e89e5f7a944611b742680bfea68deaf0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Chapter 4: MISSING TERMS The special rules governing the sale of goods make it easier to form a valid K when the certain important terms that the parties let out of their agreement. It relates to: Price, Method & Time of payment, Time of delivery, Place of delivery, Quantity of goods. 1
Chapter 4: MISSING TERMS The special rules governing the sale of goods make it easier to form a valid K when the certain important terms that the parties let out of their agreement. It relates to: Price, Method & Time of payment, Time of delivery, Place of delivery, Quantity of goods. 1
 1 - Price of the goods If no price is state in the K for the sale of goods: -Under D#38: not clear (no article) -Under CISG: Art 55, 56 provide that “The price to be charged is the same as the price for such goods under comparable circumstances in the trade concerned. ” -Under CC: Art 521 2
1 - Price of the goods If no price is state in the K for the sale of goods: -Under D#38: not clear (no article) -Under CISG: Art 55, 56 provide that “The price to be charged is the same as the price for such goods under comparable circumstances in the trade concerned. ” -Under CC: Art 521 2
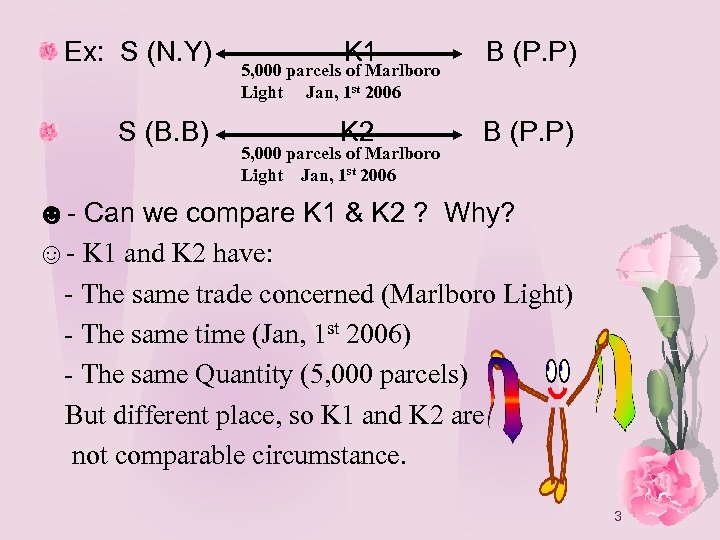 Ex: S (N. Y) S (B. B) K 1 B (P. P) K 2 B (P. P) 5, 000 parcels of Marlboro Light Jan, 1 st 2006 ☻- Can we compare K 1 & K 2 ? Why? ☺- K 1 and K 2 have: - The same trade concerned (Marlboro Light) - The same time (Jan, 1 st 2006) - The same Quantity (5, 000 parcels) But different place, so K 1 and K 2 are not comparable circumstance. 3
Ex: S (N. Y) S (B. B) K 1 B (P. P) K 2 B (P. P) 5, 000 parcels of Marlboro Light Jan, 1 st 2006 ☻- Can we compare K 1 & K 2 ? Why? ☺- K 1 and K 2 have: - The same trade concerned (Marlboro Light) - The same time (Jan, 1 st 2006) - The same Quantity (5, 000 parcels) But different place, so K 1 and K 2 are not comparable circumstance. 3
 ♣- Condition - Trade concerned (same object) - Time of conclusion of the K - Same quantity - Same location of business ☻- Study question # 8 (p: 27) Thanna K 500 m of silk, deliver in June, 1 st Soporn Thanna will pay to Soporn by meter ☻-Is this valid price term under the CISG? , D#38? 4
♣- Condition - Trade concerned (same object) - Time of conclusion of the K - Same quantity - Same location of business ☻- Study question # 8 (p: 27) Thanna K 500 m of silk, deliver in June, 1 st Soporn Thanna will pay to Soporn by meter ☻-Is this valid price term under the CISG? , D#38? 4
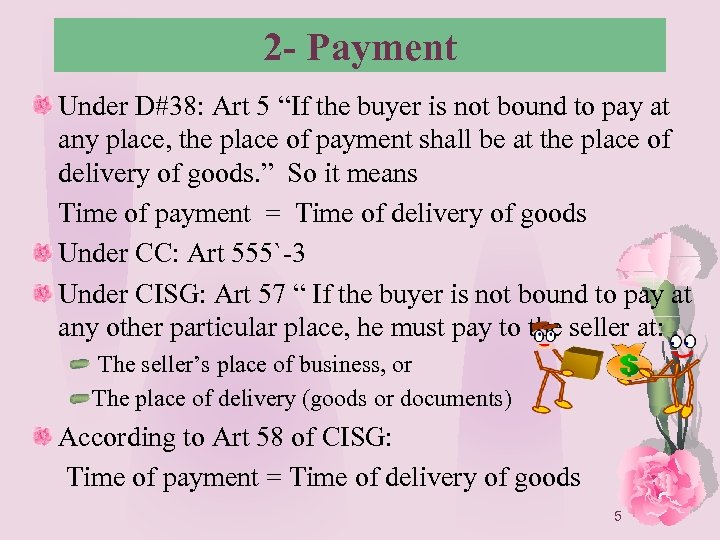 2 - Payment Under D#38: Art 5 “If the buyer is not bound to pay at any place, the place of payment shall be at the place of delivery of goods. ” So it means Time of payment = Time of delivery of goods Under CC: Art 555`-3 Under CISG: Art 57 “ If the buyer is not bound to pay at any other particular place, he must pay to the seller at: The seller’s place of business, or The place of delivery (goods or documents) According to Art 58 of CISG: Time of payment = Time of delivery of goods 5
2 - Payment Under D#38: Art 5 “If the buyer is not bound to pay at any place, the place of payment shall be at the place of delivery of goods. ” So it means Time of payment = Time of delivery of goods Under CC: Art 555`-3 Under CISG: Art 57 “ If the buyer is not bound to pay at any other particular place, he must pay to the seller at: The seller’s place of business, or The place of delivery (goods or documents) According to Art 58 of CISG: Time of payment = Time of delivery of goods 5
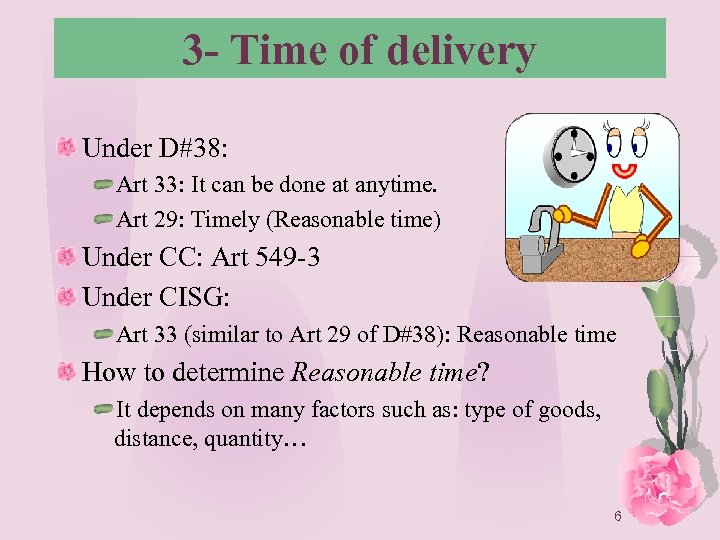 3 - Time of delivery Under D#38: Art 33: It can be done at anytime. Art 29: Timely (Reasonable time) Under CC: Art 549 -3 Under CISG: Art 33 (similar to Art 29 of D#38): Reasonable time How to determine Reasonable time? It depends on many factors such as: type of goods, distance, quantity… 6
3 - Time of delivery Under D#38: Art 33: It can be done at anytime. Art 29: Timely (Reasonable time) Under CC: Art 549 -3 Under CISG: Art 33 (similar to Art 29 of D#38): Reasonable time How to determine Reasonable time? It depends on many factors such as: type of goods, distance, quantity… 6
 4 - Place of delivery Under D#38: Art 32: Place of delivery shall be at residence of debtor. Art 30: Debtor is any party who owes an obligation to another party. Under CC: Art 549 -4 Under CISG: Art 31: Place of delivery shall be at the seller’s place of business. Ex: The seller’s place of business is in PP, but warehouse of goods in BB. The buyer in SR. Where is the place of delivery? 7
4 - Place of delivery Under D#38: Art 32: Place of delivery shall be at residence of debtor. Art 30: Debtor is any party who owes an obligation to another party. Under CC: Art 549 -4 Under CISG: Art 31: Place of delivery shall be at the seller’s place of business. Ex: The seller’s place of business is in PP, but warehouse of goods in BB. The buyer in SR. Where is the place of delivery? 7
 What’s matter? If buyer will spend $600 for transportation from PP to SR. If seller will spend $500 for transportation from BB to PP If buyer will spend $400 for transportation from BB to SR So, the seller should spend $200 to buyer & tell him to take the goods at the warehouse in BB. Result: The buyer gains $400 (600 + 200 – 400 = 400) The seller gains $300 (500 – 200 = 300) 8
What’s matter? If buyer will spend $600 for transportation from PP to SR. If seller will spend $500 for transportation from BB to PP If buyer will spend $400 for transportation from BB to SR So, the seller should spend $200 to buyer & tell him to take the goods at the warehouse in BB. Result: The buyer gains $400 (600 + 200 – 400 = 400) The seller gains $300 (500 – 200 = 300) 8
 5 - Quantity Art 17 of D#38 & Art 14 of CISG require the quantity must be writing in the K. Section 2 -306 of UCC refers to two important types of K: Requirement K: seller supplies all products to the buyer required (need) and buyer agrees to buy only from the seller. Output K: buyer buys all products the seller produced, and seller sells products only to the buyer. Read Example page 37 9
5 - Quantity Art 17 of D#38 & Art 14 of CISG require the quantity must be writing in the K. Section 2 -306 of UCC refers to two important types of K: Requirement K: seller supplies all products to the buyer required (need) and buyer agrees to buy only from the seller. Output K: buyer buys all products the seller produced, and seller sells products only to the buyer. Read Example page 37 9
 Example: Jan, 1 st Laurel needs 500 m of silk Sombo supplies Feb, 1 st Laurel needs 1500 m of silk Sombo supplies Mar, 1 st Laurel goes to France. Does he break the K ? 10
Example: Jan, 1 st Laurel needs 500 m of silk Sombo supplies Feb, 1 st Laurel needs 1500 m of silk Sombo supplies Mar, 1 st Laurel goes to France. Does he break the K ? 10
 ACCEPTANCE Under general contract law: Acceptance must be Unequivocal (mirror image). Any variation of the offer = Counter-offer. Under CC: Art : 342 -2 Under CISG: more flexibility If offeree changes an immaterial terms: Acceptance If offeree changes a material terms: Counter-offer What are material terms? Art 19 of CISG: The material terms are: Price, Place & Time of delivery, Payment, Quantity & Quality, Extent of one party’s liability to the other, and 11 Settlement of disputes.
ACCEPTANCE Under general contract law: Acceptance must be Unequivocal (mirror image). Any variation of the offer = Counter-offer. Under CC: Art : 342 -2 Under CISG: more flexibility If offeree changes an immaterial terms: Acceptance If offeree changes a material terms: Counter-offer What are material terms? Art 19 of CISG: The material terms are: Price, Place & Time of delivery, Payment, Quantity & Quality, Extent of one party’s liability to the other, and 11 Settlement of disputes.
 FORMALITY Under D#38: Ks must be in writing are: Ks involving money or items worth more than 5000 R (Art 4) Ks for loans with interest (Art 57) Personal property mortgage Ks (Art 65) Surety Ks (Art 112) Under CISG: Art 11: Ks for sale of goods do not need to be in writing. It may be proved by any means including witnesses. 12
FORMALITY Under D#38: Ks must be in writing are: Ks involving money or items worth more than 5000 R (Art 4) Ks for loans with interest (Art 57) Personal property mortgage Ks (Art 65) Surety Ks (Art 112) Under CISG: Art 11: Ks for sale of goods do not need to be in writing. It may be proved by any means including witnesses. 12
 CONSIDERATION There are no special rules of consideration that apply to sale of goods transaction. But Art 12 of D#38 provides that “The consideration from the both parties to the K must be equal, and allow the party that received less to rescind the K. ” Under Free Market Principle, K will not be rescinded simply even though one party got a “bad deal”, because the K made by the parties’ freewill. Study Question #14 (p: 43) 13
CONSIDERATION There are no special rules of consideration that apply to sale of goods transaction. But Art 12 of D#38 provides that “The consideration from the both parties to the K must be equal, and allow the party that received less to rescind the K. ” Under Free Market Principle, K will not be rescinded simply even though one party got a “bad deal”, because the K made by the parties’ freewill. Study Question #14 (p: 43) 13
 Saray K 50, 000 bottles, 100 R/1 PWC Market price 150 R/1, So does Saray be able to make 50 R more on every bottle? Under General Contract Law: Saray would be obligated to sell the price and could not rescind the K, because it turned out to be a bad deal for him. But under Art 12 of D#38, Cambodian ntract Co court could rescind the K based on the inadequacy of the consideration. 14
Saray K 50, 000 bottles, 100 R/1 PWC Market price 150 R/1, So does Saray be able to make 50 R more on every bottle? Under General Contract Law: Saray would be obligated to sell the price and could not rescind the K, because it turned out to be a bad deal for him. But under Art 12 of D#38, Cambodian ntract Co court could rescind the K based on the inadequacy of the consideration. 14


