30c0e058b8bc2171ce259db055c3da75.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 CHAPTER 4 Supply Chain, Enterprise Resources Planning, and Business Processes Engineering 4 -1 1
CHAPTER 4 Supply Chain, Enterprise Resources Planning, and Business Processes Engineering 4 -1 1
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Learning Objectives 2 • Understand the concept of the supply chain, its importance, and management. • Describe the problems of managing the supply chain and some innovative solutions. • Trace the evolution of software that support activities along the supply chain. • Define business processing reengineering (BPR) and understand its relationship with the supply chain.
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Learning Objectives 2 • Understand the concept of the supply chain, its importance, and management. • Describe the problems of managing the supply chain and some innovative solutions. • Trace the evolution of software that support activities along the supply chain. • Define business processing reengineering (BPR) and understand its relationship with the supply chain.
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Learning Objectives 3 • Describe the networked organization and identify its benefits. • Demonstrate the role of IT in supporting BPR. • Describe mass customization, cycle time reduction, self-directed teams, and empowerment. • Define business alliances and virtual corporations. • Understand the relationships among enterprise resources planning (ERP), supply chain management (SCM), and electronic commerce.
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Learning Objectives 3 • Describe the networked organization and identify its benefits. • Demonstrate the role of IT in supporting BPR. • Describe mass customization, cycle time reduction, self-directed teams, and empowerment. • Define business alliances and virtual corporations. • Understand the relationships among enterprise resources planning (ERP), supply chain management (SCM), and electronic commerce.
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban How Dell Reengineered and Managed its Supply Chain to Become #1 • The Problem – price war, and on the verge of bankruptcy • The Solution – – – – using just-in-time manufacturing using mass customization locating within 15 minutes of Dell’s suppliers doing most orders on the Web shipping by UPS selling standard computers to large corporations testing new PC models at the same time as the networks’ solutions are developed – monitor productivity and rate of return on investment, on all products 4
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban How Dell Reengineered and Managed its Supply Chain to Become #1 • The Problem – price war, and on the verge of bankruptcy • The Solution – – – – using just-in-time manufacturing using mass customization locating within 15 minutes of Dell’s suppliers doing most orders on the Web shipping by UPS selling standard computers to large corporations testing new PC models at the same time as the networks’ solutions are developed – monitor productivity and rate of return on investment, on all products 4
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban How Dell Reengineered and Managed its Supply Chain to Become #1 • What Role did IT Play? – electronic commerce with customers – extranet for suppliers – Using the Internet to create a community around its supply chain • The Results – become the number one PC seller – be considered one of the world’s bestmanaged and profitable companies 5
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban How Dell Reengineered and Managed its Supply Chain to Become #1 • What Role did IT Play? – electronic commerce with customers – extranet for suppliers – Using the Internet to create a community around its supply chain • The Results – become the number one PC seller – be considered one of the world’s bestmanaged and profitable companies 5
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Essentials of the Supply Chains • Dell case demonstrates that: – by introducing a new business model one can change the manner in which business is done and may even capture the leadership in its industry – by introducing major customer-related changes, one can improve the communication and customer services – by improving logistics system along the entire supply chain, Dell integrated its own suppliers into its supply chain, efficiently and effectively – Dell created flexible and responsive manufacturing systems – the changes are considered to be a complete reengineering – Dell supports all of the above by extensive use of electronic commerce, the Internet, extranet and intranets 6
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Essentials of the Supply Chains • Dell case demonstrates that: – by introducing a new business model one can change the manner in which business is done and may even capture the leadership in its industry – by introducing major customer-related changes, one can improve the communication and customer services – by improving logistics system along the entire supply chain, Dell integrated its own suppliers into its supply chain, efficiently and effectively – Dell created flexible and responsive manufacturing systems – the changes are considered to be a complete reengineering – Dell supports all of the above by extensive use of electronic commerce, the Internet, extranet and intranets 6
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Essentials of the Supply Chains • Supply Chain – the flow of material, information, and services from raw material suppliers through factories and warehouses to the end customers • Supply Chain Management (SCM) – to plan, organize, and coordinate all the supply chain’s activities 7
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Essentials of the Supply Chains • Supply Chain – the flow of material, information, and services from raw material suppliers through factories and warehouses to the end customers • Supply Chain Management (SCM) – to plan, organize, and coordinate all the supply chain’s activities 7
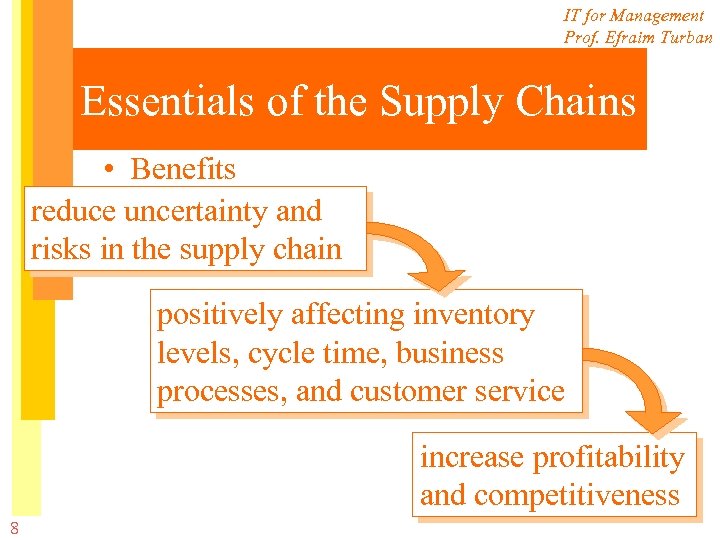 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Essentials of the Supply Chains • Benefits reduce uncertainty and risks in the supply chain positively affecting inventory levels, cycle time, business processes, and customer service increase profitability and competitiveness 8
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Essentials of the Supply Chains • Benefits reduce uncertainty and risks in the supply chain positively affecting inventory levels, cycle time, business processes, and customer service increase profitability and competitiveness 8
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Essentials of the Supply Chains • The Components of Supply Chain 9 – Upstream supply chain • includes the organization’s first-tier suppliers and their suppliers – Internal supply chain • includes all the processes used by an organization in transforming the inputs of the suppliers to outputs – Downstream supply chain • includes all the processes involved in delivering the products to final customers
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Essentials of the Supply Chains • The Components of Supply Chain 9 – Upstream supply chain • includes the organization’s first-tier suppliers and their suppliers – Internal supply chain • includes all the processes used by an organization in transforming the inputs of the suppliers to outputs – Downstream supply chain • includes all the processes involved in delivering the products to final customers
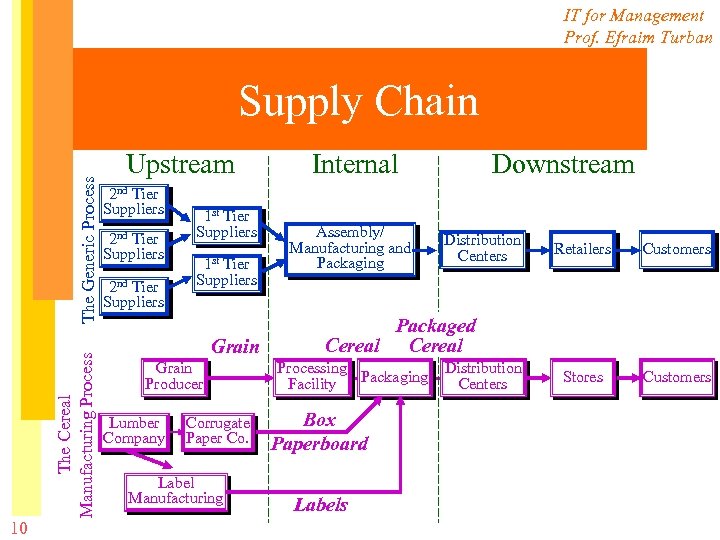 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban 10 The Cereal Manufacturing Process The Generic Process Supply Chain Upstream 2 nd Tier Suppliers 1 st Tier Suppliers Grain Producer Lumber Company Corrugate Paper Co. Label Manufacturing Internal Assembly/ Manufacturing and Packaging Downstream Distribution Centers Retailers Customers Stores Customers Packaged Cereal Processing Packaging Facility Box Paperboard Labels Distribution Centers
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban 10 The Cereal Manufacturing Process The Generic Process Supply Chain Upstream 2 nd Tier Suppliers 1 st Tier Suppliers Grain Producer Lumber Company Corrugate Paper Co. Label Manufacturing Internal Assembly/ Manufacturing and Packaging Downstream Distribution Centers Retailers Customers Stores Customers Packaged Cereal Processing Packaging Facility Box Paperboard Labels Distribution Centers
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Problems Along the Supply Chains • Uncertainties – demand forecast, which influenced by competition, prices, weather conditions, technological development, and customers’ general confidence – delivery times, which depend on several factors ranging from machine failures to road conditions and traffic jams, that way interfere with shipments • Symptoms of poor SCM 11 – poor customer service, which hinders people from getting the product or service when and where needed, or gives them a product of poor quality – High cost, low (or no) profit
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Problems Along the Supply Chains • Uncertainties – demand forecast, which influenced by competition, prices, weather conditions, technological development, and customers’ general confidence – delivery times, which depend on several factors ranging from machine failures to road conditions and traffic jams, that way interfere with shipments • Symptoms of poor SCM 11 – poor customer service, which hinders people from getting the product or service when and where needed, or gives them a product of poor quality – High cost, low (or no) profit
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Some Solutions to the Supply Chain Problems 12 • Vertical integration - building inventories • Coordination of all different activities • Use outsourcing rather than do-it-yourself during demand peaks • ‘Buy’ rather than ‘make’ production inputs whenever appropriate • Configure optimal shipping plans • Create strategic partnerships with suppliers • Use just-in-time approach to purchasing • Use fewer suppliers • Use IT to support the above
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Some Solutions to the Supply Chain Problems 12 • Vertical integration - building inventories • Coordination of all different activities • Use outsourcing rather than do-it-yourself during demand peaks • ‘Buy’ rather than ‘make’ production inputs whenever appropriate • Configure optimal shipping plans • Create strategic partnerships with suppliers • Use just-in-time approach to purchasing • Use fewer suppliers • Use IT to support the above
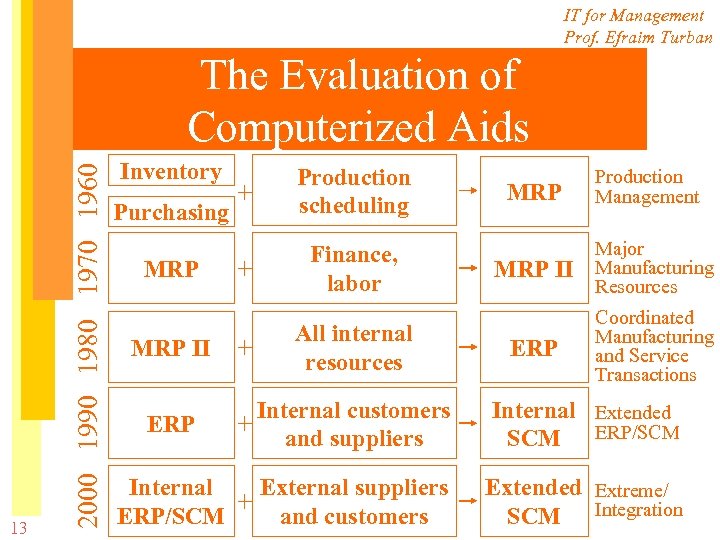 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban 13 2000 1990 1980 1970 1960 The Evaluation of Computerized Aids Inventory Purchasing MRP II + Production scheduling + Finance, labor + All internal resources MRP Production Management MRP II Major Manufacturing Resources ERP Coordinated Manufacturing and Service Transactions Internal customers + and suppliers Internal Extended SCM ERP/SCM Internal External suppliers + and customers ERP/SCM Extended Extreme/ SCM Integration ERP
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban 13 2000 1990 1980 1970 1960 The Evaluation of Computerized Aids Inventory Purchasing MRP II + Production scheduling + Finance, labor + All internal resources MRP Production Management MRP II Major Manufacturing Resources ERP Coordinated Manufacturing and Service Transactions Internal customers + and suppliers Internal Extended SCM ERP/SCM Internal External suppliers + and customers ERP/SCM Extended Extreme/ SCM Integration ERP
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Why Integration? • Tangible benefits – Inventory reduction, personnel reduction, productivity improvement, order management improvement, financial-close cycle improvements, IT cost reduction, procurement cost reduction, cash management improvements, revenue/profit increases, transportation logistics cost reduction maintenance reduction, and ontime delivery improvement 14
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Why Integration? • Tangible benefits – Inventory reduction, personnel reduction, productivity improvement, order management improvement, financial-close cycle improvements, IT cost reduction, procurement cost reduction, cash management improvements, revenue/profit increases, transportation logistics cost reduction maintenance reduction, and ontime delivery improvement 14
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Why Integration? • Intangible benefits – Information visibility, new/improved processes, customer responsiveness, standardization, flexibility, globalization, and business performance. 15
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Why Integration? • Intangible benefits – Information visibility, new/improved processes, customer responsiveness, standardization, flexibility, globalization, and business performance. 15
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Integrating the Supply Chain • After the introduction of computer-based information, companies started to integrate the links of the supply chain • New forms of organizational relationships and the information revolution, especially the Internet and electronic commerce, have brought SCM to the forefront of management attention 16
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Integrating the Supply Chain • After the introduction of computer-based information, companies started to integrate the links of the supply chain • New forms of organizational relationships and the information revolution, especially the Internet and electronic commerce, have brought SCM to the forefront of management attention 16
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Enterprise Resources Planning (ERP) • Objective – to integrate all departments and functions across a company onto a single computer system that can serve all of the enterprise’s needs • Results – productivity improvement – increases customer satisfaction 17
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Enterprise Resources Planning (ERP) • Objective – to integrate all departments and functions across a company onto a single computer system that can serve all of the enterprise’s needs • Results – productivity improvement – increases customer satisfaction 17
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban SAP - The Complete Solution 18 • SAP R/3 is comprised of four major application categories - accounting, manufacturing, sales, and human resources containing more than 70 modules • SAP R/3 allows companies to automate or eliminate many costly and error-prone manual communication procedures • SAP implementation is very complex and consequently very expensive
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban SAP - The Complete Solution 18 • SAP R/3 is comprised of four major application categories - accounting, manufacturing, sales, and human resources containing more than 70 modules • SAP R/3 allows companies to automate or eliminate many costly and error-prone manual communication procedures • SAP implementation is very complex and consequently very expensive
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Example of How R/3 Work • Step 1 : Brazilian retailer orders, via the Internet, 1, 000 shoes from International Shoe Co. A sales rep takes the order, routes it to R/3’s ordering module, R/3 checks the retailer credit, price, etc. The order is approved. • Step 2 : Simultaneously R/3’s inventory module checks the stocks and notifies the rep that half the order can be filled immediately from stock. The other half will be manufactured and delivered in 5 days directly from the factory in Taiwan. 19
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Example of How R/3 Work • Step 1 : Brazilian retailer orders, via the Internet, 1, 000 shoes from International Shoe Co. A sales rep takes the order, routes it to R/3’s ordering module, R/3 checks the retailer credit, price, etc. The order is approved. • Step 2 : Simultaneously R/3’s inventory module checks the stocks and notifies the rep that half the order can be filled immediately from stock. The other half will be manufactured and delivered in 5 days directly from the factory in Taiwan. 19
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Example of How R/3 Work 20 • Step 3 : R/3’s manufacturing module schedules the production in Taiwan and instructs the warehouse (in Chinese) to ship the shoes to Brazil and print up an invoice (in Portuguese). • Step 4 : R/3’s human resources module calculates labor requirements. Due to a shortage, the personnel manager in Taiwan is instructed to get temporary workers. • Step 5 : R/3’s material planning module notifies the purchasing manager about a shortage of purple dye. A purchase order is automatically issued.
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Example of How R/3 Work 20 • Step 3 : R/3’s manufacturing module schedules the production in Taiwan and instructs the warehouse (in Chinese) to ship the shoes to Brazil and print up an invoice (in Portuguese). • Step 4 : R/3’s human resources module calculates labor requirements. Due to a shortage, the personnel manager in Taiwan is instructed to get temporary workers. • Step 5 : R/3’s material planning module notifies the purchasing manager about a shortage of purple dye. A purchase order is automatically issued.
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Example of How R/3 Work • Step 6 : The customer logs on via the extranet to the company’s sneakers division. He can see that 500 shoes were shipped from the regional warehouse. This is done with R/3 tracing capabilities. • Step 7 : Based on data from R/3’s forecasting and financial modules, the CEO can determine both demand profitability per product. The financial module also converts all foreign moneys to $U. S. , whenever needed 21
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Example of How R/3 Work • Step 6 : The customer logs on via the extranet to the company’s sneakers division. He can see that 500 shoes were shipped from the regional warehouse. This is done with R/3 tracing capabilities. • Step 7 : Based on data from R/3’s forecasting and financial modules, the CEO can determine both demand profitability per product. The financial module also converts all foreign moneys to $U. S. , whenever needed 21
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban ERP • Pros – provides a single interface for managing all the routine activities performed in manufacturing – can integrate several hundred applications – plays critical role in getting small- and mediumsized manufacturers to focus on business processes • Cons 22 – need to change existing business processes to fit SAP’s the format – never meant to fully support supply chains – difficult to build, operate, change and maintain
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban ERP • Pros – provides a single interface for managing all the routine activities performed in manufacturing – can integrate several hundred applications – plays critical role in getting small- and mediumsized manufacturers to focus on business processes • Cons 22 – need to change existing business processes to fit SAP’s the format – never meant to fully support supply chains – difficult to build, operate, change and maintain
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban First Generation ERP • Supported routine transactional activities • Excelled in transaction management • Generated reports which provided a snapshot of the business at a point in time • Did not support the continues refining and enhancing of plans as changes and events occur, up to the very last minute before executing the plan 23
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban First Generation ERP • Supported routine transactional activities • Excelled in transaction management • Generated reports which provided a snapshot of the business at a point in time • Did not support the continues refining and enhancing of plans as changes and events occur, up to the very last minute before executing the plan 23
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Second Generation ERP • Adds decision support and business intelligence capabilities • Integration of database management systems (DBMS) and spreadsheets in Excel or Lotus 1 -2 -3 • It is Web-based • Integrates CRM and EC 24
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Second Generation ERP • Adds decision support and business intelligence capabilities • Integration of database management systems (DBMS) and spreadsheets in Excel or Lotus 1 -2 -3 • It is Web-based • Integrates CRM and EC 24
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Application Service Providers and ERP Outsourcing • Application service providers (ASP) – a software vendor that offers to lease ERPbased applications to other businesses – offerings are evident in ERP-added functions such as electronic commerce, customer relationship management (CRM), datamarts, desktop productivity, human resources information systems (HRMS), and other supply chain-related applications 25
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Application Service Providers and ERP Outsourcing • Application service providers (ASP) – a software vendor that offers to lease ERPbased applications to other businesses – offerings are evident in ERP-added functions such as electronic commerce, customer relationship management (CRM), datamarts, desktop productivity, human resources information systems (HRMS), and other supply chain-related applications 25
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Global Supply Chains 26 • IT provides EDI, communication options, online expertise in sometimes difficult and fast-changing regulations • IT can be instrumental in helping businesses find trade partners • IT facilitates outsourcing of products and services, especially IT programming, to countries with plentiful supply of labor, at low cost
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Global Supply Chains 26 • IT provides EDI, communication options, online expertise in sometimes difficult and fast-changing regulations • IT can be instrumental in helping businesses find trade partners • IT facilitates outsourcing of products and services, especially IT programming, to countries with plentiful supply of labor, at low cost
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Business Process Reengineering (BPR) • Fundamentally rethinking and radically redesigning business processes, in order to achieve dramatic improvements in quality, cost, speed and service 27
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Business Process Reengineering (BPR) • Fundamentally rethinking and radically redesigning business processes, in order to achieve dramatic improvements in quality, cost, speed and service 27
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban The Need for BPR • Three Cs 28 – Customers today know what they want, what they are willing to pay, and how to get products and services on their own terms. – Competition is continuously increasing with respect to price, quality, selection, service, and promptness of delivery. – Change continues to occur. Markets, products, services, technology, the business environment, and people keep changing, frequently in an unpredictable and significant manner.
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban The Need for BPR • Three Cs 28 – Customers today know what they want, what they are willing to pay, and how to get products and services on their own terms. – Competition is continuously increasing with respect to price, quality, selection, service, and promptness of delivery. – Change continues to occur. Markets, products, services, technology, the business environment, and people keep changing, frequently in an unpredictable and significant manner.
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Problem of the Stovepipe • “Stovepipe” because of lack of cooperation between functional areas (vertical dimension) • Business process reengineering (BPR), which undertakes a fundamental change in specific business processes, integrates information required for good decision making 29
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Problem of the Stovepipe • “Stovepipe” because of lack of cooperation between functional areas (vertical dimension) • Business process reengineering (BPR), which undertakes a fundamental change in specific business processes, integrates information required for good decision making 29
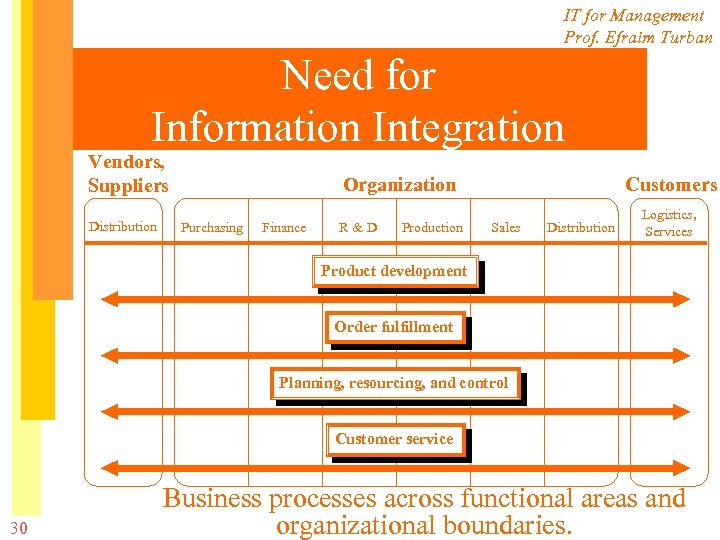 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Need for Information Integration Vendors, Suppliers Distribution Organization Purchasing Finance R&D Production Customers Sales Distribution Logistics, Services Product development Order fulfillment Planning, resourcing, and control Customer service 30 Business processes across functional areas and organizational boundaries.
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Need for Information Integration Vendors, Suppliers Distribution Organization Purchasing Finance R&D Production Customers Sales Distribution Logistics, Services Product development Order fulfillment Planning, resourcing, and control Customer service 30 Business processes across functional areas and organizational boundaries.
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban IBM Credit Corporation Reduced Cycle Time by 90% • The old process – took an average of seven days • The reengineered process – a simple DSS provides the deal structurer with the guidance needed – the program guides the generalist in finding information in the databases, plugging numbers into an evaluation model, and pulling standardized clauses - ‘boilerplate’-from a file – electronic communication and collaboration 31
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban IBM Credit Corporation Reduced Cycle Time by 90% • The old process – took an average of seven days • The reengineered process – a simple DSS provides the deal structurer with the guidance needed – the program guides the generalist in finding information in the databases, plugging numbers into an evaluation model, and pulling standardized clauses - ‘boilerplate’-from a file – electronic communication and collaboration 31
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban The Enabling Role of Information Technology in BPR • • • • 32 Shared databases, Internet client/server architecture, intranet Expert systems, neural computing Telecommunication and networks: client/server intranet Decision support systems, enterprise support systems, expert systems Wireless communication and portable computers, the web, electronic mail Interactive videodisk, desktop teleconferencing, electronic mail Tracking technology, groupware, workflow software, search engines High-performance computing systems, intelligent agents Groupware and group support systems, telecommunication, electronic mail, client/server CAD/CAM, CASE tools, online systems for JIT decision making, expert systems CAD/CAM, electronic data interchange, imaging processing Artificial intelligence, expert systems Robots, imaging technologies, object-oriented programming, expert systems, geographical information systems (GIS)
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban The Enabling Role of Information Technology in BPR • • • • 32 Shared databases, Internet client/server architecture, intranet Expert systems, neural computing Telecommunication and networks: client/server intranet Decision support systems, enterprise support systems, expert systems Wireless communication and portable computers, the web, electronic mail Interactive videodisk, desktop teleconferencing, electronic mail Tracking technology, groupware, workflow software, search engines High-performance computing systems, intelligent agents Groupware and group support systems, telecommunication, electronic mail, client/server CAD/CAM, CASE tools, online systems for JIT decision making, expert systems CAD/CAM, electronic data interchange, imaging processing Artificial intelligence, expert systems Robots, imaging technologies, object-oriented programming, expert systems, geographical information systems (GIS)
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Retooling of IT for BPR • Get a good understanding of the current installed base of information systems applications and databases • Understand the existing infrastructure in terms of computing equipment, networks, and the like, and their relationships to the current available software, procedures, and data 33
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Retooling of IT for BPR • Get a good understanding of the current installed base of information systems applications and databases • Understand the existing infrastructure in terms of computing equipment, networks, and the like, and their relationships to the current available software, procedures, and data 33
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Tools for BPR • • • 34 Simulation and visual simulation tools Flow diagrams Work analysis Rapid application development Other tools (e. g. CAD/CAM, imaging technologies, EDI, interorganizational systems and expert systems) • Integrated tool kits • Workflow software • The Web
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Tools for BPR • • • 34 Simulation and visual simulation tools Flow diagrams Work analysis Rapid application development Other tools (e. g. CAD/CAM, imaging technologies, EDI, interorganizational systems and expert systems) • Integrated tool kits • Workflow software • The Web
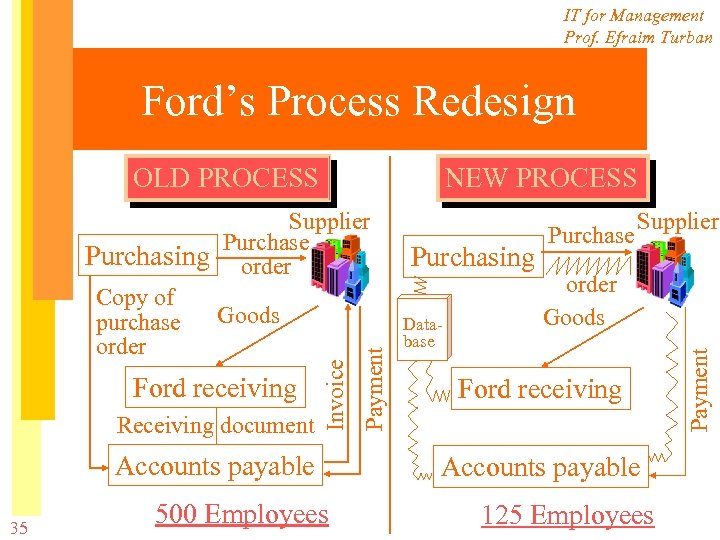 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Ford’s Process Redesign NEW PROCESS Receiving document Accounts payable 35 500 Employees Payment Ford receiving Invoice Supplier Purchase Purchasing order Copy of Goods purchase order Purchasing Database Purchase Supplier order Goods Ford receiving Accounts payable 125 Employees Payment OLD PROCESS
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Ford’s Process Redesign NEW PROCESS Receiving document Accounts payable 35 500 Employees Payment Ford receiving Invoice Supplier Purchase Purchasing order Copy of Goods purchase order Purchasing Database Purchase Supplier order Goods Ford receiving Accounts payable 125 Employees Payment OLD PROCESS
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban From Mass Production to Mass Customization • Mass production – a company produces a large quantity of an identical standard product • Mass customization – a company produces large volumes, yet customizes each product to the specifications of individual customers 36
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban From Mass Production to Mass Customization • Mass production – a company produces a large quantity of an identical standard product • Mass customization – a company produces large volumes, yet customizes each product to the specifications of individual customers 36
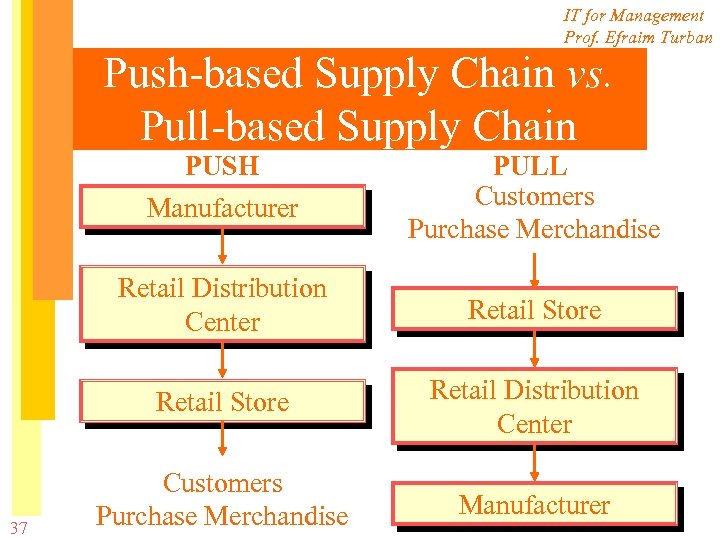 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Push-based Supply Chain vs. Pull-based Supply Chain PUSH Manufacturer Retail Distribution Center Retail Store 37 PULL Customers Purchase Merchandise Retail Distribution Center Customers Purchase Merchandise Manufacturer
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Push-based Supply Chain vs. Pull-based Supply Chain PUSH Manufacturer Retail Distribution Center Retail Store 37 PULL Customers Purchase Merchandise Retail Distribution Center Customers Purchase Merchandise Manufacturer
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Cycle Time Reduction • IT allows the combination or elimination of steps, and the expedition of various activities in the process • Telecommunications and especially the Internet and intranets cut communications time through the use of e-mail and EDI and allows collaboration in design and operations of products and services 38
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Cycle Time Reduction • IT allows the combination or elimination of steps, and the expedition of various activities in the process • Telecommunications and especially the Internet and intranets cut communications time through the use of e-mail and EDI and allows collaboration in design and operations of products and services 38
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Reengineering Organizations • An Example - Bank 39 – Customer deals with a single point of contact, the account manager – Account manager is responsible for all bank services, and provides all services to the customer, who receives a single statement for all accounts – IT provides account manager with expert advice on specialized topics, such as loans – By allowing easy access to the different databases, the account manager can answer queries, plan, and organize the work with customers
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Reengineering Organizations • An Example - Bank 39 – Customer deals with a single point of contact, the account manager – Account manager is responsible for all bank services, and provides all services to the customer, who receives a single statement for all accounts – IT provides account manager with expert advice on specialized topics, such as loans – By allowing easy access to the different databases, the account manager can answer queries, plan, and organize the work with customers
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Networked vs. Hierarchical Organization Formal Highly structured Manage Control Direct Employees a cost Information management -owned Hierarchical Organizations Risk avoidance Individual contributions 40 Networked Organization Informal Loosely structured Delegate/lead Ownership/participation Empower Employees an asset Information shared ownership Flatter Organizations Risk management Team contributions
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Networked vs. Hierarchical Organization Formal Highly structured Manage Control Direct Employees a cost Information management -owned Hierarchical Organizations Risk avoidance Individual contributions 40 Networked Organization Informal Loosely structured Delegate/lead Ownership/participation Empower Employees an asset Information shared ownership Flatter Organizations Risk management Team contributions
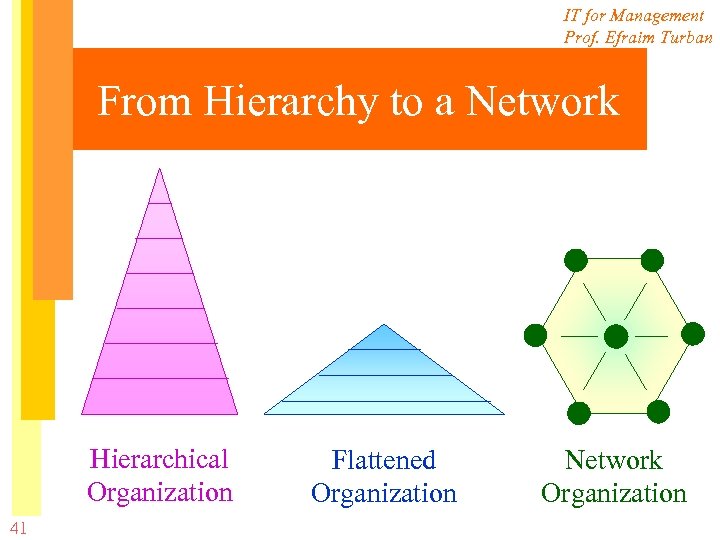 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban From Hierarchy to a Network Hierarchical Organization 41 Flattened Organization Network Organization
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban From Hierarchy to a Network Hierarchical Organization 41 Flattened Organization Network Organization
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Empowerment • The vesting of decision-making or approval authority in employees • Giving permission to the workforce to unleash, develop, and utilize their skills and knowledge to their fullest potential, for the good of the organization as well as for themselves, and providing the framework in which this can be done 42
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Empowerment • The vesting of decision-making or approval authority in employees • Giving permission to the workforce to unleash, develop, and utilize their skills and knowledge to their fullest potential, for the good of the organization as well as for themselves, and providing the framework in which this can be done 42
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Empowerment’s Relationship to Information Technology 43 • IT provides the right information, at the right time, at the right quality, and at the right cost • IT provides tools that will enhance the creativity and productivity of employees, so they can make self-decisions, as well s the quality of their work • IT provides online training, uses multimedia, and even apply intelligent computer-aided instruction to employees who need more skills and higher levels of skills
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Empowerment’s Relationship to Information Technology 43 • IT provides the right information, at the right time, at the right quality, and at the right cost • IT provides tools that will enhance the creativity and productivity of employees, so they can make self-decisions, as well s the quality of their work • IT provides online training, uses multimedia, and even apply intelligent computer-aided instruction to employees who need more skills and higher levels of skills
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Teams • Types of teams – permanent or work group teams – problem-solving teams – quality circles, participating teams – management teams – virtual teams 44 • IT plays a critical role in empowering team members and providing the necessary communication links among teams
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Teams • Types of teams – permanent or work group teams – problem-solving teams – quality circles, participating teams – management teams – virtual teams 44 • IT plays a critical role in empowering team members and providing the necessary communication links among teams
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Virtual Corporations • Virtual corporation is an organization composed of several business partners sharing costs and resources for the purpose of producing a product or service • Major attributes – excellence – opportunism – trust – technology 45 – full utilization – lack of borders – adaptability to change
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Virtual Corporations • Virtual corporation is an organization composed of several business partners sharing costs and resources for the purpose of producing a product or service • Major attributes – excellence – opportunism – trust – technology 45 – full utilization – lack of borders – adaptability to change
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban How IT Supports Virtual Corporation 46 • IT allows communication and collaboration among the dispersed business partners • Standard transactions in the interorganizational IS are supported by EDI and EFT • The Internet is the infrastructure for these and other technologies • Modern database technologies and networking permit business partners to access each other’s databases • ERP software is extensively used to support standard transactions among business partners
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban How IT Supports Virtual Corporation 46 • IT allows communication and collaboration among the dispersed business partners • Standard transactions in the interorganizational IS are supported by EDI and EFT • The Internet is the infrastructure for these and other technologies • Modern database technologies and networking permit business partners to access each other’s databases • ERP software is extensively used to support standard transactions among business partners
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Buying and Selling Along the Supply Chain • Upstream activities – Bidding – Consolidation of vendors’ catalogues in buyer’s site – Onsite specialty stores – Other purchases – Buying knowledge – Internal SCM activities • Downstream activities – Selling on your own web site – Auctions on your web site 47 • Upstream and Downstream combined
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Buying and Selling Along the Supply Chain • Upstream activities – Bidding – Consolidation of vendors’ catalogues in buyer’s site – Onsite specialty stores – Other purchases – Buying knowledge – Internal SCM activities • Downstream activities – Selling on your own web site – Auctions on your web site 47 • Upstream and Downstream combined
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Implementing EC Solutions Along the Supply Chain • Build in yourself, in house • Outsource the job • Integrate EC with ERP • Integration with CRM and DSS • Componentization 48
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban Implementing EC Solutions Along the Supply Chain • Build in yourself, in house • Outsource the job • Integrate EC with ERP • Integration with CRM and DSS • Componentization 48
 IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban 6 -49 49 Copyright 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the express written permission of the copyright owner in unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Son, Inc. Adopters of the textbook are granted permission to make back-up copies for his/her own use only, to make copies for distribution to student of the course the textbook is used in, and to modify this material to best suit their instructional needs. Under no circumstances can copies be made for resale. The publisher assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the information contained herein.
IT for Management Prof. Efraim Turban 6 -49 49 Copyright 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the express written permission of the copyright owner in unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Son, Inc. Adopters of the textbook are granted permission to make back-up copies for his/her own use only, to make copies for distribution to student of the course the textbook is used in, and to modify this material to best suit their instructional needs. Under no circumstances can copies be made for resale. The publisher assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the information contained herein.


