354baeea45582139429fedcf0f7d3bb1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Chapter 4 The Share Market and the Corporation Websites: www. asic. gov. au www. asx. com. au www. nyse. com Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 1
Chapter 4 The Share Market and the Corporation Websites: www. asic. gov. au www. asx. com. au www. nyse. com Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 1
 Learning Objectives • Understand the nature of corporations and their use of equity as a financing tool • Describe the role of the stock market Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 2
Learning Objectives • Understand the nature of corporations and their use of equity as a financing tool • Describe the role of the stock market Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 2
 Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 3
Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 3
 4. 1 Introduction • Share market – A formal exchange facilitating the issue, buying and selling of equity securities • Publicly listed corporation – A company whose shares are quoted and traded on a formal stock exchange (SX) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 4
4. 1 Introduction • Share market – A formal exchange facilitating the issue, buying and selling of equity securities • Publicly listed corporation – A company whose shares are quoted and traded on a formal stock exchange (SX) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 4
 4. 1 Introduction (cont. ) • Ordinary share – The principal form of equity issued by a corporation which bestows a claim to residual cash flows and ownership and voting rights Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 5
4. 1 Introduction (cont. ) • Ordinary share – The principal form of equity issued by a corporation which bestows a claim to residual cash flows and ownership and voting rights Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 5
 Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 6
Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 6
 4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation • The corporation differs from other business forms Ownership claims are widespread and easily transferable – Owners (shareholders) do not affect the day-today affairs of the company – Shareholder’s liability is limited to the uncalled amount of the shares – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 7
4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation • The corporation differs from other business forms Ownership claims are widespread and easily transferable – Owners (shareholders) do not affect the day-today affairs of the company – Shareholder’s liability is limited to the uncalled amount of the shares – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 7
 4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation (cont. ) • Advantages of the corporate form Can obtain large amounts of finance for a relatively cheap cost – The liquidity of securities facilitates investor diversification and encourages investment in corporate securities – Specialised management can be chosen (due to separation of ownership and control) – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 8
4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation (cont. ) • Advantages of the corporate form Can obtain large amounts of finance for a relatively cheap cost – The liquidity of securities facilitates investor diversification and encourages investment in corporate securities – Specialised management can be chosen (due to separation of ownership and control) – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 8
 4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation (cont. ) • Advantages of the corporate form (cont. ) ‘Perpetual succession’—the corporate form is unaffected by changes in management or ownership – The corporate form is suited to large-scale operations – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 9
4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation (cont. ) • Advantages of the corporate form (cont. ) ‘Perpetual succession’—the corporate form is unaffected by changes in management or ownership – The corporate form is suited to large-scale operations – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 9
 4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation (cont. ) • Disadvantages of the corporate form – The primary disadvantage arises due to the separation of ownership and control § Conflict of interest between owners (shareholders) and mangers (agents) known as agency theory Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 10
4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation (cont. ) • Disadvantages of the corporate form – The primary disadvantage arises due to the separation of ownership and control § Conflict of interest between owners (shareholders) and mangers (agents) known as agency theory Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 10
 4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation (cont. ) • Disadvantages (cont. ) – Management may not have strong incentive to act in the interests of the owners (shareholders) i. e. maximise shareholder value (share price) § Moderating influences include • • Investors’ ability to sell shares in a corporation Dismissal from the board at AGM by shareholders Threat of takeover and loss of employment Use of performance incentives like share options Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 11
4. 2 The Nature of the Corporation (cont. ) • Disadvantages (cont. ) – Management may not have strong incentive to act in the interests of the owners (shareholders) i. e. maximise shareholder value (share price) § Moderating influences include • • Investors’ ability to sell shares in a corporation Dismissal from the board at AGM by shareholders Threat of takeover and loss of employment Use of performance incentives like share options Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 11
 Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 12
Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 12
 4. 3 The Stock Exchange (SX) • Primary role • Secondary role • Derivative market role • Interest rate role • Trading and settlement role • Information role • Regulatory role Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 13
4. 3 The Stock Exchange (SX) • Primary role • Secondary role • Derivative market role • Interest rate role • Trading and settlement role • Information role • Regulatory role Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 13
 Primary role • The SX facilitates the efficient and orderly sale of new financial securities – New floats/initial public offerings (IPOs) § – Rights issue § – Initial listing of a corporation on the SX Issue of additional shares to existing shareholders on a pro-rata basis Placements § Issue of new shares to selected institutional investors Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 14
Primary role • The SX facilitates the efficient and orderly sale of new financial securities – New floats/initial public offerings (IPOs) § – Rights issue § – Initial listing of a corporation on the SX Issue of additional shares to existing shareholders on a pro-rata basis Placements § Issue of new shares to selected institutional investors Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 14
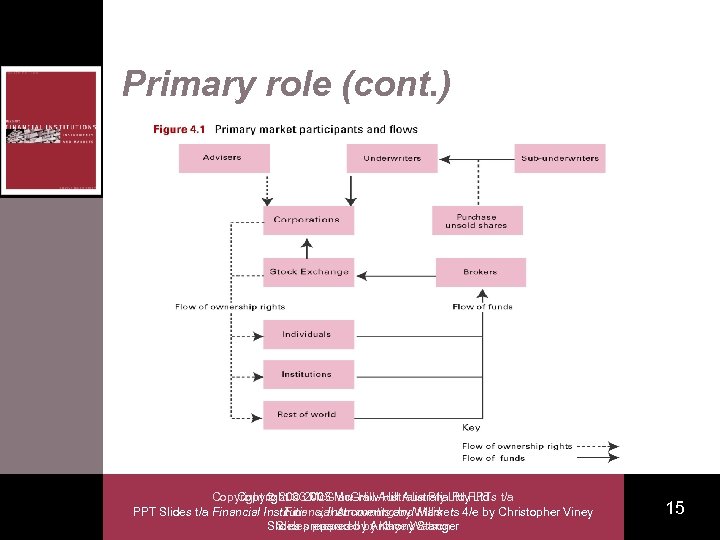 Primary role (cont. ) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 15
Primary role (cont. ) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 15
 Secondary role • The SX facilitates trading in existing shares No new funds are raised by the issuing company – An active, liquid, well organised secondary market increases the appeal of buying new shares in the primary market – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 16
Secondary role • The SX facilitates trading in existing shares No new funds are raised by the issuing company – An active, liquid, well organised secondary market increases the appeal of buying new shares in the primary market – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 16
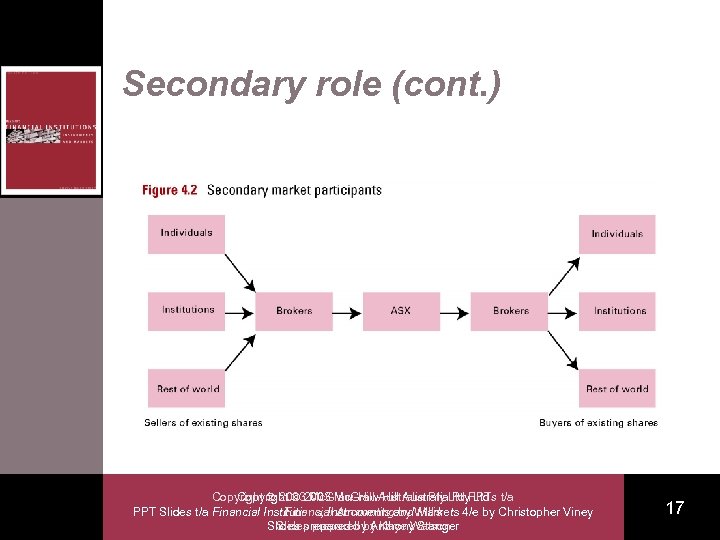 Secondary role (cont. ) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 17
Secondary role (cont. ) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 17
 Derivative market role • The SX provides a market for trading equity -related derivative products A derivative is a financial security that derives its price from an underlying commodity (gold) or financial instrument (Fosters shares) – Derivative products can be – § § Exchange-traded (standardised) Over-the-counter contracts (unstandardised) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 18
Derivative market role • The SX provides a market for trading equity -related derivative products A derivative is a financial security that derives its price from an underlying commodity (gold) or financial instrument (Fosters shares) – Derivative products can be – § § Exchange-traded (standardised) Over-the-counter contracts (unstandardised) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 18
 Derivative market role (cont. ) • The SX provides a market for trading equity -related derivative products (cont. ) – Derivatives serve as a § § – Risk management tool (hedge) Speculative instrument Derivatives traded on the ASX include § § § Options Warrants Futures contracts Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 19
Derivative market role (cont. ) • The SX provides a market for trading equity -related derivative products (cont. ) – Derivatives serve as a § § – Risk management tool (hedge) Speculative instrument Derivatives traded on the ASX include § § § Options Warrants Futures contracts Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 19
 Interest rate role • The listing, quotation and trading of debt securities on the SX, e. g. – corporate bonds, floating rate notes (FRNs), convertible notes, preference shares Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 20
Interest rate role • The listing, quotation and trading of debt securities on the SX, e. g. – corporate bonds, floating rate notes (FRNs), convertible notes, preference shares Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 20
 Interest rate role (cont. ) • This role adds value to to a debt issue due to Transparency – Ease of entry – Liquidity – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 21
Interest rate role (cont. ) • This role adds value to to a debt issue due to Transparency – Ease of entry – Liquidity – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 21
 Trading and settlement role • Shares are traded using an electronic (computer-based) trading system—Stock Exchange Automated Trading System (SEATS) Clients’ orders are executed via computer from the broker’s office – Orders are executed in order of time received and the buy/sell price – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 22
Trading and settlement role • Shares are traded using an electronic (computer-based) trading system—Stock Exchange Automated Trading System (SEATS) Clients’ orders are executed via computer from the broker’s office – Orders are executed in order of time received and the buy/sell price – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 22
 Trading and settlement role (cont. ) • Shares are traded using an electronic (computer-based) trading system—Stock Exchange Automated Trading System (SEATS) (cont. ) – SEATS has improved the speed and efficiency of trade-processing and settlement, and the dissemination of information to market participants Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 23
Trading and settlement role (cont. ) • Shares are traded using an electronic (computer-based) trading system—Stock Exchange Automated Trading System (SEATS) (cont. ) – SEATS has improved the speed and efficiency of trade-processing and settlement, and the dissemination of information to market participants Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 23
 Trading and settlement role (cont. ) • ASX CHESS (Clearing House Electronic Sub- register System) Share ownership and settlement performed electronically – Settlement of transactions within three days (T + 3) – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 24
Trading and settlement role (cont. ) • ASX CHESS (Clearing House Electronic Sub- register System) Share ownership and settlement performed electronically – Settlement of transactions within three days (T + 3) – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 24
 Trading and settlement role (cont. ) • CDI (CHESS Depositary Interest) – Electronic depositary receipts issued by the ASX representing uncertificated (scriptless) securities § § – CUFS (CHESS Unit Foreign Securities) for equity securities DI (Depositary Interest) for debt securities Overcomes problems of countries not recognising uncertificated holdings or the electronic transfer of legal title Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 25
Trading and settlement role (cont. ) • CDI (CHESS Depositary Interest) – Electronic depositary receipts issued by the ASX representing uncertificated (scriptless) securities § § – CUFS (CHESS Unit Foreign Securities) for equity securities DI (Depositary Interest) for debt securities Overcomes problems of countries not recognising uncertificated holdings or the electronic transfer of legal title Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 25
 Information role • Investor confidence in the Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) relies on informational efficiency – i. e. the current share prices should reflect all information available in the market • The ASX has a critical role in facilitating the flow of information to the market Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 26
Information role • Investor confidence in the Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) relies on informational efficiency – i. e. the current share prices should reflect all information available in the market • The ASX has a critical role in facilitating the flow of information to the market Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 26
 Information role (cont. ) • Listing rules are SX rules with which a listed entity must comply • Examples of information disclosures required by ASX listing rules – – – A change in forecasted profitability Appointment of a liquidator Declaration of a dividend Notice of a takeover bid Disclosure of directors’ interests Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 27
Information role (cont. ) • Listing rules are SX rules with which a listed entity must comply • Examples of information disclosures required by ASX listing rules – – – A change in forecasted profitability Appointment of a liquidator Declaration of a dividend Notice of a takeover bid Disclosure of directors’ interests Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 27
 Regulatory role • The aim of regulation is to ensure market participants have confidence in the integrity of market operations • Two main supervisors in Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) – Australian Securities and Investment Commission (ASIC) – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 28
Regulatory role • The aim of regulation is to ensure market participants have confidence in the integrity of market operations • Two main supervisors in Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) – Australian Securities and Investment Commission (ASIC) – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 28
 Regulatory role (cont. ) • ASX – Ensures listed companies meet specified limited levels of performance and standards of information disclosure so investors can make informed decisions § – Continuous disclosure Prescribes appropriate behaviour of broker participants on the exchange § Penalties include discipline, penalties, loss of licence Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 29
Regulatory role (cont. ) • ASX – Ensures listed companies meet specified limited levels of performance and standards of information disclosure so investors can make informed decisions § – Continuous disclosure Prescribes appropriate behaviour of broker participants on the exchange § Penalties include discipline, penalties, loss of licence Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 29
 Regulatory role (cont. ) • ASX (cont. ) – Electronic surveillance systems to monitor trading behaviour of market participants § § – Detect trades that fall outside certain limits Cross-references all trades against information on the relevant company, directors and associated parties The National Guarantee Fund (NFG) compensates investors in the event of misconduct by a stockbroker Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 30
Regulatory role (cont. ) • ASX (cont. ) – Electronic surveillance systems to monitor trading behaviour of market participants § § – Detect trades that fall outside certain limits Cross-references all trades against information on the relevant company, directors and associated parties The National Guarantee Fund (NFG) compensates investors in the event of misconduct by a stockbroker Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 30
 Regulatory role (cont. ) • ASIC Responsible for the supervision of corporations law and markets – Established in 1991 as the ASC (Australian Securities Commission) – Following ‘Wallis Inquiry’ findings, changed its name to ASIC – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 31
Regulatory role (cont. ) • ASIC Responsible for the supervision of corporations law and markets – Established in 1991 as the ASC (Australian Securities Commission) – Following ‘Wallis Inquiry’ findings, changed its name to ASIC – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 31
 Regulatory role (cont. ) • ASIC (cont. ) Responsible for market integrity and consumer protection across the financial system – Not solely confined to equity (also investments, insurance and superannuation products) – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 32
Regulatory role (cont. ) • ASIC (cont. ) Responsible for market integrity and consumer protection across the financial system – Not solely confined to equity (also investments, insurance and superannuation products) – Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 32
 Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 33
Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 33
 4. 4 The Development of Share Markets • Origins of the modern share market can be traced back to commercial activity in England in the 16 th century and the corporate form of business • In Australia, share markets developed with growth in economic activity in cities and provincial locations and operated quite independently Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 34
4. 4 The Development of Share Markets • Origins of the modern share market can be traced back to commercial activity in England in the 16 th century and the corporate form of business • In Australia, share markets developed with growth in economic activity in cities and provincial locations and operated quite independently Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 34
 4. 4 The Development of Share Markets (cont. ) • In 1937 the Australian Associated Stock Exchanges (AASE) was incorporated which eventually represented all six capital city SXs • In 1976 a joint exchange was formed between the Sydney and Melbourne exchanges which allowed members access to both trading floors Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 35
4. 4 The Development of Share Markets (cont. ) • In 1937 the Australian Associated Stock Exchanges (AASE) was incorporated which eventually represented all six capital city SXs • In 1976 a joint exchange was formed between the Sydney and Melbourne exchanges which allowed members access to both trading floors Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 35
 4. 4 The Development of Share Markets (cont. ) • 1987 saw the establishment of the Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) as a mutual organisation and a single national market • In 1998 the ASX was demutualised and became a publicly listed corporation Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 36
4. 4 The Development of Share Markets (cont. ) • 1987 saw the establishment of the Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) as a mutual organisation and a single national market • In 1998 the ASX was demutualised and became a publicly listed corporation Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 36
 Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 37
Chapter Organisation 4. 1 4. 2 4. 3 4. 4 4. 5 Introduction The Nature of the Corporation The Stock Exchange The Development of Share Markets Summary Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 37
 4. 5 Summary • The corporate form of organisation has a number of advantages (fund raising and management) and the disadvantage of the separation of ownership and control • The SX has a number of market roles – – – Primary and secondary Derivative Interest rate Trading and settlement Information Regulatory Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 38
4. 5 Summary • The corporate form of organisation has a number of advantages (fund raising and management) and the disadvantage of the separation of ownership and control • The SX has a number of market roles – – – Primary and secondary Derivative Interest rate Trading and settlement Information Regulatory Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 38
 4. 5 Summary (cont. ) • The Australian share market is regulated by the ASX and ASIC • The ASX has demutualised and is now a publicly listed corporation Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 39
4. 5 Summary (cont. ) • The Australian share market is regulated by the ASX and ASIC • The ASX has demutualised and is now a publicly listed corporation Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia. Ltd PPTs t/a Copyright Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPT Slides t/a Financial Institutions, Instruments and Willis Financial Accounting by Markets 4/e by Christopher Viney Slides prepared by Anthony Stanger Slides prepared by Kaye Watson 39


