d969379748341e33e97d93e3384f22fd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

 Chapter 4 The Future of the Financial System and the Money and Capital Markets Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2008 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Chapter 4 The Future of the Financial System and the Money and Capital Markets Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2008 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Learning Objectives ù To explore the economic, demographic, social, and technological forces reshaping the financial system today. ù To learn about recent trends in the financial system and how they may affect us in the future. ù To learn about how your behavior and decisions, along with millions of others, may plan an important role in shaping the future of the financial system 4 -3
Learning Objectives ù To explore the economic, demographic, social, and technological forces reshaping the financial system today. ù To learn about recent trends in the financial system and how they may affect us in the future. ù To learn about how your behavior and decisions, along with millions of others, may plan an important role in shaping the future of the financial system 4 -3
 Introduction ù Powerful forces are reshaping today’s financial marketplace ù Forces for change ù Powerful new trends within the financial marketplace itself ù Major changes in the structure and functioning of the economy ù New social and demographic trends ù Altering the public’s need for new financial services 4 -4
Introduction ù Powerful forces are reshaping today’s financial marketplace ù Forces for change ù Powerful new trends within the financial marketplace itself ù Major changes in the structure and functioning of the economy ù New social and demographic trends ù Altering the public’s need for new financial services 4 -4
 Financial Forces: Reshaping the Money and Capital Markets Today ù Financial innovation - the development of many new financial services and instruments ù Service proliferation - the expansion of the menu of financial services offered ù Competition - the intense struggle for the customer’s business ù Consolidation - mergers and acquisitions have created financial giants out of numerous smaller financial-service providers 4 -5
Financial Forces: Reshaping the Money and Capital Markets Today ù Financial innovation - the development of many new financial services and instruments ù Service proliferation - the expansion of the menu of financial services offered ù Competition - the intense struggle for the customer’s business ù Consolidation - mergers and acquisitions have created financial giants out of numerous smaller financial-service providers 4 -5
 Financial Forces: Reshaping the Money and Capital Markets Today ù Deregulation - the lightening or elimination of government rules brought about by a strategy of privatization of the financial sector ù Convergence - the blurring of the traditional distinctions among different types of financial-service institutions ù Homogenization - the growing similarity in the service menus offered by financial institutions 4 -6
Financial Forces: Reshaping the Money and Capital Markets Today ù Deregulation - the lightening or elimination of government rules brought about by a strategy of privatization of the financial sector ù Convergence - the blurring of the traditional distinctions among different types of financial-service institutions ù Homogenization - the growing similarity in the service menus offered by financial institutions 4 -6
 Financial Forces: Reshaping the Money and Capital Markets Today ù Globalization - the global expansion of operations and the falling of geographical barriers ù Market broadening - the expansion of traditionally local markets to become regional, national, or even international in scope ù Securitization - the pooling of loans and the issuance of securities as claims against the loan pool 4 -7
Financial Forces: Reshaping the Money and Capital Markets Today ù Globalization - the global expansion of operations and the falling of geographical barriers ù Market broadening - the expansion of traditionally local markets to become regional, national, or even international in scope ù Securitization - the pooling of loans and the issuance of securities as claims against the loan pool 4 -7
 Economic & Demographic Forces Reshaping the Financial System ù Aging population has greater needs ù Retirement ù Tax and estate planning ù Changing basic family unit ù Rise in proportion of nontraditional households (single-parent, well-educated working women, parents and children living apart, immigrants) ù Increases demand (new forms housing, daycare facilities, flexible work schedule, less expensive medical care) 4 -8
Economic & Demographic Forces Reshaping the Financial System ù Aging population has greater needs ù Retirement ù Tax and estate planning ù Changing basic family unit ù Rise in proportion of nontraditional households (single-parent, well-educated working women, parents and children living apart, immigrants) ù Increases demand (new forms housing, daycare facilities, flexible work schedule, less expensive medical care) 4 -8
 Life Cycle Hypothesis ù Life cycle hypothesis ù Aging individuals reduce expectations of lifetime income ù As retirement approaches, consumption declines to match ù As US population ages ù Tend to consume less ù Tend to save more ù Challenge ù Provide for older savers ù Including retirement and estate planning 4 -9
Life Cycle Hypothesis ù Life cycle hypothesis ù Aging individuals reduce expectations of lifetime income ù As retirement approaches, consumption declines to match ù As US population ages ù Tend to consume less ù Tend to save more ù Challenge ù Provide for older savers ù Including retirement and estate planning 4 -9
 Economic & Demographic Forces Reshaping the Financial System ù Displacement of manufacturing industries by service industries in more developed economies ù Technological innovation - the dissemination and storage of information today is broader, cheaper, faster, and more accurate ù Internationalization of markets - such as the emergence of the European Union 4 -10
Economic & Demographic Forces Reshaping the Financial System ù Displacement of manufacturing industries by service industries in more developed economies ù Technological innovation - the dissemination and storage of information today is broader, cheaper, faster, and more accurate ù Internationalization of markets - such as the emergence of the European Union 4 -10
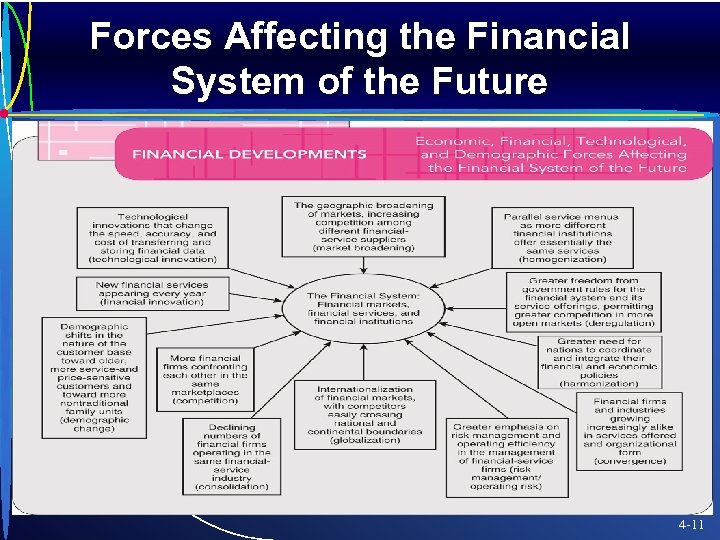 Forces Affecting the Financial System of the Future 4 -11
Forces Affecting the Financial System of the Future 4 -11
 Dealing with Risk in the Financial System: The Challenges and Opportunities ù The financial marketplaces depends on public confidence ù Induces parties to provide credit to the market ù Honesty and reliability often as important as price ù Loss of public confidence ù Produces adverse consequences for individual financial institutions ù Damages the efficiency of market processes ù Flight of funds ù Higher costs for remaining funds 4 -12
Dealing with Risk in the Financial System: The Challenges and Opportunities ù The financial marketplaces depends on public confidence ù Induces parties to provide credit to the market ù Honesty and reliability often as important as price ù Loss of public confidence ù Produces adverse consequences for individual financial institutions ù Damages the efficiency of market processes ù Flight of funds ù Higher costs for remaining funds 4 -12
 Dealing with Risk in the Financial System: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Public confidence can be promoted ù Government insurance systems ù Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) ù Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (PBGC) ù Regulation of capital – equity requirements ù Private responses - market discipline ù Developing better risk-management tools ù Derivatives ù Stress testing 4 -13
Dealing with Risk in the Financial System: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Public confidence can be promoted ù Government insurance systems ù Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) ù Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (PBGC) ù Regulation of capital – equity requirements ù Private responses - market discipline ù Developing better risk-management tools ù Derivatives ù Stress testing 4 -13
 Risk in the Financial System: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Government actions limited by problems ù Government-provided insurance can distort risk-taking ù Excess restrictions can reduce international competitiveness ù Private response limited ù Limited information disclosure ù Market investors can only approximately price these securities 4 -14
Risk in the Financial System: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Government actions limited by problems ù Government-provided insurance can distort risk-taking ù Excess restrictions can reduce international competitiveness ù Private response limited ù Limited information disclosure ù Market investors can only approximately price these securities 4 -14
 New Technology: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Financial information ù Essential to provision of financial services ù Technological revolution – analysis, storage, and transfer ù Electronic-based communications systems annually improving at accelerating pace 4 -15
New Technology: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Financial information ù Essential to provision of financial services ù Technological revolution – analysis, storage, and transfer ù Electronic-based communications systems annually improving at accelerating pace 4 -15
 New Technology: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Global integrated electronic networks ù Changing financial services design and delivery ù Internet ù Cellular phones and smart phones ù Pocket and hand-held computers ù Smart cards 4 -16
New Technology: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Global integrated electronic networks ù Changing financial services design and delivery ù Internet ù Cellular phones and smart phones ù Pocket and hand-held computers ù Smart cards 4 -16
 New Technology: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Advertising ù Transaction ù Internet banking ù Internet investment ù Purchases ù Financial transfers ù Information 4 -17
New Technology: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Advertising ù Transaction ù Internet banking ù Internet investment ù Purchases ù Financial transfers ù Information 4 -17
 New Technology: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Adjustment to technology lags the technological revolution ù Many still prefer paper transactions ù Preference for direct interaction ù Challenges ù Maximize friendliness of user interface ù Minimize operating costs and service prices ù Ensure ease of technological upgrades ù Strengthen data integrity and system security ù Manage greater level of external information 4 -18
New Technology: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Adjustment to technology lags the technological revolution ù Many still prefer paper transactions ù Preference for direct interaction ù Challenges ù Maximize friendliness of user interface ù Minimize operating costs and service prices ù Ensure ease of technological upgrades ù Strengthen data integrity and system security ù Manage greater level of external information 4 -18
 The Changing Mix of Financial-Service Suppliers: Challenges and Opportunities ù Who will offer financial services ù Erosion of traditional area separation ù Greater competition ù Price competition ù Nonprice features ù Likely remainder of differentiation will disappear ù Better-informed customers likely to be willing to move business 4 -19
The Changing Mix of Financial-Service Suppliers: Challenges and Opportunities ù Who will offer financial services ù Erosion of traditional area separation ù Greater competition ù Price competition ù Nonprice features ù Likely remainder of differentiation will disappear ù Better-informed customers likely to be willing to move business 4 -19
 The Changing Mix of Financial-Service Suppliers: Challenges and Opportunities ù Extensive delivery system ù Cost advantage ù Productivity advantage ù Emerging financial service needs ù Need for new financial institutions ù Develop to manage evolution in financial instruments ù Loans to remodel residential ù Small business loans ù Credit risk derivatives 4 -20
The Changing Mix of Financial-Service Suppliers: Challenges and Opportunities ù Extensive delivery system ù Cost advantage ù Productivity advantage ù Emerging financial service needs ù Need for new financial institutions ù Develop to manage evolution in financial instruments ù Loans to remodel residential ù Small business loans ù Credit risk derivatives 4 -20
 The Changing Mix of Financial-Service Suppliers: Challenges and Opportunities ù Securitization ù Mortgage-backed securities very successful ù Spawned other markets ù Credit card receivables ù Auto and boat loans ù Equipment leases, among others 4 -21
The Changing Mix of Financial-Service Suppliers: Challenges and Opportunities ù Securitization ù Mortgage-backed securities very successful ù Spawned other markets ù Credit card receivables ù Auto and boat loans ù Equipment leases, among others 4 -21
 Consolidations and Convergences: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Merger and acquisition activity ù Consolidation ù Convergence 4 -22
Consolidations and Convergences: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Merger and acquisition activity ù Consolidation ù Convergence 4 -22
 Consolidations and Convergences: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Advantages ù Elimination of duplication brings about substantial operating costs savings ù Broadening of services and customer segments accelerate revenue growth ù Greater diversification reduces overall risk ù Combination of expertise results in higherquality products and services ù Greater economies of scale increases the affordability of technologies ù Greater efficiency in joint marketing and crossselling 4 -23
Consolidations and Convergences: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Advantages ù Elimination of duplication brings about substantial operating costs savings ù Broadening of services and customer segments accelerate revenue growth ù Greater diversification reduces overall risk ù Combination of expertise results in higherquality products and services ù Greater economies of scale increases the affordability of technologies ù Greater efficiency in joint marketing and crossselling 4 -23
 Consolidations and Convergences: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Disadvantage ù Greater complexities of managing the firm may increase operating costs ù May have overestimated public’s demand for “one stop” financial shopping ù Smaller financial firms may provide more personalized services ù Smaller financial firms may compete effectively by outsourcing 4 -24
Consolidations and Convergences: The Challenges and Opportunities ù Disadvantage ù Greater complexities of managing the firm may increase operating costs ù May have overestimated public’s demand for “one stop” financial shopping ù Smaller financial firms may provide more personalized services ù Smaller financial firms may compete effectively by outsourcing 4 -24
 Financial Services Regulation ù Consolidation and convergence ù Major challenges for the regulatory agencies ù Safe financial system ù Stable financial system ù Regulators cannot stop the market evolution ù Challenge to merge safety and stability with market forces 4 -25
Financial Services Regulation ù Consolidation and convergence ù Major challenges for the regulatory agencies ù Safe financial system ù Stable financial system ù Regulators cannot stop the market evolution ù Challenge to merge safety and stability with market forces 4 -25
 Financial Services Regulation ù Different regulatory approaches ù Holding company ù Single regulator ù Functional regulation ù Harmonization 4 -26
Financial Services Regulation ù Different regulatory approaches ù Holding company ù Single regulator ù Functional regulation ù Harmonization 4 -26
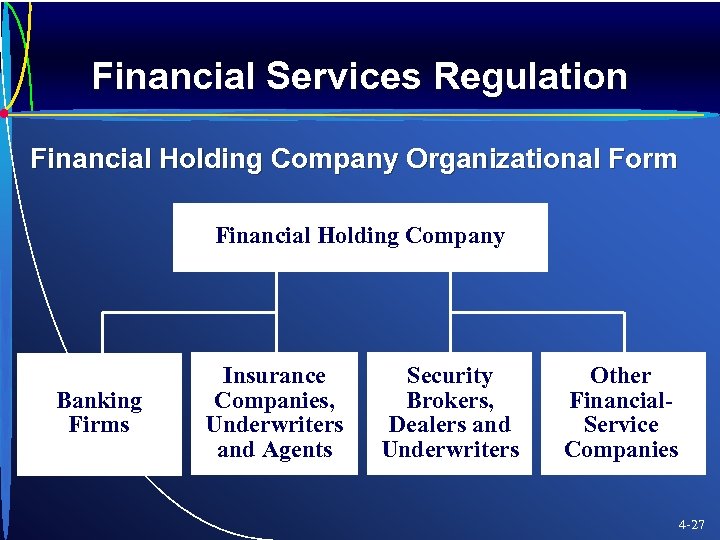 Financial Services Regulation Financial Holding Company Organizational Form Financial Holding Company Banking Firms Insurance Companies, Underwriters and Agents Security Brokers, Dealers and Underwriters Other Financial. Service Companies 4 -27
Financial Services Regulation Financial Holding Company Organizational Form Financial Holding Company Banking Firms Insurance Companies, Underwriters and Agents Security Brokers, Dealers and Underwriters Other Financial. Service Companies 4 -27
 Financial Services Regulation ù Financial Subsidiaries Organization Form Banking or Other Controlling Firm Securities Subsidiary Insurance Subsidiary Other Financial. Service Subsidiaries 4 -28
Financial Services Regulation ù Financial Subsidiaries Organization Form Banking or Other Controlling Firm Securities Subsidiary Insurance Subsidiary Other Financial. Service Subsidiaries 4 -28
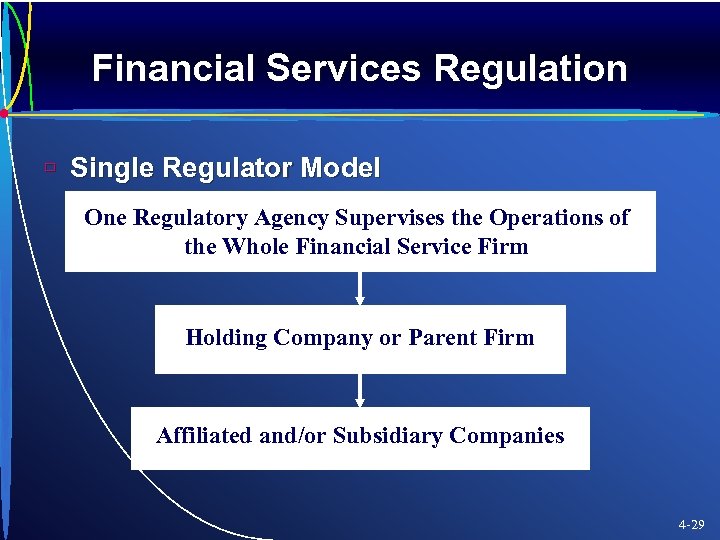 Financial Services Regulation ù Single Regulator Model One Regulatory Agency Supervises the Operations of the Whole Financial Service Firm Holding Company or Parent Firm Affiliated and/or Subsidiary Companies 4 -29
Financial Services Regulation ù Single Regulator Model One Regulatory Agency Supervises the Operations of the Whole Financial Service Firm Holding Company or Parent Firm Affiliated and/or Subsidiary Companies 4 -29
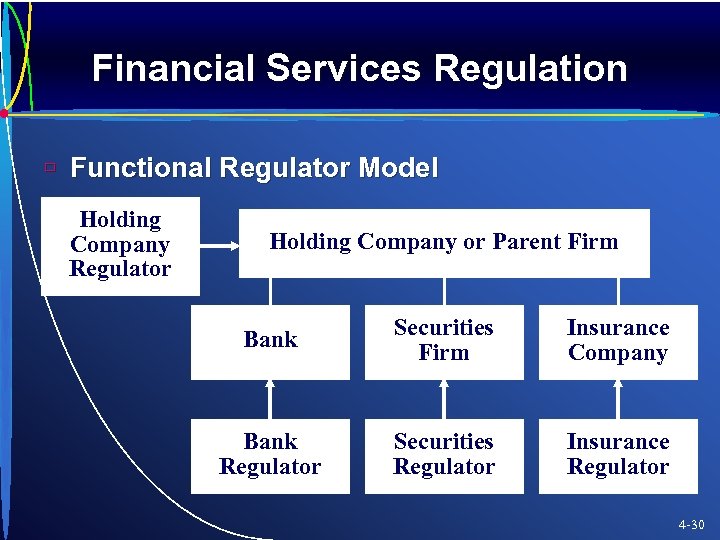 Financial Services Regulation ù Functional Regulator Model Holding Company Regulator Holding Company or Parent Firm Bank Securities Firm Insurance Company Bank Regulator Securities Regulator Insurance Regulator 4 -30
Financial Services Regulation ù Functional Regulator Model Holding Company Regulator Holding Company or Parent Firm Bank Securities Firm Insurance Company Bank Regulator Securities Regulator Insurance Regulator 4 -30
 Financial Services Regulation ù Difficulty of coordination and control in larger and more diversified financial institutions require, ù Employees who are well trained in coordination and control skills ù Strong internal auditing procedures and management information systems, and ù Continual evaluation of subsidiary firms, profit centers, and service functions for their contributions to the firm’s goals 4 -31
Financial Services Regulation ù Difficulty of coordination and control in larger and more diversified financial institutions require, ù Employees who are well trained in coordination and control skills ù Strong internal auditing procedures and management information systems, and ù Continual evaluation of subsidiary firms, profit centers, and service functions for their contributions to the firm’s goals 4 -31
 The Payments System: Current and Future ù Retail ù Small payments ù Largely between individuals and firms ù Wholesale ù Large payments ù Mainly banks, business firms, and government agencies ù Typically pass through automatic clearinghouses, fedwire and other clearinghouses 4 -32
The Payments System: Current and Future ù Retail ù Small payments ù Largely between individuals and firms ù Wholesale ù Large payments ù Mainly banks, business firms, and government agencies ù Typically pass through automatic clearinghouses, fedwire and other clearinghouses 4 -32
 The Payments System: Current and Future ùRetail payments system lags behind the wholesale payments system in converting from expensive paper transactions to electronic systems 4 -33
The Payments System: Current and Future ùRetail payments system lags behind the wholesale payments system in converting from expensive paper transactions to electronic systems 4 -33
 The Current and Future Need for Regulation of Financial Institutions ù Recent deregulatory trend likely to continue ù reduced barriers to geographic expansion ù reduced restrictions on the portfolio choices by financial institutions, ù reorganization of regulatory agencies, ù reduced barriers to the development and offering of new services to the public ù Contentious debate on new services from depository institutions ù The pace of government deregulation appears to be accelerating (GATT, NAFTA) 4 -34
The Current and Future Need for Regulation of Financial Institutions ù Recent deregulatory trend likely to continue ù reduced barriers to geographic expansion ù reduced restrictions on the portfolio choices by financial institutions, ù reorganization of regulatory agencies, ù reduced barriers to the development and offering of new services to the public ù Contentious debate on new services from depository institutions ù The pace of government deregulation appears to be accelerating (GATT, NAFTA) 4 -34
 The Current and Future Need for Regulation of Financial Institutions ù Not all government regulations will disappear ù Concern over safety ù Concern over confidence ù Shifting regulation ù Financial disclosure ù Consumer privacy protection ù Social responsibility ù Promote a level playing field 4 -35
The Current and Future Need for Regulation of Financial Institutions ù Not all government regulations will disappear ù Concern over safety ù Concern over confidence ù Shifting regulation ù Financial disclosure ù Consumer privacy protection ù Social responsibility ù Promote a level playing field 4 -35
 Shifting Regulation: Disclosure ù Require more release of information ù Potential risk ù Potential public disfavor ù Discipline of the market ù Potential gain ù Greater confidence ù More intelligent decisions ù Most economical use of resources 4 -36
Shifting Regulation: Disclosure ù Require more release of information ù Potential risk ù Potential public disfavor ù Discipline of the market ù Potential gain ù Greater confidence ù More intelligent decisions ù Most economical use of resources 4 -36
 Shifting Regulation: Privacy Protection ù Privacy protection ù Many regulations on release of information ù Fight identity theft ù Each year thousands become victim of fraud ù Information stolen to access accounts and assets ù Has been used by terrorist groups 4 -37
Shifting Regulation: Privacy Protection ù Privacy protection ù Many regulations on release of information ù Fight identity theft ù Each year thousands become victim of fraud ù Information stolen to access accounts and assets ù Has been used by terrorist groups 4 -37
 Shifting Regulation: Privacy Protection ù More customer privacy protection ù Require customer permission ù More security ù Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council ù Depository institutions beginning to require more than name and password to access information 4 -38
Shifting Regulation: Privacy Protection ù More customer privacy protection ù Require customer permission ù More security ù Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council ù Depository institutions beginning to require more than name and password to access information 4 -38
 Shifting Regulation: Social Responsibility ù Greater scrutiny of fairness ù Resources used ù Service distribution ù Nondiscrimination ù Serving all neighborhoods ù Pressure will grow ù Have all institutions ù Serve all customers 4 -39
Shifting Regulation: Social Responsibility ù Greater scrutiny of fairness ù Resources used ù Service distribution ù Nondiscrimination ù Serving all neighborhoods ù Pressure will grow ù Have all institutions ù Serve all customers 4 -39
 Shifting Regulation: Level Playing Field ù Fair and equal regulatory treatment ù Important issue for bankers ù Various institutions have differential treatment ù Taxation ù Instruments ù Services ù Differential treatment may lead to differential competitiveness ù Pressure for convergence across different types of institutions 4 -40
Shifting Regulation: Level Playing Field ù Fair and equal regulatory treatment ù Important issue for bankers ù Various institutions have differential treatment ù Taxation ù Instruments ù Services ù Differential treatment may lead to differential competitiveness ù Pressure for convergence across different types of institutions 4 -40
 Markets on the Net ù Accuity at www. bankinfo. com ù American Bankers Association at www. aba. com/Industry+Issues ù Australian Prudential Regulatory Authority at www. apra. gov. au ù Citi Identity Theft Solutions at citibank. com/us/cardserv/advice/victim. htm ù Consumer Law at www. consumerlaw. org ù Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation at http: //www. fdic. gov/consumers ù Federal Reserve System at www. federalreserve. gov 4 -41
Markets on the Net ù Accuity at www. bankinfo. com ù American Bankers Association at www. aba. com/Industry+Issues ù Australian Prudential Regulatory Authority at www. apra. gov. au ù Citi Identity Theft Solutions at citibank. com/us/cardserv/advice/victim. htm ù Consumer Law at www. consumerlaw. org ù Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation at http: //www. fdic. gov/consumers ù Federal Reserve System at www. federalreserve. gov 4 -41
 Markets on the Net ù ù ù ù ù Federal Trade Commission at www. ftc. gov Fin. Pipe at www. finpipe. com/derivglossary. htm Google at www. google. com/xhtml Government Computer News at gcn. com Hoovers at hoovers. com Identity Theft Assistance Center at identitytheftassistance. com Identity Theft 911 LLC at identitytheft 911. org Imenu at www. imenu. com Managing Automation at Managing. Automation. com 4 -42
Markets on the Net ù ù ù ù ù Federal Trade Commission at www. ftc. gov Fin. Pipe at www. finpipe. com/derivglossary. htm Google at www. google. com/xhtml Government Computer News at gcn. com Hoovers at hoovers. com Identity Theft Assistance Center at identitytheftassistance. com Identity Theft 911 LLC at identitytheft 911. org Imenu at www. imenu. com Managing Automation at Managing. Automation. com 4 -42
 Markets on the Net ù Mobile Answers at www. mobile. answers. com ù National Consumer Law Center at www. consumerlaw. org ù New York Stock Exchange at www. nyse. com ù Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation at www. pbgc. gov ù Quote. com at www. quote. com ù Rfid Journal at www. rfidjournal. com ù U. S. Bureau of the Census at www. census. gov ù Wells Fargo Bank at www. wellsfargo. com ù Yahoo at wap. oa. yahoo. com 4 -43
Markets on the Net ù Mobile Answers at www. mobile. answers. com ù National Consumer Law Center at www. consumerlaw. org ù New York Stock Exchange at www. nyse. com ù Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation at www. pbgc. gov ù Quote. com at www. quote. com ù Rfid Journal at www. rfidjournal. com ù U. S. Bureau of the Census at www. census. gov ù Wells Fargo Bank at www. wellsfargo. com ù Yahoo at wap. oa. yahoo. com 4 -43
 Chapter Review ù Introduction: The financial markets in change ù Financial forces reshaping the money and capital markets today ù Social, economic, and demographic forces reshaping the financial system 4 -44
Chapter Review ù Introduction: The financial markets in change ù Financial forces reshaping the money and capital markets today ù Social, economic, and demographic forces reshaping the financial system 4 -44
 Chapter Review ù The challenges and opportunities presented by recent trends ù Dealing with risk in the financial system: Ensuring the strength and viability of Financial institutions and increasing public confidence ù Effect of new technology on the design and delivery of financial services ù Changing mix of financial-service suppliers ù Consolidations and convergences 4 -45
Chapter Review ù The challenges and opportunities presented by recent trends ù Dealing with risk in the financial system: Ensuring the strength and viability of Financial institutions and increasing public confidence ù Effect of new technology on the design and delivery of financial services ù Changing mix of financial-service suppliers ù Consolidations and convergences 4 -45
 Chapter Review ù A new role for financial-services regulation in an age of financialservices consolidation and convergence ù The future of the payments system ù The future need for regulation of financial institutions ù Regulations that could grow ù Level playing field 4 -46
Chapter Review ù A new role for financial-services regulation in an age of financialservices consolidation and convergence ù The future of the payments system ù The future need for regulation of financial institutions ù Regulations that could grow ù Level playing field 4 -46


