5991e0152596a8c5e706e5808340bfec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Chapter 4: Troubleshoot System Startup and User Logon Problems MCDST 70 -271: Supporting Users and Troubleshooting a Microsoft Windows XP Operating System Guide to MCDST 70 -271
Objectives • Understand the Windows XP boot phases • Understand advanced startup options • Understand boot configuration and selecting an operating system • Edit the Boot. ini file • Understand the Windows XP load phase Guide to MCDST 70 -271 2

Objectives (continued) • Use the MS-DOS startup disk and the Recovery Console • Troubleshoot the startup process • Describe the Windows XP security model, and the types of logon • Troubleshoot and customize the logon process Guide to MCDST 70 -271 3
Windows XP Boot Phases • Boot phase – Takes place when computer is first powered on or – When you choose Restart from the Turn Off Computer dialog box • Load phase – Begins when boot phase is completed and a configuration is selected Guide to MCDST 70 -271 4
Power-on Self Test • First step in boot sequence for any computer with an operating system • Determines – The amount of real memory that exists – Whether or not all necessary hardware components, such as a keyboard, are present • The software for the POST resides in the system’s primary BIOS chip Guide to MCDST 70 -271 5

Power-on Self Test (continued) Guide to MCDST 70 -271 6
Initial Startup • Master Boot Record (MBR) begins boot process by looking up the partition table • Active partition contains OS files that must be loaded first • Partition boot sector is completely dependent on the operating system and file system in use Guide to MCDST 70 -271 7
Boot Loader • Files on system partition used to initiate loading of the operating system • Will display a boot menu if more than one OS is present • Ntldr, Boot. ini, Bootsect. dos, Ntdetect. com, and Ntbootdd. sys may all be present in the root directory of the startup disk Guide to MCDST 70 -271 8
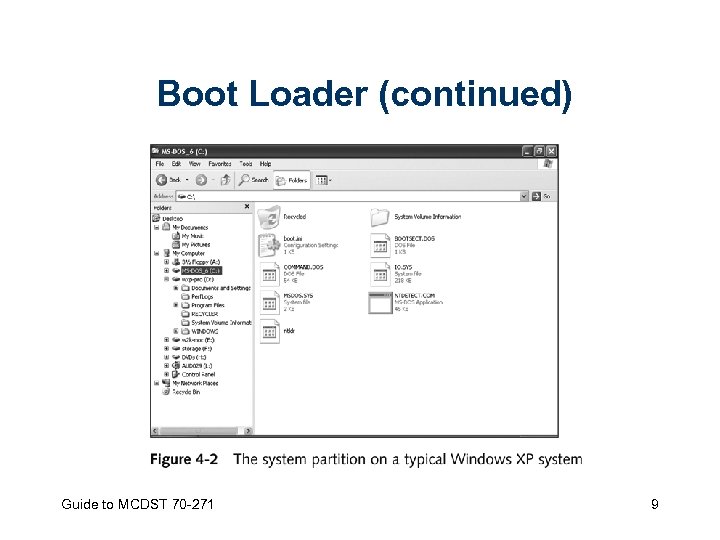
Boot Loader (continued) Guide to MCDST 70 -271 9

Selecting the Operating System • Ntldr – Reads the Boot. ini file – Displays operating system selections • Boot selection menu – Represents the point at which users can select which operating system they want to load Guide to MCDST 70 -271 10

Selecting the Operating System (continued) Guide to MCDST 70 -271 11

Detecting Hardware • Ntdetect. com – Executed by the boot loader – Used to collect a list of hardware currently installed in the computer • Ntdetect – Checks computer ID, bus/adapter type, video, keyboard, communication ports – Creates a system profile Guide to MCDST 70 -271 12
Selecting a Configuration • Once hardware is detected, the system needs to select a system configuration (hardware profile) – If a single hardware profile is defined, that is used – If two or more hardware profiles are present, the system selects a profile based on detected hardware – If the system cannot make an automatic selection, you are prompted to manually select a hardware profile Guide to MCDST 70 -271 13

Advanced Startup Options • • Safe mode Safe Mode with Networking Safe Mode with Command Prompt Enable Boot Logging Guide to MCDST 70 -271 14

Advanced Startup Options (continued) • • Enable VGA Mode Last Known Good Configuration (LKGC) Directory Services Restore Mode Debugging Mode Guide to MCDST 70 -271 15
![Boot Configuration and Selecting an Operating System • [boot loader] – Timeout setting • Boot Configuration and Selecting an Operating System • [boot loader] – Timeout setting •](https://present5.com/presentation/5991e0152596a8c5e706e5808340bfec/image-16.jpg)
Boot Configuration and Selecting an Operating System • [boot loader] – Timeout setting • Defines number of seconds system waits for user to select an operating system before loading default operating system – Default setting • Lists the path to the default operating system • [operating systems] – Lists available operating systems Guide to MCDST 70 -271 16

Editing Boot. ini • Options include – Using Control Panel to edit the file indirectly – Using a text editor to change the file directly Guide to MCDST 70 -271 17
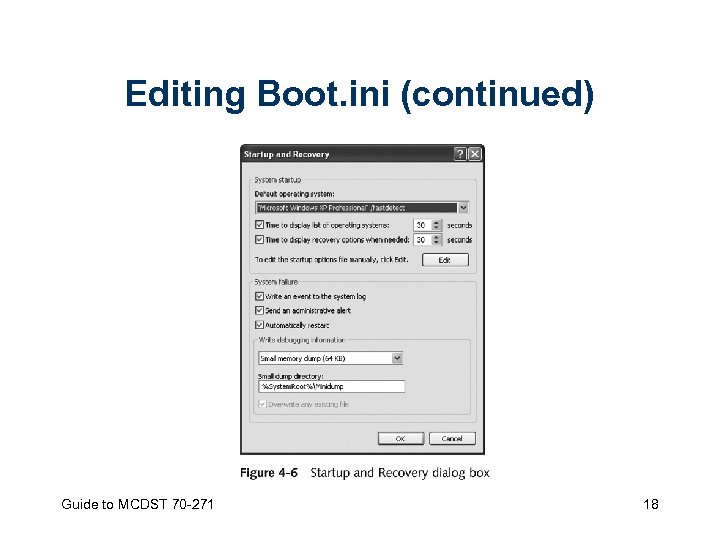
Editing Boot. ini (continued) Guide to MCDST 70 -271 18
Windows XP Load Phase • Consists of the following stages – – – Loading the kernel Initializing the kernel Services load Windows XP system startup Logging on Guide to MCDST 70 -271 19

Loading the Kernel • Boot loader – Loads Windows XP kernel (Ntoskrnl. exe) and Hardware abstraction layer (HAL; file Hal. dll) into memory • Control set – Special set of Registry values that describes a Windows XP machine’s startup configuration Guide to MCDST 70 -271 20
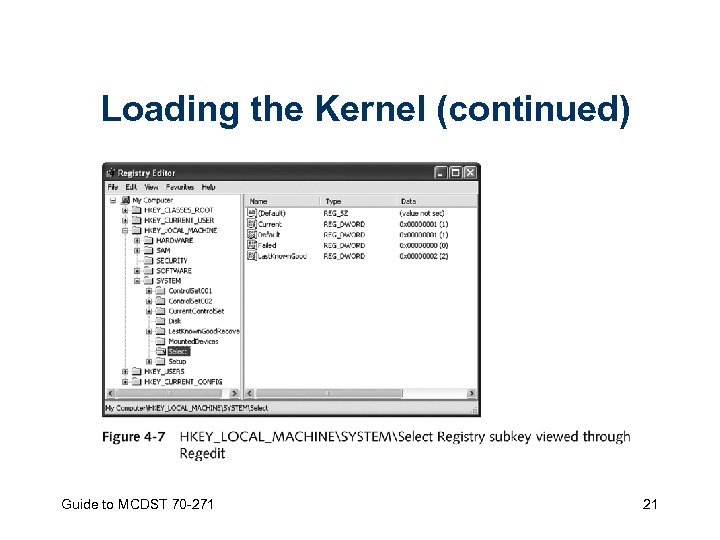
Loading the Kernel (continued) Guide to MCDST 70 -271 21
Initializing the Kernel • Error levels – Ignore: error is ignored – Normal: boot process continues – Severe: management of error depends on whether the LKGC is in use or not – Critical: management of error depends on whether the LKGC is in use or not Guide to MCDST 70 -271 22

Services Load • Autocheck – Ensures that files stored on your hard drive are always consistent – Detects and attempts to repair damaged files and directories Guide to MCDST 70 -271 23
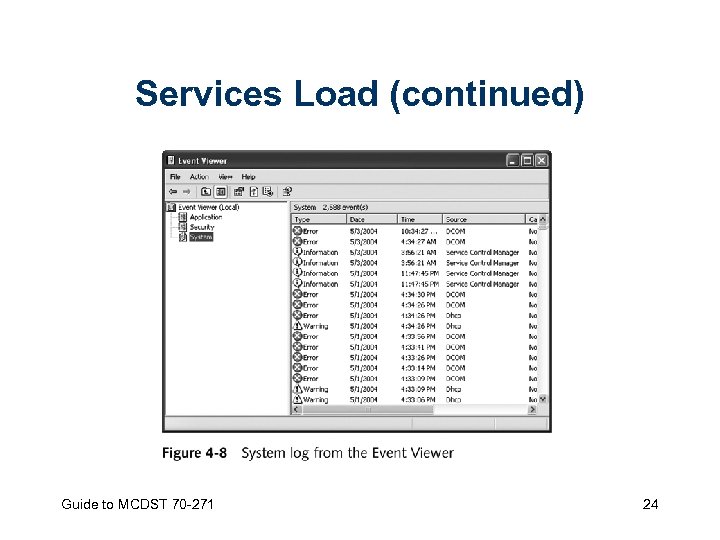
Services Load (continued) Guide to MCDST 70 -271 24

Windows XP System Startup • Windows XP system can be considered fully started once: – Windows XP services have all started – The elements in the group of processes configured to launch on startup are fired off • This phase is signaled by the appearance of the Windows XP logon screen as the. Win 32 subsystem starts winlogon. exe – Automatically launches the Local Security Authority (Lsass. exe) process Guide to MCDST 70 -271 25

Logging On • Until a user successfully logs on, the boot process is not complete until the Clone control set is copied to the LKGC set • This procedure provides values to be used the next time the machine is powered up, if the user elects to use the LKGC Guide to MCDST 70 -271 26
MS-DOS Startup Disk • Used to troubleshoot problems with Windows XP • For Windows XP systems that use only or mostly FAT partitions – Any file on a FAT partition can be edited, replaced, moved, copied, deleted, renamed, etc. • If system uses NTFS partitions – MS-DOS startup disk will be of little use Guide to MCDST 70 -271 27

Recovery Console • To access: – From a command prompt, change directories to your Windows XP CD • Run i 386winnt 32. exe /cmdcons to install the Recovery Console – Use the Windows XP CD or startup disks to start your computer • Select the Recovery Console option when you are prompted to choose repair options Guide to MCDST 70 -271 28

Troubleshooting Startup • General troubleshooting procedure – – – Use the LKGC boot option Boot into Safe Mode Uninstall or remove the suspect component Use a System Restore point if available Use the Recovery Console Guide to MCDST 70 -271 29
Troubleshooting Startup (continued) • General troubleshooting procedure – Verify the Boot. ini configuration and the presence of required system files – Install a second instance of the OS onto a different partition – Use Automated System Recovery (ASR) – Perform an upgrade install – Perform a clean install Guide to MCDST 70 -271 30

Security Within the Logon Process • Windows Welcome – Designed for use on standalone or workgroup member systems – Fast User Switching allows Windows XP Professional to switch users without logging off • Classic logon method – Logon mode is set to classic logon automatically when Windows XP system becomes a domain member Guide to MCDST 70 -271 31

Logon Identification • Before user can access Windows XP resource, he or she must log on to the system by supplying a valid user ID and password • Identification requires that user supply a valid account name Guide to MCDST 70 -271 32

Logon Authentication • Authentication – User must use some method to verify his or her identity • Access token includes the following components: – The unique SID for the account – List of groups (via group SIDs) to which the user belongs – List of rights and privileges associated with the specific user’s account Guide to MCDST 70 -271 33
Troubleshooting Logon • Domain controller – Authenticates domain logons and maintains the security policies and account database for a domain • Cached credentials – Does not represent true domain authentication – Re-uses old authentication and access token Guide to MCDST 70 -271 34

Mapped Network Drive • If unable to connect over a mapped network drive, create a new mapping to the drive • Forces a new authentication procedure and assigns the user account a current access token Guide to MCDST 70 -271 35
First Time Logons • If user has not logged on to a specific system before and domain controller is unavailable, an error message states that logon could not be performed – Check if system has correct network connectivity and contact system or network administrator to confirm an issue or problem with the network or local domain controllers – If user had logged on in the past, Windows XP Professional would have used cached credentials to provide access when the domain controller could not be reached Guide to MCDST 70 -271 36

Typing Errors • User may mistype his logon credentials or the CAPS LOCK key was engaged • If password included numbers and the numerical keypad was used, the NUM LOCK key may not have been engaged • If still unable to log on, check with the system or network administrator – May need to have the password on domain user account reset or account may be locked out due to too many repetitive logon failures Guide to MCDST 70 -271 37

Customizing the Logon Process • Winlogon – Alters the default logon process appearance and function – Controls automated logon, warning text, the display of the Shutdown button • Reasons for customizing the logon process – To change the default username – To add a security warning message Guide to MCDST 70 -271 38
Disabling the Default Username • Logon window displays the name of the last user to log on by default • Possible to change the default by altering the value of its associated Registry key or Local Security Policy value Guide to MCDST 70 -271 39

Adding a Security Warning Message • Legal. Notice. Caption – Puts a label on the title bar of the legal notice window that appears during logon • Legal. Notice. Text – Contains text information that provides the details of the warning to be issued to system users Guide to MCDST 70 -271 40

Disabling the Shutdown Button • Value named Shutdown. Without. Logon – Edited in the Registry or Local Security Policy console – Enabled by default – To disable, change its value assignment to 0 – To re-enable, reset its value to 1 Guide to MCDST 70 -271 41

Automating Logons • To set up an automated logon, these Registry value entries must be defined and set – – Default. Domain. Name Default. User. Name Default. Password Auto. Admin. Logon Guide to MCDST 70 -271 42
Summary • The Windows XP boot process – After the POST • BIOS loads the MBR, which then loads the partition boot sector – When boot menu appears • You can press F 8 to access the Windows Advanced Options Menu – After the boot loader • The kernel is loaded into memory Guide to MCDST 70 -271 43

Summary (continued) • Boot process can be altered by changing the Boot. ini file • Recovery Console used to recover system configurations and user settings in the event of a system failure • Winlogon – Controls how users identify themselves and log on – Supports a number of logon controls Guide to MCDST 70 -271 44
5991e0152596a8c5e706e5808340bfec.ppt