fc8190f3db992e147fbc4c1e1d0602e3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Chapter 4 Introduction to Automation Kanchala Sudtachat
Chapter 4 Introduction to Automation Kanchala Sudtachat
 Contents l l l Basic elements of an automated system Advanced automation function Levels of automation
Contents l l l Basic elements of an automated system Advanced automation function Levels of automation
 Defining l l l Automation is the technology by which a process or procedure is accomplished without human assistance. It is implemented using a program of instructions combined with a control system that executes the instructions. เพอใหระบบอตโนมตดำเนนการผล ตได ตองอาศย “power” ใชเพอขบเคลอนกระบวนการและดำเ นนการโปรแกรม รวมทงระบบควบคม
Defining l l l Automation is the technology by which a process or procedure is accomplished without human assistance. It is implemented using a program of instructions combined with a control system that executes the instructions. เพอใหระบบอตโนมตดำเนนการผล ตได ตองอาศย “power” ใชเพอขบเคลอนกระบวนการและดำเ นนการโปรแกรม รวมทงระบบควบคม
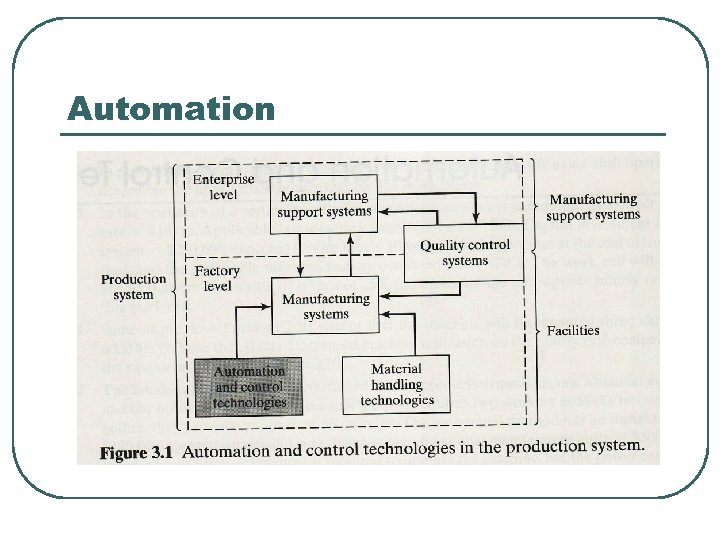 Automation
Automation
 Basic elements of an automated system 1. 2. 3. Power to accomplish the process and operate the system. A program of instructions to direct the process. A control system to actuate the instruction
Basic elements of an automated system 1. 2. 3. Power to accomplish the process and operate the system. A program of instructions to direct the process. A control system to actuate the instruction
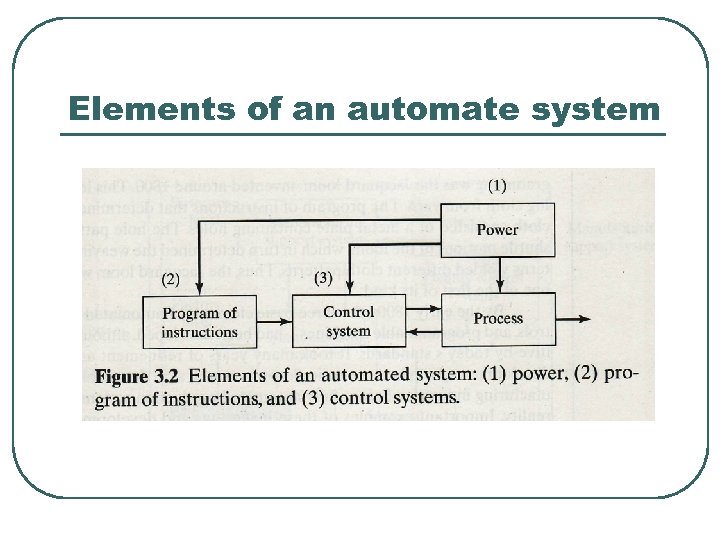 Elements of an automate system
Elements of an automate system
 Power to accomplish the automated process l l Power for the process: เปนสงทตองการเพอขบเคลอนก ระบวนการและควบคมการผลต แหลงพลงงานหลกในระบบอตโนมต คอ พลงงานไฟฟา เพราะมขอไดเปรยบมากกวาพลงงานอย างอน • มตนทนปานกลาง และเปนสวนสำคญของโครงสรางอตสา หกรรม • สามารถเปลยนไปเปนพลงงานทางเลอก
Power to accomplish the automated process l l Power for the process: เปนสงทตองการเพอขบเคลอนก ระบวนการและควบคมการผลต แหลงพลงงานหลกในระบบอตโนมต คอ พลงงานไฟฟา เพราะมขอไดเปรยบมากกวาพลงงานอย างอน • มตนทนปานกลาง และเปนสวนสำคญของโครงสรางอตสา หกรรม • สามารถเปลยนไปเปนพลงงานทางเลอก
 Power to accomplish the automated process l l l Power for the process: the power source for each operation is usually converted from electricity. Other power for automation: fossil fuels, solar energy, water and wind. Power sources are used to drive the process itself, electrical power is used for the controls that automate the operation.
Power to accomplish the automated process l l l Power for the process: the power source for each operation is usually converted from electricity. Other power for automation: fossil fuels, solar energy, water and wind. Power sources are used to drive the process itself, electrical power is used for the controls that automate the operation.
 Power to accomplish the automated process l l Process หมายถง การดำเนนการของกระบวนการผลตซงเก ดขนบน work unit Power is required for the following material handling function • Loading and unloading the work unit. • Material transport between operation.
Power to accomplish the automated process l l Process หมายถง การดำเนนการของกระบวนการผลตซงเก ดขนบน work unit Power is required for the following material handling function • Loading and unloading the work unit. • Material transport between operation.
 Power to accomplish the automated process (cont(. l Power for Automation: power is used for the following functions: • Controller unit • Power to actuate the control signals • Data acquisition and information processing: ขอมลจะถกสะสมจากกระบวนการ (process) และใชเปนขอมลนำเขา เพอควบคมการทำงานตามขนตอนท กำหนด
Power to accomplish the automated process (cont(. l Power for Automation: power is used for the following functions: • Controller unit • Power to actuate the control signals • Data acquisition and information processing: ขอมลจะถกสะสมจากกระบวนการ (process) และใชเปนขอมลนำเขา เพอควบคมการทำงานตามขนตอนท กำหนด
 Program of Instruction l l การดำเนนการผลต ตองการขนตอนการผลตมากกวาหนง ขนตอน เพอใหได product แตละหนวย ขนตอนเหลานเรยกวา “work cycle” ชนงานทผลตสำเรจใหม จะเกดขนในแตละ work cycle บางกระบวนการผลต อาจม product ผลตสำเรจมากกวาหนงชนในหนง Work cycle The particular processing steps for the
Program of Instruction l l การดำเนนการผลต ตองการขนตอนการผลตมากกวาหนง ขนตอน เพอใหได product แตละหนวย ขนตอนเหลานเรยกวา “work cycle” ชนงานทผลตสำเรจใหม จะเกดขนในแตละ work cycle บางกระบวนการผลต อาจม product ผลตสำเรจมากกวาหนงชนในหนง Work cycle The particular processing steps for the
 Program of Instruction l l Work cycle program: ประกอบดวยหนงขนตอนทมความส ำคญ ซงใชเพอรกษา parameter ของกระบวนการซงมการกำหนดไว ในกระบวนการผลต ทตองใชคนทำงานรวมดวย โดยใชคนทำหนาท load, unload งาน ดงนนงานสวนนจะไมอยใน work cycle program Work cycle program ประกอบดวยขนตอนหลากหลายขน
Program of Instruction l l Work cycle program: ประกอบดวยหนงขนตอนทมความส ำคญ ซงใชเพอรกษา parameter ของกระบวนการซงมการกำหนดไว ในกระบวนการผลต ทตองใชคนทำงานรวมดวย โดยใชคนทำหนาท load, unload งาน ดงนนงานสวนนจะไมอยใน work cycle program Work cycle program ประกอบดวยขนตอนหลากหลายขน
 Program of Instruction l l l Process parameter: คอ input ทเราปอนเขาไปในกระบวนการผลต เชน อณหภมทตองกำหนดภายในเตาของก ระบวนการheat treatment, คาพกดของแกน (x, y) ในการกำหนดตำแหนงใหกบชนงานใ นระบบ
Program of Instruction l l l Process parameter: คอ input ทเราปอนเขาไปในกระบวนการผลต เชน อณหภมทตองกำหนดภายในเตาของก ระบวนการheat treatment, คาพกดของแกน (x, y) ในการกำหนดตำแหนงใหกบชนงานใ นระบบ
 Program of Instruction l l Work cycle program: Ex. single process parameter: Maintain the temperature of a furnace at designated value for the duration of a heat treatment cycle. The single-step process is defined by more than one process parameter. Ex. Both temperature and atmosphere are controlled.
Program of Instruction l l Work cycle program: Ex. single process parameter: Maintain the temperature of a furnace at designated value for the duration of a heat treatment cycle. The single-step process is defined by more than one process parameter. Ex. Both temperature and atmosphere are controlled.
 Ex 4. 1 An Automated Turning Operation l The work cycle consists of the following steps: (1) load starting workpiece, (2) position cutting tool prior to turning, (3) turn, (4) reposition tool to a safe location at end of turning, and (5) unload finished workpiece. Identify the activity and process parameter in each step of the operation.
Ex 4. 1 An Automated Turning Operation l The work cycle consists of the following steps: (1) load starting workpiece, (2) position cutting tool prior to turning, (3) turn, (4) reposition tool to a safe location at end of turning, and (5) unload finished workpiece. Identify the activity and process parameter in each step of the operation.
 Program of Instruction l 1. 2. 3. ขอเสย ของอปกรณ Hardware ททำตามโปรแกรมคำสง อปกรณเหลานตองการเวลามากเพ อออกแบบและทำการผลต และเหมาะกบใชกบผลตภณฑ batch production การเปลยนแปลงโปรแกรมทำไดยาก และใชเวลามาก โปรแกรมอยในลกษณะรปแบบทางกาย
Program of Instruction l 1. 2. 3. ขอเสย ของอปกรณ Hardware ททำตามโปรแกรมคำสง อปกรณเหลานตองการเวลามากเพ อออกแบบและทำการผลต และเหมาะกบใชกบผลตภณฑ batch production การเปลยนแปลงโปรแกรมทำไดยาก และใชเวลามาก โปรแกรมอยในลกษณะรปแบบทางกาย
 Decision-Making l Decision-Making in the programmed work cycle • Operator interaction • Ex งานแกะสลก คนงานตองปอนขอมลรปรางลกษณ ะของชนงานทตองการแกะสลก • Different part or product styles processed by the system • Ex อตสาหกรรมทใช robot เชอมท body ของ car ตองมการตดสนใจเลอกลกษณะรอยเ
Decision-Making l Decision-Making in the programmed work cycle • Operator interaction • Ex งานแกะสลก คนงานตองปอนขอมลรปรางลกษณ ะของชนงานทตองการแกะสลก • Different part or product styles processed by the system • Ex อตสาหกรรมทใช robot เชอมท body ของ car ตองมการตดสนใจเลอกลกษณะรอยเ
 Work cycle l การโปรแกรมวงรอบการทำงาน สามารถรวบรวมและสรปลกษณะทใชก บระบบอตโนมต ไดดงน • Number of steps in work cycle • ขนตอนการทำงานทงหมดทอยใน work cycle เปนจำนวนกขนตอน • ลำดบขนตอนการทำงานใน discrete production เปน (1) load (2) process (3) unload • Manual participation in the work cycle
Work cycle l การโปรแกรมวงรอบการทำงาน สามารถรวบรวมและสรปลกษณะทใชก บระบบอตโนมต ไดดงน • Number of steps in work cycle • ขนตอนการทำงานทงหมดทอยใน work cycle เปนจำนวนกขนตอน • ลำดบขนตอนการทำงานใน discrete production เปน (1) load (2) process (3) unload • Manual participation in the work cycle
 Work cycle • Manual participation in the work cycle สวนกระบวนการผลตใดทมพนกงา นทำงานใน work cycle • Process parameters • มจำนวน process parameter ทใชในการควบคมการทำงานในแต ละขนตอนการทำงานก parameter • เปนแบบ continuous หรอ discrete • ตองมการเปลยนแปลงระหวางกระบว นการหรอไม
Work cycle • Manual participation in the work cycle สวนกระบวนการผลตใดทมพนกงา นทำงานใน work cycle • Process parameters • มจำนวน process parameter ทใชในการควบคมการทำงานในแต ละขนตอนการทำงานก parameter • เปนแบบ continuous หรอ discrete • ตองมการเปลยนแปลงระหวางกระบว นการหรอไม
 Work cycle • Operator interaction • ตวอยาง ตองการพนกงานเพอปอนขอมลท จำเปนสำหรบกระบวนการผลตในแตละ work cycle หรอไม • Variations in part or product styles • หนวยชนงานทเขาสกระบวนการผลตเหมอน กนทก work cycle หรอไม • เปนแบบ mass production (fix automation), batch production (programmable automation) หรอ different part / product styles (flexible automation)
Work cycle • Operator interaction • ตวอยาง ตองการพนกงานเพอปอนขอมลท จำเปนสำหรบกระบวนการผลตในแตละ work cycle หรอไม • Variations in part or product styles • หนวยชนงานทเขาสกระบวนการผลตเหมอน กนทก work cycle หรอไม • เปนแบบ mass production (fix automation), batch production (programmable automation) หรอ different part / product styles (flexible automation)
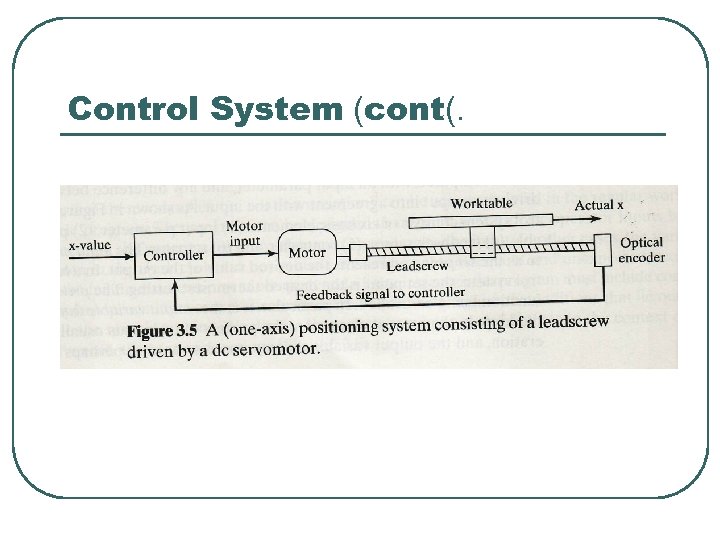
 Control System l l l A closed loop control system, also know as a feedback control system, is one in which the output variable is compared with an input parameter. Consists of six basic elements (1) input parameter, (2) process, (3) output variable, (4) feedback sensor, (5) controller and (6) actuator
Control System l l l A closed loop control system, also know as a feedback control system, is one in which the output variable is compared with an input parameter. Consists of six basic elements (1) input parameter, (2) process, (3) output variable, (4) feedback sensor, (5) controller and (6) actuator
 Control System (1) input parameter การกำหนดคาของกระบวนการ เพอให ไดคาทตองการของ output (2) process การดำเนนการหรอ หนาทในการควบคม (3) output variable สามารถแปรผนไดในบางกรณ และเปนตววดประสทธภาพในกระบวนการ เชน อณหภม , แรง, อตราการไหล (4) feedback sensor ถกใชเพอวดคา output ทแปรผน
Control System (1) input parameter การกำหนดคาของกระบวนการ เพอให ไดคาทตองการของ output (2) process การดำเนนการหรอ หนาทในการควบคม (3) output variable สามารถแปรผนไดในบางกรณ และเปนตววดประสทธภาพในกระบวนการ เชน อณหภม , แรง, อตราการไหล (4) feedback sensor ถกใชเพอวดคา output ทแปรผน
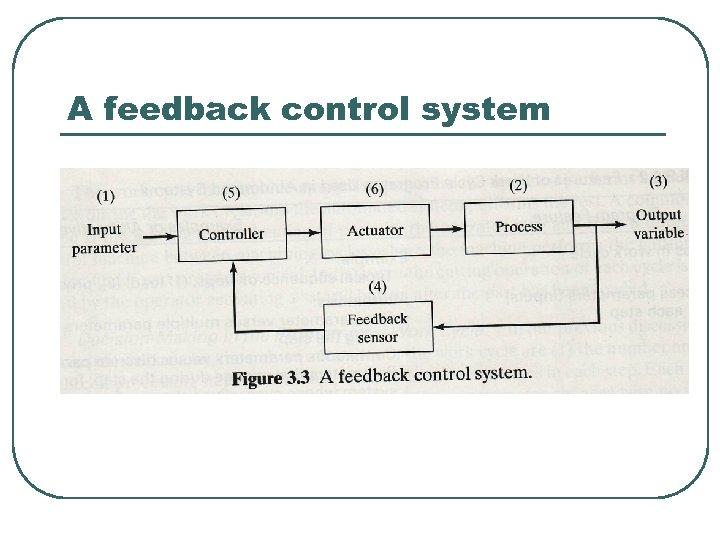 A feedback control system
A feedback control system
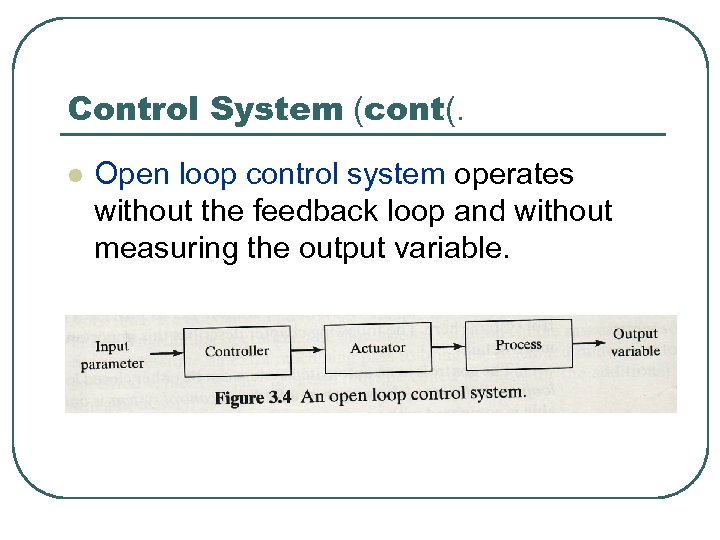 Control System (cont(. l Open loop control system operates without the feedback loop and without measuring the output variable.
Control System (cont(. l Open loop control system operates without the feedback loop and without measuring the output variable.
 Control System (cont(. l Open loop control system usually appropriate when the following conditions apply: 1. The actions per formed by control system are simple. 2. The actuating function is very reliable 3. Any reaction force opposing the actuation are small enough to have no effect on the actuation
Control System (cont(. l Open loop control system usually appropriate when the following conditions apply: 1. The actions per formed by control system are simple. 2. The actuating function is very reliable 3. Any reaction force opposing the actuation are small enough to have no effect on the actuation
 Control System (cont(.
Control System (cont(.
 Advanced Automation Functions l l ระบบอตโนมตอาจมความสามารถปฏบต งานในฟงกชนขนสง ซงใน work cycle ไมไดกำหนดเฉพาะไว ฟงกชนนเกยวของกบ safety, performance of equipment ฟงกชนของระบบมดงน • • • Safety Monitoring Maintenance and repair diagnostics Error detecting and recovery
Advanced Automation Functions l l ระบบอตโนมตอาจมความสามารถปฏบต งานในฟงกชนขนสง ซงใน work cycle ไมไดกำหนดเฉพาะไว ฟงกชนนเกยวของกบ safety, performance of equipment ฟงกชนของระบบมดงน • • • Safety Monitoring Maintenance and repair diagnostics Error detecting and recovery
 Advanced Automation Functions l Safety Monitoring: 1. To protect human workers in the vicinity of the system. 2. To protect the equipment associated with the system. l The safety monitoring is programmed to respond to unsafe condition. (1) Complete stoppage, (2) Sounding an alarm (3) Reducing speed, (4) Taking corrective action
Advanced Automation Functions l Safety Monitoring: 1. To protect human workers in the vicinity of the system. 2. To protect the equipment associated with the system. l The safety monitoring is programmed to respond to unsafe condition. (1) Complete stoppage, (2) Sounding an alarm (3) Reducing speed, (4) Taking corrective action
 Advanced Automation Functions l Maintenance and Repair Diagnostics have three modes of operation 1. Status monitoring 2. Failure diagnostics 3. Recommendation l Status monitoring serves two important functions in machine diagnostics: (1) providing information for diagnosing a current failure, (2) providing data to predict a future malfunction or failure
Advanced Automation Functions l Maintenance and Repair Diagnostics have three modes of operation 1. Status monitoring 2. Failure diagnostics 3. Recommendation l Status monitoring serves two important functions in machine diagnostics: (1) providing information for diagnosing a current failure, (2) providing data to predict a future malfunction or failure
 Advanced Automation Functions l l l Error Detection and Recovery: The error detection step uses the automated system’ s available sensor system to determine when a deviation or malfunction has occurred The possible error can be classified into: • • • Random error Systematic error Aberrations
Advanced Automation Functions l l l Error Detection and Recovery: The error detection step uses the automated system’ s available sensor system to determine when a deviation or malfunction has occurred The possible error can be classified into: • • • Random error Systematic error Aberrations
 Advanced Automation Functions l Error Recovery: the types of strategies can be classified as follows. 1. Make adjustments at the end of the current work cycle 2. Make adjustments during the current cycle 3. Stop the process to invoke corrective action 4. Stop the process and call for help
Advanced Automation Functions l Error Recovery: the types of strategies can be classified as follows. 1. Make adjustments at the end of the current work cycle 2. Make adjustments during the current cycle 3. Stop the process to invoke corrective action 4. Stop the process and call for help
 Levels of Automation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Device level Machine level Cell or system level Plant level Enterprise level
Levels of Automation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Device level Machine level Cell or system level Plant level Enterprise level
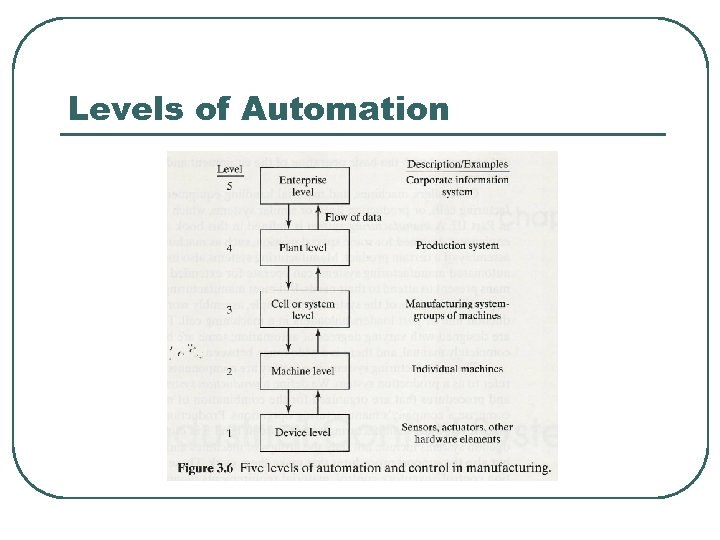 Levels of Automation
Levels of Automation


