1894799d2c6d5556e1945cebb2fa7a9c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Chapter 40 The Resurgence of Conservatism, 1980– 1992
Chapter 40 The Resurgence of Conservatism, 1980– 1992
 APUSH ‘thinking skills’ HISTORICAL CAUSATION PATTERNS OF CONTINUITY AND CHANGE PERIODIZATION COMPARISON CONTEXTUALIZATION HISTORICAL ARGUMENTATION APPROPRIATE USE OF HISTORICAL EVIDENCE INTERPRETATION SYNTHESIS
APUSH ‘thinking skills’ HISTORICAL CAUSATION PATTERNS OF CONTINUITY AND CHANGE PERIODIZATION COMPARISON CONTEXTUALIZATION HISTORICAL ARGUMENTATION APPROPRIATE USE OF HISTORICAL EVIDENCE INTERPRETATION SYNTHESIS
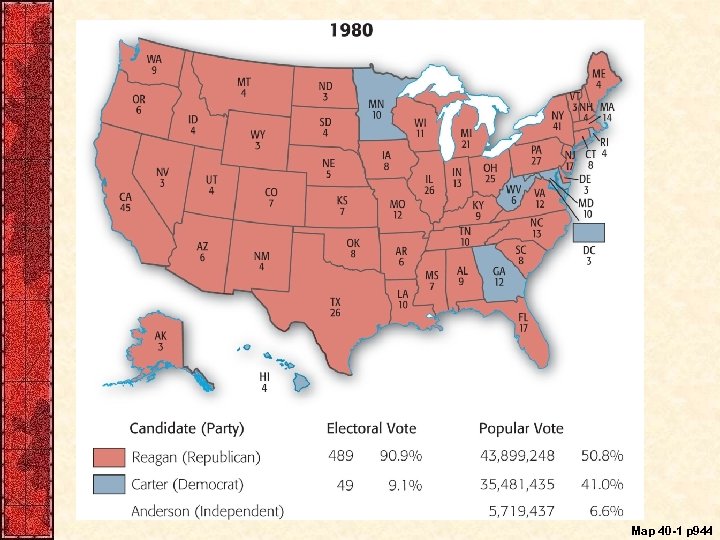
 I. The Election of Ronald Reagan, 1980 • Carter’s administration seen as bungling – Democrats renominated after “ABC” movement • Republican candidate was Ronald Reagan • 1980 Election results – 51% of the popular vote for Reagan, 41% for Carter – Electoral count 489 for Reagan; 49 for Carter – Republicans control Senate (ffirst time since 1954) – Carter’s farewell address • Stressed his effort to scale down the deadly arm race • To promote human rights and to protect the environment – Carter received the Nobel Peace Prize in 2002
I. The Election of Ronald Reagan, 1980 • Carter’s administration seen as bungling – Democrats renominated after “ABC” movement • Republican candidate was Ronald Reagan • 1980 Election results – 51% of the popular vote for Reagan, 41% for Carter – Electoral count 489 for Reagan; 49 for Carter – Republicans control Senate (ffirst time since 1954) – Carter’s farewell address • Stressed his effort to scale down the deadly arm race • To promote human rights and to protect the environment – Carter received the Nobel Peace Prize in 2002
 I. The Election of Ronald Reagan, 1980 (con’t) • Reagan’s philosophy – During campaign attacked ‘big government’ – Sided with the New Right on social issues – Championed “forgotten man” against big business – Supported “common man” against big government – Condemned federal favoritism for minorities • Questioned welfare programs & affirmative-action policies – Aimed to win over from the Democratic column • Southern & working-class whites (Reagan Democrats) – Drew on the ideas of the “neoconservatives” • Wanted free-market liberated from government restraints
I. The Election of Ronald Reagan, 1980 (con’t) • Reagan’s philosophy – During campaign attacked ‘big government’ – Sided with the New Right on social issues – Championed “forgotten man” against big business – Supported “common man” against big government – Condemned federal favoritism for minorities • Questioned welfare programs & affirmative-action policies – Aimed to win over from the Democratic column • Southern & working-class whites (Reagan Democrats) – Drew on the ideas of the “neoconservatives” • Wanted free-market liberated from government restraints
 p 943
p 943
 Map 40 -1 p 944
Map 40 -1 p 944
 II. The Reagan Revolution • Reagan’s arrival in Washington was triumphal – Devoted to fiscal fitness, leaner federal government – Sought to dismantle the welfare state – Sought to reverse political evolution of government – Assembled a cabinet of “the best and the rightest” – He took dead aim at the bloated federal budget – Found an ally GB Conservative Margaret Thatcher, • Small gov’t kept their nations safer from communism. – Reagan’s proposwed budget • Cut social programs • Increased military spending – Democratic boil weevils supported his plan
II. The Reagan Revolution • Reagan’s arrival in Washington was triumphal – Devoted to fiscal fitness, leaner federal government – Sought to dismantle the welfare state – Sought to reverse political evolution of government – Assembled a cabinet of “the best and the rightest” – He took dead aim at the bloated federal budget – Found an ally GB Conservative Margaret Thatcher, • Small gov’t kept their nations safer from communism. – Reagan’s proposwed budget • Cut social programs • Increased military spending – Democratic boil weevils supported his plan
 p 944
p 944

 III. The Battle of the Budget • Congress accepted Reagan’s budget proposals • Next Reagan proposal- substantial tax cuts – Congress approved a set of far-reaching tax reforms • Lowered individual tax rates, estate taxes • Reaganomics (supply-side economics) – Reagan’s supply-side economics theory • • Stable economy + tax cuts = economic growth Recession, then economic recovery in 1983 Income gaps widened between the richest & poorest Massive military expenditures ($2 trillion dollars) – Federal budget deficits topped $100 billion in 1982
III. The Battle of the Budget • Congress accepted Reagan’s budget proposals • Next Reagan proposal- substantial tax cuts – Congress approved a set of far-reaching tax reforms • Lowered individual tax rates, estate taxes • Reaganomics (supply-side economics) – Reagan’s supply-side economics theory • • Stable economy + tax cuts = economic growth Recession, then economic recovery in 1983 Income gaps widened between the richest & poorest Massive military expenditures ($2 trillion dollars) – Federal budget deficits topped $100 billion in 1982
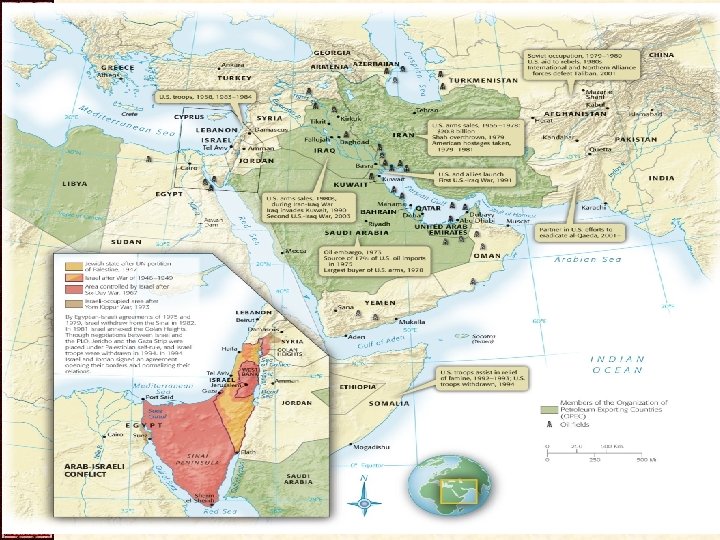
 IV. Reagan Renews the Cold War • Relations with the Soviets were strained – Reagan” USSR=“focus of evil in the modern world” – Enormously expanded U. S. military capabilities • Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI)—popularly “Star Wars” – We supported “Solidarity” movement in Poland – Kremlin inertia – 3 leaders died between 1982 -1985 – USSR downed Korean airliner (Sept 1983) – Arms-control negotiations with Soviets had stopped – 1984 Soviet-bloc athletes boycotted L. A. Olympics
IV. Reagan Renews the Cold War • Relations with the Soviets were strained – Reagan” USSR=“focus of evil in the modern world” – Enormously expanded U. S. military capabilities • Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI)—popularly “Star Wars” – We supported “Solidarity” movement in Poland – Kremlin inertia – 3 leaders died between 1982 -1985 – USSR downed Korean airliner (Sept 1983) – Arms-control negotiations with Soviets had stopped – 1984 Soviet-bloc athletes boycotted L. A. Olympics
 p 946
p 946
 V. Troubles Abroad • Volatile Middle Eastern pot continued to boil – Israel strained its bonds of friendship with U. S. • New settlements established in West Bank (1981 -2) • Israel invaded neighboring Lebanon (June 1982) – US peace keepers attacked (1983) • Central America and the Caribbean – Sandinistas lead successful leftist Nicaragua revolution – Provided covert aid contras and “advisers” to area – Invaded Grenada to stop a revolution (Oct 1983)
V. Troubles Abroad • Volatile Middle Eastern pot continued to boil – Israel strained its bonds of friendship with U. S. • New settlements established in West Bank (1981 -2) • Israel invaded neighboring Lebanon (June 1982) – US peace keepers attacked (1983) • Central America and the Caribbean – Sandinistas lead successful leftist Nicaragua revolution – Provided covert aid contras and “advisers” to area – Invaded Grenada to stop a revolution (Oct 1983)
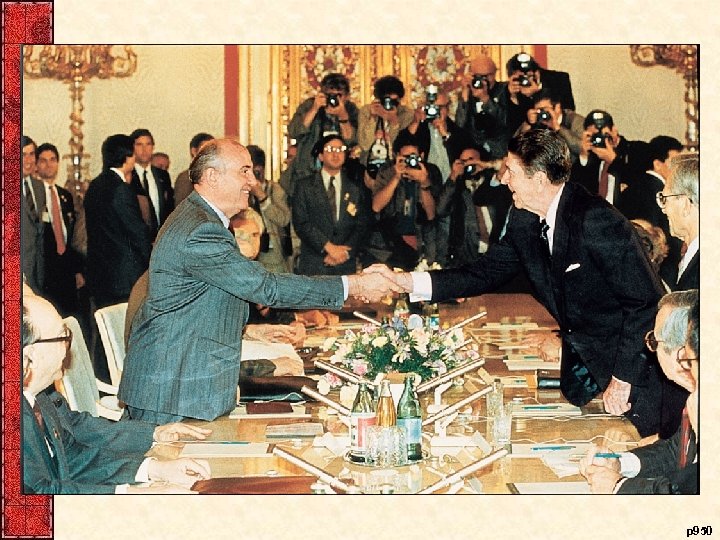
 VI. Round Two for Reagan • Reagan again the candidate for Republicans • Democratic candidate was Walter Mondale • 1984 Election results – Reagan: 525 electoral votes to Mondale 13 – Reagan-52, 609, 797 votes to Mondale-36, 450, 613 • Reagan’s 2 nd term focused on foreign policy – Gorbachev, new charismatic Soviet leader • Glasnost –“openness” and Perestroika—“restructuring” • USSR needed to end cold war to change – Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty (1987 -88) – Other moves in foreign policy by Reagan • Supported democracy in Philippines (1986 -87) • Retaliatory bombing against Libya in (1986)
VI. Round Two for Reagan • Reagan again the candidate for Republicans • Democratic candidate was Walter Mondale • 1984 Election results – Reagan: 525 electoral votes to Mondale 13 – Reagan-52, 609, 797 votes to Mondale-36, 450, 613 • Reagan’s 2 nd term focused on foreign policy – Gorbachev, new charismatic Soviet leader • Glasnost –“openness” and Perestroika—“restructuring” • USSR needed to end cold war to change – Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty (1987 -88) – Other moves in foreign policy by Reagan • Supported democracy in Philippines (1986 -87) • Retaliatory bombing against Libya in (1986)

 p 950
p 950
 VII. The Iran-Contra Imbroglio • Reagan had two major foreign policy problems – American hostages in Lebanon – Left-wing Sandinista government in Nicaragua • The Iran-Contra affair (1986 -88) – U. S. diplomats secretly arranged arms sales to Iran • Iranian money diverted to Nicaraguan rebels (Contras) – Violated a congressional ban on aid to Nicaraguan rebels • The ‘Teflon president’ – Reagan remained very popular and beloved
VII. The Iran-Contra Imbroglio • Reagan had two major foreign policy problems – American hostages in Lebanon – Left-wing Sandinista government in Nicaragua • The Iran-Contra affair (1986 -88) – U. S. diplomats secretly arranged arms sales to Iran • Iranian money diverted to Nicaraguan rebels (Contras) – Violated a congressional ban on aid to Nicaraguan rebels • The ‘Teflon president’ – Reagan remained very popular and beloved
 p 950
p 950
 VIII. Reagan’s Economic Legacy • Reagan vowed to Change America by 1=Rolling back big government • Cut back on government regulations – Trade deficit grew rapidly • Cut back on the ‘welfare state’ – Growing gap between rich and poor 2=Supporting supply-side economics • Lowering taxes (he did) • Balancing the budget (He didn’t) – Decrease in taxes, increase in military spending » $200 billion yearly deficit • Ensured the perpetuation of his political values
VIII. Reagan’s Economic Legacy • Reagan vowed to Change America by 1=Rolling back big government • Cut back on government regulations – Trade deficit grew rapidly • Cut back on the ‘welfare state’ – Growing gap between rich and poor 2=Supporting supply-side economics • Lowering taxes (he did) • Balancing the budget (He didn’t) – Decrease in taxes, increase in military spending » $200 billion yearly deficit • Ensured the perpetuation of his political values
 IX. The Religious Right • 1980 s - religion pervaded American politics – Moral Majority led by Jerry Falwell • Conspicuous coalition of conservative Christians • Aggressive political advocate of conservative causes • Religious right: – Were sometimes called “movement conservatives” – They were a reaction to sixties radicalism • Against sexual permissiveness, abortion, feminism, gays • Emphasized that ‘personal matters’ were political matters • Mirrored the tactics of 1960 s civil disobedience protesters
IX. The Religious Right • 1980 s - religion pervaded American politics – Moral Majority led by Jerry Falwell • Conspicuous coalition of conservative Christians • Aggressive political advocate of conservative causes • Religious right: – Were sometimes called “movement conservatives” – They were a reaction to sixties radicalism • Against sexual permissiveness, abortion, feminism, gays • Emphasized that ‘personal matters’ were political matters • Mirrored the tactics of 1960 s civil disobedience protesters
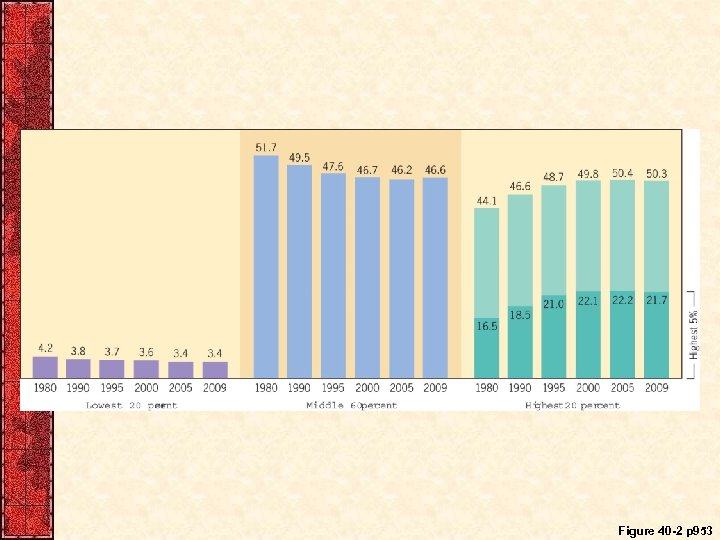 Figure 40 -2 p 953
Figure 40 -2 p 953
 p 953
p 953
 X. Conservatism in the Courts • Reagan’s used courts for “cultural wars” – He named three conservative-minded justices • SCOTUS repudiated affirmative action / abortion – Made it very nard to prove discrimination – Restricted access to abortion
X. Conservatism in the Courts • Reagan’s used courts for “cultural wars” – He named three conservative-minded justices • SCOTUS repudiated affirmative action / abortion – Made it very nard to prove discrimination – Restricted access to abortion
 p 954
p 954
 XI. Referendum on Reaganism in 1988 • Republicans lost control of the Senate in 1986 – Democrats upset at Iran-Contra scandal – Democrats Saving & Loans bailout ($500 b) – Black Monday- stock market plunge (Oct 1987) • 1988 Democrats nominate Michael Dukakis • Republicans nominated VP George H. W. Bush • 1988 Election results – Popular votes Bush 47, 946, 422, Dukakis 41, 016, 429 – Electoral College Bush 426 , Dukakis 111
XI. Referendum on Reaganism in 1988 • Republicans lost control of the Senate in 1986 – Democrats upset at Iran-Contra scandal – Democrats Saving & Loans bailout ($500 b) – Black Monday- stock market plunge (Oct 1987) • 1988 Democrats nominate Michael Dukakis • Republicans nominated VP George H. W. Bush • 1988 Election results – Popular votes Bush 47, 946, 422, Dukakis 41, 016, 429 – Electoral College Bush 426 , Dukakis 111
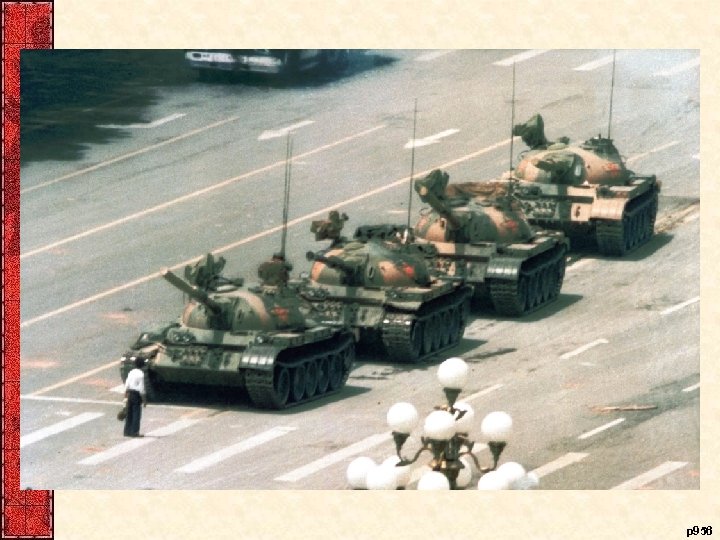
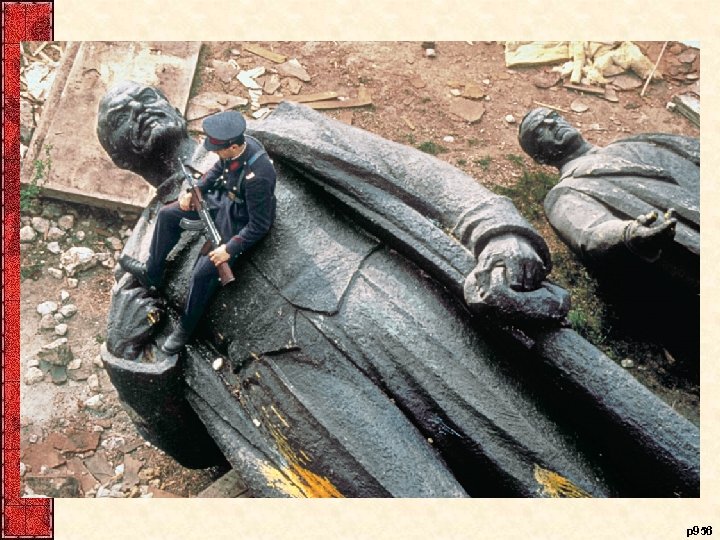
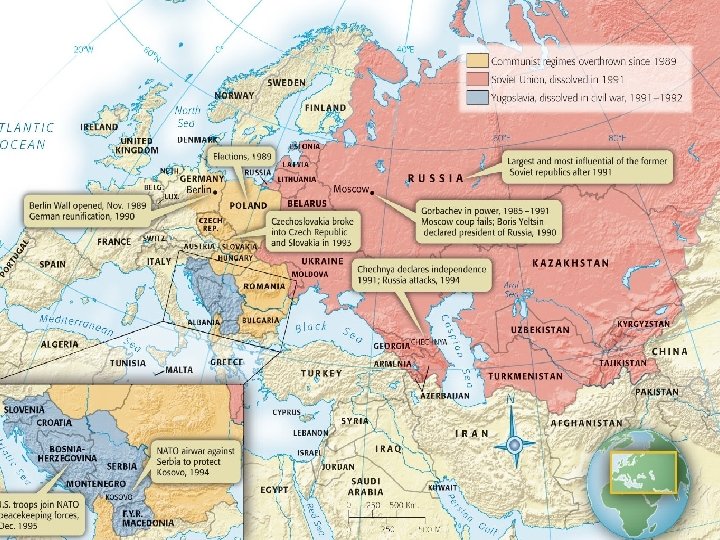
 XII. George H. W. Bush and the End of the Cold War Bush’s deepest commitment was to public service • Democracy worldwide had arrived – China (Spring 1989) • Prodemocracy demonstrations n Tiananmen Square – Eastern Europe (1988 -1992) • Germany’s Berlin Wall opened (Dec 1988) • Poland toppled communist government (Aug 1989) – Then Hungary, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, and Romania • Germany reunited (Oct 1990) – The Soviet Union (1988 -1992) • Failed Coup (Aug 1991), USSR collapses (Jan 1992) – Fifteen republics loosely confederated (CIS) • Many political, military, economic unknowns
XII. George H. W. Bush and the End of the Cold War Bush’s deepest commitment was to public service • Democracy worldwide had arrived – China (Spring 1989) • Prodemocracy demonstrations n Tiananmen Square – Eastern Europe (1988 -1992) • Germany’s Berlin Wall opened (Dec 1988) • Poland toppled communist government (Aug 1989) – Then Hungary, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, and Romania • Germany reunited (Oct 1990) – The Soviet Union (1988 -1992) • Failed Coup (Aug 1991), USSR collapses (Jan 1992) – Fifteen republics loosely confederated (CIS) • Many political, military, economic unknowns
 50 AY utes SS in PE 5 m PO & rd wo Was the “Reagan Revolution” successful?
50 AY utes SS in PE 5 m PO & rd wo Was the “Reagan Revolution” successful?
 p 955
p 955
 p 956
p 956
 p 956
p 956
 p 958
p 958
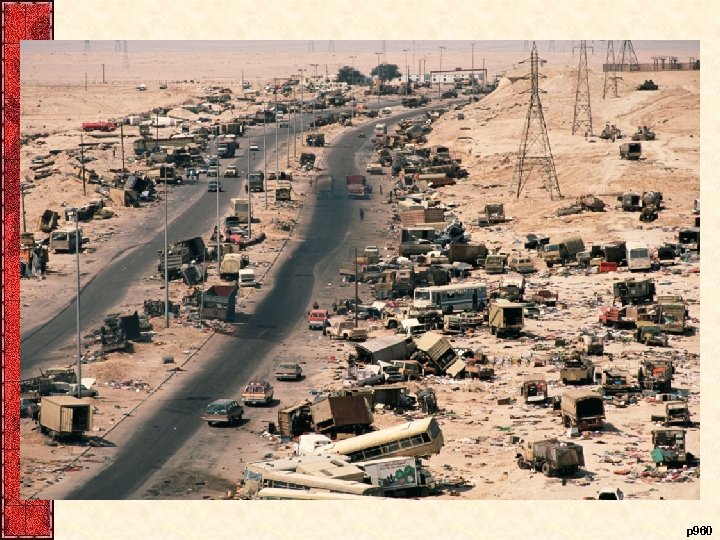
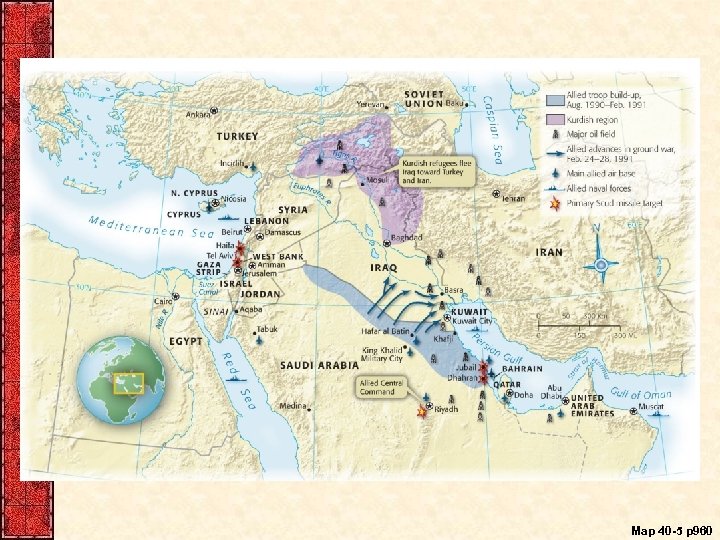
 XIII. The Persian Gulf Crisis • End of the Cold War didn’t end of all wars – United States invaded Panama in December 1989 – Iraq(Saddam Hussein) invaded Kuwait(1990) • UN Security Council OK’d military force • First Persian Gulf War – US ( & 28 other nations) attacked Iraqi troops – A month of ‘smart’ bombing, then ground troops • Desert Storm (the “hundred-hour war”) – Kuwait was liberated – Saddam had survived to menace the world another day
XIII. The Persian Gulf Crisis • End of the Cold War didn’t end of all wars – United States invaded Panama in December 1989 – Iraq(Saddam Hussein) invaded Kuwait(1990) • UN Security Council OK’d military force • First Persian Gulf War – US ( & 28 other nations) attacked Iraqi troops – A month of ‘smart’ bombing, then ground troops • Desert Storm (the “hundred-hour war”) – Kuwait was liberated – Saddam had survived to menace the world another day
 p 960
p 960
 Map 40 -5 p 960
Map 40 -5 p 960
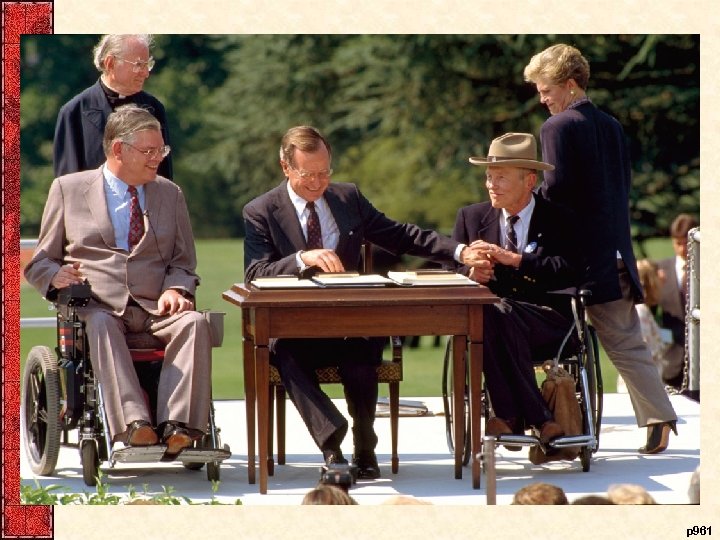
 XIV. Bush on the Home Front • Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) 1990 • Signed a major water projects bill in 1992 – Distribution of subsidized federal water in the West • Environment, urban areas, then agriculture priorities • The explosive “social issues” – Challenged targeted racial college scholarships – Opposed abortion (a growing ‘gender gap’) • Nominated Clarence Thomas for SCOTUS • Bush’s political health damaged by economy – 7% unemployment, Fed deficit $250 b • 1990 Bush agreed to a budget with tax increases – Said “Read my lips—no new taxes” in 1988 campa. Ign
XIV. Bush on the Home Front • Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) 1990 • Signed a major water projects bill in 1992 – Distribution of subsidized federal water in the West • Environment, urban areas, then agriculture priorities • The explosive “social issues” – Challenged targeted racial college scholarships – Opposed abortion (a growing ‘gender gap’) • Nominated Clarence Thomas for SCOTUS • Bush’s political health damaged by economy – 7% unemployment, Fed deficit $250 b • 1990 Bush agreed to a budget with tax increases – Said “Read my lips—no new taxes” in 1988 campa. Ign
 p 961
p 961
 p 963
p 963


