4c7f8f30790db4911f43bcfc91a5036e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 157

 Chapter 4: network layer
Chapter 4: network layer

 Two key network-layer functions
Two key network-layer functions
 Connection setup
Connection setup
 Network service model
Network service model
 Network layer service models:
Network layer service models:


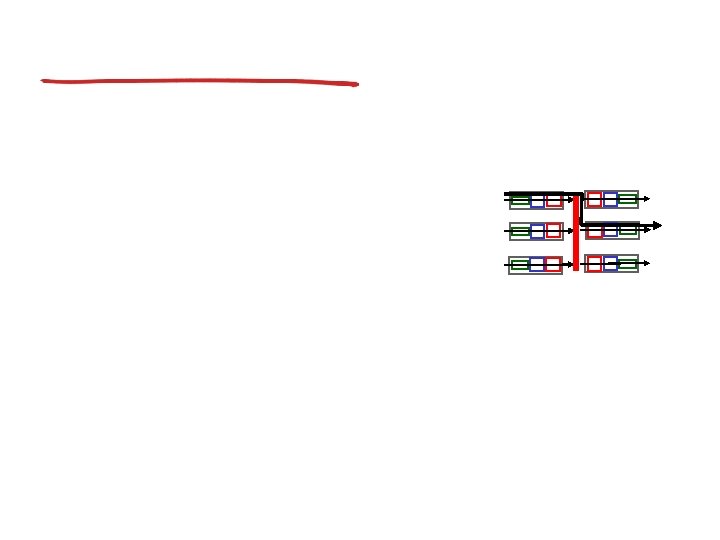
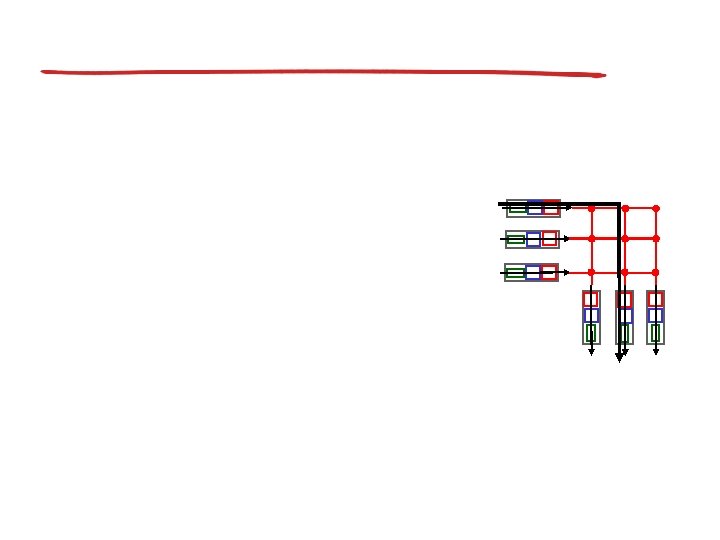
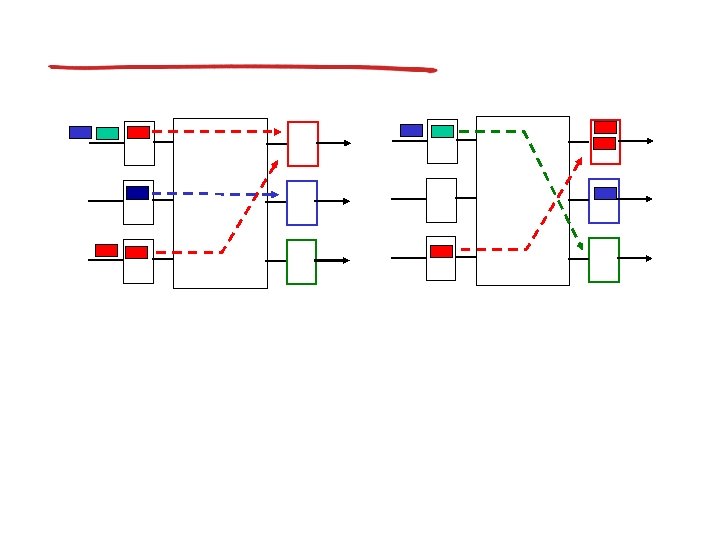
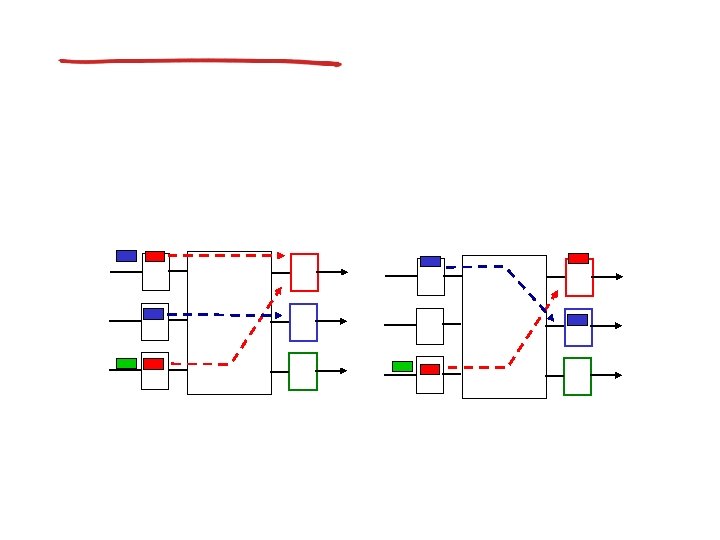
 Virtual circuits
Virtual circuits
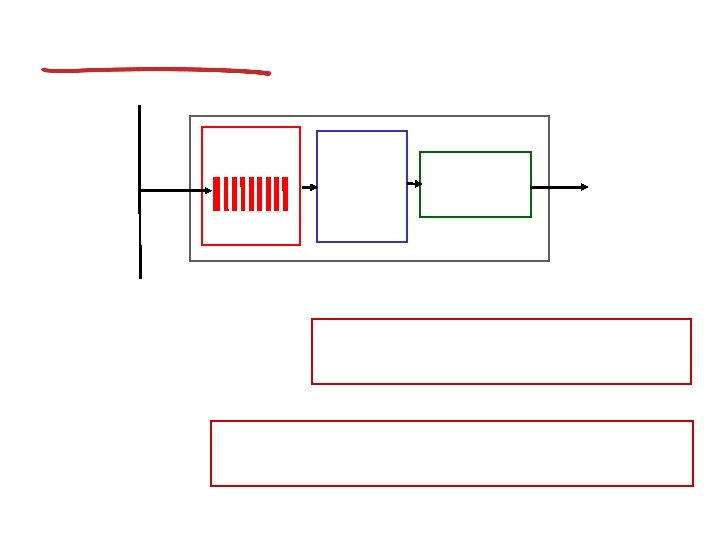
 VC implementation
VC implementation
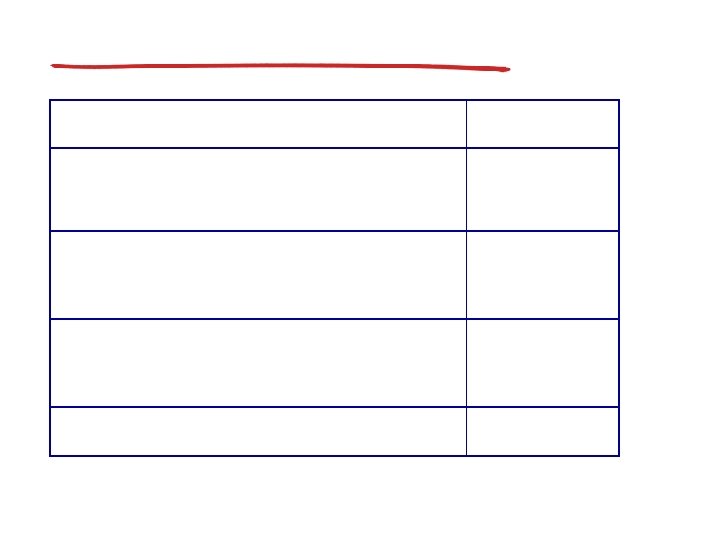
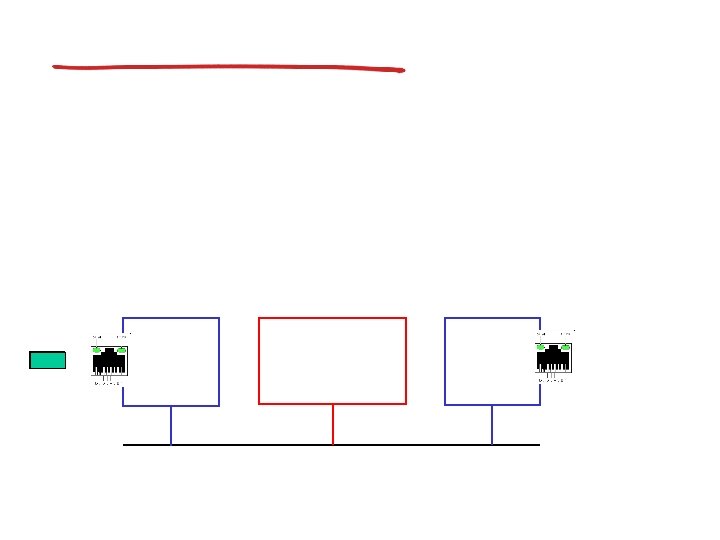
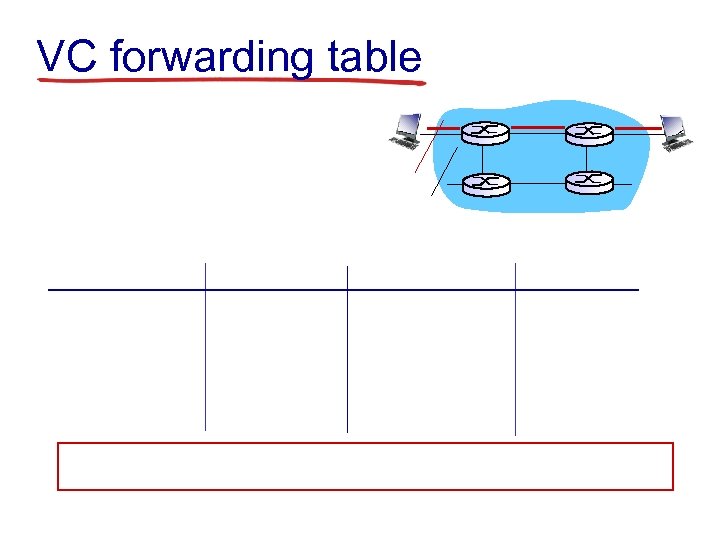 VC forwarding table
VC forwarding table
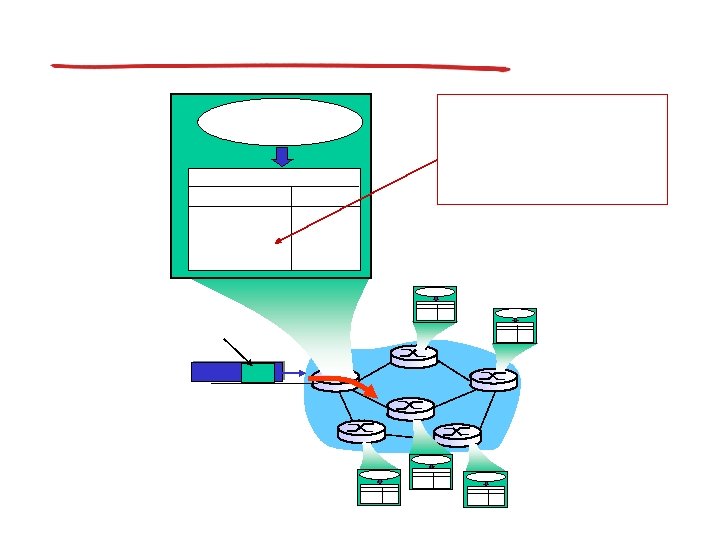
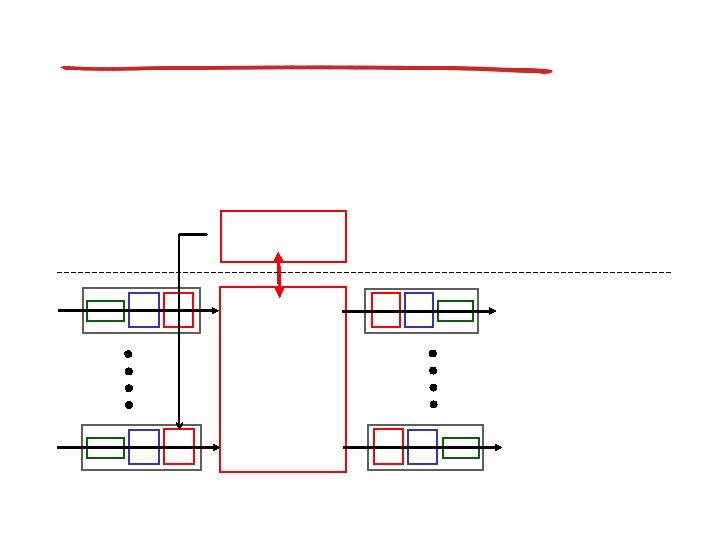
 Longest prefix matching
Longest prefix matching
 Datagram or VC network: why?
Datagram or VC network: why?

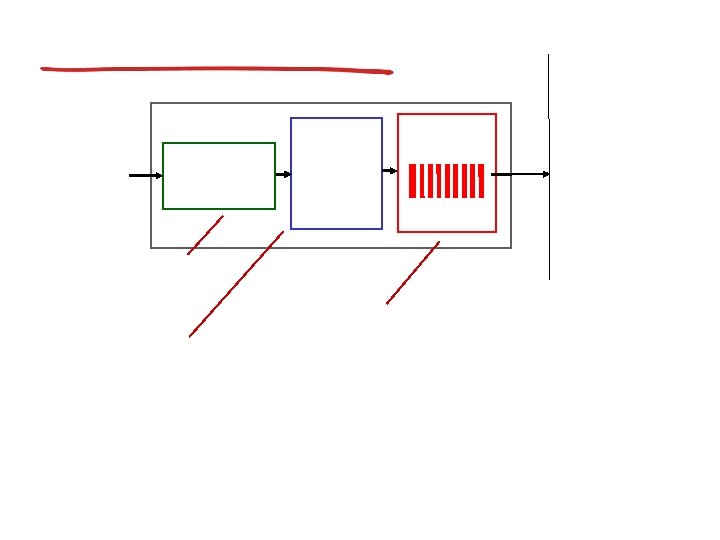
 How much buffering?
How much buffering?

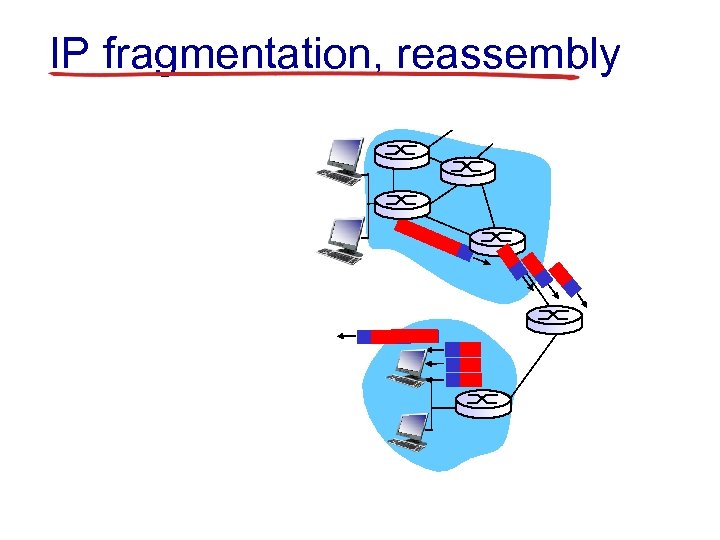 IP fragmentation, reassembly
IP fragmentation, reassembly
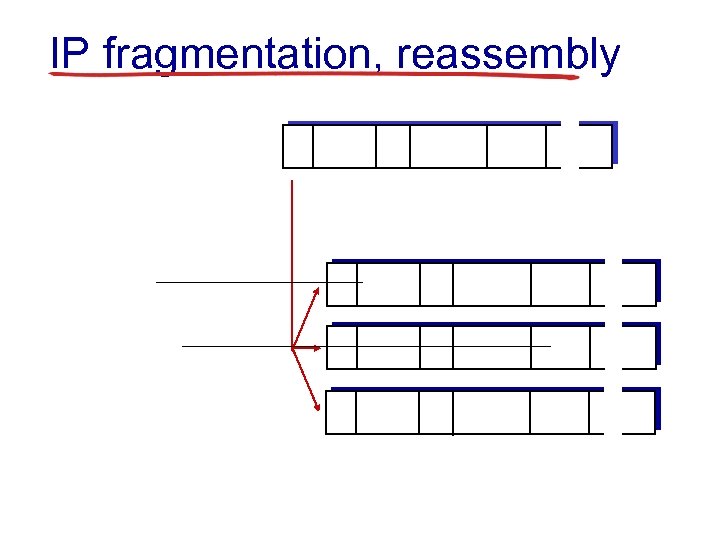 IP fragmentation, reassembly
IP fragmentation, reassembly

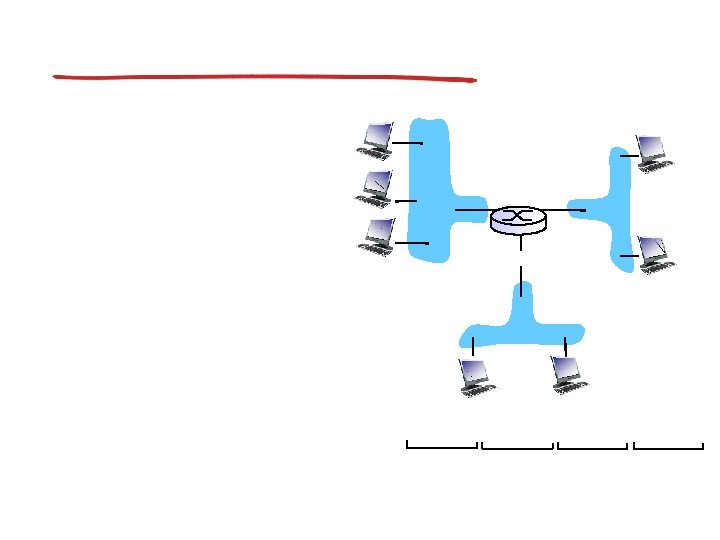
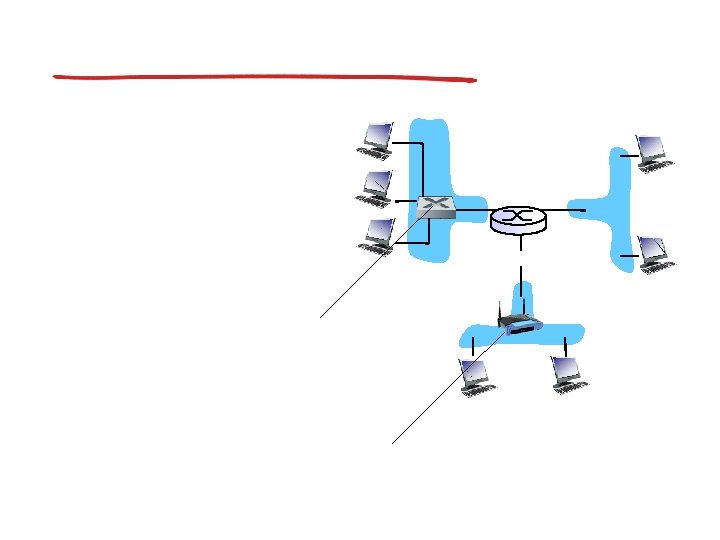
 Subnets
Subnets
 Subnets
Subnets
 Subnets
Subnets
 IP addressing: CIDR
IP addressing: CIDR
 IP addresses: how to get one?
IP addresses: how to get one?

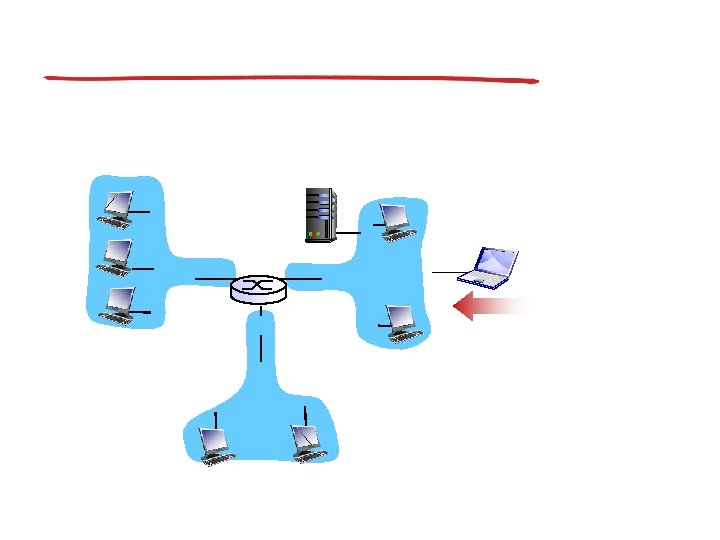
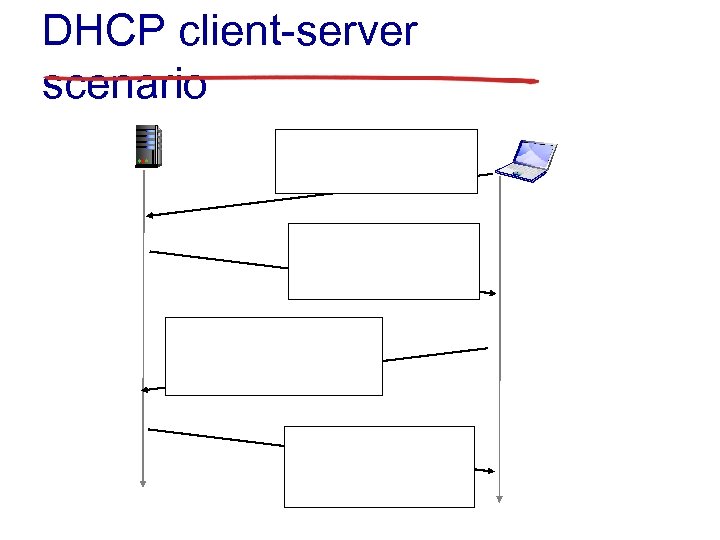 DHCP client-server scenario
DHCP client-server scenario
 DHCP: more than IP addresses
DHCP: more than IP addresses
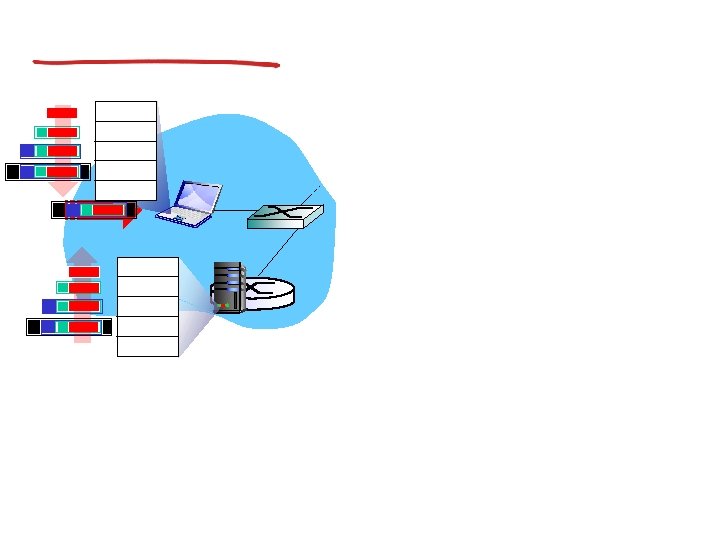
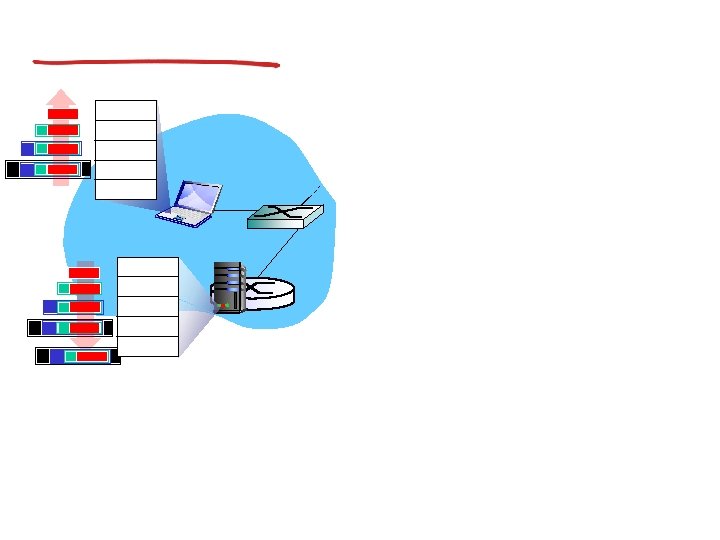
 IP addresses: how to get one?
IP addresses: how to get one?

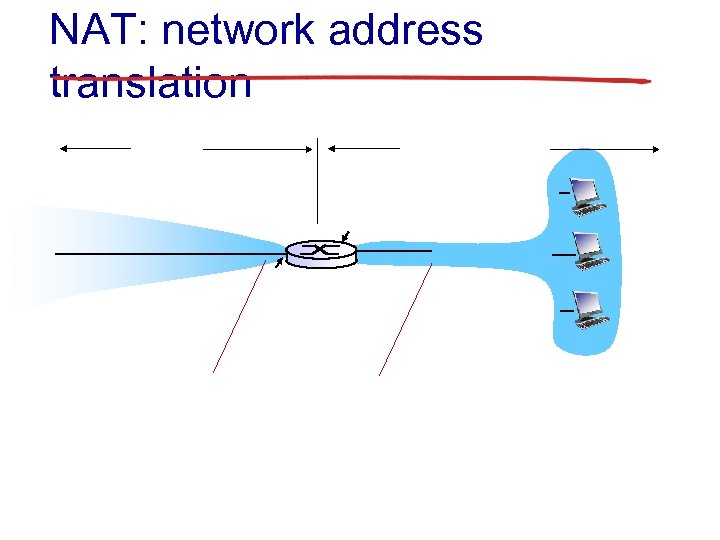 NAT: network address translation
NAT: network address translation
 NAT: network address translation
NAT: network address translation
 NAT: network address translation
NAT: network address translation
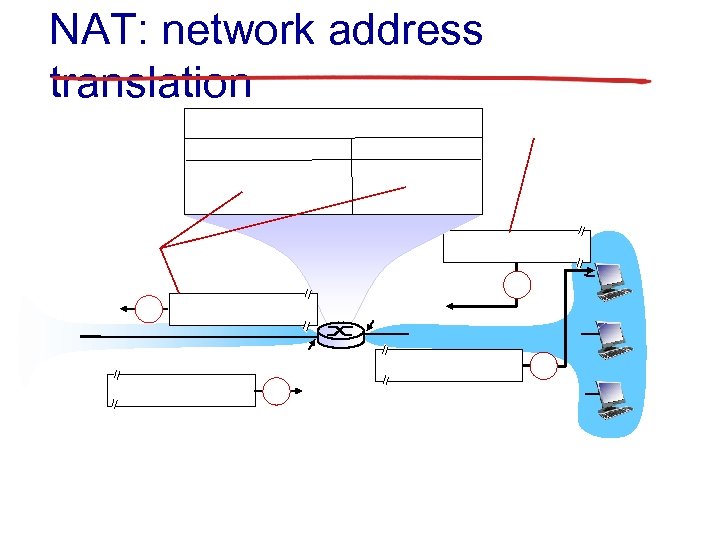 NAT: network address translation
NAT: network address translation
 NAT: network address translation
NAT: network address translation
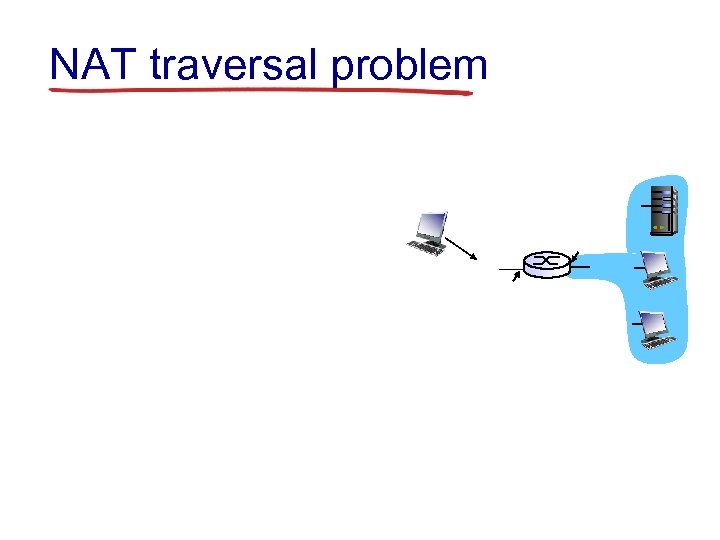 NAT traversal problem
NAT traversal problem
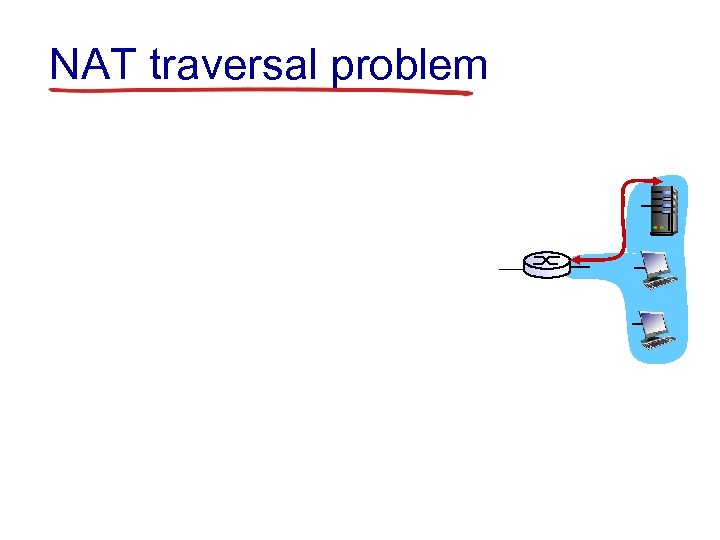 NAT traversal problem
NAT traversal problem
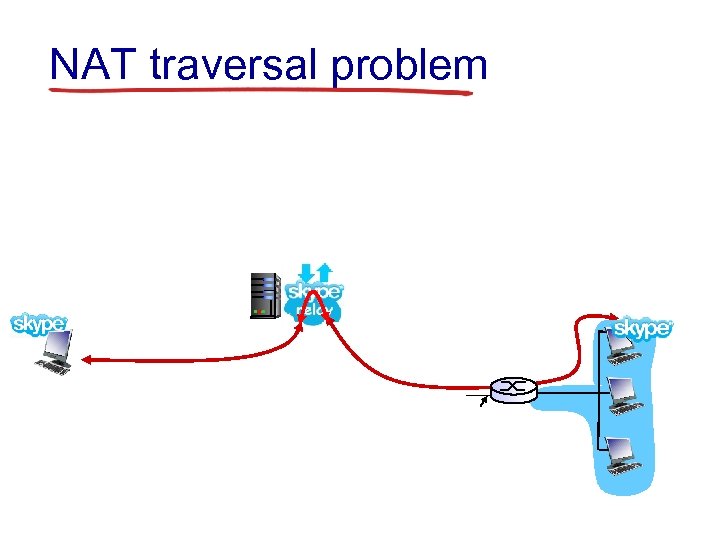 NAT traversal problem
NAT traversal problem


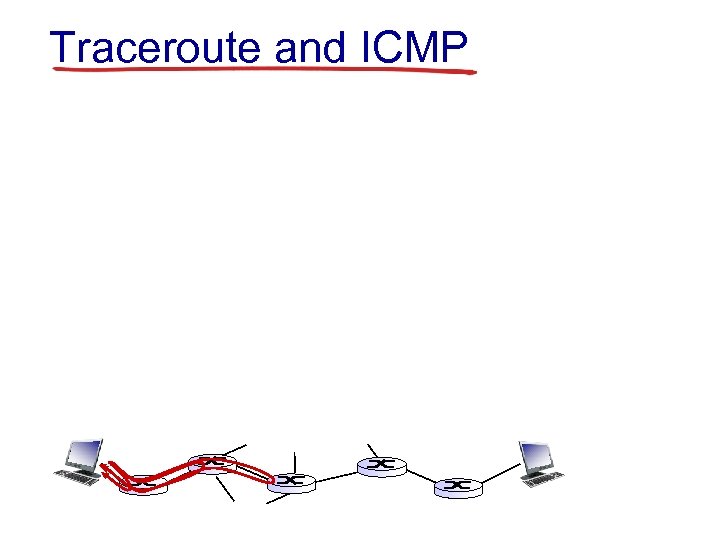 Traceroute and ICMP
Traceroute and ICMP
 IPv 6: motivation
IPv 6: motivation
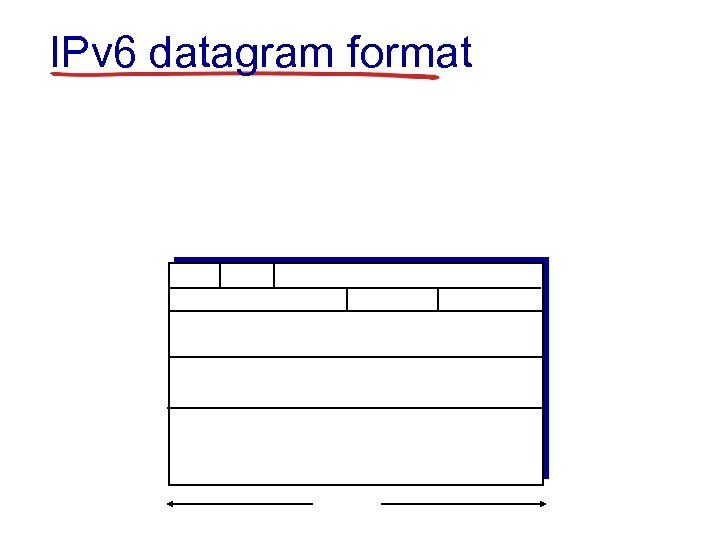 IPv 6 datagram format
IPv 6 datagram format
 Other changes from IPv 4
Other changes from IPv 4
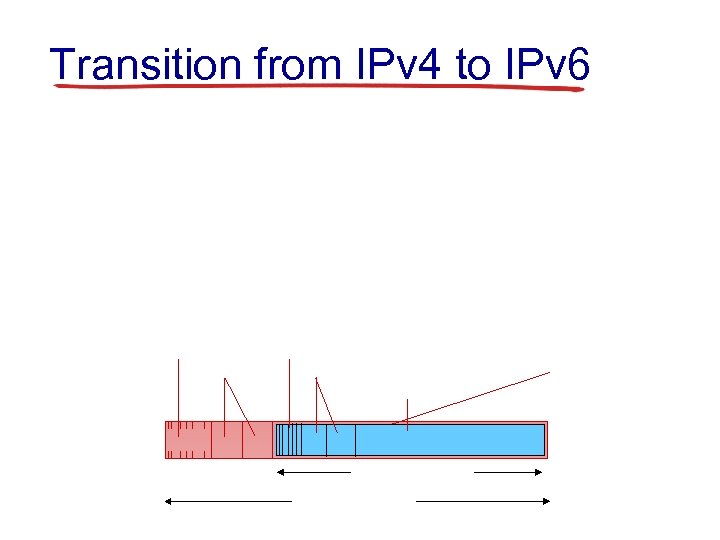 Transition from IPv 4 to IPv 6
Transition from IPv 4 to IPv 6
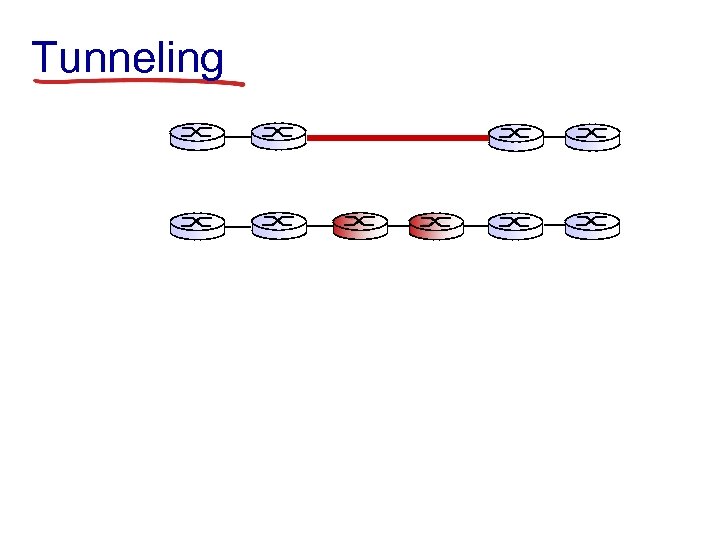 Tunneling
Tunneling
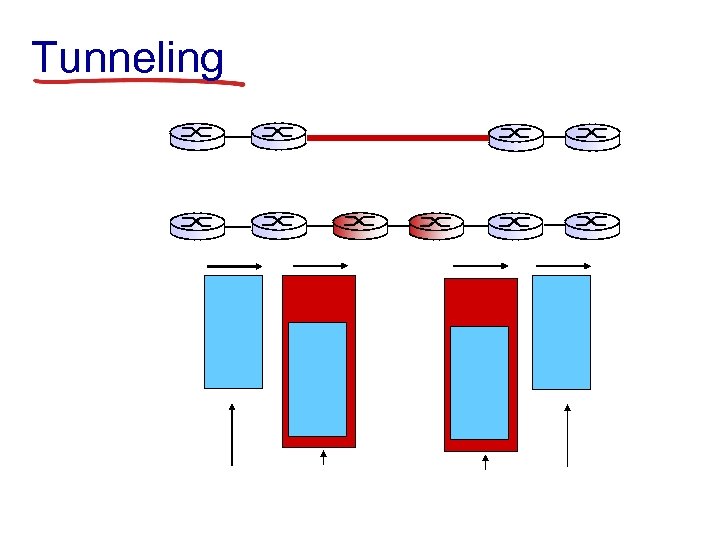 Tunneling
Tunneling
 IPv 6: adoption
IPv 6: adoption

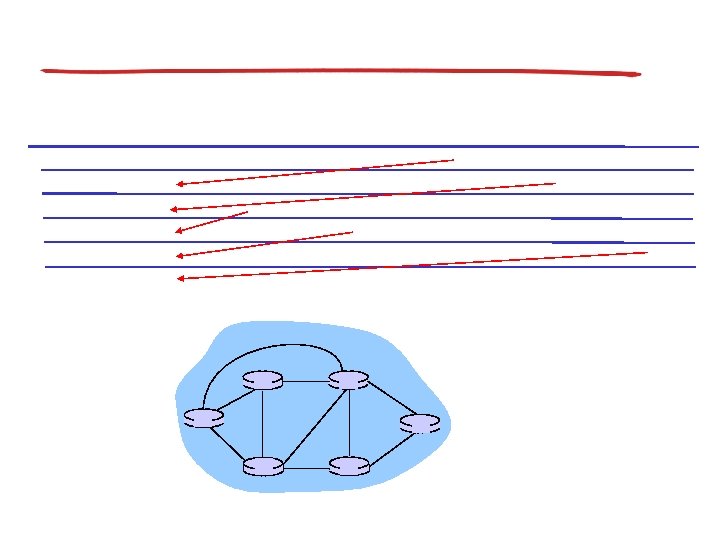
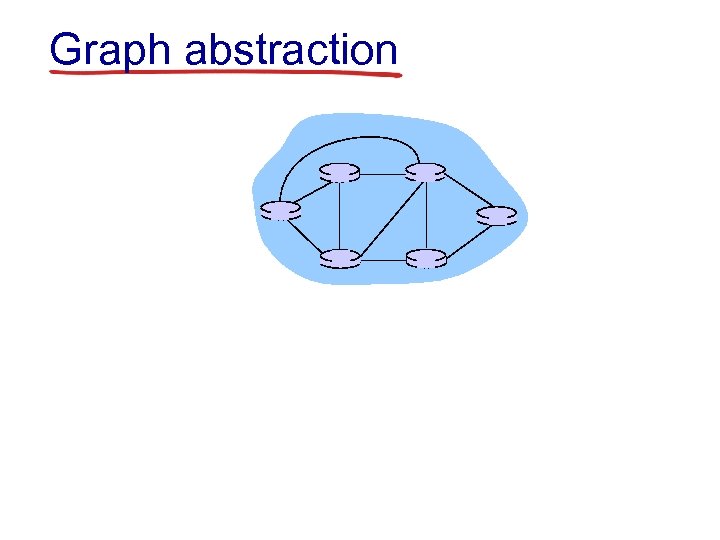 Graph abstraction
Graph abstraction
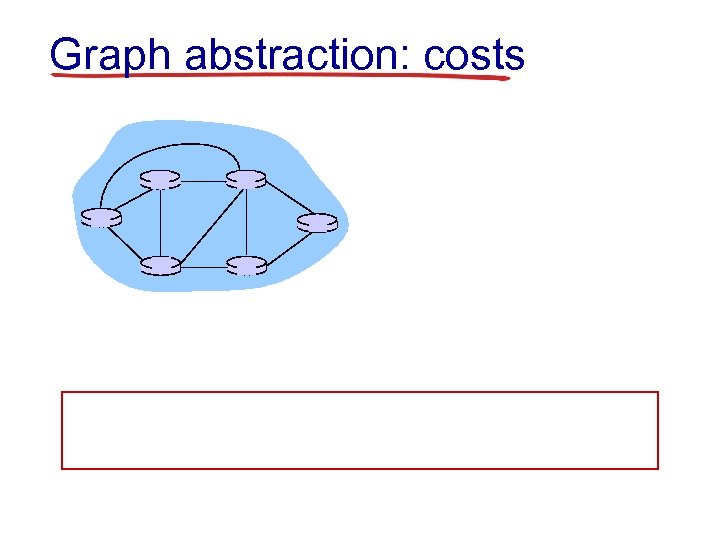 Graph abstraction: costs
Graph abstraction: costs




 Distance vector algorithm
Distance vector algorithm
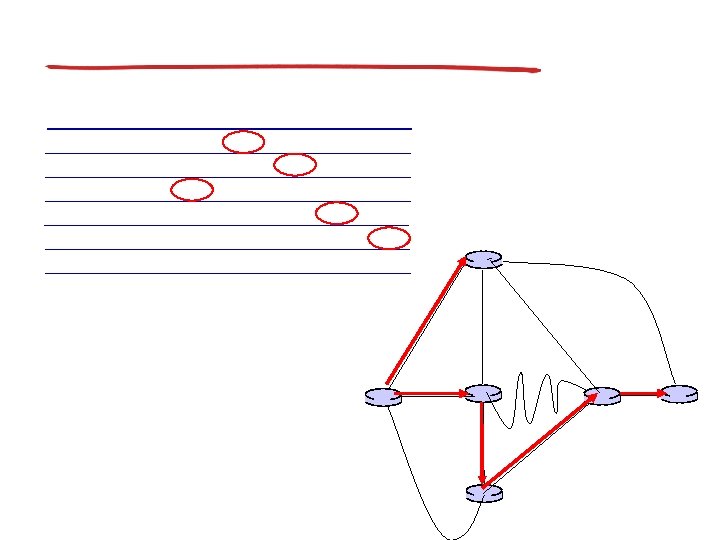
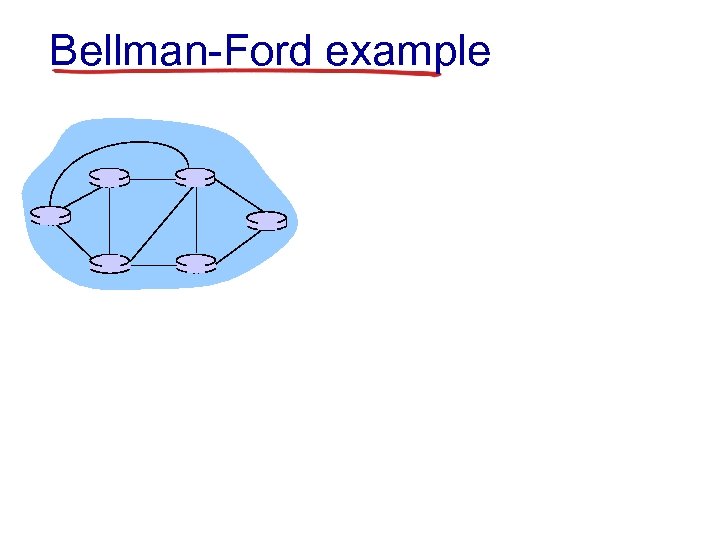 Bellman-Ford example
Bellman-Ford example
 Distance vector algorithm
Distance vector algorithm
 Distance vector algorithm
Distance vector algorithm
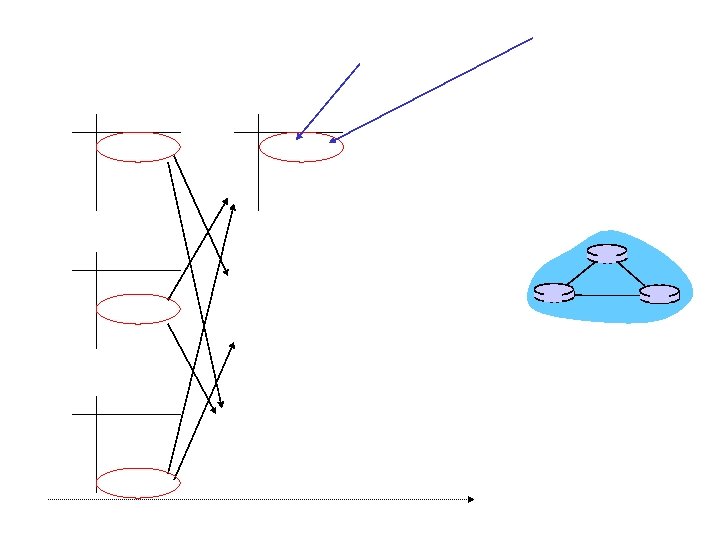
 Distance vector algorithm
Distance vector algorithm
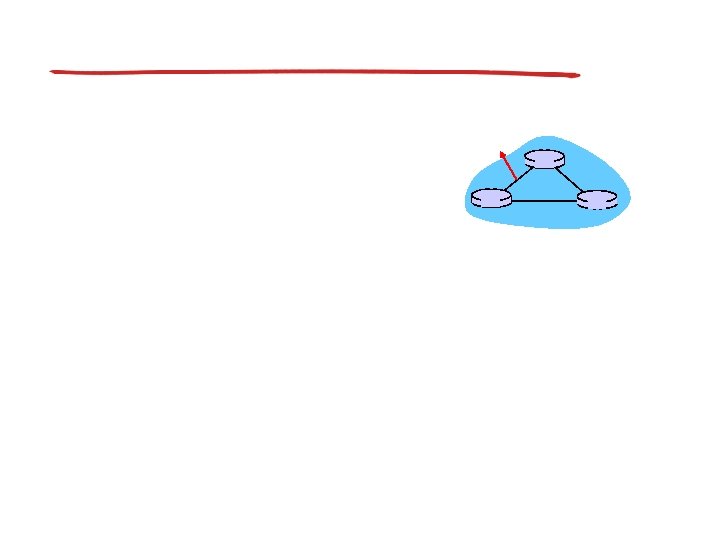
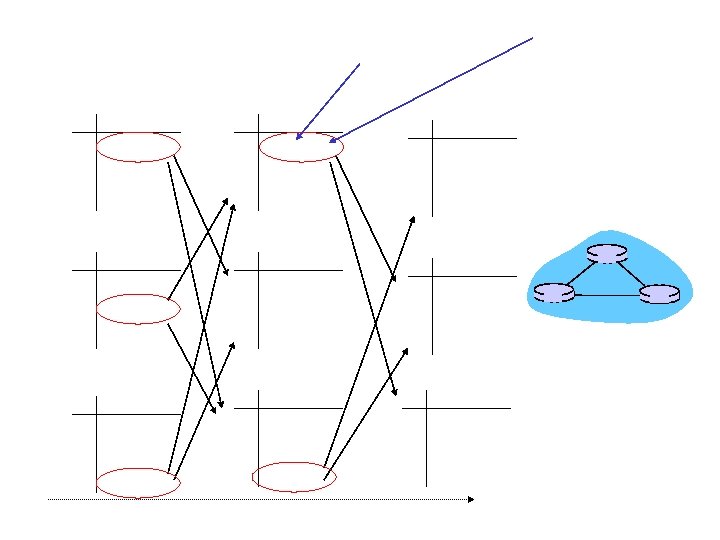





 Hierarchical routing
Hierarchical routing
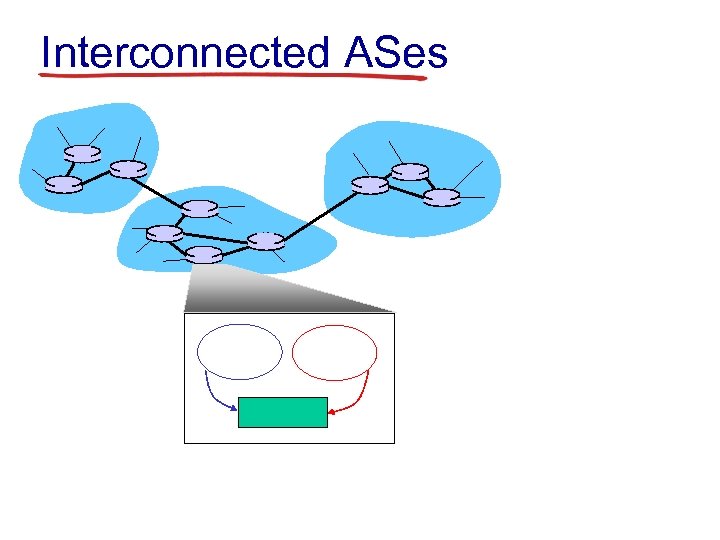 Interconnected ASes
Interconnected ASes
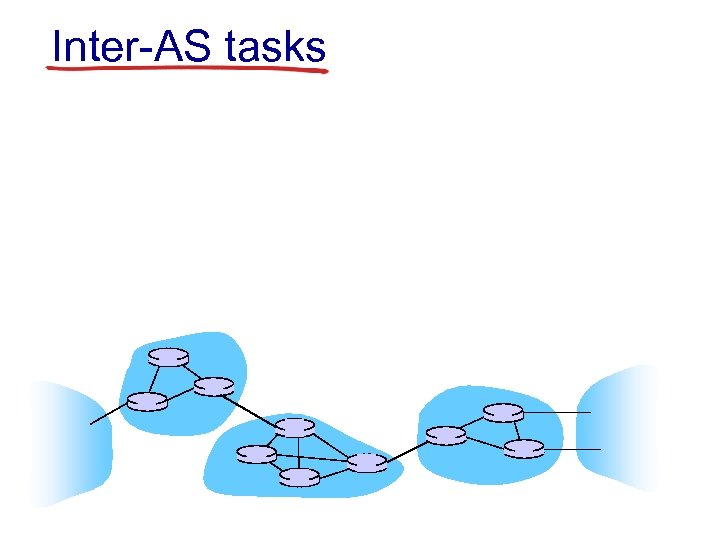 Inter-AS tasks
Inter-AS tasks


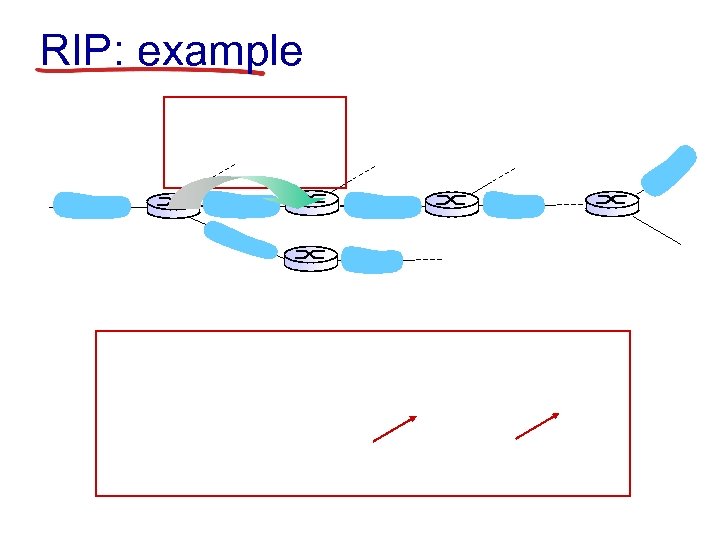 RIP: example
RIP: example



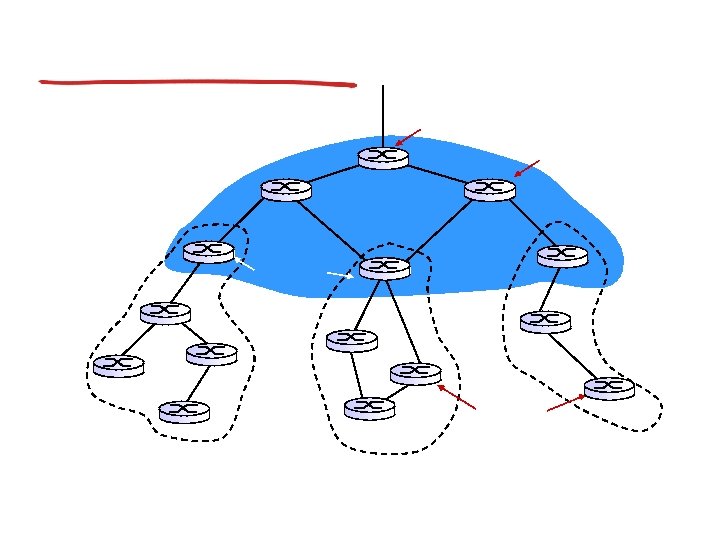
 Hierarchical OSPF
Hierarchical OSPF

 BGP basics
BGP basics
 Path attributes and BGP routes
Path attributes and BGP routes
 BGP route selection
BGP route selection


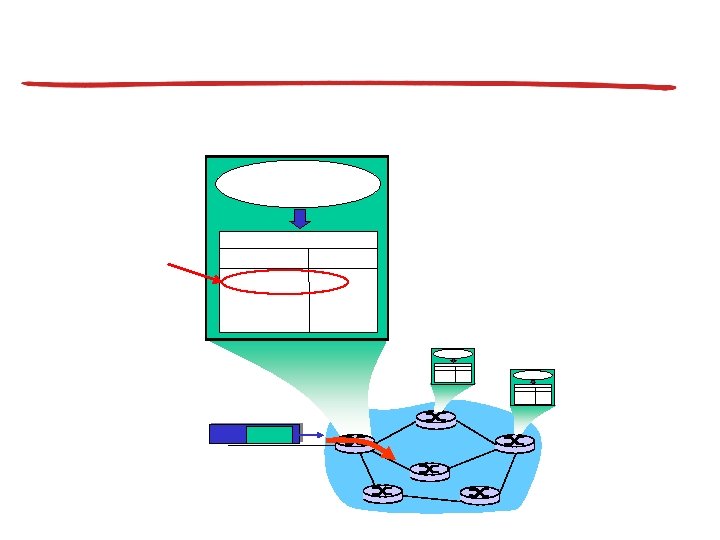

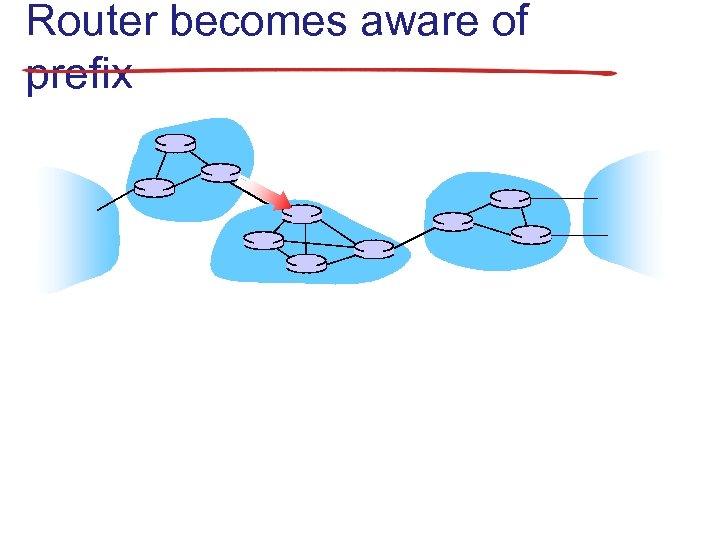 Router becomes aware of prefix
Router becomes aware of prefix
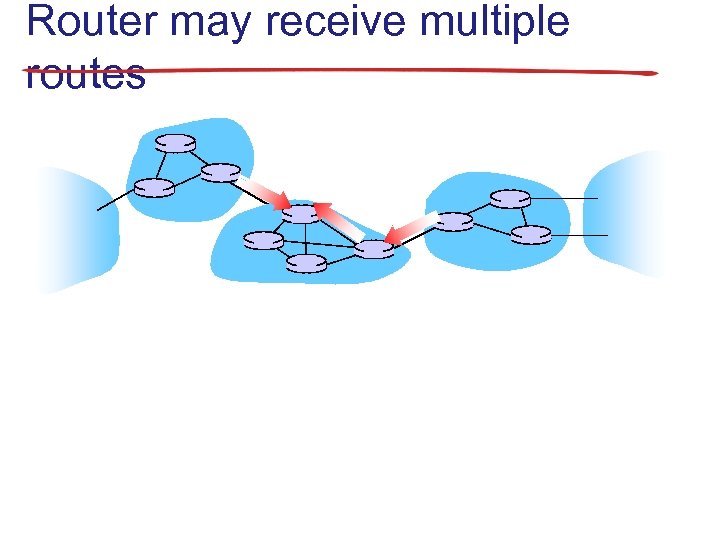 Router may receive multiple routes
Router may receive multiple routes
 Select best BGP route to prefix
Select best BGP route to prefix
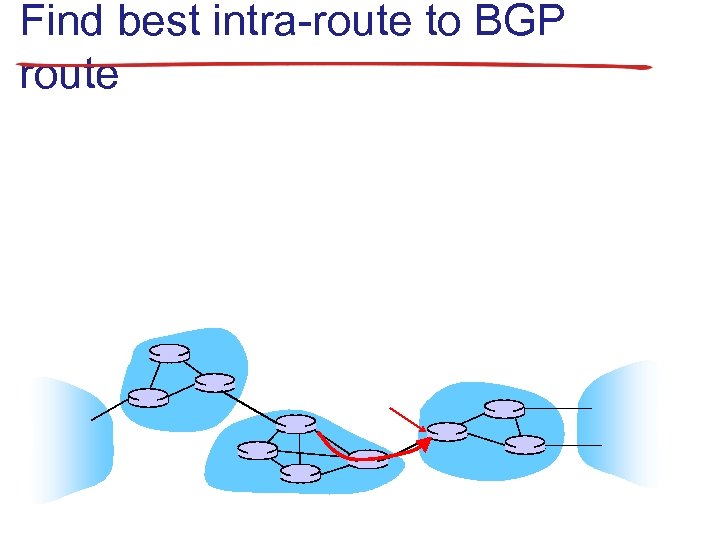 Find best intra-route to BGP route
Find best intra-route to BGP route
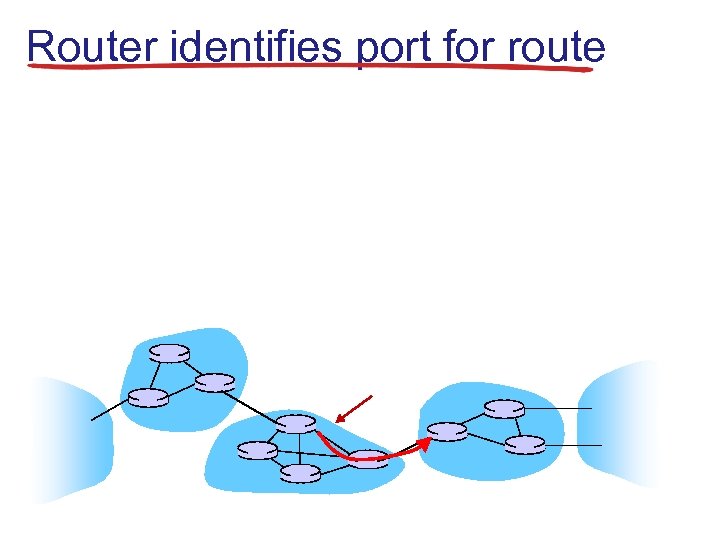 Router identifies port for route
Router identifies port for route
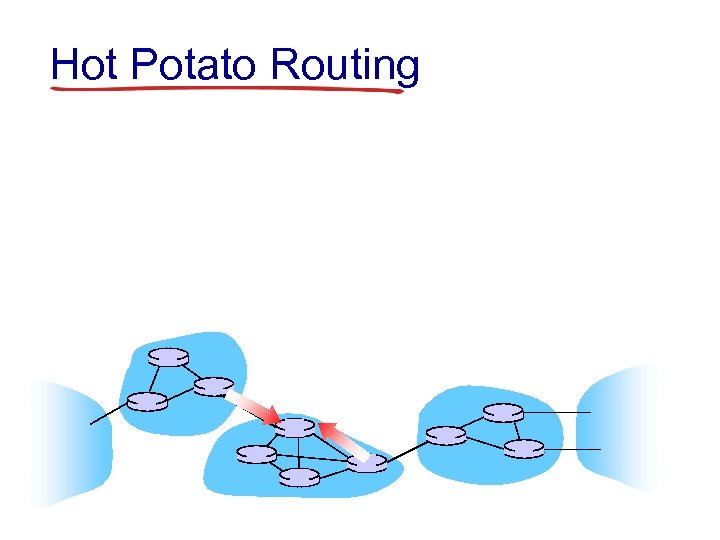 Hot Potato Routing
Hot Potato Routing

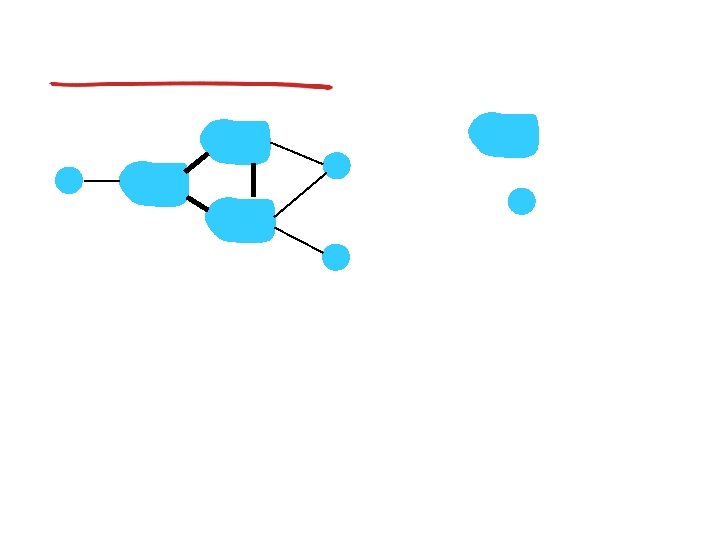
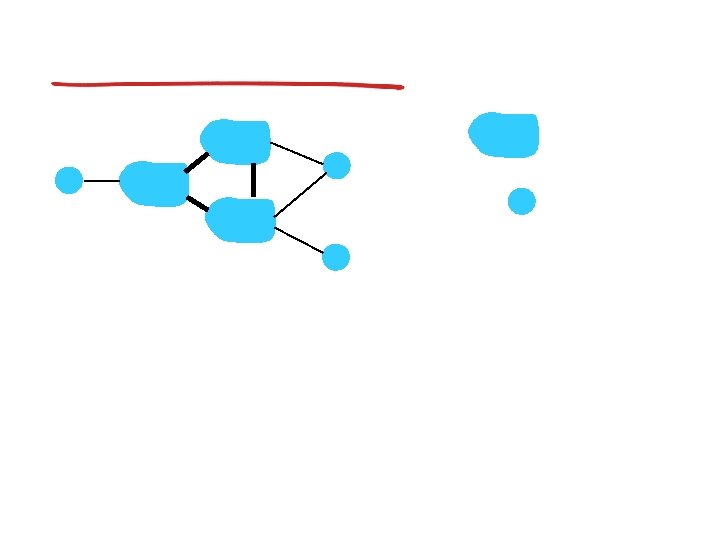


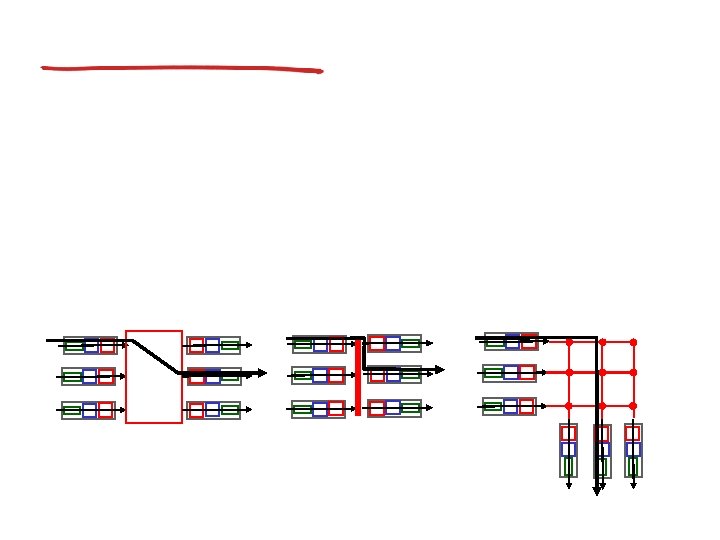
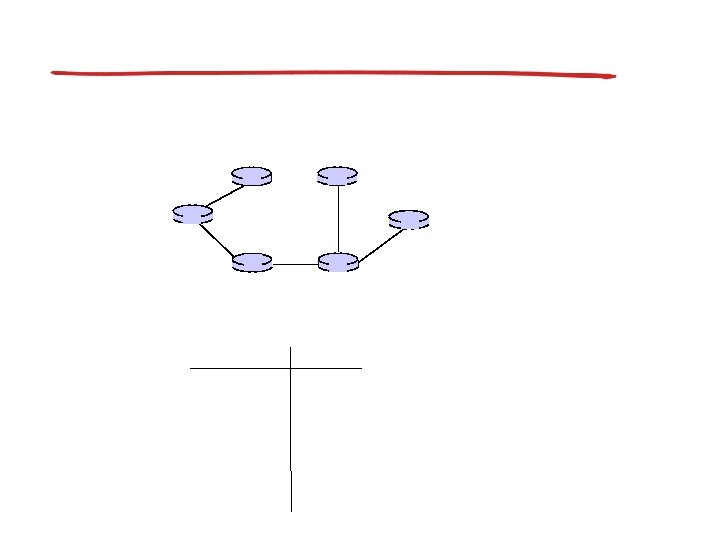
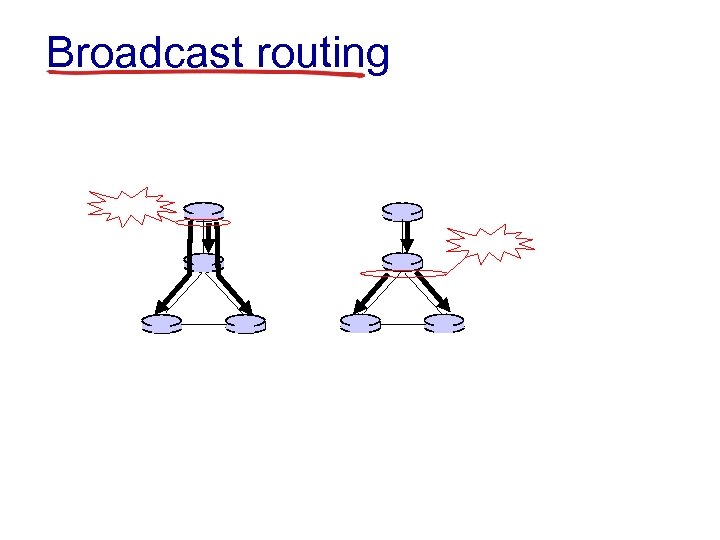 Broadcast routing
Broadcast routing
 In-network duplication
In-network duplication
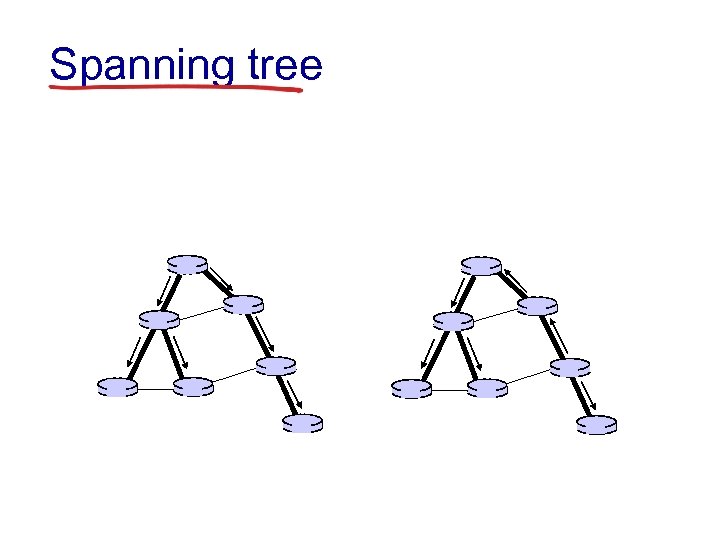 Spanning tree
Spanning tree
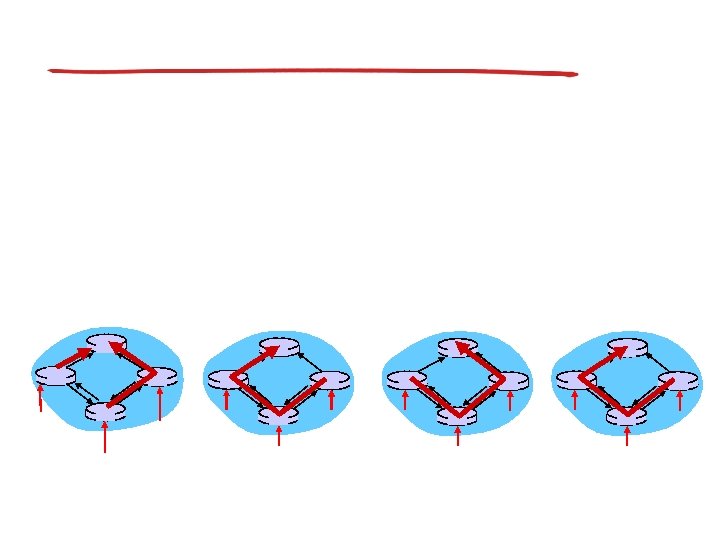
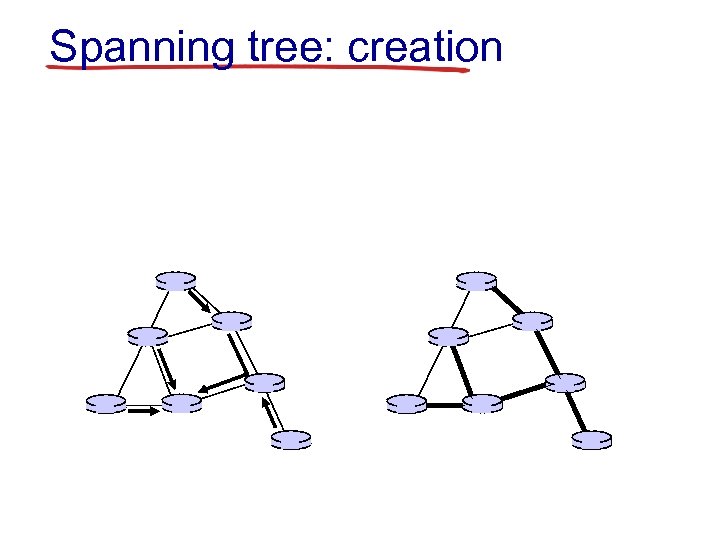 Spanning tree: creation
Spanning tree: creation
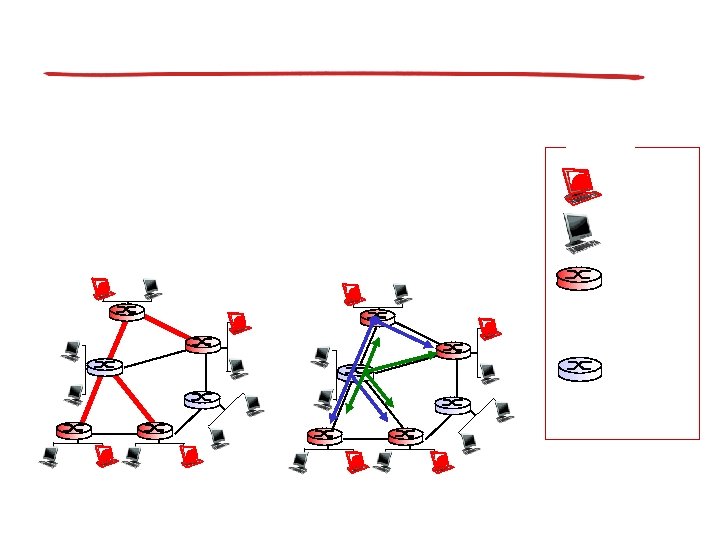

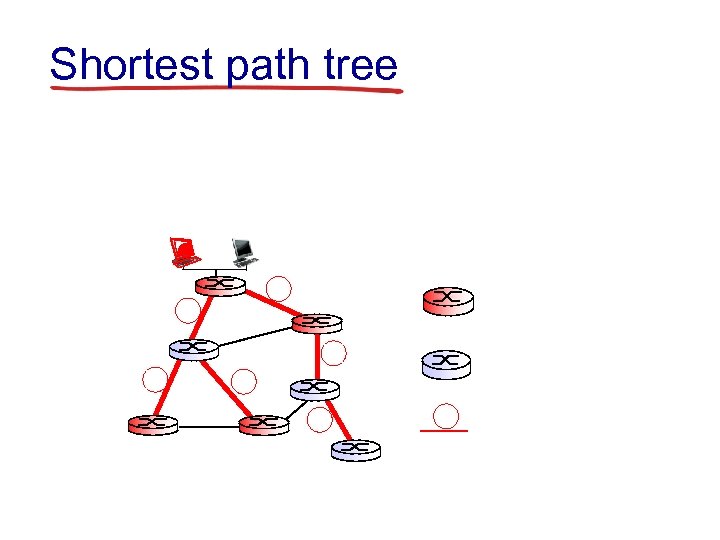 Shortest path tree
Shortest path tree
 Reverse path forwarding
Reverse path forwarding
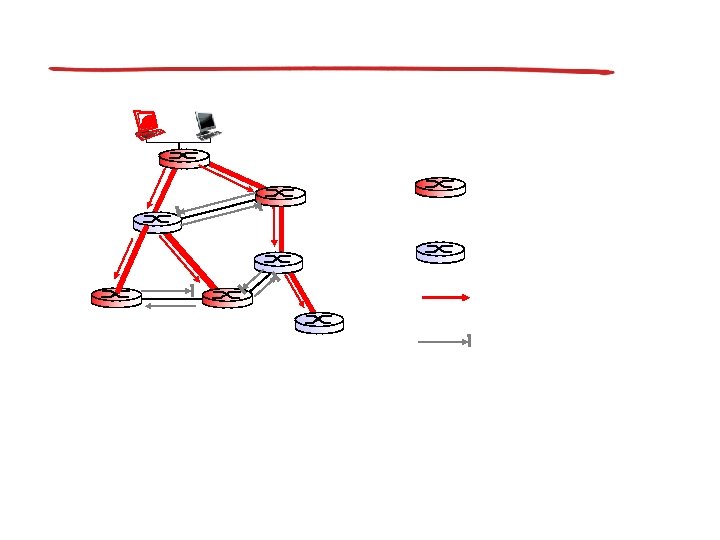
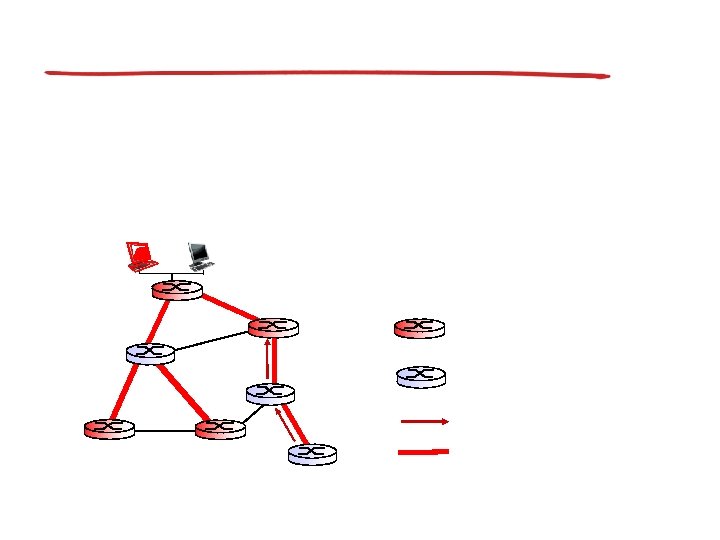

 Center-based trees
Center-based trees
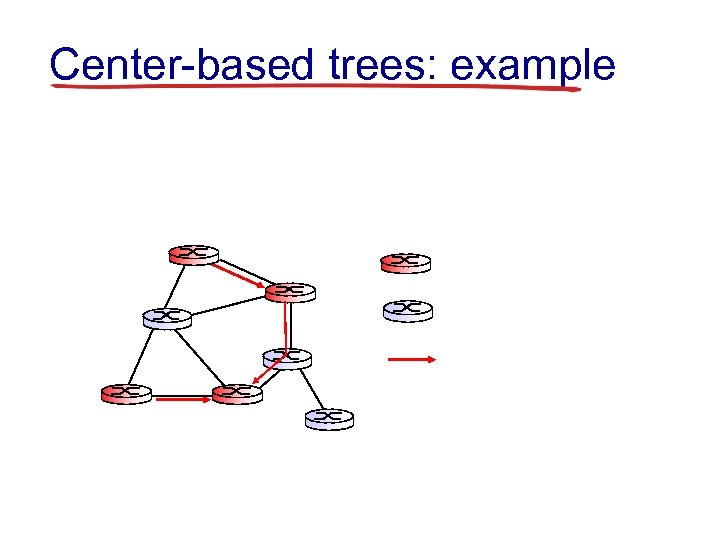 Center-based trees: example
Center-based trees: example

 DVMRP: continued…
DVMRP: continued…
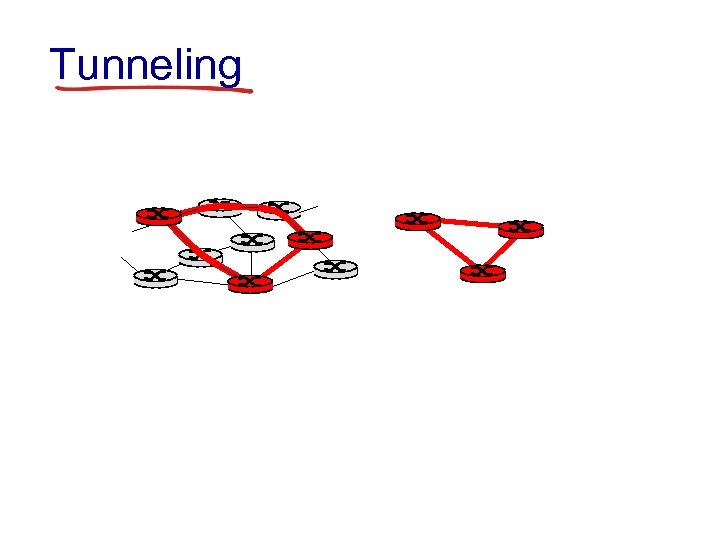 Tunneling
Tunneling



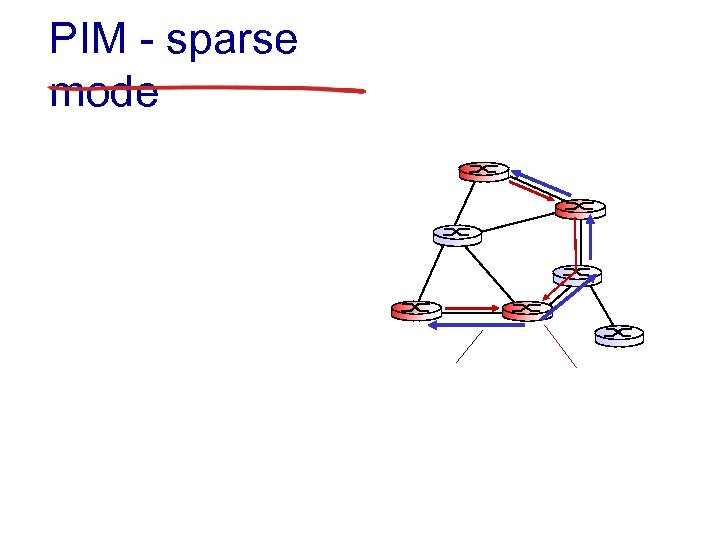 PIM - sparse mode
PIM - sparse mode
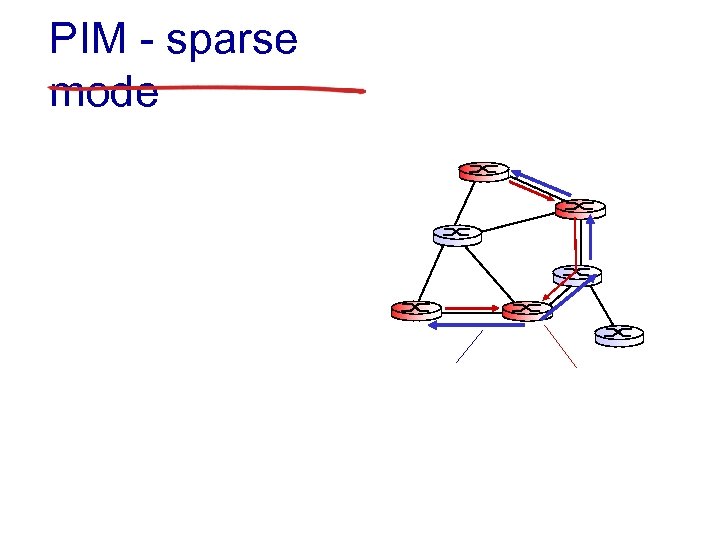 PIM - sparse mode
PIM - sparse mode



