12a5017047ed9b9721fad8349d6885ad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 Chapter 4 The Internal Assessment Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 11 th Edition Fred David Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 1
Chapter 4 The Internal Assessment Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 11 th Edition Fred David Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 1
 Chapter Outline The Nature of an Internal Audit The Resource-Based View (RBV) Integrating Strategy & Culture Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 2
Chapter Outline The Nature of an Internal Audit The Resource-Based View (RBV) Integrating Strategy & Culture Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 2
 Chapter Outline (cont’d) Management Marketing Opportunity Analysis Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 3
Chapter Outline (cont’d) Management Marketing Opportunity Analysis Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 3
 Chapter Outline (cont’d) Finance/Accounting Production/Operations Research & Development Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 4
Chapter Outline (cont’d) Finance/Accounting Production/Operations Research & Development Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 4
 Chapter Outline (cont’d) Management Information Systems The Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 5
Chapter Outline (cont’d) Management Information Systems The Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 5
 Internal Assessment The biggest levers you’ve got to change a company are strategy, structure, and culture. If I could pick two, I’d pick strategy and culture. – Wayne Leonard, CEO, Entergy Weak leadership can wreck the soundest strategy. – Sun Zi Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 6
Internal Assessment The biggest levers you’ve got to change a company are strategy, structure, and culture. If I could pick two, I’d pick strategy and culture. – Wayne Leonard, CEO, Entergy Weak leadership can wreck the soundest strategy. – Sun Zi Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 6
 Nature of an Internal Audit Functional Areas of Business -- Strengths -- Weaknesses Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 7
Nature of an Internal Audit Functional Areas of Business -- Strengths -- Weaknesses Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 7
 Nature of an Internal Audit Basis for Objectives & Strategies n n n Internal strengths/weaknesses External opportunities/threats Clear statement of mission Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 8
Nature of an Internal Audit Basis for Objectives & Strategies n n n Internal strengths/weaknesses External opportunities/threats Clear statement of mission Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 8
 Key Internal Forces Functional Business Areas: §Vary by organization §Divisions have differing strengths & weaknesses Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 9
Key Internal Forces Functional Business Areas: §Vary by organization §Divisions have differing strengths & weaknesses Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 9
 Key Internal Forces Distinctive Competencies: §Firm’s strengths that cannot be easily matched or imitated by competitors Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 10
Key Internal Forces Distinctive Competencies: §Firm’s strengths that cannot be easily matched or imitated by competitors Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 10
 Key Internal Forces Distinctive Competencies: §Building competitive advantage involves taking advantage of distinctive competencies Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 11
Key Internal Forces Distinctive Competencies: §Building competitive advantage involves taking advantage of distinctive competencies Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 11
 Key Internal Forces Distinctive Competencies: §Strategies designed to improve on a firm’s weaknesses and turn to strengths Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 12
Key Internal Forces Distinctive Competencies: §Strategies designed to improve on a firm’s weaknesses and turn to strengths Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 12
 Internal Audit Parallels process of external audit • Information from: • Management • Marketing • Finance/accounting • Production/operations • Research & Development • Management information Systems Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 13
Internal Audit Parallels process of external audit • Information from: • Management • Marketing • Finance/accounting • Production/operations • Research & Development • Management information Systems Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 13
 Internal Audit Involvement in performing an internal strategic-management audit provides vehicle for understanding nature and effect of decisions in other functional business areas of the firm Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 14
Internal Audit Involvement in performing an internal strategic-management audit provides vehicle for understanding nature and effect of decisions in other functional business areas of the firm Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 14
 Internal Audit Key to Organizational Success Coordination & understanding among managers from all functional areas Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 15
Internal Audit Key to Organizational Success Coordination & understanding among managers from all functional areas Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 15
 Internal Audit Functional Relationships Number and complexity increases relative to organization size Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 16
Internal Audit Functional Relationships Number and complexity increases relative to organization size Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 16
 Internal Audit Financial Ratio Analysis Exemplifies complexity of relationships among functional areas of the business Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 17
Internal Audit Financial Ratio Analysis Exemplifies complexity of relationships among functional areas of the business Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 17
 Resource Based View (RBV) Approach to Competitive Advantage Internal resources are more important than external factors Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 18
Resource Based View (RBV) Approach to Competitive Advantage Internal resources are more important than external factors Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 18
 Resource Based View (RBV) 3 All Encompassing Categories 1. Physical resources 2. Human resources 3. Organizational resources Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 19
Resource Based View (RBV) 3 All Encompassing Categories 1. Physical resources 2. Human resources 3. Organizational resources Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 19
 Resource Based View (RBV) Empirical Indicators § Rare § Hard to imitate § Not easily substitutable Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 20
Resource Based View (RBV) Empirical Indicators § Rare § Hard to imitate § Not easily substitutable Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 20
 Integrating Strategy & Culture Organizational Culture Pattern of behavior developed by an organization as it learns to cope with its problem of external adaptation and internal integration…is considered valid and taught to new members Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 21
Integrating Strategy & Culture Organizational Culture Pattern of behavior developed by an organization as it learns to cope with its problem of external adaptation and internal integration…is considered valid and taught to new members Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 21
 Integrating Strategy & Culture Organizational Culture § Resistant to change § May represent: § Strength § Weakness Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 22
Integrating Strategy & Culture Organizational Culture § Resistant to change § May represent: § Strength § Weakness Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 22
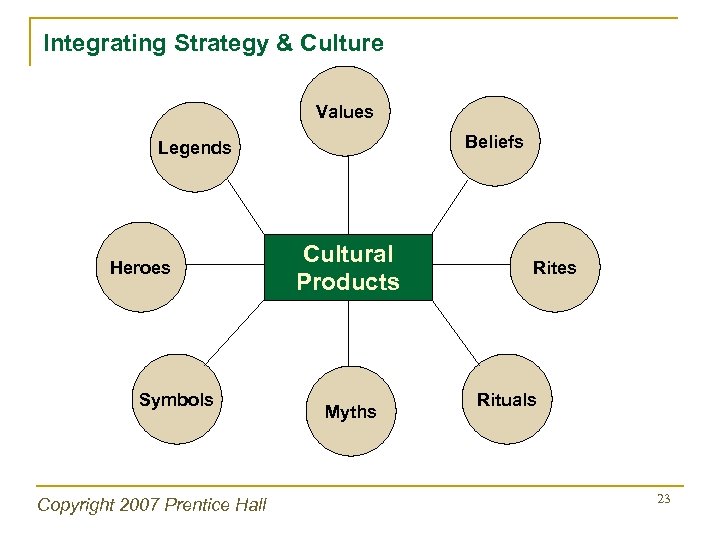 Integrating Strategy & Culture Values Beliefs Legends Heroes Symbols Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Cultural Products Myths Rites Rituals 23
Integrating Strategy & Culture Values Beliefs Legends Heroes Symbols Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Cultural Products Myths Rites Rituals 23
 Integrating Strategy & Culture Organizational Culture Can Inhibit Strategic Management § Miss external changes due to strongly held beliefs § Natural tendency to “hold the course” even during times of strategic change Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 24
Integrating Strategy & Culture Organizational Culture Can Inhibit Strategic Management § Miss external changes due to strongly held beliefs § Natural tendency to “hold the course” even during times of strategic change Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 24
 U. S. Versus Foreign Cultures To successfully compete in world markets, U. S. managers must obtain a better knowledge of historical, cultural, and religious forces that motivate and drive people in other countries. Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 25
U. S. Versus Foreign Cultures To successfully compete in world markets, U. S. managers must obtain a better knowledge of historical, cultural, and religious forces that motivate and drive people in other countries. Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 25
 Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 26
Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 26
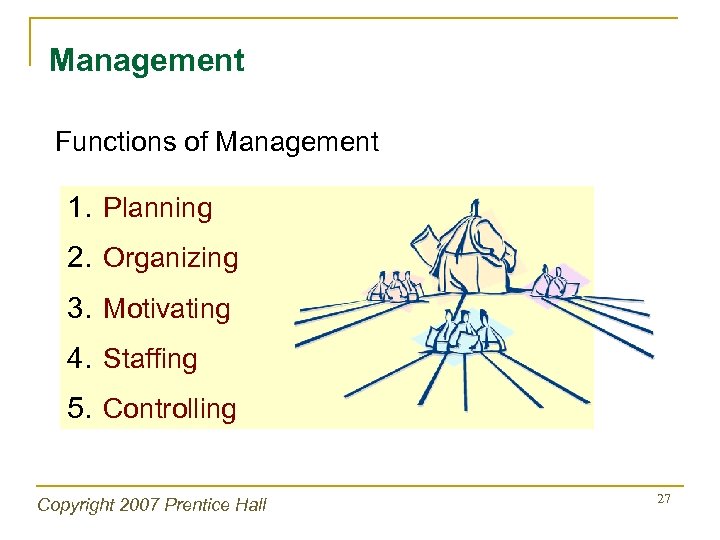 Management Functions of Management 1. Planning 2. Organizing 3. Motivating 4. Staffing 5. Controlling Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 27
Management Functions of Management 1. Planning 2. Organizing 3. Motivating 4. Staffing 5. Controlling Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 27
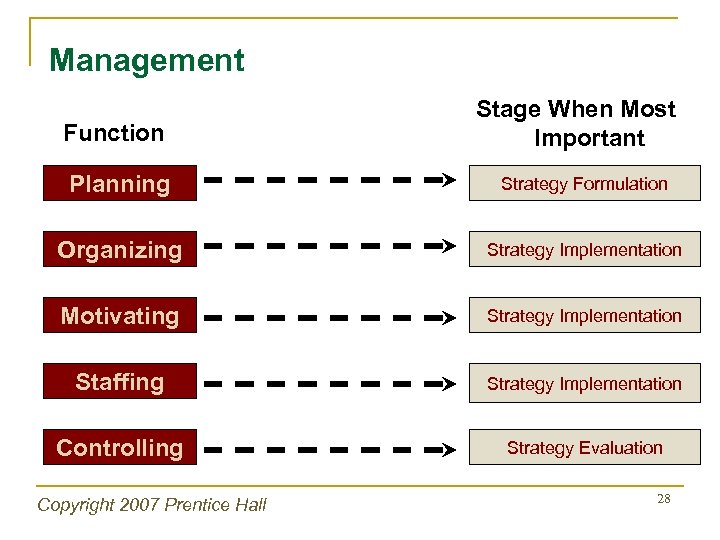 Management Function Stage When Most Important Planning Strategy Formulation Organizing Strategy Implementation Motivating Strategy Implementation Staffing Strategy Implementation Controlling Strategy Evaluation Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 28
Management Function Stage When Most Important Planning Strategy Formulation Organizing Strategy Implementation Motivating Strategy Implementation Staffing Strategy Implementation Controlling Strategy Evaluation Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 28
 Management Planning § Beginning of management process § Bridge between present & future § Improves likelihood of attaining desired results Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 29
Management Planning § Beginning of management process § Bridge between present & future § Improves likelihood of attaining desired results Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 29
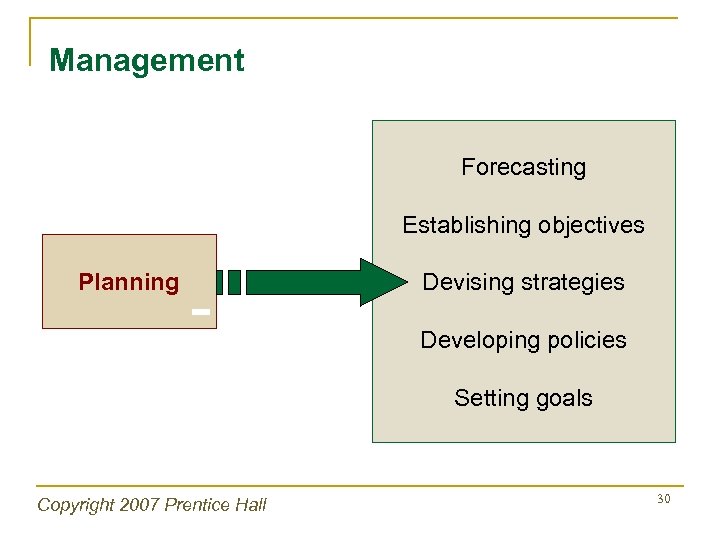 Management Forecasting Establishing objectives Planning Devising strategies Developing policies Setting goals Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 30
Management Forecasting Establishing objectives Planning Devising strategies Developing policies Setting goals Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 30
 Management Organizing § Achieves coordinated effort § Defines task & authority relationships § Departmentalization § Delegation of authority Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 31
Management Organizing § Achieves coordinated effort § Defines task & authority relationships § Departmentalization § Delegation of authority Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 31
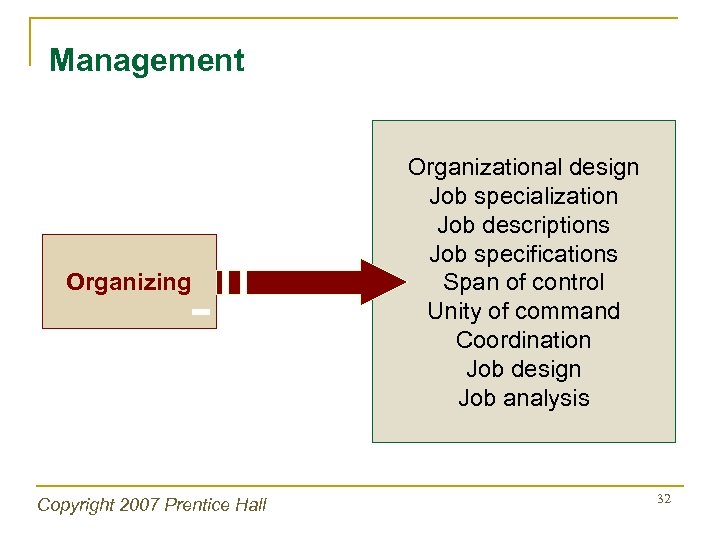 Management Organizing Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Organizational design Job specialization Job descriptions Job specifications Span of control Unity of command Coordination Job design Job analysis 32
Management Organizing Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Organizational design Job specialization Job descriptions Job specifications Span of control Unity of command Coordination Job design Job analysis 32
 Management Motivating § Influencing to accomplish specific objectives § Communication – major component Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 33
Management Motivating § Influencing to accomplish specific objectives § Communication – major component Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 33
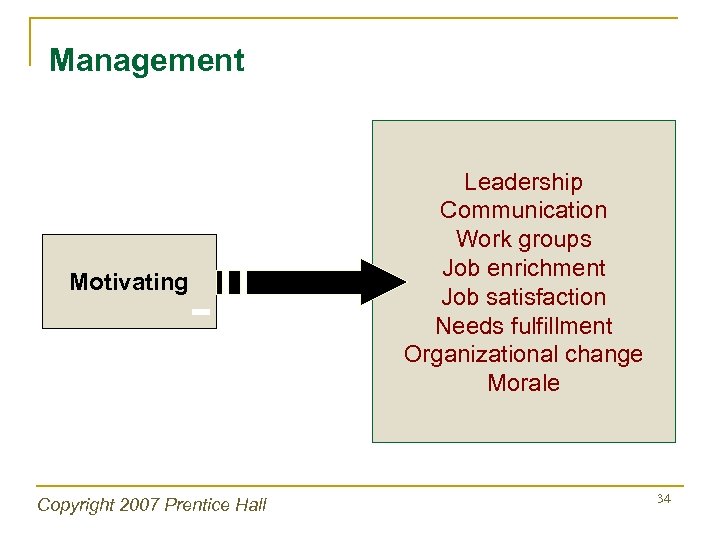 Management Motivating Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Leadership Communication Work groups Job enrichment Job satisfaction Needs fulfillment Organizational change Morale 34
Management Motivating Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Leadership Communication Work groups Job enrichment Job satisfaction Needs fulfillment Organizational change Morale 34
 Management Staffing § Personnel management § Human resources management Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 35
Management Staffing § Personnel management § Human resources management Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 35
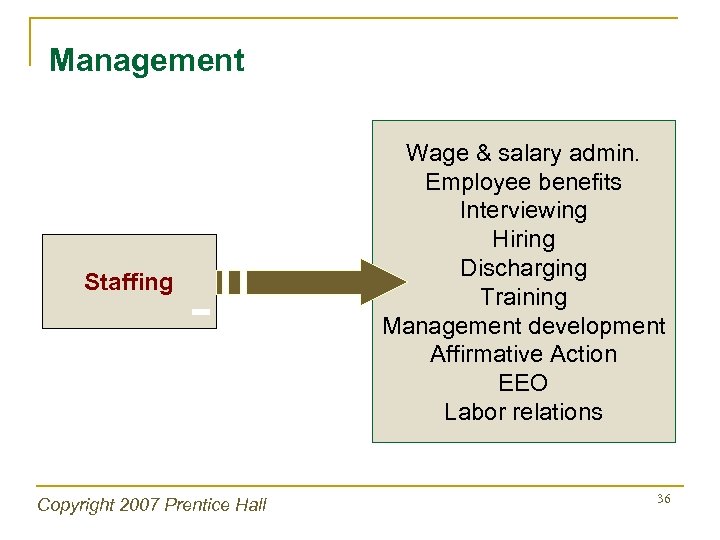 Management Staffing Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Wage & salary admin. Employee benefits Interviewing Hiring Discharging Training Management development Affirmative Action EEO Labor relations 36
Management Staffing Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Wage & salary admin. Employee benefits Interviewing Hiring Discharging Training Management development Affirmative Action EEO Labor relations 36
 Management Controlling § Establishing performance standards § Ensure actual operations conform to planned operations § Taking corrective actions Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 37
Management Controlling § Establishing performance standards § Ensure actual operations conform to planned operations § Taking corrective actions Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 37
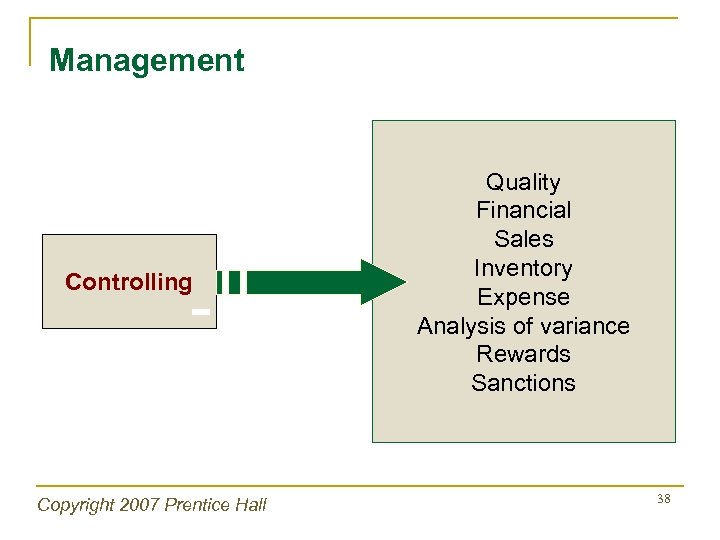 Management Controlling Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Quality Financial Sales Inventory Expense Analysis of variance Rewards Sanctions 38
Management Controlling Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Quality Financial Sales Inventory Expense Analysis of variance Rewards Sanctions 38
 Management Audit Checklist • Does the firm use strategic management concepts? • Are objectives/goals measurable? Well communicated? • Do managers at all levels plan effectively? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 39
Management Audit Checklist • Does the firm use strategic management concepts? • Are objectives/goals measurable? Well communicated? • Do managers at all levels plan effectively? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 39
 Management Audit Checklist • Do managers delegate well? • Is the organization’s structure appropriate? • Are job descriptions clear? • Are job specifications clear? • Is employee morale high? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 40
Management Audit Checklist • Do managers delegate well? • Is the organization’s structure appropriate? • Are job descriptions clear? • Are job specifications clear? • Is employee morale high? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 40
 Management Audit Checklist • Is employee absenteeism low? • Is employee turnover low? • Are the reward mechanisms effective? • Are the organization’s control mechanisms effective? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 41
Management Audit Checklist • Is employee absenteeism low? • Is employee turnover low? • Are the reward mechanisms effective? • Are the organization’s control mechanisms effective? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 41
 Marketing Customer Needs/Wants for Products/Services 1. Defining 2. Anticipating 3. Creating 4. Fulfilling Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 42
Marketing Customer Needs/Wants for Products/Services 1. Defining 2. Anticipating 3. Creating 4. Fulfilling Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 42
 Marketing Functions 1. Customer analysis 2. Selling products/services 3. Product & service planning 4. Pricing 5. Distribution 6. Marketing research 7. Opportunity analysis Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 43
Marketing Functions 1. Customer analysis 2. Selling products/services 3. Product & service planning 4. Pricing 5. Distribution 6. Marketing research 7. Opportunity analysis Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 43
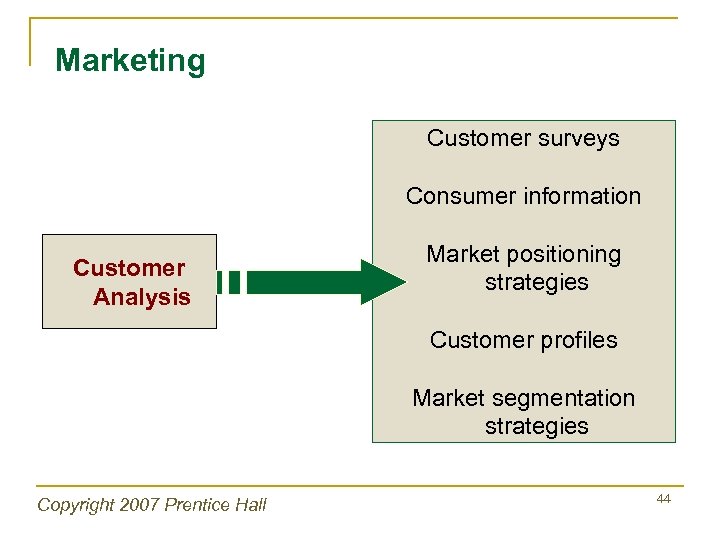 Marketing Customer surveys Consumer information Customer Analysis Market positioning strategies Customer profiles Market segmentation strategies Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 44
Marketing Customer surveys Consumer information Customer Analysis Market positioning strategies Customer profiles Market segmentation strategies Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 44
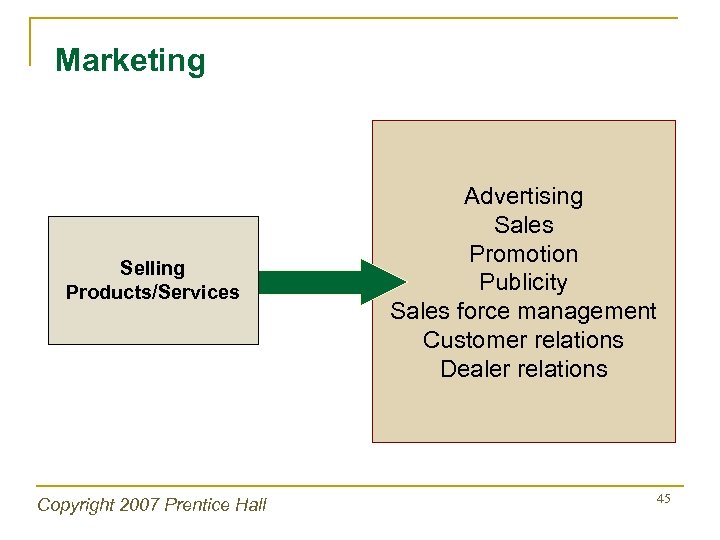 Marketing Selling Products/Services Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Advertising Sales Promotion Publicity Sales force management Customer relations Dealer relations 45
Marketing Selling Products/Services Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Advertising Sales Promotion Publicity Sales force management Customer relations Dealer relations 45
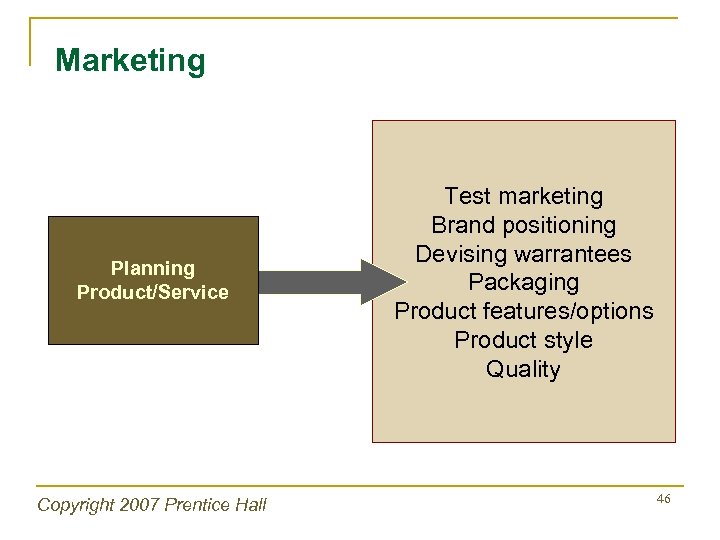 Marketing Planning Product/Service Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Test marketing Brand positioning Devising warrantees Packaging Product features/options Product style Quality 46
Marketing Planning Product/Service Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Test marketing Brand positioning Devising warrantees Packaging Product features/options Product style Quality 46
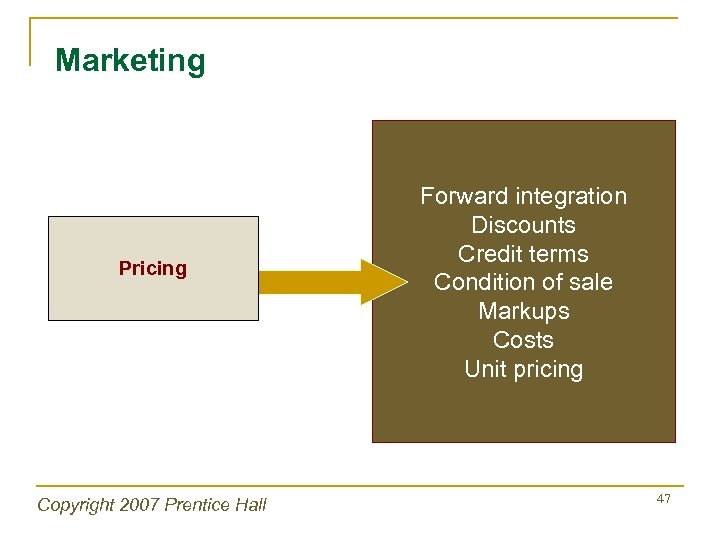 Marketing Pricing Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Forward integration Discounts Credit terms Condition of sale Markups Costs Unit pricing 47
Marketing Pricing Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Forward integration Discounts Credit terms Condition of sale Markups Costs Unit pricing 47
 Marketing Distribution Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Warehousing Channels Coverage Retail site locations Sales territories Inventory levels Transportation 48
Marketing Distribution Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Warehousing Channels Coverage Retail site locations Sales territories Inventory levels Transportation 48
 Marketing Research Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Data collection Data input Data analysis Support business functions 49
Marketing Research Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Data collection Data input Data analysis Support business functions 49
 Marketing Assessing costs Opportunity Analysis Assessing benefits Assessing risks Cost/benefit/risk analysis Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 50
Marketing Assessing costs Opportunity Analysis Assessing benefits Assessing risks Cost/benefit/risk analysis Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 50
 Marketing Opportunity Analysis 1. Are markets segmented effectively? 2. Is the organization positioned well among competitors? 3. Has the firm’s market share been increasing? 4. Are the distribution channels reliable & cost effective? 5. Is the sales force effective? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 51
Marketing Opportunity Analysis 1. Are markets segmented effectively? 2. Is the organization positioned well among competitors? 3. Has the firm’s market share been increasing? 4. Are the distribution channels reliable & cost effective? 5. Is the sales force effective? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 51
 Marketing Opportunity Analysis 6. Does the firm conduct market research? 7. Are product quality & customer service good? 8. Are the firm’s products/services priced appropriately? 9. Does the firm have effective promotion, advertising, & publicity strategies? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 52
Marketing Opportunity Analysis 6. Does the firm conduct market research? 7. Are product quality & customer service good? 8. Are the firm’s products/services priced appropriately? 9. Does the firm have effective promotion, advertising, & publicity strategies? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 52
 Marketing Opportunity Analysis 10. Are the marketing planning & budgeting effective? 11. Do the firm’s marketing managers have adequate experience and training? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 53
Marketing Opportunity Analysis 10. Are the marketing planning & budgeting effective? 11. Do the firm’s marketing managers have adequate experience and training? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 53
 Finance/Accounting § Determining financial strengths & weaknesses key to strategy formation Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 54
Finance/Accounting § Determining financial strengths & weaknesses key to strategy formation Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 54
 Finance/Accounting Functions 1. Investment decision (Capital budgeting) 2. Financing decision 3. Dividend decision Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 55
Finance/Accounting Functions 1. Investment decision (Capital budgeting) 2. Financing decision 3. Dividend decision Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 55
 Basic Financial Ratios Firm’s ability to meet its short-term obligations Liquidity Ratios Current ratio Quick (or acid test) ratio Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 56
Basic Financial Ratios Firm’s ability to meet its short-term obligations Liquidity Ratios Current ratio Quick (or acid test) ratio Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 56
 Basic Financial Ratios Extent of debt financing Leverage Ratios Debt-to-total assets Debt-to-equity Long-term debt-to-equity Times-interest earned Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 57
Basic Financial Ratios Extent of debt financing Leverage Ratios Debt-to-total assets Debt-to-equity Long-term debt-to-equity Times-interest earned Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 57
 Basic Financial Ratios Effective use of firm’s resources Activity Ratios Inventory-turnover Fixed assets turnover Total assets turnover Accounts receivable turnover Average collection period Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 58
Basic Financial Ratios Effective use of firm’s resources Activity Ratios Inventory-turnover Fixed assets turnover Total assets turnover Accounts receivable turnover Average collection period Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 58
 Basic Financial Ratios Effectiveness shown by returns on sales & investment Profitability Ratios Gross profit margin Operating profit margin Net profit margin Return on total assets (ROA) Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 59
Basic Financial Ratios Effectiveness shown by returns on sales & investment Profitability Ratios Gross profit margin Operating profit margin Net profit margin Return on total assets (ROA) Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 59
 Basic Financial Ratios Effectiveness shown by returns on sales & investment Profitability Ratios (cont’d) Ratios Return on stockholders equity (ROE) Earnings per share Price-earnings ratio Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 60
Basic Financial Ratios Effectiveness shown by returns on sales & investment Profitability Ratios (cont’d) Ratios Return on stockholders equity (ROE) Earnings per share Price-earnings ratio Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 60
 Basic Financial Ratios Firm’s ability to maintain economic position Growth Ratios Sales Net income Earnings per share Dividends per share Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 61
Basic Financial Ratios Firm’s ability to maintain economic position Growth Ratios Sales Net income Earnings per share Dividends per share Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 61
 Finance/Accounting Audit • Where is the firm strong/weak as indicated by financial ratio analysis? • Can the firm raise short-term capital as needed? • Can the firm raise long-term capital as needed through debt and/or equity? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 62
Finance/Accounting Audit • Where is the firm strong/weak as indicated by financial ratio analysis? • Can the firm raise short-term capital as needed? • Can the firm raise long-term capital as needed through debt and/or equity? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 62
 Finance/Accounting Audit • Does the firm have sufficient working capital? • Are capital budgeting procedures effective? • Are dividend payout policies reasonable? • Are the firm’s financial managers experienced & well trained? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 63
Finance/Accounting Audit • Does the firm have sufficient working capital? • Are capital budgeting procedures effective? • Are dividend payout policies reasonable? • Are the firm’s financial managers experienced & well trained? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 63
 Finance/Accounting Audit Effective Financial Analysis Requires: 1. Analysis of how the ratios have changed over time 2. How the ratios compare to industry norms 3. How the ratios compare with key competitors Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 64
Finance/Accounting Audit Effective Financial Analysis Requires: 1. Analysis of how the ratios have changed over time 2. How the ratios compare to industry norms 3. How the ratios compare with key competitors Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 64
 Production/Operations Functions § Process § Capacity § Inventory § Workforce § Quality Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 65
Production/Operations Functions § Process § Capacity § Inventory § Workforce § Quality Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 65
 Production/Operations Process Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Facility design Technology selection Facility layout Process flow analysis Facility location Line balancing Process control 66
Production/Operations Process Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Facility design Technology selection Facility layout Process flow analysis Facility location Line balancing Process control 66
 Production/Operations Capacity Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Forecasting Facilities planning Aggregate planning Scheduling Capacity planning Queuing analysis 67
Production/Operations Capacity Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Forecasting Facilities planning Aggregate planning Scheduling Capacity planning Queuing analysis 67
 Production/Operations Inventory Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Raw materials Work in process Finished goods Materials handling 68
Production/Operations Inventory Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Raw materials Work in process Finished goods Materials handling 68
 Production/Operations Workforce Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Job design Work measurement Job enrichment Work standards Motivation techniques 69
Production/Operations Workforce Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Job design Work measurement Job enrichment Work standards Motivation techniques 69
 Production/Operations Quality Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Quality control Sampling Testing Quality assurance Cost Control 70
Production/Operations Quality Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall Quality control Sampling Testing Quality assurance Cost Control 70
 Production/Operations Audit • Are suppliers of materials, parts, etc. reliable and reasonable? • Are facilities, equipment & machinery in good condition? • Are inventory-control policies and procedures effective? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 71
Production/Operations Audit • Are suppliers of materials, parts, etc. reliable and reasonable? • Are facilities, equipment & machinery in good condition? • Are inventory-control policies and procedures effective? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 71
 Production/Operations Audit • Are quality-control policies & procedures effective? • Are facilities, resources, and markets strategically located? • Does the firm have technological competencies? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 72
Production/Operations Audit • Are quality-control policies & procedures effective? • Are facilities, resources, and markets strategically located? • Does the firm have technological competencies? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 72
 Research & Development Functions § Development of new products before competitors § Improving product quality § Improving manufacturing processes to reduce costs Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 73
Research & Development Functions § Development of new products before competitors § Improving product quality § Improving manufacturing processes to reduce costs Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 73
 Research & Development Financing as many projects as possible Use percent-of-sales method R&D Budgets Budgeting relative to competitors How many successful new products are needed Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 74
Research & Development Financing as many projects as possible Use percent-of-sales method R&D Budgets Budgeting relative to competitors How many successful new products are needed Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 74
 Research & Development Audit • Are the R&D facilities adequate? • If R&D is outsourced, is it cost effective? • Are the R&D personnel well qualified? • Are R&D resources allocated effectively? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 75
Research & Development Audit • Are the R&D facilities adequate? • If R&D is outsourced, is it cost effective? • Are the R&D personnel well qualified? • Are R&D resources allocated effectively? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 75
 Research & Development Audit • Are MIS and computer systems adequate? • Is communication between R&D & other organizational units effective? • Are present products technologically competitive? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 76
Research & Development Audit • Are MIS and computer systems adequate? • Is communication between R&D & other organizational units effective? • Are present products technologically competitive? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 76
 Management Information Systems Purpose § Improve performance of an enterprise by improving the quality of managerial decisions. Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 77
Management Information Systems Purpose § Improve performance of an enterprise by improving the quality of managerial decisions. Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 77
 Management Information Systems n n n Information Systems CIO/CTO Security User-friendly E-commerce Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 78
Management Information Systems n n n Information Systems CIO/CTO Security User-friendly E-commerce Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 78
 Management Information Systems Audit • Do managers use the information system to make decisions? • Is there a CIO or Director of Information Systems position in the firm? • Is data updated regularly? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 79
Management Information Systems Audit • Do managers use the information system to make decisions? • Is there a CIO or Director of Information Systems position in the firm? • Is data updated regularly? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 79
 Management Information Systems Audit • Do managers from all functional areas contribute input to the information system? • Are there effective passwords for entry into the firm’s information system? • Are strategists of the firm familiar with the information systems of rival firms? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 80
Management Information Systems Audit • Do managers from all functional areas contribute input to the information system? • Are there effective passwords for entry into the firm’s information system? • Are strategists of the firm familiar with the information systems of rival firms? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 80
 Management Information Systems Audit • Is the information system user-friendly? • Do all users understand the competitive advantages that information can provide? • Are computer training workshops provided for users? • Is the firm’s system being improved? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 81
Management Information Systems Audit • Is the information system user-friendly? • Do all users understand the competitive advantages that information can provide? • Are computer training workshops provided for users? • Is the firm’s system being improved? Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 81
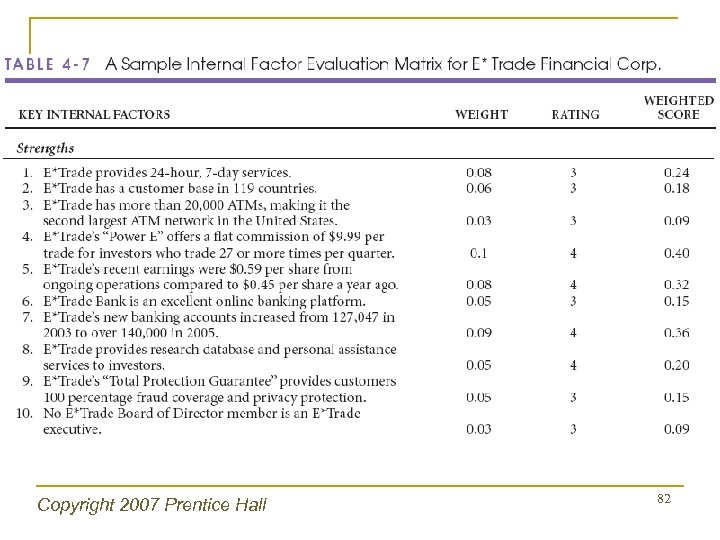 Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 82
Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 82
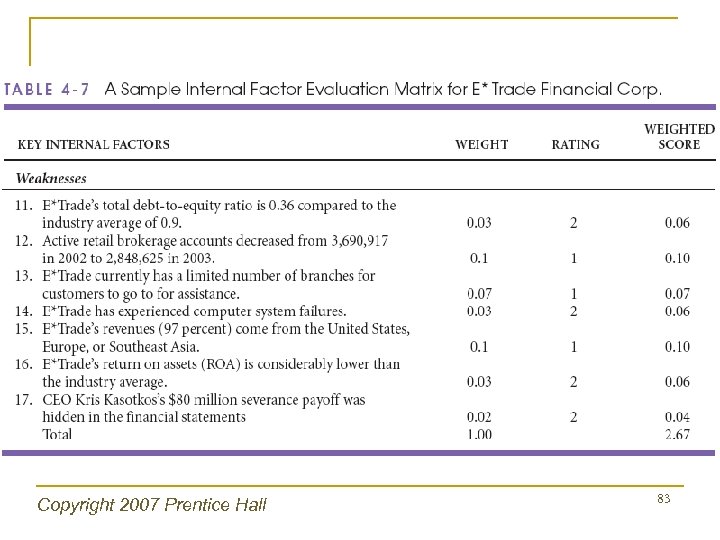 Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 83
Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 83
 For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Activity Ratios Cost/Benefit Analysis Capital Budgeting Cultural Products Communication Distinctive Competencies Controlling Distribution Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 84
For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Activity Ratios Cost/Benefit Analysis Capital Budgeting Cultural Products Communication Distinctive Competencies Controlling Distribution Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 84
 For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Dividend Decision Functions of Finance/Accounting Empirical Indicators Functions of Management Financial Ratio Analysis Functions of Marketing Financing Decision Functions of Production/ Operations Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 85
For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Dividend Decision Functions of Finance/Accounting Empirical Indicators Functions of Management Financial Ratio Analysis Functions of Marketing Financing Decision Functions of Production/ Operations Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 85
 For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Growth Ratios Investment Decision Human Resource Management Leverage Ratios Internal Audit Liquidity Ratios Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix Management Information Systems Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 86
For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Growth Ratios Investment Decision Human Resource Management Leverage Ratios Internal Audit Liquidity Ratios Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix Management Information Systems Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 86
 For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Motivating Personnel Management Opportunity Analysis Planning Organizational Culture Pricing Organizing Product & Service Planning Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 87
For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Motivating Personnel Management Opportunity Analysis Planning Organizational Culture Pricing Organizing Product & Service Planning Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 87
 For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Production/Operations Functions Selling Profitability Ratios Staffing Research & Development Synergy Resource Based View (RBV) Test Marketing Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 88
For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Production/Operations Functions Selling Profitability Ratios Staffing Research & Development Synergy Resource Based View (RBV) Test Marketing Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 88
 For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Value Chain Analysis (VCA) Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 89
For Review (Chapter 4) Key Terms & Concepts Value Chain Analysis (VCA) Copyright 2007 Prentice Hall 89


