e690734dc07283403a2343585e750e15.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 CHAPTER 4 INDUSTRIAL HAZARD
CHAPTER 4 INDUSTRIAL HAZARD
 CONTENT Ergonomics Health and Toxic Substances Environmental Control and Noise Flammable and Explosive Materials Fire Protection Material Handling and Storage Personal Protection and First Aid Electrical Hazards Mechanical Hazards
CONTENT Ergonomics Health and Toxic Substances Environmental Control and Noise Flammable and Explosive Materials Fire Protection Material Handling and Storage Personal Protection and First Aid Electrical Hazards Mechanical Hazards
 Ergonomics “Ergonomics is a multidisciplinary science that studies human physical and psychological capabilities and limitations. This body of knowledge can be used to design or modify the workplace, equipment, products, or work procedures to improve human performance and reduce the likelihood of injury and illness” “Ergonomik adalah kepelbagaian-bidang sains yang mempelajari kemampuan dan batasan fizikal dan psikologi manusia… Digunakan untuk merekacipta atau merombak tempat kerja, peralatan, produk-produk, atau prosedur kerja untuk menambah-baik persembahan manusia…. Mengurangkan kebarangkalian kecederaan dan kesakitan…” (Source: ref. Work-Related)
Ergonomics “Ergonomics is a multidisciplinary science that studies human physical and psychological capabilities and limitations. This body of knowledge can be used to design or modify the workplace, equipment, products, or work procedures to improve human performance and reduce the likelihood of injury and illness” “Ergonomik adalah kepelbagaian-bidang sains yang mempelajari kemampuan dan batasan fizikal dan psikologi manusia… Digunakan untuk merekacipta atau merombak tempat kerja, peralatan, produk-produk, atau prosedur kerja untuk menambah-baik persembahan manusia…. Mengurangkan kebarangkalian kecederaan dan kesakitan…” (Source: ref. Work-Related)
 “Ergonomics bloopers: Never assume that people use product according to plan”
“Ergonomics bloopers: Never assume that people use product according to plan”
 Designing Safety Features into Workplace Machines Example of the application of ergonomics principles in the design of machine controls: ü Design of punch press footswitches A properly designed standard footswitch for activating a mechanical power press has a cover to prevent the operator or other personnel from accidentally stepping on the pedal or switch.
Designing Safety Features into Workplace Machines Example of the application of ergonomics principles in the design of machine controls: ü Design of punch press footswitches A properly designed standard footswitch for activating a mechanical power press has a cover to prevent the operator or other personnel from accidentally stepping on the pedal or switch.
 Controlling the Work Environment -Physical environment that surrounds the worker in the workplace: -Temperature of work environment -Humidity -Pollution
Controlling the Work Environment -Physical environment that surrounds the worker in the workplace: -Temperature of work environment -Humidity -Pollution
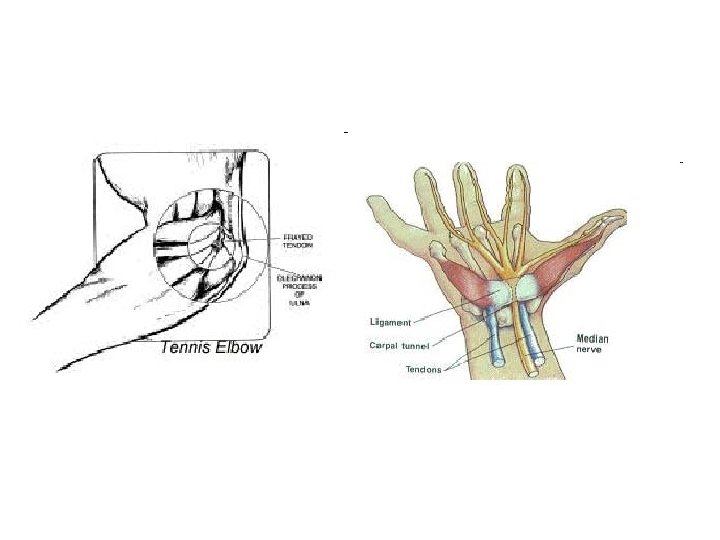
 Workplace Musculoskeletal Disorders ü Carpal Tunnel Syndrome ü a medical condition in which the median nerve is compressed at the wrist, leading to pain, paresthesias, and muscle weakness in the forearm and hand. üCumulative Trauma Disorders / Repetitive Strain Injuries ü caused by repetitive tasks, is any of a loose group of conditions resulting from overuse of a tool, eg. computer, guitar or knife üMusculoskeletal Disorders (MSD) ü Caused either by the work itself or by the employees' working environment. They can also result from fractures sustained in an accident. Typically, MSDs affect the back, neck, shoulders and upper limbs; less often they affect the lower limbs
Workplace Musculoskeletal Disorders ü Carpal Tunnel Syndrome ü a medical condition in which the median nerve is compressed at the wrist, leading to pain, paresthesias, and muscle weakness in the forearm and hand. üCumulative Trauma Disorders / Repetitive Strain Injuries ü caused by repetitive tasks, is any of a loose group of conditions resulting from overuse of a tool, eg. computer, guitar or knife üMusculoskeletal Disorders (MSD) ü Caused either by the work itself or by the employees' working environment. They can also result from fractures sustained in an accident. Typically, MSDs affect the back, neck, shoulders and upper limbs; less often they affect the lower limbs
 Health and Toxic Substances -Health hazard carry a great deal of impact because the potential harm to exposed employees is great and the cost of correction of a single health hazard is high. -Health deals with the long term chronic exposure effects. (remember the 3 case-studies in chapter 1!) -Safety deals with the more obvious acute effects that do their damage immediately. (acute=rapid effect) -Toxic substances must be controlled for the health of the workers as well as to avoid OSHA citation.
Health and Toxic Substances -Health hazard carry a great deal of impact because the potential harm to exposed employees is great and the cost of correction of a single health hazard is high. -Health deals with the long term chronic exposure effects. (remember the 3 case-studies in chapter 1!) -Safety deals with the more obvious acute effects that do their damage immediately. (acute=rapid effect) -Toxic substances must be controlled for the health of the workers as well as to avoid OSHA citation.
 Toxic Substances Irritants (Iritasi) -Inflame the surfaces of the parts of the body by their corrosive action. -Effect skin, moister surface especially the lungs. Example: -dust -ammonia -chlorine gas -acid mists
Toxic Substances Irritants (Iritasi) -Inflame the surfaces of the parts of the body by their corrosive action. -Effect skin, moister surface especially the lungs. Example: -dust -ammonia -chlorine gas -acid mists
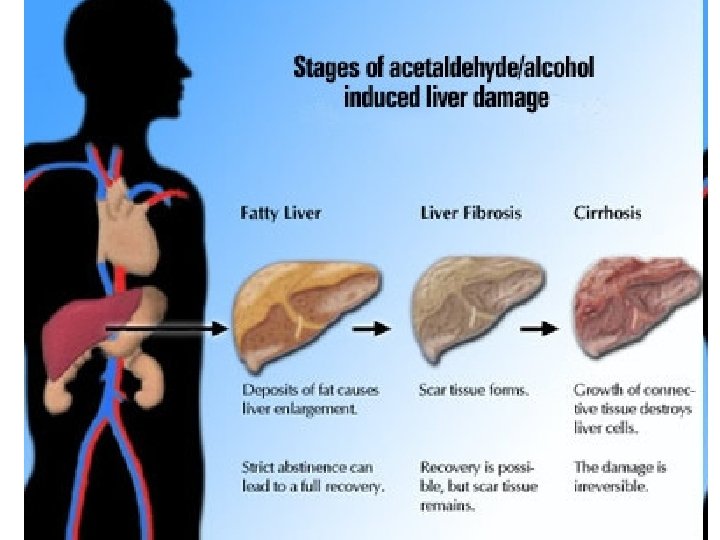
 Toxic Substances Systemic Poisons (Keracunan sistem dalaman) -Attack vital organs or systems of organs such as liver damage n etc. Example: -lead -carbon disulfide -Methyl alcohol (methanol)
Toxic Substances Systemic Poisons (Keracunan sistem dalaman) -Attack vital organs or systems of organs such as liver damage n etc. Example: -lead -carbon disulfide -Methyl alcohol (methanol)
 Toxic Substances Depressants -Certain substances act as depressants or narcotics on the central nervous system. -Affecting safety and health because interfere with the concentration of workers who operate machinery. Example: -Ethyl alcohol ( the ‘drinking’ variety of alcohol) -Acetylene -Benzene
Toxic Substances Depressants -Certain substances act as depressants or narcotics on the central nervous system. -Affecting safety and health because interfere with the concentration of workers who operate machinery. Example: -Ethyl alcohol ( the ‘drinking’ variety of alcohol) -Acetylene -Benzene
 Toxic Substances Carcinogens -Substances that are known to cause or are suspected to cause cancer. Example: -Vinyl chloride (cause a form of cancer of the liver) -Polyvinyl chloride
Toxic Substances Carcinogens -Substances that are known to cause or are suspected to cause cancer. Example: -Vinyl chloride (cause a form of cancer of the liver) -Polyvinyl chloride
 Toxic Substances Air Contaminants -Gases easily contaminate the air because air consists of gases and gases readily mix. Eg; carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide and chlorine. -Vapors are also gases (liquids or solids) that release small quantities of gases into the surrounding air. Eg; Gasoline and solvents -Dusts (solid particles) Eg: Asbestos, coal, cotton and radioactive dusts
Toxic Substances Air Contaminants -Gases easily contaminate the air because air consists of gases and gases readily mix. Eg; carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide and chlorine. -Vapors are also gases (liquids or solids) that release small quantities of gases into the surrounding air. Eg; Gasoline and solvents -Dusts (solid particles) Eg: Asbestos, coal, cotton and radioactive dusts
 Toxic Substances Air Contaminants -Fumes are also solid particles, but are generally too fine to be called dust. Eg: Metal fumes
Toxic Substances Air Contaminants -Fumes are also solid particles, but are generally too fine to be called dust. Eg: Metal fumes
 Environmental Control and Noise -Environmental control: Involve strategies for dealing with air contaminants problem, chiefly through ventilation. -Industrial Noise : Phenomenon that requires an understanding of the physics of sound-wave energy.
Environmental Control and Noise -Environmental control: Involve strategies for dealing with air contaminants problem, chiefly through ventilation. -Industrial Noise : Phenomenon that requires an understanding of the physics of sound-wave energy.
 Ventilation -Ventilation is the most obvious engineering solution to an aircontaminant problem. -The most desirable way to deal with air contaminant is: ü change the process (isolate or enclose it) so that the contaminant is no longer produced. ü change the material used
Ventilation -Ventilation is the most obvious engineering solution to an aircontaminant problem. -The most desirable way to deal with air contaminant is: ü change the process (isolate or enclose it) so that the contaminant is no longer produced. ü change the material used
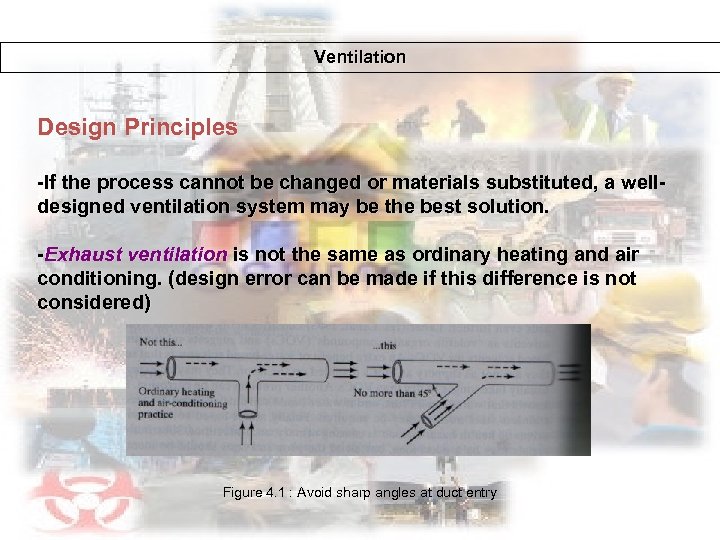 Ventilation Design Principles -If the process cannot be changed or materials substituted, a welldesigned ventilation system may be the best solution. -Exhaust ventilation is not the same as ordinary heating and air conditioning. (design error can be made if this difference is not considered) Figure 4. 1 : Avoid sharp angles at duct entry
Ventilation Design Principles -If the process cannot be changed or materials substituted, a welldesigned ventilation system may be the best solution. -Exhaust ventilation is not the same as ordinary heating and air conditioning. (design error can be made if this difference is not considered) Figure 4. 1 : Avoid sharp angles at duct entry
 Ventilation Makeup Air -Open windows and doors (traditional way to makeup air) -Recirculate the exhaust air after filtration and decontamination -Introduce the makeup air right at the point at which the contamination is taking place -Use a heat exchanger to recapture the energy of the exhaust air and transfer it to the incoming make up air.
Ventilation Makeup Air -Open windows and doors (traditional way to makeup air) -Recirculate the exhaust air after filtration and decontamination -Introduce the makeup air right at the point at which the contamination is taking place -Use a heat exchanger to recapture the energy of the exhaust air and transfer it to the incoming make up air.
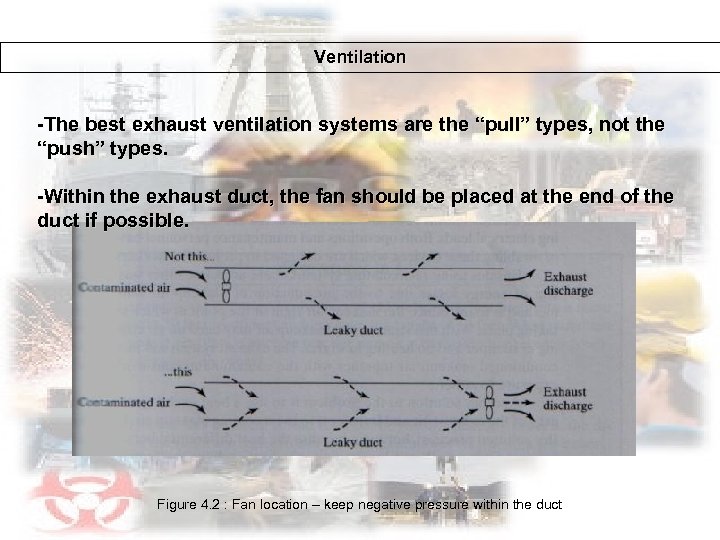 Ventilation -The best exhaust ventilation systems are the “pull” types, not the “push” types. -Within the exhaust duct, the fan should be placed at the end of the duct if possible. Figure 4. 2 : Fan location – keep negative pressure within the duct
Ventilation -The best exhaust ventilation systems are the “pull” types, not the “push” types. -Within the exhaust duct, the fan should be placed at the end of the duct if possible. Figure 4. 2 : Fan location – keep negative pressure within the duct
 ` Industrial Noise -Noise exposure cause a health problem -Noise can be defined as unwanted sound -In industrial sense, noise means excessive sound or harmful sound -Sound level meter can be used to measure sound levels Noise prevention: a) Personal protective equipment b) elimination of the source of the noise
` Industrial Noise -Noise exposure cause a health problem -Noise can be defined as unwanted sound -In industrial sense, noise means excessive sound or harmful sound -Sound level meter can be used to measure sound levels Noise prevention: a) Personal protective equipment b) elimination of the source of the noise
 Flammable and Explosive Materials Flammable liquids (such as gasoline) have a flash point below 37. 70 C (1000 F). Combustible liquids have a flash point at or higher than flammable liquids. Explosive range or flammable range defines the concentration of a vapor or gas in air that can ignite from a source.
Flammable and Explosive Materials Flammable liquids (such as gasoline) have a flash point below 37. 70 C (1000 F). Combustible liquids have a flash point at or higher than flammable liquids. Explosive range or flammable range defines the concentration of a vapor or gas in air that can ignite from a source.
 Classes of flammable and combustible liquids Flammable Liquids Class I-A Class I-B Class I-C Flash point below 730 F, boiling point below 1000 F. Flash point below 730 F, boiling point at or above 1000 F. Flash point at or above 730 F, but below 1000 F. Combustible Liquids Class III-A Class III-B Flash point at or above 1000 F, but below 1400 F. Flash point at or above 1400 F, but below 2000 F. Flash point at or above 2000 F.
Classes of flammable and combustible liquids Flammable Liquids Class I-A Class I-B Class I-C Flash point below 730 F, boiling point below 1000 F. Flash point below 730 F, boiling point at or above 1000 F. Flash point at or above 730 F, but below 1000 F. Combustible Liquids Class III-A Class III-B Flash point at or above 1000 F, but below 1400 F. Flash point at or above 1400 F, but below 2000 F. Flash point at or above 2000 F.
 Explosives are classified according to degree of hazard. Class A is the most hazardous ( nitroglycerin, black powder and dynamite). Class B explosives include propellants, photographic, flash powders and some special fireworks. Class C explosives are manufactured articles that contain explosives in restricted quantities.
Explosives are classified according to degree of hazard. Class A is the most hazardous ( nitroglycerin, black powder and dynamite). Class B explosives include propellants, photographic, flash powders and some special fireworks. Class C explosives are manufactured articles that contain explosives in restricted quantities.
 Fire Protection -Effective fire prevention requires anticipation of fire sources. -Cause of industrial fires are : ü Overheated bearings or hot machinery and processes. ü Clogged or dirty ventilation filters or ducts (when the clogging material is a flammable or combustible air contaminant). Prevention : ØEffective preventive maintenance ØStrategy in housekeeping
Fire Protection -Effective fire prevention requires anticipation of fire sources. -Cause of industrial fires are : ü Overheated bearings or hot machinery and processes. ü Clogged or dirty ventilation filters or ducts (when the clogging material is a flammable or combustible air contaminant). Prevention : ØEffective preventive maintenance ØStrategy in housekeeping
 Emergency Evacuation Alarm systems Fire Detection Systems -Smoke alarms and other detection devices -Most detection systems are delicate instruments and will not withstand the rigors of the industrial environment -Conditions to be considered are dust, corrosive atmospheres, weather exposure, heat from processes and mechanical damage.
Emergency Evacuation Alarm systems Fire Detection Systems -Smoke alarms and other detection devices -Most detection systems are delicate instruments and will not withstand the rigors of the industrial environment -Conditions to be considered are dust, corrosive atmospheres, weather exposure, heat from processes and mechanical damage.
 Fire Brigades Some firms may adopt a strategy in which employees are organized into brigade to fight fire themselves. They have to consider : ü Employee fitness ü Firefighter training ü Protective Clothing and Apparatus
Fire Brigades Some firms may adopt a strategy in which employees are organized into brigade to fight fire themselves. They have to consider : ü Employee fitness ü Firefighter training ü Protective Clothing and Apparatus
 Fire Extinguishers -Fire extinguishers are still the most effective method of immediately controlling a very local fire before disastrous consequences ensue. -Fire protection field classifies fires into four categories. -Wrong application of extinguishment medium to a fire can do more harm than good.
Fire Extinguishers -Fire extinguishers are still the most effective method of immediately controlling a very local fire before disastrous consequences ensue. -Fire protection field classifies fires into four categories. -Wrong application of extinguishment medium to a fire can do more harm than good.
 Fire Extinguishers Figure 4. 3 : Four Classes of Fires and Appropriate Extinguishing Media
Fire Extinguishers Figure 4. 3 : Four Classes of Fires and Appropriate Extinguishing Media
 Another type of fire protection systems are: ü Standpipe and Hose Systems ü Automatic Sprinkler Systems ü Fixed Extinguishing Systems
Another type of fire protection systems are: ü Standpipe and Hose Systems ü Automatic Sprinkler Systems ü Fixed Extinguishing Systems
 Material Handling and Storage -Handling of material in manufacturing plant can be as hazardous as the industrial process itself. -General hazards of material-handling equipment are : Ø Being struck by an industrial truck or conveyor Ø Automatic or remote control nature (conveyor accidents) -Material storage standards; bags, containers, or bundles stored in tiers shall be “stacked, blocked, interlocked, and limited in height so that they are stable and secure against sliding or collapse. ”
Material Handling and Storage -Handling of material in manufacturing plant can be as hazardous as the industrial process itself. -General hazards of material-handling equipment are : Ø Being struck by an industrial truck or conveyor Ø Automatic or remote control nature (conveyor accidents) -Material storage standards; bags, containers, or bundles stored in tiers shall be “stacked, blocked, interlocked, and limited in height so that they are stable and secure against sliding or collapse. ”
 Industrial Trucks -Category of material-handling equipment -Important factors that should be consider in reducing hazards regarding industrial trucks: Ø Truck selection Ø Operations Ø Forklift driver training Ø Passengers Ø Parking and maintenance
Industrial Trucks -Category of material-handling equipment -Important factors that should be consider in reducing hazards regarding industrial trucks: Ø Truck selection Ø Operations Ø Forklift driver training Ø Passengers Ø Parking and maintenance
 Personal Protection and First Aid -Personal protective equipment (PPE) must be properly selected to match the hazard. -Employer must be trained to use PPE properly. -Example: ü Hearing protection ü Eye and face protection ü Respiratory protection ü Head protection
Personal Protection and First Aid -Personal protective equipment (PPE) must be properly selected to match the hazard. -Employer must be trained to use PPE properly. -Example: ü Hearing protection ü Eye and face protection ü Respiratory protection ü Head protection
 Hearing Protection -Important factor in selecting a type of noise protection is probably effectiveness in reducing decibel level of noise exposure. Various types of ear protection: ü Cotton balls ü Swedish wools ü Earplugs ü Molded Ear Caps ü Earmuffs ü Helmets
Hearing Protection -Important factor in selecting a type of noise protection is probably effectiveness in reducing decibel level of noise exposure. Various types of ear protection: ü Cotton balls ü Swedish wools ü Earplugs ü Molded Ear Caps ü Earmuffs ü Helmets
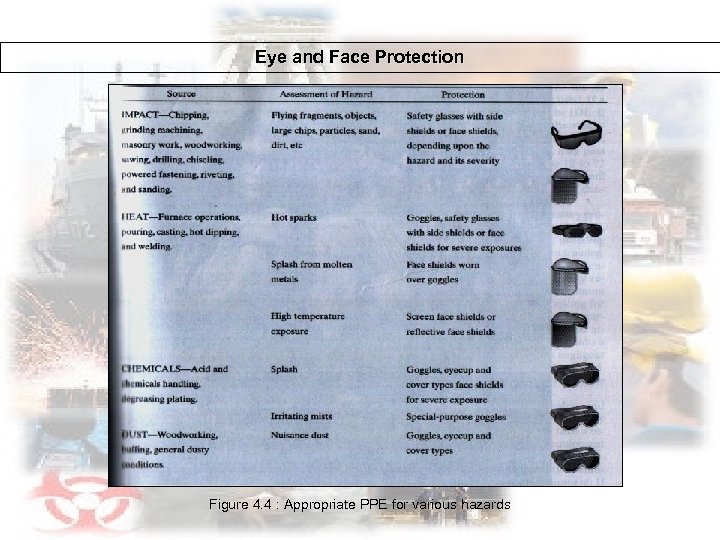 Eye and Face Protection Figure 4. 4 : Appropriate PPE for various hazards
Eye and Face Protection Figure 4. 4 : Appropriate PPE for various hazards
 Respiratory Protection Classification of respiratory protection devices; 1. Air-purifying devices (a) Dust mask (b) Quarter mask (c) Half mask (d) Full-face mask (e) Gas mask (f ) Mouthpiece respirator 2. Atmosphere-supplying respirators (a) Air line respirator (b) Hose mask (c) Self-contained breathing apparatus
Respiratory Protection Classification of respiratory protection devices; 1. Air-purifying devices (a) Dust mask (b) Quarter mask (c) Half mask (d) Full-face mask (e) Gas mask (f ) Mouthpiece respirator 2. Atmosphere-supplying respirators (a) Air line respirator (b) Hose mask (c) Self-contained breathing apparatus
 Head Protection -Implementation of hard hat rules Figure 4. 3 : Various types of hard hat
Head Protection -Implementation of hard hat rules Figure 4. 3 : Various types of hard hat
 First Aid -First-aid station may satisfy several additional functions besides providing immediate care for the injured. -First aid station is often used for : ØMedical tests ØScreening examinations ØMonitoring of acute and chronic effects of health hazards -Provision of emergency showers and emergency eyewash stations on job sites
First Aid -First-aid station may satisfy several additional functions besides providing immediate care for the injured. -First aid station is often used for : ØMedical tests ØScreening examinations ØMonitoring of acute and chronic effects of health hazards -Provision of emergency showers and emergency eyewash stations on job sites
 Electrical Hazards -Electricity is the flow of negatively charged particles called electrons through an electrically conductive material. Sources of electrical hazards are: Ø Equipment failure Ø Improper wiring Ø Insulation failure Ø Static electricity discharge Ø Using metal ladders to work on electrical equipment Ø Working on electrical equipment without ensuring that the power has been shut off Ø Lightning strikes
Electrical Hazards -Electricity is the flow of negatively charged particles called electrons through an electrically conductive material. Sources of electrical hazards are: Ø Equipment failure Ø Improper wiring Ø Insulation failure Ø Static electricity discharge Ø Using metal ladders to work on electrical equipment Ø Working on electrical equipment without ensuring that the power has been shut off Ø Lightning strikes
 Reduction of Electrical Hazards Method of reducing electrical hazards: Ø Grounding of electrical equipment -safeguard people from electrical shock -reduce the probability of a fire -protect equipment from damage Ø Humidification Ø Use antistatic materials Ø Ionizers Ø Double insulation
Reduction of Electrical Hazards Method of reducing electrical hazards: Ø Grounding of electrical equipment -safeguard people from electrical shock -reduce the probability of a fire -protect equipment from damage Ø Humidification Ø Use antistatic materials Ø Ionizers Ø Double insulation
 Mechanical Hazards Mechanical hazards are those associated with power-driven machines, whether automated or manually operated
Mechanical Hazards Mechanical hazards are those associated with power-driven machines, whether automated or manually operated
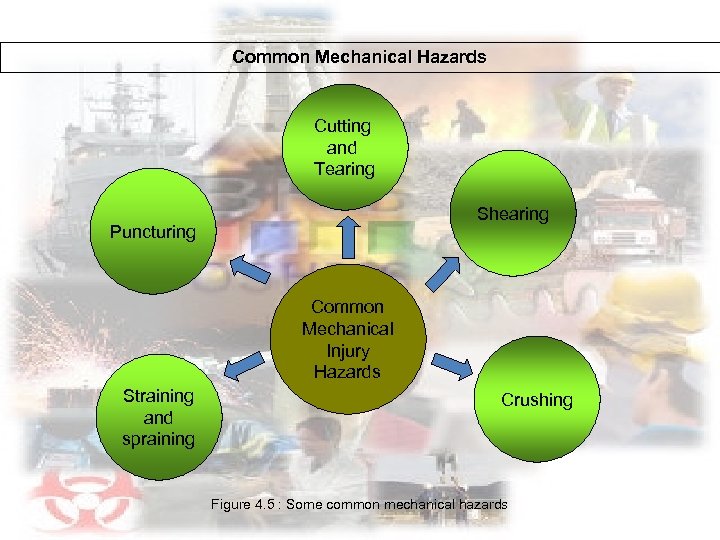 Common Mechanical Hazards Cutting and Tearing Shearing Puncturing Common Mechanical Injury Hazards Straining and spraining Crushing Figure 4. 5 : Some common mechanical hazards
Common Mechanical Hazards Cutting and Tearing Shearing Puncturing Common Mechanical Injury Hazards Straining and spraining Crushing Figure 4. 5 : Some common mechanical hazards
 Safeguarding Machine safeguarding is to minimize the risk of accidents of machineoperator contact. The contact can be: Ø An individual making the contact with the machine-usually the moving part Ø From the machine via flying metal chips, chemical and hot splashes, and circular saw kickbacks Ø Caused by the direct result of a machine malfunction, including mechanical and electrical failure
Safeguarding Machine safeguarding is to minimize the risk of accidents of machineoperator contact. The contact can be: Ø An individual making the contact with the machine-usually the moving part Ø From the machine via flying metal chips, chemical and hot splashes, and circular saw kickbacks Ø Caused by the direct result of a machine malfunction, including mechanical and electrical failure
 OSHA’s Requirement for Machine Guarding OSHA’s requirement for machine guarding are summarized as follows: a) Types of guarding b) General requirements for machine guards c) Guarding the point of operation d) Machines requiring point of operation guards e) Exposure of blades f) Anchoring fixed machinery
OSHA’s Requirement for Machine Guarding OSHA’s requirement for machine guarding are summarized as follows: a) Types of guarding b) General requirements for machine guards c) Guarding the point of operation d) Machines requiring point of operation guards e) Exposure of blades f) Anchoring fixed machinery
 Quiz 3 • Give one example of the effect of toxic substances to human.
Quiz 3 • Give one example of the effect of toxic substances to human.
 Thank You To be continued on next lecture
Thank You To be continued on next lecture


