0bfd868ec7da3284290d3189b73ef486.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Chapter 4 Telecommunications and the Internet Dr. Hassan Ismail 1
Chapter 4 Telecommunications and the Internet Dr. Hassan Ismail 1
 Chapter 4 Objectives • Understand the role of telecommunications in organizations • Understand the evolution of computer networks • Understand the Internet and how it works • Understand basic Internet services • Understand the use of the World Wide Web 2
Chapter 4 Objectives • Understand the role of telecommunications in organizations • Understand the evolution of computer networks • Understand the Internet and how it works • Understand basic Internet services • Understand the use of the World Wide Web 2
 The Role of Telecommunications and Networks in Organizations • Definitions – Telecommunications – the transmission of all forms of information, including digital data, voice, fax, sound, and video, from one location to another over some type of network – Network – a group of computers and associated peripheral devices connected by a communication channel capable of sharing information and other resources (e. g. , like a printer) between users – Bandwidth – the carrying capacity of telecommunications networks 3
The Role of Telecommunications and Networks in Organizations • Definitions – Telecommunications – the transmission of all forms of information, including digital data, voice, fax, sound, and video, from one location to another over some type of network – Network – a group of computers and associated peripheral devices connected by a communication channel capable of sharing information and other resources (e. g. , like a printer) between users – Bandwidth – the carrying capacity of telecommunications networks 3
 The Role of Telecommunications and Networks in Organizations • Interpersonal Communication Applications – E-mail and Groupware – Voice mail & Facsimile (fax) – Teleconferencing, Data conferencing and Videoconferencing – Common business applications: • Distance learning, • E-learning • E-commerce • E-business • Telemedicine 4
The Role of Telecommunications and Networks in Organizations • Interpersonal Communication Applications – E-mail and Groupware – Voice mail & Facsimile (fax) – Teleconferencing, Data conferencing and Videoconferencing – Common business applications: • Distance learning, • E-learning • E-commerce • E-business • Telemedicine 4
 Electronic Mail and Groupware • E-mail: Eliminates telephone tag and costly long-distance telephone charges • Groupware: Enables work groups at different locations to participate in discussion forums and work on shared documents and projects 5
Electronic Mail and Groupware • E-mail: Eliminates telephone tag and costly long-distance telephone charges • Groupware: Enables work groups at different locations to participate in discussion forums and work on shared documents and projects 5
 Voice Mail and Fax • Voice mail: Digitizes spoken message and transmits it over a network • Fax: Digitizes and transmits documents over telephone lines 6
Voice Mail and Fax • Voice mail: Digitizes spoken message and transmits it over a network • Fax: Digitizes and transmits documents over telephone lines 6
 Teleconferencing, data conferencing, and videoconferencing • Teleconferencing: Ability to confer with a group of people simultaneously • Data conferencing: Two or more users can edit and modify data files simultaneously • Videoconferencing: Participants are able to see each other over video screens 7
Teleconferencing, data conferencing, and videoconferencing • Teleconferencing: Ability to confer with a group of people simultaneously • Data conferencing: Two or more users can edit and modify data files simultaneously • Videoconferencing: Participants are able to see each other over video screens 7
 Common business applications • Distance learning: Education or training delivered • E-learning: Instruction delivered online using the • E-Commerce: buying or selling online using • E-business: use the internet technology to support business. • Telemedicine: exchange of medical information from one location to another via a computer network. over a distance to individuals in one or more locations Internet or private networks the Internet or private networks 8
Common business applications • Distance learning: Education or training delivered • E-learning: Instruction delivered online using the • E-Commerce: buying or selling online using • E-business: use the internet technology to support business. • Telemedicine: exchange of medical information from one location to another via a computer network. over a distance to individuals in one or more locations Internet or private networks the Internet or private networks 8
 Network Topologies • Star network • Ring network • Bus network 9
Network Topologies • Star network • Ring network • Bus network 9
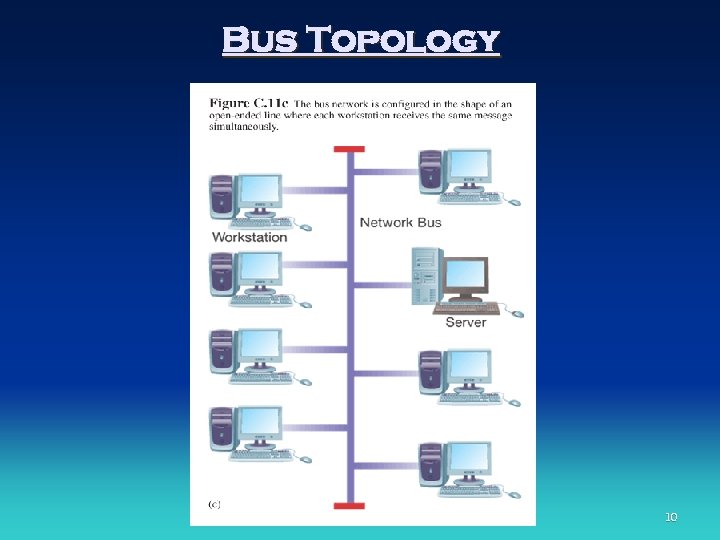 Bus Topology 10
Bus Topology 10
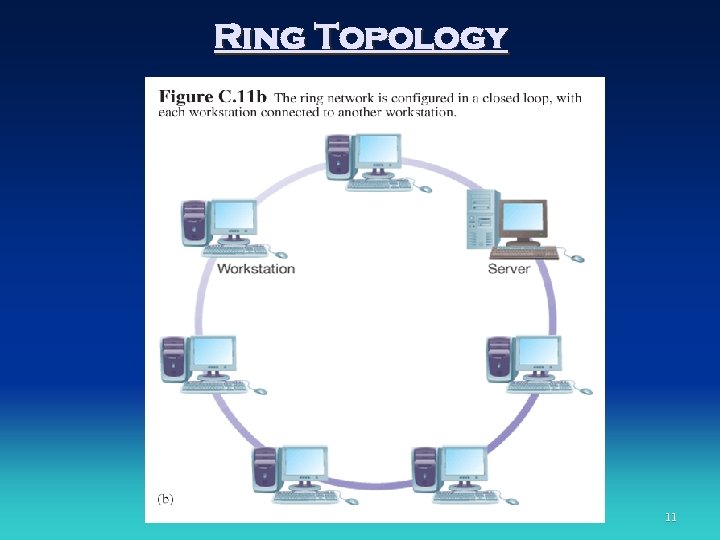 Ring Topology 11
Ring Topology 11
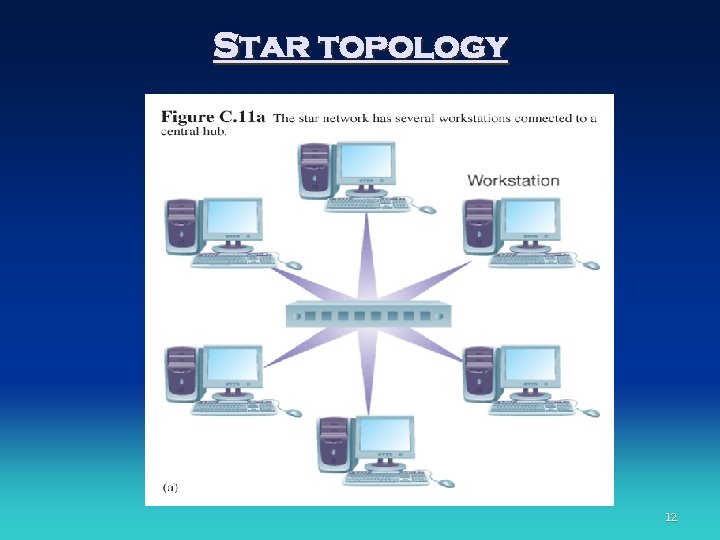 Star topology 12
Star topology 12
 Evolution of Computer Networking • Sharing Information – Senders and receivers that have something to share – Transmission media: cable to send the message – Rules or protocols: dictating communication between senders and receivers. 13
Evolution of Computer Networking • Sharing Information – Senders and receivers that have something to share – Transmission media: cable to send the message – Rules or protocols: dictating communication between senders and receivers. 13
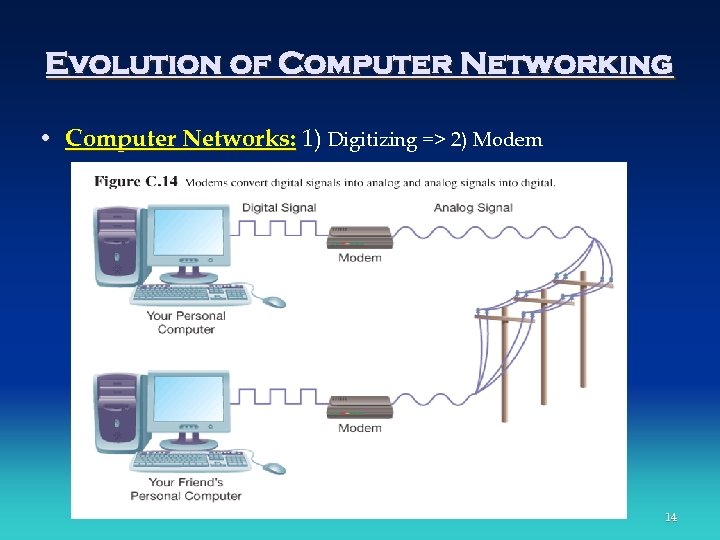 Evolution of Computer Networking • Computer Networks: 1) Digitizing => 2) Modem 14
Evolution of Computer Networking • Computer Networks: 1) Digitizing => 2) Modem 14
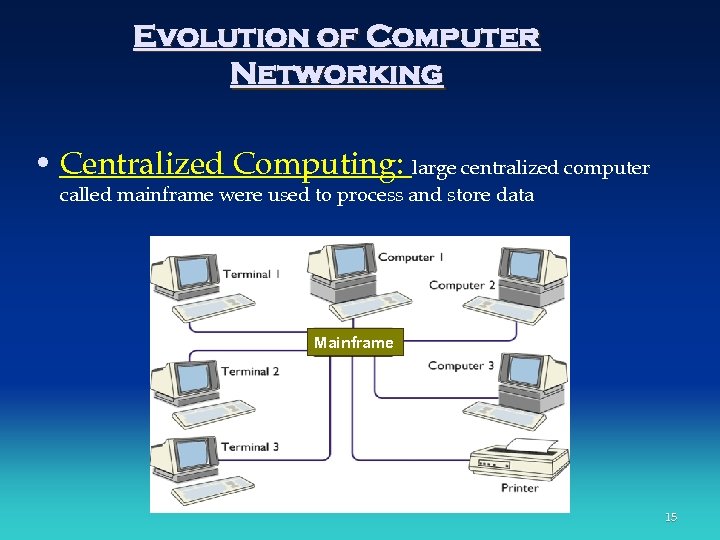 Evolution of Computer Networking • Centralized Computing: large centralized computer called mainframe were used to process and store data Mainframe 15
Evolution of Computer Networking • Centralized Computing: large centralized computer called mainframe were used to process and store data Mainframe 15
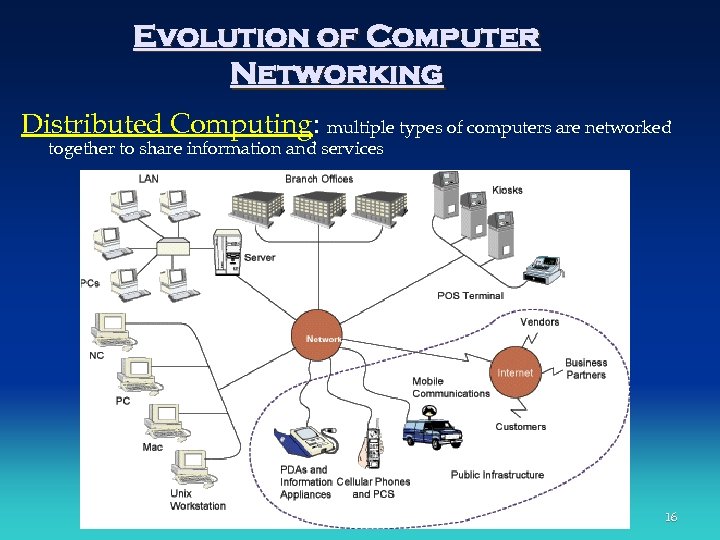 Evolution of Computer Networking Distributed Computing: multiple types of computers are networked together to share information and services 16
Evolution of Computer Networking Distributed Computing: multiple types of computers are networked together to share information and services 16
 Evolution of Computer Networking Collaborative Computing: two or more networked computers are used to accomplish a common processing task. (1) (2) (3) 1. Requests record to change 3. Returns changed record 2. Returns requested record 17
Evolution of Computer Networking Collaborative Computing: two or more networked computers are used to accomplish a common processing task. (1) (2) (3) 1. Requests record to change 3. Returns changed record 2. Returns requested record 17
 Evolution of Computer Networking • Types of Networks – Private Branch Exchange (PBX) – Local Area Network (LAN) – Wide Area Network (WAN) – Personal Area Networks (PANs): 18
Evolution of Computer Networking • Types of Networks – Private Branch Exchange (PBX) – Local Area Network (LAN) – Wide Area Network (WAN) – Personal Area Networks (PANs): 18
 Evolution of Computer Networking • Types of Networks – Private Branch Exchange (PBX): • Central switching system • Handle firm’s voice and digital communications 19
Evolution of Computer Networking • Types of Networks – Private Branch Exchange (PBX): • Central switching system • Handle firm’s voice and digital communications 19
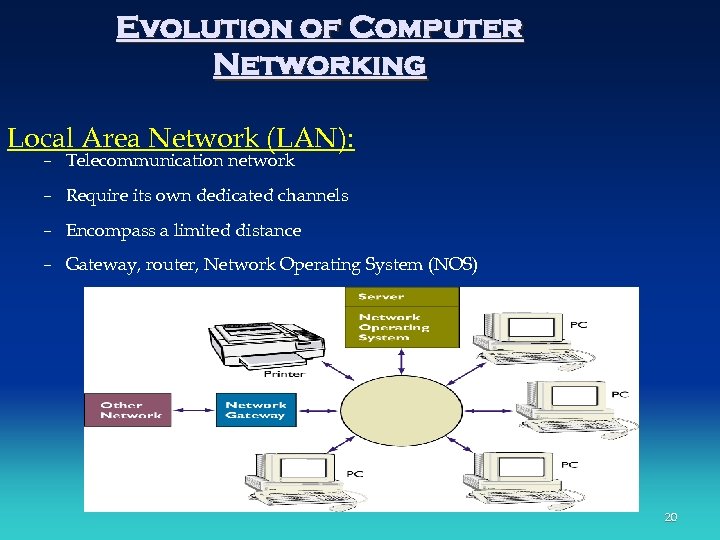 Evolution of Computer Networking Local Area Network (LAN): – Telecommunication network – Require its own dedicated channels – Encompass a limited distance – Gateway, router, Network Operating System (NOS) 20
Evolution of Computer Networking Local Area Network (LAN): – Telecommunication network – Require its own dedicated channels – Encompass a limited distance – Gateway, router, Network Operating System (NOS) 20
 Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Telecommunication network • Span large geographical distance • Consist of variety of cable, satellite, and microwave technologies • Switched lines, dedicated lines 21
Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Telecommunication network • Span large geographical distance • Consist of variety of cable, satellite, and microwave technologies • Switched lines, dedicated lines 21
 …WAN types • Global Networks: spans multiple countries and may include several organizations • Enterprise Networks: WAN connecting networks of single organization • Value-Added Networks (VANs): private, third-party managed networks (lease communication lines rather than investing in dedicated network equipment). • Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs): network for city-wide area 22
…WAN types • Global Networks: spans multiple countries and may include several organizations • Enterprise Networks: WAN connecting networks of single organization • Value-Added Networks (VANs): private, third-party managed networks (lease communication lines rather than investing in dedicated network equipment). • Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs): network for city-wide area 22
 Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Telecommunication network • Span large geographical distance • Consist of variety of cable, satellite, and microwave technologies • Switched lines, dedicated lines 23
Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Telecommunication network • Span large geographical distance • Consist of variety of cable, satellite, and microwave technologies • Switched lines, dedicated lines 23
 Personal Area Networks (PAN) emerging technology uses wireless communication to exchange data through short-range radio communication for short-distance (exp: Bluetooth) 24
Personal Area Networks (PAN) emerging technology uses wireless communication to exchange data through short-range radio communication for short-distance (exp: Bluetooth) 24
 The Internet • How did the Internet Get Started? – ARPANET • U. S. Defense • Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) – NSFNET • National Science Foundation 25
The Internet • How did the Internet Get Started? – ARPANET • U. S. Defense • Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) – NSFNET • National Science Foundation 25
 The Internet • Internet Technologies – Packet-Switching Technology – TCP/IP • Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol • IP Datagram – Connecting Independent Networks • Routers • Backbone Network 26
The Internet • Internet Technologies – Packet-Switching Technology – TCP/IP • Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol • IP Datagram – Connecting Independent Networks • Routers • Backbone Network 26
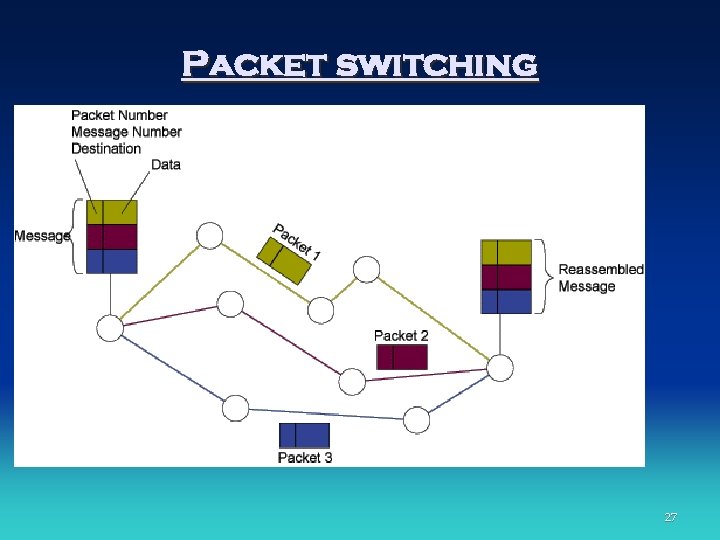 Packet switching 27
Packet switching 27
 The Internet • Web Domain Names and Addresses – Uniform Resource Locator (URL) – Common domain extensions • . edu. org. mil. com. net • . ca. th. no (country codes) – IP Addresses 28
The Internet • Web Domain Names and Addresses – Uniform Resource Locator (URL) – Common domain extensions • . edu. org. mil. com. net • . ca. th. no (country codes) – IP Addresses 28
 The Internet • Who Manages the Internet? – Domain Name System (DNS) – a system used to associate Internet host names with their Internet IP addresses – The Internet Registry – provides central maintenance of the DNS root database, used to associated Internet hostnames with their IP addresses. 29
The Internet • Who Manages the Internet? – Domain Name System (DNS) – a system used to associate Internet host names with their Internet IP addresses – The Internet Registry – provides central maintenance of the DNS root database, used to associated Internet hostnames with their IP addresses. 29
 The Internet • Who Manages the Internet? – Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) – a non-profit corporation manages IP addresses, domain names, and root server system management – Inter. NIC Registration Service – assigns Internet addresses 30
The Internet • Who Manages the Internet? – Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) – a non-profit corporation manages IP addresses, domain names, and root server system management – Inter. NIC Registration Service – assigns Internet addresses 30
 The Internet • How Do You connect to the Internet? – Internet Service Providers (ISPs): which will give you username and password to access to the internet. – Network Access Points (NAPs): within which ISPs can connect to one another. – Internet backbone: which is the collection of main backbone network connections and telecommunications lines comprising the Internet. 31
The Internet • How Do You connect to the Internet? – Internet Service Providers (ISPs): which will give you username and password to access to the internet. – Network Access Points (NAPs): within which ISPs can connect to one another. – Internet backbone: which is the collection of main backbone network connections and telecommunications lines comprising the Internet. 31
 The Internet • How Fast Is Your Connection? – – – – Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) Digital Subsciber Line (DSL) Cable Modems Satellite Connections T 1 Lines Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) 32
The Internet • How Fast Is Your Connection? – – – – Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) Digital Subsciber Line (DSL) Cable Modems Satellite Connections T 1 Lines Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) 32
 The Internet • Security in the Internet Age – Encryption – Firewalls – Authentication 33
The Internet • Security in the Internet Age – Encryption – Firewalls – Authentication 33
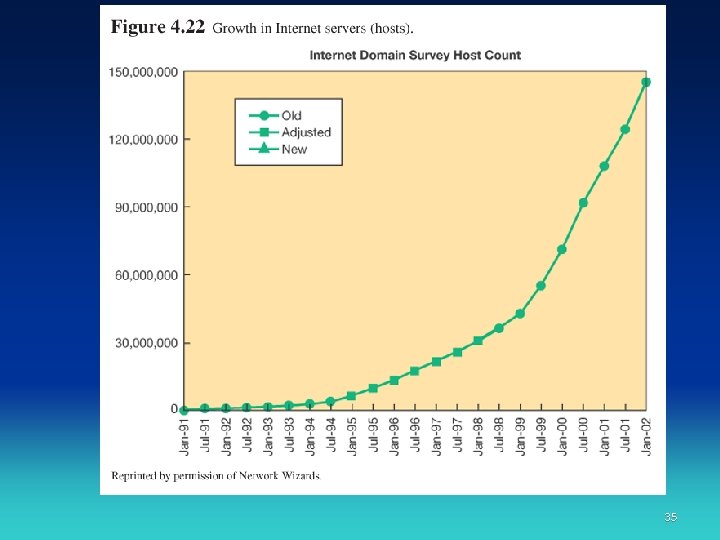
 The Internet • State of the Internet • What are people doing on the Internet? – E-mail – What next for the Internet? • Internet 2 • Abilene network backbone 34
The Internet • State of the Internet • What are people doing on the Internet? – E-mail – What next for the Internet? • Internet 2 • Abilene network backbone 34
 35
35
 The Internet • Internet Tools (see table in page 119) – E-mail – Telnet – File transfer – Listserv – Usenet – Archie – WAIS – Gopher – Voice over IP 36
The Internet • Internet Tools (see table in page 119) – E-mail – Telnet – File transfer – Listserv – Usenet – Archie – WAIS – Gopher – Voice over IP 36
 World Wide Web • • Web browser Hypertext Hyperlinks Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Web servers Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Uniform Resource Locator (URL) 37
World Wide Web • • Web browser Hypertext Hyperlinks Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Web servers Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Uniform Resource Locator (URL) 37
 World Wide Web • World Wide Web Architecture • World Wide Web Applications – – Electronic brochure Online ordering Electronic marketplaces Online customer service 38
World Wide Web • World Wide Web Architecture • World Wide Web Applications – – Electronic brochure Online ordering Electronic marketplaces Online customer service 38


