4860b4fb9c48451f81b55cfff8f58b77.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Chapter 5 B 2 B E-Commerce

Learning Objectives 1. Describe the B 2 B field. 2. Describe the major types of B 2 B models. 3. Discuss the characteristics and models of the sell-side marketplace, including auctions. 4. Describe the sell-side intermediaries. 5. Describe the characteristics of the buy-side marketplace and e-procurement. 6. Explain how reverse auctions work in B 2 B. 7. Describe B 2 B aggregation and group purchasing models. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Learning Objectives 8. Describe other procurement methods. 9. Define exchanges and describe their major types. 10. Describe B 2 B portals. 11. Describe third-party exchanges. 12. Describe how B 2 B can benefit from social networking and Web 2. 0. 13. Describe Internet marketing in B 2 B, including organizational buyer behavior. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B ECommerce • business-to-business e-commerce (B 2 B EC) Transactions between businesses conducted electronically over the Internet, extranets, intranets, or private networks; also known as e. B 2 B (electronic B 2 B) or just B 2 B. • Market size : (12 trillion by 2012) • Leading items: chemicals, computer electronics, food, office products, motor vehicles, …etc Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

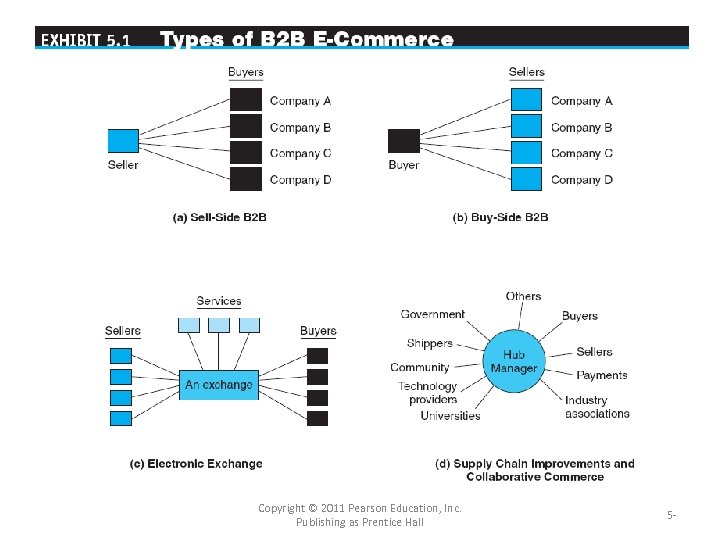
Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B ECommerce • THE BASIC TYPES OF B 2 B E-MARKETPLACES AND SERVICES – One-to-Many and Many-to-One: Private EMarketplaces • company-centric EC E-commerce that focuses on a single company’s buying needs (many-to-one or buy-side) or selling needs (one-tomany or sell-side). • (IS and participants) are controlled by individual sellside or buy-side Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B ECommerce – Many-to-Many: Exchanges (public e-marketplace) • exchanges (trading communities or trading exchanges) Many-to-many e-marketplaces, usually owned and run by a third party or a consortium, in which many buyers and many sellers meet electronically to trade with each other. • public e-marketplaces Third-party exchanges open to all interested parties (sellers and buyers). – Supply Chain Improvers and Collaborative Commerce • Hub manager • Not just buying and selling. • Collaborative Commerce: Communication, design, planning, and information sharing among business partners Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

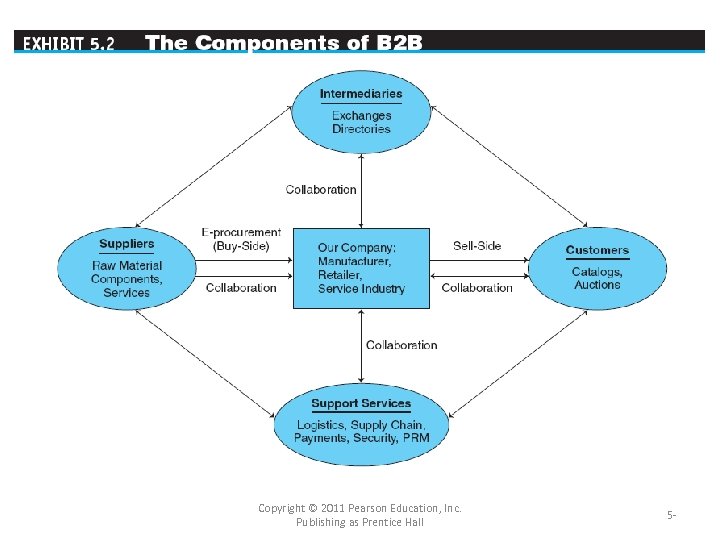
Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B ECommerce • B 2 B CHARACTERISTICS (qualities) – Parties to the Transaction: Sellers, Buyers, and Intermediaries • Can be conducted directly between a customer and a manufacturer or by an • online intermediary An online third party that brokers a transaction online between a buyer and a seller; may be virtual or click-and-mortar. Distributors or wholesalers Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B ECommerce – Types of Transactions • spot buying The purchase of goods and services as they are needed, usually at prevailing market prices. • strategic (systematic) sourcing Purchases involving long-term contracts that usually are based on private negotiations between sellers and buyers. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B ECommerce • Types of Materials Traded – direct materials Materials used in the production of a product (e. g. , steel in a car or paper in a book). – indirect materials Materials used to support production (e. g. , office supplies or lightbulbs). They are used in activities that support production maintenance, repair, and operation (MRO) Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B ECommerce – The Direction of the Trades • vertical marketplaces Markets that deal with one industry or industry segment (ex: steel, chemicals, cars, electronics, hospital supplies). • horizontal marketplaces Markets that concentrate on a service, material, or a product that is used in all types of industries (e. g. , office supplies, PCs, travel services). • SUPPLY CHAIN RELATIONSHIPS IN B 2 B The use of business-to-business electronic commerce is generally a part of existing supply chains that are used to make them more efficient. Used in acquisition of material, processing, packaging, moving Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Thu 10 -4 Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B E-Commerce • SERVICE INDUSTRIES ONLINE IN B 2 B – Travel and hospitality services – Real estate – Financial services – EFT payment – Online financing – online business loans – Other online services – consulting, law firms, health organizations Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -
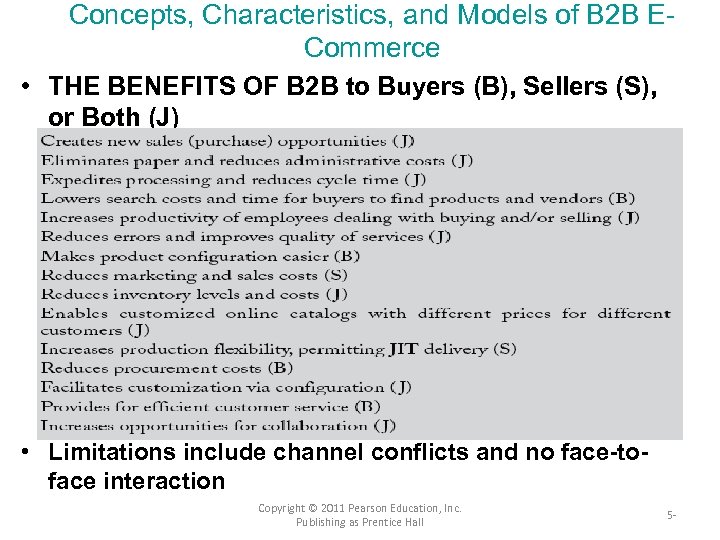
Concepts, Characteristics, and Models of B 2 B ECommerce • THE BENEFITS OF B 2 B to Buyers (B), Sellers (S), or Both (J) • Limitations include channel conflicts and no face-toface interaction Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

One-to-Many: Sell-Side E-Marketplaces • sell-side e-marketplace A Web-based marketplace in which one company sells to many business buyers from e-catalogs or auctions, frequently over an extranet. The major types of B 2 B sell-side transactions include selling from electronic catalogs, selling through forward auctions and one-to-one selling (Negotiation) – B 2 B Sellers: click and mortar: Distributors or wholesalers OR pure online – Customer Service: GE used SW agent to respond to million calls. Cost per call dropped to $0. 2 instead of $5 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

One-to-Many: Sell-Side E-Marketplaces • SELLING FROM CATALOGS – The most common sell-side method – Ex: MS sells over $60 billion SW to distributors over extranet. – Benefits: Lower order processing costs, a faster ordering cycle, fewer errors, lower search costs for buyers/sellers, lower logistics costs, and customization options. – Limitations: how to attract buyers, channel conflicts

Selling via Distributors and Other Intermediaries • Manufacturers use intermediaries to distribute their products to a large number of smaller buyers. • The intermediaries buy products from many manufacturers and aggregate them into one catalog from which they sell to customers or to retailers (Ex: Sam’s club of wallmart) • E-distributors sell in horizontal or vertical markets. • Now, many of these distributors also are selling online via Webstores. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Selling via E-auction • Companies use forward auction (on their Web site) to liquidate unneeded capital assets • Benefits of USING AUCTIONS ON THE SELL SIDE – Revenue generation – Cost savings – Increased “stickiness” - loyalty – Member acquisition and retention– registered users • AUCTIONING FROM THE COMPANY’S OWN SITE – Used by large companies like GM Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Selling via E-auction • USING INTERMEDIARIES IN AUCTIONS – Example: Liquidation. com • The benefits of using an intermediary - lack of new required resources - HW, bandwidth. IT personnel - fast time to market - outsourcing of billing/collections. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

One-from-Many: Buy-Side E-Marketplaces and EProcurement • buy-side e-marketplace A corporate-based acquisition site that uses reverse auctions, negotiations, group purchasing, or any other e-procurement method. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

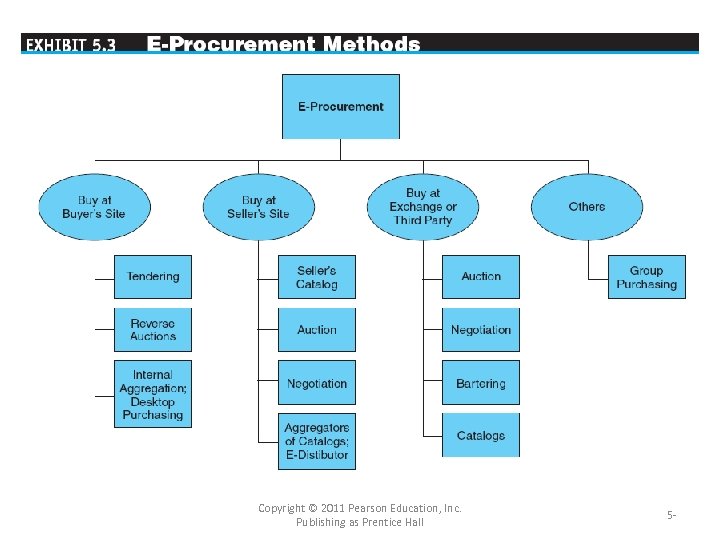
One-from-Many: Buy-Side E-Marketplaces and EProcurement • E-procurement The electronic acquisition of goods and services for organizations. • PROCUREMENT TYPES – Use Internet technology in: • E-Sourcing – identify supplier to a specific product • E-Tendering – send requests to suppliers and receive response • E-Reverse auctioning • E-Informing – gather and distribute purchasing info Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

Sun 13 -4 One-from-Many: Buy-Side EMarketplaces and E-Procurement • INEFFICIENCIES IN TRADITIONAL PROCUREMENT MANAGEMENT – procurement management The planning, organizing, and coordinating of all the activities related to purchasing goods and services needed to accomplish the organization’s mission. – maverick buying Unplanned purchases of items needed quickly, often at non-prenegotiated higher prices. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

One-from-Many: Buy-Side E-Marketplaces and EProcurement • E-procurement benefits Increased productivity, lower purchase prices, improved information flow, minimized maverick purchasing, improved payment processes, faster purchasing, reduced processing costs, and finding new suppliers/vendors. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -

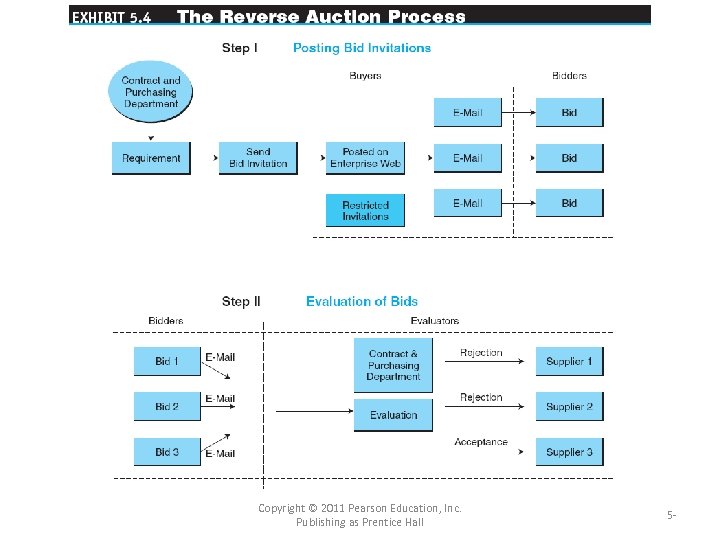
Buy-Side E-Marketplaces: Reverse Auctions • Reverse auction: Companies place their RFQ information online and allow bidders to access that information and place bids. • request for quote (RFQ) The “invitation” to participate in a tendering (bidding) system. • CONDUCTING REVERSE AUCTIONS – E-Tendering by Governments Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5 -
4860b4fb9c48451f81b55cfff8f58b77.ppt