bfff30628d5ac7c073fd42c569ac7197.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Chapter 4 Marketing Research: Gather, Analyze, and Use Information
Chapter 4 Marketing Research: Gather, Analyze, and Use Information
 Chapter Objectives 1. List and explain the steps in the marketing research process. 2. Differentiate between the types and sources of primary and secondary data. 3. Fully cover the methods by which marketing researchers collect primary data. Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n Educat 4 -2
Chapter Objectives 1. List and explain the steps in the marketing research process. 2. Differentiate between the types and sources of primary and secondary data. 3. Fully cover the methods by which marketing researchers collect primary data. Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n Educat 4 -2
 Marketing Research Does anyone else find this disturbing? 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Two Home Chapters Index Design 7 -3 Heavy Users Consume 17 Pounds Per Year!!
Marketing Research Does anyone else find this disturbing? 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Two Home Chapters Index Design 7 -3 Heavy Users Consume 17 Pounds Per Year!!
 The Marketing Research Function Marketing research - The planning, collection, and analysis of data relevant to marketing decision making and the communication of the results of analysis to company decision makers. Two key roles of MR: n Determine how effective the current marketing mix is and drive changes where needed n Explore new opportunities in the marketplace 7 -4
The Marketing Research Function Marketing research - The planning, collection, and analysis of data relevant to marketing decision making and the communication of the results of analysis to company decision makers. Two key roles of MR: n Determine how effective the current marketing mix is and drive changes where needed n Explore new opportunities in the marketplace 7 -4
 Marketing Research 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter One Decisions That Draw on Marketing Research Segmentation: deciding which segments should be targeted & their benefits Product: determining features, packaging, branding Distribution: determining number and type of retailers Advertising & Promotion: determining how much to spend and on which media outlets Personal selling: setting goals and sales force territories and number of sales staff Home Index 7 -5 Chapters Design Price: setting pricing level, responding to competitors, using pricing strategies Customer Satisfaction: deciding on how to measure it and developing a strategy to respond
Marketing Research 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter One Decisions That Draw on Marketing Research Segmentation: deciding which segments should be targeted & their benefits Product: determining features, packaging, branding Distribution: determining number and type of retailers Advertising & Promotion: determining how much to spend and on which media outlets Personal selling: setting goals and sales force territories and number of sales staff Home Index 7 -5 Chapters Design Price: setting pricing level, responding to competitors, using pricing strategies Customer Satisfaction: deciding on how to measure it and developing a strategy to respond
 Marketing Research 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter One Marketing Research and the 4 P’s: Holiday Inn Express Product • What kind of hotel would “sell” in the marketplace? • What should the hotel chain be named? • What brand elements should be created? Place • Where should hotels be located? Home Chapters Index Design 7 -6 Promotion • What advertising appeals would be most successful? • How should the hotel be positioned? • What media would be the most effective? Price • How much should be charged for room nights?
Marketing Research 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter One Marketing Research and the 4 P’s: Holiday Inn Express Product • What kind of hotel would “sell” in the marketplace? • What should the hotel chain be named? • What brand elements should be created? Place • Where should hotels be located? Home Chapters Index Design 7 -6 Promotion • What advertising appeals would be most successful? • How should the hotel be positioned? • What media would be the most effective? Price • How much should be charged for room nights?
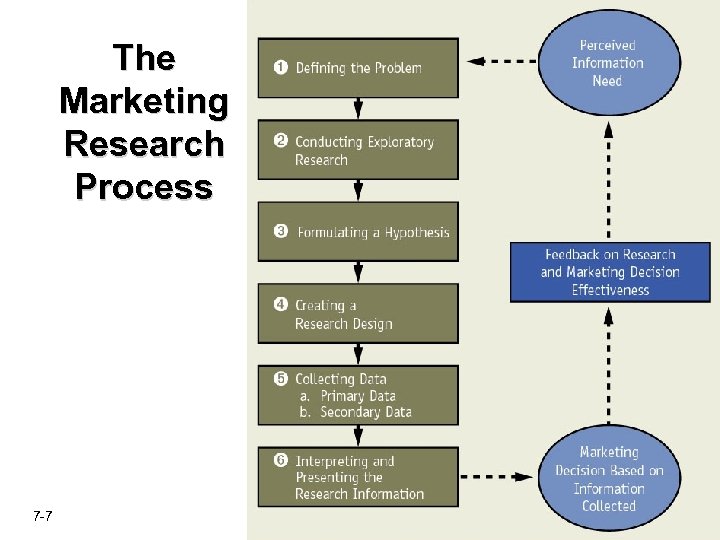 The Marketing Research Process 7 -7
The Marketing Research Process 7 -7
 Step 1: Define the Problem üWhat does the marketer want to know? üAvoid confusing symptoms of a problem (ex: declining sales) with the problem itself (ex: price disadvantage) üDefining the problem helps to prevent the all-too-common tendency to spend resources attempting to answer “interesting, but not necessary” questions 7 -8
Step 1: Define the Problem üWhat does the marketer want to know? üAvoid confusing symptoms of a problem (ex: declining sales) with the problem itself (ex: price disadvantage) üDefining the problem helps to prevent the all-too-common tendency to spend resources attempting to answer “interesting, but not necessary” questions 7 -8
 Step 2: Conduct exploratory research Exploratory Research – An informal investigation seeking to discover the cause of a problem by discussing it with informed internal and external sources üCan include evaluation of company records such as sales and profit analyses üCan also include sales and profit analyses of competitors’ products 7 -9
Step 2: Conduct exploratory research Exploratory Research – An informal investigation seeking to discover the cause of a problem by discussing it with informed internal and external sources üCan include evaluation of company records such as sales and profit analyses üCan also include sales and profit analyses of competitors’ products 7 -9
 Step 3: Formulate a Hypothesis üDoes the marketer have a theory about the problem that can be tested? üSets the stage for more in-depth research by further clarifying what researchers need to test üNot all marketing research tests specific hypotheses 7 -10
Step 3: Formulate a Hypothesis üDoes the marketer have a theory about the problem that can be tested? üSets the stage for more in-depth research by further clarifying what researchers need to test üNot all marketing research tests specific hypotheses 7 -10
 Step 4: Create a Research Design - A series of decisions that, taken together, comprise a master plan or model for conducting marketing research üMust ensure that the study will measure what the marketer intends to measure üMust also ensure an appropriate selection of respondents (“sample”) 7 -11
Step 4: Create a Research Design - A series of decisions that, taken together, comprise a master plan or model for conducting marketing research üMust ensure that the study will measure what the marketer intends to measure üMust also ensure an appropriate selection of respondents (“sample”) 7 -11
 Designing the Sample n Probability sampling: üEach member of the population has some known chance of being included üSample is representative of population, and inferences about population are justified n Nonprobability sample üPersonal judgment used in selecting respondents üSome members of population have no chance of being included so sample is not representative of population Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n 4 -12 Educat
Designing the Sample n Probability sampling: üEach member of the population has some known chance of being included üSample is representative of population, and inferences about population are justified n Nonprobability sample üPersonal judgment used in selecting respondents üSome members of population have no chance of being included so sample is not representative of population Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n 4 -12 Educat
 Step 5: Collect Data Secondary data - data from previously published or compiled sources (ex: Census data). Data is not specifically for the problem at hand Primary data - data collected for the first time specifically for a marketing research study (ex: focus group) 7 -13
Step 5: Collect Data Secondary data - data from previously published or compiled sources (ex: Census data). Data is not specifically for the problem at hand Primary data - data collected for the first time specifically for a marketing research study (ex: focus group) 7 -13
 Marketing Research Secondary Data 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Four Secondary Data - data from previously published or compiled sources (ex: Census data) • Someone else has done initial research who had a similar or identical problem Home Chapters Index Design 7 -14
Marketing Research Secondary Data 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Four Secondary Data - data from previously published or compiled sources (ex: Census data) • Someone else has done initial research who had a similar or identical problem Home Chapters Index Design 7 -14
 Secondary Data Sources n Government Data üCompanies’ most important source of marketing data üCensus information available at no charge n Private Data (examples) üStarch Readership Reports – measures ads üA. C. Nielsen’s Sales. Net scanner data from supermarkets n Online Sources of Secondary Data üCyberspace simplifies the search for secondary data üOnline data can cost less and take less time 7 -15
Secondary Data Sources n Government Data üCompanies’ most important source of marketing data üCensus information available at no charge n Private Data (examples) üStarch Readership Reports – measures ads üA. C. Nielsen’s Sales. Net scanner data from supermarkets n Online Sources of Secondary Data üCyberspace simplifies the search for secondary data üOnline data can cost less and take less time 7 -15
 Searching for Gold: Data Mining n Data mining -- Includes sophisticated analysis techniques to take advantage of the massive amount of transaction information now available n Analysts sift through data to identify unique patterns of behavior among different customer groups for use in target marketing Ex: Amazon targeting potential buyers of American Idol Season One box set Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n 4 -16 Educat
Searching for Gold: Data Mining n Data mining -- Includes sophisticated analysis techniques to take advantage of the massive amount of transaction information now available n Analysts sift through data to identify unique patterns of behavior among different customer groups for use in target marketing Ex: Amazon targeting potential buyers of American Idol Season One box set Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n 4 -16 Educat
 Marketing Research Advantages of Secondary Data 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Four Home Chapters Index Design 7 -17 + Can be obtained quickly + Is usually inexpensive or even free + Might provide a solution to a problem without using an primary data + Is usually available from various sources
Marketing Research Advantages of Secondary Data 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Four Home Chapters Index Design 7 -17 + Can be obtained quickly + Is usually inexpensive or even free + Might provide a solution to a problem without using an primary data + Is usually available from various sources
 Marketing Research Disadvantages of Secondary Data 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Four Home Chapters Index Design 7 -18 - The right data needed to make decisions might not be available - The data might be outdated - The source might be questionable - data may have been “perfumed” or company not competent - The way the data was collected may have been incorrect
Marketing Research Disadvantages of Secondary Data 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Four Home Chapters Index Design 7 -18 - The right data needed to make decisions might not be available - The data might be outdated - The source might be questionable - data may have been “perfumed” or company not competent - The way the data was collected may have been incorrect
 Marketing Research Primary Data 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Four Home Chapters Index Design 7 -19 Primary Data – data collected for the first time specifically for a marketing research study. • Directly acquired from customer/end user • Can be expensive • Generally for specific use related to research issue • Assumption is that no one has had this exact problem before • Includes surveys, focus groups, interviews, observation studies, test marketing, and more
Marketing Research Primary Data 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter Four Home Chapters Index Design 7 -19 Primary Data – data collected for the first time specifically for a marketing research study. • Directly acquired from customer/end user • Can be expensive • Generally for specific use related to research issue • Assumption is that no one has had this exact problem before • Includes surveys, focus groups, interviews, observation studies, test marketing, and more
 Primary Data 1. Interviews ü Best means for obtaining detailed info about consumers ü Usually in person, but can be via technology ü Can be slow & expensive 2. Focus Groups - an information gathering procedure that typically brings together 8 to 12 individuals to discuss a given subject ü Can provide quick and relatively inexpensive insights ü May not produce completely honest responses 7 -20
Primary Data 1. Interviews ü Best means for obtaining detailed info about consumers ü Usually in person, but can be via technology ü Can be slow & expensive 2. Focus Groups - an information gathering procedure that typically brings together 8 to 12 individuals to discuss a given subject ü Can provide quick and relatively inexpensive insights ü May not produce completely honest responses 7 -20
 Primary Data 3. Mail Surveys ü Are cost effective and provides anonymity that may encourage candid answers. ü Usually low response rates and long time to conduct 4. Online Methods – Surveys, Observing chats, Observing surfing, Online Focus Groups ü Benefits include the lack of geographic restrictions, faster turn-around time, and dramatically lower costs 7 -21
Primary Data 3. Mail Surveys ü Are cost effective and provides anonymity that may encourage candid answers. ü Usually low response rates and long time to conduct 4. Online Methods – Surveys, Observing chats, Observing surfing, Online Focus Groups ü Benefits include the lack of geographic restrictions, faster turn-around time, and dramatically lower costs 7 -21
 Primary Data 5. Experimental Method ü A researcher manipulates test group(s) and compares the results with those of a control group ü The most common example is test marketing ü Expensive to conduct 6. Observation Method ü Researchers actually view the research subjects ü Useful in helping to understand consumer behavior ü Includes counting passing cars or people meters recording household TV-viewing habits 7 -22
Primary Data 5. Experimental Method ü A researcher manipulates test group(s) and compares the results with those of a control group ü The most common example is test marketing ü Expensive to conduct 6. Observation Method ü Researchers actually view the research subjects ü Useful in helping to understand consumer behavior ü Includes counting passing cars or people meters recording household TV-viewing habits 7 -22
 Observation Methods Copyri Wireless users at the ght Connection Court are 2009 Pearso easily observed n 4 -23 Educat Unobtrusive measures such as Garbology look for physical evidence that remains after some action has been taken
Observation Methods Copyri Wireless users at the ght Connection Court are 2009 Pearso easily observed n 4 -23 Educat Unobtrusive measures such as Garbology look for physical evidence that remains after some action has been taken
 Marketing Research 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter One Marketing Research Brainstorming Q. What types of Marketing Research may have been used in the development of the following products: ü Red Bull ü NASCAR Hall of Fame ü Breathe-Right Strips ü Ugg Boots üAmerican Idol Home Chapters Index Design 7 -24
Marketing Research 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter One Marketing Research Brainstorming Q. What types of Marketing Research may have been used in the development of the following products: ü Red Bull ü NASCAR Hall of Fame ü Breathe-Right Strips ü Ugg Boots üAmerican Idol Home Chapters Index Design 7 -24
 Challenges to gathering primary data in foreign countries üDifferences in sophistication of research operations üInfrastructure/transportation challenges üLack of phones and/or low literacy rates üLocal customs and cultural differences üLanguage translation difficulties Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n 4 -25 Educat
Challenges to gathering primary data in foreign countries üDifferences in sophistication of research operations üInfrastructure/transportation challenges üLack of phones and/or low literacy rates üLocal customs and cultural differences üLanguage translation difficulties Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n 4 -25 Educat
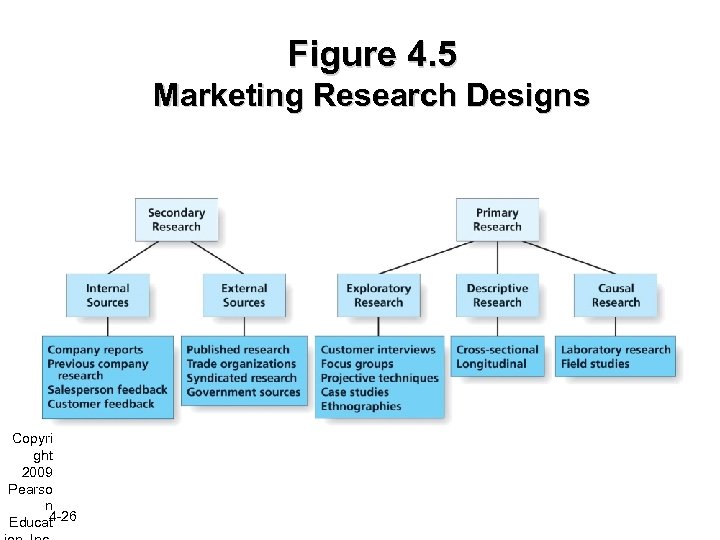 Figure 4. 5 Marketing Research Designs Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n 4 -26 Educat
Figure 4. 5 Marketing Research Designs Copyri ght 2009 Pearso n 4 -26 Educat
 Step 6: Interpret and Present Research Information üFindings must be presented to decisionmakers in a format that allows them to make effective judgments 7 -27
Step 6: Interpret and Present Research Information üFindings must be presented to decisionmakers in a format that allows them to make effective judgments 7 -27
 Honda launches a unique vehicle targeting a specific sought after customer segment. What role do you think Marketing Research played? 7 -28
Honda launches a unique vehicle targeting a specific sought after customer segment. What role do you think Marketing Research played? 7 -28
 Marketing Research 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter One Home Chapters Index Design 7 -29 Exercise -- Averting Failures via MR Scenario – As a world-class MR firm with a knack for seeing the future, what proactive Marketing Research would you have done which would have prevented/lessened the following failures? Include the type of research you would have conducted and the marketing actions you would have recommended. Group/Product 1. Microsoft Zune – gaining little market share 2. Powerade - dominated by Gatorade 3. 2006 Winter Olympics TV viewing – very low 4. TWA Airlines – bankrupt & absorbed by AA 5. Blockbuster Video – sales down, stores
Marketing Research 6 th Edition - Mc. Daniel / Gates Chapter One Home Chapters Index Design 7 -29 Exercise -- Averting Failures via MR Scenario – As a world-class MR firm with a knack for seeing the future, what proactive Marketing Research would you have done which would have prevented/lessened the following failures? Include the type of research you would have conducted and the marketing actions you would have recommended. Group/Product 1. Microsoft Zune – gaining little market share 2. Powerade - dominated by Gatorade 3. 2006 Winter Olympics TV viewing – very low 4. TWA Airlines – bankrupt & absorbed by AA 5. Blockbuster Video – sales down, stores


