101d2ea9d290b19ae7583877584b1a61.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Chapter 5 Demand: the benefit side of the market Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 1

The law of demand • The quantity demanded of a good or service declines as its price rises and increases as its price falls, ceteris paribus. Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 2

The law of demand • The benefit of an activity equals the highest price we’d be willing to pay to pursue it (i. e. the reservation price). • As the cost of an activity rises and exceeds the reservation price, less of the activity will be pursued. Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 3

The law of demand • The origins of demand – What determines ‘tastes’ or ‘preferences’? § Biology § Culture § Peer influences Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 4

The law of demand • Thinking as an economist – Needs vs. wants – Why have many Australian cities made watering restrictions permanent? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 5

Translating wants into demand • How should we allocate our incomes among the various goods and services that are available? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 6

Translating wants into demand • Measuring wants: The concept of utility – Utility § The satisfaction people derive from their consumption activities. – Assumption § People allocate their income to maximise their satisfaction or total utility. Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 7

Translating wants into demand • How much of a free good should we use? § The cost of waiting is worth it if people get free goods. § How many free sausages will an individual want to consume? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 8

Alice’s total utility from sausage consumption Sausage quantity (sausages/hour) Total utility (utils/hour) 0 0 1 50 2 90 3 120 4 140 5 150 6 140 How many sausages should Alice consume if the sausage is ‘free’? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 9
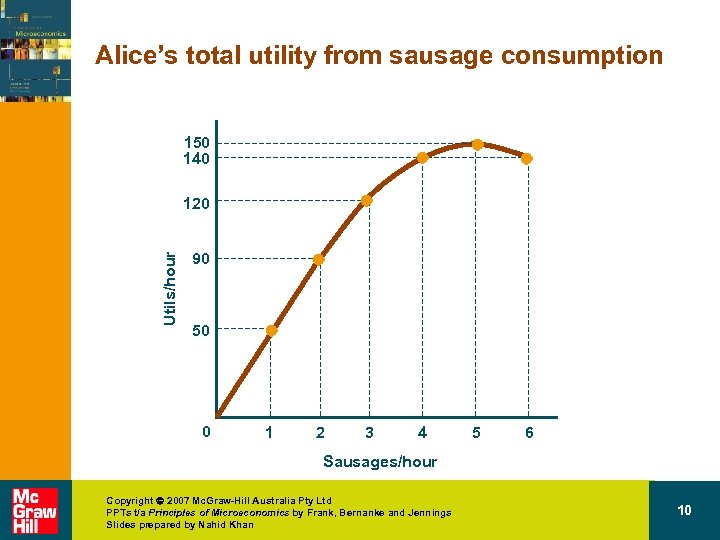
Alice’s total utility from sausage consumption 150 140 Utils/hour 120 90 50 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sausages/hour Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 10

Translating wants into demand • What should Alice do when she gets to the front of the line? • What do you think? – Is the time spent in the line relevant to how many sausages to order? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 11
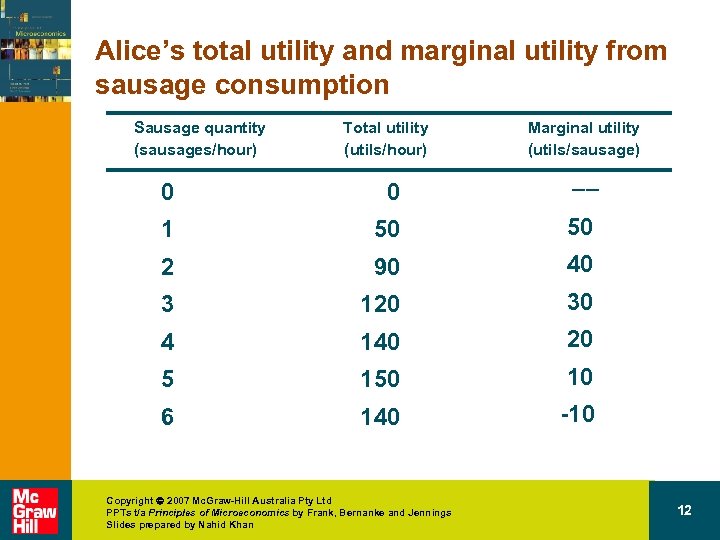
Alice’s total utility and marginal utility from sausage consumption Sausage quantity (sausages/hour) Total utility (utils/hour) Marginal utility (utils/sausage) __ 0 0 1 50 50 2 90 40 3 120 30 4 140 20 5 150 10 6 140 -10 Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 12
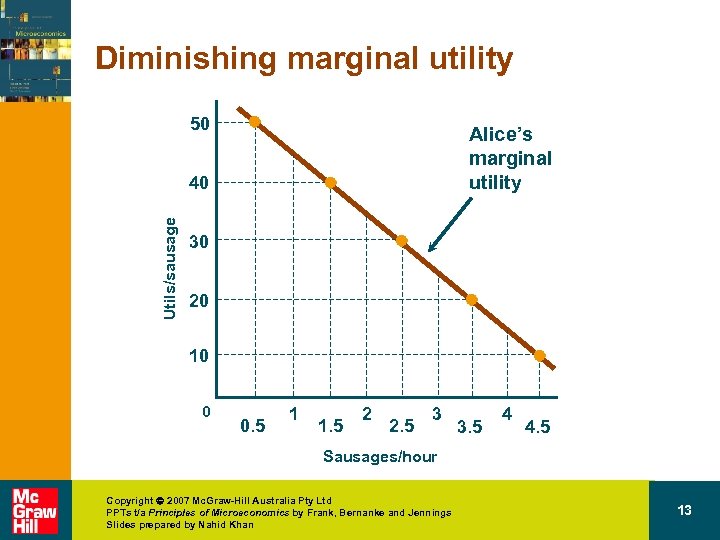
Diminishing marginal utility 50 Alice’s marginal utility Utils/sausage 40 30 20 10 0 0. 5 1 1. 5 2 2. 5 3 3. 5 4 4. 5 Sausages/hour Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 13

Translating wants into demand • The law of diminishing marginal utility – The tendency for the additional utility gained from consuming an additional unit of a good in a given period of time to diminish as consumption increases beyond some point. Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 14

Translating wants into demand • How should we allocate a fixed income between two goods? – Assume § § § Two goods: beef and venison sausages Price of venison sausages equals $2/kg Price of beef sausages equals $1/kg Alice’s budget = $400/yr Currently Alice is buying 200 kg of beef and 100 kg of venison sausages each year Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 15

Translating wants into demand • Question – Is Alice maximising her total utility? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 16
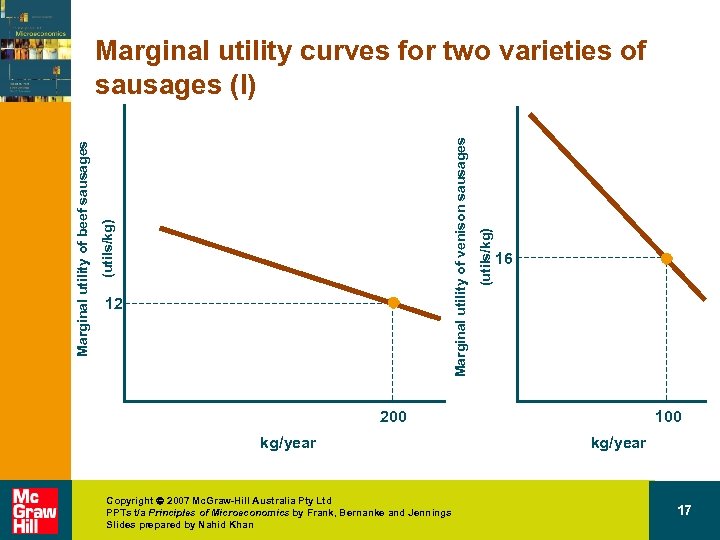
12 (utils/kg) Marginal utility of venison sausages (utils/kg) Marginal utility of beef sausages Marginal utility curves for two varieties of sausages (I) 16 200 kg/year Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 100 kg/year 17

Translating wants into demand • Marginal utility beef/kg – 12/1 = 12 utils/$ • Marginal utility venison/kg – 16/2 = 8 utils/$ Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 18

Translating wants into demand • If Alice spends $2 less on venison, utils will decline by 16. • If Alice spends $2 more on beef, utils will increase by 24. • So … – Alice should buy more beef. Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 19
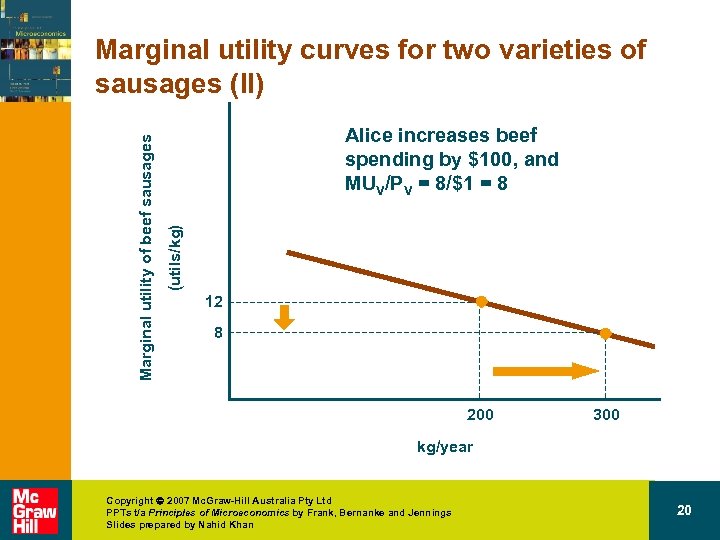
Alice increases beef spending by $100, and MUV/PV = 8/$1 = 8 (utils/kg) Marginal utility of beef sausages Marginal utility curves for two varieties of sausages (II) 12 8 200 300 kg/year Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 20
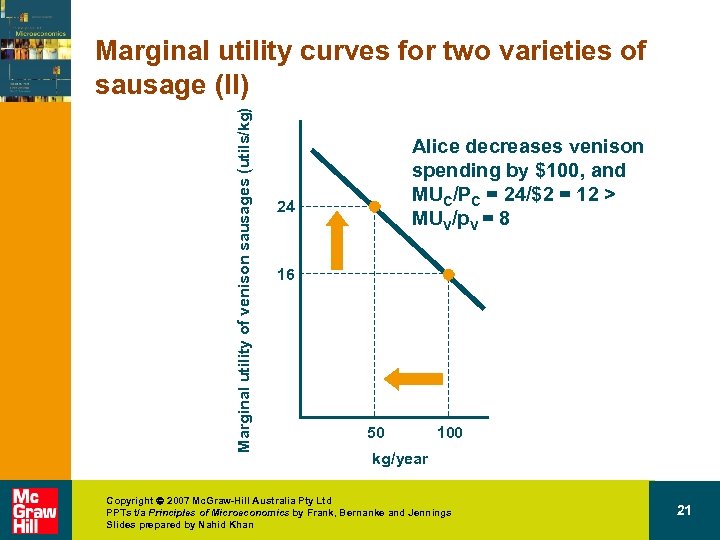
Marginal utility of venison sausages (utils/kg) Marginal utility curves for two varieties of sausage (II) Alice decreases venison spending by $100, and MUC/PC = 24/$2 = 12 > MUV/p. V = 8 24 16 50 100 kg/year Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 21
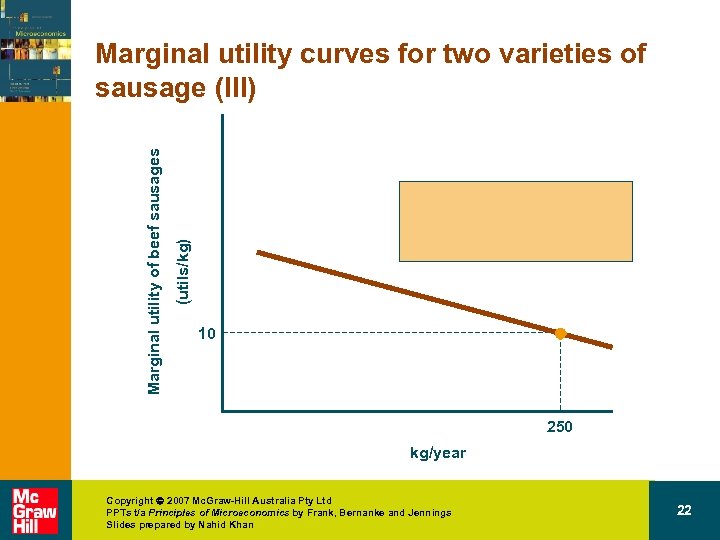
(utils/kg) Marginal utility of beef sausages Marginal utility curves for two varieties of sausage (III) 10 250 kg/year Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 22
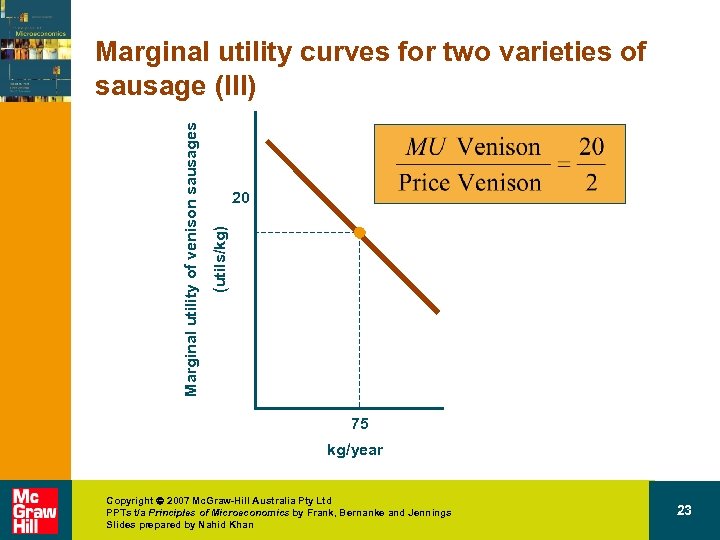
20 (utils/kg) Marginal utility of venison sausages Marginal utility curves for two varieties of sausage (III) 75 kg/year Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 23

Translating wants into demand • The rational spending rule – Spending should be allocated across goods so that the marginal utility per dollar is the same for each good. Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 24

Translating wants into demand • The rational spending rule – How is the rational spending rule related to the cost-benefit principle? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 25

Translating wants into demand • Income and substitution effects revisited – How should Alice respond to a reduction in the price of venison sausages? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 26
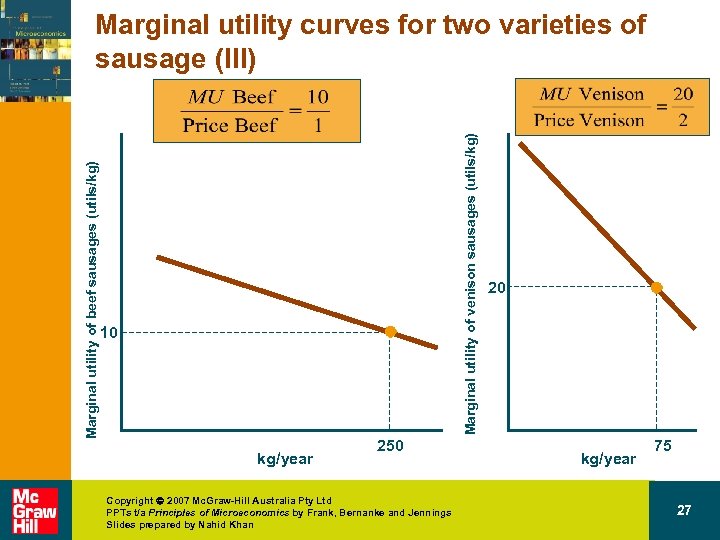
Marginal utility of venison sausages (utils/kg) Marginal utility of beef sausages (utils/kg) Marginal utility curves for two varieties of sausage (III) 10 kg/year 250 Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 20 kg/year 75 27

Translating wants into demand • Assume – Budget = $400 – PC = $2 & PV = $1 – QC = 75 & QV = 250 Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 28

Translating wants into demand • Assume – Price of venison falls to $1. Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 29

Applying the rational spending rule • Substitution at work • When the price of a good or service goes up, rational consumers generally turn to less expensive substitutes. • Thinking as an Economist – Why is the average size of a wealthy resident’s house in Seattle twice that of one in Manhattan? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 30

Applying the rational spending rule • Thinking as an economist – Why do new car sales continue to boom, despite rising real petrol prices? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 31

Applying the rational spending rule • Income differences at work • Thinking as an economist – How does strong growth in incomes help explain the steadily increasing proportion of Australian domestic expenditure spent on imported goods? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 32

Applying the rational spending rule • The importance of income differences – Why are waiting lines longer in poorer suburbs? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 33
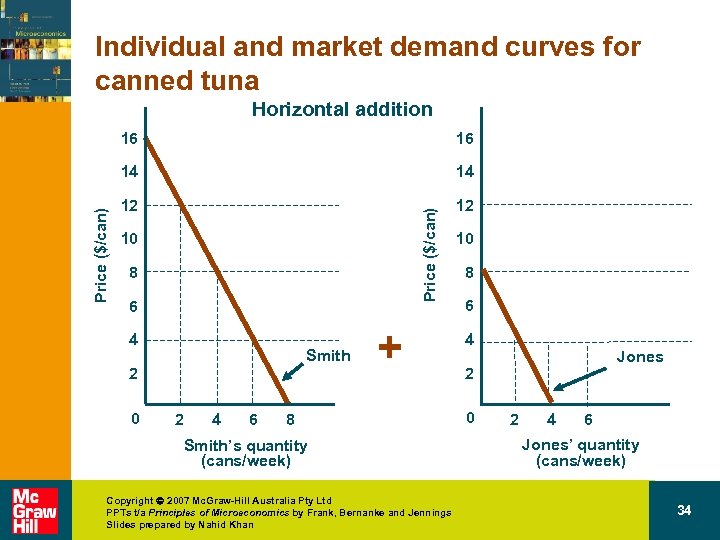
Individual and market demand curves for canned tuna Horizontal addition 14 12 12 Price ($/can) 16 14 Price ($/can) 16 10 8 6 4 Smith 2 0 2 4 6 + 8 Smith’s quantity (cans/week) Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 10 8 6 4 Jones 2 0 2 4 6 Jones’ quantity (cans/week) 34
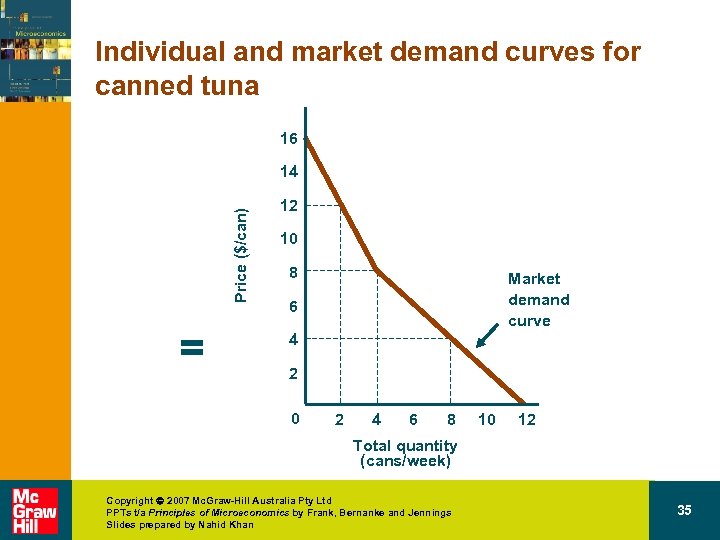
Individual and market demand curves for canned tuna 16 Price ($/can) 14 = 12 10 8 Market demand curve 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Total quantity (cans/week) Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 35
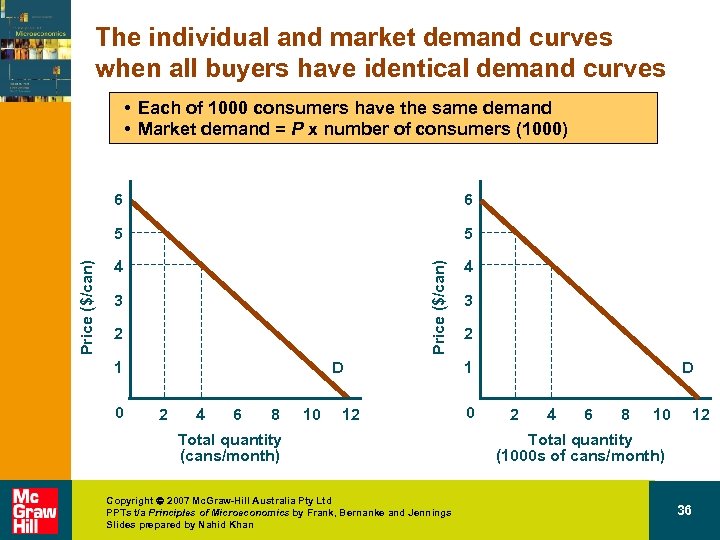
The individual and market demand curves when all buyers have identical demand curves • Each of 1000 consumers have the same demand • Market demand = P x number of consumers (1000) 5 4 4 Price ($/can) 6 5 Price ($/can) 6 3 2 1 0 D 2 4 6 8 10 12 Total quantity (cans/month) Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 3 2 1 0 D 2 4 6 8 10 12 Total quantity (1000 s of cans/month) 36

Demand consumer surplus • Consumer surplus – The difference between a buyer’s reservation price for a good and the price actually paid. Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 37

Price ($/unit) Calculating consumer surplus A market with a ‘digital’ demand curve 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Demand 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Units/day Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 38
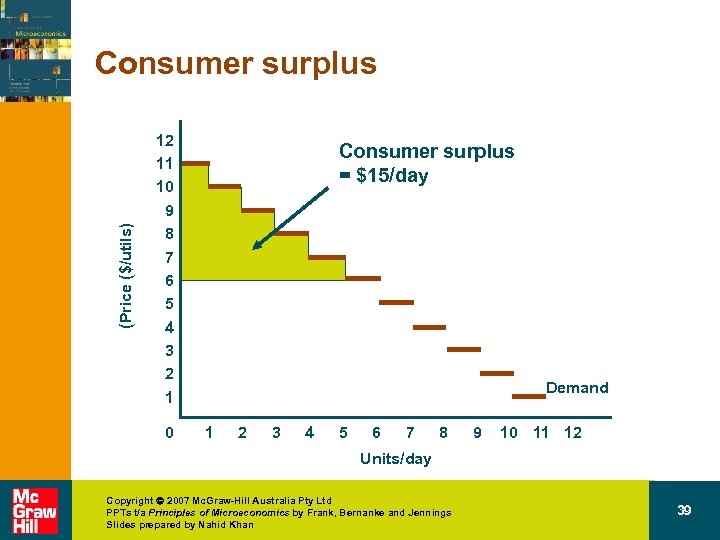
(Price ($/utils) Consumer surplus 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Consumer surplus = $15/day Demand 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Units/day Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 39

Demand consumer surplus • Question – How much will residents of the mountain village benefit from being able to participate in the market for fish if the road linking them to the coast is built? Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 40
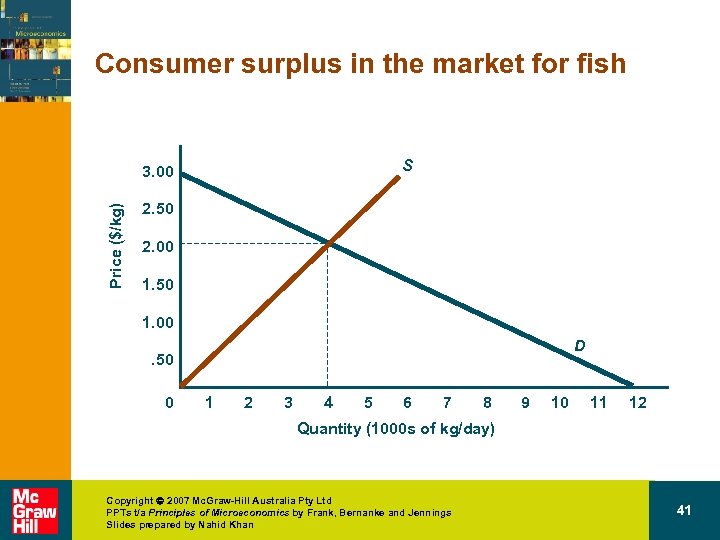
Consumer surplus in the market for fish S Price ($/kg) 3. 00 2. 50 2. 00 1. 50 1. 00 D . 50 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Quantity (1000 s of kg/day) Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 41
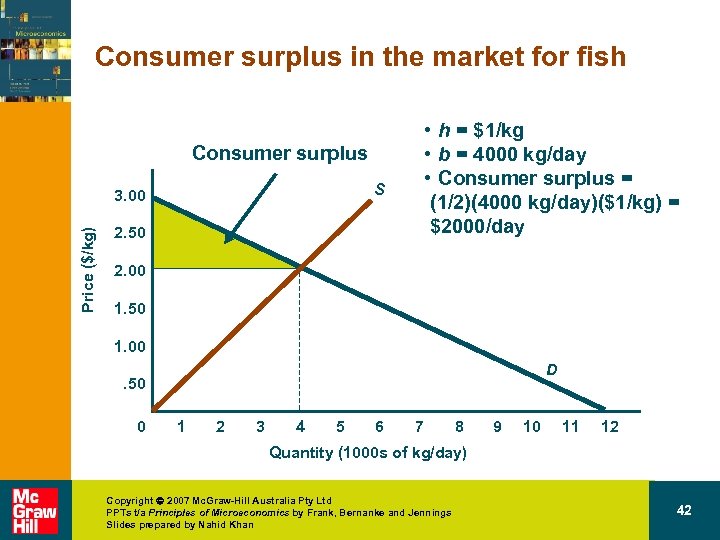
Consumer surplus in the market for fish • h = $1/kg • b = 4000 kg/day • Consumer surplus = (1/2)(4000 kg/day)($1/kg) = $2000/day Consumer surplus S Price ($/kg) 3. 00 2. 50 2. 00 1. 50 1. 00 D . 50 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Quantity (1000 s of kg/day) Copyright 2007 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Principles of Microeconomics by Frank, Bernanke and Jennings Slides prepared by Nahid Khan 42
101d2ea9d290b19ae7583877584b1a61.ppt