76c5c3213db17d0a8f7ea6cead8bdca3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Chapter 5 Designing Services 5 -1
Chapter 5 Designing Services 5 -1
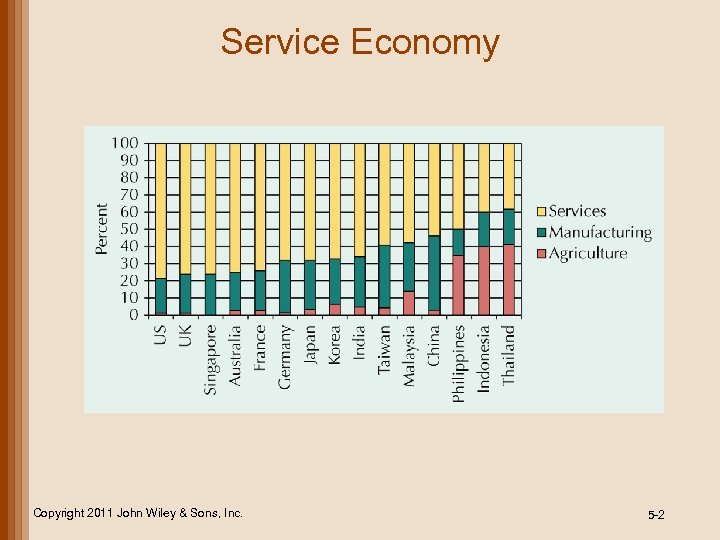 Service Economy Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -2
Service Economy Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -2
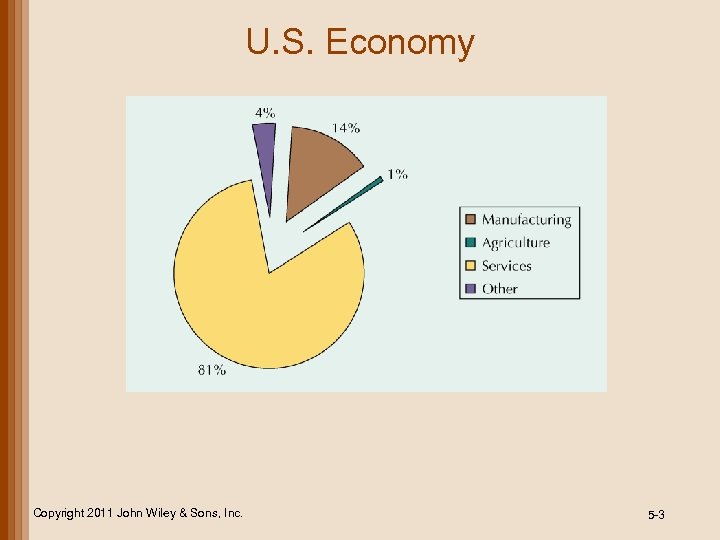 U. S. Economy Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -3
U. S. Economy Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -3
 Characteristics of Services • Services – Acts, performances or relationships that produce time, form or psychological utilities • Goods – tangible objects • Facilitating services – accompany almost all purchases of goods • Facilitating goods – accompany almost all service purchases Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -4
Characteristics of Services • Services – Acts, performances or relationships that produce time, form or psychological utilities • Goods – tangible objects • Facilitating services – accompany almost all purchases of goods • Facilitating goods – accompany almost all service purchases Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -4
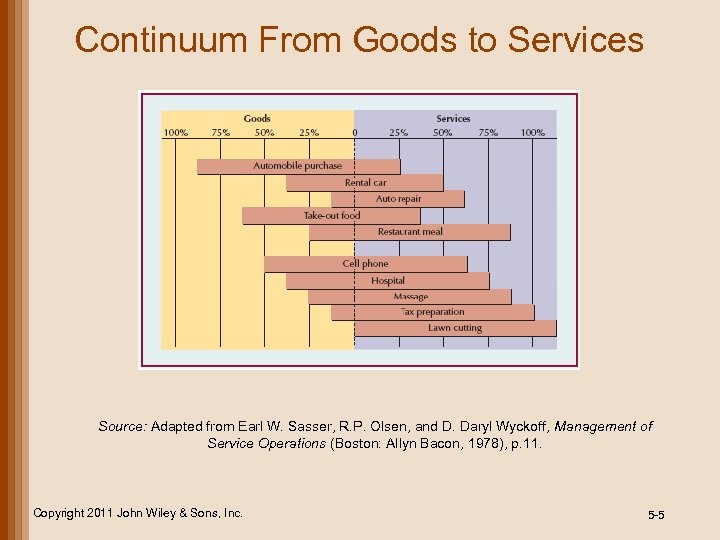 Continuum From Goods to Services Source: Adapted from Earl W. Sasser, R. P. Olsen, and D. Daryl Wyckoff, Management of Service Operations (Boston: Allyn Bacon, 1978), p. 11. Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -5
Continuum From Goods to Services Source: Adapted from Earl W. Sasser, R. P. Olsen, and D. Daryl Wyckoff, Management of Service Operations (Boston: Allyn Bacon, 1978), p. 11. Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -5
 Characteristics of Services • • Service are intangible Service output is variable Services have higher customer contact Services are perishable Service and service delivery are inseparable Services are consumed more often than products Services can be easily emulated Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -6
Characteristics of Services • • Service are intangible Service output is variable Services have higher customer contact Services are perishable Service and service delivery are inseparable Services are consumed more often than products Services can be easily emulated Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -6
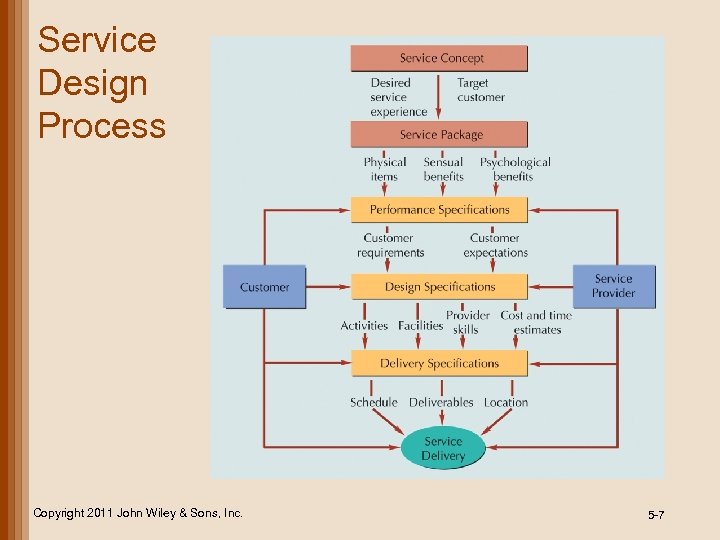 Service Design Process Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -7
Service Design Process Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -7
 Service Design Process • Service concept – purpose of a service; it defines target market and customer experience • Service package – mixture of physical items, sensual benefits, and psychological benefits • Service specifications – performance specifications – design specifications – delivery specifications Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -8
Service Design Process • Service concept – purpose of a service; it defines target market and customer experience • Service package – mixture of physical items, sensual benefits, and psychological benefits • Service specifications – performance specifications – design specifications – delivery specifications Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -8
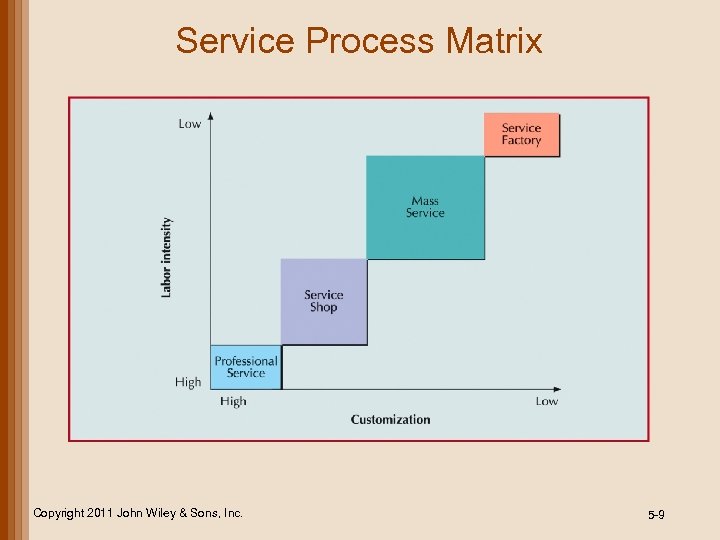 Service Process Matrix Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -9
Service Process Matrix Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -9
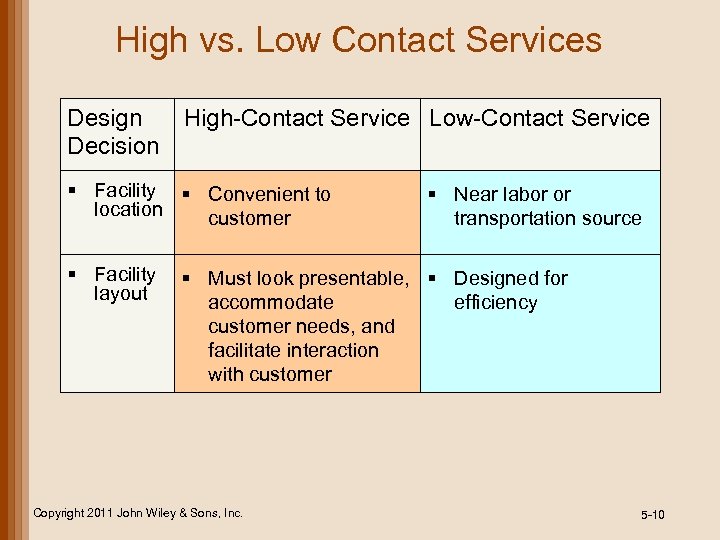 High vs. Low Contact Services Design Decision High-Contact Service Low-Contact Service § Facility § Convenient to location customer § Facility layout § Near labor or transportation source § Must look presentable, § Designed for accommodate efficiency customer needs, and facilitate interaction with customer Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -10
High vs. Low Contact Services Design Decision High-Contact Service Low-Contact Service § Facility § Convenient to location customer § Facility layout § Near labor or transportation source § Must look presentable, § Designed for accommodate efficiency customer needs, and facilitate interaction with customer Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -10
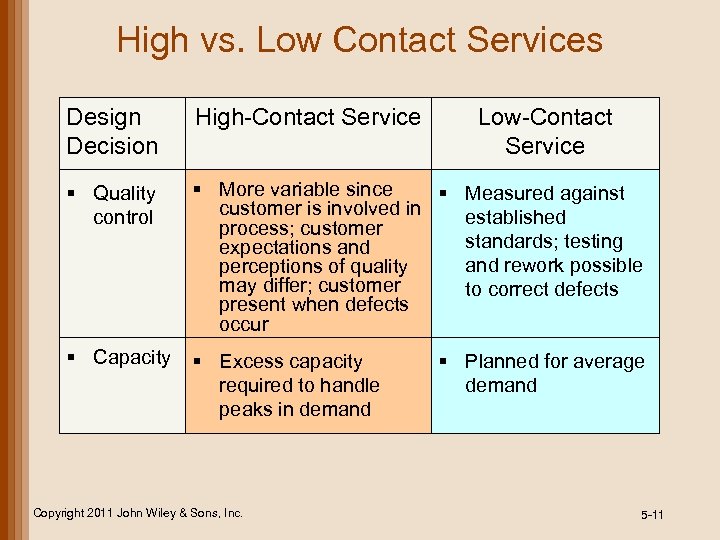 High vs. Low Contact Services Design Decision High-Contact Service § Quality control § More variable since § Measured against customer is involved in established process; customer standards; testing expectations and rework possible perceptions of quality may differ; customer to correct defects present when defects occur § Capacity § Excess capacity required to handle peaks in demand Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Low-Contact Service § Planned for average demand 5 -11
High vs. Low Contact Services Design Decision High-Contact Service § Quality control § More variable since § Measured against customer is involved in established process; customer standards; testing expectations and rework possible perceptions of quality may differ; customer to correct defects present when defects occur § Capacity § Excess capacity required to handle peaks in demand Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Low-Contact Service § Planned for average demand 5 -11
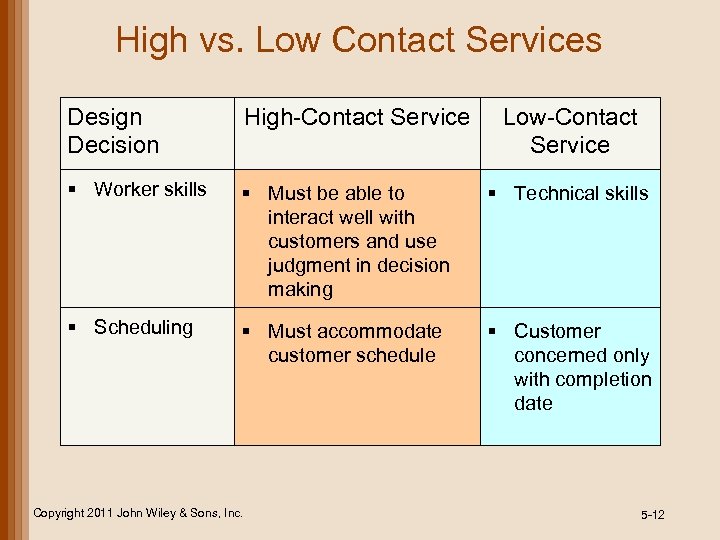 High vs. Low Contact Services Design Decision High-Contact Service § Worker skills § Must be able to interact well with customers and use judgment in decision making § Technical skills § Scheduling § Must accommodate customer schedule § Customer concerned only with completion date Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Low-Contact Service 5 -12
High vs. Low Contact Services Design Decision High-Contact Service § Worker skills § Must be able to interact well with customers and use judgment in decision making § Technical skills § Scheduling § Must accommodate customer schedule § Customer concerned only with completion date Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Low-Contact Service 5 -12
 Tools for Service Design • Service blueprinting • • line of influence line of interaction line of visibility line of support • Front-office/Backoffice activities Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. • Servicescapes • space and function • ambient conditions • signs, symbols, and artifacts • Quantitative techniques 5 -13
Tools for Service Design • Service blueprinting • • line of influence line of interaction line of visibility line of support • Front-office/Backoffice activities Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. • Servicescapes • space and function • ambient conditions • signs, symbols, and artifacts • Quantitative techniques 5 -13
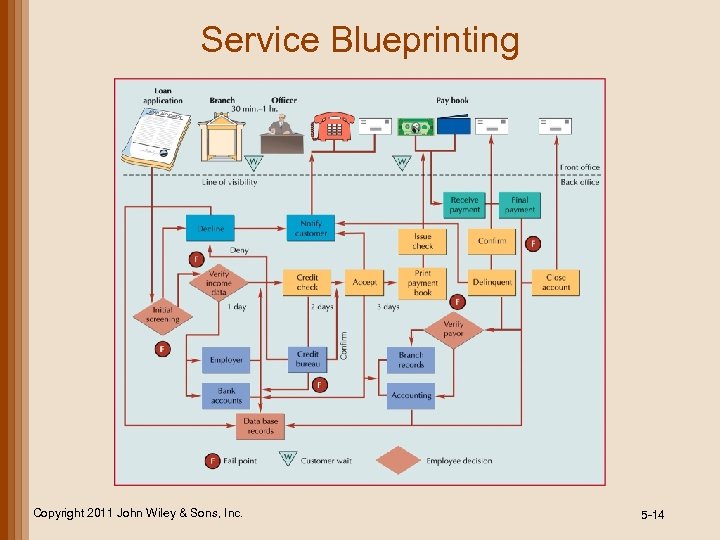 Service Blueprinting Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -14
Service Blueprinting Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -14
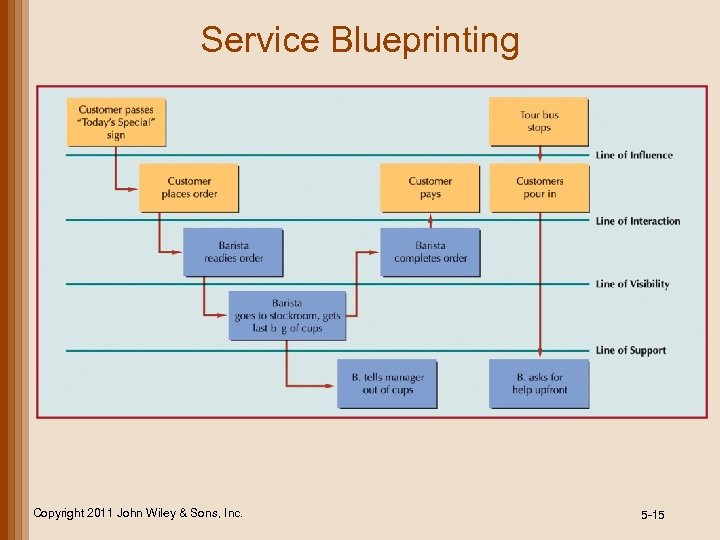 Service Blueprinting Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -15
Service Blueprinting Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -15
 Tools for Service Design • Service blueprinting • Front-office/ – Courtesy – Responsiveness – Usability • Back-office activities – Efficiency – Productivity – Standardization Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. • Servicescapes • space and function • ambient conditions • signs, symbols, and artifacts • Quantitative techniques 5 -16
Tools for Service Design • Service blueprinting • Front-office/ – Courtesy – Responsiveness – Usability • Back-office activities – Efficiency – Productivity – Standardization Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. • Servicescapes • space and function • ambient conditions • signs, symbols, and artifacts • Quantitative techniques 5 -16
 Elements of Waiting Line Analysis • Arrival rate (λ) • frequency at which customers arrive at a waiting line according to a probability distribution, usually Poisson • Service rate (μ) • time required to serve a customer, usually described by negative exponential distribution • Service rate must be higher than arrival rate (λ < μ) • Queue discipline • order in which customers are served • Infinite queue • can be of any length; length of a finite queue is limited Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -17
Elements of Waiting Line Analysis • Arrival rate (λ) • frequency at which customers arrive at a waiting line according to a probability distribution, usually Poisson • Service rate (μ) • time required to serve a customer, usually described by negative exponential distribution • Service rate must be higher than arrival rate (λ < μ) • Queue discipline • order in which customers are served • Infinite queue • can be of any length; length of a finite queue is limited Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -17
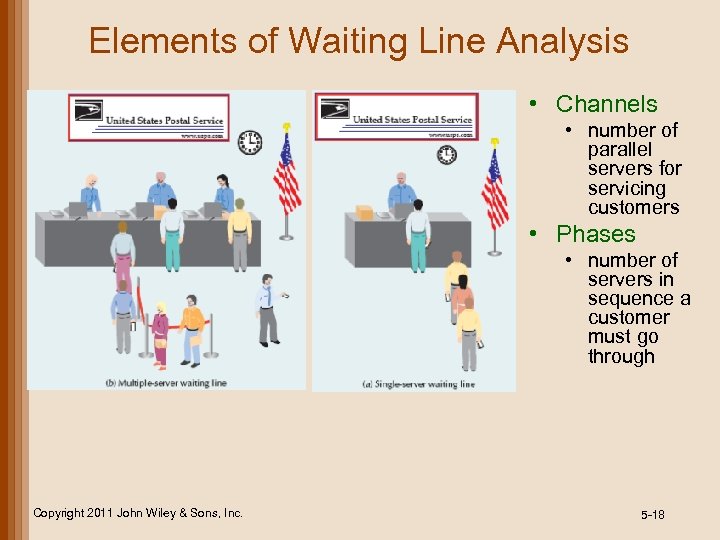 Elements of Waiting Line Analysis • Channels • number of parallel servers for servicing customers • Phases • number of servers in sequence a customer must go through Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -18
Elements of Waiting Line Analysis • Channels • number of parallel servers for servicing customers • Phases • number of servers in sequence a customer must go through Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -18
 Operating Characteristics • Operating characteristics are assumed to approach a steady state Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -19
Operating Characteristics • Operating characteristics are assumed to approach a steady state Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -19
 Psychology of Waiting • Cartoon film characters • magazines and newspapers • televisions • mirrors • express lanes for few purchases in super markets Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -20
Psychology of Waiting • Cartoon film characters • magazines and newspapers • televisions • mirrors • express lanes for few purchases in super markets Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -20
 Waiting Line Models Basic Single-Server Model • Assumptions • Poisson arrival rate • exponential service times • first-come, first-served queue discipline • infinite queue length • infinite calling population Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. • Computations • λ = mean arrival rate • μ = mean service rate • n = number of customers in line 5 -21
Waiting Line Models Basic Single-Server Model • Assumptions • Poisson arrival rate • exponential service times • first-come, first-served queue discipline • infinite queue length • infinite calling population Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. • Computations • λ = mean arrival rate • μ = mean service rate • n = number of customers in line 5 -21
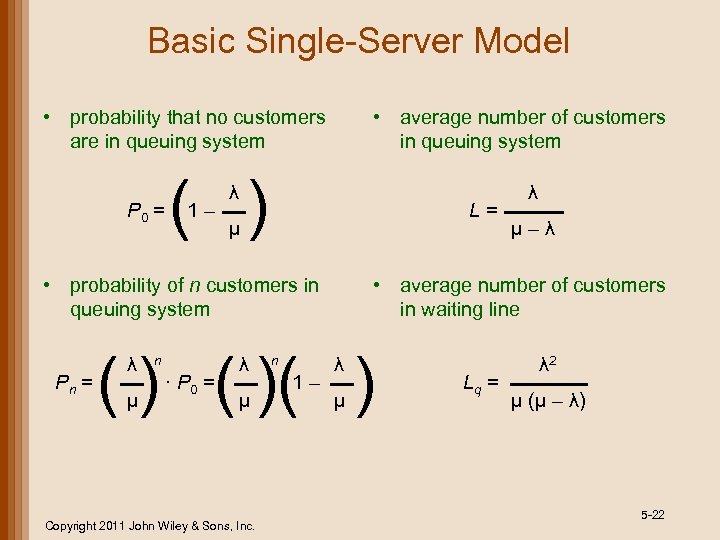 Basic Single-Server Model • average number of customers in queuing system • probability that no customers are in queuing system P 0 = ( ) 1– λ L= μ Pn = ( )( ) μ n ∙ P 0 = λ μ Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. n 1– μ–λ • average number of customers in waiting line • probability of n customers in queuing system λ λ λ μ Lq = λ 2 μ (μ – λ) 5 -22
Basic Single-Server Model • average number of customers in queuing system • probability that no customers are in queuing system P 0 = ( ) 1– λ L= μ Pn = ( )( ) μ n ∙ P 0 = λ μ Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. n 1– μ–λ • average number of customers in waiting line • probability of n customers in queuing system λ λ λ μ Lq = λ 2 μ (μ – λ) 5 -22
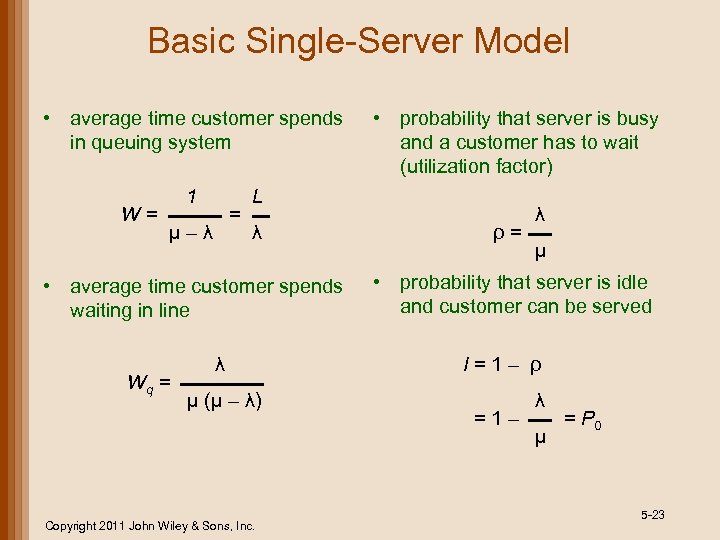 Basic Single-Server Model • average time customer spends in queuing system W= 1 = μ–λ L λ • average time customer spends waiting in line Wq = • probability that server is busy and a customer has to wait (utilization factor) λ μ (μ – λ) Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ρ= λ μ • probability that server is idle and customer can be served I=1– ρ =1– λ μ = P 0 5 -23
Basic Single-Server Model • average time customer spends in queuing system W= 1 = μ–λ L λ • average time customer spends waiting in line Wq = • probability that server is busy and a customer has to wait (utilization factor) λ μ (μ – λ) Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ρ= λ μ • probability that server is idle and customer can be served I=1– ρ =1– λ μ = P 0 5 -23
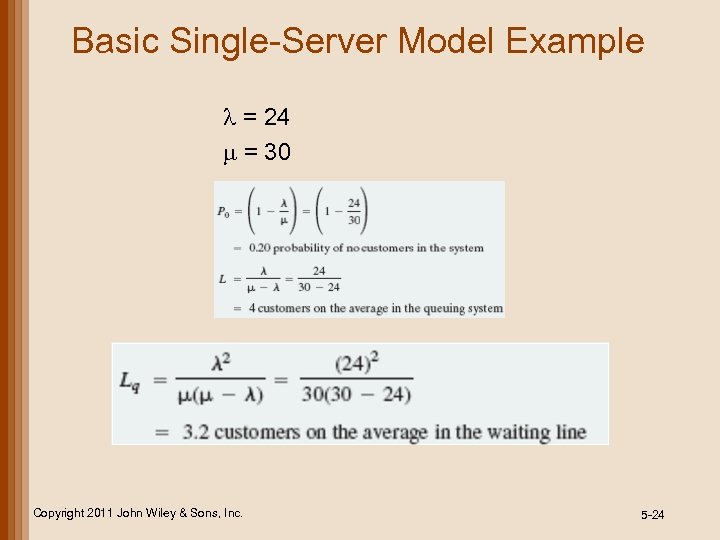 Basic Single-Server Model Example l = 24 m = 30 Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -24
Basic Single-Server Model Example l = 24 m = 30 Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -24
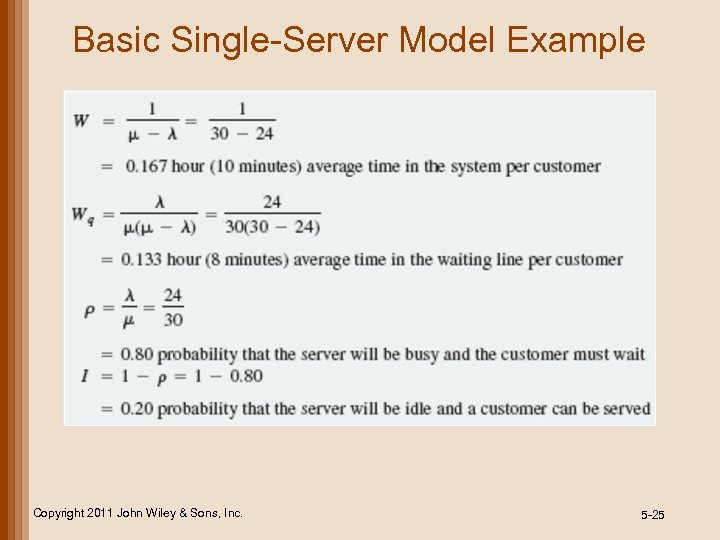 Basic Single-Server Model Example Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -25
Basic Single-Server Model Example Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -25
 Service Improvement Analysis • Waiting time (8 min. ) is too long • hire assistant for cashier? • increased service rate • hire another cashier? • reduced arrival rate • Is improved service worth the cost? Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -26
Service Improvement Analysis • Waiting time (8 min. ) is too long • hire assistant for cashier? • increased service rate • hire another cashier? • reduced arrival rate • Is improved service worth the cost? Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -26
 Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w. Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w 1 -27 5 -27
Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w. Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w 1 -27 5 -27
 This is not very good service. Although another window (server) might reduce waiting time, the service time in excess of 2 minutes is still too long; it should probably be less than 1 minute. Thus, the process of filling orders needs to be improved. 5 -28
This is not very good service. Although another window (server) might reduce waiting time, the service time in excess of 2 minutes is still too long; it should probably be less than 1 minute. Thus, the process of filling orders needs to be improved. 5 -28
 5 -29
5 -29
 Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w. Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w 1 -30 5 -30
Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w. Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. w 1 -30 5 -30
 5 -31
5 -31
 5 -32
5 -32
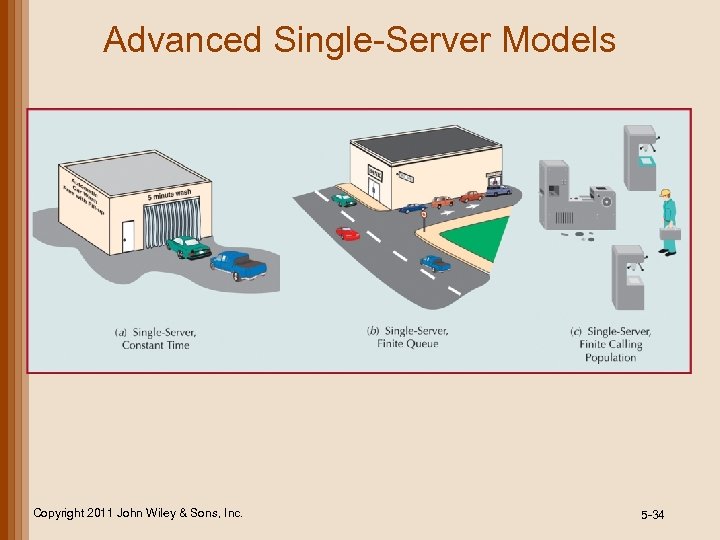
 Advanced Single-Server Models • Constant service times • occur most often when automated equipment or machinery performs service • Finite queue lengths • occur when there is a physical limitation to length of waiting line • Finite calling population • number of “customers” that can arrive is limited Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -33
Advanced Single-Server Models • Constant service times • occur most often when automated equipment or machinery performs service • Finite queue lengths • occur when there is a physical limitation to length of waiting line • Finite calling population • number of “customers” that can arrive is limited Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -33
 Advanced Single-Server Models Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -34
Advanced Single-Server Models Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -34
 Basic Multiple-Server Model • Single waiting line and service facility with several independent servers in parallel • Same assumptions as single-server model • sμ > λ • s = number of servers • servers must be able to serve customers faster than they arrive Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -35
Basic Multiple-Server Model • Single waiting line and service facility with several independent servers in parallel • Same assumptions as single-server model • sμ > λ • s = number of servers • servers must be able to serve customers faster than they arrive Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 -35
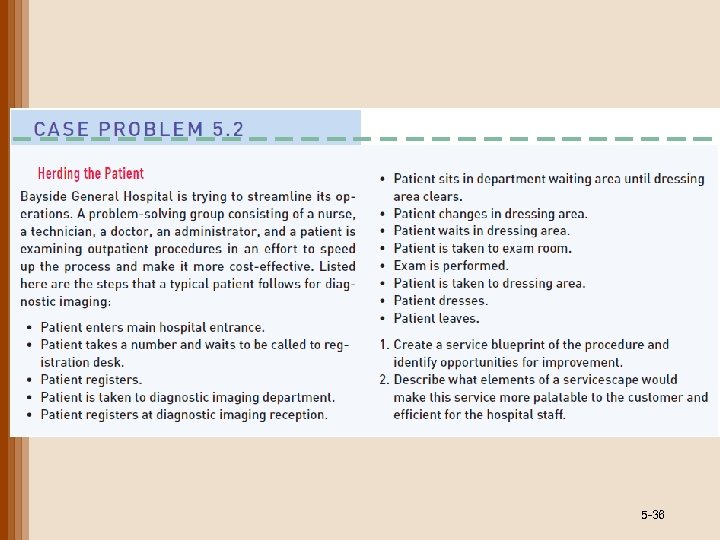 5 -36
5 -36


