7dc95fb1fdd24267c6bcab53083ec0ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 86
 Chapter 4 Managing the Information Systems Infrastructure 4 -1 Google (v. )- …to use the Google search engine to obtain information…on the World Wide Web. Merriam-Webster IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Chapter 4 Managing the Information Systems Infrastructure 4 -1 Google (v. )- …to use the Google search engine to obtain information…on the World Wide Web. Merriam-Webster IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 4 -2 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge infrastructure. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 4 -2 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge infrastructure. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 4 -3 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge infrastructure. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 4 -3 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge infrastructure. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Infrastructure 4 -4 Interconnection of basic facilities and services enabling an area to function properly Streets Power, telephone, water, and sewage lines Schools Retail stores Law enforcement IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Infrastructure 4 -4 Interconnection of basic facilities and services enabling an area to function properly Streets Power, telephone, water, and sewage lines Schools Retail stores Law enforcement IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 The IS Infrastructure 4 -5 Google’s newest data center—The Dalles, OR Why there? Fiber-optic network connectivity Access to water for cooling needs Cheap, uninterrupted power from a nearby hydroelectric dam IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
The IS Infrastructure 4 -5 Google’s newest data center—The Dalles, OR Why there? Fiber-optic network connectivity Access to water for cooling needs Cheap, uninterrupted power from a nearby hydroelectric dam IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
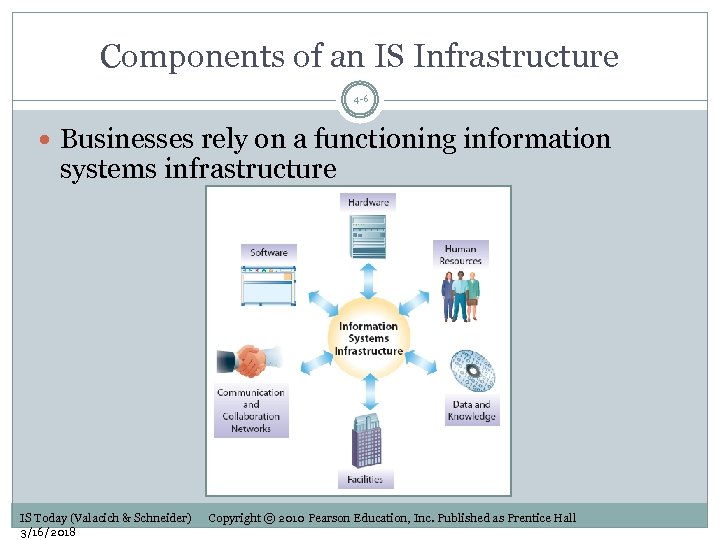 Components of an IS Infrastructure 4 -6 Businesses rely on a functioning information systems infrastructure IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Components of an IS Infrastructure 4 -6 Businesses rely on a functioning information systems infrastructure IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 4 -7 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge infrastructure. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 4 -7 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge infrastructure. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
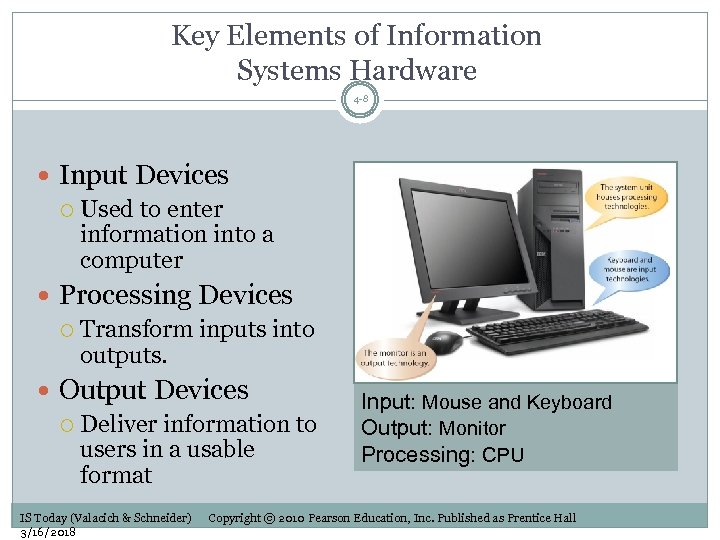 Key Elements of Information Systems Hardware 4 -8 Input Devices Used to enter information into a computer Processing Devices Transform inputs into outputs. Output Devices Deliver information to users in a usable format IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Input: Mouse and Keyboard Output: Monitor Processing: CPU Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Key Elements of Information Systems Hardware 4 -8 Input Devices Used to enter information into a computer Processing Devices Transform inputs into outputs. Output Devices Deliver information to users in a usable format IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Input: Mouse and Keyboard Output: Monitor Processing: CPU Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Input Technologies 4 -9 Entering text and numbers: keyboard Selecting and pointing: mouse, touch screen, touch pad Entering batch data: scanner, bar code reader Entering audio and video: microphone, digital camera IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Input Technologies 4 -9 Entering text and numbers: keyboard Selecting and pointing: mouse, touch screen, touch pad Entering batch data: scanner, bar code reader Entering audio and video: microphone, digital camera IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
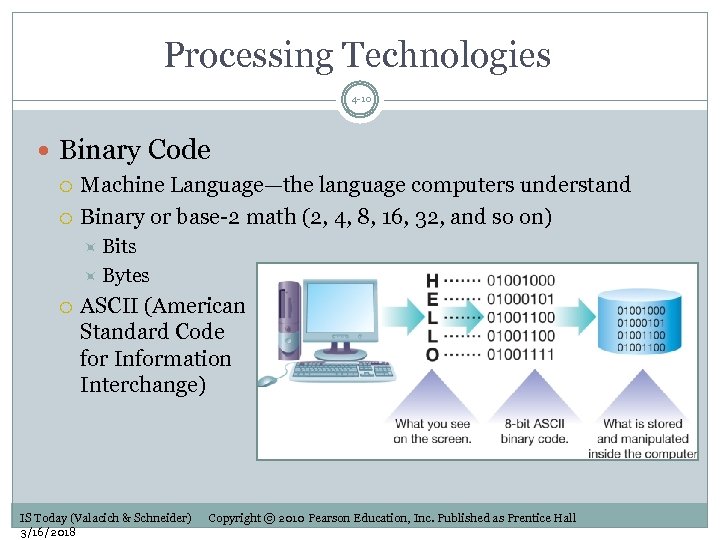 Processing Technologies 4 -10 Binary Code Machine Language—the language computers understand Binary or base-2 math (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and so on) Bits Bytes ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Processing Technologies 4 -10 Binary Code Machine Language—the language computers understand Binary or base-2 math (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and so on) Bits Bytes ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
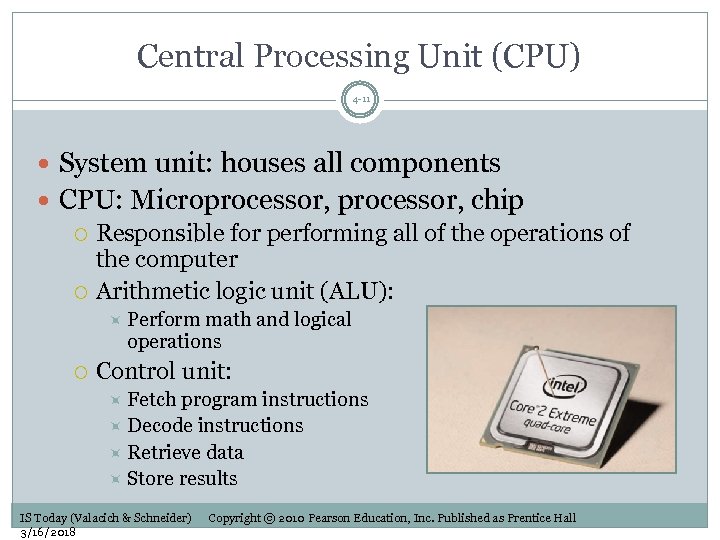 Central Processing Unit (CPU) 4 -11 System unit: houses all components CPU: Microprocessor, chip Responsible for performing all of the operations of the computer Arithmetic logic unit (ALU): Perform math and logical operations Control unit: Fetch program instructions Decode instructions Retrieve data Store results IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Central Processing Unit (CPU) 4 -11 System unit: houses all components CPU: Microprocessor, chip Responsible for performing all of the operations of the computer Arithmetic logic unit (ALU): Perform math and logical operations Control unit: Fetch program instructions Decode instructions Retrieve data Store results IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
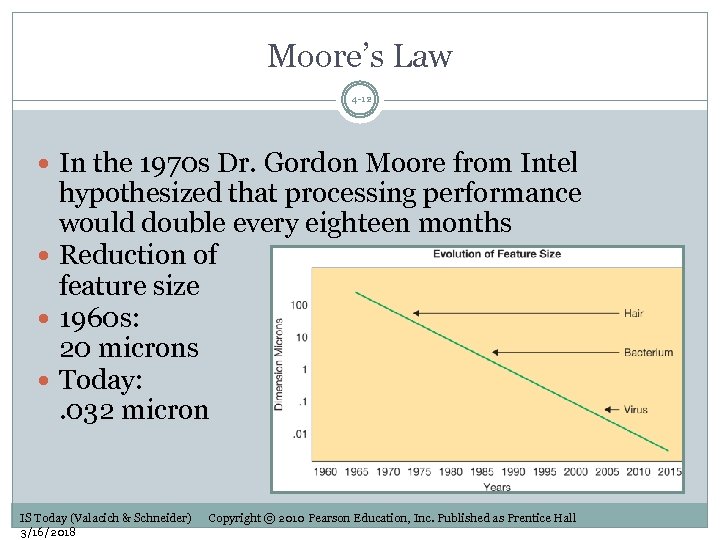 Moore’s Law 4 -12 In the 1970 s Dr. Gordon Moore from Intel hypothesized that processing performance would double every eighteen months Reduction of feature size 1960 s: 20 microns Today: . 032 micron IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Moore’s Law 4 -12 In the 1970 s Dr. Gordon Moore from Intel hypothesized that processing performance would double every eighteen months Reduction of feature size 1960 s: 20 microns Today: . 032 micron IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Primary Storage 4 -13 For temporary storage to support computer processing Registers and cache (volatile) Store data for immediate use by the CPU Random-access memory (RAM) (volatile) Store programs and data currently in use Read-only memory (ROM) (nonvolatile) Store programs and data automatically loaded when the computer is turned on Basis input/output system (BIOS) IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Primary Storage 4 -13 For temporary storage to support computer processing Registers and cache (volatile) Store data for immediate use by the CPU Random-access memory (RAM) (volatile) Store programs and data currently in use Read-only memory (ROM) (nonvolatile) Store programs and data automatically loaded when the computer is turned on Basis input/output system (BIOS) IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
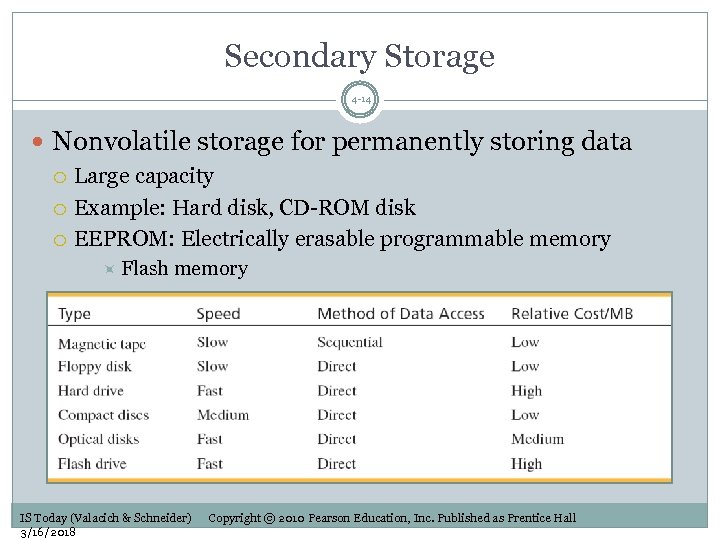 Secondary Storage 4 -14 Nonvolatile storage for permanently storing data Large capacity Example: Hard disk, CD-ROM disk EEPROM: Electrically erasable programmable memory Flash memory IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Secondary Storage 4 -14 Nonvolatile storage for permanently storing data Large capacity Example: Hard disk, CD-ROM disk EEPROM: Electrically erasable programmable memory Flash memory IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Output Devices: Video Output 4 -15 Used to display information from a computer Monitors Projectors Video card (graphics card) Tells monitor which dots to activate IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Output Devices: Video Output 4 -15 Used to display information from a computer Monitors Projectors Video card (graphics card) Tells monitor which dots to activate IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Printers and Plotters 4 -16 Plotter Uses pens to transfer engineering designs to drafting paper Dot Matrix Used for voluminous information Ink-jet Sprays ink onto paper Laser Uses electrostatic process to force ink onto paper IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Printers and Plotters 4 -16 Plotter Uses pens to transfer engineering designs to drafting paper Dot Matrix Used for voluminous information Ink-jet Sprays ink onto paper Laser Uses electrostatic process to force ink onto paper IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Audio Output 4 -17 Sound card and speakers Sound card translates digits into sound Also used to capture sound IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Audio Output 4 -17 Sound card and speakers Sound card translates digits into sound Also used to capture sound IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
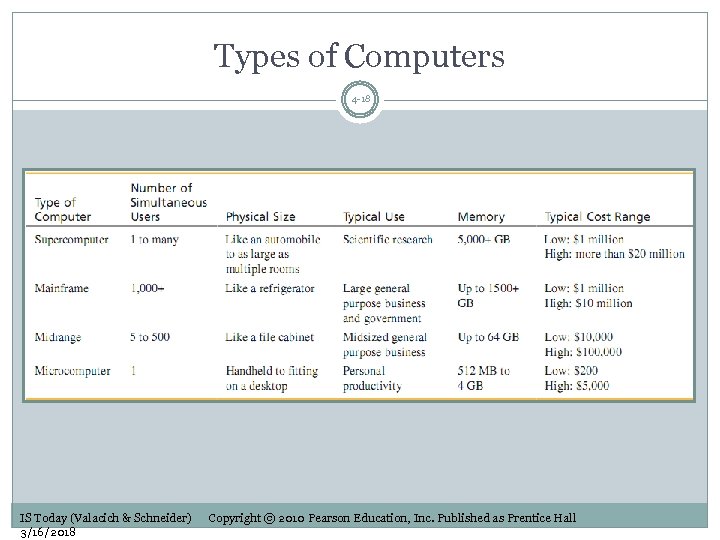 Types of Computers 4 -18 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Types of Computers 4 -18 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Hardware Infrastructure Trends Supercomputers IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Hardware Infrastructure Trends Supercomputers IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 On-Demand Computing 4 -20 Dealing with fluctuating computing needs Available resources allocated based on user needs Utility computing On-demand computing rented from external provider Paid on as-needed basis Storage service provider Scalability IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
On-Demand Computing 4 -20 Dealing with fluctuating computing needs Available resources allocated based on user needs Utility computing On-demand computing rented from external provider Paid on as-needed basis Storage service provider Scalability IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
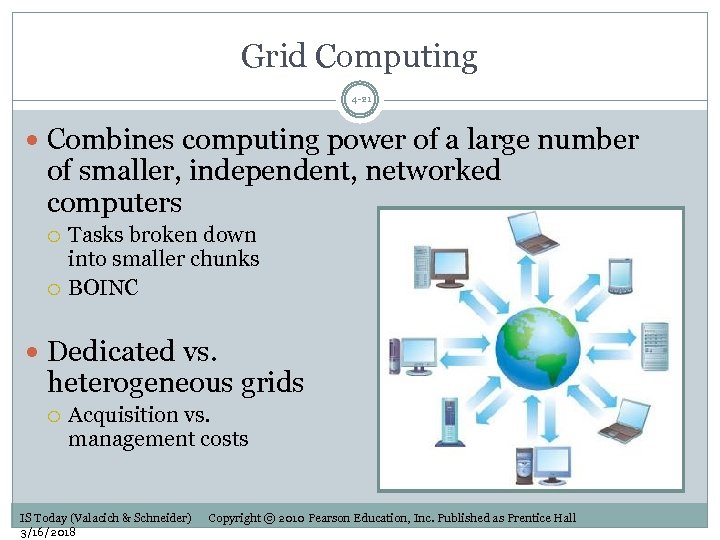 Grid Computing 4 -21 Combines computing power of a large number of smaller, independent, networked computers Tasks broken down into smaller chunks BOINC Dedicated vs. heterogeneous grids Acquisition vs. management costs IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Grid Computing 4 -21 Combines computing power of a large number of smaller, independent, networked computers Tasks broken down into smaller chunks BOINC Dedicated vs. heterogeneous grids Acquisition vs. management costs IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
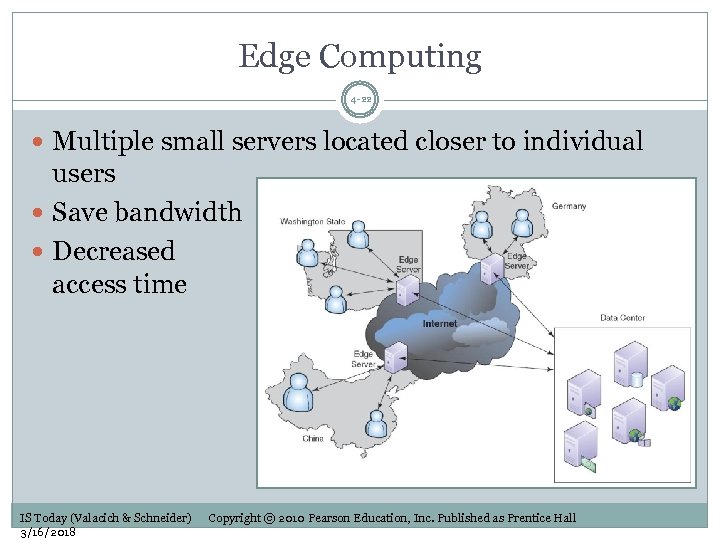 Edge Computing 4 -22 Multiple small servers located closer to individual users Save bandwidth Decreased access time IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Edge Computing 4 -22 Multiple small servers located closer to individual users Save bandwidth Decreased access time IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Green Computing 4 -23 Use computers more efficiently Large organizations with significant computing needs Save money using: Virtualization Virtual machines can be configured to run on a single computer IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Green Computing 4 -23 Use computers more efficiently Large organizations with significant computing needs Save money using: Virtualization Virtual machines can be configured to run on a single computer IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 4 -24 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 4 -24 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
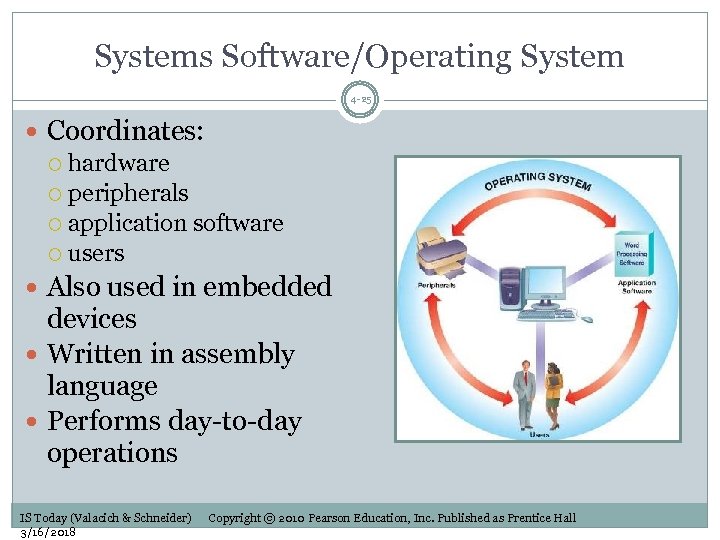 Systems Software/Operating System 4 -25 Coordinates: hardware peripherals application software users Also used in embedded devices Written in assembly language Performs day-to-day operations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Systems Software/Operating System 4 -25 Coordinates: hardware peripherals application software users Also used in embedded devices Written in assembly language Performs day-to-day operations IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
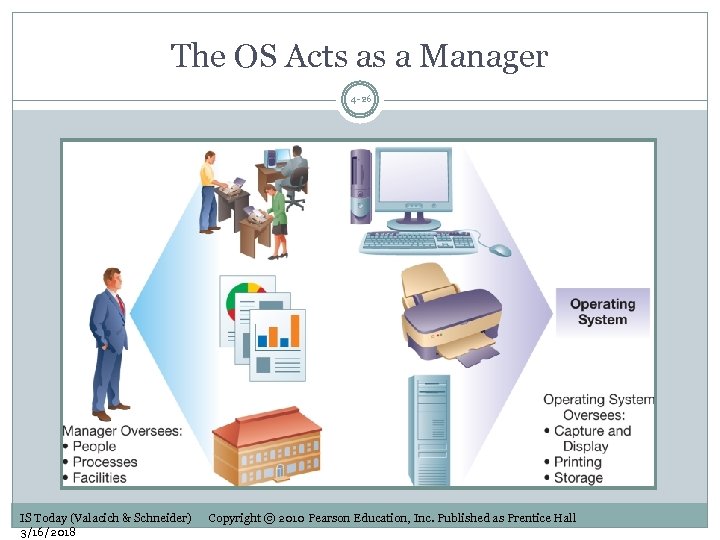 The OS Acts as a Manager 4 -26 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
The OS Acts as a Manager 4 -26 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Interfaces: Command vs. GUI 4 -27 Provided by operating system Interface types: Command line interface Requires typing text commands Graphical user interface (GUI) Windows Vista Mac OS X Linux (KDE or GNOME) IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Interfaces: Command vs. GUI 4 -27 Provided by operating system Interface types: Command line interface Requires typing text commands Graphical user interface (GUI) Windows Vista Mac OS X Linux (KDE or GNOME) IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Application Software 4 -28 For performing specific user tasks Writing a business letter Processing payroll Application software interacts with systems software IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Application Software 4 -28 For performing specific user tasks Writing a business letter Processing payroll Application software interacts with systems software IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Software Infrastructure Trends 4 -29 Open-source software Open-source movement aided by the advent of the Internet Source code is freely available for use and/or modification Open-source operating system Linux Used in embedded systems to personal computers to supercomputers IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Software Infrastructure Trends 4 -29 Open-source software Open-source movement aided by the advent of the Internet Source code is freely available for use and/or modification Open-source operating system Linux Used in embedded systems to personal computers to supercomputers IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Open-Source Application Software 4 -30 Open-source application software Apache Web server Firefox Web browser Open. Office Drawback: Obtaining customer support may be difficult IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Open-Source Application Software 4 -30 Open-source application software Apache Web server Firefox Web browser Open. Office Drawback: Obtaining customer support may be difficult IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Application Service Providers 4 -31 ASPs provide on-demand software access over the Web Specific software located on the ASP’s server Accessed using Web-enabled interfaces Software as a service (Saa. S) Benefits: Reduced need to maintain or upgrade software Fixed monthly fee for services Reliability IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Application Service Providers 4 -31 ASPs provide on-demand software access over the Web Specific software located on the ASP’s server Accessed using Web-enabled interfaces Software as a service (Saa. S) Benefits: Reduced need to maintain or upgrade software Fixed monthly fee for services Reliability IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Service Oriented Architecture 4 -32 Used to integrate business processes across organizations Business processes are broken down into distinct services Enables rapid reaction to changing business conditions Reusable nature of services reduces cost of developing new applications IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Service Oriented Architecture 4 -32 Used to integrate business processes across organizations Business processes are broken down into distinct services Enables rapid reaction to changing business conditions Reusable nature of services reduces cost of developing new applications IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 4 -33 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge infrastructure. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 4 -33 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge infrastructure. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
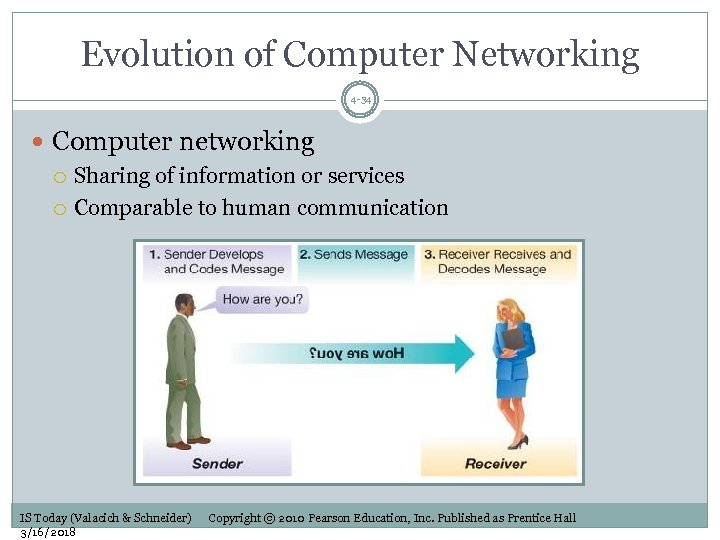 Evolution of Computer Networking 4 -34 Computer networking Sharing of information or services Comparable to human communication IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Evolution of Computer Networking 4 -34 Computer networking Sharing of information or services Comparable to human communication IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Messages, Senders, and Receivers 4 -35 Components of communication: Senders and receivers with something to share A transmission medium to send the message Protocols (rules) dictating communication IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Messages, Senders, and Receivers 4 -35 Components of communication: Senders and receivers with something to share A transmission medium to send the message Protocols (rules) dictating communication IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
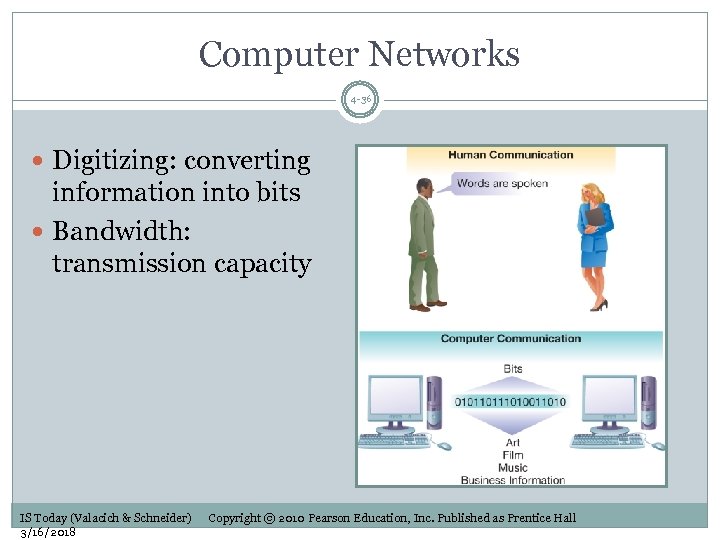 Computer Networks 4 -36 Digitizing: converting information into bits Bandwidth: transmission capacity IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Computer Networks 4 -36 Digitizing: converting information into bits Bandwidth: transmission capacity IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
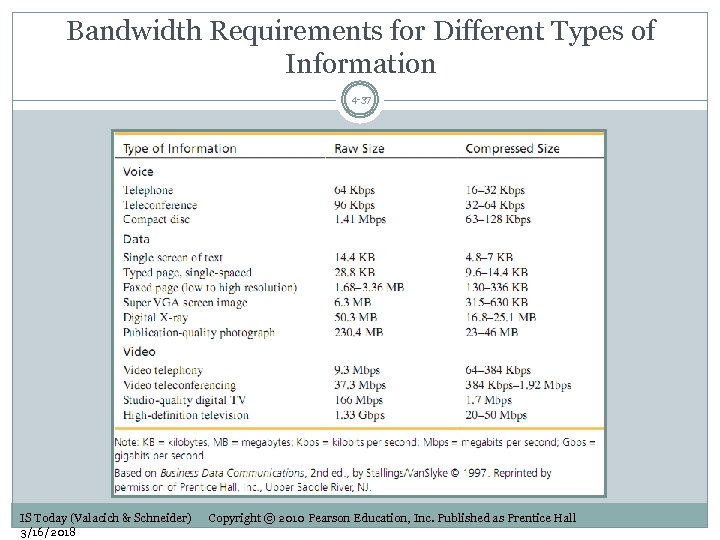 Bandwidth Requirements for Different Types of Information 4 -37 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Bandwidth Requirements for Different Types of Information 4 -37 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
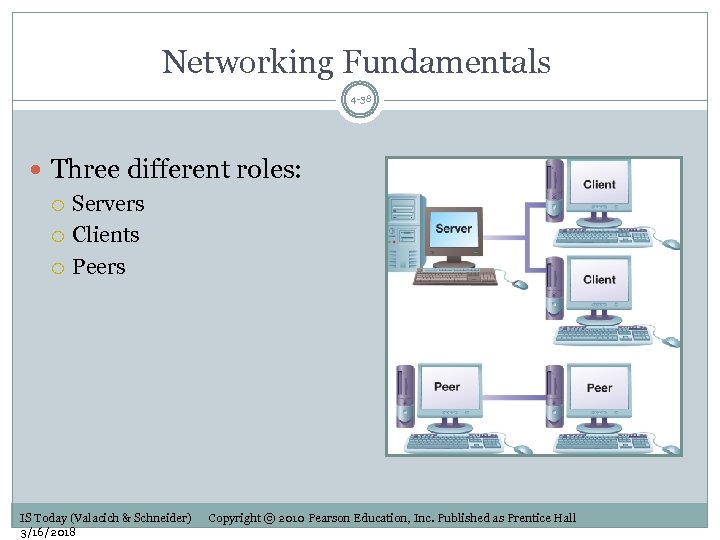 Networking Fundamentals 4 -38 Three different roles: Servers Clients Peers IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Networking Fundamentals 4 -38 Three different roles: Servers Clients Peers IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
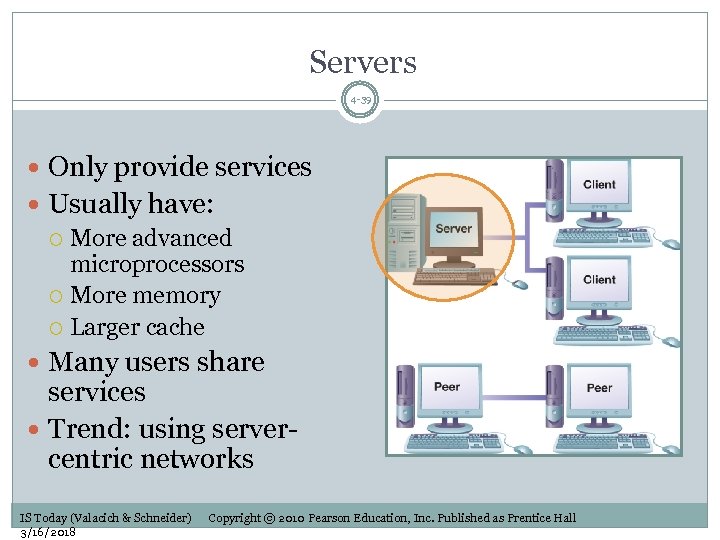 Servers 4 -39 Only provide services Usually have: More advanced microprocessors More memory Larger cache Many users share services Trend: using servercentric networks IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Servers 4 -39 Only provide services Usually have: More advanced microprocessors More memory Larger cache Many users share services Trend: using servercentric networks IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
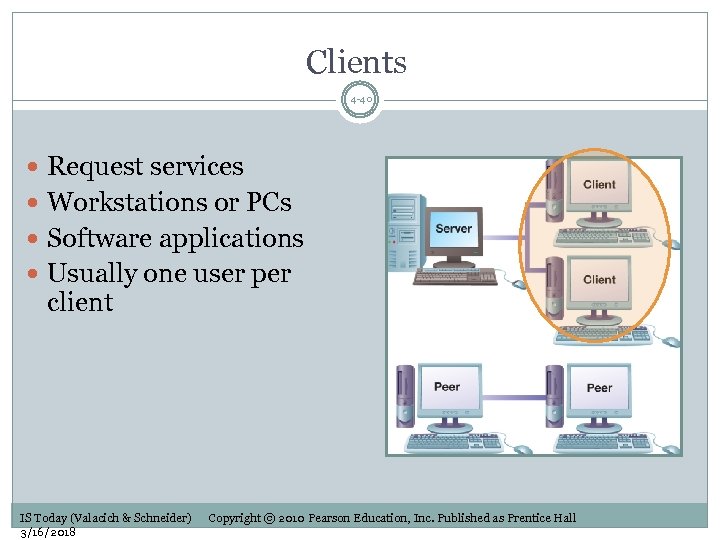 Clients 4 -40 Request services Workstations or PCs Software applications Usually one user per client IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Clients 4 -40 Request services Workstations or PCs Software applications Usually one user per client IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
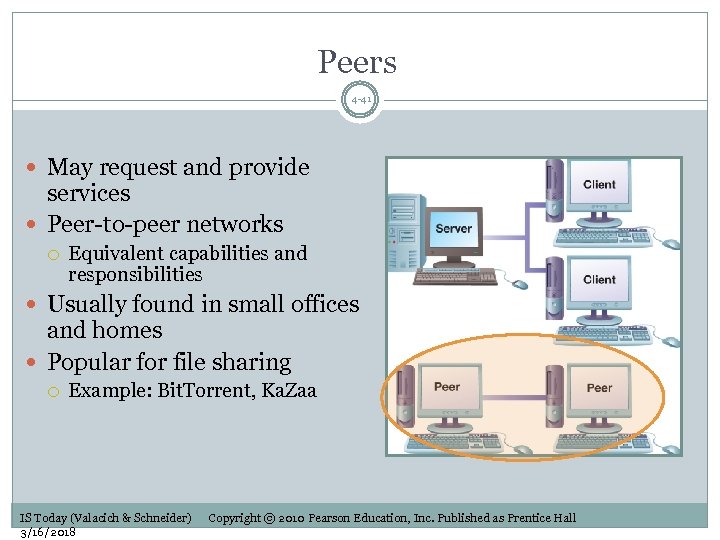 Peers 4 -41 May request and provide services Peer-to-peer networks Equivalent capabilities and responsibilities Usually found in small offices and homes Popular for file sharing Example: Bit. Torrent, Ka. Zaa IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Peers 4 -41 May request and provide services Peer-to-peer networks Equivalent capabilities and responsibilities Usually found in small offices and homes Popular for file sharing Example: Bit. Torrent, Ka. Zaa IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
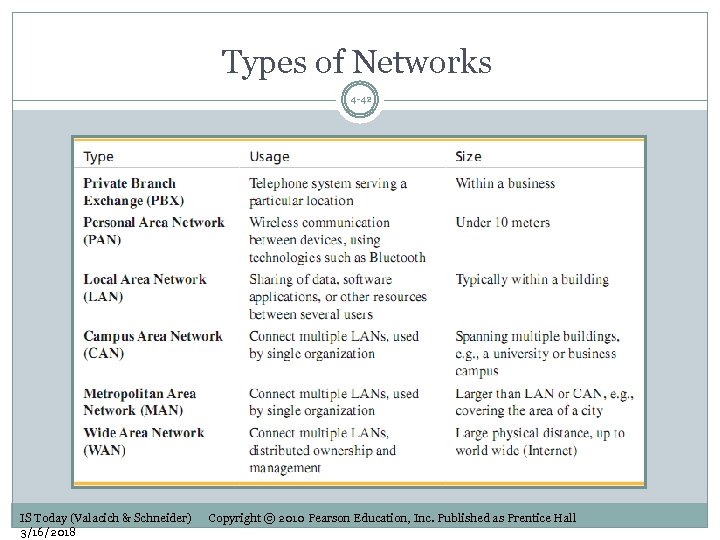 Types of Networks 4 -42 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Types of Networks 4 -42 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
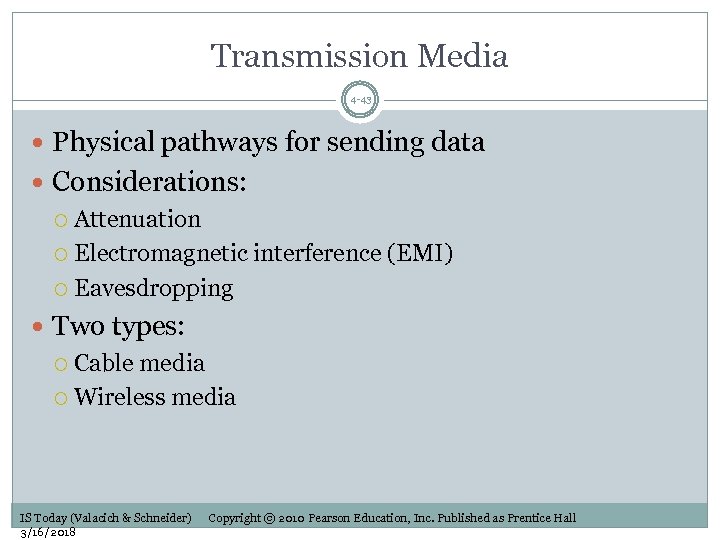 Transmission Media 4 -43 Physical pathways for sending data Considerations: Attenuation Electromagnetic interference (EMI) Eavesdropping Two types: Cable media Wireless media IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Transmission Media 4 -43 Physical pathways for sending data Considerations: Attenuation Electromagnetic interference (EMI) Eavesdropping Two types: Cable media Wireless media IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
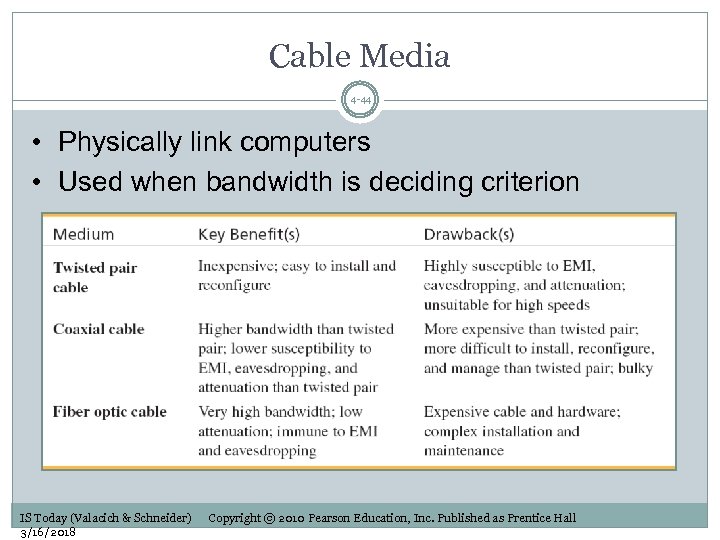 Cable Media 4 -44 • Physically link computers • Used when bandwidth is deciding criterion IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Cable Media 4 -44 • Physically link computers • Used when bandwidth is deciding criterion IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
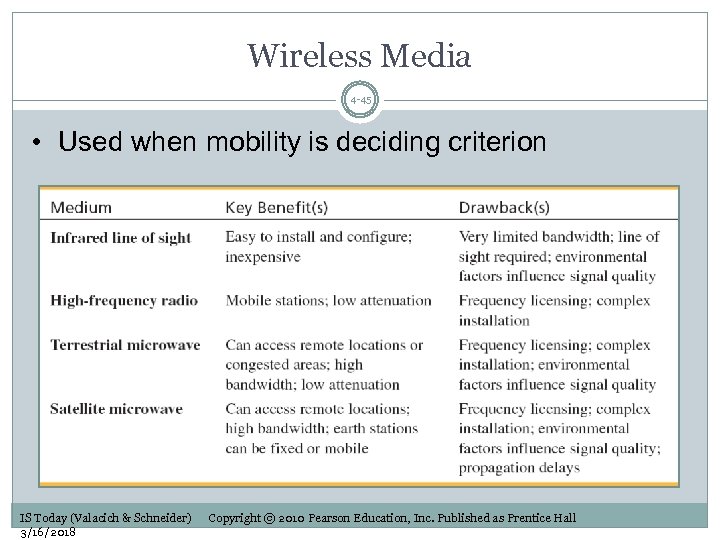 Wireless Media 4 -45 • Used when mobility is deciding criterion IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Wireless Media 4 -45 • Used when mobility is deciding criterion IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Applications of Wireless Media 4 -46 Wireless local area networks (WLANs) Wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) Bluetooth Ultra Low Power (ULP) Bluetooth Terrestrial microwave Satellite microwave Access remote locations Global positioning system (GPS) Used to triangulate position anywhere on earth IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Applications of Wireless Media 4 -46 Wireless local area networks (WLANs) Wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) Bluetooth Ultra Low Power (ULP) Bluetooth Terrestrial microwave Satellite microwave Access remote locations Global positioning system (GPS) Used to triangulate position anywhere on earth IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 How Did the Internet Get Started? 4 -47 Internet—derived from internetworking 1960 s—U. S. Defense Advanced Research Project (DARPA) ARPANET—WAN that linked universities and research centers 1986—U. S. National Science Foundation NSFNET—became major component of the Internet IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
How Did the Internet Get Started? 4 -47 Internet—derived from internetworking 1960 s—U. S. Defense Advanced Research Project (DARPA) ARPANET—WAN that linked universities and research centers 1986—U. S. National Science Foundation NSFNET—became major component of the Internet IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
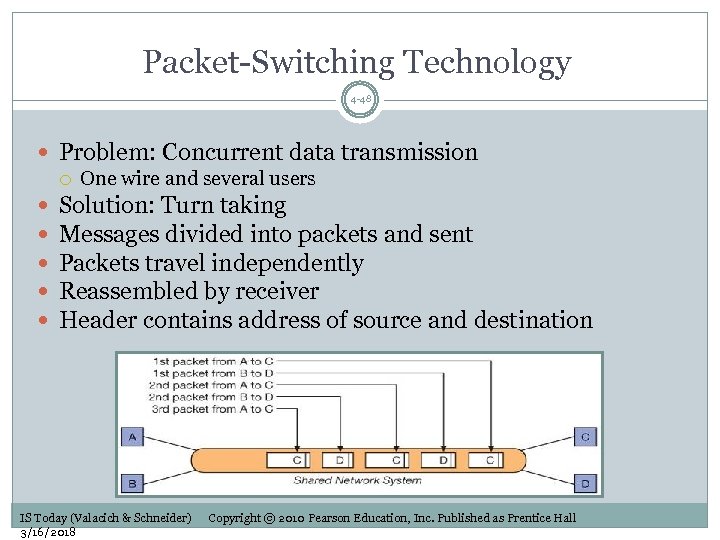 Packet-Switching Technology 4 -48 Problem: Concurrent data transmission One wire and several users Solution: Turn taking Messages divided into packets and sent Packets travel independently Reassembled by receiver Header contains address of source and destination IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Packet-Switching Technology 4 -48 Problem: Concurrent data transmission One wire and several users Solution: Turn taking Messages divided into packets and sent Packets travel independently Reassembled by receiver Header contains address of source and destination IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 TCP/IP 4 -49 Protocol of the Internet TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) Breaks information into packets Manages transfer of packets between computers IP (Internet Protocol) Defines how the packet must be formed Contains destination address Routers forward packets between networks IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
TCP/IP 4 -49 Protocol of the Internet TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) Breaks information into packets Manages transfer of packets between computers IP (Internet Protocol) Defines how the packet must be formed Contains destination address Routers forward packets between networks IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 IP Datagram 4 -50 Data packet that conforms to the IP specifications Relies on IP address Unique address assigned to computers and routers TCP helps IP deliver packets: Checks for lost datagrams Puts received datagrams in correct order Discards duplicate datagrams IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
IP Datagram 4 -50 Data packet that conforms to the IP specifications Relies on IP address Unique address assigned to computers and routers TCP helps IP deliver packets: Checks for lost datagrams Puts received datagrams in correct order Discards duplicate datagrams IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 World Wide Web 4 -51 World Wide Web (WWW) Graphical user interface to the Internet One of the most powerful uses of the Internet Web browser Software application used to locate and display Web pages Microsoft Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Flock IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
World Wide Web 4 -51 World Wide Web (WWW) Graphical user interface to the Internet One of the most powerful uses of the Internet Web browser Software application used to locate and display Web pages Microsoft Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Flock IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 History of the World Wide Web 4 -52 Gopher—early menu driven tool Web invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991 Introduced hypertext Hyperlinks—links to other related documents HTML—standard method for specifying Web pages Tags specify formatting Web pages stored on Web servers HTTP—used for processing requests Web pages have unique URL address IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
History of the World Wide Web 4 -52 Gopher—early menu driven tool Web invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991 Introduced hypertext Hyperlinks—links to other related documents HTML—standard method for specifying Web pages Tags specify formatting Web pages stored on Web servers HTTP—used for processing requests Web pages have unique URL address IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Web Domain Names and Addresses 4 -53 Domain name Top-level domain Host name IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Web Domain Names and Addresses 4 -53 Domain name Top-level domain Host name IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
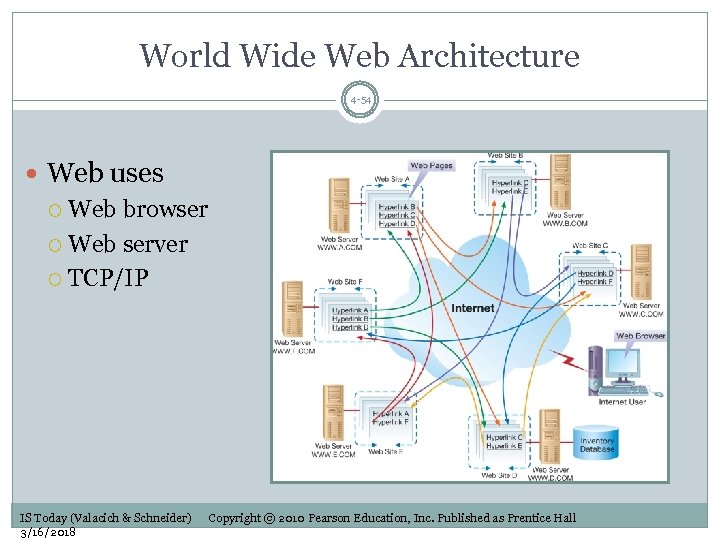 World Wide Web Architecture 4 -54 Web uses Web browser Web server TCP/IP IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
World Wide Web Architecture 4 -54 Web uses Web browser Web server TCP/IP IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Managing the Communication and Collaboration Infrastructure 4 -55 Diverse communication needs Convergence Increasing mobility Convergence of functionality of devices Cell phone and PDA Convergence within underlying infrastructures IP convergence Voice over IP Videoconferencing over IP IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Managing the Communication and Collaboration Infrastructure 4 -55 Diverse communication needs Convergence Increasing mobility Convergence of functionality of devices Cell phone and PDA Convergence within underlying infrastructures IP convergence Voice over IP Videoconferencing over IP IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 IP Convergence: Vo. IP 4 -56 Use of Internet technologies for placing telephone calls High quality of transmission possible Ability to call from any place with Internet connection IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
IP Convergence: Vo. IP 4 -56 Use of Internet technologies for placing telephone calls High quality of transmission possible Ability to call from any place with Internet connection IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 IP Convergence: Videoconferencing over IP 4 -57 IP used to transmit video data Desktop videoconferencing HP Halo meeting room: $400, 000 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
IP Convergence: Videoconferencing over IP 4 -57 IP used to transmit video data Desktop videoconferencing HP Halo meeting room: $400, 000 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Increasing Mobility 4 -58 Knowledge workers require access to information from anywhere Communication devices Wireless devices capable of connecting to organization’s internal network Wireless security concerns IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Increasing Mobility 4 -58 Knowledge workers require access to information from anywhere Communication devices Wireless devices capable of connecting to organization’s internal network Wireless security concerns IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Learning Objectives 4 -59 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives 4 -59 1. List the essential information systems infrastructure components and describe why they are necessary for satisfying an organization’s informational needs. Describe the components of an organization’s hardware infrastructure and highlight current trends. 2. 3. Describe the components of an organization’s software infrastructure and highlight current trends. 4. Describe the components of an organization’s communications and collaboration infrastructure and highlight current trends. 5. Describe the components of an organization’s data and knowledge. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
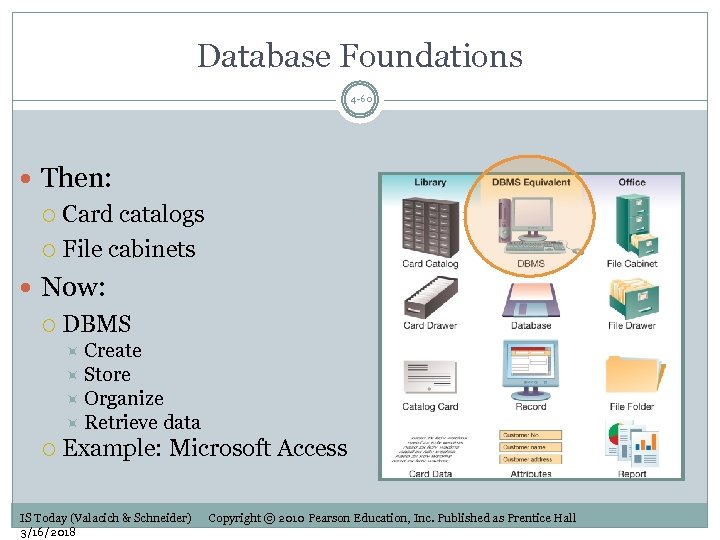 Database Foundations 4 -60 Then: Card catalogs File cabinets Now: DBMS Create Store Organize Retrieve data Example: Microsoft Access IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Database Foundations 4 -60 Then: Card catalogs File cabinets Now: DBMS Create Store Organize Retrieve data Example: Microsoft Access IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Database 4 -61 Database Collection of related data organized in a way to facilitate searches Entities Something you collect data about Examples: people, books IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Database 4 -61 Database Collection of related data organized in a way to facilitate searches Entities Something you collect data about Examples: people, books IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Record 4 -62 Contains data about a single entity Similar to catalog card IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Record 4 -62 Contains data about a single entity Similar to catalog card IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Attributes 4 -63 Specific characteristic describing the entities Examples: name and social security number are attributes of a person IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Attributes 4 -63 Specific characteristic describing the entities Examples: name and social security number are attributes of a person IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
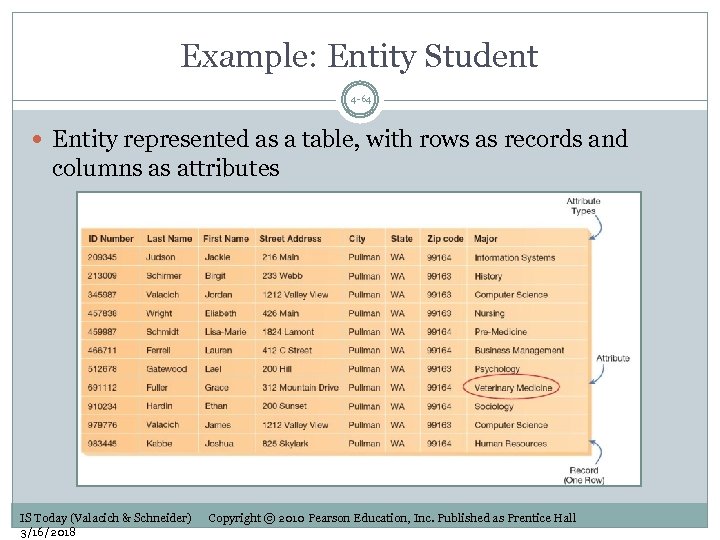 Example: Entity Student 4 -64 Entity represented as a table, with rows as records and columns as attributes IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Example: Entity Student 4 -64 Entity represented as a table, with rows as records and columns as attributes IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Advantages of the Database Approach 4 -65 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Program-data independence Minimal data redundancy Improved data consistency Improved data sharing Increased productivity of application development IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Advantages of the Database Approach 4 -65 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Program-data independence Minimal data redundancy Improved data consistency Improved data sharing Increased productivity of application development IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Advantages of the Database Approach (cont’d) 4 -66 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Enforcement of standards Improved security Improved data quality Improved data accessibility Reduced program maintenance IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Advantages of the Database Approach (cont’d) 4 -66 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Enforcement of standards Improved security Improved data quality Improved data accessibility Reduced program maintenance IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Costs and Risks of the Database Approach 4 -67 New, specialized personnel Installation and management cost and complexity 3. Conversion costs 4. Need for explicit backup and recovery 5. Organizational conflict 1. 2. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Costs and Risks of the Database Approach 4 -67 New, specialized personnel Installation and management cost and complexity 3. Conversion costs 4. Need for explicit backup and recovery 5. Organizational conflict 1. 2. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Effective Management of Databases 4 -68 Two components Data Structure of data Captured in a data model Entity-relationship diagram Data dictionary Specifies data types and other information about attributes Used to enforce business rules IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Effective Management of Databases 4 -68 Two components Data Structure of data Captured in a data model Entity-relationship diagram Data dictionary Specifies data types and other information about attributes Used to enforce business rules IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Effective Management of Databases 4 -69 Database Administrator (DBA) Responsible for development and management of databases Works with system analysts and programmers Works with users and managers Implements security features Grants access rights One of the key actors in creating a successful database IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Effective Management of Databases 4 -69 Database Administrator (DBA) Responsible for development and management of databases Works with system analysts and programmers Works with users and managers Implements security features Grants access rights One of the key actors in creating a successful database IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Entering Data 4 -70 Forms Enter data about a record Field in a form corresponds to attribute in a record Used to add, modify, or delete data IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Entering Data 4 -70 Forms Enter data about a record Field in a form corresponds to attribute in a record Used to add, modify, or delete data IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Querying Data 4 -71 Query: Used to retrieve information Structured Query Language (SQL) Example: Display students who earned an “A” Writing SQL queries can become very complex IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Querying Data 4 -71 Query: Used to retrieve information Structured Query Language (SQL) Example: Display students who earned an “A” Writing SQL queries can become very complex IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
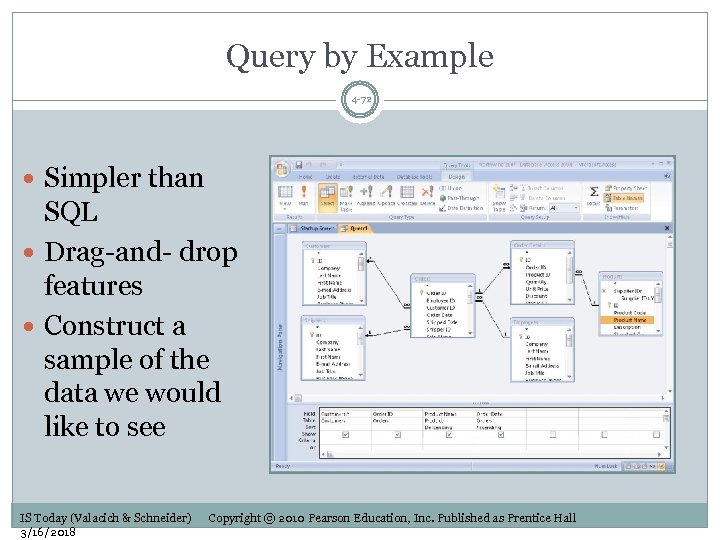 Query by Example 4 -72 Simpler than SQL Drag-and- drop features Construct a sample of the data we would like to see IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Query by Example 4 -72 Simpler than SQL Drag-and- drop features Construct a sample of the data we would like to see IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
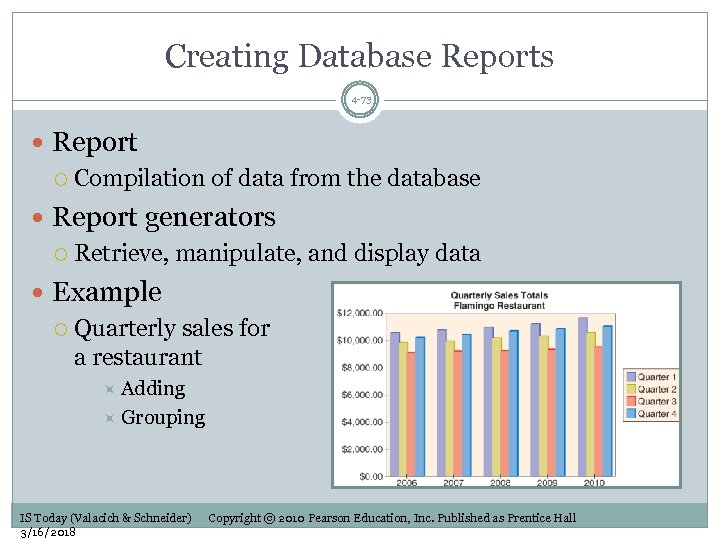 Creating Database Reports 4 -73 Report Compilation of data from the database Report generators Retrieve, manipulate, and display data Example Quarterly sales for a restaurant Adding Grouping IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Creating Database Reports 4 -73 Report Compilation of data from the database Report generators Retrieve, manipulate, and display data Example Quarterly sales for a restaurant Adding Grouping IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 How Organizations Get the Most from Their Data 4 -74 Online transaction processing (OLTP) Immediate automated responses to user requests Designed to handle multiple concurrent transactions Speed of transaction processing is important Linking Web site applications to databases Information provided is dynamic and customized, rather than static Tweaking of database to get optimal performance IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
How Organizations Get the Most from Their Data 4 -74 Online transaction processing (OLTP) Immediate automated responses to user requests Designed to handle multiple concurrent transactions Speed of transaction processing is important Linking Web site applications to databases Information provided is dynamic and customized, rather than static Tweaking of database to get optimal performance IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
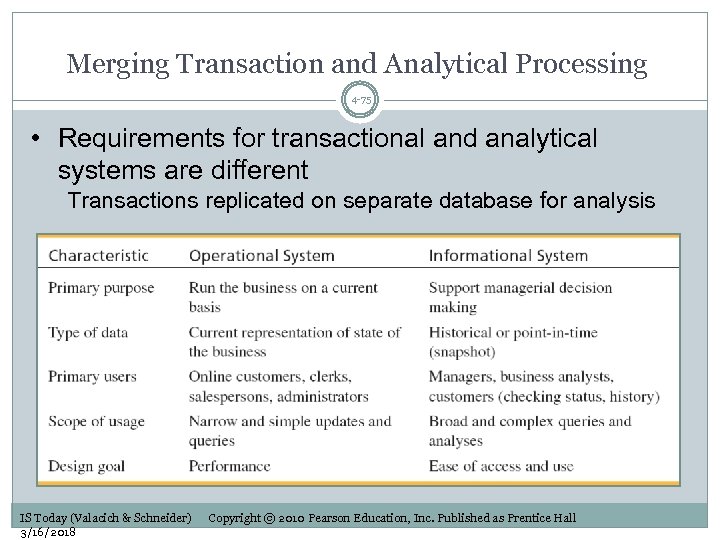 Merging Transaction and Analytical Processing 4 -75 • Requirements for transactional and analytical systems are different Transactions replicated on separate database for analysis IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Merging Transaction and Analytical Processing 4 -75 • Requirements for transactional and analytical systems are different Transactions replicated on separate database for analysis IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
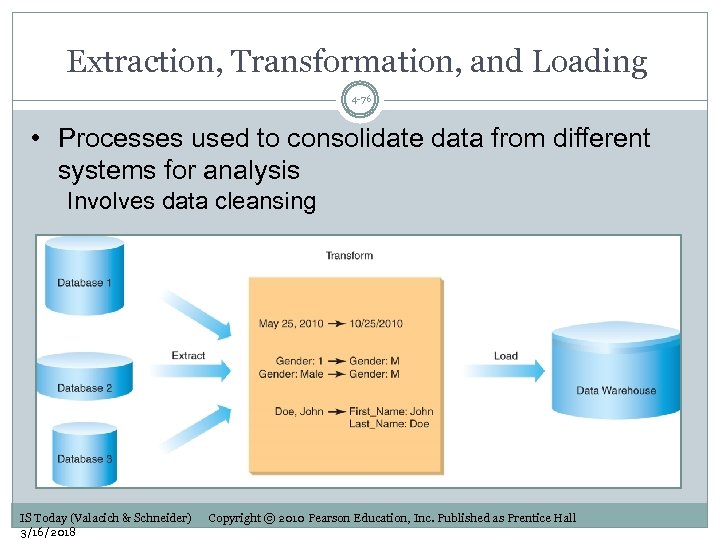 Extraction, Transformation, and Loading 4 -76 • Processes used to consolidate data from different systems for analysis Involves data cleansing IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Extraction, Transformation, and Loading 4 -76 • Processes used to consolidate data from different systems for analysis Involves data cleansing IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Data Warehouses and Data Marts 4 -77 Data Warehouse Integration of multiple large databases and other information sources into a single repository Pull together, integrate, and share critical corporate data throughout the firm Data Mart Data warehouse that is limited in scope Customized for the decision support applications of a particular end-user group IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Data Warehouses and Data Marts 4 -77 Data Warehouse Integration of multiple large databases and other information sources into a single repository Pull together, integrate, and share critical corporate data throughout the firm Data Mart Data warehouse that is limited in scope Customized for the decision support applications of a particular end-user group IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 End of Chapter Content 4 -78 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
End of Chapter Content 4 -78 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Opening Case: Managing in the Digital World: “I Googled You!” 4 -79 January 1996—Brin and Page create Back. Rub Mission: to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful Tremendous growth Unique services Gmail Google Scholar Goog 411 Open. Social Android Google Chrome IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Opening Case: Managing in the Digital World: “I Googled You!” 4 -79 January 1996—Brin and Page create Back. Rub Mission: to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful Tremendous growth Unique services Gmail Google Scholar Goog 411 Open. Social Android Google Chrome IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Cookies: Harmless Identifiers or Privacy Violations? 4 -80 Cookies are used in many ways Cookies are benign, and let certain Web site features work correctly What is the concern about cookies? Downloaded onto user’s computer without their knowledge or consent Can be used to track preferences, but marketers try to target you before the Internet Cookie information can be aggregated by companies, public distrust Be aware of Web sites’ privacy policies IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Cookies: Harmless Identifiers or Privacy Violations? 4 -80 Cookies are used in many ways Cookies are benign, and let certain Web site features work correctly What is the concern about cookies? Downloaded onto user’s computer without their knowledge or consent Can be used to track preferences, but marketers try to target you before the Internet Cookie information can be aggregated by companies, public distrust Be aware of Web sites’ privacy policies IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Black. Berry 4 -81 Research in Motion (RIM) introduced Black. Berry in 1999 More than 3 million users in March 2006 NTP Inc. sued RIM claiming patent infringement NTP sent notice of their wireless communications patents to wireless companies (including RIM) Department of Defense argued that loss of Black. Berry Network would be threat to national security RIM agreed to pay NTP $612. 5 million February 11, 2008: Blackberry e—mail outage Showed how dependent people have become on mobile communications IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Black. Berry 4 -81 Research in Motion (RIM) introduced Black. Berry in 1999 More than 3 million users in March 2006 NTP Inc. sued RIM claiming patent infringement NTP sent notice of their wireless communications patents to wireless companies (including RIM) Department of Defense argued that loss of Black. Berry Network would be threat to national security RIM agreed to pay NTP $612. 5 million February 11, 2008: Blackberry e—mail outage Showed how dependent people have become on mobile communications IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Google’s Larry Page and Sergey Brin 4 -82 Started operation out of dorm room, then moved to a friend’s garage 1 st quarter results as a public company: $805. 9 million Brin and Page are worth $12. 8 billion each Google. org—addresses world’s most pressing problems Google has gone green Plan: to be carbon neutral Climate Savers Computing Initiative Recharge. IT Plug-In Hybrid Car Initiative IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Google’s Larry Page and Sergey Brin 4 -82 Started operation out of dorm room, then moved to a friend’s garage 1 st quarter results as a public company: $805. 9 million Brin and Page are worth $12. 8 billion each Google. org—addresses world’s most pressing problems Google has gone green Plan: to be carbon neutral Climate Savers Computing Initiative Recharge. IT Plug-In Hybrid Car Initiative IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
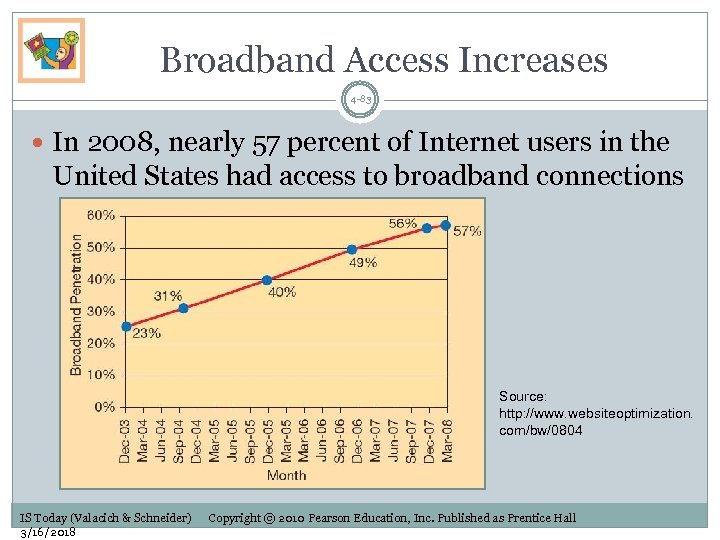 Broadband Access Increases 4 -83 In 2008, nearly 57 percent of Internet users in the United States had access to broadband connections Source: http: //www. websiteoptimization. com/bw/0804 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Broadband Access Increases 4 -83 In 2008, nearly 57 percent of Internet users in the United States had access to broadband connections Source: http: //www. websiteoptimization. com/bw/0804 IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Autonomic Computing 4 -84 Autonomic computing Self-managing systems requiring minimal human intervention to operate Self-configuring Self-optimizing Self-healing Self-protecting IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Autonomic Computing 4 -84 Autonomic computing Self-managing systems requiring minimal human intervention to operate Self-configuring Self-optimizing Self-healing Self-protecting IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 TV for the Visually Impaired 4 -85 Problem: Patients with macular degeneration have difficulty seeing high frequency waves in the visual spectrum, especially TV Solution: Researchers designed an algorithm that specifically increases contrast over the middle- and low- frequency ranges that patients can still see Results: Analog Devices is building a prototype that they hope can be installed on all TVs. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
TV for the Visually Impaired 4 -85 Problem: Patients with macular degeneration have difficulty seeing high frequency waves in the visual spectrum, especially TV Solution: Researchers designed an algorithm that specifically increases contrast over the middle- and low- frequency ranges that patients can still see Results: Analog Devices is building a prototype that they hope can be installed on all TVs. IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
 Movie Industry 4 -86 Movie Production CGI (computer-generated imagery, also known as computer graphics, CG) Post production Independent filmmakers can produce studio-quality films without having to rely on expensive lighting, film development, or post-production facilities Theaters Digital projectors Reduces distribution costs by up to 90 percent New 3 -D technologies (3 ality) IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall
Movie Industry 4 -86 Movie Production CGI (computer-generated imagery, also known as computer graphics, CG) Post production Independent filmmakers can produce studio-quality films without having to rely on expensive lighting, film development, or post-production facilities Theaters Digital projectors Reduces distribution costs by up to 90 percent New 3 -D technologies (3 ality) IS Today (Valacich & Schneider) 3/16/2018 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Published as Prentice Hall


