses include education, training, research, and business Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 30

Virtual Reality (VR) • Mimics sensory reality • Some sophisticated VR software includes use of goggles, gloves, earphones, and a moving base • Business use of VR is expected to grow dramatically for design and testing of new products, and for marketing Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 31

System Software • Manages computer resources and performs routine tasks not specific to any application – Copying and pasting sections and files – Printing documents – Allocating memory • Developed to partner with application software Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 32

Operating Systems (O/S) • Most important system software – Developed for a certain microprocessor or microprocessors – Addresses technical details such as registers and RAM addresses – Plays the role of “traffic cop” or the “boss” of computer resources Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 33
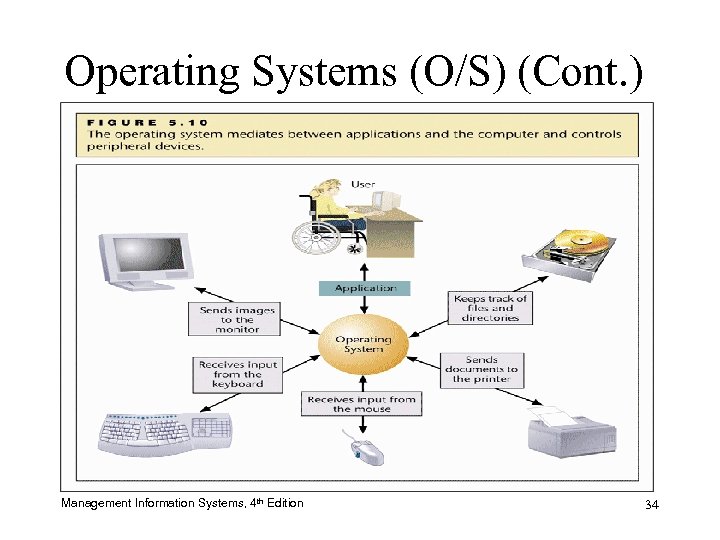
Operating Systems (O/S) (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 34
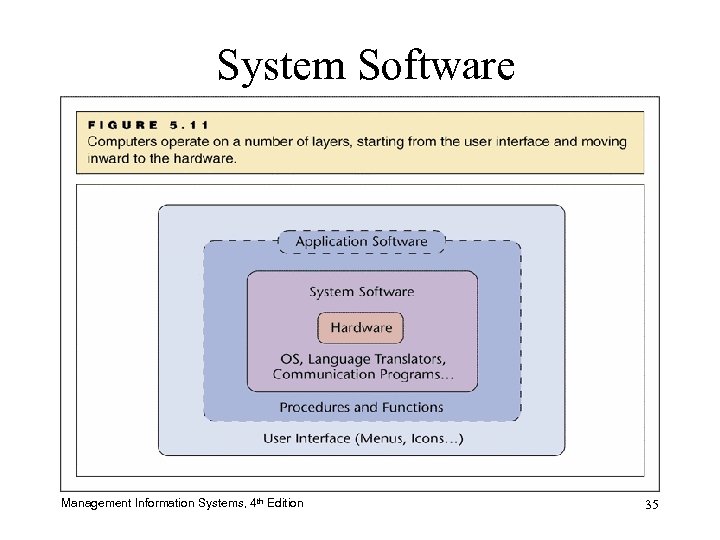
System Software Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 35

Operating System Functions • Systems Management • User Interface • Memory Allocation • Multitasking, Multiprogramming, and Multiprocessing • Times and Statistics • Increasing Services from O/Ss Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 36
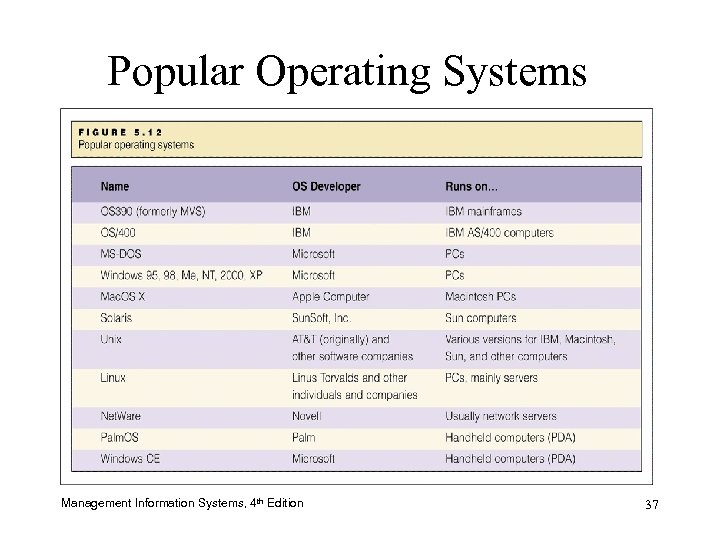
Popular Operating Systems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 37

Data Communication Programs • Controls and supports data communication activities in a network – Setting up rules that govern transmission and reception of data – Connecting and disconnecting communication links – Assigning priorities among terminals in a network – Detecting and correcting transmission errors Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 38

Linux and the Open Source Revolution • Proprietary software: source code of the software public • Open source software: source code can be obtained free of charge • Contains fewer bugs because thousands of independent programmers review the code Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 39
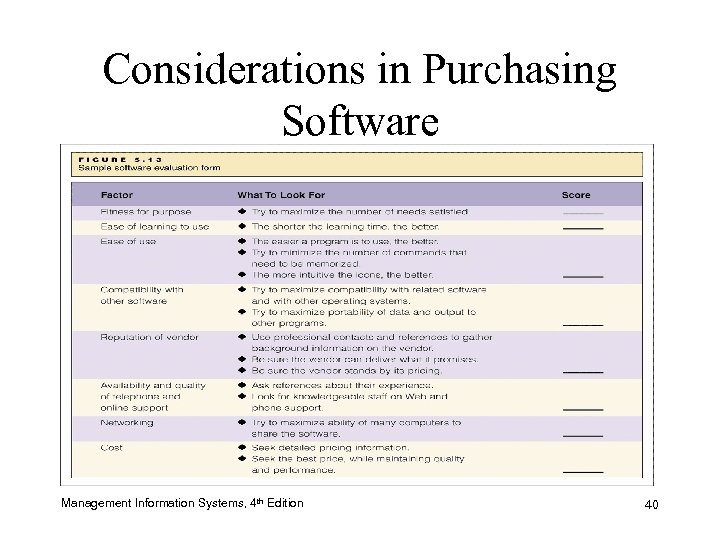
Considerations in Purchasing Software Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 40
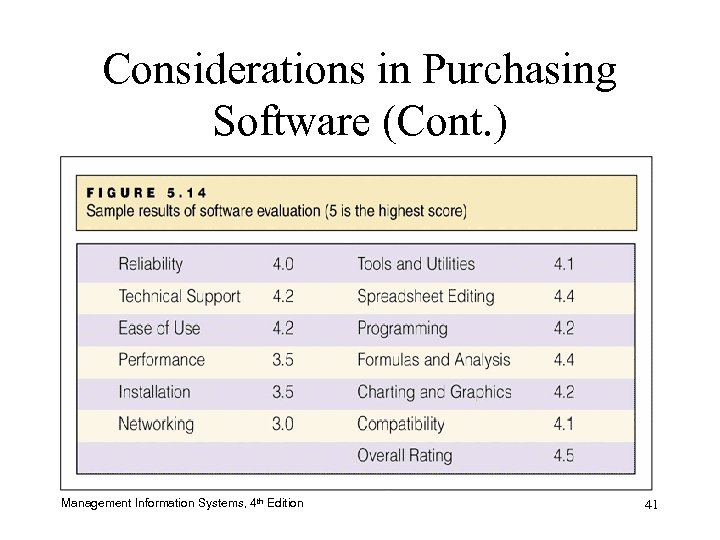
Considerations in Purchasing Software (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 41

Summary • Software developments and the impact on business • Application software versus operating system software • Tailored software versus off-the-shelf software • Major developments in application and system software • Evaluation of package software Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 42
5bd4dcdac713882b51b7a37c182f1549.ppt