402bd1d01e06c24af8f7540c542ec2ad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 Chapter 5 -6 Review Language and Religion
Chapter 5 -6 Review Language and Religion
 Introduction 1. 7, 299 languages in the world today 2. Only 10 are spoken by at least 100 million people 3. Language is the means through which cultural values (religion, ethnicity) are spread 4. Geographers look at similarities to understand diffusion around the world 5. Is ENGLISH the language of power? Globalization? 6. People are trying to preserve local diversity and identity through language
Introduction 1. 7, 299 languages in the world today 2. Only 10 are spoken by at least 100 million people 3. Language is the means through which cultural values (religion, ethnicity) are spread 4. Geographers look at similarities to understand diffusion around the world 5. Is ENGLISH the language of power? Globalization? 6. People are trying to preserve local diversity and identity through language
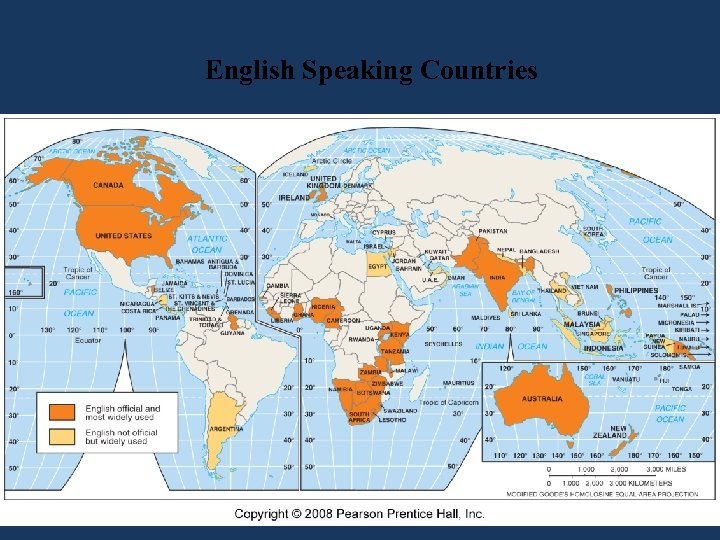 English Speaking Countries
English Speaking Countries
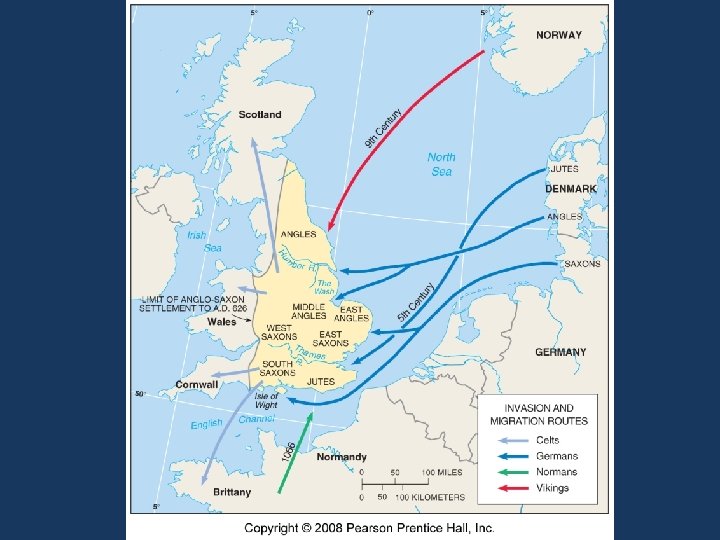
 Origin of English 1. Celts invaded by Anglos & Saxons who were German tribes. 2. Combined with Normans (French) and Vikings to produce English. a. French was the official language for 300 years (10661362) Dialects 1. Dialect – variation of a language, distinguished by vocabulary, spelling and pronunciation. 2. Geographers study dialect to show distinctive differences in the environment in which groups live 3. A language with many dialects, one may be the standard language 4. BRP=British Received Pronunciation—preferred dialect – London, Oxford & Cambridge.
Origin of English 1. Celts invaded by Anglos & Saxons who were German tribes. 2. Combined with Normans (French) and Vikings to produce English. a. French was the official language for 300 years (10661362) Dialects 1. Dialect – variation of a language, distinguished by vocabulary, spelling and pronunciation. 2. Geographers study dialect to show distinctive differences in the environment in which groups live 3. A language with many dialects, one may be the standard language 4. BRP=British Received Pronunciation—preferred dialect – London, Oxford & Cambridge.
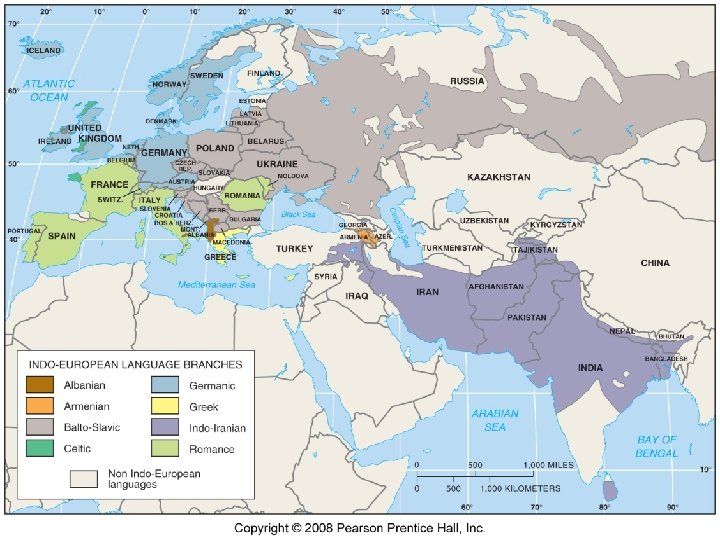
 Key Issue 2: Why Is English Related to Other Languages? Indo-European Branches 1. Language family (trunk) is a collection of languages related through ancestral language that existed before recorded history 2. Language branch is within the family a collection of languages related through common ancestral language 3. Indo-European is divided into eight branches: a. Indo-Iranian – South Asia b. Romance – southwestern Europe and Latin America c. Germanic – northwestern Europe and North America (English) d. Balto-Slavic – Eastern Europe 4. Albanian, Armenian, Greek, and Celtic are used less often 5. Language group is a collection of languages within a branch, common origins, recent past
Key Issue 2: Why Is English Related to Other Languages? Indo-European Branches 1. Language family (trunk) is a collection of languages related through ancestral language that existed before recorded history 2. Language branch is within the family a collection of languages related through common ancestral language 3. Indo-European is divided into eight branches: a. Indo-Iranian – South Asia b. Romance – southwestern Europe and Latin America c. Germanic – northwestern Europe and North America (English) d. Balto-Slavic – Eastern Europe 4. Albanian, Armenian, Greek, and Celtic are used less often 5. Language group is a collection of languages within a branch, common origins, recent past
 Diffusion 1. Language diffuses primarily through conquest and warfare 2. Native languages triumph due to farming over hunting 3. After generations of isolation, distinct languages emerge
Diffusion 1. Language diffuses primarily through conquest and warfare 2. Native languages triumph due to farming over hunting 3. After generations of isolation, distinct languages emerge
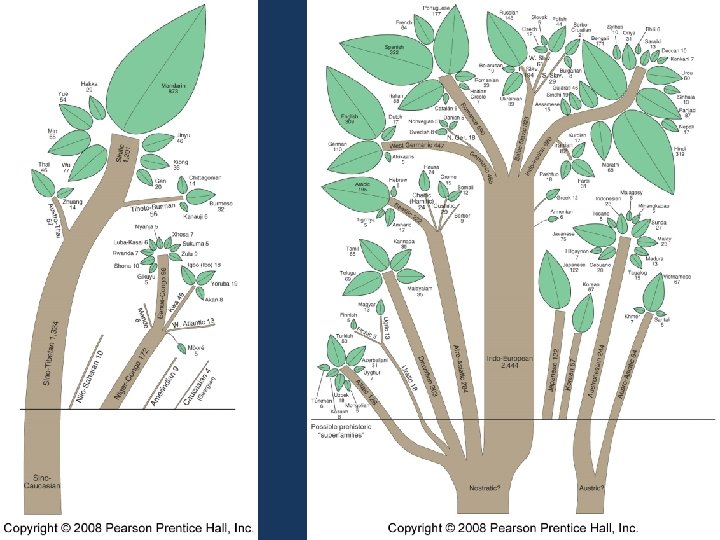
 Key Issue 3: Where Are Other Language Families Distributed? Classification of Languages 1. Indo-European Family such as English – spoken by 48% 2. Sino-Tibetan Family such as Mandarin – 26% 3. Afro-Asiatic such as Arabic – 6% 4. Language families form the trunks of the trees a. Branches are languages related through common ancestral language b. Individual languages are the leaves 5. The larger the trunk and leaves, the more speakers there are 6. Superfamilies are shown as the roots – existence speculative
Key Issue 3: Where Are Other Language Families Distributed? Classification of Languages 1. Indo-European Family such as English – spoken by 48% 2. Sino-Tibetan Family such as Mandarin – 26% 3. Afro-Asiatic such as Arabic – 6% 4. Language families form the trunks of the trees a. Branches are languages related through common ancestral language b. Individual languages are the leaves 5. The larger the trunk and leaves, the more speakers there are 6. Superfamilies are shown as the roots – existence speculative
 Key Issue 4: Why Do People Preserve Local Languages? Preserving Language Diversity 1. Distribution of a language is a measure of the fate of an ethnic group 2. 516 languages nearly extinct a. 46 in Africa, 170 in the Americas, 78 in Asia, 12 in Europe 210 in the Pacific b. 1500 s Peru – 500 languages now only 92 3. Only 300 languages safe from extinction 4. Hebrew disappears by 400 BC a. 1948 – Hebrew becomes official language of the new Israel b. Used to unify the new country c. Had to be revived with 4, 000 new words
Key Issue 4: Why Do People Preserve Local Languages? Preserving Language Diversity 1. Distribution of a language is a measure of the fate of an ethnic group 2. 516 languages nearly extinct a. 46 in Africa, 170 in the Americas, 78 in Asia, 12 in Europe 210 in the Pacific b. 1500 s Peru – 500 languages now only 92 3. Only 300 languages safe from extinction 4. Hebrew disappears by 400 BC a. 1948 – Hebrew becomes official language of the new Israel b. Used to unify the new country c. Had to be revived with 4, 000 new words

 Global Dominance of English 1. Lingua franca – language of international communication 2. Pidgin language – simplified lingua franca to communicate with another language 3. More than 90% of students in EU learn English 4. 500 million people speak English as a second language 5. Most effective way to participate in global economy is participate in global culture 6. English is expansion diffusion – spreads in a snowball effect
Global Dominance of English 1. Lingua franca – language of international communication 2. Pidgin language – simplified lingua franca to communicate with another language 3. More than 90% of students in EU learn English 4. 500 million people speak English as a second language 5. Most effective way to participate in global economy is participate in global culture 6. English is expansion diffusion – spreads in a snowball effect
 Introduction – Religion 1. Geographers watch how one religion diffuses across space and may conflict with others 2. Geographers also observe how religion derives from the environment and modify it 3. Spatial connections: place of origin, diffusion, process of diffusion, why more widespread 4. Universalizing Religion – attempt to be global, appeal to all people wherever they live 5. Ethnic Religion – appeals to one group living in one place – 24% of the population
Introduction – Religion 1. Geographers watch how one religion diffuses across space and may conflict with others 2. Geographers also observe how religion derives from the environment and modify it 3. Spatial connections: place of origin, diffusion, process of diffusion, why more widespread 4. Universalizing Religion – attempt to be global, appeal to all people wherever they live 5. Ethnic Religion – appeals to one group living in one place – 24% of the population
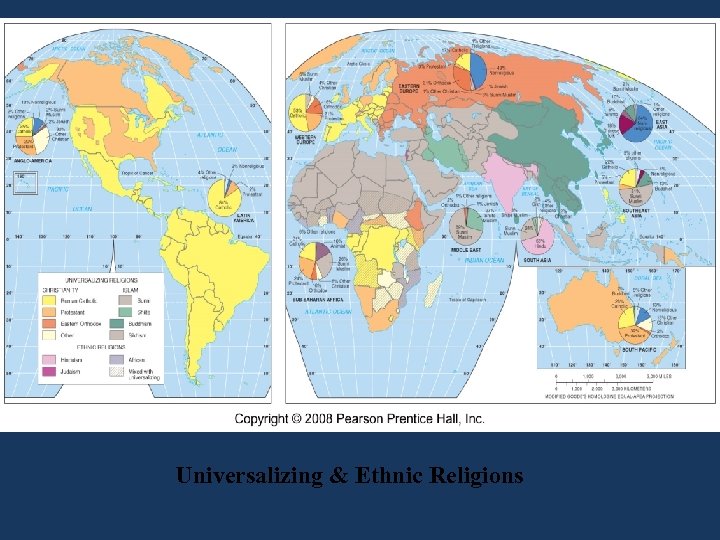 Universalizing & Ethnic Religions
Universalizing & Ethnic Religions
 Ethnic Religions 1. 860 million adherents of Hindu – world’s third largest religion 2. 97% clustered in one country, India – thus, an ethnic religion 3. Hindus believe it is up to the individual to worship God 4. Path varies – devotion, action, knowledge, renunciation 5. You alone are responsible for your actions… and consequences
Ethnic Religions 1. 860 million adherents of Hindu – world’s third largest religion 2. 97% clustered in one country, India – thus, an ethnic religion 3. Hindus believe it is up to the individual to worship God 4. Path varies – devotion, action, knowledge, renunciation 5. You alone are responsible for your actions… and consequences
 Key Issue 2: Why Do Religions Have Different Distributions? Origin of Christianity 1. Jesus was born in Bethlehem between 8 BC and 4 BC 2. He died on a cross about 30 AD in Jerusalem A. Preached the coming of the Kingdom of God 3. Christian Bible documented miracles/deeds performed by Jesus 4. Resurrection provides hope for salvation 5. Roman Catholics believe God conveys his belief through seven sacraments: a. Baptism, Confirmation, Penance, Anointing the sick, Matrimony, Holy Orders, Eucharist 6. Eastern Orthodox accepted seven sacraments but rejected other doctrines added after 700 AD 7. Protestants split in 1500 s when Martin Luther posted 95 theses a. Individuals have responsibility for salvation trough communication with God b. Grace is achieved through faith rather than sacraments
Key Issue 2: Why Do Religions Have Different Distributions? Origin of Christianity 1. Jesus was born in Bethlehem between 8 BC and 4 BC 2. He died on a cross about 30 AD in Jerusalem A. Preached the coming of the Kingdom of God 3. Christian Bible documented miracles/deeds performed by Jesus 4. Resurrection provides hope for salvation 5. Roman Catholics believe God conveys his belief through seven sacraments: a. Baptism, Confirmation, Penance, Anointing the sick, Matrimony, Holy Orders, Eucharist 6. Eastern Orthodox accepted seven sacraments but rejected other doctrines added after 700 AD 7. Protestants split in 1500 s when Martin Luther posted 95 theses a. Individuals have responsibility for salvation trough communication with God b. Grace is achieved through faith rather than sacraments
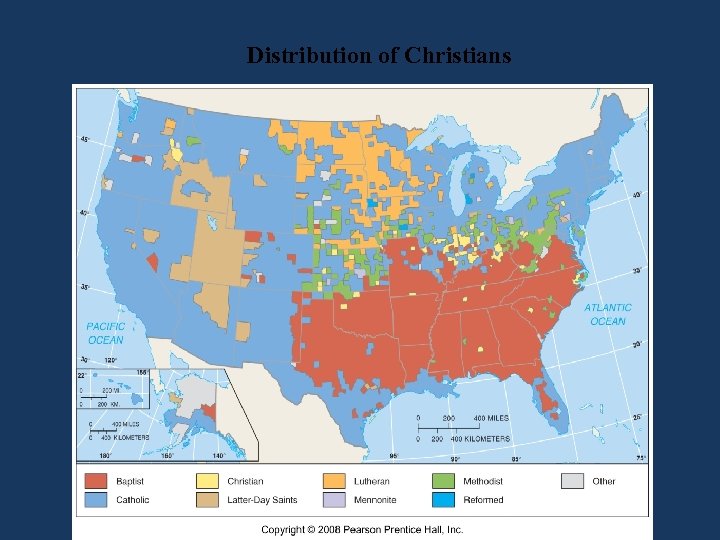 Distribution of Christians
Distribution of Christians
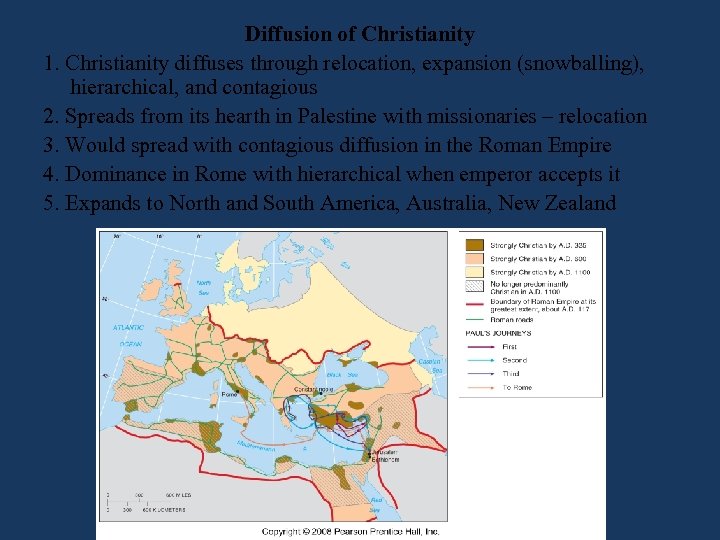 Diffusion of Christianity 1. Christianity diffuses through relocation, expansion (snowballing), hierarchical, and contagious 2. Spreads from its hearth in Palestine with missionaries – relocation 3. Would spread with contagious diffusion in the Roman Empire 4. Dominance in Rome with hierarchical when emperor accepts it 5. Expands to North and South America, Australia, New Zealand
Diffusion of Christianity 1. Christianity diffuses through relocation, expansion (snowballing), hierarchical, and contagious 2. Spreads from its hearth in Palestine with missionaries – relocation 3. Would spread with contagious diffusion in the Roman Empire 4. Dominance in Rome with hierarchical when emperor accepts it 5. Expands to North and South America, Australia, New Zealand
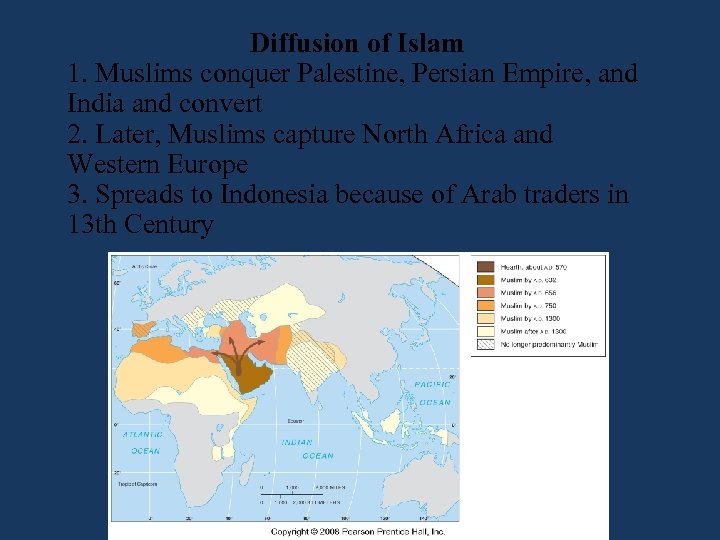 Diffusion of Islam 1. Muslims conquer Palestine, Persian Empire, and India and convert 2. Later, Muslims capture North Africa and Western Europe 3. Spreads to Indonesia because of Arab traders in 13 th Century
Diffusion of Islam 1. Muslims conquer Palestine, Persian Empire, and India and convert 2. Later, Muslims capture North Africa and Western Europe 3. Spreads to Indonesia because of Arab traders in 13 th Century
 Key Issue 3: Why Do Religions Organize Space in Distinctive Patterns? Places of Worship 1. Christian church more important than buildings in other religions 2. Usually the largest and tallest building placed in a prominent location 3. Muslim masques are places for community gathering 4. Hindus – important religious functions are performed in the home – temples are shrines 5. Buddhist – pagodas contain relics of Buddha but not for worship
Key Issue 3: Why Do Religions Organize Space in Distinctive Patterns? Places of Worship 1. Christian church more important than buildings in other religions 2. Usually the largest and tallest building placed in a prominent location 3. Muslim masques are places for community gathering 4. Hindus – important religious functions are performed in the home – temples are shrines 5. Buddhist – pagodas contain relics of Buddha but not for worship
 Key Issue 4: Why Do Territorial Conflicts Arise Among Religious Groups? Religion vs. Government 1. North America and Western Europe believe economic development and religion are compatible 2. Less developed countries view it differently – Muslims, Hindus, etc.
Key Issue 4: Why Do Territorial Conflicts Arise Among Religious Groups? Religion vs. Government 1. North America and Western Europe believe economic development and religion are compatible 2. Less developed countries view it differently – Muslims, Hindus, etc.
 Taliban 1. US backs their govt. in Afghanistan to prevent another Russian invasion 2. Taliban creates Ministry for the Promotion of Virtue and the Prevention of Vice a. Men beaten for shaving their beards b. Stoned for committing adultery c. Homosexuals were buried alive d. Prostitutes were hanged in front of audiences e. Thieves had their hands cut off f. Women had their fingers cut off for wearing nail polish g. Banned western activities like TV, music, even flying kites
Taliban 1. US backs their govt. in Afghanistan to prevent another Russian invasion 2. Taliban creates Ministry for the Promotion of Virtue and the Prevention of Vice a. Men beaten for shaving their beards b. Stoned for committing adultery c. Homosexuals were buried alive d. Prostitutes were hanged in front of audiences e. Thieves had their hands cut off f. Women had their fingers cut off for wearing nail polish g. Banned western activities like TV, music, even flying kites
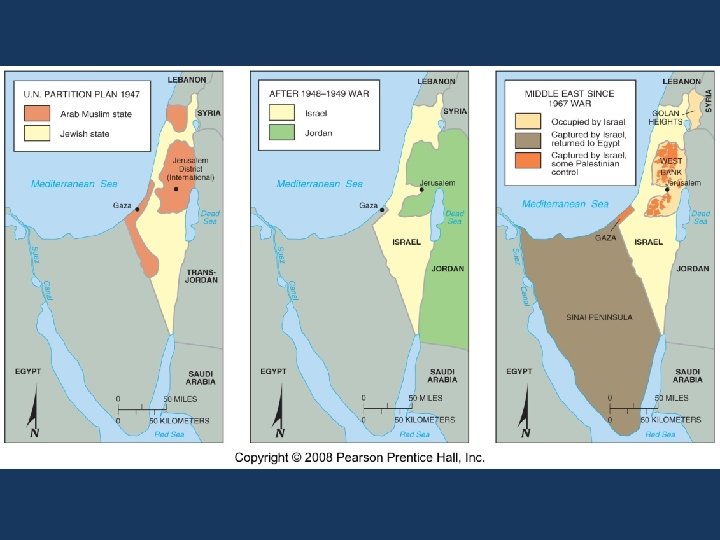
 Jews vs. Muslims 1. British announces they’re leaving Palestine; UN sets up two independent countries a. One Jewish, one Muslim; Jerusalem would international open to all 2. 1948 – UK withdrawals, Jews declare all territory the state of Israel a. Next day, neighboring Arab states invade b. Old City Jerusalem becomes part of Jordan; new city belongs to Israel 3. 1967 Six-Day War – Israel gains West Bank, Gaza Strip, Golan Heights, Sinai Pen. , Jerusalem a. Israel returns Sinai and Egyptian President assassinated for “recognizing” Israel 4. Fatah Party will recognize Israel if they return all land obtained in 1967 5. Hamas Party does not recognize Israel; will fight for ALL the land 6. Jerusalem – as long as one religion controls city, there will not be peace
Jews vs. Muslims 1. British announces they’re leaving Palestine; UN sets up two independent countries a. One Jewish, one Muslim; Jerusalem would international open to all 2. 1948 – UK withdrawals, Jews declare all territory the state of Israel a. Next day, neighboring Arab states invade b. Old City Jerusalem becomes part of Jordan; new city belongs to Israel 3. 1967 Six-Day War – Israel gains West Bank, Gaza Strip, Golan Heights, Sinai Pen. , Jerusalem a. Israel returns Sinai and Egyptian President assassinated for “recognizing” Israel 4. Fatah Party will recognize Israel if they return all land obtained in 1967 5. Hamas Party does not recognize Israel; will fight for ALL the land 6. Jerusalem – as long as one religion controls city, there will not be peace
 Chapter 7 -9 Review Ethnicity, Political Geography, and Development
Chapter 7 -9 Review Ethnicity, Political Geography, and Development
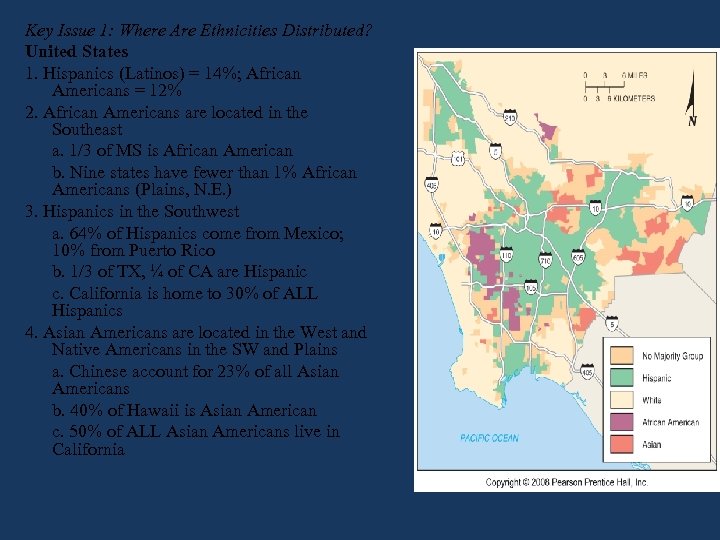 Key Issue 1: Where Are Ethnicities Distributed? United States 1. Hispanics (Latinos) = 14%; African Americans = 12% 2. African Americans are located in the Southeast a. 1/3 of MS is African American b. Nine states have fewer than 1% African Americans (Plains, N. E. ) 3. Hispanics in the Southwest a. 64% of Hispanics come from Mexico; 10% from Puerto Rico b. 1/3 of TX, ¼ of CA are Hispanic c. California is home to 30% of ALL Hispanics 4. Asian Americans are located in the West and Native Americans in the SW and Plains a. Chinese account for 23% of all Asian Americans b. 40% of Hawaii is Asian American c. 50% of ALL Asian Americans live in California
Key Issue 1: Where Are Ethnicities Distributed? United States 1. Hispanics (Latinos) = 14%; African Americans = 12% 2. African Americans are located in the Southeast a. 1/3 of MS is African American b. Nine states have fewer than 1% African Americans (Plains, N. E. ) 3. Hispanics in the Southwest a. 64% of Hispanics come from Mexico; 10% from Puerto Rico b. 1/3 of TX, ¼ of CA are Hispanic c. California is home to 30% of ALL Hispanics 4. Asian Americans are located in the West and Native Americans in the SW and Plains a. Chinese account for 23% of all Asian Americans b. 40% of Hawaii is Asian American c. 50% of ALL Asian Americans live in California
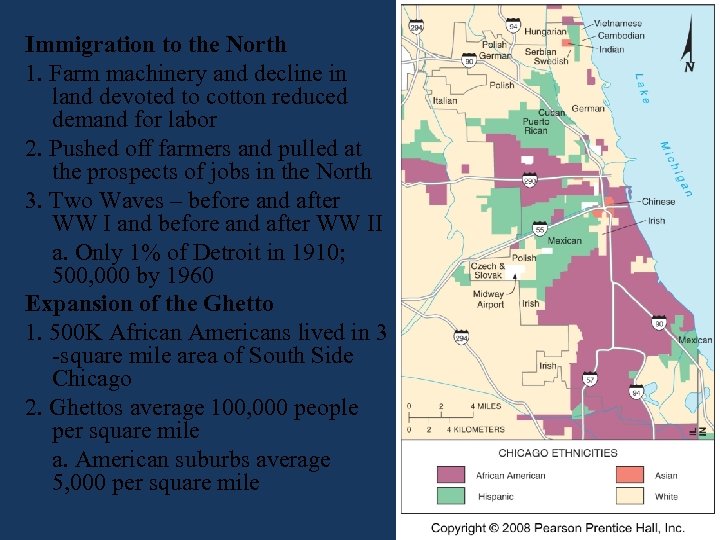 Immigration to the North 1. Farm machinery and decline in land devoted to cotton reduced demand for labor 2. Pushed off farmers and pulled at the prospects of jobs in the North 3. Two Waves – before and after WW I and before and after WW II a. Only 1% of Detroit in 1910; 500, 000 by 1960 Expansion of the Ghetto 1. 500 K African Americans lived in 3 -square mile area of South Side Chicago 2. Ghettos average 100, 000 people per square mile a. American suburbs average 5, 000 per square mile
Immigration to the North 1. Farm machinery and decline in land devoted to cotton reduced demand for labor 2. Pushed off farmers and pulled at the prospects of jobs in the North 3. Two Waves – before and after WW I and before and after WW II a. Only 1% of Detroit in 1910; 500, 000 by 1960 Expansion of the Ghetto 1. 500 K African Americans lived in 3 -square mile area of South Side Chicago 2. Ghettos average 100, 000 people per square mile a. American suburbs average 5, 000 per square mile
 Difference Between Ethnicity & Race 1. Asian as a race & Asian American as ethnicity are the same group 2. African American- Black is different & can be from other places, like L. A. a. Some American blacks trace their heritage to someplace other than Africa 3. Hispanic or Latino is not a race 4. Traits that are race can be transmitted genetically 5. Racism is the belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities and racial differences produce an inherent superiority of a particular race 6. Ethnicity derives from distinctive features of a particular place on Earth 7. Geographers don’t like to classify humans by race because they are not rooted to a place 8. Race does matter because it determines where people live attend school, recreate, etc.
Difference Between Ethnicity & Race 1. Asian as a race & Asian American as ethnicity are the same group 2. African American- Black is different & can be from other places, like L. A. a. Some American blacks trace their heritage to someplace other than Africa 3. Hispanic or Latino is not a race 4. Traits that are race can be transmitted genetically 5. Racism is the belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities and racial differences produce an inherent superiority of a particular race 6. Ethnicity derives from distinctive features of a particular place on Earth 7. Geographers don’t like to classify humans by race because they are not rooted to a place 8. Race does matter because it determines where people live attend school, recreate, etc.
 White Flight 1. Brown v Board of Education of Topeka (1954) – separate schools was unconstitutional a. Racial separation branded minority children as inferior – inherently unequal 2. Rather than integrate, whites left the cities a. White flight – whites leaving in anticipation of blacks immigrating in b. Detroit’s white population dropped by 1 million in 25 years 3. 1950 Detroit – 1. 7 million white, 300, 000 black 4. 2000 Detroit – 200, 000 white, 800, 000 black 5. Kerner Commission – US cities were divided into two unequal societies
White Flight 1. Brown v Board of Education of Topeka (1954) – separate schools was unconstitutional a. Racial separation branded minority children as inferior – inherently unequal 2. Rather than integrate, whites left the cities a. White flight – whites leaving in anticipation of blacks immigrating in b. Detroit’s white population dropped by 1 million in 25 years 3. 1950 Detroit – 1. 7 million white, 300, 000 black 4. 2000 Detroit – 200, 000 white, 800, 000 black 5. Kerner Commission – US cities were divided into two unequal societies
 Nationalities 1. Identity with a group of people who share legal attachments and personal allegiance to a particular country. 2. Similar to ethnicity – shared cultural values. Different from race 3. Most U. S. immigrants identify themselves by ethnicity rather than nationality. 4. Does Quebec have a different ethnicity or nationality from Canada?
Nationalities 1. Identity with a group of people who share legal attachments and personal allegiance to a particular country. 2. Similar to ethnicity – shared cultural values. Different from race 3. Most U. S. immigrants identify themselves by ethnicity rather than nationality. 4. Does Quebec have a different ethnicity or nationality from Canada?
 Nation-States 1. Self determination- ethnicities govern themselves 2. Nation-State – Correspond to geographical area of a ethnicity. a. WW II – Germany wanted to unite all German speaking people. b. Denmark – almost all Dutch speakers but what about Greenland? Faeroe Islands? c. Many borders redrawn after WW I based on ethnicity Nationalism 1. Loyalty to state, one nation above all others – a. Emphasize shared values 2. Mass media – independent news is a risk to nationalism – what about US? a. Nearly every country regulates communications – mail, phone, TV, etc. 3. Protest – should burning the flag be illegal?
Nation-States 1. Self determination- ethnicities govern themselves 2. Nation-State – Correspond to geographical area of a ethnicity. a. WW II – Germany wanted to unite all German speaking people. b. Denmark – almost all Dutch speakers but what about Greenland? Faeroe Islands? c. Many borders redrawn after WW I based on ethnicity Nationalism 1. Loyalty to state, one nation above all others – a. Emphasize shared values 2. Mass media – independent news is a risk to nationalism – what about US? a. Nearly every country regulates communications – mail, phone, TV, etc. 3. Protest – should burning the flag be illegal?
 Multinational States 1. Multiethnic States – more than 1 ethnicity. 2. Multinational States – 2 distinct ethnicities coexisting peacefully a. Usually one nationality tries to dominate the other b. U. K. is multinational Wales, Scotland, England, N. Ireland. – very different historically 3. Former USSR – 15 republics now 15 independent states; 20% non-Russian 4. Russia is now largest multinational state. 39 nationalities- some want independence a. Chechnya (near Georgia) Sunni Muslims, has petroleum b. Armenia – the most ethnically homogenous country in the region. c. Many Moldovans want to merge with Romania d. Kazakhstan – 53% Muslim, 30% Christian but still peaceful – why? e. Tajikistan – Muslims aligned with Christians fighting Tajik communists f. Azeris and Armenians are in border conflicts – Armenia divides Azerbaijan 5. Georgia Ossetians vs. Abkhazians – Ossetians want to be united with Russia a. Russia invades to help South Ossetia and Abkhazia separate in August 2008 b. Troops remain as “guests” of the new countries
Multinational States 1. Multiethnic States – more than 1 ethnicity. 2. Multinational States – 2 distinct ethnicities coexisting peacefully a. Usually one nationality tries to dominate the other b. U. K. is multinational Wales, Scotland, England, N. Ireland. – very different historically 3. Former USSR – 15 republics now 15 independent states; 20% non-Russian 4. Russia is now largest multinational state. 39 nationalities- some want independence a. Chechnya (near Georgia) Sunni Muslims, has petroleum b. Armenia – the most ethnically homogenous country in the region. c. Many Moldovans want to merge with Romania d. Kazakhstan – 53% Muslim, 30% Christian but still peaceful – why? e. Tajikistan – Muslims aligned with Christians fighting Tajik communists f. Azeris and Armenians are in border conflicts – Armenia divides Azerbaijan 5. Georgia Ossetians vs. Abkhazians – Ossetians want to be united with Russia a. Russia invades to help South Ossetia and Abkhazia separate in August 2008 b. Troops remain as “guests” of the new countries
 Introduction – Political Geography 1. We take for granted the division of our planets surface into a collection of spaces 2. Power is gained through connections among states for economic reasons 3. There were only about 50 countries in the 1940 s; 192 today 4. State – An area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government. 5. Sovereignty – Independence from the control of its internal affairs by other states 6. Country – Synonym for state
Introduction – Political Geography 1. We take for granted the division of our planets surface into a collection of spaces 2. Power is gained through connections among states for economic reasons 3. There were only about 50 countries in the 1940 s; 192 today 4. State – An area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government. 5. Sovereignty – Independence from the control of its internal affairs by other states 6. Country – Synonym for state
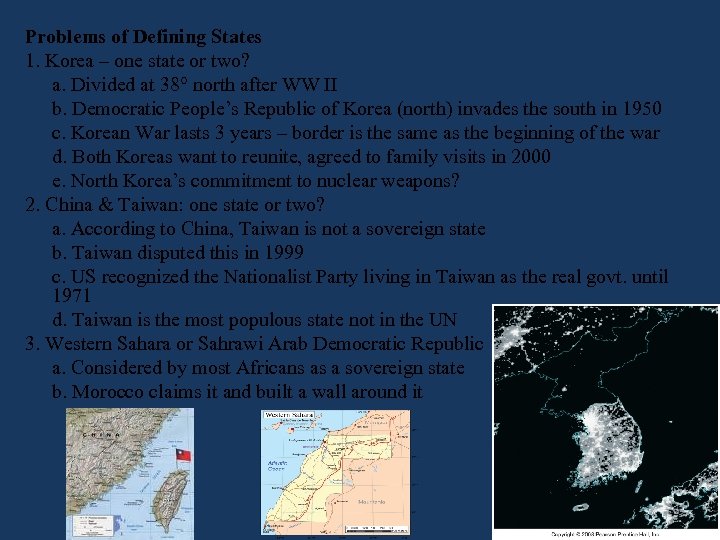 Problems of Defining States 1. Korea – one state or two? a. Divided at 38 north after WW II b. Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (north) invades the south in 1950 c. Korean War lasts 3 years – border is the same as the beginning of the war d. Both Koreas want to reunite, agreed to family visits in 2000 e. North Korea’s commitment to nuclear weapons? 2. China & Taiwan: one state or two? a. According to China, Taiwan is not a sovereign state b. Taiwan disputed this in 1999 c. US recognized the Nationalist Party living in Taiwan as the real govt. until 1971 d. Taiwan is the most populous state not in the UN 3. Western Sahara or Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic a. Considered by most Africans as a sovereign state b. Morocco claims it and built a wall around it
Problems of Defining States 1. Korea – one state or two? a. Divided at 38 north after WW II b. Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (north) invades the south in 1950 c. Korean War lasts 3 years – border is the same as the beginning of the war d. Both Koreas want to reunite, agreed to family visits in 2000 e. North Korea’s commitment to nuclear weapons? 2. China & Taiwan: one state or two? a. According to China, Taiwan is not a sovereign state b. Taiwan disputed this in 1999 c. US recognized the Nationalist Party living in Taiwan as the real govt. until 1971 d. Taiwan is the most populous state not in the UN 3. Western Sahara or Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic a. Considered by most Africans as a sovereign state b. Morocco claims it and built a wall around it
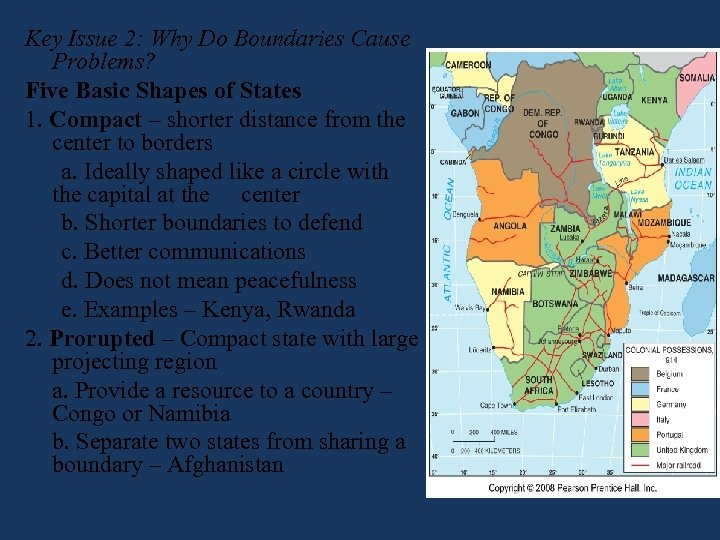 Key Issue 2: Why Do Boundaries Cause Problems? Five Basic Shapes of States 1. Compact – shorter distance from the center to borders a. Ideally shaped like a circle with the capital at the center b. Shorter boundaries to defend c. Better communications d. Does not mean peacefulness e. Examples – Kenya, Rwanda 2. Prorupted – Compact state with large projecting region a. Provide a resource to a country – Congo or Namibia b. Separate two states from sharing a boundary – Afghanistan
Key Issue 2: Why Do Boundaries Cause Problems? Five Basic Shapes of States 1. Compact – shorter distance from the center to borders a. Ideally shaped like a circle with the capital at the center b. Shorter boundaries to defend c. Better communications d. Does not mean peacefulness e. Examples – Kenya, Rwanda 2. Prorupted – Compact state with large projecting region a. Provide a resource to a country – Congo or Namibia b. Separate two states from sharing a boundary – Afghanistan
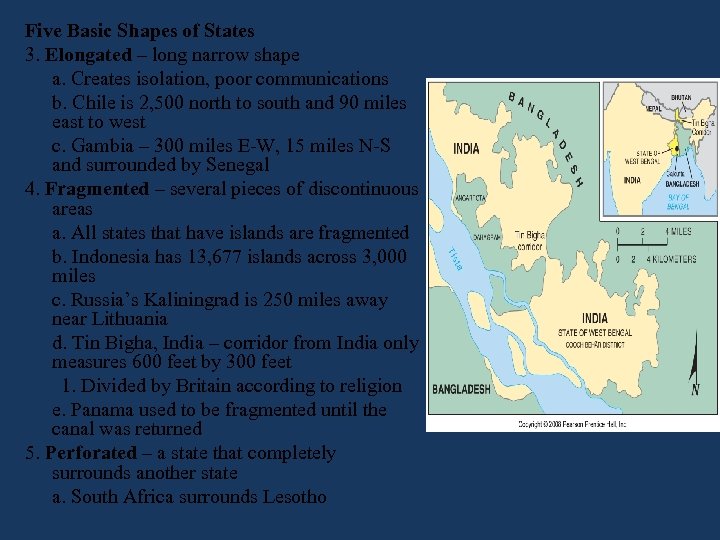 Five Basic Shapes of States 3. Elongated – long narrow shape a. Creates isolation, poor communications b. Chile is 2, 500 north to south and 90 miles east to west c. Gambia – 300 miles E-W, 15 miles N-S and surrounded by Senegal 4. Fragmented – several pieces of discontinuous areas a. All states that have islands are fragmented b. Indonesia has 13, 677 islands across 3, 000 miles c. Russia’s Kaliningrad is 250 miles away near Lithuania d. Tin Bigha, India – corridor from India only measures 600 feet by 300 feet 1. Divided by Britain according to religion e. Panama used to be fragmented until the canal was returned 5. Perforated – a state that completely surrounds another state a. South Africa surrounds Lesotho
Five Basic Shapes of States 3. Elongated – long narrow shape a. Creates isolation, poor communications b. Chile is 2, 500 north to south and 90 miles east to west c. Gambia – 300 miles E-W, 15 miles N-S and surrounded by Senegal 4. Fragmented – several pieces of discontinuous areas a. All states that have islands are fragmented b. Indonesia has 13, 677 islands across 3, 000 miles c. Russia’s Kaliningrad is 250 miles away near Lithuania d. Tin Bigha, India – corridor from India only measures 600 feet by 300 feet 1. Divided by Britain according to religion e. Panama used to be fragmented until the canal was returned 5. Perforated – a state that completely surrounds another state a. South Africa surrounds Lesotho
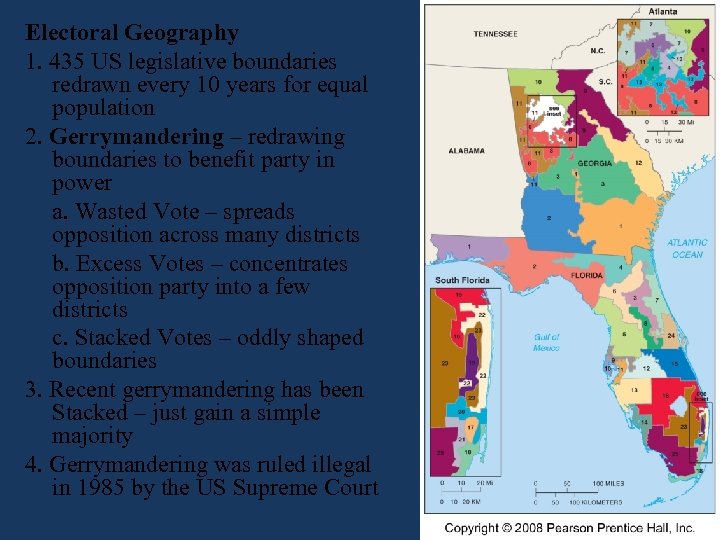 Electoral Geography 1. 435 US legislative boundaries redrawn every 10 years for equal population 2. Gerrymandering – redrawing boundaries to benefit party in power a. Wasted Vote – spreads opposition across many districts b. Excess Votes – concentrates opposition party into a few districts c. Stacked Votes – oddly shaped boundaries 3. Recent gerrymandering has been Stacked – just gain a simple majority 4. Gerrymandering was ruled illegal in 1985 by the US Supreme Court
Electoral Geography 1. 435 US legislative boundaries redrawn every 10 years for equal population 2. Gerrymandering – redrawing boundaries to benefit party in power a. Wasted Vote – spreads opposition across many districts b. Excess Votes – concentrates opposition party into a few districts c. Stacked Votes – oddly shaped boundaries 3. Recent gerrymandering has been Stacked – just gain a simple majority 4. Gerrymandering was ruled illegal in 1985 by the US Supreme Court
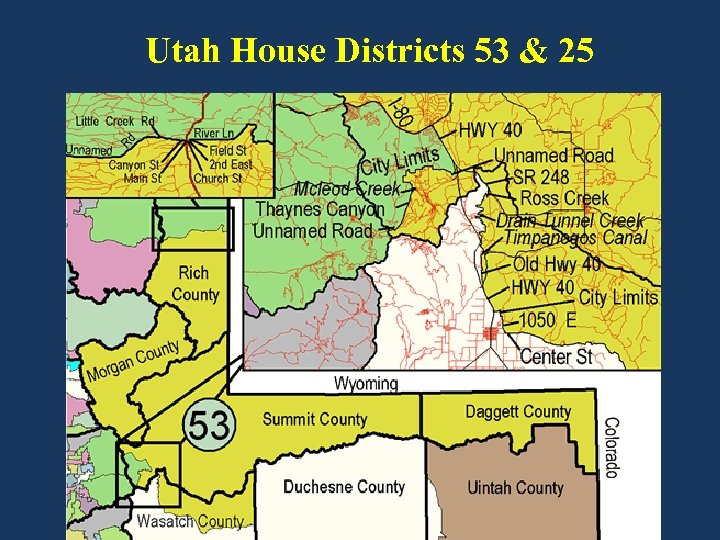 Utah House Districts 53 & 25
Utah House Districts 53 & 25
 Economic Cooperation 1. The world has moved to a pattern of multiple superpowers a. Economic power instead of military b. Leading power is a union of states – European Union 2. 2004 – eight former communist states join EU 3. Goal – promote development through economic cooperation 4. Free trade – goods, services, capital, people move freely between members 5. Common currency – eliminated different prices, interest rates
Economic Cooperation 1. The world has moved to a pattern of multiple superpowers a. Economic power instead of military b. Leading power is a union of states – European Union 2. 2004 – eight former communist states join EU 3. Goal – promote development through economic cooperation 4. Free trade – goods, services, capital, people move freely between members 5. Common currency – eliminated different prices, interest rates
 Supranationalism 1. Political, economic, and/or cultural cooperation among states to promote shared objectives 2. States tend to give up political power to a higher authority to pursue common objectives a. Political, economic, military, or environmental goals b. Ex. EU, NAFTA, UN NATO, Warsaw Pact, OPEC Devolution 1. Granting of powers from central government to government at regional or local level 2. Regions within a state demand gain political strength at the expense of the central government – breakup of a state - balkanization 3. Growing autonomy within a state a. Ex. Yugoslavia, USSR, Czechoslovakia, British India b. UK, Canada, Spain, India/Pakistan
Supranationalism 1. Political, economic, and/or cultural cooperation among states to promote shared objectives 2. States tend to give up political power to a higher authority to pursue common objectives a. Political, economic, military, or environmental goals b. Ex. EU, NAFTA, UN NATO, Warsaw Pact, OPEC Devolution 1. Granting of powers from central government to government at regional or local level 2. Regions within a state demand gain political strength at the expense of the central government – breakup of a state - balkanization 3. Growing autonomy within a state a. Ex. Yugoslavia, USSR, Czechoslovakia, British India b. UK, Canada, Spain, India/Pakistan
 Key Issue 1: Why Does Development Vary Among Countries? Economic Indicators of Development 1. Human Development Index (HDI) – measure of economic, social, and demographic levels a. Economic Factor = PCI (Gross Domestic Product Per Capita) b. Social Factors = Literacy Rate c. Amount of Education (primary, secondary and tertiary years total, %) d. Demographic Factor = Life Expectancy 2. GDP per capita – value of the total output of goods and services produced in a year divided by the number of people a. $15/hour in MDCs vs. $2/hour in LDCs b. 18 countries with per capita GDP lower than $1000; 15 in Africa c. Some progress in LDCs: $800 in 1990 to $4400 in 2005; 450% increase 3. Misleading? US per capita GDP = $40, 000 but 1/8 live in poverty
Key Issue 1: Why Does Development Vary Among Countries? Economic Indicators of Development 1. Human Development Index (HDI) – measure of economic, social, and demographic levels a. Economic Factor = PCI (Gross Domestic Product Per Capita) b. Social Factors = Literacy Rate c. Amount of Education (primary, secondary and tertiary years total, %) d. Demographic Factor = Life Expectancy 2. GDP per capita – value of the total output of goods and services produced in a year divided by the number of people a. $15/hour in MDCs vs. $2/hour in LDCs b. 18 countries with per capita GDP lower than $1000; 15 in Africa c. Some progress in LDCs: $800 in 1990 to $4400 in 2005; 450% increase 3. Misleading? US per capita GDP = $40, 000 but 1/8 live in poverty
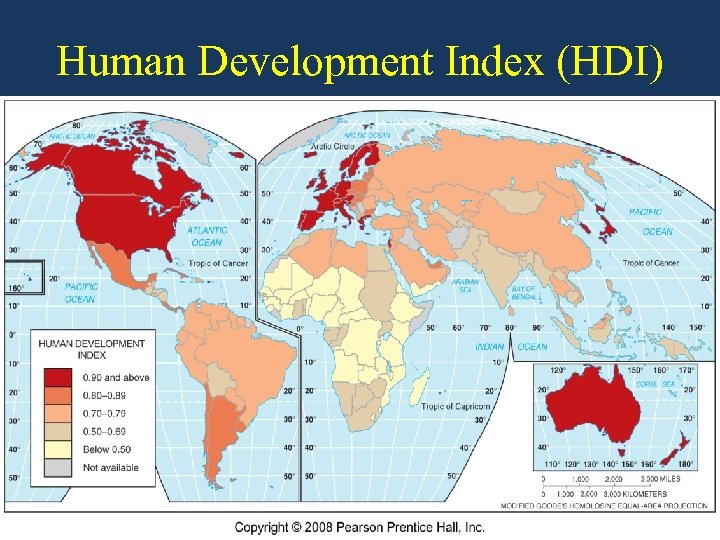 Human Development Index (HDI)
Human Development Index (HDI)
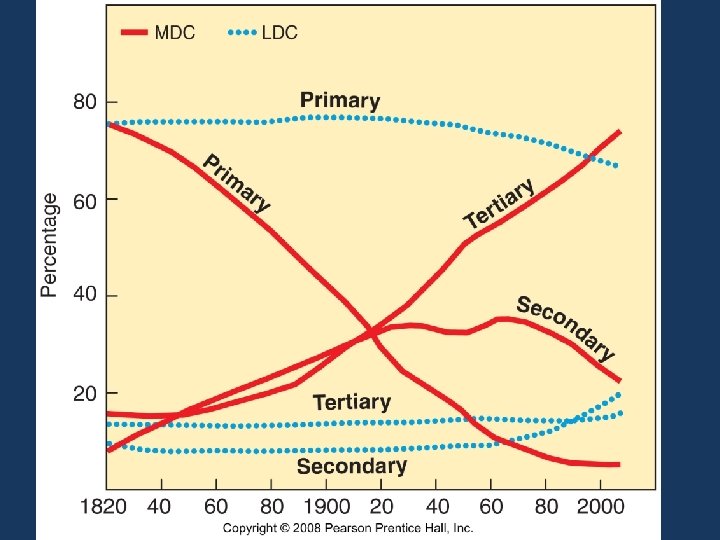
 Types of Jobs 1. Primary – extract materials from the Earth – agriculture, mining, fishing, etc. 2. Secondary – manufacturing, assemble raw materials into consumer goods 3. Tertiary – selling consumer goods – retail, banking, law, education, government 4. LDCs – 60+% in agriculture; 5% in MDCs a. Low primary sector means low number of farmers can produce enough food 5. MDCs – primary and secondary jobs have decreased, tertiary has increased a. Continues to increase for demand of goods and services
Types of Jobs 1. Primary – extract materials from the Earth – agriculture, mining, fishing, etc. 2. Secondary – manufacturing, assemble raw materials into consumer goods 3. Tertiary – selling consumer goods – retail, banking, law, education, government 4. LDCs – 60+% in agriculture; 5% in MDCs a. Low primary sector means low number of farmers can produce enough food 5. MDCs – primary and secondary jobs have decreased, tertiary has increased a. Continues to increase for demand of goods and services
 Consumer Goods 1. Wealth in MDCs purchases goods and services – transportation, communication a. Automobile provide access to jobs and services b. Automobile distribute products c. Telephones enhance interaction with suppliers and customers d. Computers facilitate sharing info with suppliers and customers 2. Greater exposure means MDCs have more cultural diversity than LDCs 3. Ironically, cell phone ownership is higher in LDCs
Consumer Goods 1. Wealth in MDCs purchases goods and services – transportation, communication a. Automobile provide access to jobs and services b. Automobile distribute products c. Telephones enhance interaction with suppliers and customers d. Computers facilitate sharing info with suppliers and customers 2. Greater exposure means MDCs have more cultural diversity than LDCs 3. Ironically, cell phone ownership is higher in LDCs
 Social Indicators of Development 1. MDCs use their wealth to build schools, hospitals, welfare services, etc. a. MDCs are better educated, healthier, and better protected b. As such, the population can be more economically productive 2. The higher the development the better the education a. Measured in student/teacher ratio and literacy rate b. MDCs = 10 years of school vs. 2 in LDCs c. Student/teacher ratio is double in LDCs 3. Health care expenditures – 8% of GDP in MDCs vs. 6% in LDCs a. More money means more hospitals, doctors, and nurses b. Many countries provide health care at no cost c. US actually resembles LDCs in individual costs 4. MDCs also provide help to elderly, sick, poor, disabled, orphaned, veterans, widows, single parents, or unemployed 5. MDCs may need to increase taxes to keep, though
Social Indicators of Development 1. MDCs use their wealth to build schools, hospitals, welfare services, etc. a. MDCs are better educated, healthier, and better protected b. As such, the population can be more economically productive 2. The higher the development the better the education a. Measured in student/teacher ratio and literacy rate b. MDCs = 10 years of school vs. 2 in LDCs c. Student/teacher ratio is double in LDCs 3. Health care expenditures – 8% of GDP in MDCs vs. 6% in LDCs a. More money means more hospitals, doctors, and nurses b. Many countries provide health care at no cost c. US actually resembles LDCs in individual costs 4. MDCs also provide help to elderly, sick, poor, disabled, orphaned, veterans, widows, single parents, or unemployed 5. MDCs may need to increase taxes to keep, though
 Demographic Indicators of Development 1. Life Expectancy – avg. number of years are infant can expect to live at current mortality rates a. MDCs mid 70’s; LDCs early 40’s 2. Infant Mortality – MDCs >1%; LDCs 6% 3. Natural Increase Rate (NIR) – LDCs = 1. 5%; MDCs = 1/10 of 1% a. Means they building new schools, etc. instead of building better for existing pop. 4. Crude Birth Rate (CBR) - LDCs = 24 per 1, 000; MDCs 11 per l, 000 5. CDR does not indicate society’s level of development a. Diffusion of medical technology b. MDCs hive older populations
Demographic Indicators of Development 1. Life Expectancy – avg. number of years are infant can expect to live at current mortality rates a. MDCs mid 70’s; LDCs early 40’s 2. Infant Mortality – MDCs >1%; LDCs 6% 3. Natural Increase Rate (NIR) – LDCs = 1. 5%; MDCs = 1/10 of 1% a. Means they building new schools, etc. instead of building better for existing pop. 4. Crude Birth Rate (CBR) - LDCs = 24 per 1, 000; MDCs 11 per l, 000 5. CDR does not indicate society’s level of development a. Diffusion of medical technology b. MDCs hive older populations
 Key Issue 2: Where Are More and Less Developed Countries Distributed? Anglo-America (HDI 0. 94) Western Europe (HDI 0. 93) Japan (HDI 0. 94) Eastern Europe (HDI 0. 80) Latin America (HDI 0. 80) East Asia (HDI 0. 76) Middle East (HDI 0. 68) Southeast Asia (HDI 0. 58)
Key Issue 2: Where Are More and Less Developed Countries Distributed? Anglo-America (HDI 0. 94) Western Europe (HDI 0. 93) Japan (HDI 0. 94) Eastern Europe (HDI 0. 80) Latin America (HDI 0. 80) East Asia (HDI 0. 76) Middle East (HDI 0. 68) Southeast Asia (HDI 0. 58)
 Key Issue 3: Where Does Level of Development Vary by Gender? Gender-Related Development Index 1. The U. N hasn’t found a single country where women are treated as well as men 2. Gender-Related Development (GDI) – same formula as HDI adjusted for gender 3. GDI penalizes a country for large disparities between men and women a. Norway is the highest at 0. 96
Key Issue 3: Where Does Level of Development Vary by Gender? Gender-Related Development Index 1. The U. N hasn’t found a single country where women are treated as well as men 2. Gender-Related Development (GDI) – same formula as HDI adjusted for gender 3. GDI penalizes a country for large disparities between men and women a. Norway is the highest at 0. 96
 Key Issue 4: Why Do Less Developed Countries Face Obstacles to Development? 1. Looking much better for LDCs: a. IMR down from 85 to 60 b. NIR down from 2. 1 to 1. 5 c. PCI up from $500 to $4, 500 2. 1/5 of people living in MDCs consume 5/6 of world’s goods a. 14% of people live in Africa but consume 1% 3. Americans spend more on cosmetics than the cost of providing 2 billion kids schools 4. Europeans spend more on ice cream than the cost to provide 2 billion toilets 5. Two problems for LDCs – funding and policy to promote development
Key Issue 4: Why Do Less Developed Countries Face Obstacles to Development? 1. Looking much better for LDCs: a. IMR down from 85 to 60 b. NIR down from 2. 1 to 1. 5 c. PCI up from $500 to $4, 500 2. 1/5 of people living in MDCs consume 5/6 of world’s goods a. 14% of people live in Africa but consume 1% 3. Americans spend more on cosmetics than the cost of providing 2 billion kids schools 4. Europeans spend more on ice cream than the cost to provide 2 billion toilets 5. Two problems for LDCs – funding and policy to promote development


