71d41b2d08af64d6013d2c79bc4eaca5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
Chapter 48. Nervous System AP Biology 3/16/2018

Why do animals need a nervous system? Remember to think about the bunny… AP Biology 3/16/2018

What characteristics do animals need in a nervous system? § fast § accurate § reset quickly Poor bunny! AP Biology 3/16/2018
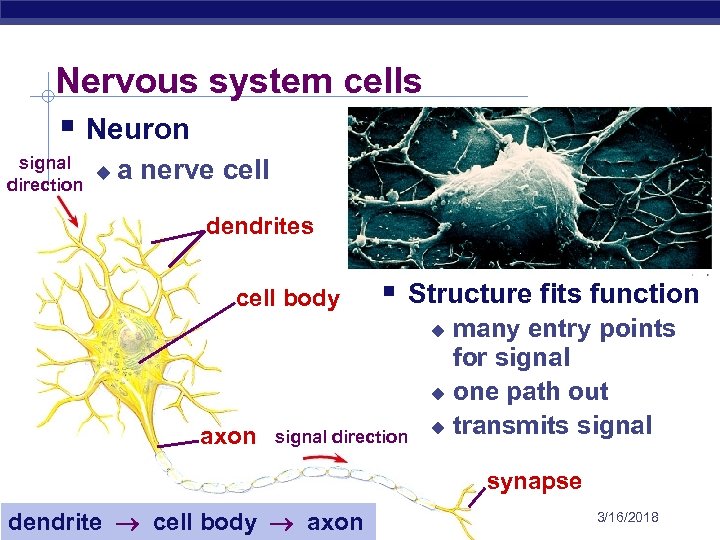
Nervous system cells § Neuron signal u direction a nerve cell dendrites cell body § Structure fits function many entry points for signal u one path out u transmits signal u axon signal direction synapse AP Biology dendrite cell body axon 3/16/2018
Transmission of a signal § How is a signal transmitted down neuron? Think Dominoes! AP Biology 3/16/2018

Transmission of a signal § Dominoes u start the signal § knock down line of dominoes by tipping 1 st one send message u propagate the signal § do dominoes move down the line? no, just a wave through them! u re-set the system § before you can do it again, have to set up dominoes again reset the axon AP Biology 3/16/2018

Transmission of a nerve signal § Neuron has similar system channels are set up u once 1 st is opened, the rest open in succession u § all or nothing response an action travels along neuron u have to re-set channels so neuron can react again u AP Biology 3/16/2018
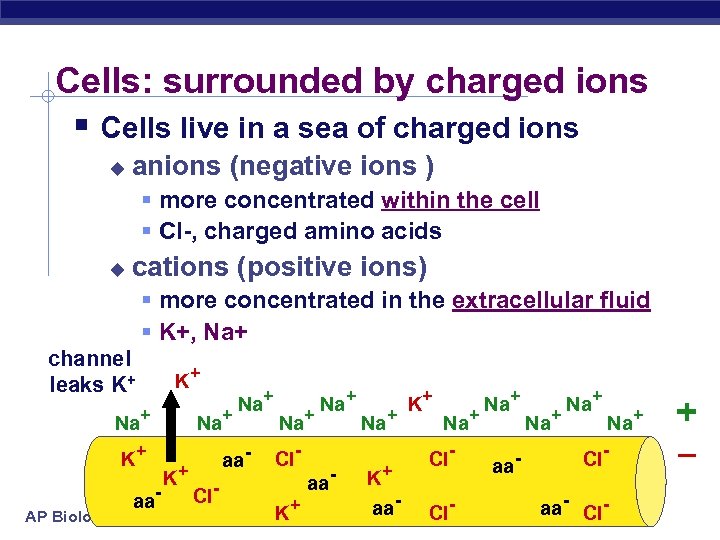
Cells: surrounded by charged ions § Cells live in a sea of charged ions u anions (negative ions ) § more concentrated within the cell § Cl-, charged amino acids u cations (positive ions) § more concentrated in the extracellular fluid § K+, Na+ K+ AP Biology aa- Na+ K+ Na+ aa. Cl- Na+ Cl. K+ Na+ aa- Na+ K+ aa- K+ Na+ Cl. Cl- Na+ aa- Na+ Na+ Claa- Cl 3/16/2018 – K+ + channel leaks K+

Cells have voltage! § Opposite charges on opposite sides of cell membrane u membrane is polarized § negative inside; positive outside § charge gradient § stored energy (like a battery) + + + + – – – – – – – + + + + AP Biology 3/16/2018
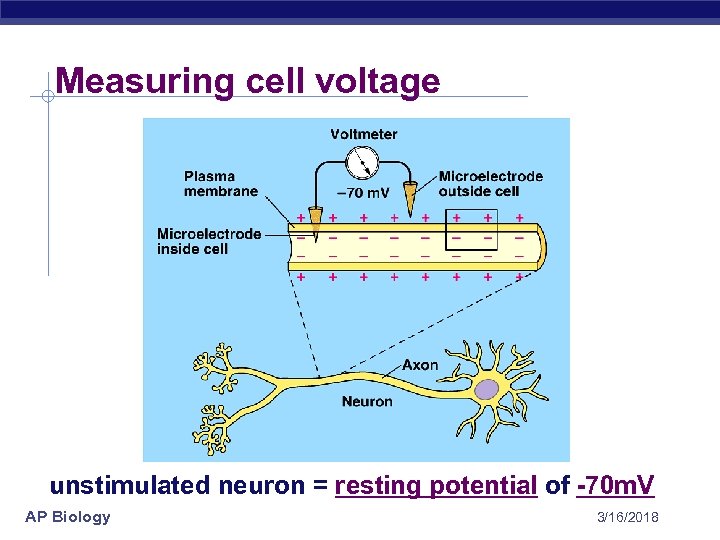
Measuring cell voltage unstimulated neuron = resting potential of -70 m. V AP Biology 3/16/2018
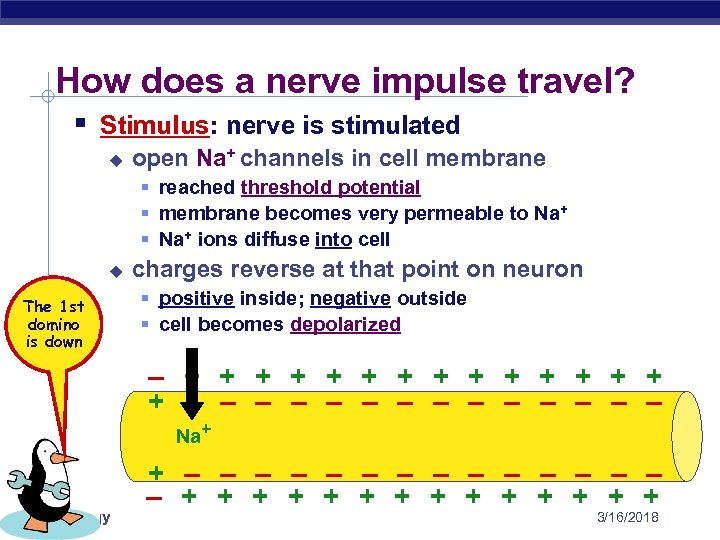
How does a nerve impulse travel? § Stimulus: nerve is stimulated u open Na+ channels in cell membrane § reached threshold potential § membrane becomes very permeable to Na+ § Na+ ions diffuse into cell u The 1 st domino is down charges reverse at that point on neuron § positive inside; negative outside § cell becomes depolarized – + + + + – – – – Na+ AP Biology + – – – – + + + + 3/16/2018
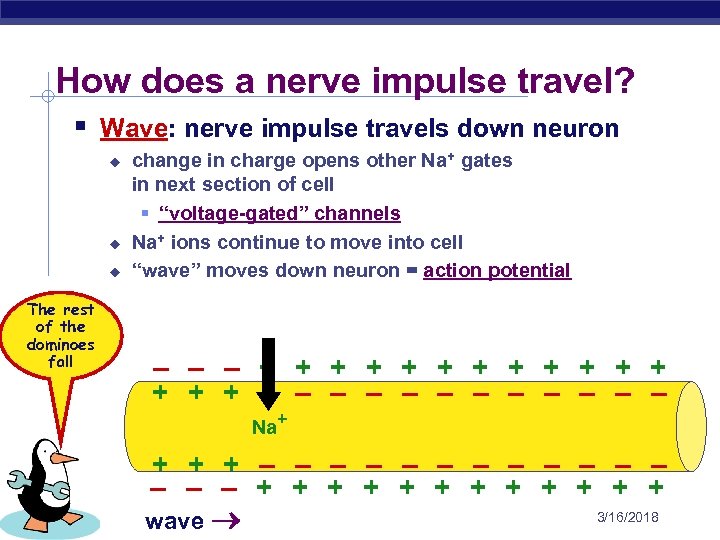
How does a nerve impulse travel? § Wave: nerve impulse travels down neuron u u u The rest of the dominoes fall change in charge opens other Na+ gates in next section of cell § “voltage-gated” channels Na+ ions continue to move into cell “wave” moves down neuron = action potential – – – + + + + – – – Na+ + – – – – + + + AP Biology wave 3/16/2018
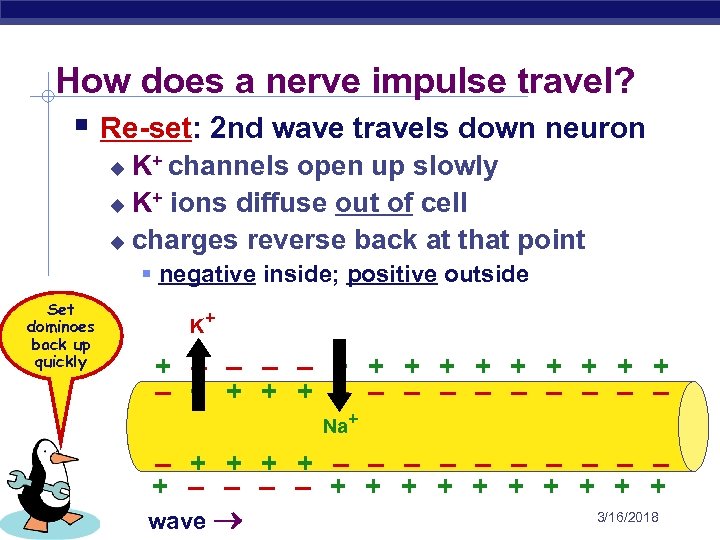
How does a nerve impulse travel? § Re-set: 2 nd wave travels down neuron K+ channels open up slowly u K+ ions diffuse out of cell u charges reverse back at that point u § negative inside; positive outside Set dominoes back up quickly K+ + – – + + + + + – – – – – Na+ – + + – – – – – + + + + + AP Biology wave 3/16/2018
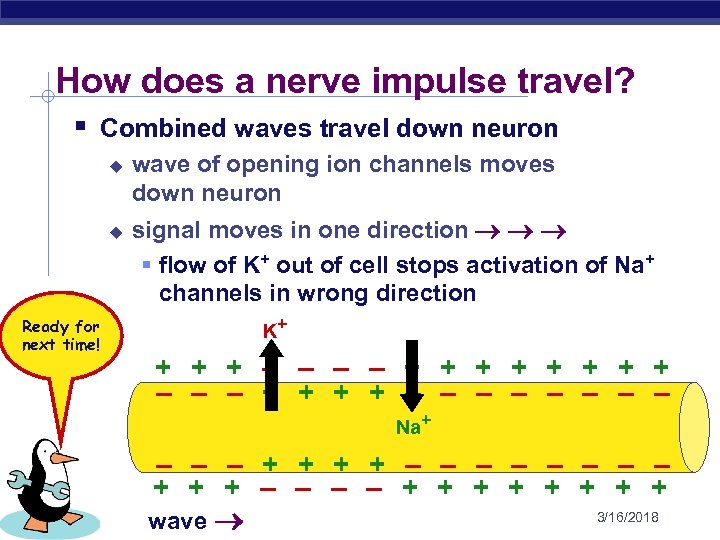
How does a nerve impulse travel? § Combined waves travel down neuron u u Ready for next time! wave of opening ion channels moves down neuron signal moves in one direction § flow of K+ out of cell stops activation of Na+ channels in wrong direction K+ + – – + + + + – – – – Na+ – – – + + – – – – + + + + AP Biology wave 3/16/2018
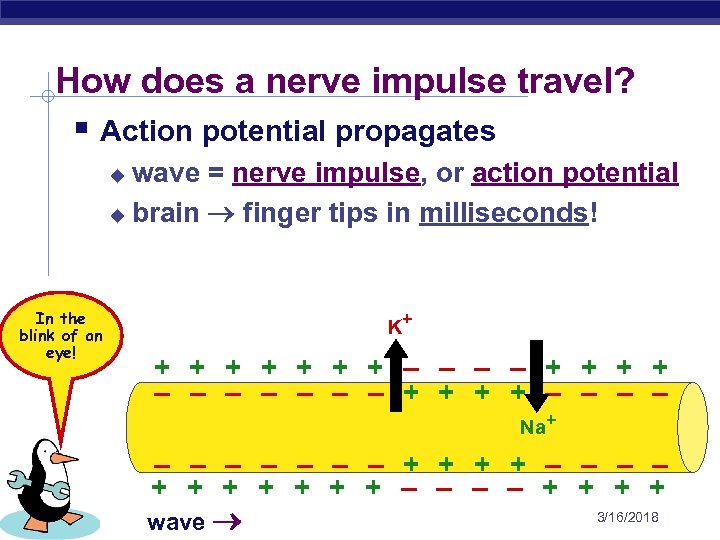
How does a nerve impulse travel? § Action potential propagates wave = nerve impulse, or action potential u brain finger tips in milliseconds! u In the blink of an eye! K+ + + + – – – – Na+ – – – – + + + + AP Biology wave 3/16/2018
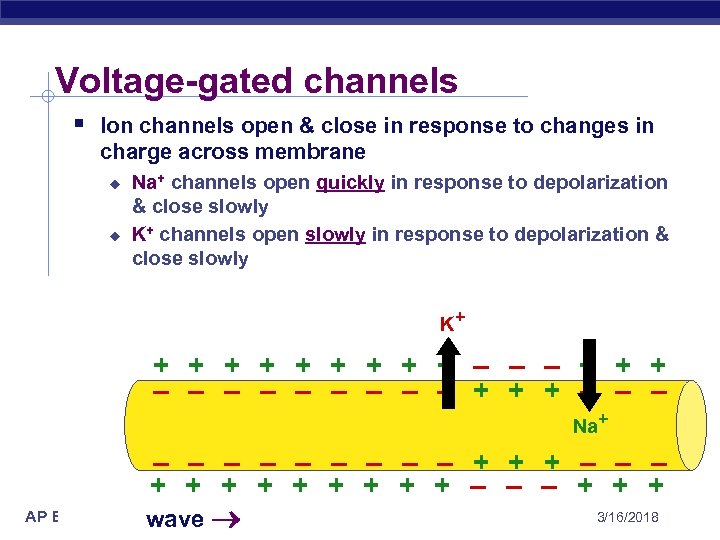
Voltage-gated channels § Ion channels open & close in response to changes in charge across membrane u u Na+ channels open quickly in response to depolarization & close slowly K+ channels open slowly in response to depolarization & close slowly K+ + + + + – – – – – + + + – – – Na+ – – – – – + + + + + – – – + + + AP Biology wave 3/16/2018
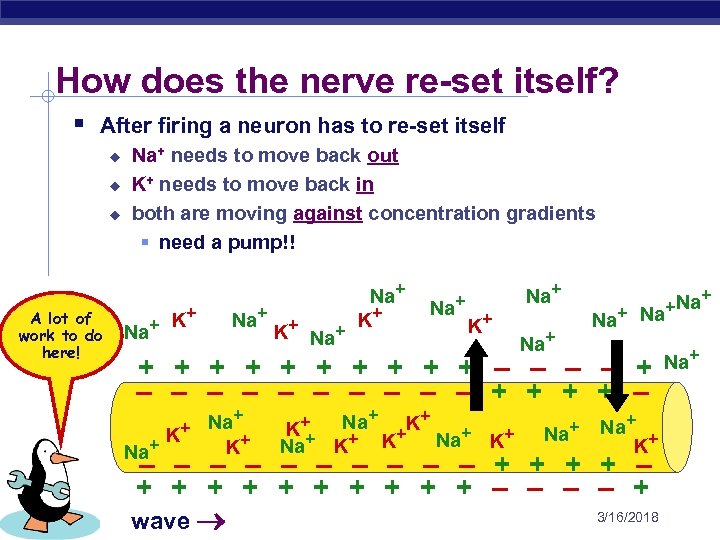
How does the nerve re-set itself? § After firing a neuron has to re-set itself u u u A lot of work to do here! Na+ needs to move back out K+ needs to move back in both are moving against concentration gradients § need a pump!! + + K Na Na+ + K+ K Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na + + + + + – – – – – + + Na +K K+ Na+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ Na K Na+ K+ – – – – – + + + + + – – + AP Biology wave 3/16/2018 Na+ +
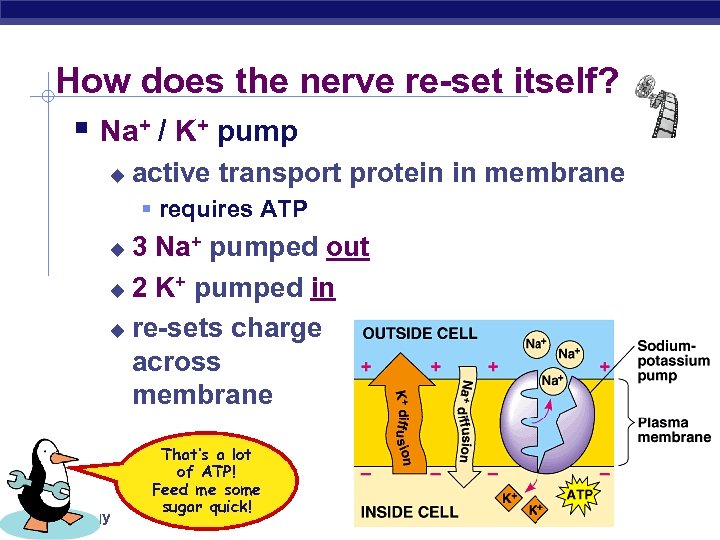
How does the nerve re-set itself? § Na+ / K+ pump u active transport protein in membrane § requires ATP 3 Na+ pumped out u 2 K+ pumped in u re-sets charge across membrane u AP Biology That’s a lot of ATP! Feed me some sugar quick! 3/16/2018
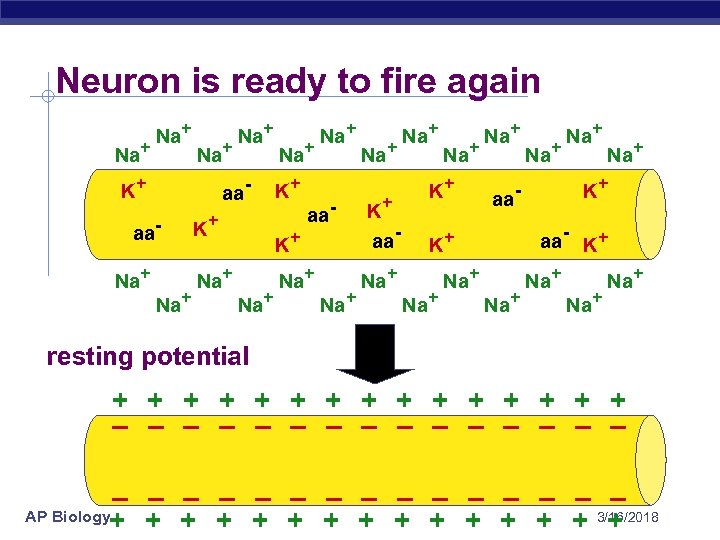
Neuron is ready to fire again Na+ Na+ K+ aa- aa. Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ aa- K+ Na+ Na+ K+ aa. Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ aa- K+ K+ Na+ Na+ resting potential + + + + – – – – – – – – AP Biology + + + + 3/16/2018 +
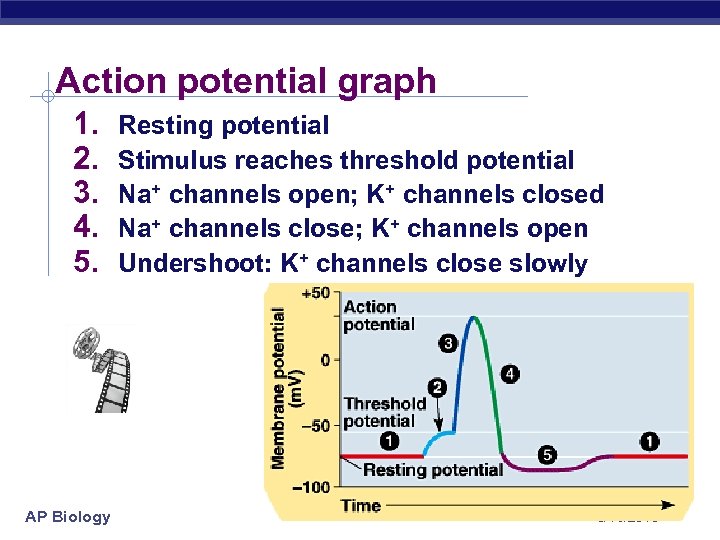
Action potential graph 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. AP Biology Resting potential Stimulus reaches threshold potential Na+ channels open; K+ channels closed Na+ channels close; K+ channels open Undershoot: K+ channels close slowly 3/16/2018

In a nutshell: AP Biology 3/16/2018
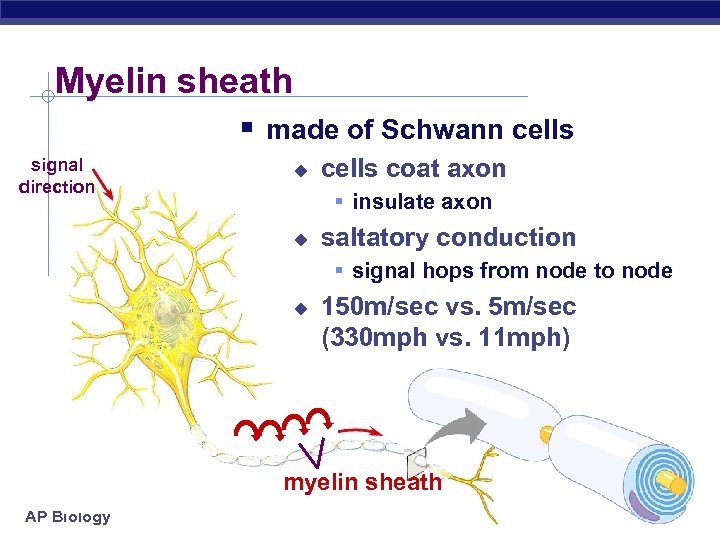
Myelin sheath § made of Schwann cells signal direction u cells coat axon § insulate axon u saltatory conduction § signal hops from node to node u 150 m/sec vs. 5 m/sec (330 mph vs. 11 mph) myelin sheath AP Biology 3/16/2018
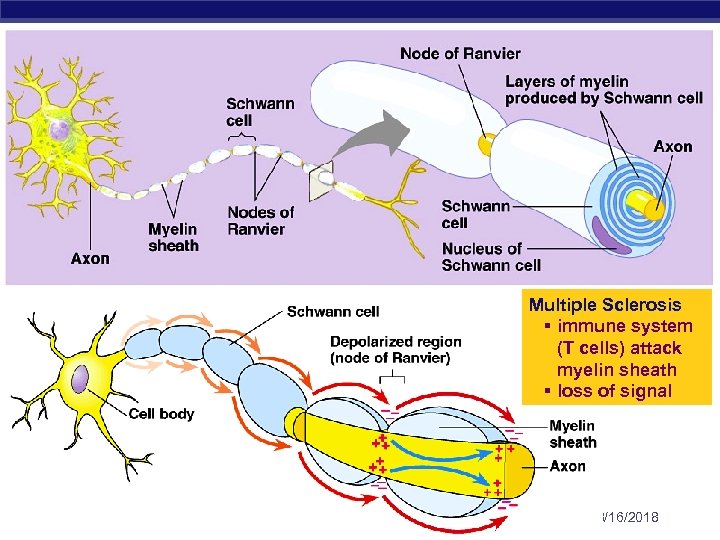
Multiple Sclerosis § immune system (T cells) attack myelin sheath § loss of signal AP Biology 3/16/2018

What happens at the end of the axon? Impulse has to jump the synapse! u u junction between neurons has to jump quickly from one cell to next How does the wave jump the gap? Synapse AP Biology 3/16/2018
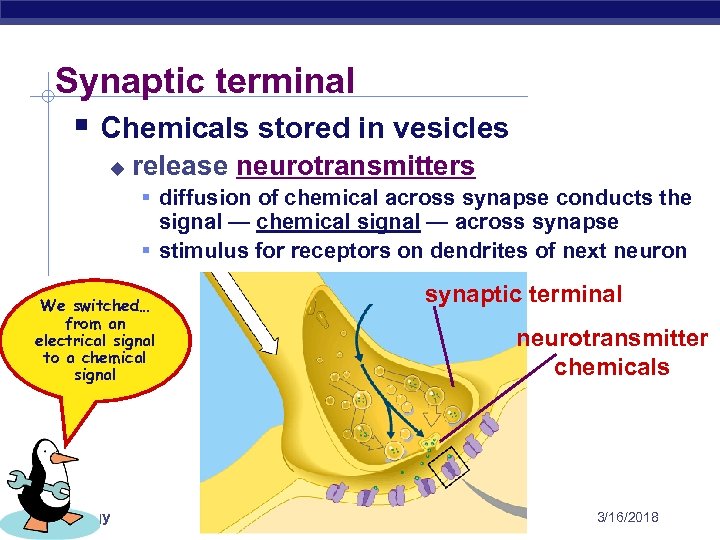
Synaptic terminal § Chemicals stored in vesicles u release neurotransmitters § diffusion of chemical across synapse conducts the signal — chemical signal — across synapse § stimulus for receptors on dendrites of next neuron We switched… from an electrical signal to a chemical signal AP Biology synaptic terminal neurotransmitter chemicals 3/16/2018
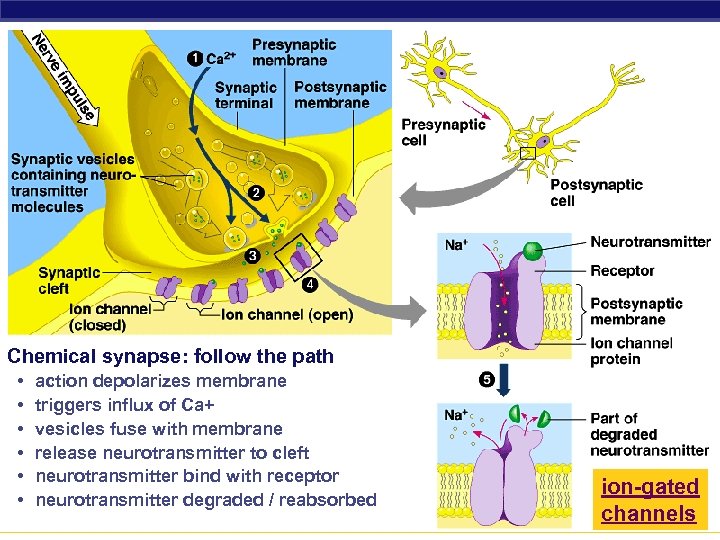
Chemical synapse: follow the path • • • action depolarizes membrane triggers influx of Ca+ vesicles fuse with membrane release neurotransmitter to cleft neurotransmitter bind with receptor neurotransmitter degraded / reabsorbed AP Biology ion-gated channels 3/16/2018
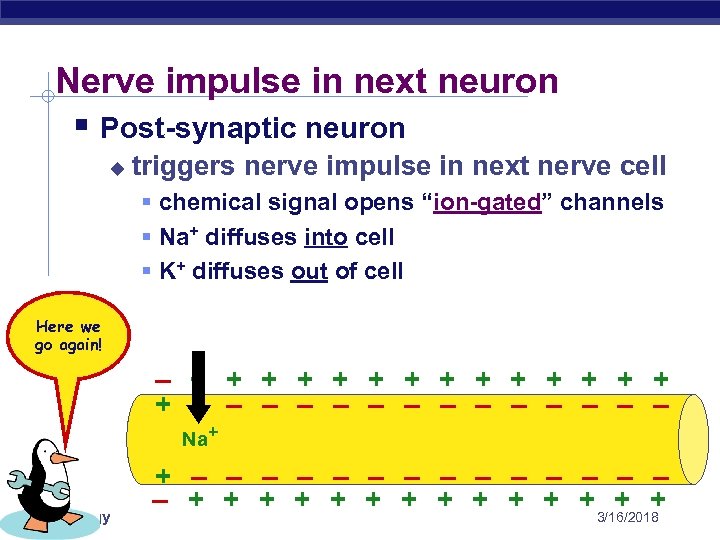
Nerve impulse in next neuron § Post-synaptic neuron u triggers nerve impulse in next nerve cell § chemical signal opens “ion-gated” channels § Na+ diffuses into cell § K+ diffuses out of cell Here we go again! – + + + + – – – – Na+ AP Biology + – – – – + + + 3/16/2018 + +

Again, in summary: AP Biology 3/16/2018
AP Biology 3/16/2018

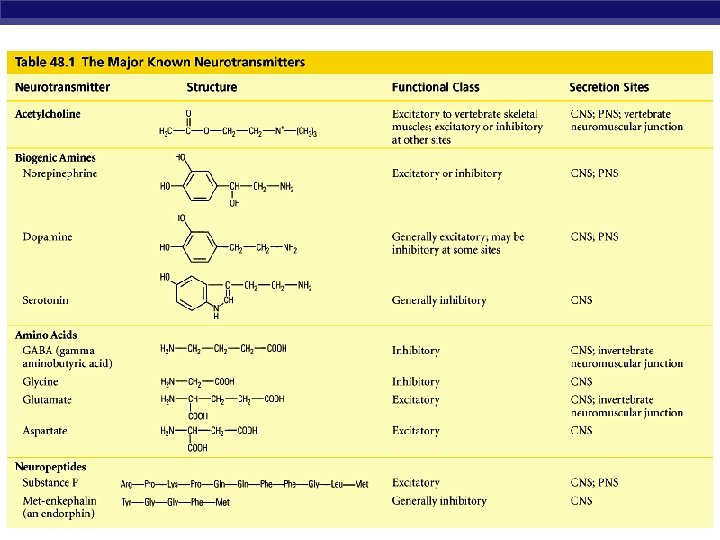
Neurotransmitters § Acetylcholine u transmit signal to skeletal muscle § Epinephrine (adrenaline) & norepinephrine u fight-or-flight response § Dopamine u u widespread in brain affects sleep, mood, attention & learning lack of dopamine in brain associated with Parkinson’s disease excessive dopamine linked to schizophrenia § Serotonin u AP Biologyu widespread in brain affects sleep, mood, attention & learning 3/16/2018

Neurotransmitters § Weak point of nervous system u any substance that affects neurotransmitters or mimics them affects nerve function § gases: nitric oxide, carbon monoxide § mood altering drugs: w stimulants n amphetamines, caffeine, nicotine w depressants § hallucinogenic drugs § Prozac § poisons AP Biology 3/16/2018
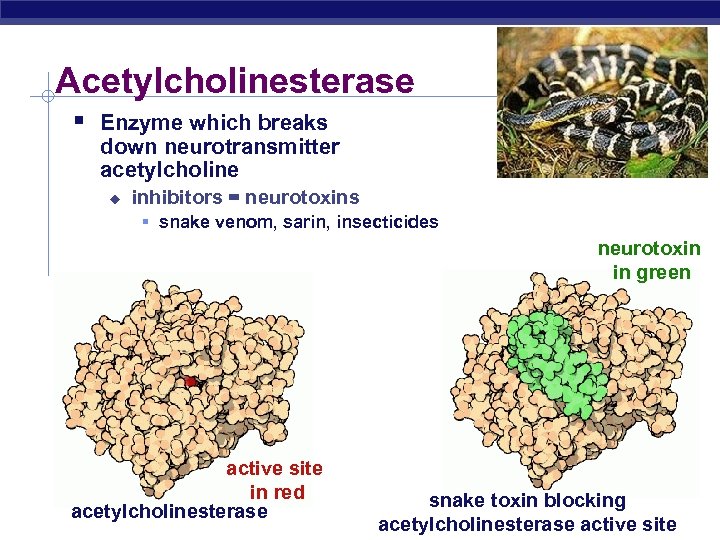
Acetylcholinesterase § Enzyme which breaks down neurotransmitter acetylcholine u inhibitors = neurotoxins § snake venom, sarin, insecticides neurotoxin in green active site in red acetylcholinesterase AP Biology snake toxin blocking 3/16/2018 acetylcholinesterase active site
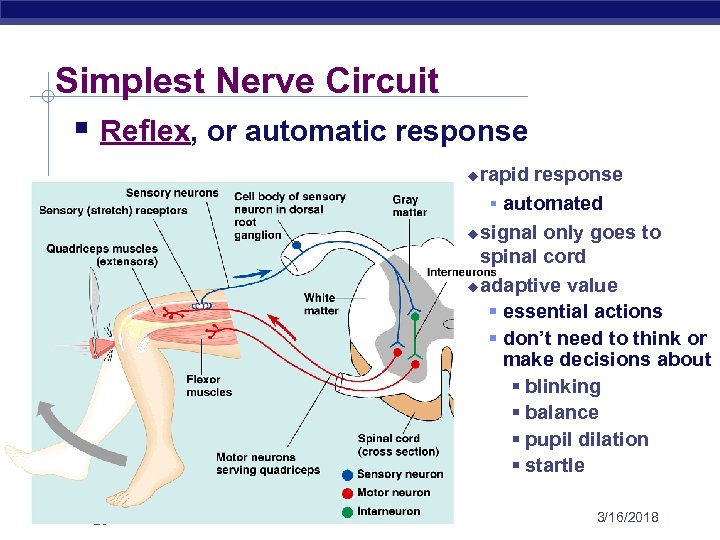
Simplest Nerve Circuit § Reflex, or automatic response rapid response § automated u signal only goes to spinal cord u adaptive value § essential actions § don’t need to think or make decisions about § blinking § balance § pupil dilation § startle u AP Biology 3/16/2018

Any Questions? ? AP Biology 3/16/2018
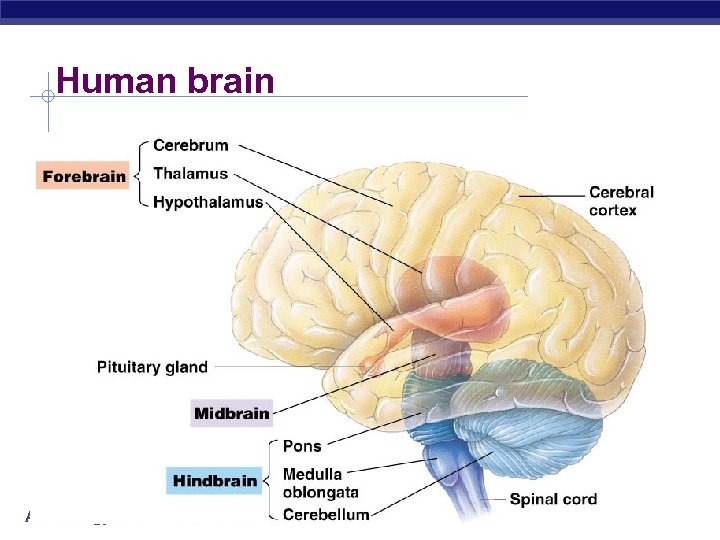
Human brain AP Biology 3/16/2018

Evolutionary older structures § Evolutionary older structures of the brain regulate essential autonomic & integrative functions u brainstem § pons § medulla oblongata § midbrain cerebellum u thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus u AP Biology 3/16/2018
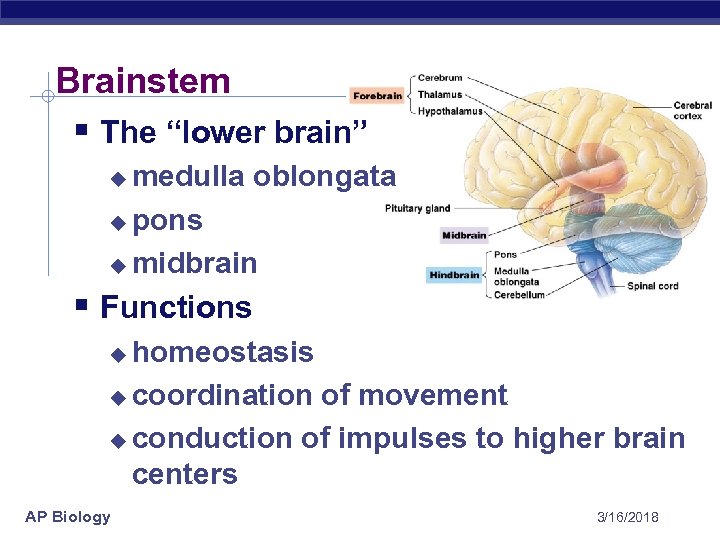
Brainstem § The “lower brain” medulla oblongata u pons u midbrain u § Functions homeostasis u coordination of movement u conduction of impulses to higher brain centers u AP Biology 3/16/2018

Medulla oblongata & Pons § Controls autonomic homeostatic functions breathing u heart & blood vessel activity u swallowing u vomiting u digestion u § Relays information to & from higher brain centers AP Biology 3/16/2018
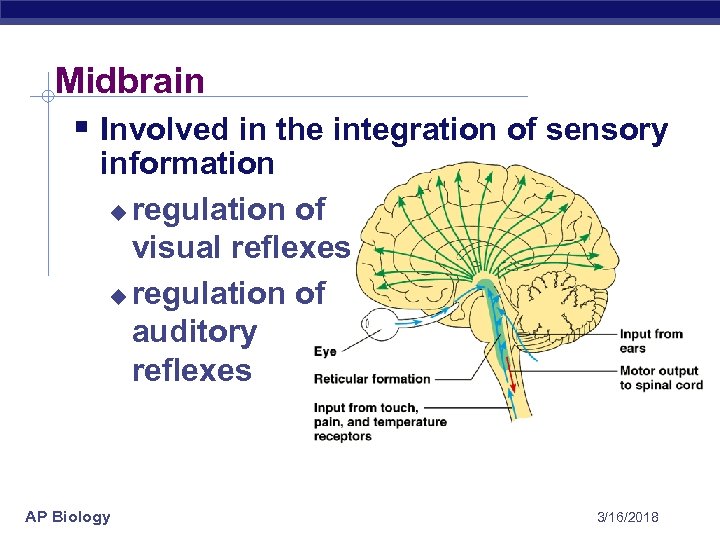
Midbrain § Involved in the integration of sensory information u regulation of visual reflexes u regulation of auditory reflexes AP Biology 3/16/2018
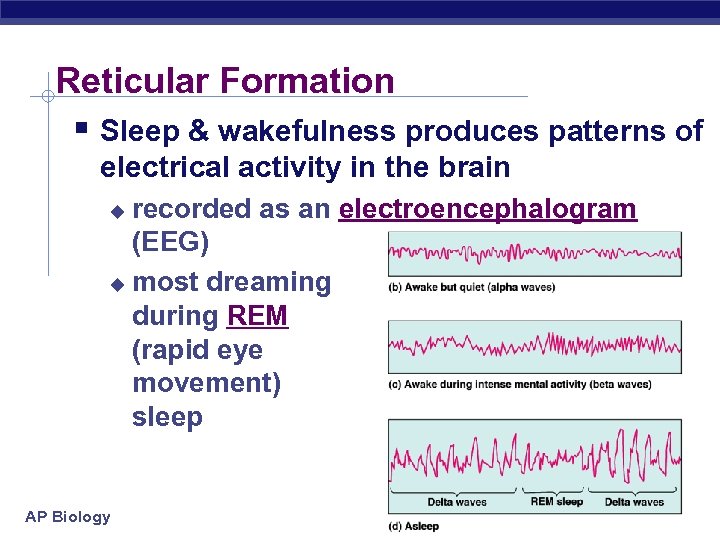
Reticular Formation § Sleep & wakefulness produces patterns of electrical activity in the brain recorded as an electroencephalogram (EEG) u most dreaming during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep u AP Biology 3/16/2018
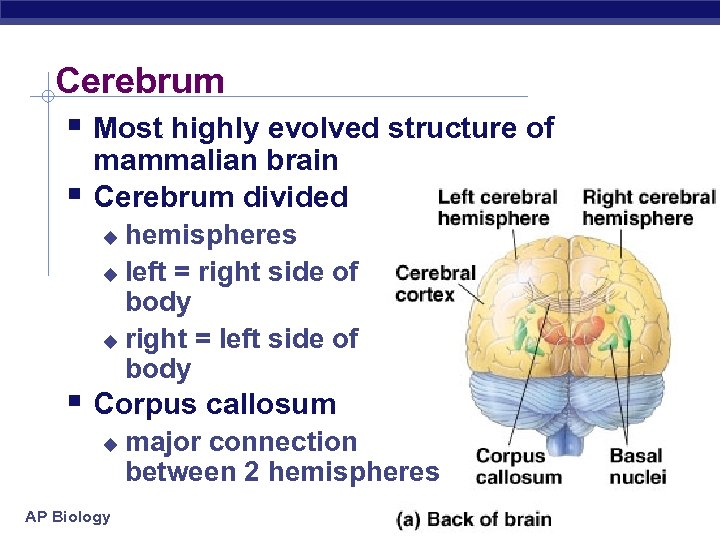
Cerebrum § Most highly evolved structure of § mammalian brain Cerebrum divided hemispheres u left = right side of body u right = left side of body u § Corpus callosum u AP Biology major connection between 2 hemispheres 3/16/2018
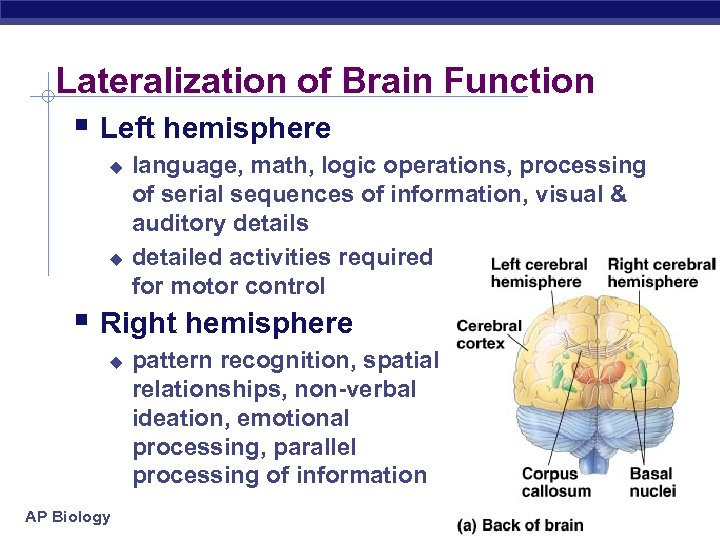
Lateralization of Brain Function § Left hemisphere u u language, math, logic operations, processing of serial sequences of information, visual & auditory details detailed activities required for motor control § Right hemisphere u AP Biology pattern recognition, spatial relationships, non-verbal ideation, emotional processing, parallel processing of information 3/16/2018
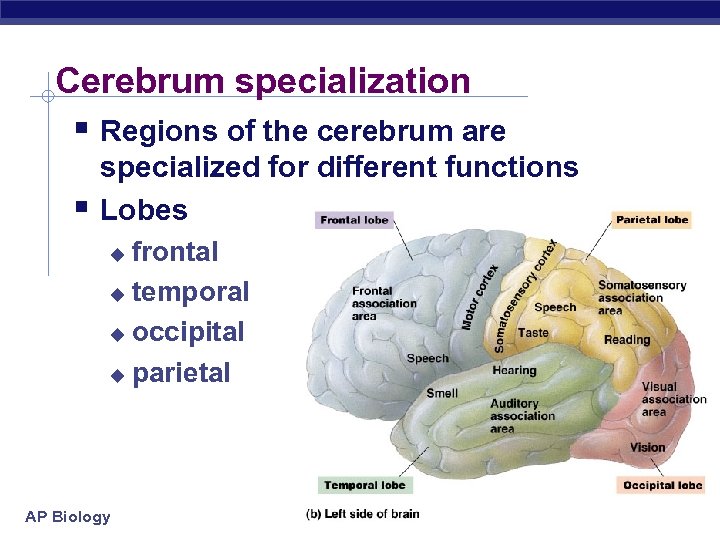
Cerebrum specialization § Regions of the cerebrum are § specialized for different functions Lobes frontal u temporal u occipital u parietal u AP Biology 3/16/2018
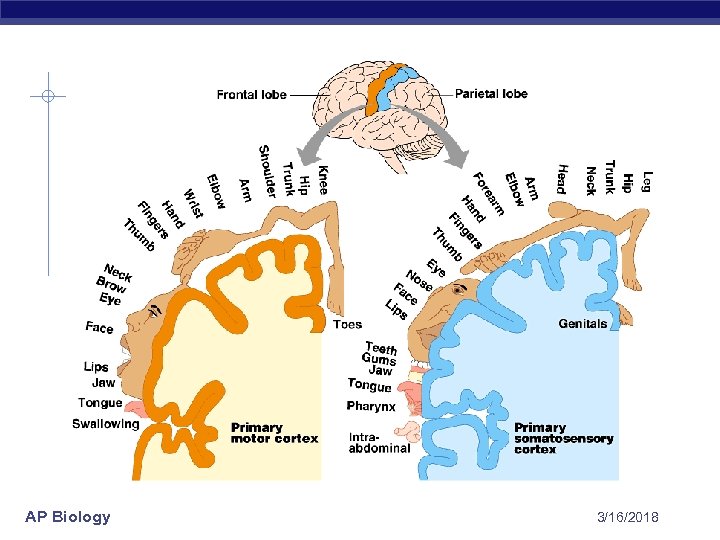
AP Biology 3/16/2018
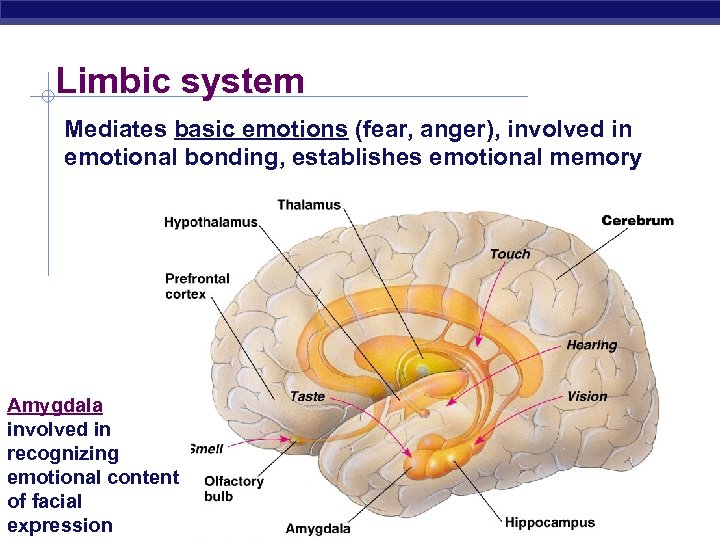
Limbic system Mediates basic emotions (fear, anger), involved in emotional bonding, establishes emotional memory Amygdala involved in recognizing emotional content of facial AP Biology expression 3/16/2018

Any Questions? ? AP Biology 3/16/2018
71d41b2d08af64d6013d2c79bc4eaca5.ppt